Abstract
Two-dimensional graphene oxide (GO)-based lamellar membranes have been widely developed for desalination, water purification, gas separation, and pervaporation. However, membranes with a well-organized multilayer structure and controlled pore size remain a challenge. Herein, an easy and efficient method is used to fabricate MoO2@GO and WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes with controlled structure and interlayer spacing. Such membranes show good separation for salt and heavy metal ions due to the intensive stacking interaction and electrostatic attraction. The as-prepared composite membranes showed high rejection rates (˃70%) toward small metal ions such as sodium (Na+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions. In addition, both membranes also showed high rejection rates ˃99% for nickel (Ni2+) and lead (Pb2+) ions with good water permeability of 275 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 bar−1. We believe that our fabricated membranes will have a bright future in next generation desalination and water purification membranes.
1. Introduction
Water scarcity is one of ongoing issue in the world that directly affects billions of people each year [1,2,3,4]. Therefore, a lot of investment is devoted to this cause to find a suitable solution. The development of more efficient and low-cost water purification membranes has become of fundamental importance [5]. The current membrane market is dominated by polymeric membranes. However, these membranes suffer from fouling and stability issues. Therefore, achieving high-performance separation membranes with controlled pore size, shape, and number of diffusion channels in the separation layer is some of the challenges. Consequently, exploring new membrane materials with advanced properties becomes a central task for the membrane community.
Recently, GO have attracted enormous attention as a filter material in membrane technology for desalination, organic solvent nanofiltration, pervaporation, and gas separation applications [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. GO contains various oxygen functional groups on its edges and basal plane. Due to these functional groups, it can easily be dispersed into water without the use of any stabilizing agent and can form a uniform dispersion. This property makes it much easier to assemble into a membrane or thin film [14,15]. Further, due to these functionalities it has a strong ability to separate inorganic and organic contaminations from water. Moreover, these functional groups provide many reactive handles for a variety of surface-modification reactions, which can be used to develop a series of functionalized or composite membranes with significantly enhanced separation performance [16,17,18,19,20]. Recently, the interlayer distances between GO nanosheets have been controlled by integrating GO with other functional materials such as carbon nanotubes, metal-organic frameworks, MXene, layered double hydroxide, zeolite, nanoparticles, metal oxide, clay, and polymers, which have been of great interest in water purification, desalination, gas separation, and organic nanofiltration applications [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Further, interlayer spacing between 2D sheets is also controlled by the reduction of GO sheets using thermal treatment, the green method, and a chemical approach [30,31,32]. However, controlling nanopore structure and interlayer spacing is still a challenging task for the scientific community [7,33].
Herein, an easy and efficient method is used to fabricate MoO2@GO (400 ± 20 nm) and WO3@GO (420 ± 20 nm)-based nanocomposite membranes for salt and heavy metal separation. Due to the intensive stacking interaction and electrostatic attraction, the as-prepared membranes show a high rejection for various metal ions such as Na+, and Mg2+ (˃70%) with a pure water permeability of ˃345 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 bar−1. Further, both membranes showed high rejection rates (˃99%) for Pb2+ and Ni2+ ions. We hope that such GO-based nanocomposite membranes with controlled pore structures can be ideal candidates for the next generation water purification, wastewater treatment, and desalination applications on a large scale.
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of GO Nanosheets
The GO nanosheets were synthesized by reported method [34]. Initially, 3.0 g of graphite nanoflakes (325 mesh), 1.5 g of sodium nitrate, and 96 mL of concentrated sulfuric acid were mixed together in ice bath with continuous stirring. Then, 9.0 g of potassium permanganate was slowly added to the mixture at below 20 °C and stirred for 90 min. The mixture was then stirred again for 2 h at 35 °C. Now, 138 mL of deionized (DI) water is added dropwise to the mixture at a temperature below 5 °C to avoid overheating. After that, 420 mL of DI was further added along with 3 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide to obtain a suspension of graphite oxide. The as-prepared product was washed several times with 3% hydrochloric acid and then dialyzed for up to 5 days to remove metallic contamination from suspension. After that, graphite oxide suspension was exfoliated to GO suspension with help of tip sonication (135 W, 1 h). Furthermore, small pieces and multilayer flakes were removed from GO suspension with help of centrifuge machine (6000 rpm for 30 min). After purification and separation, GO suspensions were dried and used for fabrication and characterization of membranes.
