A New Approach to the Development of Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Water Treatment: Mixed Polymer Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. Membrane Mechanical Resistance
2.3.2. Membranes Morphology
2.3.3. Membranes Hydrophilicity
2.3.4. Membranes Porosity
2.3.5. Membranes Permeability
3. Results and Discussion
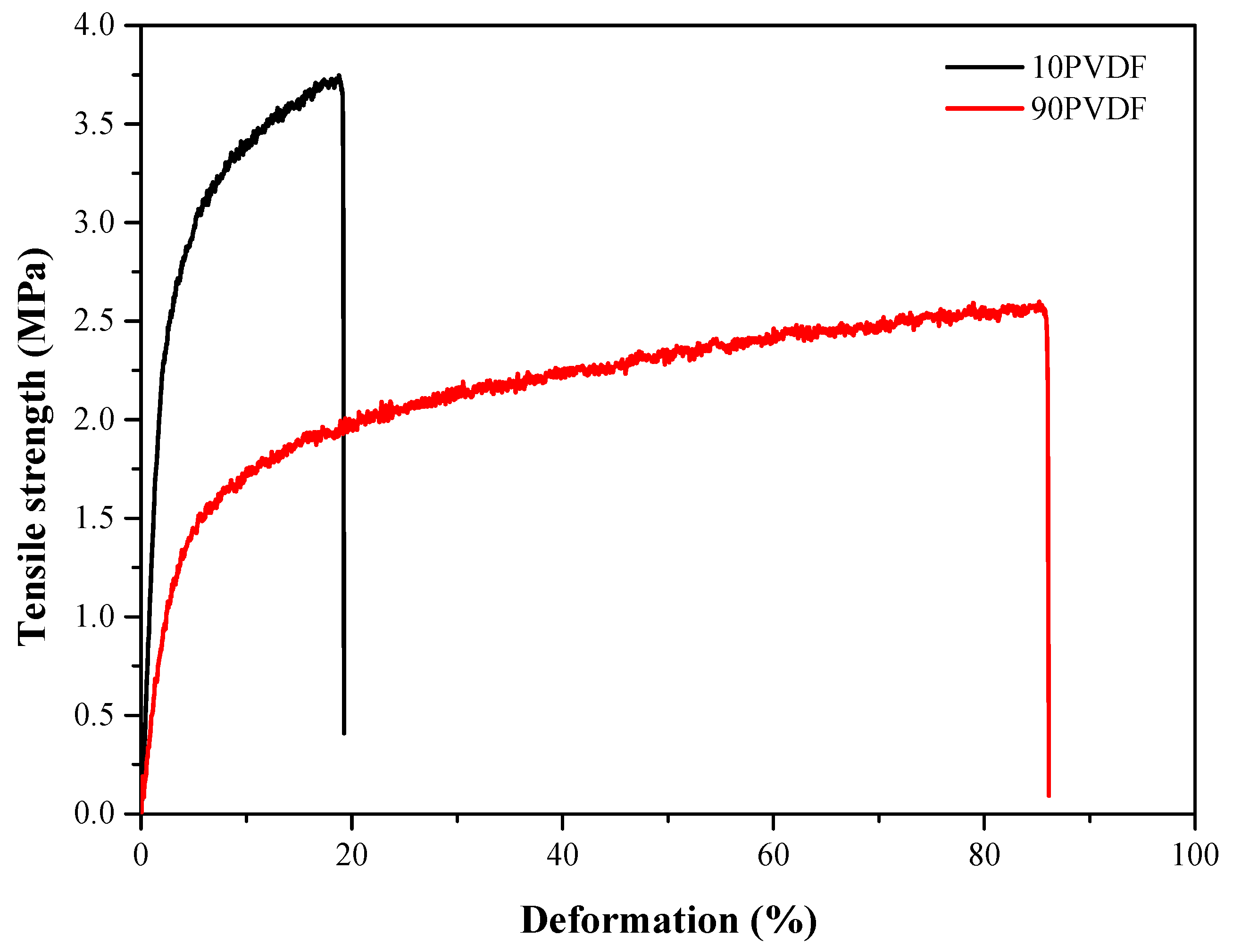
3.1. Mechanical Resistance
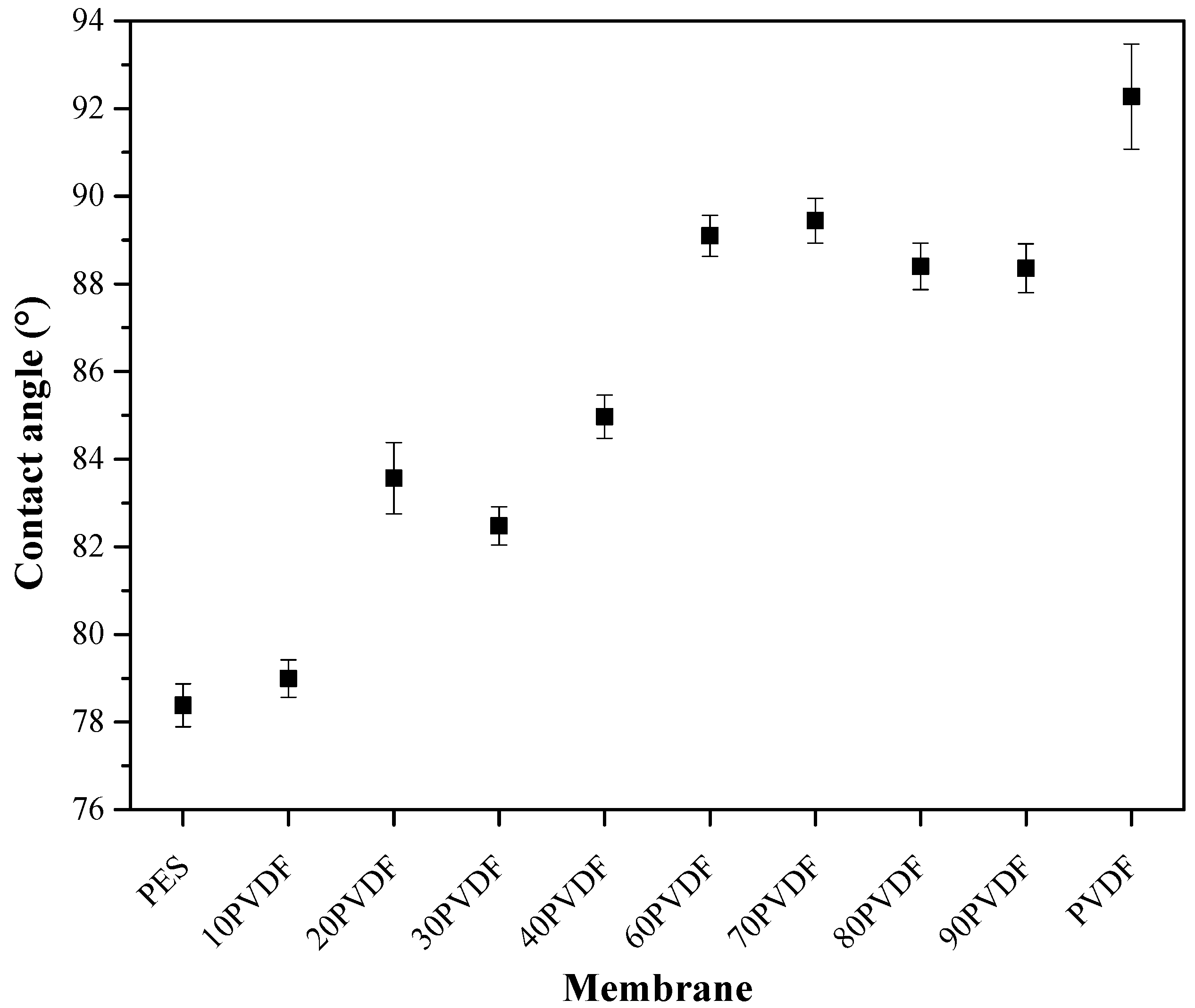
3.2. Hydrophilicity
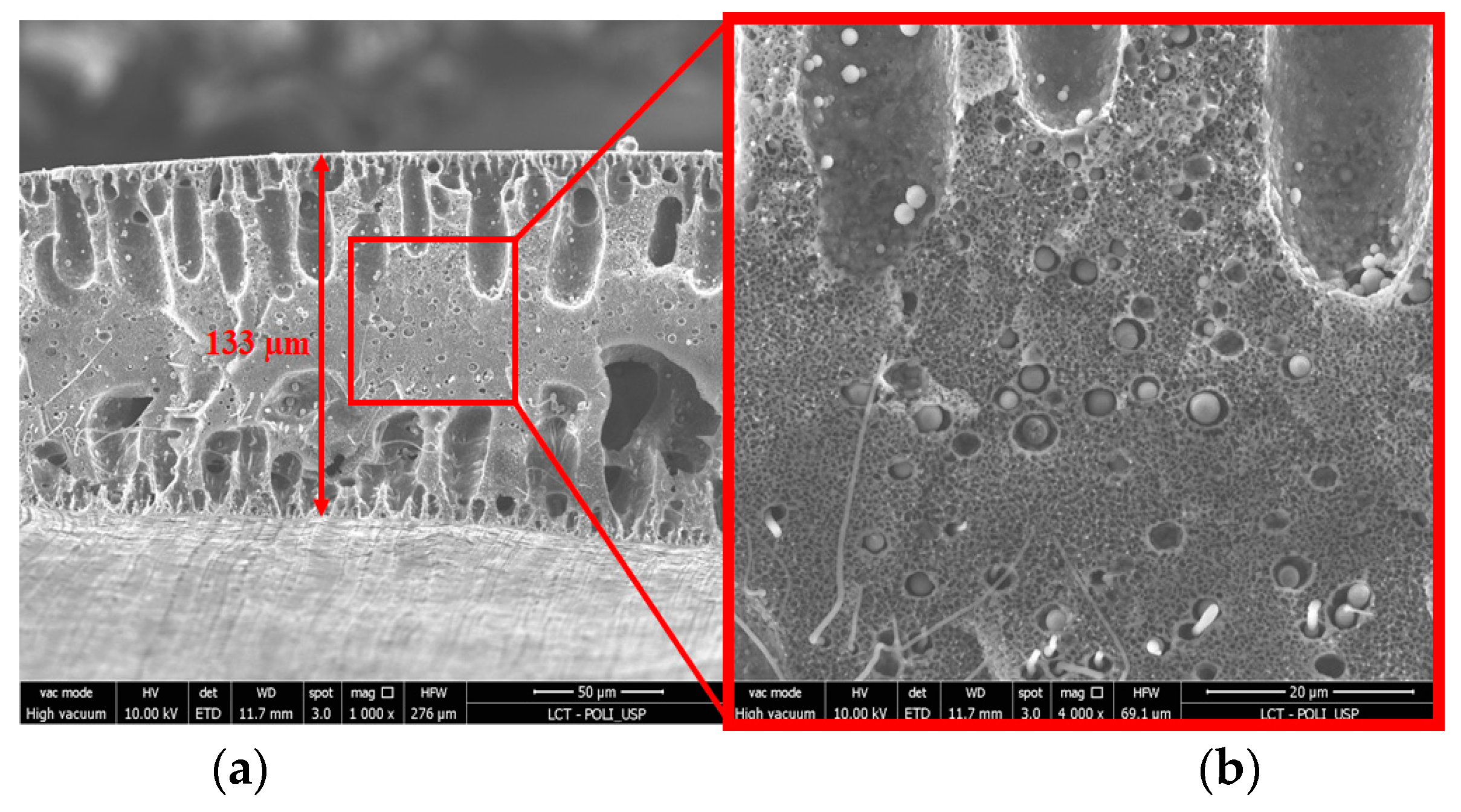
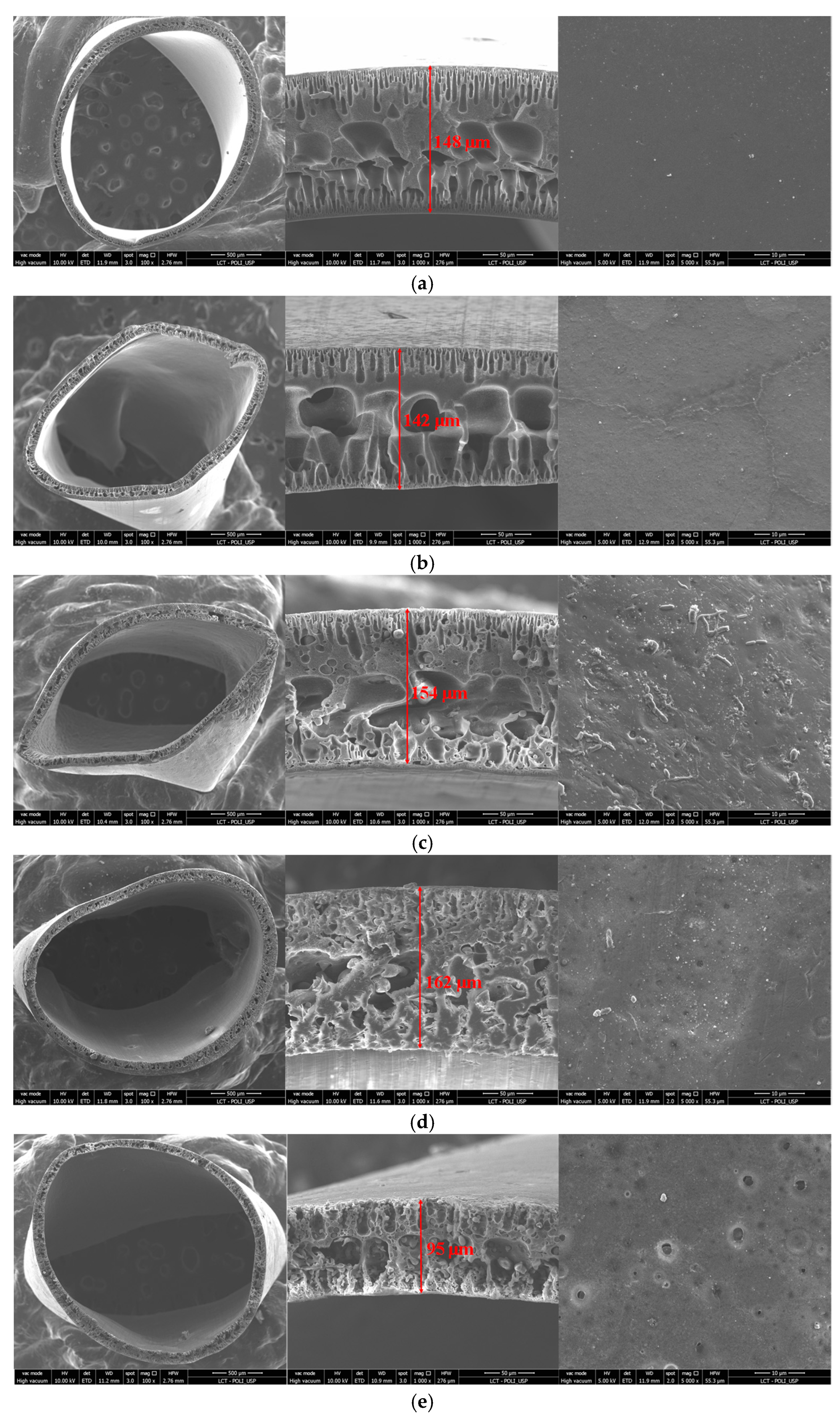
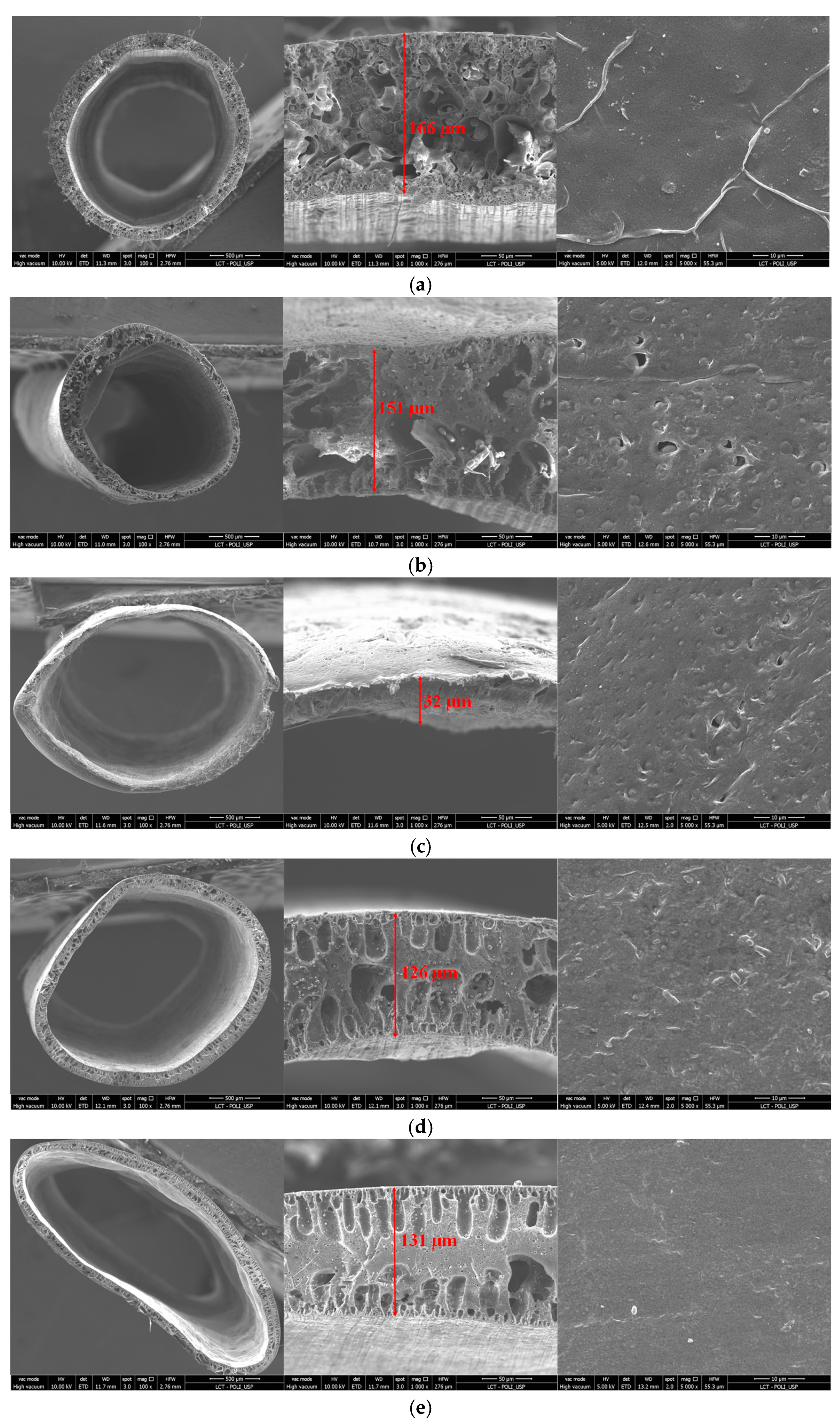
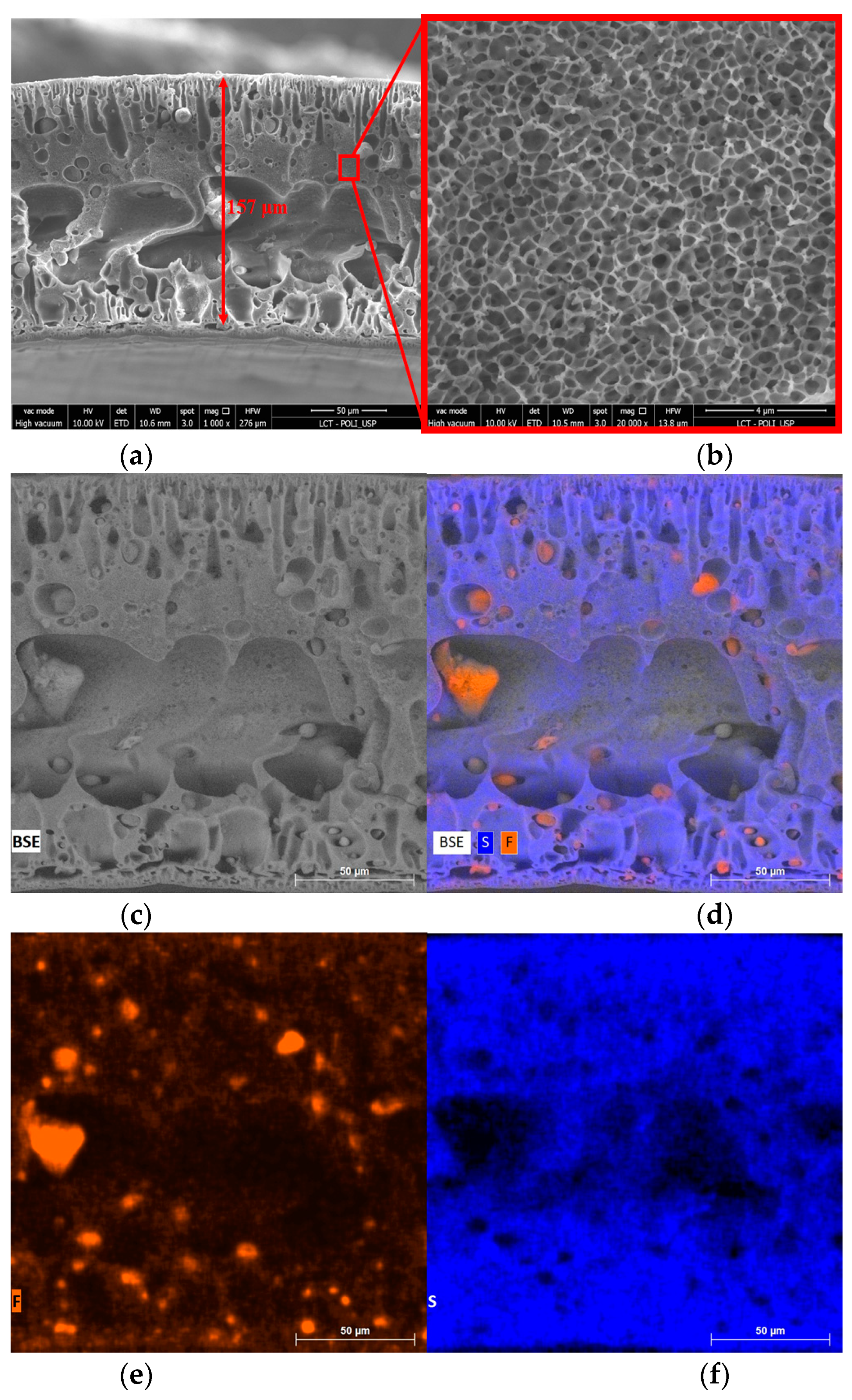
3.3. Membrane Morphology and Composition
3.4. Permeability and Porosity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2017: Special Focus on Inequalities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Mierzwa, J.C.; da Silva, M.C.C.; Veras, L.R.V.; Subtil, E.L.; Rodrigues, R.; Li, T.; Landenberger, K.R. Enhancing spiral-wound ultrafiltration performance for direct drinking water treatment through operational procedures improvement: A feasible option for the Sao Paulo Metropolitan Region. Desalination 2012, 307, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espíndola, J.C.; Mierzwa, J.C.; Amaral, M.C.; De Andrade, L.H. Water Reuse through Membrane Technologies for a Dairy Plant Using Water Pinch Simulation Software. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, I.; Fachrul, R.; Ito, T.; Ohmukai, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Development of a hydrophilic polymer membrane containing silver nanoparticles with both organic antifouling and antibacterial properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 387–388, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Jiang, T.; Liang, R.; Qin, W. Polymeric membrane ion-selective electrodes with anti-biofouling properties by surface modification of silver nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 328, 129014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.-F.; Boo, C.; Lu, X.; Zhou, X.; Yu, H.-Q.; Elimelech, M. Surface functionalization of reverse osmosis membranes with sulfonic groups for simultaneous mitigation of silica scaling and organic fouling. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lemos, H.G.; Ragio, R.A.; Conceição, A.C.S.; Venancio, E.C.; Mierzwa, J.C.; Subtil, E.L. Assessment of mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) incorporated with graphene oxide (GO) for co-treatment of wastewater and landfill leachate (LFL) in a membrane bioreactor (MBR). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sharma, A.; Awasthi, K.K.; Awasthi, A. Metal oxides nanocomposite membrane for biofouling mitigation in wastewater treatment. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 21, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Nazam, N.; Rizvi, S.M.; Ahmad, K.; Baig, M.H.; Lee, E.J.; Choi, I. Mechanistic Insights into the Antimicrobial Actions of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Implications for Multidrug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Li, N. Preparation of hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride/polyvinyl alcohol ultrafiltration membrane via polymer/non-solvent co-induced phase separation method towards enhance anti-fouling performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subtil, E.L.; Gonçalves, J.; Lemos, H.G.; Venancio, E.C.; Mierzwa, J.C.; dos Santos de Souza, J.; Alves, W.; Le-Clech, P. Preparation and characterization of a new composite conductive polyethersulfone membrane using polyaniline (PANI) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO). Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.S.; Pourghorbani, R. Preparation of PVDF/PES Blend Membranes for Cold Sterilization of Water and Milk. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2013, 32, E141–E152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.S.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Nady, N.; Elmarghany, M.R.; Sabry, M.N. PES/PVDF blend membrane and its composite with graphene nanoplates: Preparation, characterization, and water desalination via membrane distillation. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 166, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1557; Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength and Young’s Modulus of Fibers. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008.
