Effect of Electrode Type on Electrospun Membrane Morphology Using Low-Concentration PVA Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterizations
2.3. Solution Preparation for Electrospinning
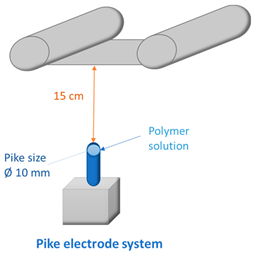
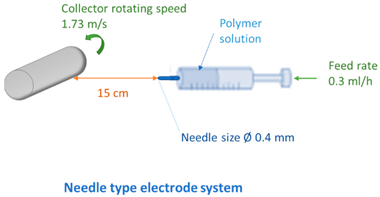
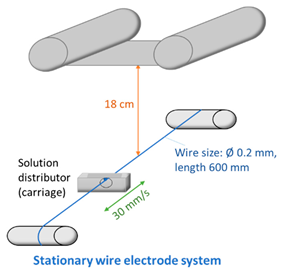
2.4. Fabrication of Membranes
3. Results and Discussion
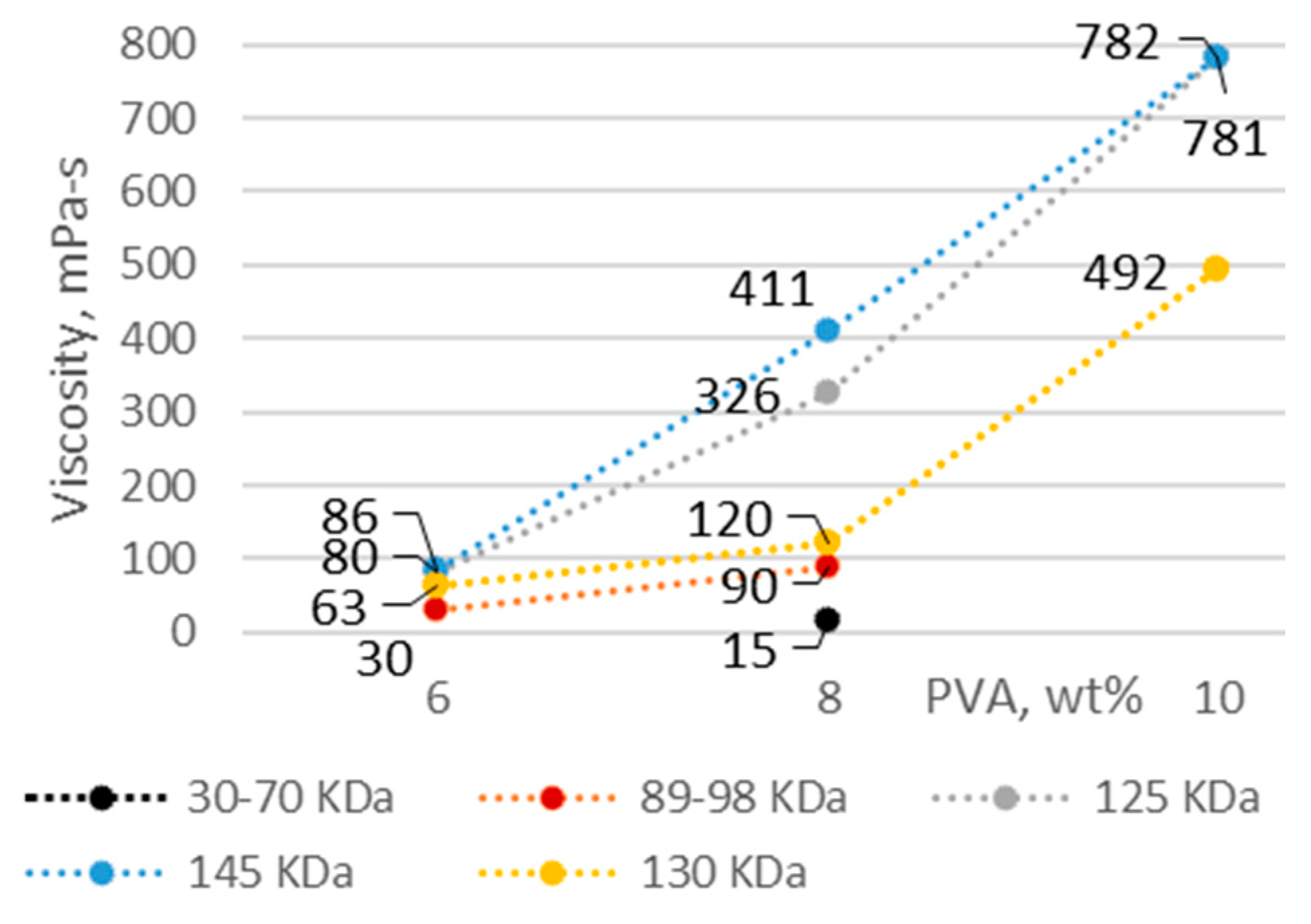
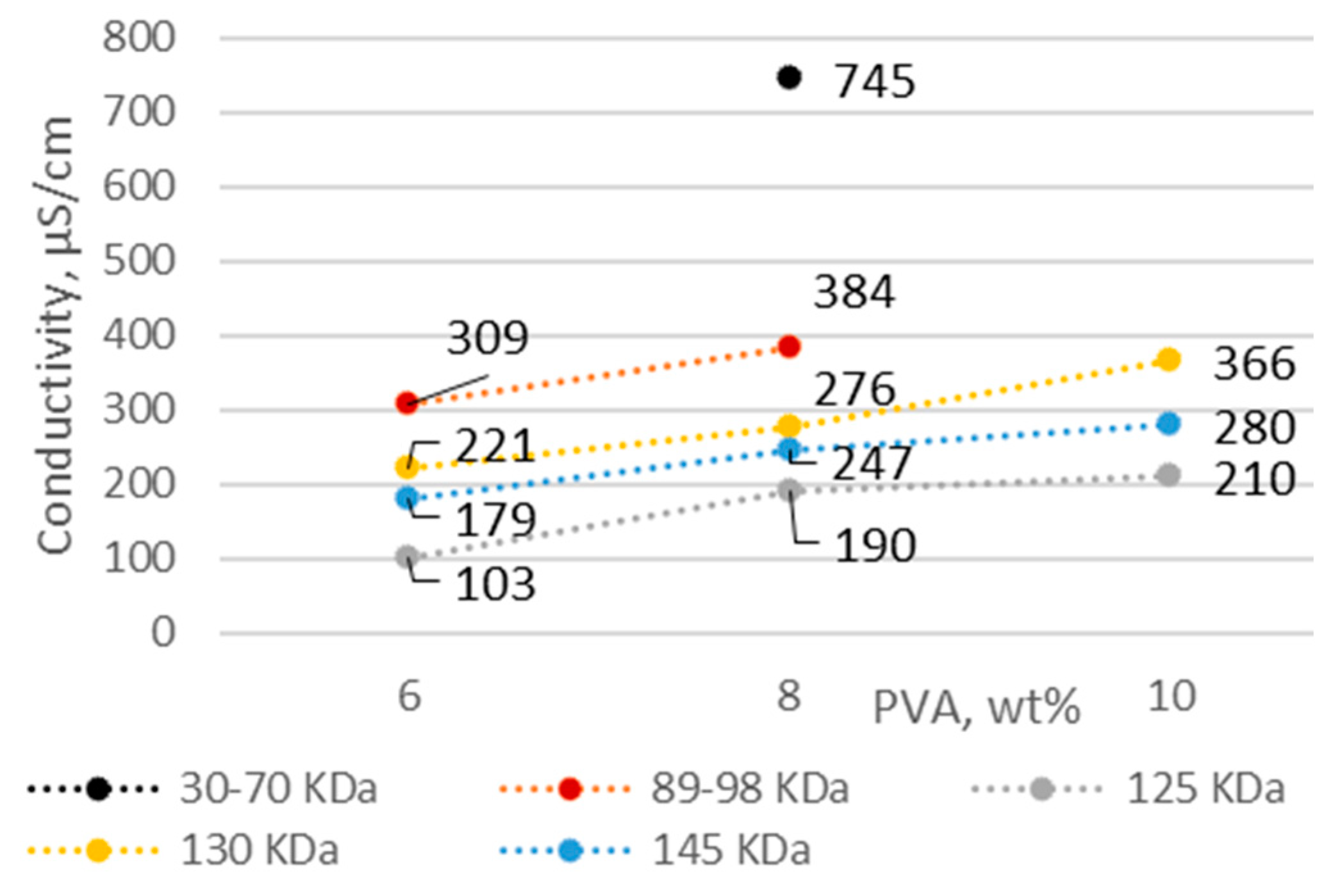
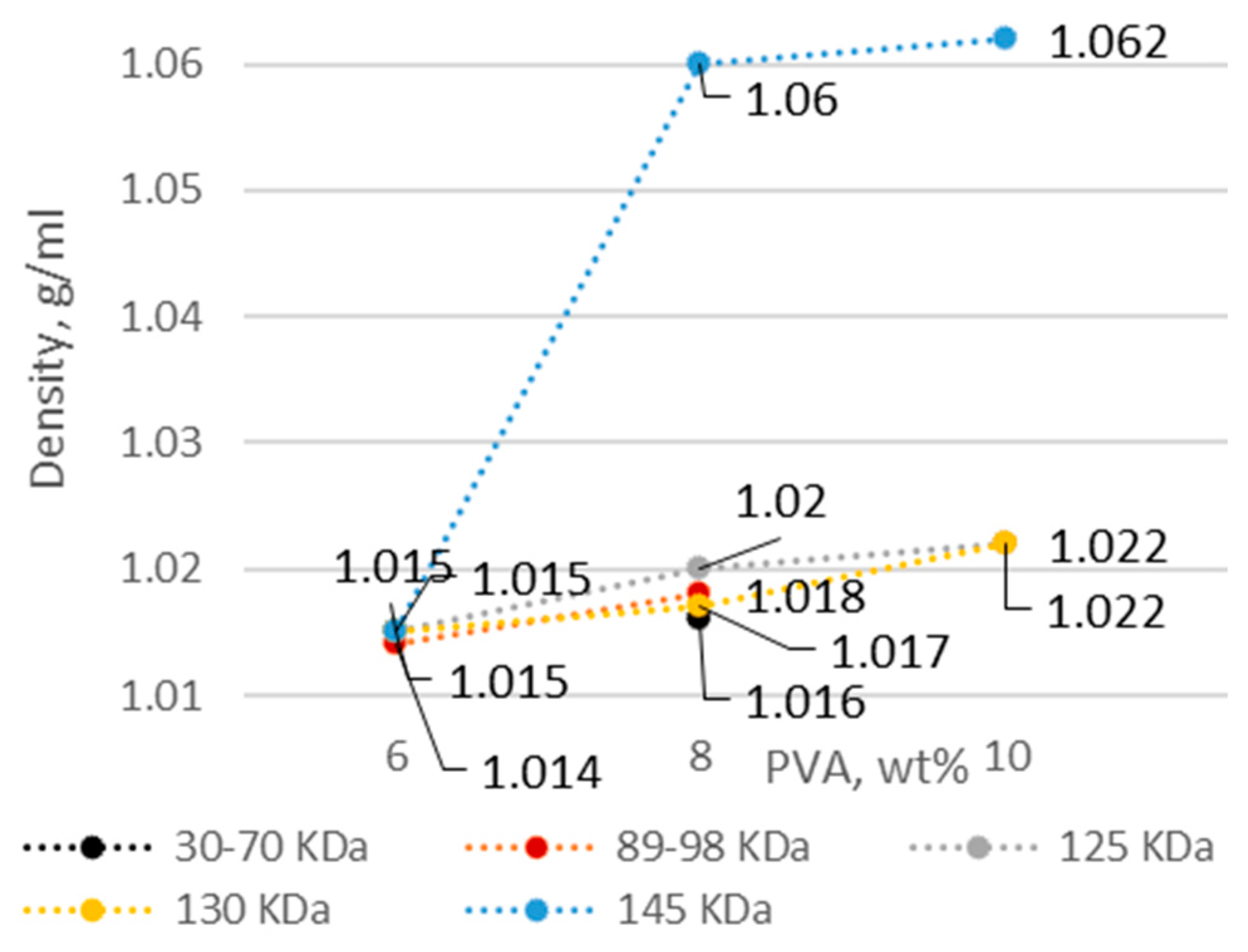
3.1. PVA Solution Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Electrode Type and Distance between Electrodes on Membrane Morphology
3.3. Membrane Morphology Depends on Concentration and Molecular Weight
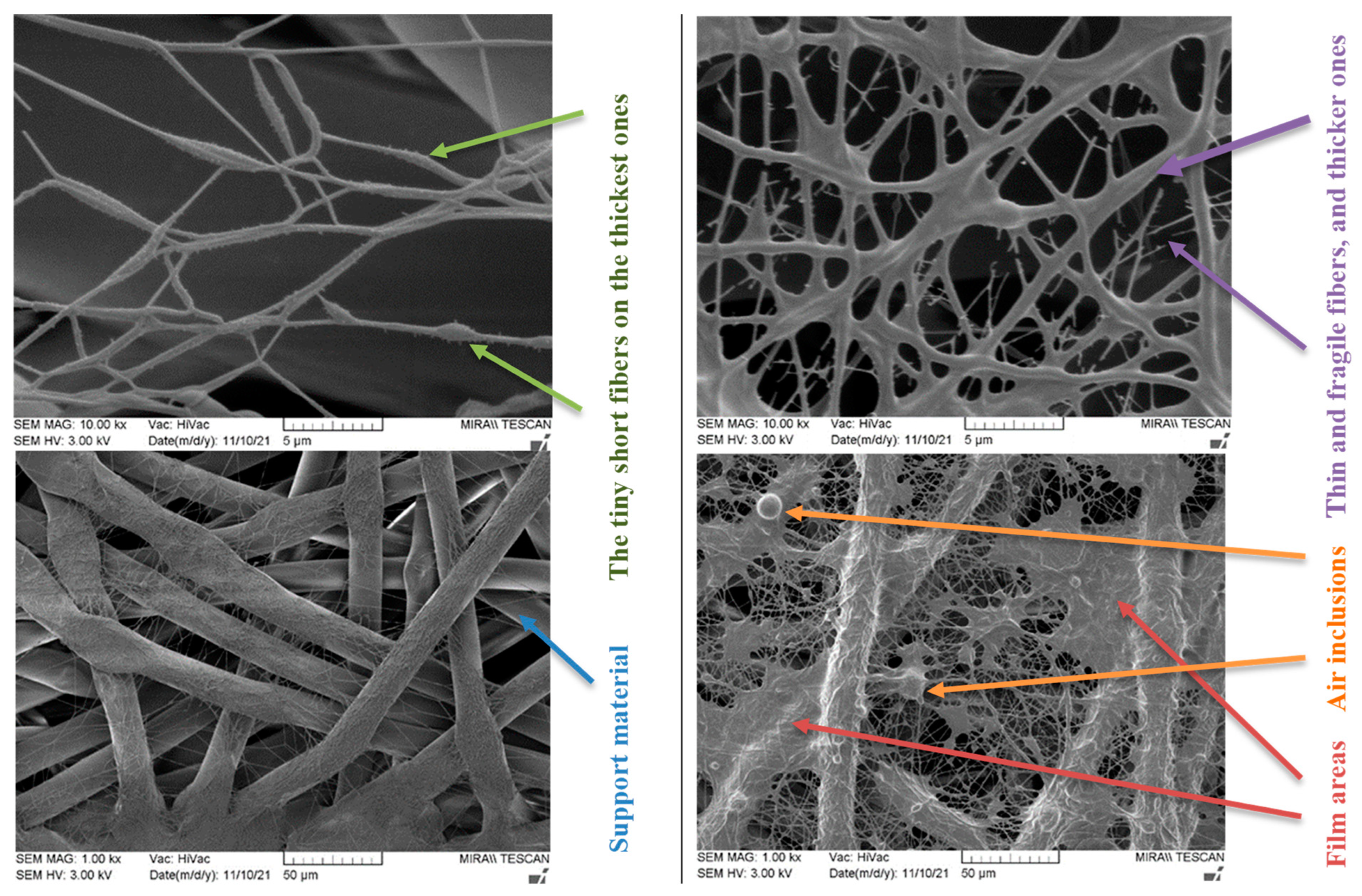
3.4. Fiber Diameter Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Afshari, M. Electrospun Nanofibers; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 1–8. ISBN 9780081009079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, R.F.; Naderi, N.; Gheibi, A. Blowing-Assisted Electrospinning. U.S. Patent US10138574B2, 27 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-X.; He, J.-H. Bubble Electrospinning with an Auxiliary Electrode and an Auxiliary Air Flow. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerond, M.; Subramanian, A.; Skene, W.; Cicoira, F. Combining Electrospinning and Electrode Printing for the Fabrication of Stretchable Organic Electrochemical Transistors. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 708914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiajia, T.; Chengheng, W.; Suping, C.; Zi, Q.; Borovskikh, P.; Shchegolkov, A.; Lu, C.; Wei, D.; Jing, S.; Hongsong, F. Combining of Electrospinning and Electrospraying to Prepare Biomimetic Neural Scaffold with Synergistic Cues of Topography and Electro-Transduction. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 5148–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Montini, B.; Florencia, A.; Abraham, G. Combination of electrospinning with other techniques for the fabrication of 3D polymeric and composite nanofibrous scaffolds with improved cellular interactions. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 172002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.W. Overview of membrane science and technology. In Membrane Technology and Applications; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2004; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanunpanich, N.; Hongsik, B.; Inn-Kyu, K. Membrane Morphology: Phase Inversion to Electrospinning. Membr. J. 2005, 15, 85–104, 1226-0088(pISSN), 2288-7253(eISSN). [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.H.; Kang, H.W. Advanced electrospinning using circle electrodes for freestanding PVDF nanofiber film fabrication. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtera, J.; Vysloužilová, L.; Komarek, J.; Skřivánek, J.; Žabka, P.; Beran, J.; Lukas, D. Protrusion of the Rod Electrode in the Electrospinning Process. J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 2015, 301636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J. A Review on Existing Technology of Electrospinning at Large Scale. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Information Technology and Scientific Management, Tianjin, China, 20–21 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Omer, S.; Forgách, L.; Zelkó, R.; Sebe, I. Scale-up of Electrospinning: Market Overview of Products and Devices for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Purposes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forward, K.M.; Rutledge, G.C. Free surface electrospinning from a wire electrode. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 183, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Jia, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, K.; Guan, Z.; Wang, L. Comparisons of Fibers Properties between Vertical and Horizontal Type Electrospinning Systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena, Virginia Beach, VA, USA, 18–21 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad, E.A.; Woodrow, K.A. Manufacturing scale-up of electrospun poly (vinyl alcohol) fibers containing tenofovir for vaginal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.-Y.; Boaretti, C.; Lorenzetti, A.; Martucci, A.; Roso, M.; Modesti, M. Effects of Solvent and Electrospinning Parameters on the Morphology and Piezoelectric Properties of PVDF Nanofibrous Membrane. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Clark, R.L. Controllable porous polymer particles generated by electrospraying. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcinkaya, B.; Cengiz Callioglu, F. The Effect of Supporting Material Type on the Nanofiber Morphology. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference NanoCon 2011, Brno, Czech Republic, 21–23 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sebe, I.; Kallai-Szabo, B.; Zelko, R.; Szabo, D. Polymers and formulation strategies of nanofibrous systems for drug delivery application and tissue engineering. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Jiang, W.; Shen, L.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun Hybrid Films for Fast and Convenient Delivery of Active Herb Extracts. Membranes 2022, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A. Electrospun Nanofibers as Carriers of Microorganisms, Stem Cells, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids in Therapeutic and Other Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun-Seo, P. Electrospinning and its applications. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 1, 043002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partheniadis, I.; Nikolakakis, I.; Laidmae, I.; Heinamaki, J. A Mini-Review: Needleless Electrospinning of Nanofibers for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Processes 2020, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng-Ming, H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumsiņa, E.; Zelča, Z.; Kukle, S. Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) and Poly (Vinyl. Alcohol)/Zinc Oxide Composite Nanofibre. Webs: Quality Control with Conductometer. In Proceedings of the 11th International Scientific and Practical Conference, Rezekne, Latvia, 15–17 June 2017; Rezekne Higher Education Institution: Rezekne, Latvia, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jēgina, S.; Šutka, A.; Kukle, S.; Zelča, Z. The Effect of Sodium Chlorophyllin on Polyvinyl Alcohol Electrospun Nanofiber Diameters. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference of Young Scientists on Energy Issues (CYSENI 2016), Kaunas, Lithuania, 26–27 May 2016; Lithuanian Energy Institute: Kaunas, Lithuania, 2016; pp. 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Zelca, Z.; Kukle, S.; Janceva, S.; Vilcena, L. Propolis Integration Methods into Solutions for Highly Loaded Propolis Fibers by Needleless Electrospinning. Molecules 2022, 27, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rwei, S.P.; Huang, C.C. Electrospinning PVA solution-rheology and morphology analyses. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, S.; Xu, H.; Dong, Y.; Okahisa, Y. Reconstruction of Fibroin Nanofibers (FNFs) via Electrospinning: Fabrication of Poly(vinyl alcohol)/FNFs Composite Nanofibers from Aqueous Solution. Polymers 2022, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higham, A.K.; Tang, C.; Landry, A.M.; Pridgeon, M.C.; Lee, E.M.; Andrady, A.L.; Khan, S.A. Foam electrospinning: A multiple jet, needle-less process for nanofiber production. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanya, T.M.; Arshad, A.B.; Lin, P.T.; Widakdo, J.; Makari, H.K.; Austria, H.F.M.; Hu, C.-C.; Lai, J.-Y.; Hung, W.-S. A review of recent progress in polymeric electrospun nanofiber membranes in addressing safe water global issues. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 9638–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Molecular Weight, kDa | PVA Content in Solution, wt.% | Mixing Temp., °C | Stirring Time, h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8PVA30_70 | 30–70 | 8 | 10–120 | 3 |