2.2. Preparation of MoO2@GO Composite Membranes
The MoO2@GO composite was prepared according to modified reported method (Scheme 1) [35]. The 100 mL aqueous solution of phosphomolybdic acid (PMA, 15 mL) was mixed with 100 mL of GO suspension (3.0 mgmL−1) in 100 mL of DI water with continuous stirring. Further, 1.25 mL of hydrazine (80%) was added to the reaction mixture and was continuously mixed for 1 h. Then, the mixture was transferred to Teflon-autoclave (Bioland, China) and kept at 180 °C overnight. After that, the as-prepared black precipitate of MoO2@GO composite was separated and washed with DI water and ethanol. Finally, the composite was dried and used for fabrication of MoO2@GO nanocomposite membranes using the vacuum filtration method, as shown in Scheme 1.
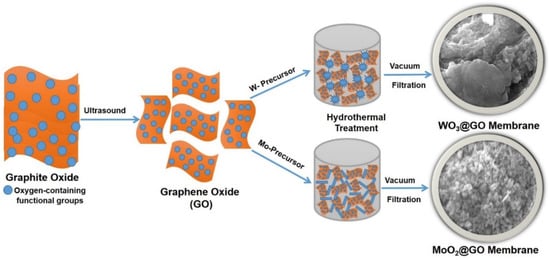
Scheme 1.
Preparation of WO3@GO and MoO2@GO nanocomposite membranes on polyether sulfone support, involving a multi-step process and hydrothermal treatment of W and Mo precursors with GO nanosheets.
2.3. Preparation of WO3@GO Nanocomposite Membranes
The WO3@GO nanocomposite was prepared according to reported hydrothermal method, as shown in Scheme 1 [36]. 1.0 g of Na2WO4·H2O and 0.2 g of NaCl were mixed with 40 mL of GO dispersion (10 mg/mL), respectively, with continuous stirring for 4 h until a uniform dispersion was obtained. At this stage, the pH of the mixture is maintained at level 2, with the help of a 3 M hydrochloric acid solution. After that, the resulting mixture was transferred to a hydrothermal reactor (Teflon-autoclave) and kept overnight at 180 °C. Finally, the black precipitate of WO3@GO nanocomposite was separated and washed several times with DI water and ethanol, respectively, to avoid contamination. The as-obtained composite was used for preparation of membranes using the vacuum filtration method, as shown in Scheme 1.
2.4. Characterization of Materials and Membranes
The scanning electron microscope (Nova NanoSEM 430, Peabody, MA, USA) was used to study the surface morphology of GO-based membranes at 15 kV and 10 kV. The surface chemistry and elemental composition of membranes were studied using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ESCALAB250, 150 W spot size, 500 µm, Waltham, MA, USA) using Al Kα radiation; all spectra were calibrated to the binding energy of adventitious carbon (284.6 eV). While the Bruker DektakXT stylus profiler (Bremen, Germany) was used to measure the thicknesses of GO-based membranes. The X-ray diffractometer (D-MAX/2400, Malvern, UK) was used to measure the interlayer distance between GO nanosheets at λ = 0.154 nm. Conductivity meter (MP513 Lab, Rinch industrial Co. Ltd. Shanghai, China) was used for the measurement of salt ions concentration.
2.5. Water Permeance and Separation Efficiency of GO-Based Membranes
The vacuum filtration assembly, with an effective area of 14.5 cm−2, was used to measure DI water permeance and salt separation at room temperature under a pressure difference of 1.0 bar. The 250 mL of feed solution are used for measurements. The water permeance of membranes was calculated according to Equation (1).
where J is permeance of membrane in L m−1 h−1 bar−1, V is volume of permeate water in liters, A is area of membrane, P is pressure in bars, and Δt is time of permeate in h.
