SPEEK and SPPO Blended Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sulfonation of PEEK
2.3. Designing of the Blended Membranes
2.4. Characterizations
2.4.1. Instrumentations
2.4.2. Ion Exchange Capacity, Water Uptake and Membrane Swelling
2.4.3. Chemical Stability of Membranes
2.4.4. Proton Conductivity Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR
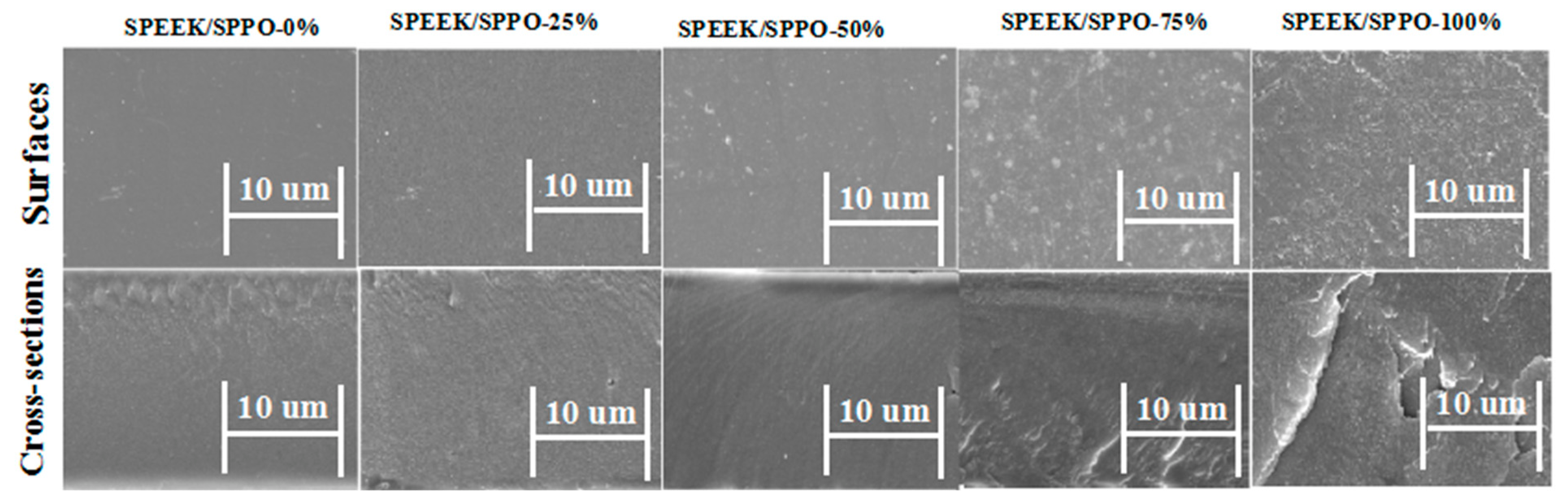
3.2. Morphology of Membranes
3.3. Ion Exchange Capacity (IEC)
3.4. Water Uptake and Membrane Swelling
3.5. Mechanical Stability
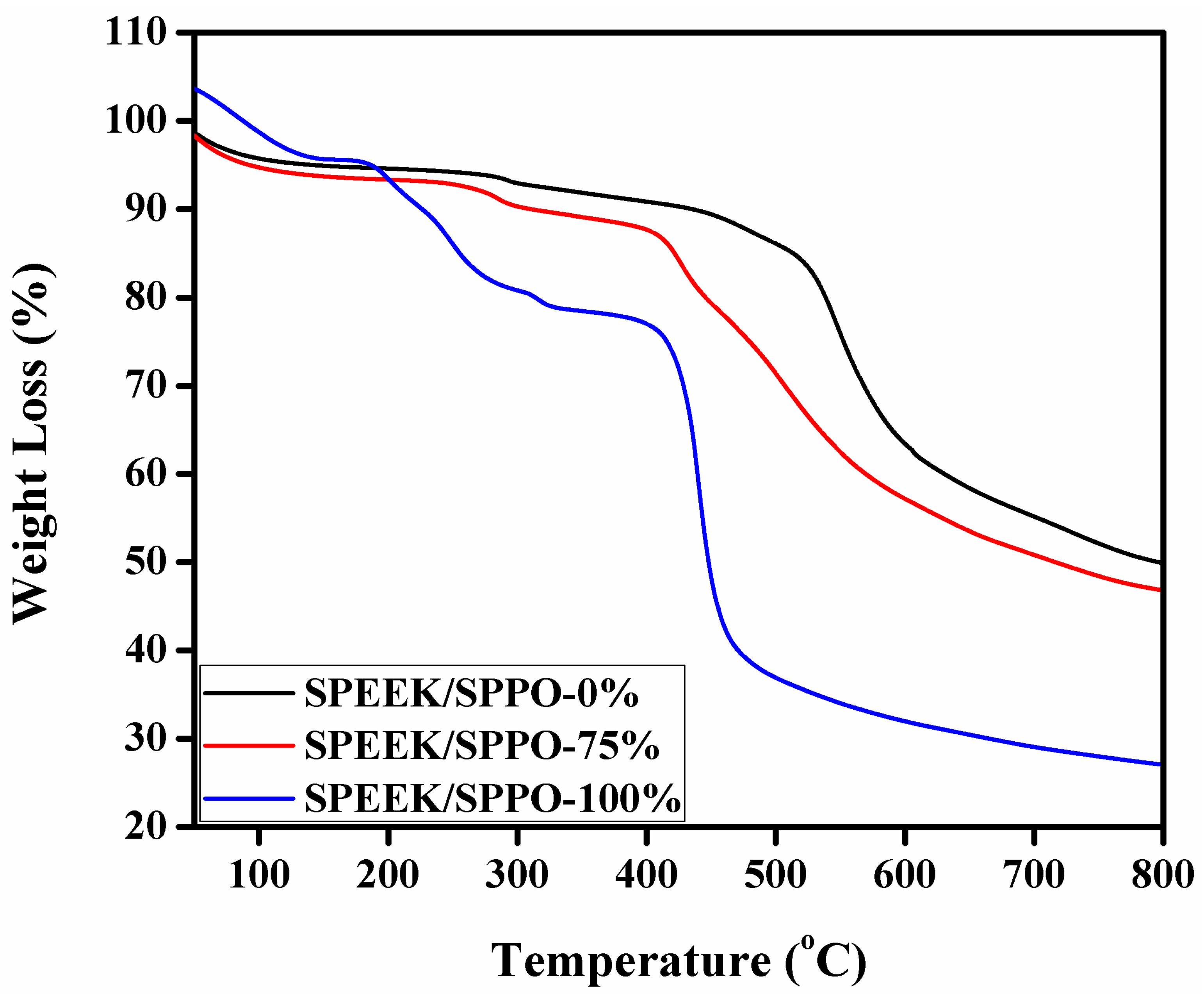
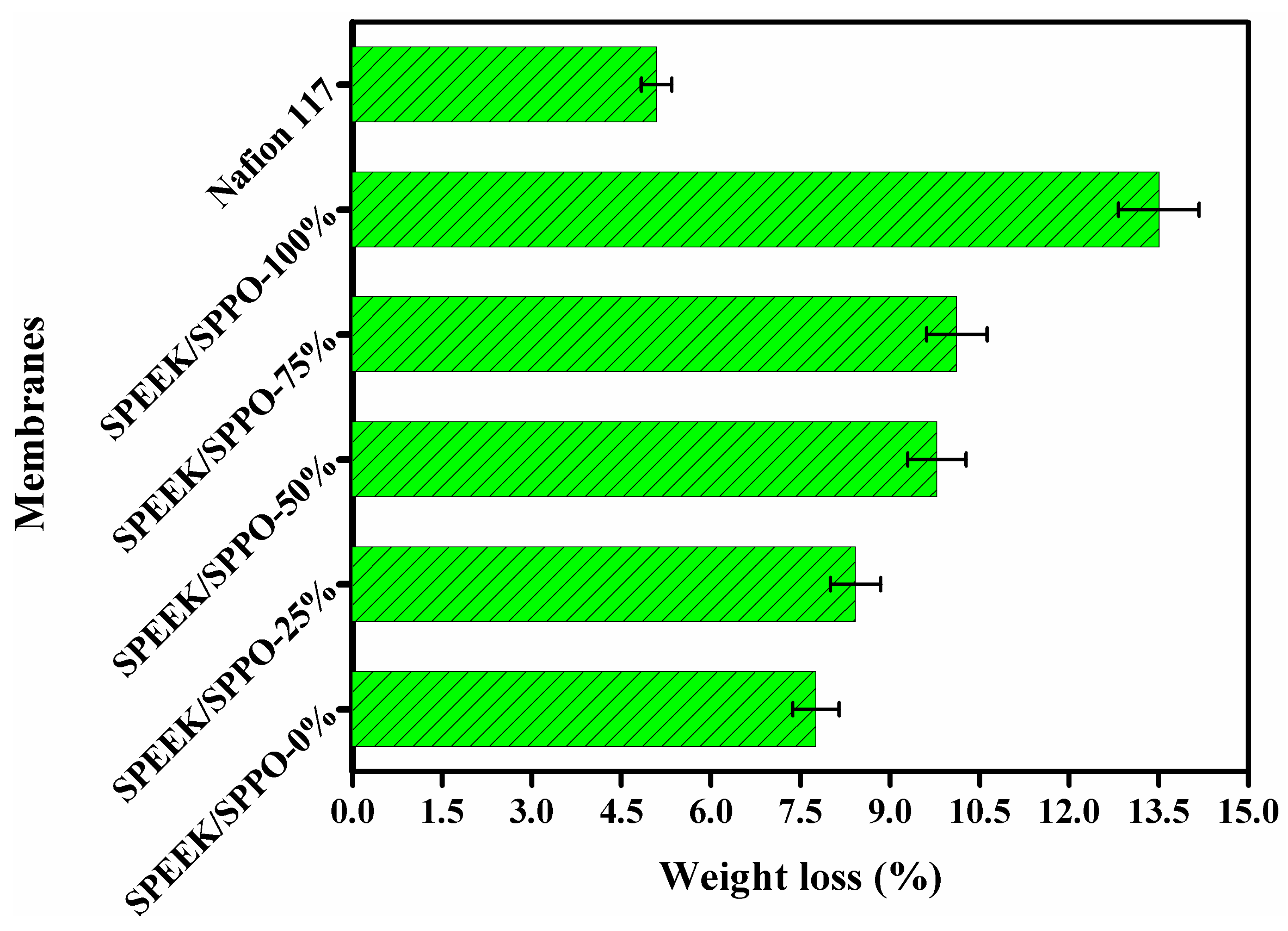
3.6. Thermal and Chemical Stability
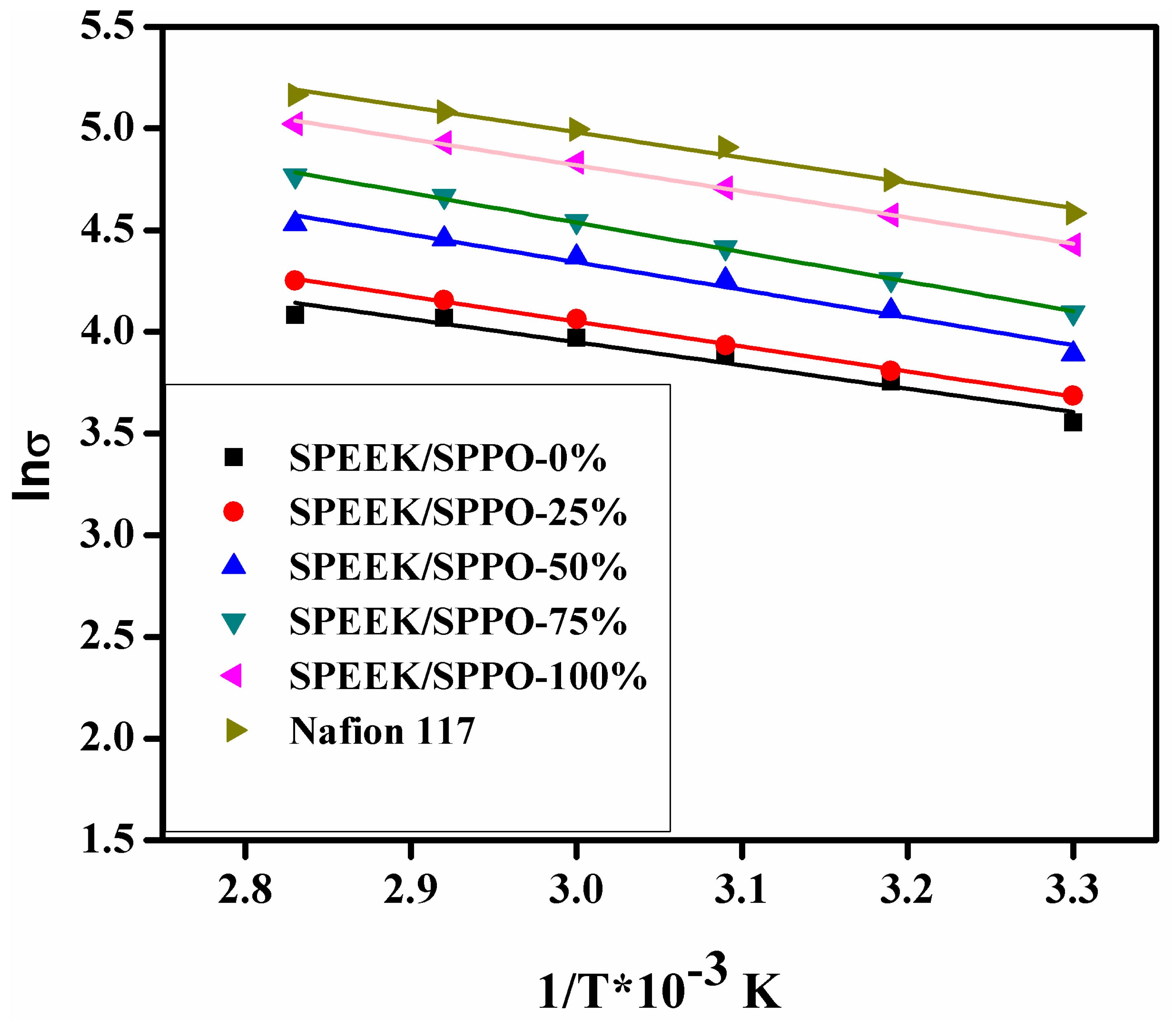
3.7. Proton Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Codes | Full names |
| IEM | Ion exchange membranes |
| PEM | Proton exchange membrane |
| SPEEK | Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) |
| SPPO | Sulfonated poly(phenylene) oxide |
References
- O’Hayre, R.; Cha, S.-K.; Colella, W.; Prinz, F.B. Fuel Cell Fundamentals; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Laberty-Robert, C.; Valle, K.; Pereira, F.; Sanchez, C. Design and properties of functional hybrid organic-inorganic membranes for fuel cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 961–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Ling, L.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Trifluoromethanesulfonimide-based hygroscopic semi-interpenetrating polymer network for enhanced proton conductivity of nafion-based proton exchange membranes at low humidity. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogungbemi, E.; Ijaodola, O.; Khatib, F.N.; Wilberforce, T.; El Hassan, Z.; Thompson, J.; Ramadan, M.; Olabi, A.G. Fuel cell membranes–pros and cons. Energy 2019, 172, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izhan Noor Azam, A.M.; Choon, P.M.; Masdar, M.S.; Zainoodin, A.M.; Husaini, T. Performance and water transport behaviour in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.S.; Soni, U.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, D.; Choudhary, V. Semi-interpenetrating polymer networks of poly (vinyl alcohol)-functionalized nanocrystals/sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) (pva-fncs/speek) as fuel cell membrane. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; Alaswad, A.; Palumbo, A.; Dassisti, M.; Olabi, A.G. Advances in stationary and portable fuel cell applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 16509–16522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alaswad, A.; Baroutaji, A.; Achour, H.; Carton, J.; Al Makky, A.; Olabi, A.G. Developments in fuel cell technologies in the transport sector. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 16499–16508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Shi, Z.; Glass, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, D.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wang, H.; Shen, J. A review of pem hydrogen fuel cell contamination: Impacts, mechanisms, and mitigation. J. Power Sources 2007, 165, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayahi, A.; Ismail, A.F.; Ilbeygi, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ghasemi, M.; Norddin, M.N.A.M.; Matsuura, T. Effect of operating temperature on the behavior of promising speek/csmm electrolyte membrane for dmfcs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 106, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikala, S.; Meenakshi, S.; Bhat, S.D.; Sahu, A.K. Functionalized bentonite clay-speek based composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 135, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakasabai, P.; Vijay, P.; Deshpande, A.P.; Varughese, S. Crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)/sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) blend membranes for fuel cell applications—Surface energy characteristics and proton conductivity. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grot, W. Fluorinated Ionomers; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Satyapal, S. Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. In 5th International Conference on Polymer Batteries & Fuel Cells; US Department of Energy: Argonne, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Epping Martin, K.; Kopasz, J. The us does high temperature membrane effort. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffin, G.A.; Haugen, G.M.; Hamrock, S.J.; Di Noto, V. Interplay between structure and relaxations in perfluorosulfonic acid proton conducting membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 822–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyatake, K.; Zhou, H.; Matsuo, T.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. Proton conductive polyimide electrolytes containing trifluoromethyl groups: Synthesis, properties, and dmfc performance. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4961–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chul Gil, S.; Chul Kim, J.; Ahn, D.; Jang, J.