Functionalization and Surface Modification of Mesoporous Hydrophobic Membranes by Oligomers and Target Additives via Environmental Crazing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nanocomposite Membranes and Their Surface Modification
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Estimation of Volume Porosity
2.3.2. Low-Temperature Strain Recovery
2.3.3. Estimation of the Composition of the Composite Membranes
2.3.4. Tensile Tests
2.3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3.6. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with X-ray Spectral Analysis
2.3.8. Wettability and Water Contact Angles of Membranes
2.3.9. Water Vapor Permeability and Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR)
2.3.10. Gas Permeability Measurements
2.3.11. Assessment of Antibacterial Activity of Nanocomposite Membranes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Crazing of PP, HDPE, and PET
3.2. Structure of Membranes
3.3. Liquid Supported Nanocomposite Membranes Containing PPG and PEG
3.4. Nanocomposite Open-Porous HDPE-Based Membranes Containing PVA and Salicylic Acid
3.5. Performance of PP, HDPE, and PET Membranes with Hydrophilic Oligomers
3.5.1. Water Vapor Permeability and Wettability
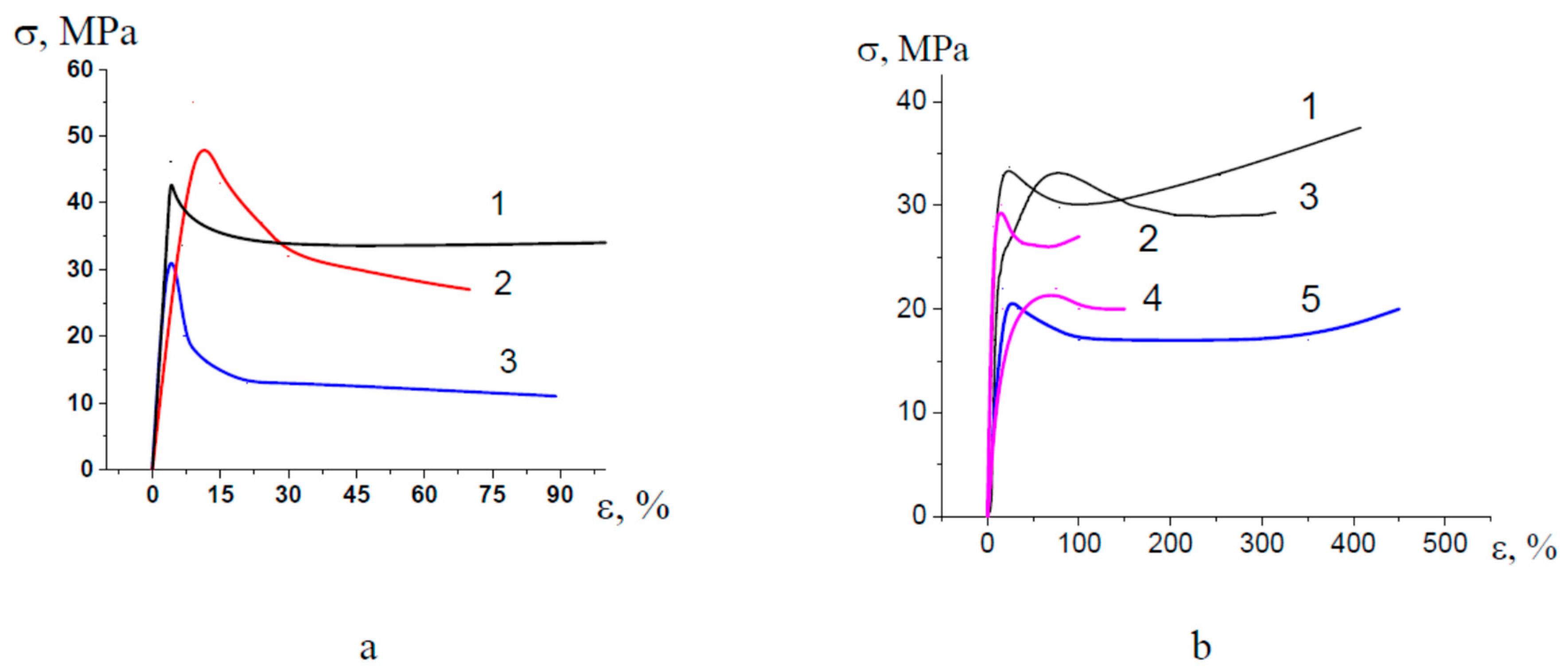
3.5.2. Mechanical Properties
3.5.3. Gas Permeability of Liquid-Supported PP-PEG Membranes
3.6. Performance of Nanocomposite HDPE-PVA, HDPE-SA, HDPE-PVA-SA Membranes
3.6.1. Water Vapor Permeability and Wettability
3.6.2. Antibacterial Properties
3.6.3. Sensing Characteristics
3.6.4. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tan, X.; Rodrigue, D. A Review on Porous Polymeric Membrane Preparation. Part II: Production Techniques with Polyethylene, Polydimethylsiloxane, Polypropylene, Polyimide, and Polytetrafluoroethylene. Polymers 2019, 11, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himma, N.F.; Anisah, S.; Prasetya, N.; Wenten, I.G. Advances in preparation, modification, and application of polypropylene membrane. J. Polym. Eng. 2016, 36, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.; Mazinani, S.; Gharehaghaji, A.A. A review on emerging developments in thermal and moisture management by membrane-based clothing systems towards personal comfort. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, M.; Candan, Z. An Insight into the Next-Generation Smart Membranes. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokanova, L.G.; Nechaev, A.N.; Apel, P.Y. The Effect of Surfactants’ Concentration on the Geometry of the Formed Pores by Etching of the Polyethelene Naphtalate Films Irradiated with High-Energy Ions. Colloid J. 2014, 76, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukanina, K.I.; Grigor’ev, K.I.; Tenchurin, T.K.; Shepelev, A.D.; Chvalun, S.N. Nonwoven Materials Produced by Electrospinning for Modern Medical Technologies (Review). Fibre Chem. 2017, 49, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Song, H.-S. Lamellar crystalline structure of hard elastic HDPE films and its influence on microporous membrane formation. Polymer 2006, 47, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, G.; MacInnis, K.; Olah, A.; Baer, E. Formation of microporous membranes by biaxial orientation of compatibilized PP/Nylon 6 blends. Polymer 2017, 123, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffar, A.; Carreau, P.J.; Ajji, A.; Kamal, M.R. Development of polypropylene microporous hydrophilic membranes by blending with PP-g-MA and PP-g-AA. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 462, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandavasu, C.; Xanthos, M.; Sirkar, K.K.; Gogos, C.G. Fabrication of microporous polymeric membranes by melt processing of immiscible blends. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xu, R.; Lei, C. Uniaxial stretching induced pore nucleation and growth in row-nucleated crystalline hard-elastic polypropylene film: The effect of activation volume and stretching work. Polymer 2018, 158, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castejon, P.; Habibi, K.; Saffar, A.; Ajji, A.; Martínez, A.B.; Arencón, D. Polypropylene-Based Porous Membranes: Influence of Polymer Composition, Extrusion Draw Ratio and Uniaxial Strain. Polymers 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Ji, Y.; Meng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, L. Strain and temperature dependence of deformation mechanism of lamellar stacks in HDPE and its guidance on microporous membrane preparation. Polymer 2016, 105, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Q. Toward uniform pore-size distribution and high porosity of isotactic polypropylene microporous membrane by adding a small amount of ultrafine full-vulcanized powder rubber. Polymer 2016, 103, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lei, C.; Cai, Q.; Xu, R.; Hu, B.; Shi, W.; Peng, X. Study of structure and properties of polypropylene microporous membrane by hot stretching. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Elimelech, M.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling membranes for sustainable water purification: Strategies and mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-Y.; Xue, Y.-R.; Yang, H.-C.; Wu, J.; Xu, Z.K. Surface and Interface Engineering of Polymer Membranes: Where We Are and Where to Go. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggenberger, O.M.; Ying, C.; Mayer, M. Surface coatings for solid-state nanopores. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Jons, S.D. Chemistry and fabrication of polymeric nanofiltration membranes: A review. Polymer 2016, 103, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volynskii, A.L.; Bakeev, N.F. Surface Phenomena in the Structural and Mechanical Behaviour of Solid Polymers; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. 552. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Wang, H. Current understanding of surface effects in microcutting. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Argon, A.S.; Cohen, R.E. Enhanced Case-II diffusion of diluents into glassy polymers undergoing plastic flow. Polymer 2001, 42, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimchuk, E.S.; Efimov, A.V.; Nikitin, L.N.; Nikonorova, N.I.; Volynskii, A.L.; Khokhlov, A.R.; Bakeev, N.F. Preparation of nanoporous polyolefin films in supercritical carbon dioxide. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 8, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarysheva, A.Y.; Bagrov, D.V.; Bakirov, A.V.; Yarysheva, L.M.; Chvalun, S.N.; Volynskii, A.L. Effect of initial polypropylene structure on its deformation via crazing mechanism in a liquid medium. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 100, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarysheva, A.Y.; Rukhlya, E.G.; Yarysheva, L.M.; Bagrov, D.V.; Volynskii, A.L.; Bakeev, N.F. The structural evolution of high-density polyethylene during crazing in liquid medium. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 66, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarysheva, A.Y.; Bakirov, A.V.; Yarysheva, L.M.; Arzhakov, M.S.; Arzhakova, O.V.; Chvalun, S.N. Unique structure and new thermophysical properties of poly(ethylene oxide) in nanocomposites based on nanoporous polypropylene matrices. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzhakova, O.V.; Dolgova, A.A.; Yarysheva, A.Y.; Zezin, A.A. Controlled green synthesis of hybrid organo-inorganic nanomaterials based on poly(ethylene terephthalate) and silver nanoparticles by x-ray radiolysis. Express Polym. Lett. 2021, 15, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarysheva, A.Y.; Yarysheva, L.M.; Drozdov, F.V.; Arzhakova, O.V.; Muzafarov, A.M. Controlled wettability of polymers via environmental crazing. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 40, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodi, G. Standard Test Methods for Water Vapor Transmission of Materials. Available online: http://www.manufacturingsolutionscenter.org/moisture-vapor-transmission.html (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Piddok, L.J.V. Techniques used for the determination of antibacterial resistance and sensitivity in bacteria. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 68, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da C Andrade, E.N.; Randall, R.F.Y.; Makin, M.J. The Rehbinder Effect. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 1950, 63, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarence, J.W.; Holly, F. Stress-enhanced transport of toluene in poly aryl ether ether ketone (PEEK). J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1996, 34, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed.; The “Gold Book”; McNaught, A.D., Wilkinson, A., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Large Contact Angles of Plant and Animal Surfaces. Nature 1945, 155, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JUTA Group. Available online: http://www.juta.cz (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Mega Flex. Available online: https://mega-flex.ru (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Liu, S.L.; Shao, L.; Chua, M.L.; Lau, C.H.; Wang, H.; Quan, S. Recent progress in the design of advanced PEO-containing membranes for CO2 removal. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Antibacterial Activity of Some Flavonoids and Organic Acids Widely Distributed in Plants. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Polymer/Additive | WCA, ° | WVTR, g/(m2 day) |
|---|---|---|
| PP | 98 | 0 |
| PP-PEG | 65 | 1254 |
| PP-PPG | 45 | 249 |
| PET | 83 | 0 |
| PET-PEG | 57 | 1660 |
| PET-PPG | 38↔/27↕ | 604 |
| HDPE | 98 | 0 |
| HDPE-PPG | 50 | 302 |
| Permeability P, Barrer | |||||
| H2 | CO2 | CH4 | N2 | Ar | He |
| 7 | 11.3 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 1.7 | 7.2 |
| Selectivity, α | |||||
| H2/CO2 | H2/CH4 | H2/N2 | H2/Ar | H2/He | |
| 0.6 | 5.4 | 14.0 | 4.1 | 1.0 | |
| CO2/H2 | CO2/CH4 | CO2/N2 | CO2/Ar | CO2/He | |
| 1.6 | 8.7 | 22.6 | 6.6 | 1.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yarysheva, A.Y.; Klyamkin, S.N.; Yarysheva, L.M.; Arzhakova, O.V. Functionalization and Surface Modification of Mesoporous Hydrophobic Membranes by Oligomers and Target Additives via Environmental Crazing. Membranes 2023, 13, 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050466
Yarysheva AY, Klyamkin SN, Yarysheva LM, Arzhakova OV. Functionalization and Surface Modification of Mesoporous Hydrophobic Membranes by Oligomers and Target Additives via Environmental Crazing. Membranes. 2023; 13(5):466. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050466
Chicago/Turabian StyleYarysheva, Alena Yu., Semen N. Klyamkin, Larisa M. Yarysheva, and Olga V. Arzhakova. 2023. "Functionalization and Surface Modification of Mesoporous Hydrophobic Membranes by Oligomers and Target Additives via Environmental Crazing" Membranes 13, no. 5: 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050466
APA StyleYarysheva, A. Y., Klyamkin, S. N., Yarysheva, L. M., & Arzhakova, O. V. (2023). Functionalization and Surface Modification of Mesoporous Hydrophobic Membranes by Oligomers and Target Additives via Environmental Crazing. Membranes, 13(5), 466. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13050466