The rejection (R) of salt solution in percentage was calculated according to Equation (2).
where R is rejection of salts in percentage, Cp is concentration of permeate, and Cf is concentration of feed solution.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Membranes
GO was prepared according to the modified method [37], while the MoO2@GO and WO3@GO-based nanocomposites were prepared according to the reported method in the literature [35,38]. Further, such nanocomposites were used for the preparation of membranes (Scheme 1). Certain amounts of the MoO2@GO and WO3@GO nanocomposite were dispersed into DI water with the help of tip sonication and were then filtered through a polyether sulfone (PES) support in a vacuum filtration assembly. The thickness of membranes can be controlled by controlling the volume and concentration of respective nanocomposites in dispersion.
The scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to study the surface morphology of the pristine GO, MoO2@GO, and WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes. The coating of MoO2@GO and WO3@GO nanocomposites on PES support can be shown in Figure 1a–d, respectively. Figure 1a,b clearly shows that the MoO2 particles are well dispersed on the surface of GO sheets in small bead form and also cross-link between GO sheets compared to a pristine GO membrane (Figure 1e), while the WO3@GO nanocomposite membrane exhibited numerous randomly oriented WO3 particles attached to the surface of the GO sheets (Figure 1c,d). Both composite membranes (Figure 1a,c) showed different surface morphology compared to the pristine GO (Figure 1e).
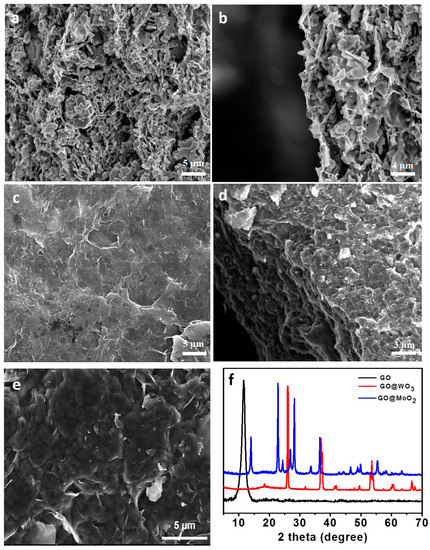
Figure 1.
Surface and cross-sectional images of (a,b) MoO2@GO and (c,d) WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes, respectively. (e) Surface SEM image of pristine GO membrane. (f) XRD pattern of GO-based membranes.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to characterize the structure and interlayer space of the MoO2@GO and WO3@GO-based nanocomposite membranes (Figure 1f). The XRD pattern well matched the JCPDS No 78-1073 monoclinic MoO2 (cell parameters, a = 5.660 Å, b = 4.860 Å, c = 5.545 Å, and β = 120.94 u). No diffraction peak was obtained for any impurities, suggesting a pure and highly crystalline MoO2. However, due to the weak crystallinity of the graphene sheets, the diffraction peak for GO is not clearly visible in the pattern, which also overlaps with 26.8° for MoO2 [35,39]. In addition, GO sheets are capable of showing a broad peak in the range of 0–20°, but due to the high intensity of the peak (110), the peak suppressed this feature [40]. This issue was also observed in the XRD pattern of the WO3@GO nanocomposite (26.1°). No clear diffraction peak of the GO is exhibited, which is due to the small amount of GO in the product and the fewer atomic numbers of carbon [41].
Further, we determined the surface chemistry of the composite membranes using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), as shown in Figure 2a–c. The pure GO membrane showed four peaks at 284.6, 286.2, 287.1, and 288.4 eV, which are attributed to C-C/C = C, C-O, C = O, and O-C = O bonds, respectively (Figure 2a). After the GO was cross-linked with MoO2, the intensity of the C-O peak drastically decreased (Figure 2b). The content of C-C/C = C groups increased from 41% to 82%, which indicates that the sp3/sp2-hybridized carbon structures are restored [42]. So, in the case of MoO2@GO nanocomposite membranes, the three C 1 s centered peaks were observed at 284.6, 286.4, and 287.7 eV, which were attributed to C-C, C-O, and C = O bonds, respectively. The C-O/C-C ratio of the pristine GO membrane decreased from 0.44 to 0.39 for the MoO2@GO composite membrane, which confirmed the reduction of the GO membrane. XPS studies on the WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes were also carried out (Figure 2c). The three C1s peaks of C-C, C-O, and C = O were observed at 284.5, 285.8, and 287.7 eV, respectively, which showed a lower intensity than the pure GO-based membranes. The C-O/C-C ratio was also calculated for the WO3@GO composite membrane, which confirmed the reduction of the GO membrane and the C/O ratio, decreasing from 0.44 to 0.35 in the case of the WO3@GO composite membrane. The carboxylic peaks of both composite membranes showed a lower intensity compared to the pristine GO membrane, due to thermal reduction treatment.