-S.; Kim, H.; Chul Jung, J.; Lim, S.; Jung, D.-H.; Lee, W. Thermally crosslinked sulfonated polyethersulfone proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deimede, V.; Voyiatzis, G.A.; Kallitsis, J.K.; Qingfeng, L.; Bjerrum, N.J. Miscibility behavior of polybenzimidazole/sulfonated polysulfone blends for use in fuel cell applications. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 7609–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollá, S.; Compañ, V. Polymer blends of speek for dmfc application at intermediate temperatures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 5121–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Xiao, M.; Meng, Y. Preparation and properties of sulfonated poly (fluorenyl ether ketone) membrane for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) membranes for direct methanol fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 226, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaysom, C.; Ladewig, B.P.; Lu, G.M.; Wang, L. Preparation and characterization of sulfonated polyethersulfone for cation-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 368, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Theoretical studies on the morphological and electrical properties of blended pes/speek nanofiltration membranes using different sulfonation degree of speek. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 334, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Bi, C.; Dai, H. Sulfonated poly (tetramethydiphenyl ether ether ketone) membranes for vanadium redox flow battery application. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Yin, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L. Effect of degree of sulfonation and casting solvent on sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Power Sources 2015, 285, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, X.D.; Chen, N. A comparative study of nafion and sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) membrane performance for iron-chromium redox flow battery. Ionics 2019, 25, 4219–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, F.; Pünt, I.; Van der Vegt, N.; Strathmann, H.; Wessling, M. Cation permeable membranes from blends of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) and poly (ether sulfone). J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 199, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.; Hong, Y.T.; Kim, S.C. Phase separation and morphology control of polymer blend membranes