Pollution and Cleaning of PDMS Pervaporation Membranes after Recovering Ethyl Acetate from Aqueous Saline Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Materials
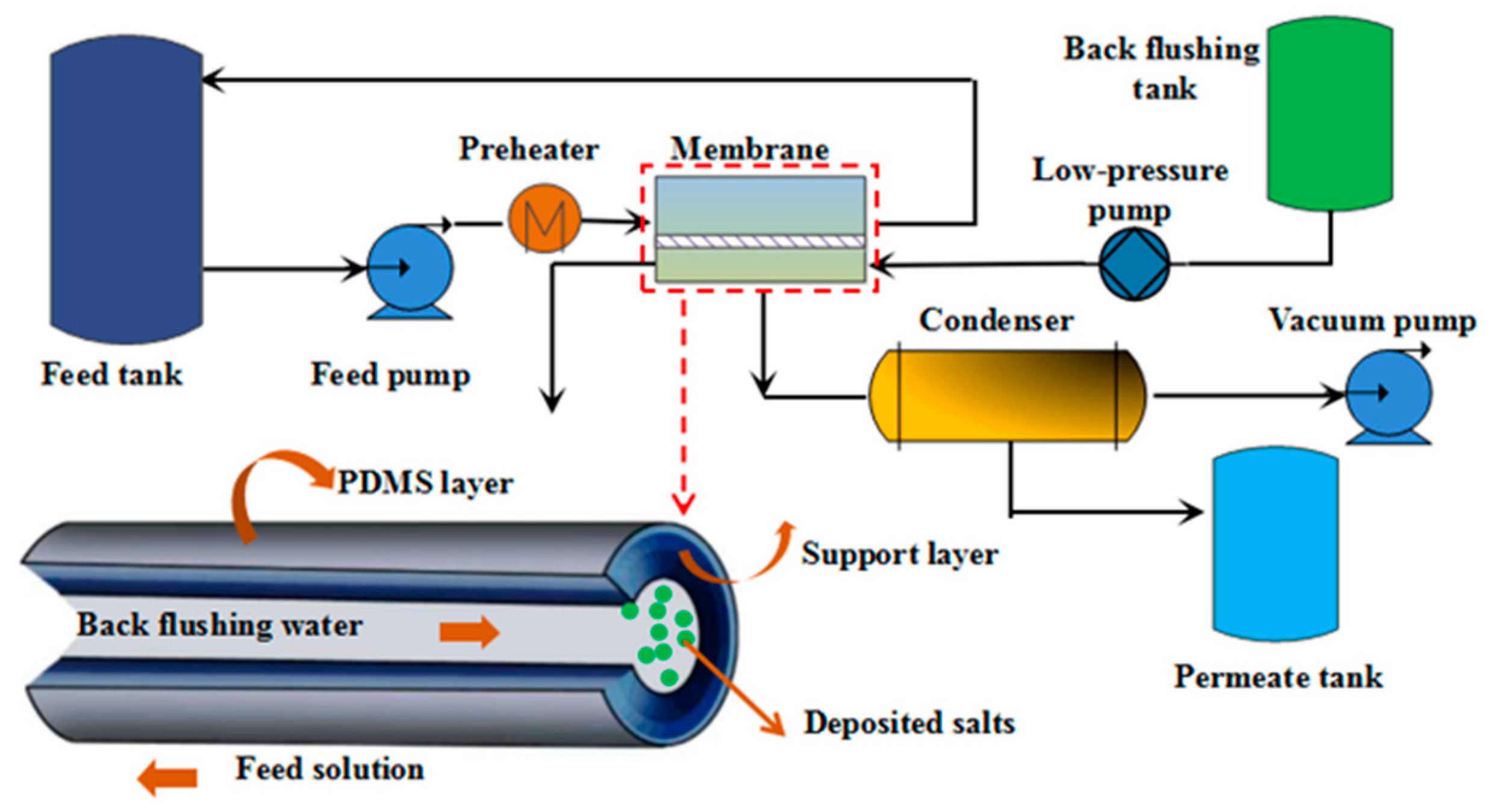
2.2. Experimental Device
2.3. Experimental Procedures and Tests
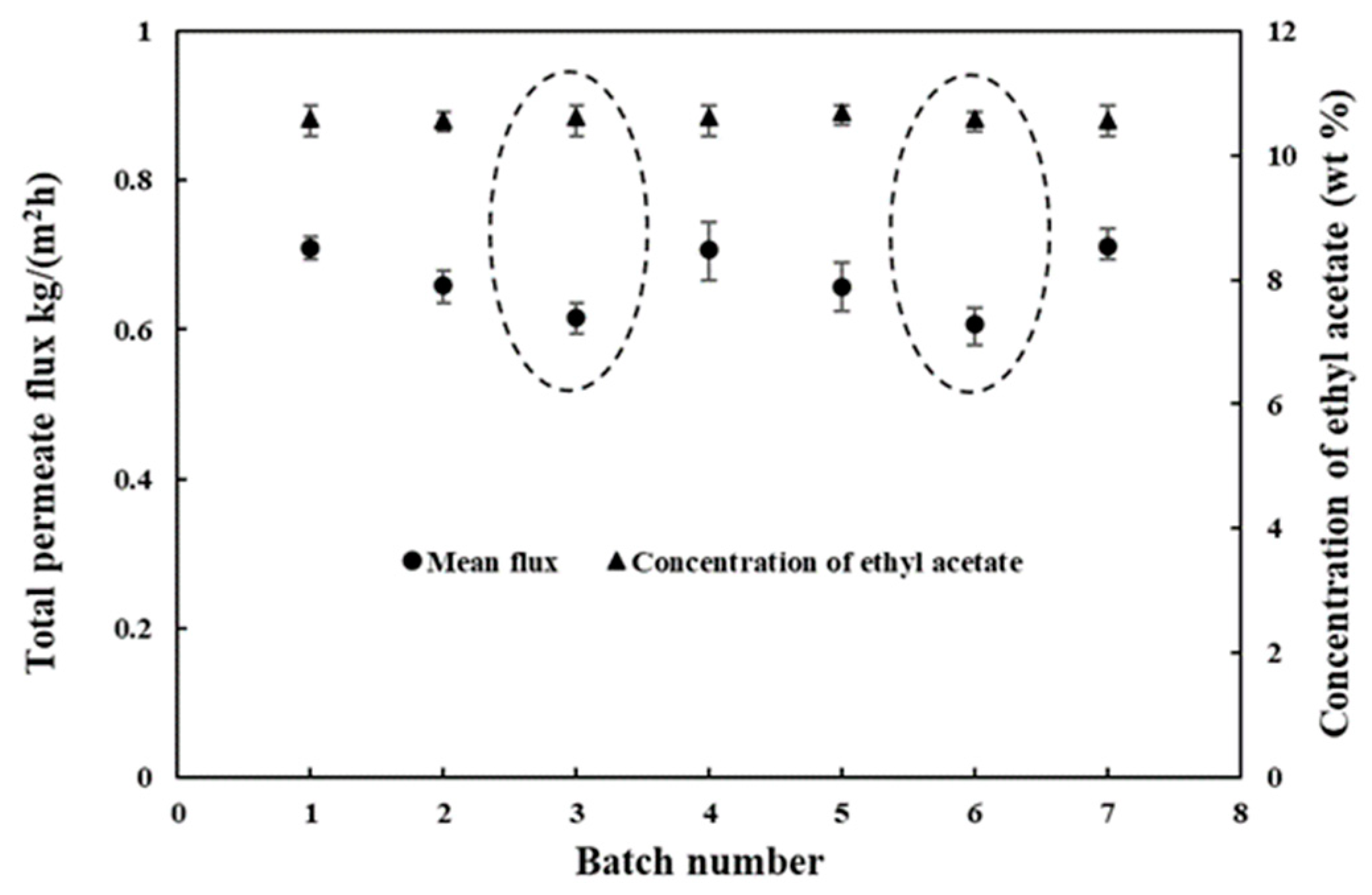
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Salts on the PV Performance
3.1.1. Pervaporation Performance of the PDMS Membrane in the Presence of Salt
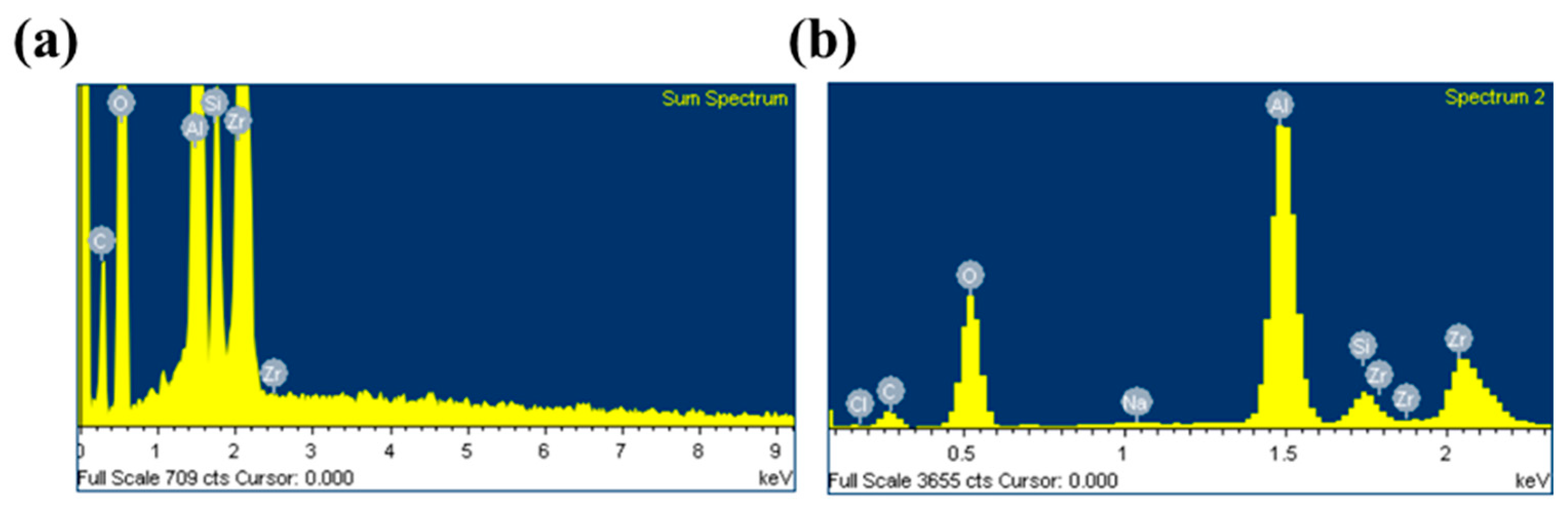
3.1.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy–Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analysis (SEM–EDX) Observation of the Virgin and Fouled Membranes
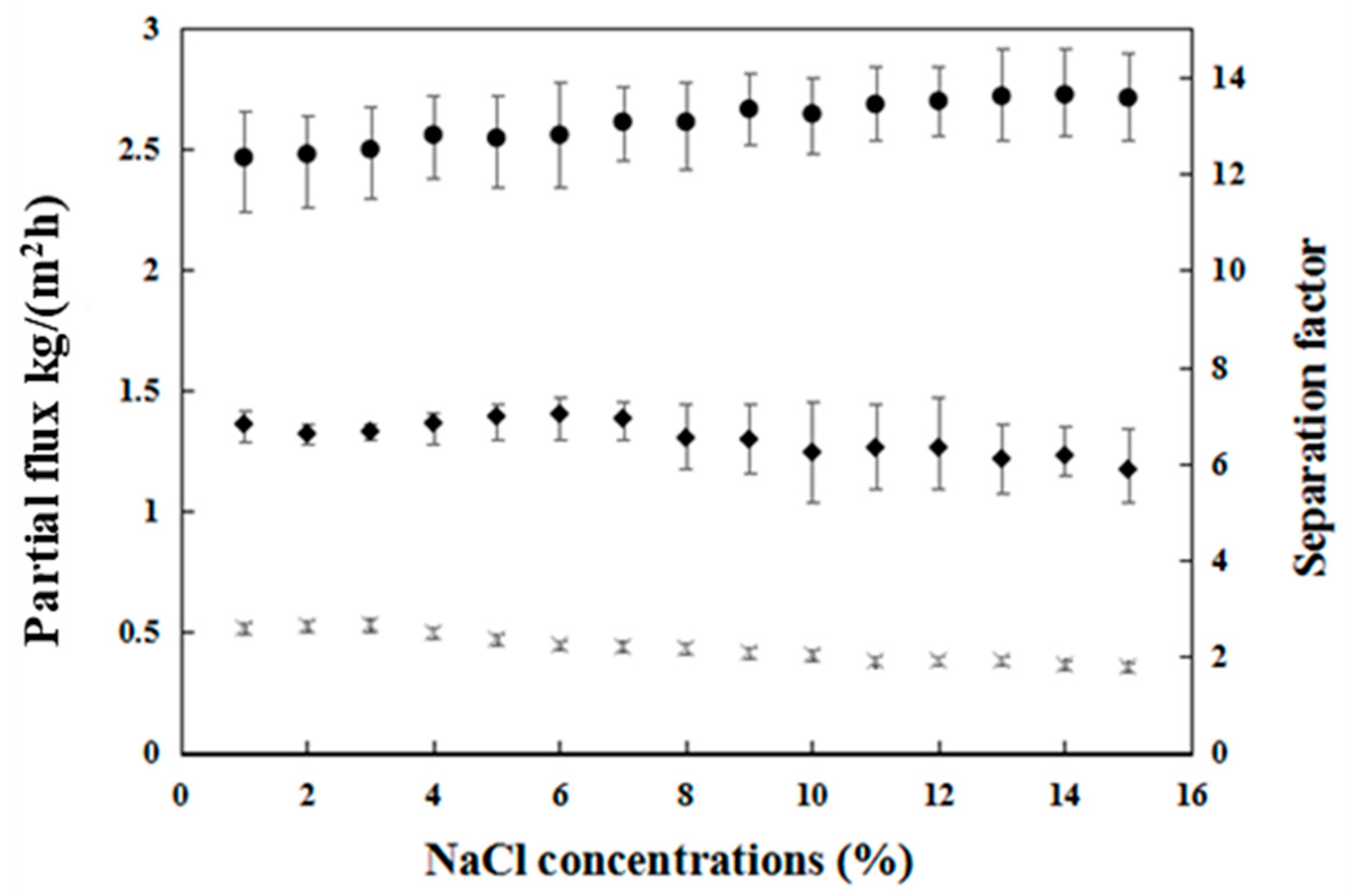
3.1.3. Influence of NaCl Concentration on Pervaporation Performance
3.1.4. Influence of Various Salt Species on the Pervaporation Performance
3.2. Membrane Cleaning
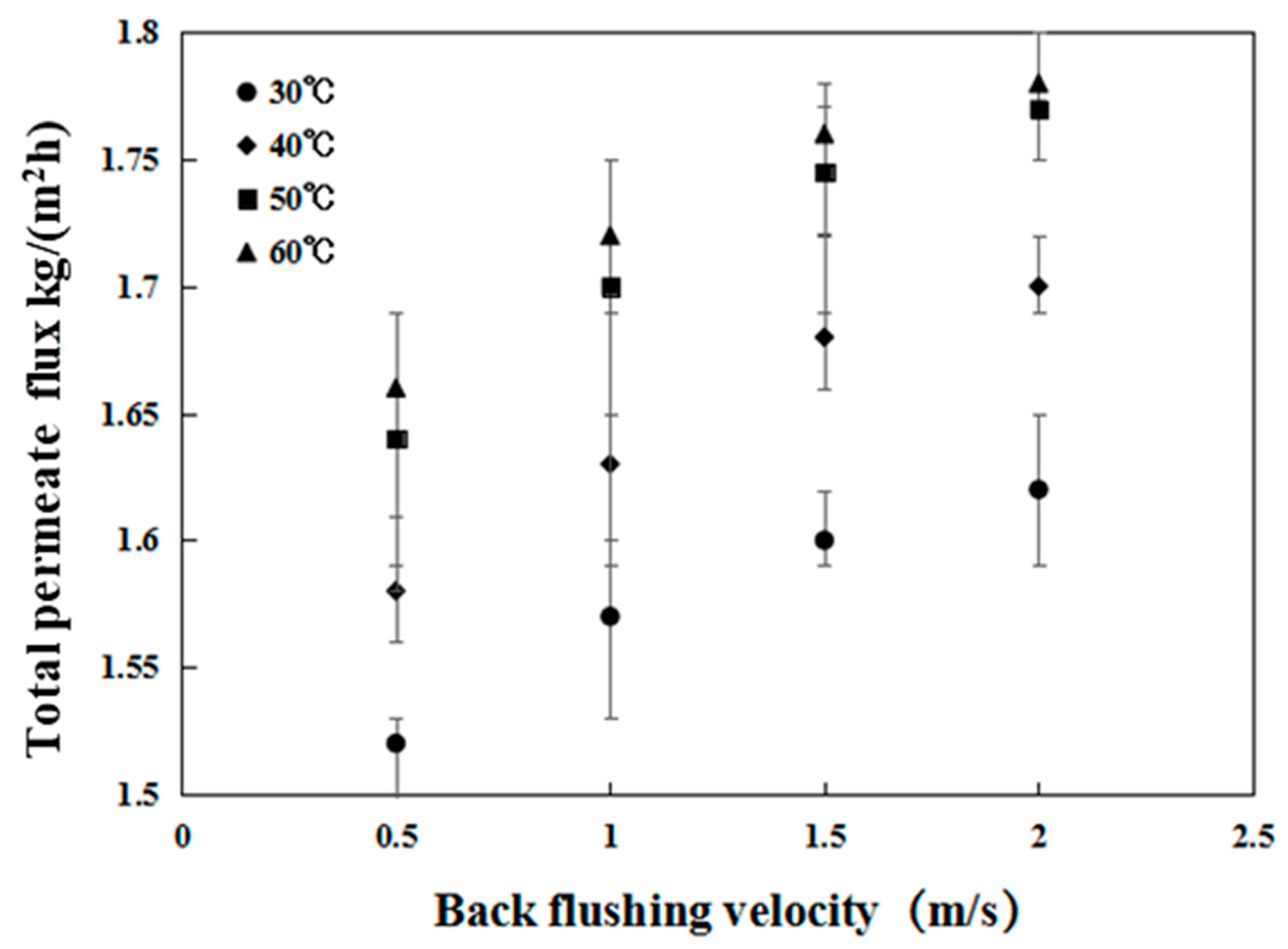
3.2.1. Effect of the Crossflow Velocity and Temperature on Permeate Flux Recovery
3.2.2. Effect of the Permeation Time tp and Backflushing Duration tb
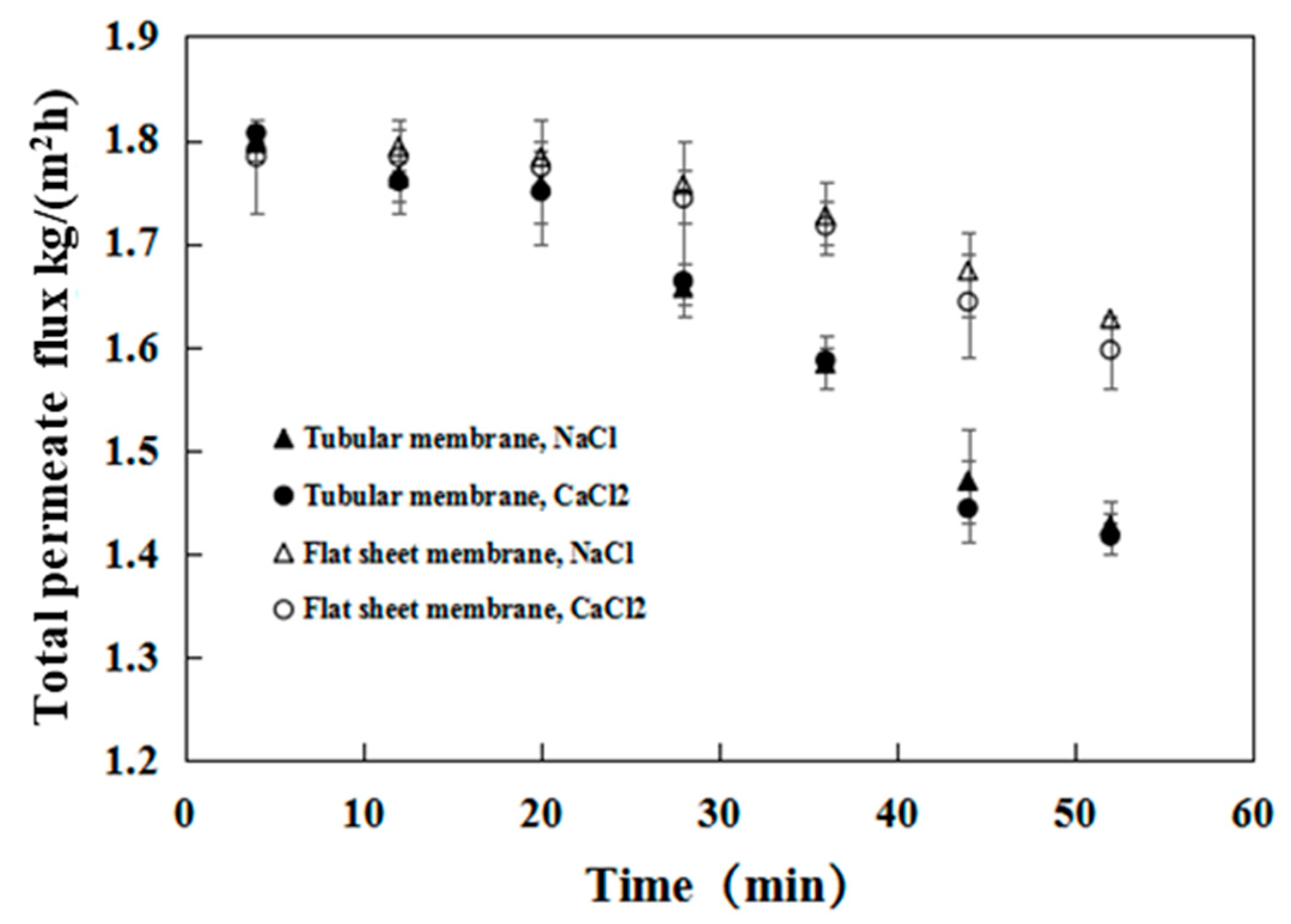
3.3. Treatment of Organic, Saline Wastewater in a Pilot Plant
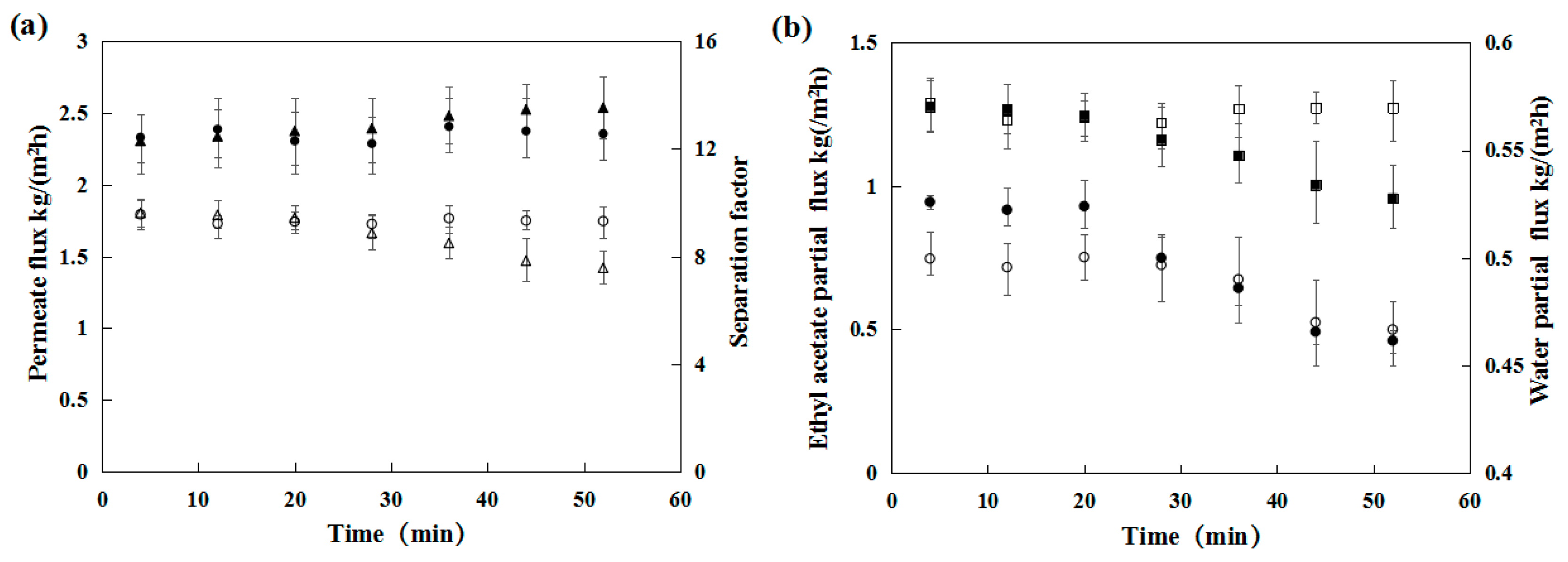
3.3.1. Variation in the Main Components during the Pervaporation Process