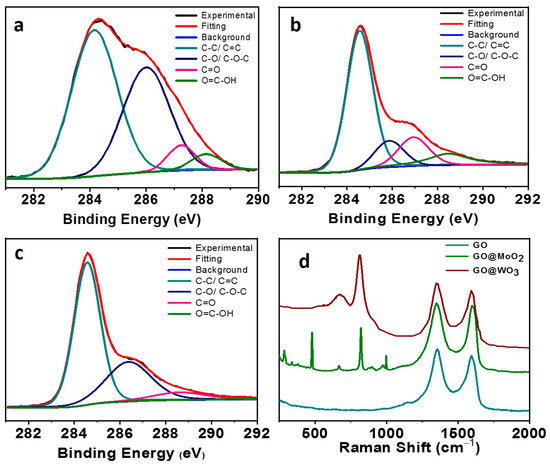
Figure 2.
(a–c) C 1 s XPs spectra of GO, (a) MoO2@GO, (b) and WO3@GO (c) nanocomposite membranes, respectively. (d) Raman studies of pristine GO, MoO2@GO, and WO3@GO-based membranes.
Further, Raman studies were carried out for the MoO2@GO and WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes (Figure 2d). Raman studies confirmed the synthesis of both composites. The two distinctive bands at 1359 and 1602 cm−1 were observed for the pristine GO membranes, these bands are then assigned to the D and G bands of the GO, respectively. As for the MoO2@GO composite membranes, the peaks at 991, 820, 664, 339, and 285 cm−1 are observed and assigned to the Mo = O stretching, O-Mo-O bending, and O-Mo-O wagging vibration modes of MoO2, respectively. While in the case of the WO3@GO composite membrane, the peaks observed at 705 and 814 cm−1 are assigned to the O-W-O stretching mode of WO3 (Figure 2d).
3.2. Water Permeance and Salt Rejection Performance
First, we evaluated the water permeance of our fabricated membranes by using 250 mL of DI water as shown in Table 1. The MoO2@GO nanocomposite membrane (400 ± 20 nm) showed a water permeance of ~410 ± 20 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, while the WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes exhibited a higher water permeance of ~445 ± 20 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, as shown in Figure 3a. Overall, both nanocomposite membranes showed an almost ten times higher permeance compared to pure GO-based membranes reported in the literature. Irregular stacking within MoO2@GO and WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes could present a more tortuous path to the flow of water, as compared to pure GO membranes. The water permeance of such membranes is possibly due to the larger interlayer space produced due to MoO2 and WO3 particles, irregular nanochannels, and the fact that the GO sheets of composite membranes may not be assembled entirely flat. This is different from corrugation, which has been reported for individual GO sheets. Further, we have studied the water permeance of using different thicknesses of both composite membranes (Table 1). First, we used MoO2@GO nanocomposite membranes with various thicknesses (400 ± 20 nm, 640 ± 20 nm, and 850 ± 20 nm). The 850 nm-thick composite membrane showed less permeance ~ 195 ± 20 L m−2 h−1 bar−1 as we increased the thickness from 400 ± 20 nm to 850 ± 20 nm, as shown in Figure 3b. The same trend has also been observed for the WO3@GO composite membrane. However, WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes with 900 ± 20 nm still showed a very high permeance 240 ± 20 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, which is several magnitudes higher than the results reported on GO-based membranes in the literature.

Table 1.
The water permeance of MoO2@GO and WO3@GO-based composite membranes with various thicknesses.
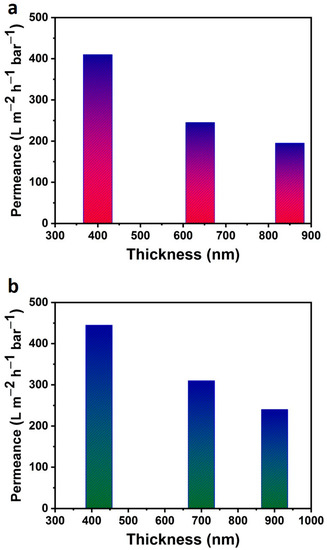
Figure 3.
