Fouling Reduction and Thermal Efficiency Enhancement in Membrane Distillation Using a Bilayer-Fluorinated Alkyl Silane–Carbon Nanotube Membrane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
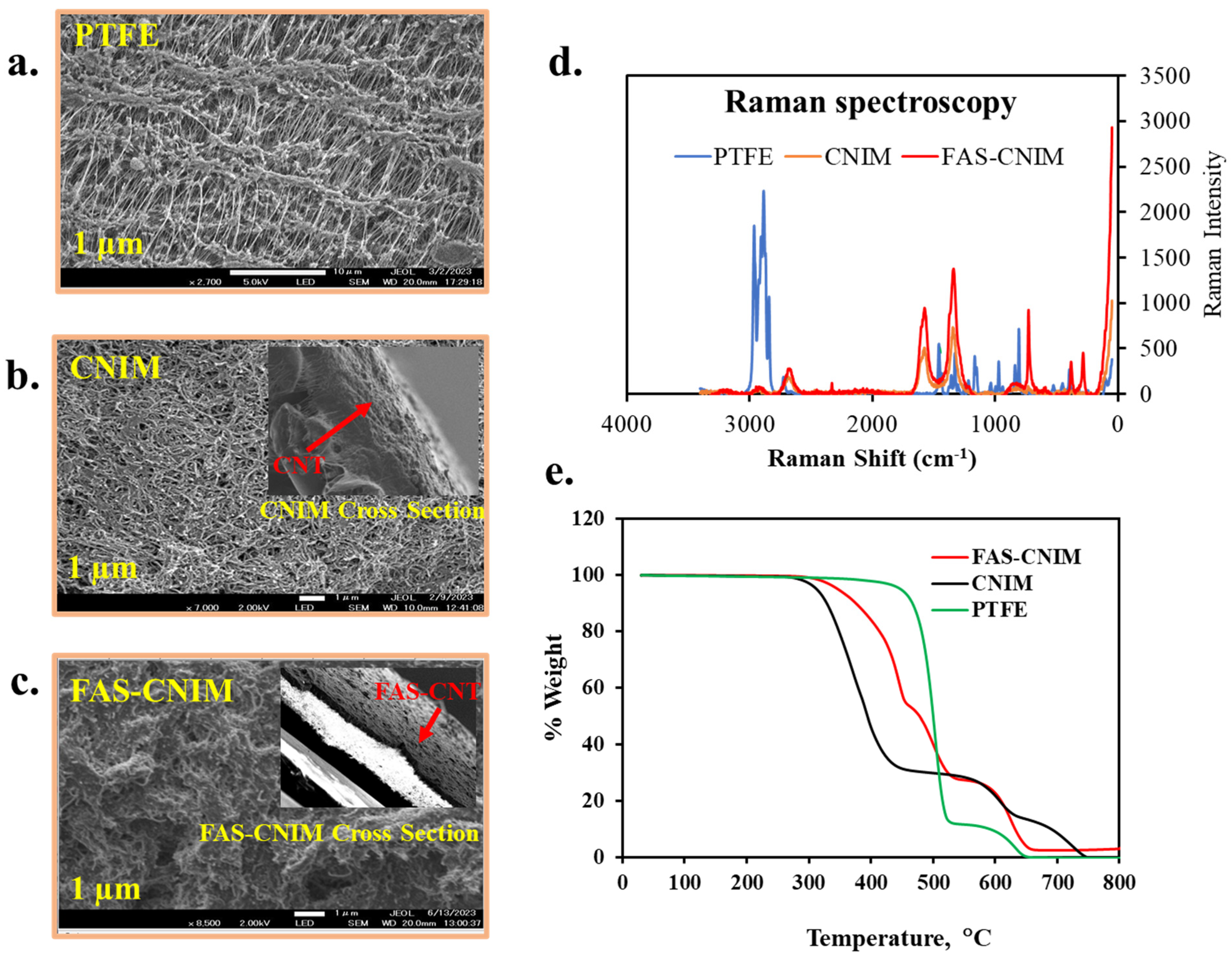
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.4. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Desalination Performance of FAS-CNIM
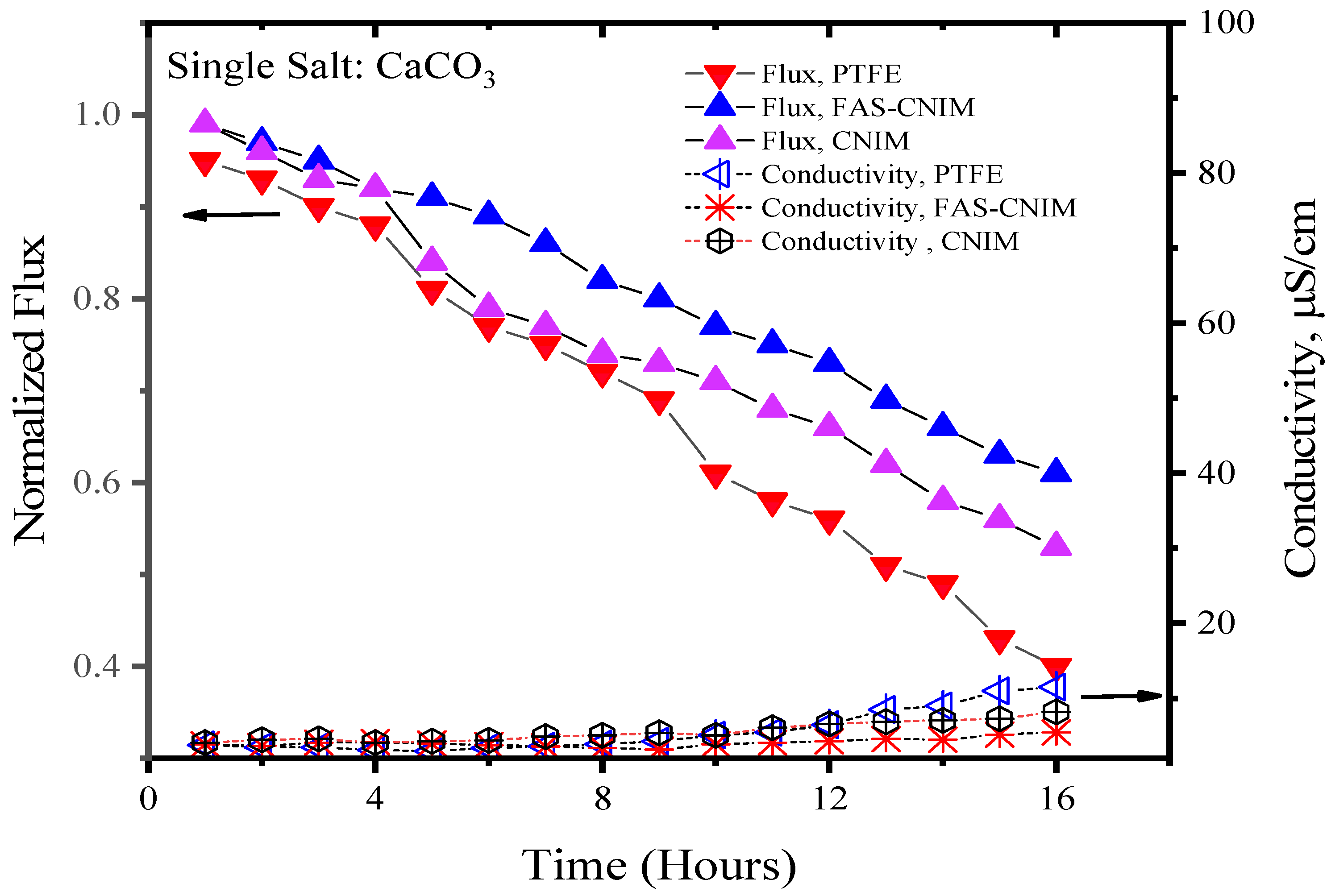
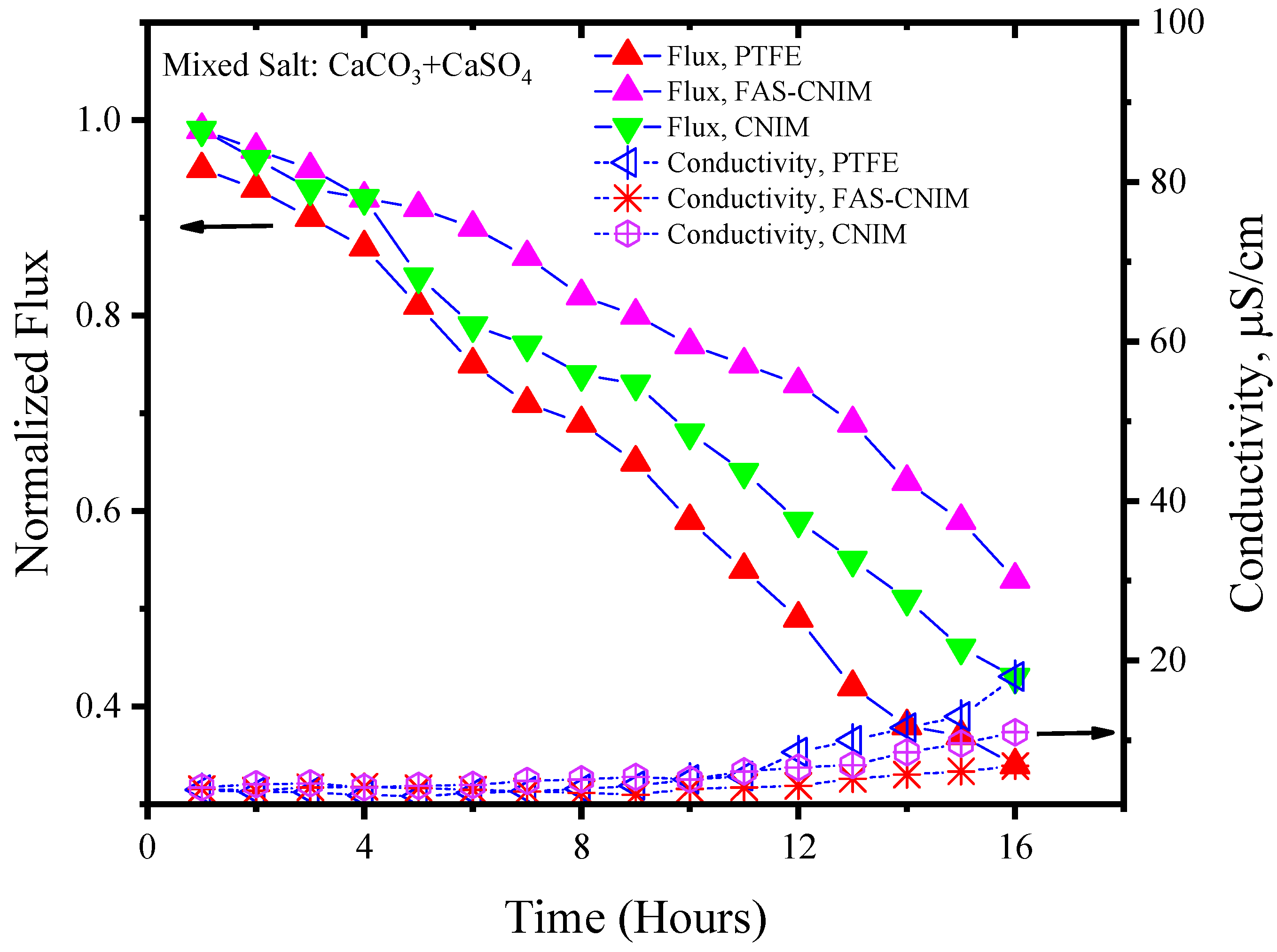
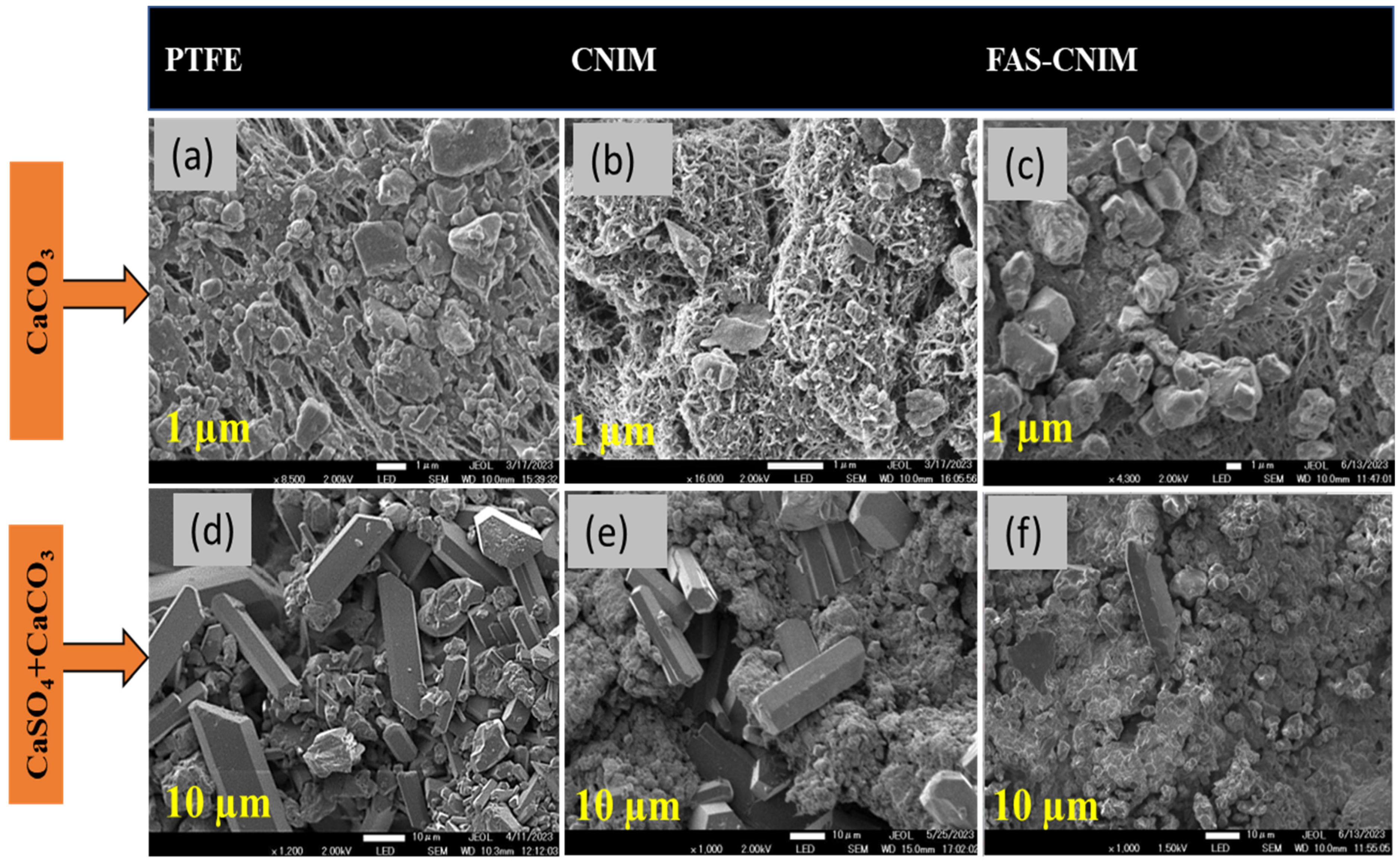
3.2. Fouling Characteristics of Membranes
