In-Depth Analysis of the Extracorporeal Proteome Adsorbed to Dialysis Membranes during Hemodialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Protein Elution and Quantification
2.3. Protein Digestion and Cleanup
2.4. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (LC–MS)
2.5. Mass Spectrometry Data Analysis
2.6. Biological Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.7. Data Analysis and Availability
3. Results
3.1. Extracorporal Proteome on Hemodialyzer Membranes
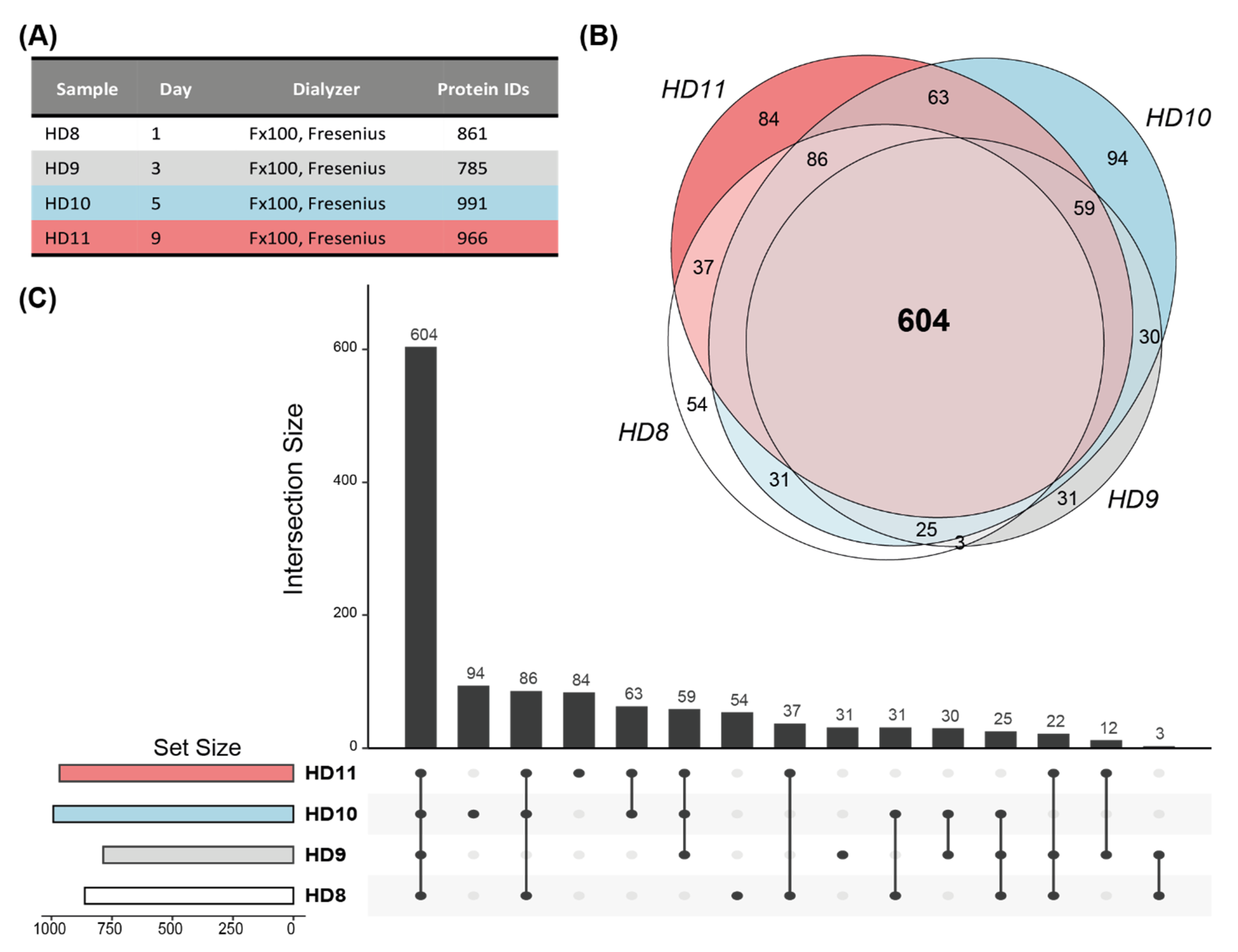
3.2. Patient-Specific Extracorporeal Proteome
3.3. Enrichment of Cellular Components, Molecular Functions and Molecular Size of the HD Membrane Proteome
3.4. Membrane-Specific Extracorporeal Proteome
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bello, A.K.; Levin, A.; Lunney, M.; Osman, M.A.A.; Ye, F.; Ashuntantang, G.E.E.; Bellorin-Font, E.; Gharbi, M.B.; Davison, S.N.; Ghnaimat, M.; et al. Status of care for end stage kidney disease in countries and regions worldwide: International cross sectional survey. BMJ 2019, 367, l5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Moio, M.R.; Fois, A.; Sofronie, A.; Gendrot, L.; Cabiddu, G.; D’Alessandro, C.; Cupisti, A. The Diet and Haemodialysis Dyad: Three Eras, Four Open Questions and Four Paradoxes. A Narrative Review, Towards a Personalized, Patient-Centered Approach. Nutrients 2017, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, Y.; Qian, Q. Protein Nutrition and Malnutrition in CKD and ESRD. Nutrients 2017, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavone, B.; Sirolli, V.; Bucci, S.; Libardi, F.; Felaco, P.; Amoroso, L.; Sacchetta, P.; Urbani, A.; Bonomini, M. Adsorption and carbonylation of plasma proteins by dialyser membrane material: In vitro and in vivo proteomics investigations. Blood Transfus 2010, 8 (Suppl. S3), s113–s119. [Google Scholar]
- Tomo, T. Biocompatibility of Hemodiafilters. Contrib. Nephrol. 2017, 189, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Urbani, A.; Lupisella, S.; Sirolli, V.; Bucci, S.; Amoroso, L.; Pavone, B.; Pieroni, L.; Sacchetta, P.; Bonomini, M. Proteomic analysis of protein adsorption capacity of different haemodialysis membranes. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratochwill, K. The Extracorporeal Proteome-The Significance of Selective Protein Removal During Dialysis Therapy. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2018, 12, e1800078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münch, J.; Ständker, L.; Forssmann, W.-G.; Kirchhoff, F. Discovery of modulators of HIV-1 infection from the human peptidome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronci, M.; Leporini, L.; Felaco, P.; Sirolli, V.; Pieroni, L.; Greco, V.; Aceto, A.; Urbani, A.; Bonomini, M. Proteomic Characterization of a New asymmetric Cellulose Triacetate Membrane for Hemodialysis. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2018, 12, e1700140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, M.; Piscitani, L.; Di Liberato, L.; Sirolli, V. Biocompatibility of Surface-Modified Membranes for Chronic Hemodialysis Therapy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harm, S.; Schildböck, C.; Hartmann, J. Cytokine Removal in Extracorporeal Blood Purification: An in vitro Study. Blood Purif. 2020, 49, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monard, C.; Rimmelé, T.; Ronco, C. Extracorporeal Blood Purification Therapies for Sepsis. Blood Purif. 2019, 47 (Suppl. S3), 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankawi, G.; Neri, M.; Zhang, J.; Breglia, A.; Ricci, Z.; Ronco, C. Extracorporeal techniques for the treatment of critically ill patients with sepsis beyond conventional blood purification therapy: The promises and the pitfalls. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbani, A.; Sirolli, V. Proteomic investigations on the effect of different membrane materials on blood protein adsorption during haemodialysis. Blood Transfus 2012, 10 (Suppl. S2), s101–s112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonomini, M.; Sirolli, V.; Pieroni, L.; Felaco, P.; Amoroso, L.; Urbani, A. Proteomic Investigations into Hemodialysis Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29508–29521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongboonkerd, V. Proteomics in extracorporeal blood purification and peritoneal dialysis. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Bowry, S. Nanoscale modulation of the pore dimensions, size distribution and structure of a new polysulfone-based high-flux dialysis membrane. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2001, 24, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayols, S. rrvgo: A Bioconductor Package to Reduce and Visualize Gene Ontology Terms. 2020. Available online: https://ssayols.github.io/rrvgo (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Herzog, R.; Boehm, M.; Unterwurzacher, M.; Wagner, A.; Parapatics, K.; Májek, P.; Mueller, A.C.; Lichtenauer, A.; Bennett, K.L.; Alper, S.L.; et al. Effects of alanyl-glutamine treatment on the peritoneal dialysis effluent proteome reveal pathomechanism-associated molecular signatures. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosova, M.; Schaefer, B.; Bermejo, J.L.; Tarantino, S.; Lasitschka, F.; Macher-Goeppinger, S.; Sinn, P.; Warady, B.A.; Zaloszyc, A.; Parapatics, K.; et al. Complement Activation in Peritoneal Dialysis-Induced Arteriolopathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, L.; Mortera, S.L.; Greco, V.; Sirolli, V.; Ronci, M.; Felaco, P.; Fucci, G.; De Fulviis, S.; Massoud, R.; Condò, S.; et al. Biocompatibility assessment of haemodialysis membrane materials by proteomic investigations. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, M.; Pieroni, L.; Di Liberato, L.; Sirolli, V.; Urbani, A. Examining hemodialyzer membrane performance using proteomic technologies. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomini, M. Proteomics and Protein Adsorption on Hemodialysis Membranes. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2017, 11, 1700112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, J.; Richtrova, P.; Hricinova, A.; Tuma, Z.; Moravec, J.; Lysak, D.; Matejovic, M. Proteomic profiling of blood-dialyzer interactome reveals involvement of lectin complement pathway in hemodialysis-induced inflammatory response. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y. Proteomic study provides new clues for complications of hemodialysis caused by dialysis membrane. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yang, K.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J. Proteomics Investigations into Serum Proteins Adsorbed by High-Flux and Low-Flux Dialysis Membranes. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mares, J.; Thongboonkerd, V.; Tuma, Z.; Moravec, J.; Matejovic, M. Specific adsorption of some complement activation proteins to polysulfone dialysis membranes during hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Bi, L.-J.; Tao, S.-C.; Xu, X.-D.; Zhang, Z.-P.; Kitazato, K.; Zhang, X.-E. Proteomic analysis of multiple myeloma: Current status and future perspectives. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2011, 5, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reule, S.; Sexton, D.J.; Solid, C.A.; Chen, S.-C.; Foley, R.N. ESRD due to Multiple Myeloma in the United States, 2001–2010. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Klein, J.B. Proteomics and autoimmune kidney disease. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 161, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]