(a,b) Water permeance of MoO2@GO (a) and WO3@GO (b) nanocomposite membranes at variable thicknesses.
Further, as-prepared MoO2@GO and WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes were used for the separation of salt ions from water, as shown in Figure 4a,b. Both composite membranes showed better rejection and permeance than the pristine GO-based membranes, as shown in Table 2. The performance of the filtration membrane in terms of its rejection of the ion solutions depends on the steric effect and the electrostatic interactions between the surface of the membrane and the ions. In our case, due to the comparable size of the ions and the pore size of the membrane, the main parameter that must be considered will be the electric interactions. Thus, as an exploratory study, we tested the retentions of our membrane with four kinds of salt NaCl, MgCl2, Ni(NO3) 2, and PbCl2, at the concentration of 0.01 M under a pressure of 1 bar. A high rejection of Ni(NO3)2 was achieved up to ~99 ± 1%, while the NaCl and MgCl2 showed less rejection (Figure 4a,b). The rejection sequence of the salt Ni(NO3)2 > PbCl2 ˃ (MgCl2) > (NaCl) was achieved for both nanocomposite membranes. The rejection of Ni2+ is higher than that of the Na+ and Mg2+ ion. This could be explained by the Donnan exclusion effect, which is usually applied to explain the retention mechanism for charged NF membranes. According to the Donnan exclusion theory, the rejection rate is related to the valences of the ion species, following the order of Zco-ions/Z counter-ions (Z refers to the valence). Such behavior is typical for negatively charged NF membranes. Our GO composite membranes are negatively charged due to the carboxylic groups at the edges and holes of the GO sheets. To maintain the electroneutrality of the solutions at each side of the GO composite membrane, the counter-ions Na+ and Mg2+ etc., have to be rejected as well. Moreover, the presence of counter-ions, which could bind part of the surface charge, may weaken the repulsive force, resulting in a higher retention for divalent cationic metal ions (Ni2+) compared to other salts. As a result, the retention sequence of different salt solutions was obtained as Ni(NO3)2 ˃ PbCl2> MgCl2 > NaCl. It should be noted that the salt rejections for our fabricated MoO2@GO and WO3@GO based nanocomposite membranes are higher than for pristine GO-based membranes, as shown in Table 2.
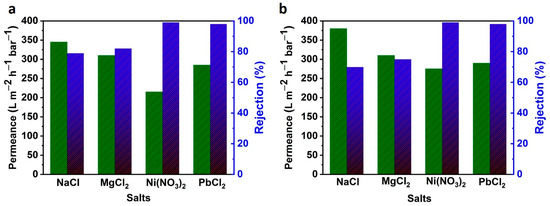
Figure 4.
The salts separation performance of (a) MoO2@GO and (b) WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes, respectively, at transmembrane pressure of 1 bar.

Table 2.
Separation performance of the GO nanocomposite membranes for various salts at 25 °C.