3.3.2. Pollution and Cleaning during the Pilot-Scale Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fatima, S.; Govardhan, B.; Kalyani, S.; Sridhar, S. Extraction of volatile organic compounds from water and wastewater by vacuum-driven membrane process: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, L.; Rahdar, A.; Bazrafshan, E.; Dahmardeh, H.; Susan, M.; Hasan, A.B.; Kyzas, G.Z. Petroleum hydrocarbon removal from wastewaters: A review. Processes 2020, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, M.T.; Geretto, M.; Pulliero, A.; Izzotti, A. Odor emissions: A public health concern for health risk perception. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhibbu-din, I. Ozone Formation Potential and Toxicity Potential of VOCs emissions from a Nigerian petroleum products depot. Anthropog. Pollut. 2020, 4, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ying, Q. Attribution of tropospheric ozone to NOx and VOC emissions: Considering ozone formation in the transition regime. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, K.A.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Karim, Z.A.; Abdullah, M.S.; Hafeez, A. A review of technologies for the phenolic compounds recovery and phenol removal from wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. 2021, 151, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Banat, F.; Alsafar, H.; Hasan, S.W. Algae biotechnology for industrial wastewater treatment, bioenergy production, and high-value bioproducts. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniaz, P.; Ardekani, N.T.; Makarem, M.A.; Rahimpour, M.R. Water and wastewater treatment systems by novel integrated membrane distillation (MD). ChemEngineering 2019, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benedict, D.J.; Parulekar, S.J.; Tsai, S.P. Pervaporation-assisted esterification of lactic and succinic acids with downstream ester recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heintz, A.; Stephan, W. A generalized solution-diffusion model of the pervaporation process through composite membranes Part II. Concentration polarization, coupled diffusion and the influence of the porous support layer. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 89, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, D.J.; Roth, L.H.; McAloon, J. Ethanol production by continuous fermentation–pervaporation: A preliminary economic analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 166, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Cocchini, U.; Nicolella, C.; Livingston, A.G. Countercurrent transport of organic and water molecules through thin film composite membranes in aqueous-aqueous extractive membrane processes. Part 1: Experimental