| 6PVA89_98 | 89–98 | 6 | ||
| 8PVA89_98 | 8 | |||
| 6PVA125 | 125 | 6 | 90–100 | 2 |
| 8PVA125 | 8 | |||
| 10PVA125 | 10 | |||
| 6PVA130 | 130 | 6 | 75–90 | |
| 8PVA130 | 8 | |||
| 10PVA130 | 10 | |||
| 6PVA145 | 145 | 6 | 90–110 | |
| 8PVA145 | 8 | 5–13 | ||
| 10PVA145 | 10 |
| Electrode Type | Pike | Needle | Wire | 5 Wires | Cylinder | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight, kDa | PVA Solution Concentration, wt.% | Electrospinning Voltage, kV | ||||
| 125 kDa | 6 | 30 | 54 | 66 | ||
| 8 | 26 | 49 | 66 | |||
| 10 | 26 | 46 | 66 | |||
| 130 kDa | 6 | 27 | 10 | 40 | 55 | 67 |
| 8 | 27 | 57 | 66 | |||
| 10 | 29 | 10 | 60 | 58 | 58 | |
| 145 kDa | 6 | 29 | - | 57 | ||
| 8 | 29 | 49 | 57 | |||
| 10 | 27 | 45 | 60 | |||
| Pike | Needle | Wire | Rotating Wires | Cylinder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
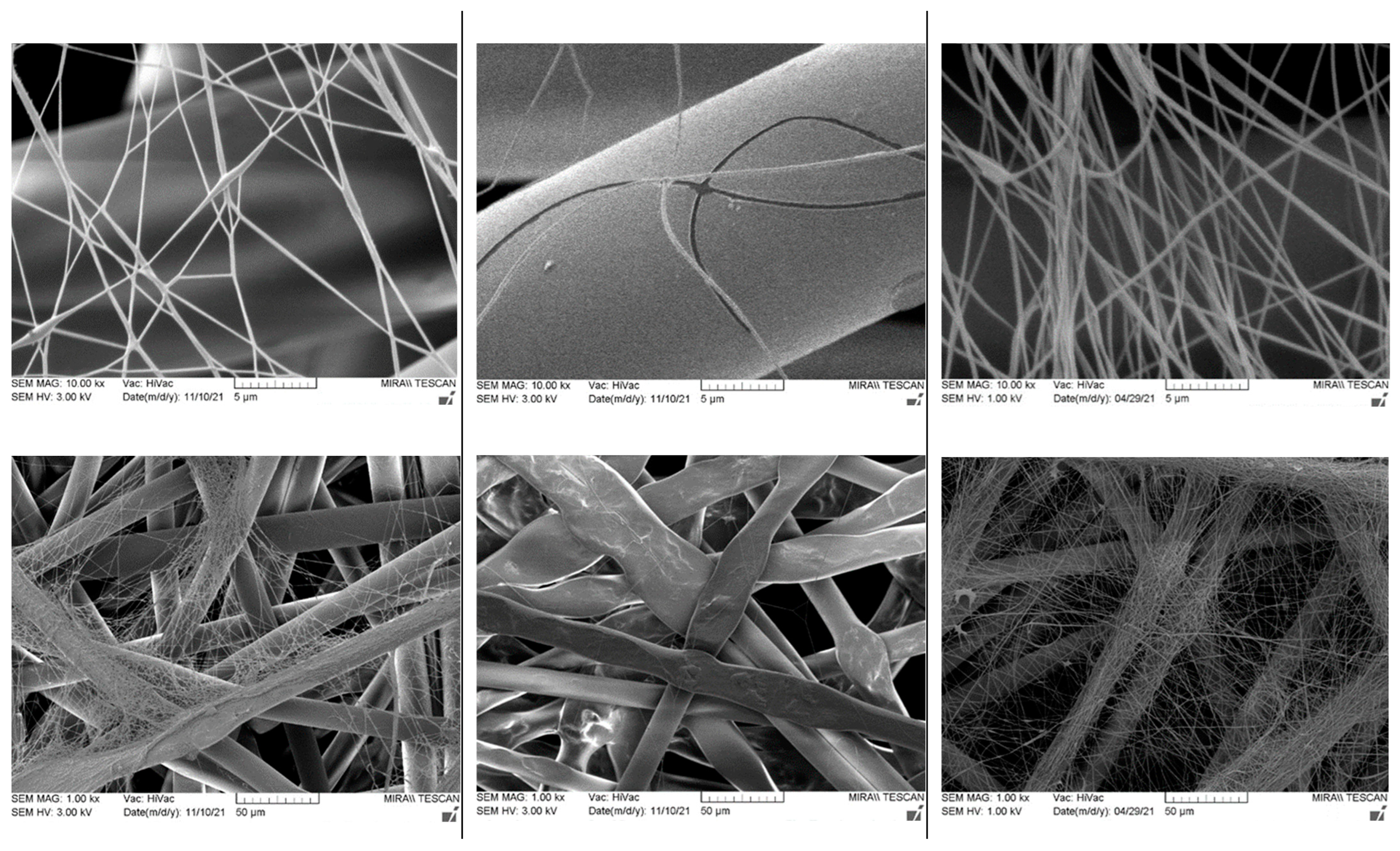
 |  |  |  |  |
| Converse type | Horizontal type | Converse type | Converse type | Converse type |
 |  | |||
 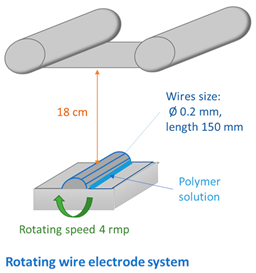 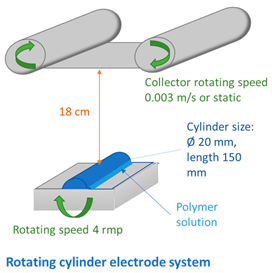 | ||||
| Electrode Type | Pike | Needle | Wire | 5 Wires | Cylinder | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight, kDa | PVA Solution Concentration, wt.% | Electrospinning Voltage, kV | ||||
| 125 kDa | 6 | G | A | A | ||
| 8 | G | G | G | |||
| 10 | G | G | G | |||
| 130 kDa | 6 | A | G | G | B | B |
