MOF-Derived Nanoporous Carbon Incorporated in the Cation Exchange Membrane for Gradient Power Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CEMs
2.2.1. Synthesis of sPPO
2.2.2. Preparation of HZCs
2.2.3. Synthesis of the Nanocomposite CEM
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Physicochemical and Electrochemical Properties of Membrane
2.4.1. Swelling Degree (SD)
2.4.2. Ion-Exchange Capacity (IEC)
2.4.3. Permselectivity
2.4.4. Electrical Resistance
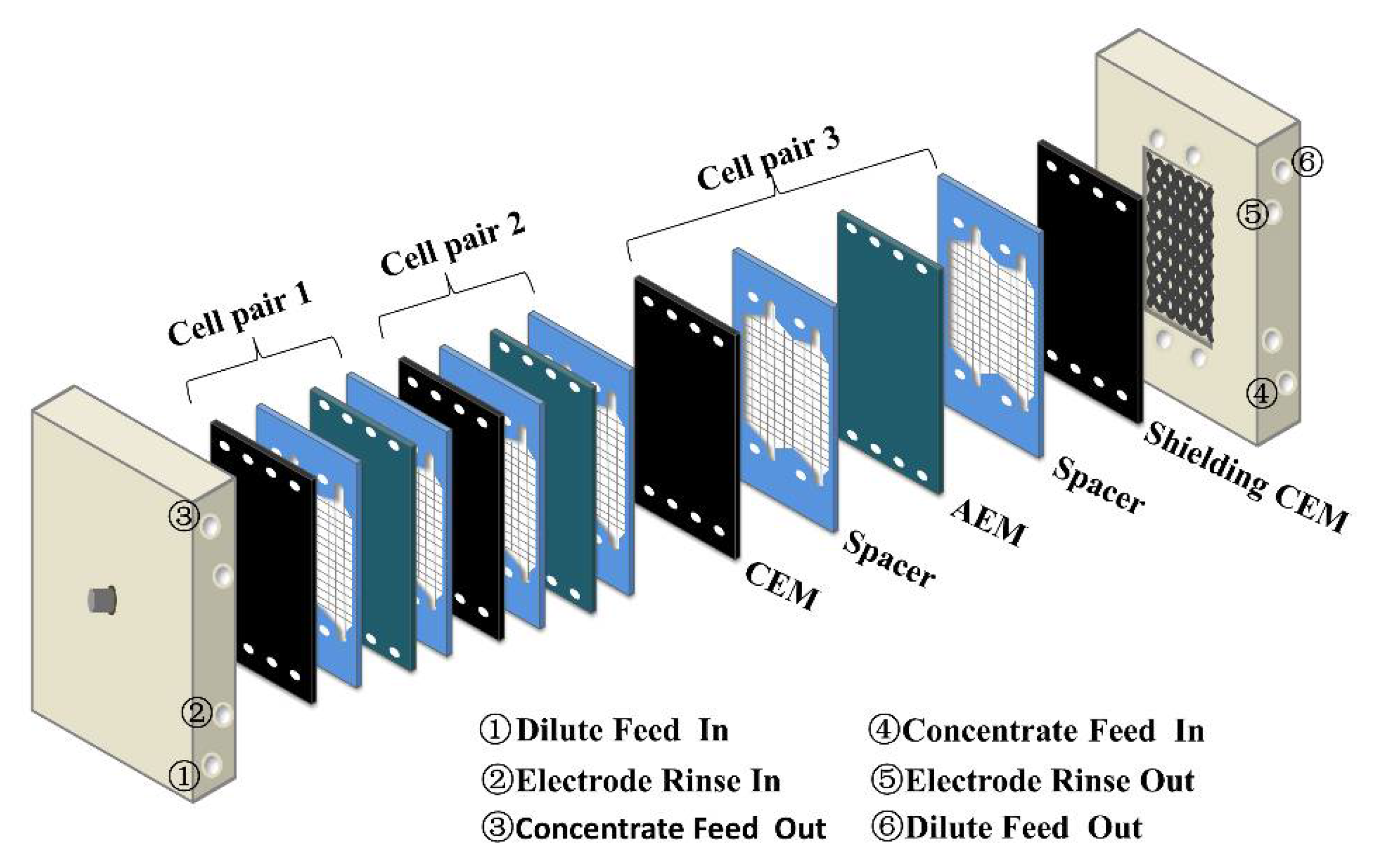
2.5. Power Generation of the Nanocomposite Membrane
3. Results and Discussion
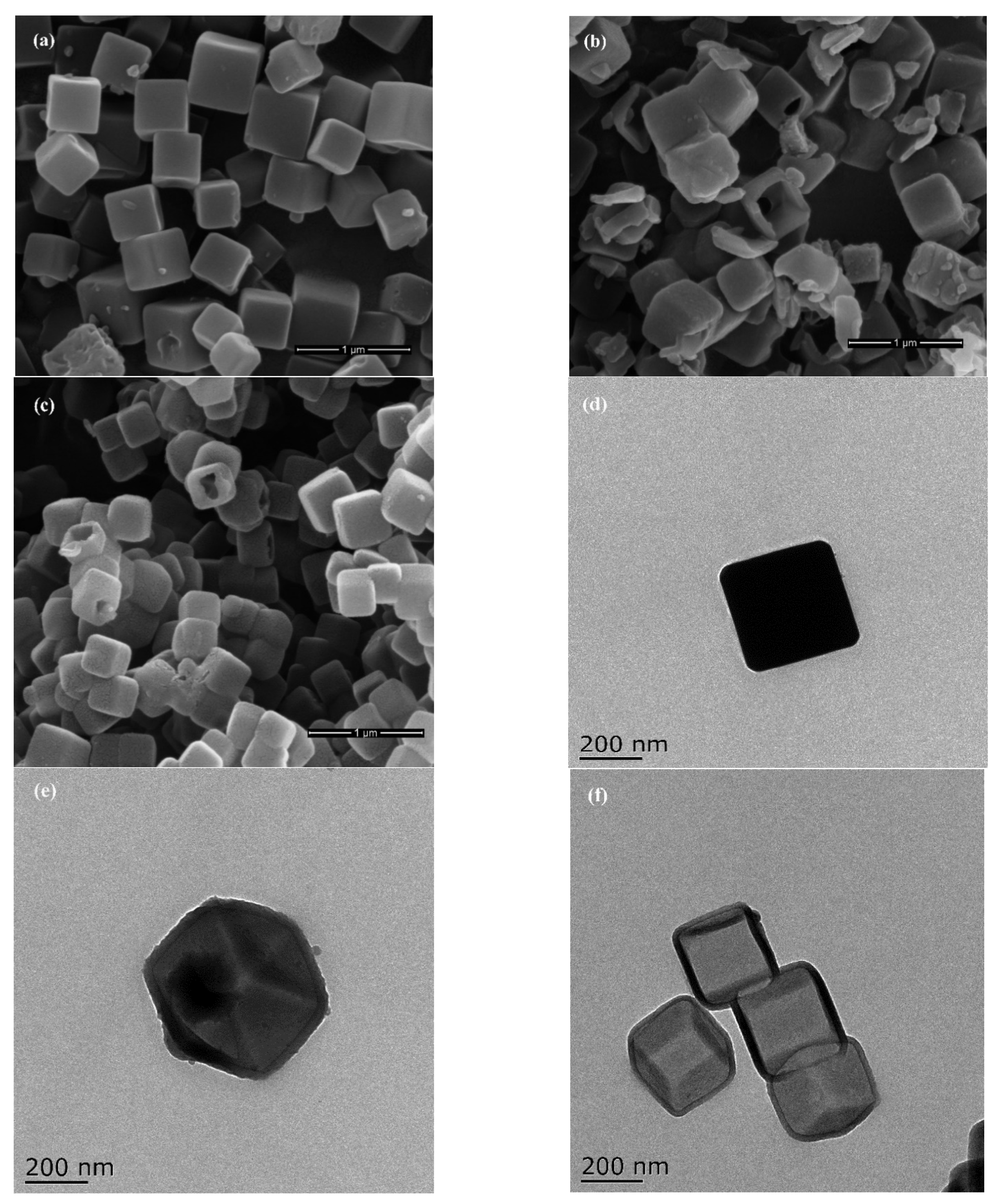
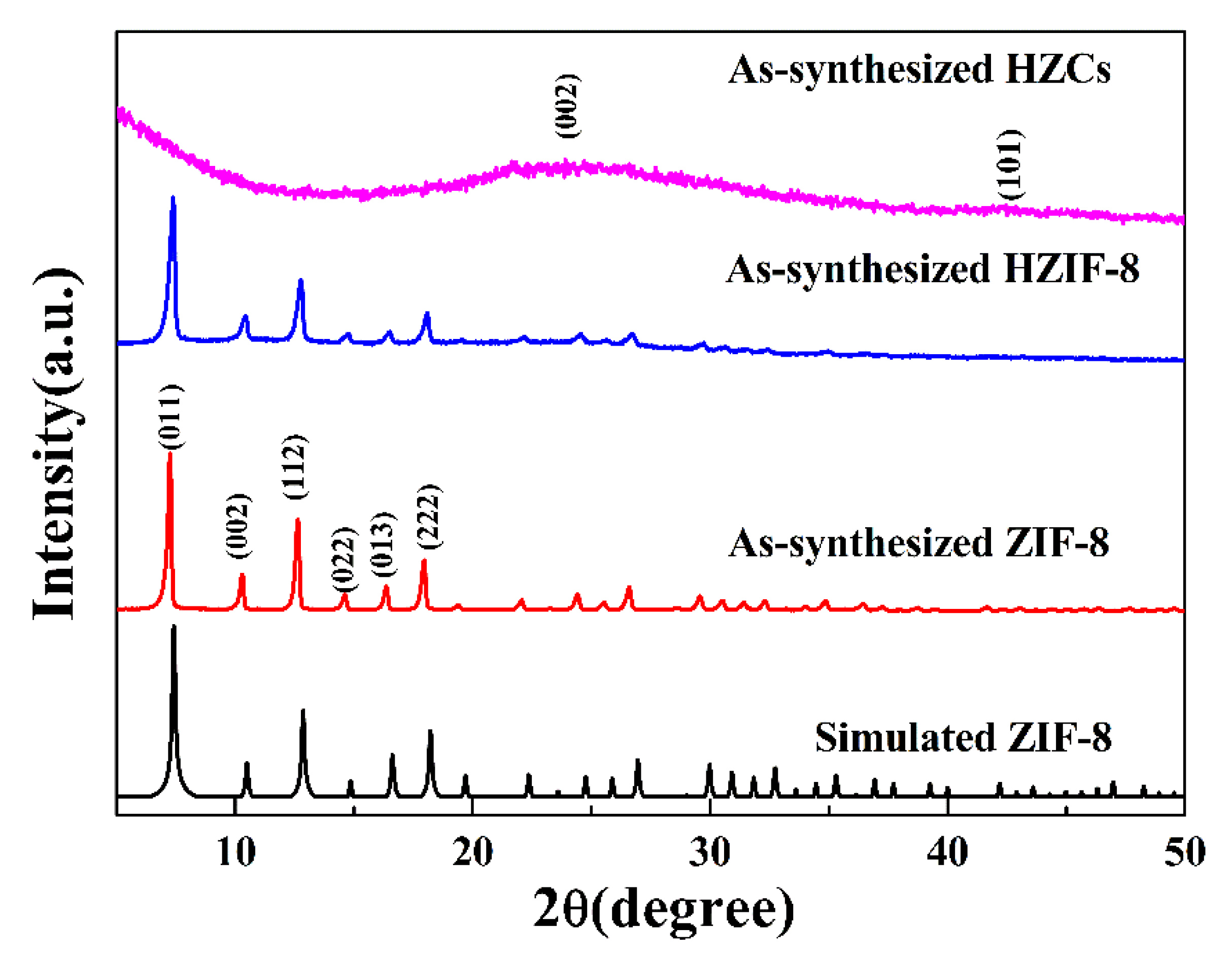
3.1. MOF-Derived Nanoporous Carbon Characterization
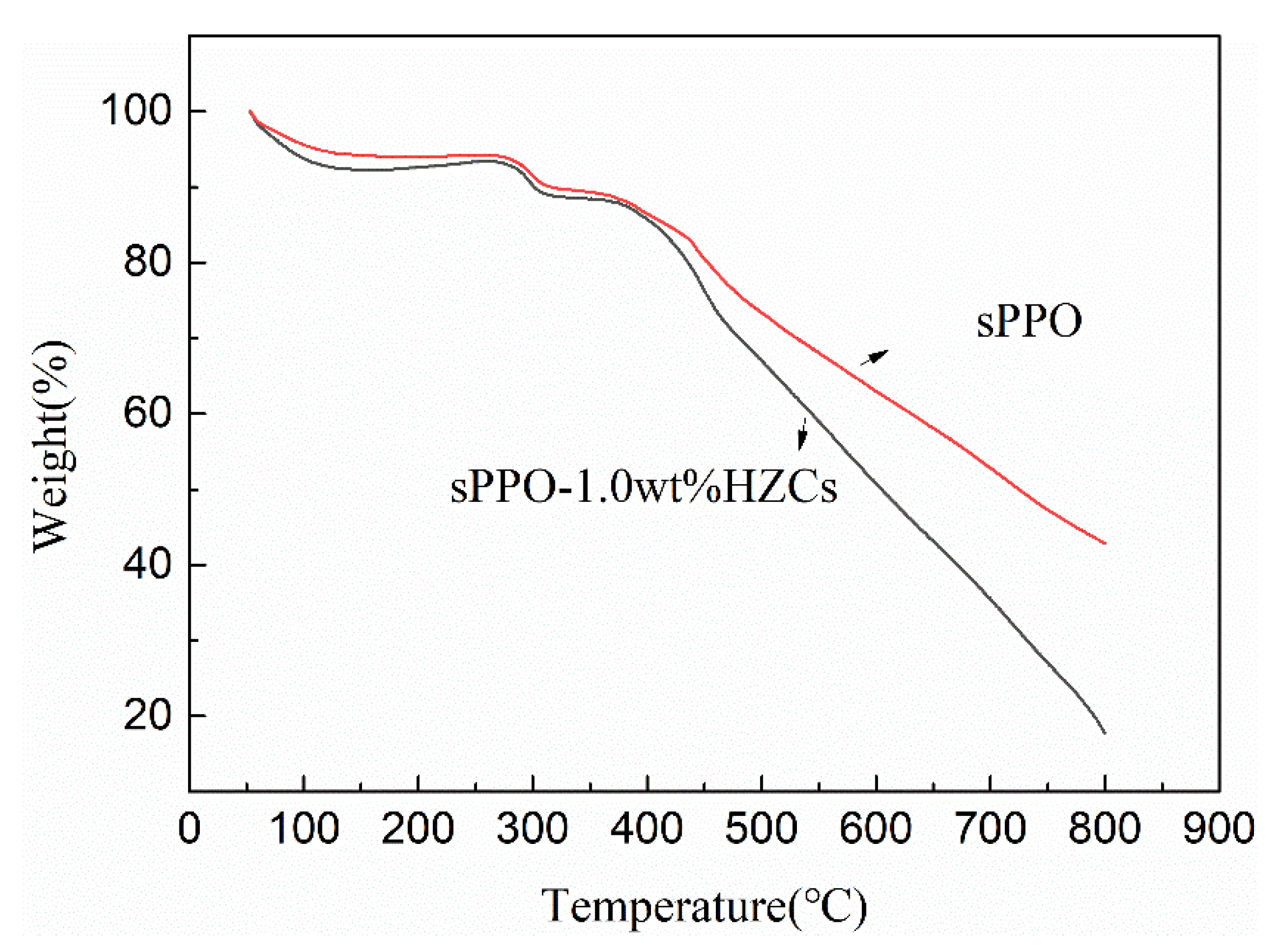
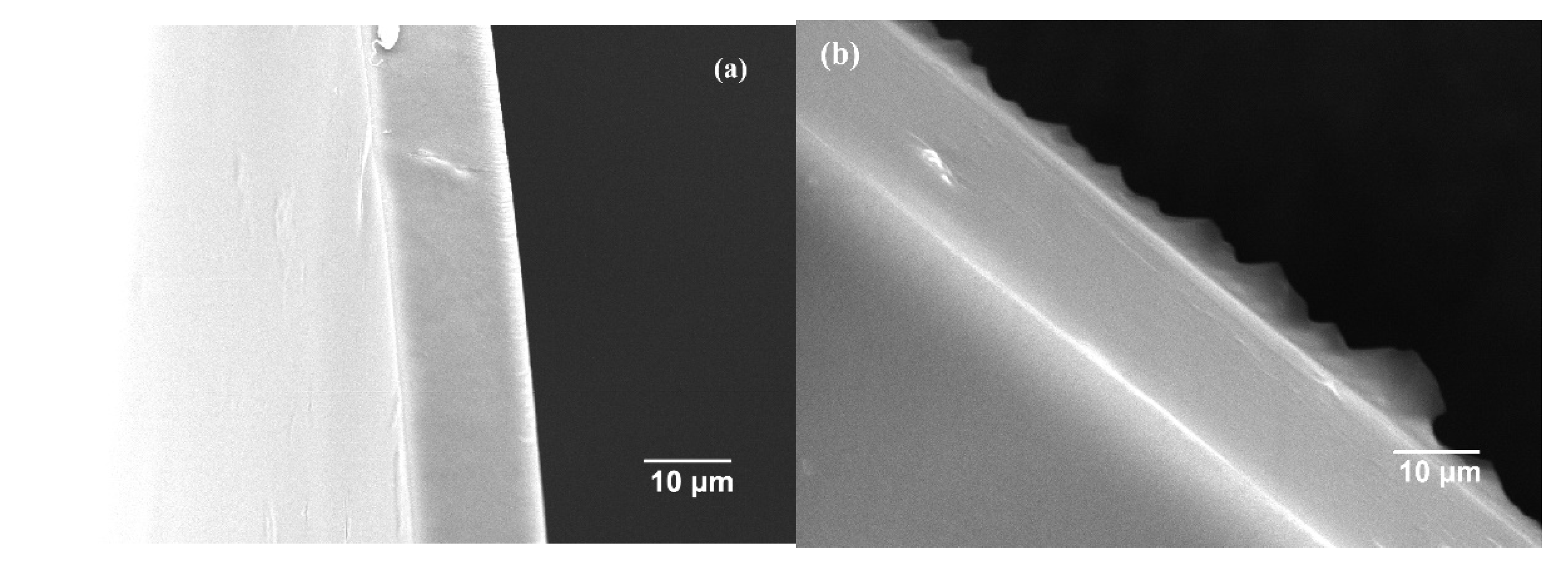
3.2. Membrane Characterization
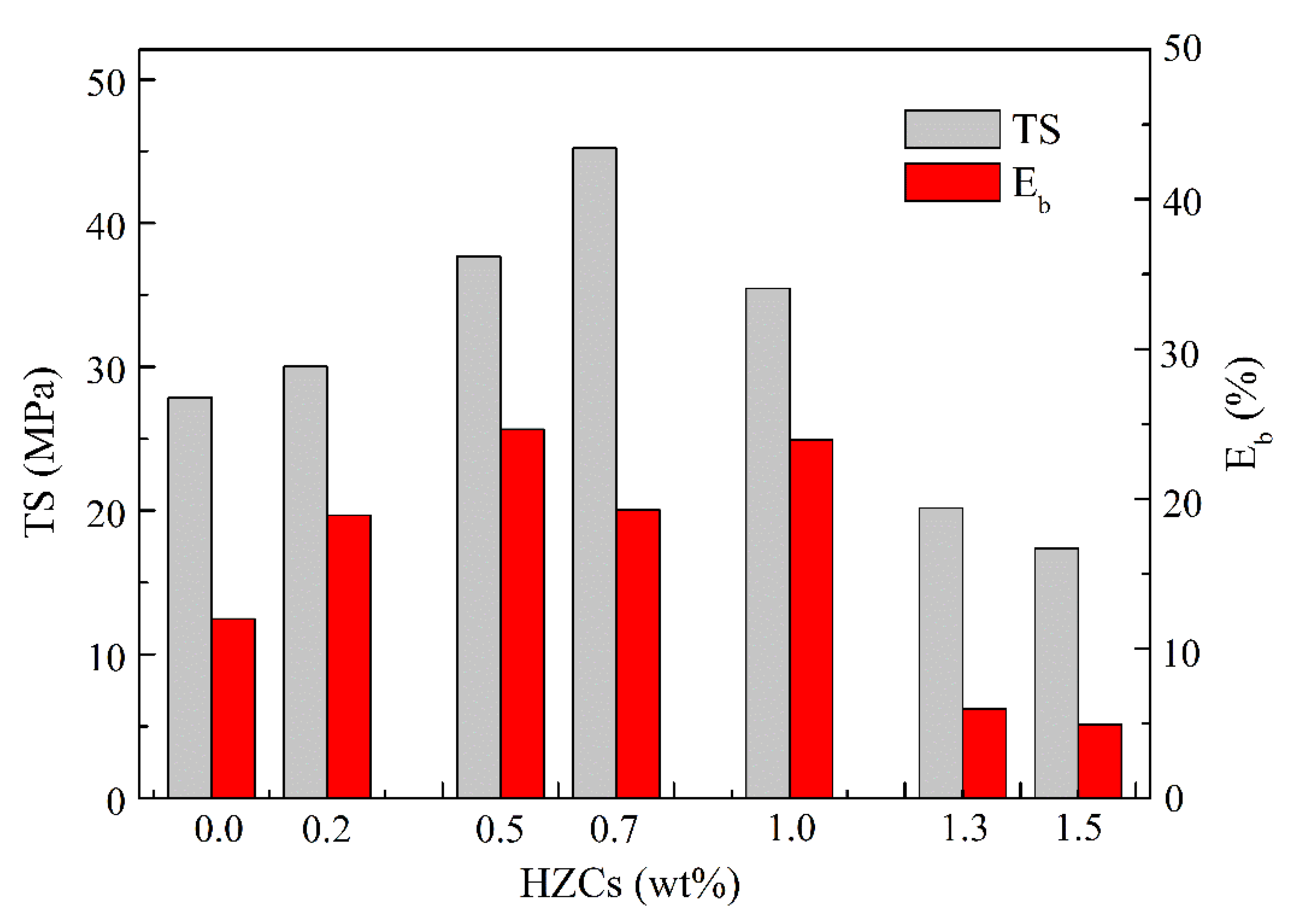
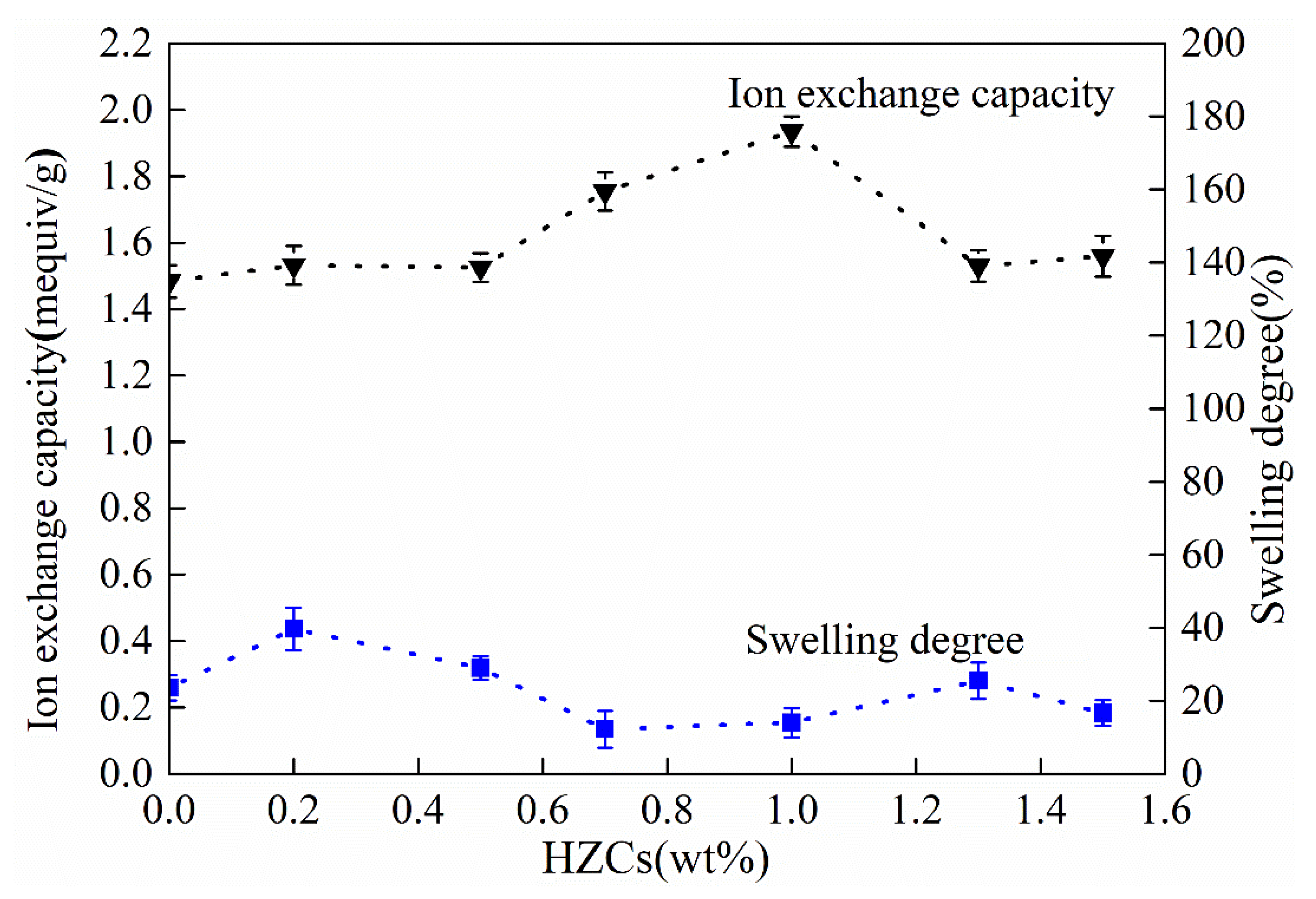
3.3. Physicochemical and Electrochemical Properties of the Membrane
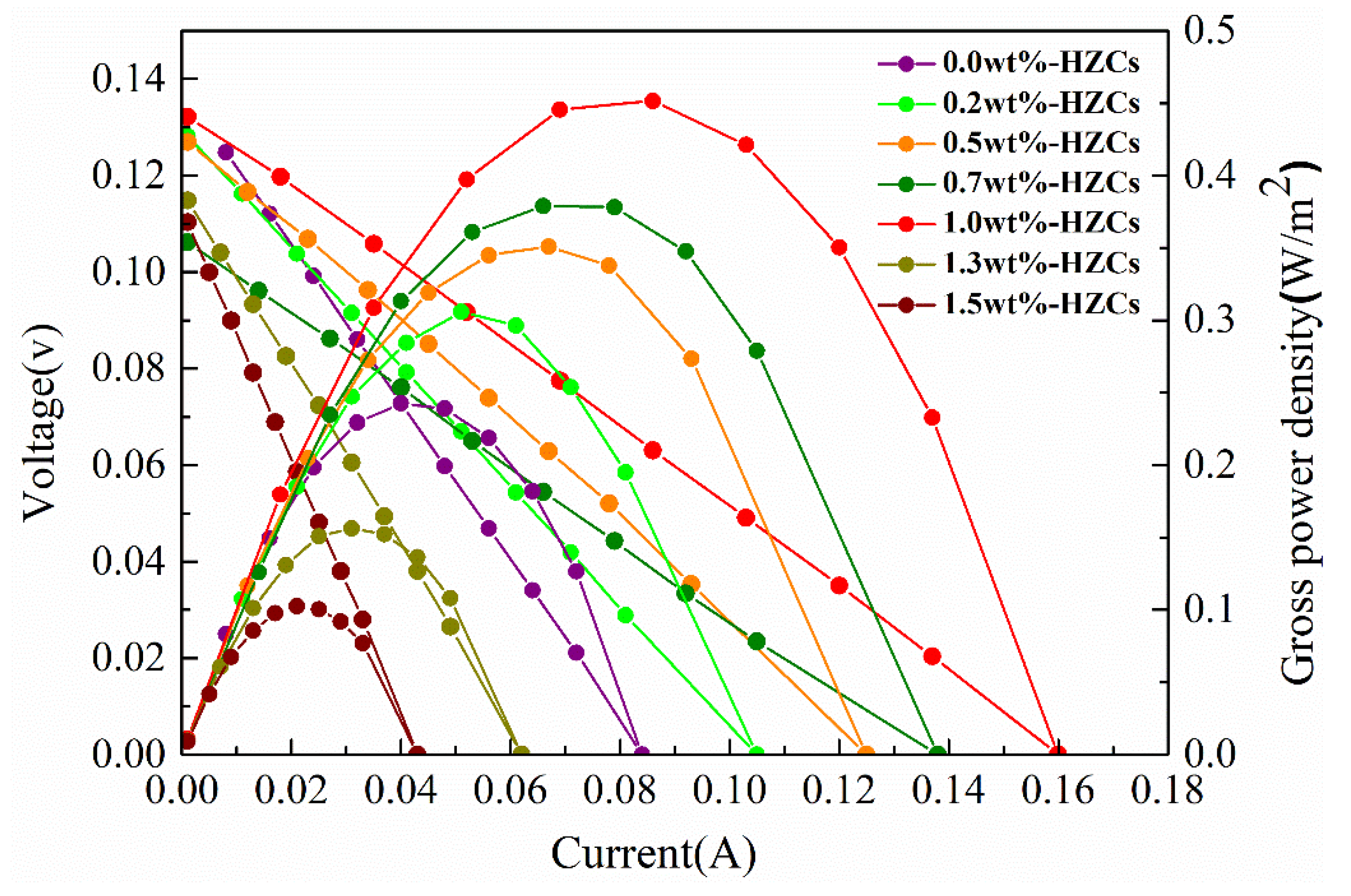
3.4. Power Generation Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IEMs | Ion exchange membranes |
| RED | Reverse electrodialysis |
| SGP | Ssalinity gradient power |
| MOF | Metal organic framework |
| ZIF | Hollow zeolitic imidazolate framework |