characterization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 4087–4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovaua, S.; Gaykawad, S.; Straathof, A.J.J.; van der Bruggen, B. Influence of fermentation by-products on the purification of ethanol from water using pervaporation. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.; Sanz, M.T.; Beltrán, S. Concentration by pervaporation of brown crab volatile compounds from dilute model solutions: Evaluation of PDMS membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- García, V.; Pongrácz, E.; Muurinen, E.; Keiski, R.L. Recovery of n-butanol from salt containing solutions by pervaporation. Desalination 2009, 241, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipnizki, F.; Hausmanns, S.; Field, R.W. Influence of impermeable components on the permeation of aqueous 1-propanol mixtures in hydrophobic pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 228, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, R.; Rao, A.K.; Khan, A.A. Processing of liquid propellant reaction liquors by pervaporation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 72, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwijnenberg, H.J.; Koops, G.H.; Wessling, M. Solar driven membrane pervaporation for desalination processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 250, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Xu, T.; Yang, W. Separation of aqueous salt solution by pervaporation through hybrid organic–inorganic membrane: Effect of operating conditions. Desalination 2003, 273, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Shieh, J.J.; Huang, R.Y.M. A pseudophase-change solution-diffusion model for pervaporation. I. Single component permeation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.V. Separation of liquids by pervaporation through polymeric membranes. Russ. Chem. Bull. 1994, 43, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawski, W.; Krajewski, S.R. Sweeping gas pervaporation with hollow-fiber ionexchange membranes. Desalination 2004, 162, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazinha, C.; Alves, V.D.; Viegas, R.M.C.; Grespo, J.G. Aroma recovery by integration of sweeping gas pervaporation and liquid absorption in membrane contactors. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, P.; Wang, H. Interplay of the factors affecting water flux and salt rejection in membrane distillation: A state-of-the-art critical review. Water 2020, 12, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Bai, K.; Lu, J.; Yang, Z.; Yin, D. Influences of inorganic salts on the pervaporation properties of zeolite NaA membranes on macroporous supports. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 192, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, J.; Sai, P.S.T.; Balakrishnan, A.R. Effect of inorganic salts on the isobaric vapor–liquid equilibrium of the ethyl acetate–ethanol system. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2013, 58, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
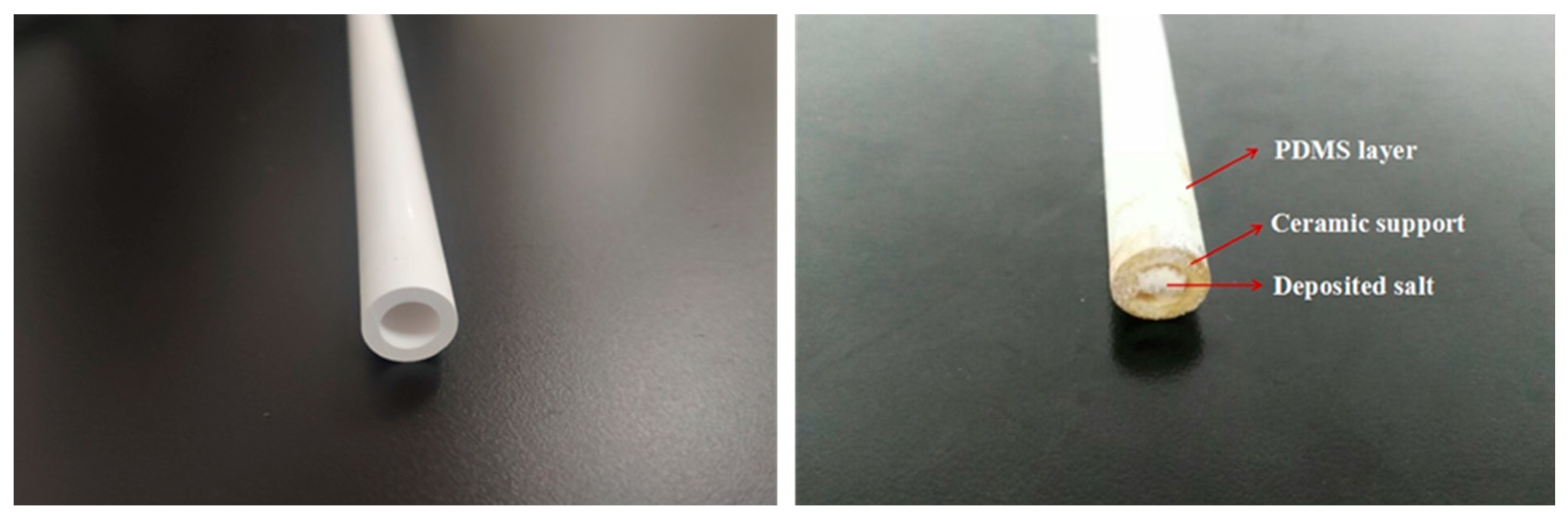
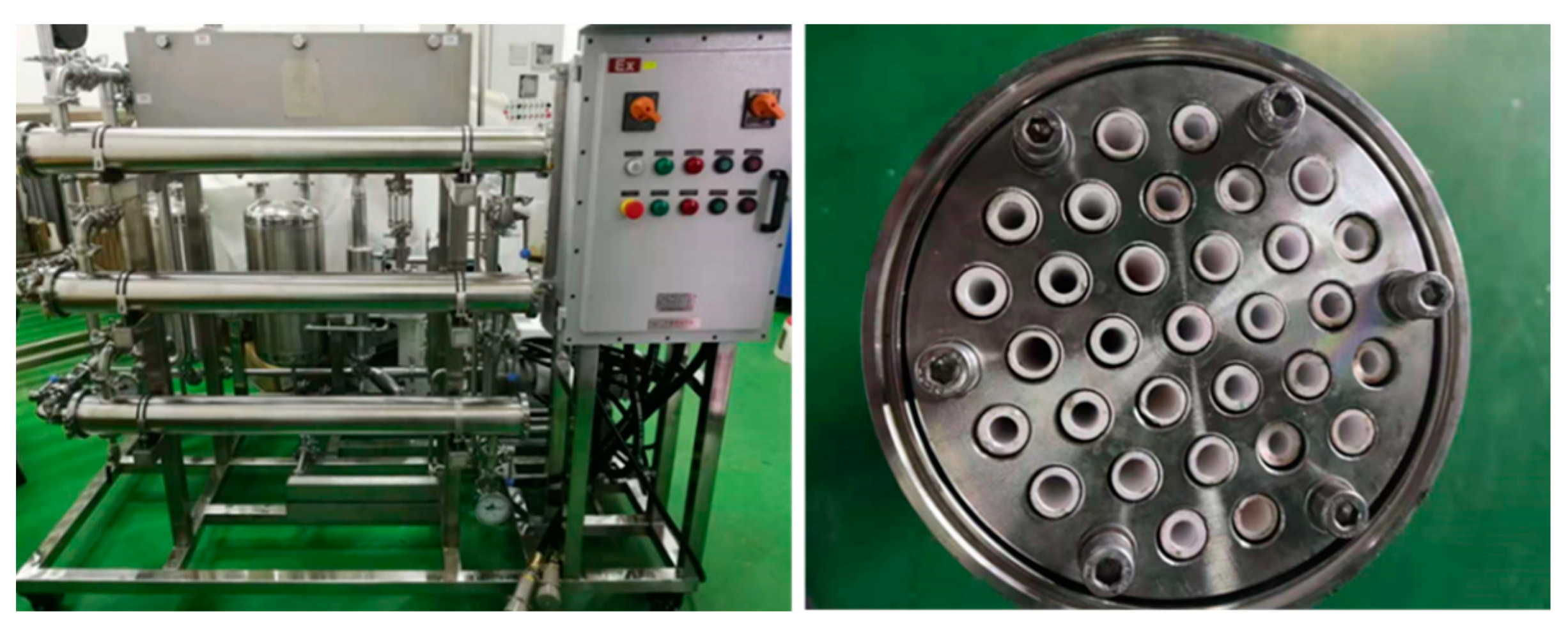
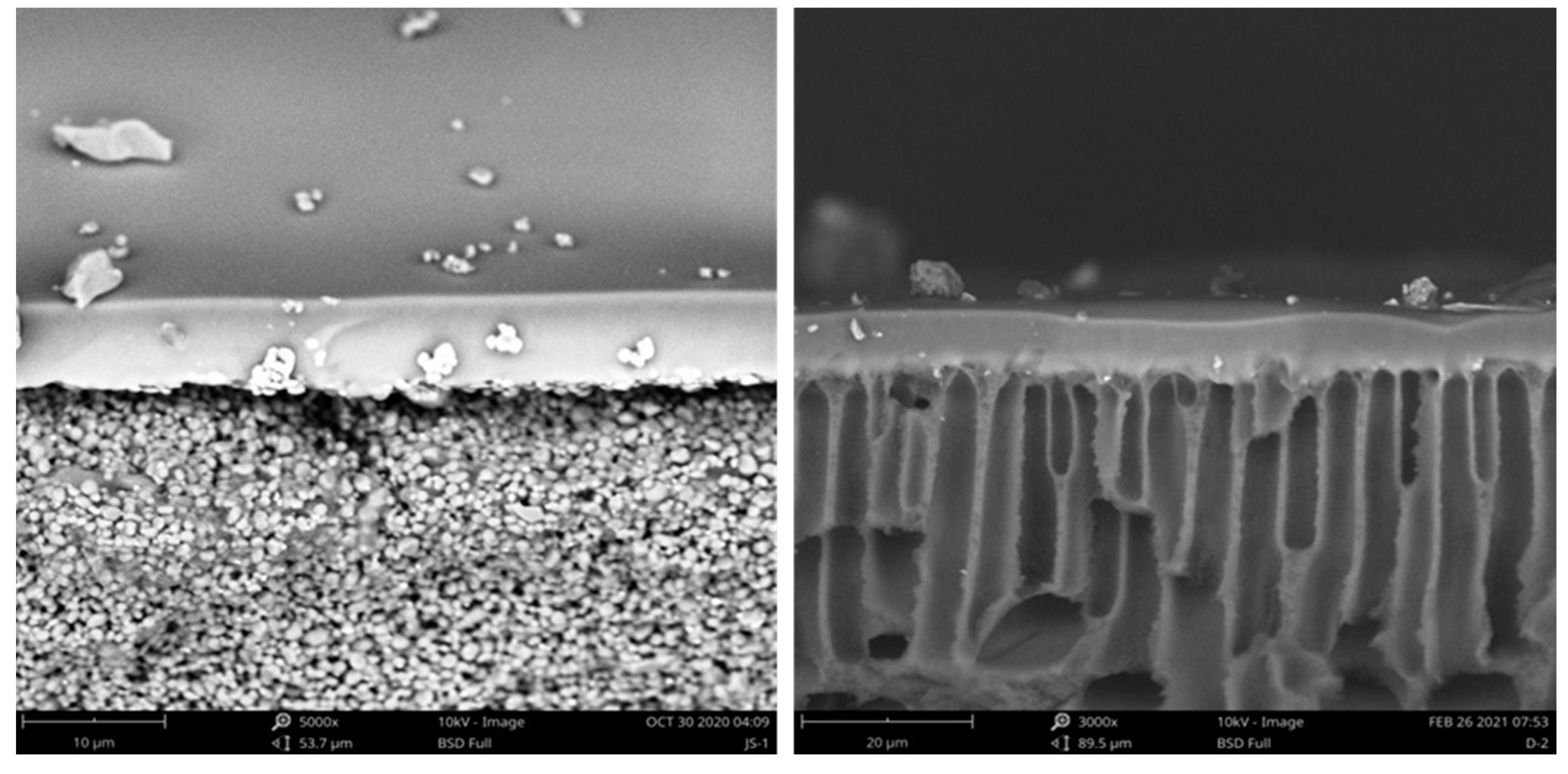


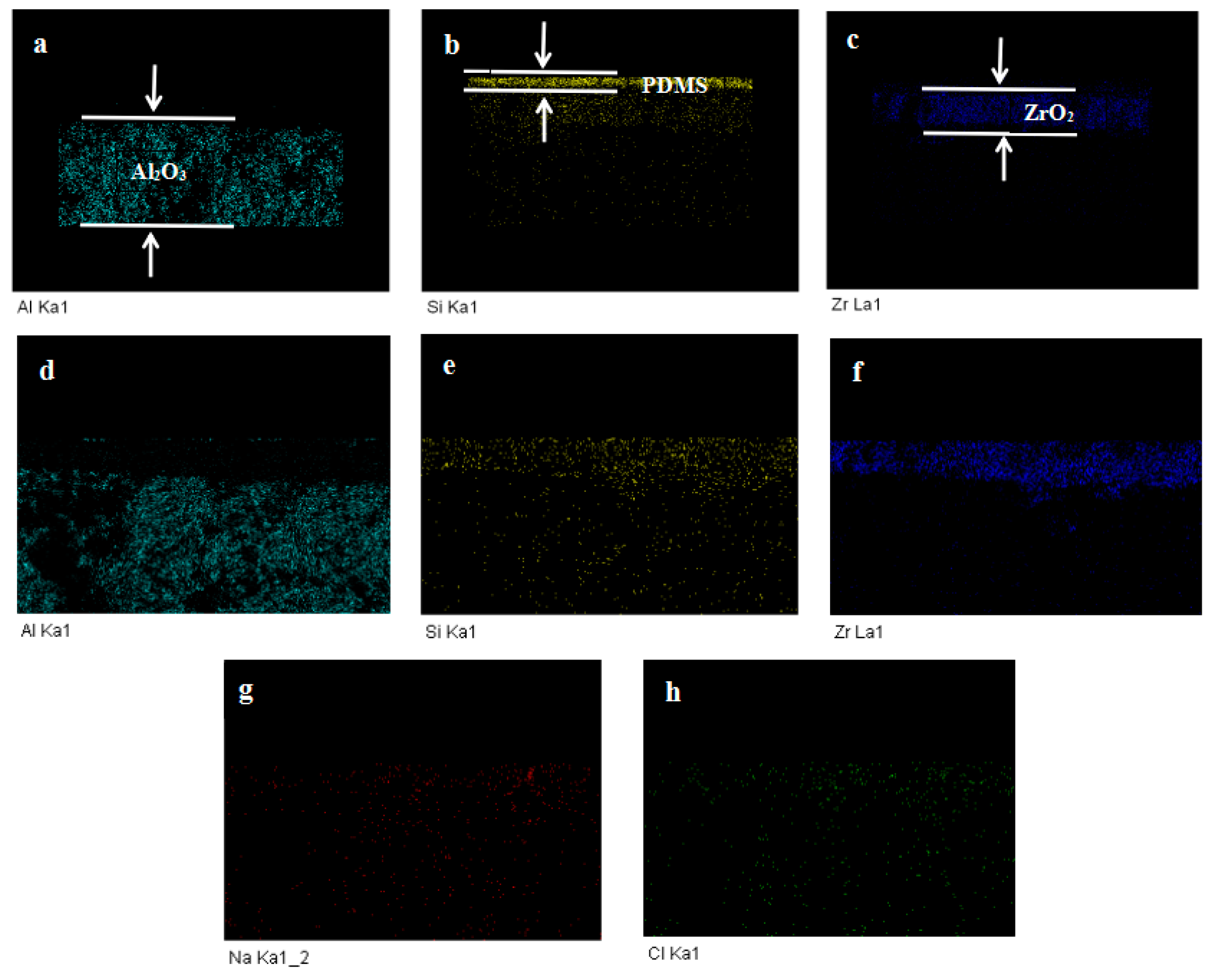

| Membrane | Flat Sheet PV Membrane | Tubular PV Membrane | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Support layer | Activate layer | Support layer | Activate layer |
| PEI | PDMS | Al2O3/ZrO2 | PDMS | |
| Thickness (um) | 30 | 8 | 1200 | 8 |
| Pore size (nm) | 50 | - | 200 | - |
| Membrane area (m2) | 0.033 | 0.00785 | ||
| Element | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| C K | 17.21 | 27.51 |
| O K | 43.15 | 51.79 |
| Al K | 22.02 | 15.68 |
| Si K | 2.78 | 1.9 |
| Zr L | 14.84 | 3.12 |
| Total | 100 |
| Element | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| C K | 15.5 | 25.64 |
| O K | 42.08 | 52.25 |
| Na K | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| Al K | 21.72 | 15.99 |
| Si K | 2.77 | 1.96 |
| Cl K | 0.47 | 0.27 |
| Zr L | 17.31 | 3.77 |
| Total | 100 |