4. Conclusions
We have fabricated high-performance MoO2@GO and WO3@GO nanocomposite membranes for a water purification and desalination application. Such membranes were characterized with the help of XRD, SEM, and XPS techniques. Further, we measured the rejection efficiency of both membranes for different salts such as NaCl, MgCl2, Ni(NO3)2, and PbCl2 with variable sizes and molecular masses. The as-prepared WO3@GO nanocomposite showed a better separation efficiency (~99%) for Ni(NO3)2 salt along with a good water permeance of ~275 ± 10 L m−2 h−1 bar−1, compared to the pristine GO and MoO2@GO composite membranes. We hope that this work provides a new approach to designing high-performance GO composite membranes with asymmetric filler distribution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.S. and F.H.M.; methodology, F.S.; software, M.A.K.; validation, M.A.K., M.I. and A.I.; formal analysis, F.S.; investigation, A.A.M.; resources, F.H.M. and K.H.C.; data curation, A.A.M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.S. and M.A.K.; writing—review and editing, M.I. and A.I.; visualization, K.H.T.; supervision, K.H.T., J.H.L. and K.H.C.; project administration, J.H.L.; K.H.T. and K.H.C.; funding acquisition, K.H.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research work is financially supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea grant funded by the Korea Government (MIST) (NRF-2022R1A2C2004771).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This research work is financially supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea grant funded by the Korea Government (MIST) (NRF-2022R1A2C2004771). F.S is thankful for Begum Nusrat Bhutto (BNB) Women University, Sukkur Pakistan for their research facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ma, T.; Sun, S.; Fu, G.; Hall, J.; Ni, Y.; He, L.; Yi, J.; Zhao, N.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; et al. Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolan, F.; Lamontagne, J.; Link, R.; Hejazi, M.; Reed, P.; Edmonds, J. Evaluating the economic impact of water scarcity in a changing world. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armendáriz-Ontiveros, M.M.; Villegas-Peralta, Y.; Madueño-Moreno, J.; Álvarez-Sánchez, J.; Dévora-Isiordia, G.; Sánchez-Duarte, R.; Madera-Santana, T. Modification of thin film composite membrane by chitosan-silver particles to improve desalination and anti-biofouling performance. Membranes 2022, 12, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed, M.M.; Abulnour, A.; Tewfik, S.; Sorour, M.; Hani, H.; Shaalan, H. Reverse osmosis membrane zero liquid discharge for agriculture drainage water desalination: Technical, economic, and environmental assessment. Membranes 2022, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, F.; Memon, F.H.; Ullah, S.; Mazumder, M.J.; Al-Ahmed, A.; Khan, F.; Thebo, K.H. Recent development in laminar transition metal dichalcogenides-based membranes towards water desalination: A Review. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202200107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjhi, F.A.; Janwery, D.; Chandio, I.; Ullah, S.; Rehman, F.; Memon, A.; Hakami, J.; Khan, F.; Boczkaj, G.; Thebo, K. Recent advances in graphene oxide-Based membranes for heavy metal ions separation. ChemBioEng Rev. 2022, 9, 574–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Rehman, F.; Khan, M.A.; Memon, F.; Soomro, F.; Iqbal, M.; Yang, J.; Thebo, K. Functionalized graphene oxide-based lamellar membranes with tunable nanochannels for ionic and molecular separation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 32410–32417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, X.; Thebo, K.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Controlling reduction degree of graphene oxide membranes for improved water permeance. Bull. Sci. 2018, 63, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Chepeleva, A.; Liamin, V.; Kuzminova, A.; Mazur, A.; Semenov, K.; Penkova, A. Novel PDMS-b-PPO membranes modified with graphene oxide for efficient pervaporation ethanol dehydration. Membranes 2022, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, Y.Y.; Robertson, E.; Cortez, R.; Vlassiouk, I.; Bucinell, R.; Olsson, K.; Kilby, L. Using Al3+ to tailor graphene oxide nanochannels: Impact on membrane stability and permeability. Membranes 2022, 12, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandio, I.; Janjhi, F.; Memon, A.; Memon, S.; Ali, Z.; Thebo, K.; Pirzado, A.; Hakro, A.; Khan, W. Ultrafast ionic and molecular sieving through graphene oxide based composite membranes. Desalination 2021, 500, 114848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjhi, F.A.; Chandio, I.; Memon, A.A.; Ahmed, Z.; Thebo, K.H.; Pirzado, A.A.A.; Hakro, A.A.; Iqbal, M. Functionalized graphene oxide based membranes for ultrafast molecular separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 117969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Aamir, M.; Thebo, K.; Akhtar, J. Laminar graphene oxide membranes towards selective ionic and molecular separations: Challenges and progress. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ying, Y.; Peng, X.J. Graphene oxide nanosheet: An emerging star material for novel separation membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13772–13782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Wei, Q.; Huang, K.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Green synthesis of graphene oxide by seconds timescale water electrolytic oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Mi, B. Enabling graphene oxide nanosheets as water separation membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3715–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. Free-standing graphene oxide-palygorskite nanohybrid membrane for Oil/Water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8247–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, W.-N.; Liu, D.; Nie, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, F.; Biswas, P.; Fortner, J.D. Engineered crumpled graphene oxide nanocomposite membrane assemblies for advanced water treatment processes. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6846–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chung, T.