| ZIF-8 | Zeolite imidazolate framework-8 |
| HZIF-8 | ZIF-8 cubic nanocrystals and hollow ZIF-8 |
| HZCs | Hollow zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived nanoporous carbons |
| sPPO | A sulfonated poly (2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) |
| CEM | Cation exchange membrane |
| AEM | Anion exchange membrane |
| SD | Swelling degree |
| IEC | Ion exchange capacity |
| PDDA | Poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride |
| PVA | Poly (vinyl alcohol) |
| PPO | Poly (2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) |
| CTAB | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide |
References
- Kim, J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.K. Energy harvesting from salinity gradient by reverse electrodialysis with anodic alumina nanopores. Energy 2013, 51, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Chen, Y.S. Nanocomposite reverse electrodialysis (RED) ion-exchange membranes for salinity gradient power generation. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 460, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, N.Y.; Elimelech, M. Thermodynamic and energy efficiency analysis of power generation from natural salinity gradients by pressure retarded osmosis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5230–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, J.N.; Leitz, F.B. Electric power from differences in salinity: The dialytic Battery. Science 1976, 191, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsen, T.; Holt, T. The potential for power production from salinity gradients by pressure retarded osmosis. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 335, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugolecki, P.; Nymeijer, K.; Metz, S.; Wessling, M. Current status of ion exchange membranes for power generation from salinity gradients. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 319, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Park, T. Electrochemical characterizations and reverse electrodialysis performance of hybrid anion exchange membranes for salinity gradient energy. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 817, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Park, T.; Dhadake, Y. Property evaluation of custom-made ion exchange membranes for electrochemical performance in reverse electrodialysis application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 850, 113437–113444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, M.; Bandura, B. Renewable energy by reverse