of sulfonated and nonsulfonated polysulfones for direct methanol fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohil, G.; Nagarale, R.; Binsu, V.; Shahi, V.K. Preparation and characterization of monovalent cation selective sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) and poly (ether sulfone) composite membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Okamoto, K.-I. Preparation and properties of cross-linked sulfonated poly (arylene ether sulfone)/sulfonated polyimide blend membranes for fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Sarikhani, K.; Majedi, F.S.; Khanbabaei, G. Electrochemical investigation of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/clay nanocomposite membranes for moderate temperature fuel cell applications. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2450–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, N.Y.; Harrison, W.L.; Badami, A.S.; Roy, A.; Lane, O.; Cromer, F.; Dong, L.; McGrath, J.E. Hydrocarbon and partially fluorinated sulfonated copolymer blends as functional membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argun, A.A.; Ashcraft, J.N.; Hammond, P.T. Highly conductive, methanol resistant polyelectrolyte multilayers. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Wang, K.; Kaliaguine, S. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) for proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 229, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.I.; Fernandez-Garcia, J.; Zhu, Q.-L. Fabrication of doubly charged anion-exchange membranes for enhancing hydroxide conductivity. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Li, X.; Fernandez-Garcia, J.; Lashari, M.H.; Rehman, A.; Elboughdiri, N.; Kolsi, L.; Ghernaout, D. Effect of different quaternary ammonium groups on the hydroxide conductivity and stability of anion exchange membranes. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7994–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Shanableh, A.; Fernandez, J.; Lashari, M.H.; Shahida, S.; Manzoor, S.; Zafar, S.; Rehman, A.; Elboughdiri, N. Synthesis of dmea-grafted anion exchange membrane for adsorptive discharge of methyl orange from wastewaters. Membranes 2021, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Khraisheh, M.; AlMomani, F. Innovative BPPO anion exchange membranes formulation using diffusion dialysis-enhanced acid regeneration system. Membranes 2021, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Su, J.; Guo, L. Preparation and characterization of high-performance anion exchange membranes for acid recovery. Desal. Water Treat. 