| tp (Min) | tb (Min) | Recovered Flux kg/(m2 h) | Recovery of the Initial Flux (%) | Separation Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No backflushing | 1.58 | - | 12.7 | |
| 30 | 5 | 1.72 | 98.3 | 12.1 |
| 30 | 10 | 1.71 | 98.9 | 12.1 |
| 60 | 5 | 1.65 | 95.6 | 12.3 |
| 60 | 10 | 1.65 | 95.6 | 12.4 |
| 90 | 5 | 1.61 | 93.3 | 12.4 |
| 90 | 10 | 1.60 | 92.2 | 12.5 |
| Detection Items | Unit | Detection Value |
|---|---|---|
| Turbidity | NTU | 7.3 |
| pH | 7.6 | |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) | g/L | 25.6 |
| K+ | mg/L | 56.2 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 2400 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 78.1 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 15.2 |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mg/L | |
| Ethyl acetate | wt.% | 0.65 |
| Time (min) | Ethyl Acetate Concentration (wt.%) | Na+ Content (g/L) | EA Flux kg/(m2 h) | Water Flux kg/(m2 h) | EA Permeance (GPU *) | Separation Factor (EA/Water) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retentate | Permeate | Retentate | Permeate | |||||
| 0 | 0.65 | - | 2.4 | - | - | - | - | |
| 30 | 0.42 | 11.32 | 2.3 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.85 | 1350 | 19.5 |
| 60 | 0.27 | 8.35 | 2.4 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.71 | 1228 | 21.6 |
| 90 | 0.15 | 3.86 | 2.4 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.61 | 719 | 14.8 |