-S. Nanometric graphene oxide framework membranes with enhanced heavy hetal removal via nanofiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10235–10242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D.; Song, X.; Bai, H. A new nanocomposite forward osmosis membrane custom-designed for treating shale gas wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P Sun Ma, R.; Ma, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, K.; Sasaki, T.; Zhu, H. Highly selective charge-guided ion transport through a hybrid membrane consisting of anionic graphene oxide and cationic hydroxide nanosheet superlattice units. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; He, G.; Xing, R.; Pan, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Wang, B. Incorporating zwitterionic graphene oxides into sodium alginate membrane for efficient water/alcohol separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Uliana, A.; Tian, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Volodin, A.; Simoens, K.; Yuan, S.; Li, J.; et al. Mussel-inspired architecture of high-flux loose nanofiltration membrane functionalized with antibacterial reduced graphene oxide–copper nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28990–29001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, G. WO3 nanorods/graphene nanocomposites for high-efficiency visible-light-driven photocatalysis and NO2 gas sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 8525–8531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatamian, M.; Khodakarampoor, N.; Oskoui, M.S.; Kazemian, N. Synthesis and characterization of RGO/zeolite composites for the removal of arsenic from contaminated water. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35352–35360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madau, L.; Schumacher, J.; Ghosh, M.; Ochedowski, O.; Meyer, J.; Lebius, H.; Ban-d, B.; Toimil-Molares, M.; Trautmann, C.; Lammertink, R.; et al. Fabrication of nanoporous graphene/polymer composite membranes. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 10487–10493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, F.H.; Rehman, F.; Lee, J.; Soomro, F.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, S.; Ali, A.; Thebo, K.; Choi, K. Transition metal dichalcogenide-based membranes for water desalination, gas separation, and energy storage. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, I.; Memon, F.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, K.; Ahmed, R.; Soomro, F.; Rehman, F.; Memon, A.; Thebo, K.; Choi, K. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for water purification and antibacterial applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Mehmood, M.; Ahmed, J.; Majeed, A.; Thebo, K. CVD grown defect rich-MWCNTs with anchored CoFe alloy nanoparticles for OER activity. Mater. Lett. 2020, 259, 126831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Cheng, H.-M. The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 2012, 50, 3210–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizighannad, S.; Mitra, S. Stepwise reduction of graphene oxide (GO) and its effects on chemical and colloidal properties. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yan, L.; Bangal, P. Chemical reduction of graphene oxide to graphene by sulfur-containing compounds. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 19885–19890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, W.; Li, Z. Controlling interlayer spacing of graphene oxide membranes by external Pressure Regulation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9309–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thebo, K.H.; Qian, X.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.; Cheng, H.; Ren, W. Highly stable graphene-oxide-based membranes with superior permeability. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, X.; Luo, W.; Huang, Y. Self-assembled hierarchical MoO2/graphene nanoarchitectures and their application as a high-performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7100–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Xu, L.; Shang, S.; Zhou, X.; Meng, L. Visible light induced methylene blue dye degradation photo-catalyzed by WO3/graphene nanocomposites and the mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15235–15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Pei, S.; Ren, W.; Gao, L.; Cheng, H.-M. Efficient preparation of large-area graphene oxide sheets for transparent conductive films. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5245–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cheng, Z.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhao, H. Facile synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/hexagonal WO3 nanosheets composites with enhanced H2S sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 230, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Di, X.; Ma, C.; Zhu, C.; Gao, P.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Ouyang, Q. Graphene-MoO2 hierarchical nanoarchitectures: In situ reduction synthesis and high rate cycling performance as lithium-ion battery anodes. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17659–17663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petnikota, S.; Teo, K.; Chen, L.; Sim, A.; Marka, S.; Reddy, M.; Srikanth, V.; Adams, S.; Chowdari, B. Exfoliated graphene oxide/MoO2 composites as anode materials in lithium-ion batteries: An insight into intercalation of Li and conversion mechanism of MoO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10884–10896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-M.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-W.; Kwak, D.-H.; Park, H.-C.; Kim, M.-C.; Hwang, B.-M.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.-H.; Hong, S.; et al. Two-dimensional nanocomposites based on tungsten oxide nanoplates and graphene nanosheets for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 163, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thebo, K.H.; Qian, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W.J. Reduced graphene oxide/metal oxide nanoparticles composite membranes for highly efficient molecular separation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).