electrodialysis. Desalination 2007, 205, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfer, F.; Lemckert, C.; Anissimov, Y.G. Osmotic power with Pressure Retarded Osmosis: Theory, performance and trends—A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 453, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, B.; Hong, J.G.; Chen, Y.S. A novel hybrid poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA)/poly (2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) (PPO) membranes for reverse electrodialysis power system. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 239, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.G.; Glabman, S.; Chen, Y.S. Effect of inorganic filler size on electrochemical performance of nanocomposite cation exchange membranes for salinity gradient power generation. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 482, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Yu, S.; Xu, X.; Bao, R.; Xu, J.; Qu, W. Preparation of organic–inorganic hybrid cation-exchange membranes via blending method and their electrochemical characterization. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 328, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.S. Fouling resistant nanocomposite cation exchange membrane with enhanced power generation for reverse electrodialysis. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 516, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, J.G.; Chen, Y.S. Evaluation of electrochemical properties and reverse electrodialysis performance for porous cation exchange membranes with sulfate-functionalized iron oxide. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 473, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Duan, J.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Li, N. Investigation of highly efficient adsorbent based on Ni-MOF-74 in the separation of CO2 from natural gas. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 419, 129653–129661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Qiu, M.; Yang, H.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Recent advances on preparation and environmental applications of MOF-derived carbons in catalysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143333–143358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, Y. Polyaniline nanowires aligned on MOFs-derived nanoporous carbon as high-performance electrodes for supercapacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 390, 138804–138812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, R.