| 120 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 2.5 | 0 | 0.003 | 0.48 | 147 | 14.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Pan, Y.; Shen, C.; Zuo, C.; Ding, X.; Liu, G.; Xing, W.; Jin, W. Pollution and Cleaning of PDMS Pervaporation Membranes after Recovering Ethyl Acetate from Aqueous Saline Solutions. Membranes 2022, 12, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040404
Sun X, Pan Y, Shen C, Zuo C, Ding X, Liu G, Xing W, Jin W. Pollution and Cleaning of PDMS Pervaporation Membranes after Recovering Ethyl Acetate from Aqueous Saline Solutions. Membranes. 2022; 12(4):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040404
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xuefei, Yang Pan, Chunxiang Shen, Chengye Zuo, Xiaobin Ding, Gongping Liu, Weihong Xing, and Wanqin Jin. 2022. "Pollution and Cleaning of PDMS Pervaporation Membranes after Recovering Ethyl Acetate from Aqueous Saline Solutions" Membranes 12, no. 4: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040404
APA StyleSun, X., Pan, Y., Shen, C., Zuo, C., Ding, X., Liu, G., Xing, W., & Jin, W. (2022). Pollution and Cleaning of PDMS Pervaporation Membranes after Recovering Ethyl Acetate from Aqueous Saline Solutions. Membranes, 12(4), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040404