| 8 | G | G | G | |||
| 10 | G | G | G | G | G | |
| 145 kDa | 6 | G | X | G | ||
| 8 | G | G | G | |||
| 10 | G | G | G | |||
| 6PVA125 (Cylinder) | 6PVA130 (Cylinder) | 6PVA130 (Wire) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 201.8 | 168.4 | 117.0 |
| −/+ | 7.7 | 7.6 | 5.2 |
| Relative error | 4% | 5% | 4% |
| Minimum | 53 | 26 | 27 |
| Maximum | 421 | 413 | 320 |
| Amplitude | 368 | 387 | 293 |
| Median | 200 | 157 | 119 |
| Mode | 132 | 136 | 133 |
| Standard deviation | 75.3 | 73.9 | 50.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zelca, Z.; Krumme, A.; Kukle, S.; Viirsalu, M.; Vilcena, L. Effect of Electrode Type on Electrospun Membrane Morphology Using Low-Concentration PVA Solutions. Membranes 2022, 12, 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060609
Zelca Z, Krumme A, Kukle S, Viirsalu M, Vilcena L. Effect of Electrode Type on Electrospun Membrane Morphology Using Low-Concentration PVA Solutions. Membranes. 2022; 12(6):609. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060609
Chicago/Turabian StyleZelca, Zane, Andres Krumme, Silvija Kukle, Mihkel Viirsalu, and Laimdota Vilcena. 2022. "Effect of Electrode Type on Electrospun Membrane Morphology Using Low-Concentration PVA Solutions" Membranes 12, no. 6: 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060609
APA StyleZelca, Z., Krumme, A., Kukle, S., Viirsalu, M., & Vilcena, L. (2022). Effect of Electrode Type on Electrospun Membrane Morphology Using Low-Concentration PVA Solutions. Membranes, 12(6), 609. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12060609