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Hollow ZIFs-derived nanoporous carbon for efficient capacitive deionization. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 273, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.H.; Ma, Y.F.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Jiang, Z.J. Spindle-like MOFs-derived porous carbon filled sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone): A high performance proton exchange membrane for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2021, 636, 119585–119597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, A.R.; Madaeni, S.S.; Xu, T.W.; Wu, L.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Na, W.; Zolanvari, S.A.; Babayi, A.; Ghasemi, J.; et al. Preparation, optimization and characterization of novel ion exchange membranes by blending of chemically modified PVDF and SPPO. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 90, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Zhang, Y.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Tailor-Made Anion-exchange membranes for salinity gradient power generation using reverse electrodialysis. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Carné-Sánchez, A.; Malgras, V.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, J.-S.; et al. Hollow carbon nanobubbles: Monocrystalline MOF nanobubbles and their pyrolysis. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, S.; Im, H.; Heo, Y.; Kim, J. Crosslinked sulfonated poly(vinyl alcohol)/sulfonated multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 380, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Zhang, B.P.; Glabman, S.; Uzal, N.; Dou, X.M.; Zhang, H.G.; Wei, X.Z.; Chen, Y.S. Potential ion exchange membranes and system performance in reverse electrodialysis for power generation: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 486, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Nanomaterials | The Blank Membrane | a The Physicochemical Properties of Nanocomposite Membranes | Gross Power Density of the Blank Membrane (W/m2) | Maximum Gross Power Density of the Nanocomposite Membrane (W/m2) | Improved Ratio of Power Density (%) | Refs. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permselectivity (%) | IEC (meq/g) | SD (%) | Area Resistance (Ω/m2) | ||||||
| 0.7 wt.%-Fe2O3–SO42− | sPPO | 87.65 | 1.40 | 26.00 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 1.3 | 32.65 | [2] |
| PDDA | PVA | 59 | 1.48 | 17.50 | 0.77 | b 0.34 | c 0.58 | 70.59 | [7] |
| 5.0 wt.%-sPVA | sPPO | 87 | 1.98 | 48 | 1.55 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 10.87 | [11] |