| Sample # | # Protein ID Multi-Consensus | # Protein ID Individual | Dialyzer | Membrane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1493 | 911 | Diacap Pro 19H, Braun | Polysulfone |
| 2 | 1504 | 1105 | Leoceed, 21HX, Asahi Kasei | Polysulfone |
| 3 | 1493 | 892 | Fx 100, Fresenius | Helixone |
| 4 | 1439 | 747 | Leoceed, 21HX, Asahi Kasei | Polysulfone |
| 5 | 1376 | 617 | Fx 100, Fresenius | Helixone |
| 6 | 1342 | 826 | Fx100, Fresenius | Helixone |
| 7 | 1381 | 749 | Leoceed, 21HX, Asahi Kasei | Polysulfone |
| 8 | 1322 | 861 | Fx100, Fresenius | Helixone |
| Study | Year | # Filters/Patients | # Proteins Identified | Method to Elute Proteins from Membranes (Wash/Elution Buffer/Elution Procedure) | Proteomic Method | Ref # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mares et al. | 2009 | 15/5 | 57 (153 spots) | 80 mL 3 mM EDTA 30 min/80 ml 40% acetic acid/30 min circulation (+7000 Da cut-off filter) | 2-DGE-MALDI-TOF/TOF | [27] |
| Urbani et al. | 2012 | 12/6 | 73 | 1 L saline/80 mL CSB (6 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 0.4% SDS, 1 mM DTT)/1 h circulation | 2-DGE-MALDI-TOF/TOF + LC–MS/MS (DIA) | [14] |
| Pieroni et al. | 2015 | 6/3 | 65 | 1 L saline/80 mL CSB (6 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 0.4% SDS, 1 mM DTT)/1 h circulation | LC–MS/MS (DIA) | [21] |
| Han et al. | 2017 | 4/2 | 668 (single-peptide IDs not excluded) | -/1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride/ /overnight (+10,000 Da cut-off filter) | dimethyl labeling- LC–MS/MS (DDA) | [26] |
| Yang et al. | 2017 | 4/4 | 462 (single-peptide IDs not excluded) | -/1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride/ overnight (+10,000 Da cut-off filter) | LC–MS/MS (DDA) | [25] |
| Ronci et al. | 2018 | 8/4 | 67–130 | 3 L saline/180 mL CSB (6 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 0.4% SDS, 1 mM DTT)/1 h circulation | LC–MS/MS (DDA) | [9] |
| This study | 2022 | 11/8 | 1648/1736 | 3 L saline 30 min/125 mL CSB (6 M urea, 2 M thiourea, 0.4% SDS, 1 mM DTT, PI, PPI, pH 8.5)/1 h circulation | LC–MS/MS (DDA) | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daniel-Fischer, L.; Sobieszek, I.J.; Wagner, A.; Sacnun, J.M.; Watschinger, B.; Aufricht, C.; Kratochwill, K.; Herzog, R. In-Depth Analysis of the Extracorporeal Proteome Adsorbed to Dialysis Membranes during Hemodialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111120
Daniel-Fischer L, Sobieszek IJ, Wagner A, Sacnun JM, Watschinger B, Aufricht C, Kratochwill K, Herzog R. In-Depth Analysis of the Extracorporeal Proteome Adsorbed to Dialysis Membranes during Hemodialysis. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111120
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaniel-Fischer, Lisa, Isabel J. Sobieszek, Anja Wagner, Juan Manuel Sacnun, Bruno Watschinger, Christoph Aufricht, Klaus Kratochwill, and Rebecca Herzog. 2022. "In-Depth Analysis of the Extracorporeal Proteome Adsorbed to Dialysis Membranes during Hemodialysis" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111120
APA StyleDaniel-Fischer, L., Sobieszek, I. J., Wagner, A., Sacnun, J. M., Watschinger, B., Aufricht, C., Kratochwill, K., & Herzog, R. (2022). In-Depth Analysis of the Extracorporeal Proteome Adsorbed to Dialysis Membranes during Hemodialysis. Membranes, 12(11), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111120