- ISO 15989; Plastic-Film and Sheeting-Measurement of Water-Contact Angle of Corona Treated Films. American National Standards Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Kumar, R.V.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Elaboration of novel tubular ceramic membrane from inexpensive raw materials by extrusion method and its performance in microfiltration of synthetic oily wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Su, Q.; Li, S.; Wen, G.; Huang, T. Aging of PVDF and PES ultrafiltration membranes by sodium hypochlorite: Effect of solution pH. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 104, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Abdullah, S.Z.; Bérubé, P.; Le-Clech, P. Ageing of membranes for water treatment: Linking changes to performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 503, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Tang, X.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Zhang, P.; Cui, Z.; Matsuyama, H. Fabrication of PVDF/EVOH blend hollow fiber membranes with hydrophilic property via thermally induced phase process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 122031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruigómez, I.; Vera, L.; González, E.; Rodríguez-Sevilla, J. Pilot plant study of a new rotating hollow fibre membrane module for improved performance of an anaerobic submerged MBR. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ladegaard Skov, A.; Liu, S.-H.; Yu, L.-Y.; Xu, Z.-l. A Facile Way to Prepare Hydrophilic Homogeneous PES Hollow Fiber Membrane via Non-Solvent Assisted Reverse Thermally Induced Phase Separation (RTIPS) Method. Polymers 2019, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.-W.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Xu, Z.-L.; Tang, Y.-J. Interfacial polymerization on PES hollow fiber membranes using mixed diamines for nanofiltration removal of salts containing oxyanions and ferric ions. Desalination 2016, 394, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xiao, C.; An, S.; Hu, X. Preparation and properties of PVDF/PVA hollow fiber membranes. Desalination 2010, 250, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Shi, L.; Fane, A.G.; Debowski, M. Performance improvement of PVDF hollow fiber-based membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.-L.; Alsalhy Qusay, F. Polyethersulfone (PES) hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes prepared by PES/non-solvent/NMP solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 233, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Yin, J.; Deng, B. Seven-bore hollow fiber membrane (HFM) for ultrafiltration (UF). Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 128, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsalhy, Q.F.; Salih, H.A.; Simone, S.; Zablouk, M.