| d 0.5 wt.%-SiO2–SO3H | sPPO | 81.40 | 0.99 | 33 | 0.95 | 1.08 | 1.3 | 20.37 | [12] |
| 0.5 wt.%-O-MWCNT | sPPO | 95.2 | 2.27 | 41 | 0.5 | 0.36 | 0.48 | 33.33 | [14] |
| 1.0 wt.%-HZCs | sPPO | 77.61 | 1.94 | 14.01 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.45 | 87.50 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, R.; Chen, Y. MOF-Derived Nanoporous Carbon Incorporated in the Cation Exchange Membrane for Gradient Power Generation. Membranes 2022, 12, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030322
Sun X, Liu Y, Xu R, Chen Y. MOF-Derived Nanoporous Carbon Incorporated in the Cation Exchange Membrane for Gradient Power Generation. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030322
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xia, Ying Liu, Ruibo Xu, and Yongsheng Chen. 2022. "MOF-Derived Nanoporous Carbon Incorporated in the Cation Exchange Membrane for Gradient Power Generation" Membranes 12, no. 3: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030322
APA StyleSun, X., Liu, Y., Xu, R., & Chen, Y. (2022). MOF-Derived Nanoporous Carbon Incorporated in the Cation Exchange Membrane for Gradient Power Generation. Membranes, 12(3), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030322