2021, 209, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Su, J.; Guo, L. Development of triethanolamine functionalized-anion exchange membrane for adsorptive removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. Desal. Water Treat. 2021, 209, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Shanableh, A.; Elboughdiri, N.; Kriaa, K.; Ghernaout, D.; Ghareba, S.; Khraisheh, M.; Lashari, M.H. Higher acid recovery efficiency of novel functionalized inorganic/organic composite anion exchange membranes from acidic wastewater. Membranes 2021, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Zheng, C.; Mondal, A.N.; Hossain, M.M.; Wu, B.; Emmanuel, K.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Preparation of anion exchange membranes from bppo and dimethylethanolamine for electrodialysis. Desalination 2017, 402, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.I.; Mondal, A.N.; Tong, B.; Jiang, C.; Emmanuel, K.; Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Development of BPPO-based anion exchange membranes for electrodialysis desalination applications. Desalination 2016, 391, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, A.N.; Zheng, C.; Cheng, C.; Hossain, M.M.; Khan, M.I.; Yao, Z.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Effect of novel polysiloxane functionalized poly(amps-co-cea) membranes for base recovery from alkaline waste solution via diffusion dialysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 5256–95267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Khraisheh, M.; Almomani, F. Fabrication and characterization of pyridinium functionalized anion exchange membranes for acid recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Khraisheh, M. Synthesis and characterization of stable anion exchange membranes for desalination applications. Desal. Water Treat. 2018, 113, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinh, V.D.C.; Thuc, V.D.; Kim, D. Chemically sustainable fuel cells via layer-by-layer fabrication of sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) membranes containing cerium oxide nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 634, 119430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Sui, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, B.; Cong, C.; Meng, X.; Zhou, Q. Sandwich-structure pi/speek/pi proton exchange membrane developed for achieving the high durability on excellent proton conductivity and stability. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 120116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Zhang, S. Synthesis of poly(arylene ether sulfone)s with locally and densely sulfonated pentiptycene pendants as highly conductive polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9876–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Bi, D.; Lin, H.; Shao, K.; Fu, T.; Zhong, S.; Na, H. Blend membranes based on disulfonated poly(aryl ether ether ketone)s (speek) and poly(amide imide) (pai) for direct methanol fuel cell usages. Polymer 2007, 48, 3090–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Exploration of highly sulfonated polyethersulfone (spes) as a membrane material with the aid of dual-layer hollow fiber fabrication technology for protein separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 309, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, J.; Kim, B.H.; Henkensmeier, D.; Jang, J.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; et al. Facile preparation of a long-term durable nano- and micro-structured polymer blend membrane for a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46516–46522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, G.; Xu, D.; Zhao, C.; Ma, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, S.; Jiang, H.; Sun, H.; et al. Cross-linked membranes based on sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone) (speek)/nafion for direct methanol fuel cells (dmfcs). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 11025–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Constructing proton-conductive highways within an ionomer membrane by embedding sulfonated polymer brush modified graphene oxide. J. Power Sources 2015, 286, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I. Comparison of different quaternary ammonium groups on desalination performance of BPPO-based anion exchange membranes. Desal. Water Treat. 2018, 108, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Mondal, A.N.; Cheng, C.; Pan, J.; Emmanuel, K.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Porous BPPO-based membranes modified by aromatic amine for acid recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Mondal, A.N.; Emmanuel, K.; Hossain, M.M.; Afsar, N.U.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Preparation of pyrrolidinium-based anion-exchange membranes for acid recovery via diffusion dialysis. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakangura, E.; Ge, L.; Muhammad, M.; Pan, J.