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Poly(ether sulfone) (PES) hollow-fiber membranes prepared from various spinning parameters. Desalination 2014, 345, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Chen, K.; Xiao, C.; Ji, D.; Ling, H.; Li, M.; Liu, H. Improving pressure durability and fractionation property via reinforced PES loose nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for textile wastewater treatment. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 108, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Li, T.; Fan, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. Construction of rough and porous surface of hydrophobic PTFE powder-embedded PVDF hollow fiber composite membrane for accelerated water mass transfer of membrane distillation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 108, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, R.A.; Medeiros, V.d.N.; Silva, B.I.A.; Araújo, E.M.; Lira, H.d.L. Study of the influence of viscosity on the morphology of polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes/additives. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Xiao, C.; Ji, D. Robust preparation and reinforcement mechanism study of PVDF hollow fiber membrane with homogeneous fibers. Polym. Test. 2022, 108, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Membrane | PVDF (%) | PES (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PES | 0 | 100 |
| PVDF | 100 | 0 |
| 10PVDF | 10 | 90 |
| 20PVDF | 20 | 80 |
| 30PVDF | 30 | 70 |
| 40PVDF | 40 | 60 |
| 60PVDF | 60 | 40 |
| 70PVDF | 70 | 30 |
| 80PVDF | 80 | 20 |
| 90PVDF | 90 | 10 |
| Membrane | Tensile Strength at Break (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PES | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 65.6 ± 12.8 | 109.9 ± 7.9 |
| 10PVDF | 3.9 ± 0.3 | 15.4 ± 4.3 | 105.5 ± 13.6 |
| 20PVDF | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 14.1 ± 7.4 | 78.8 ± 20.3 |
| 30PVDF | 3.3 ± 0.2 | 26.4 ± 6.2 | 69.5 ± 12.4 |
| 40PVDF | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 29.7 ± 7.4 | 82.7 ± 4.4 |
| 60PVDF | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 47.6 ± 11.4 | 44.9 ± 0.2 |
| 70PVDF | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 107.7 ± 16.2 | 32.8 ± 4.7 |
| 80PVDF | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 101.8 ± 10.9 | 14.9 ± 1.9 |
| 90PVDF | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 105.6 ± 25.9 | 33.5 ± 7.2 |
| PVDF | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 176.6 ± 40.3 | 27.5 ± 5.2 |
| Membrane | Diameter (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Standard Deviation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | 2.13 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.01 |
| PVDF | 2.28 | 0.30 | 0.15 | 0.02 |
| 10PVDF | 1.98 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.01 |
| 20PVDF | 2.00 | 0.47 | 0.14 | 0.01 |
| 30PVDF | 2.14 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.01 |
| 40PVDF | 1.91 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| 60PVDF | 1.65 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| 70PVDF | 2.29 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.04 |
| 80PVDF | 2.14 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.01 |
| 90PVDF | 2.08 | 0.21 | 0.12 | 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva Biron, D.; Espíndola, J.C.; Subtil, E.L.; Mierzwa, J.C. A New Approach to the Development of Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Water Treatment: Mixed Polymer Matrices. Membranes 2023, 13, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070613
da Silva Biron D, Espíndola JC, Subtil EL, Mierzwa JC. A New Approach to the Development of Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Water Treatment: Mixed Polymer Matrices. Membranes. 2023; 13(7):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070613
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva Biron, Dionísio, Jonathan Cawettiere Espíndola, Eduardo Lucas Subtil, and José Carlos Mierzwa. 2023. "A New Approach to the Development of Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Water Treatment: Mixed Polymer Matrices" Membranes 13, no. 7: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070613
APA Styleda Silva Biron, D., Espíndola, J. C., Subtil, E. L., & Mierzwa, J. C. (2023). A New Approach to the Development of Hollow Fiber Membrane Modules for Water Treatment: Mixed Polymer Matrices. Membranes, 13(7), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13070613