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. Sandwich structure sppo/bppo proton exchange membranes for fuel cells: Morphology–electrochemical properties relationship. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Membranes | SPEEK (g) | SPPO (g) | IEC (mmol/g) | WR (%) | MS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPEEK/SPPO-0% | 100 | 0 | 1.23 | 22.92 | 7.53 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-25% | 75 | 25 | 1.35 | 43.06 | 11.39 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-50% | 50 | 50 | 1.46 | 47.51 | 16.22 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-75% | 25 | 75 | 1.69 | 59.58 | 21.62 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-100% | 0 | 100 | 2.0 | 64.57 | 25.49 |
| Membranes | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|
| SPEEK/SPPO-0% | 14.36 | 3.89 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-25% | 7.58 | 6.79 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-50% | 14.27 | 8.00 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-75% | 11.48 | 11.35 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-100% | 20.42 | 41.91 |
| Sr. No. | Ea (eV) |
|---|---|
| SPEEK/SPPO-0% | 9.49 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-25% | 10.31 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-50% | 11.29 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-75% | 12.05 |
| SPEEK/SPPO-100% | 10.68 |
| Nafion 117 | 10.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, M.I.; Shanableh, A.; Shahida, S.; Lashari, M.H.; Manzoor, S.; Fernandez, J. SPEEK and SPPO Blended Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Membranes 2022, 12, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030263
Khan MI, Shanableh A, Shahida S, Lashari MH, Manzoor S, Fernandez J. SPEEK and SPPO Blended Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030263
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Muhammad Imran, Abdallah Shanableh, Shabnam Shahida, Mushtaq Hussain Lashari, Suryyia Manzoor, and Javier Fernandez. 2022. "SPEEK and SPPO Blended Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells" Membranes 12, no. 3: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030263
APA StyleKhan, M. I., Shanableh, A., Shahida, S., Lashari, M. H., Manzoor, S., & Fernandez, J. (2022). SPEEK and SPPO Blended Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Membranes, 12(3), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030263