3.3. Energy Efficiency of MD Process
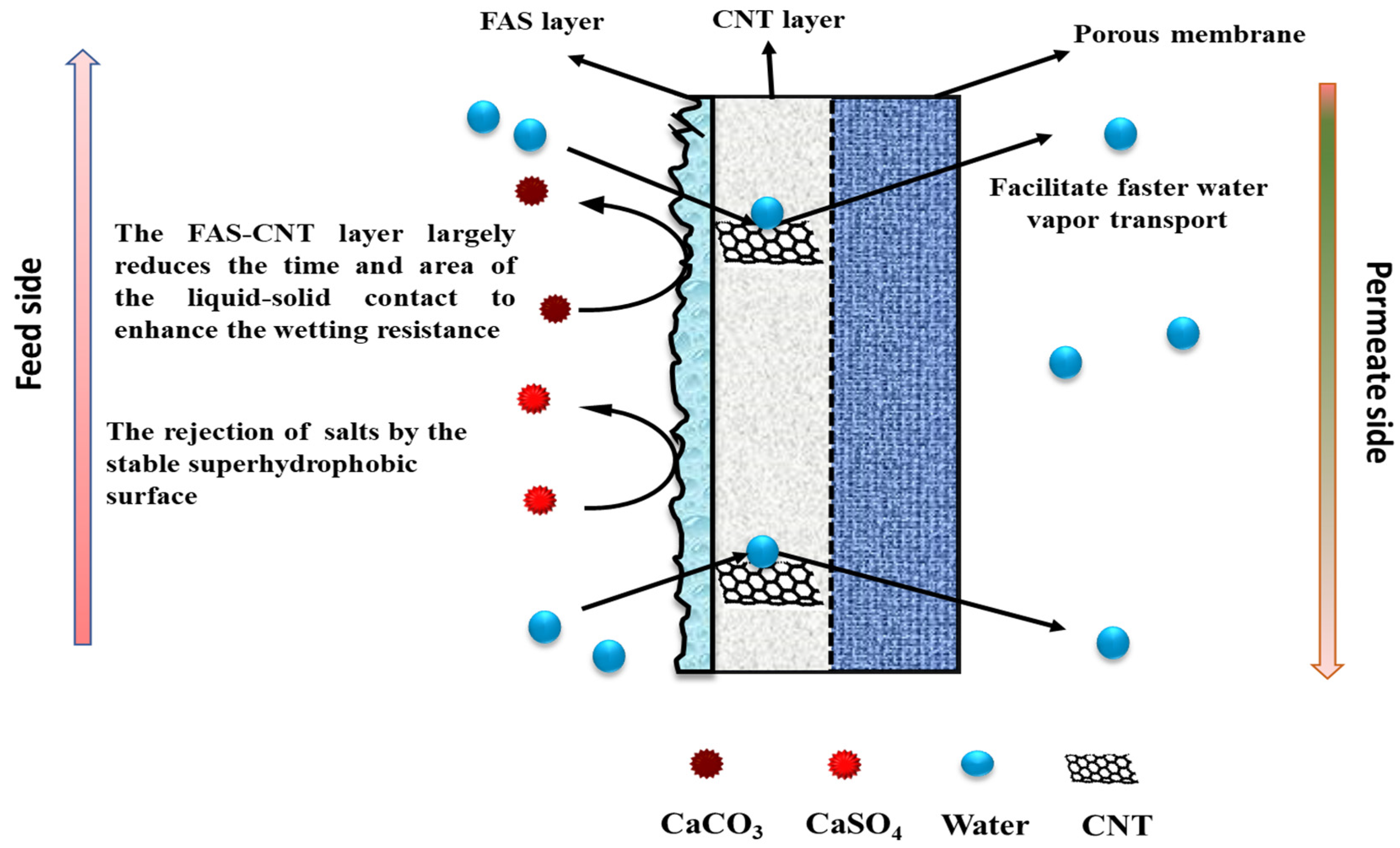
4. Mechanism of Permeation in FAS-CNIM
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, P.; Farnood, R.; Kumar, V. Superhydrophobic modification of electrospun nanofibrous Si@ PVDF membranes for desalination application in vacuum membrane distillation. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Mao, Y.; Mo, B.; Pan, Y.; Xu, R.; Ji, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Plasma-assisted facile fabrication of omniphobic graphene oxide membrane with anti-wetting property for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 668, 121207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaid, K.; Sayed, E.T.; Yousef, B.A.; Rabaia, M.K.H.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Olabi, A.G. Recent progress on the utilization of waste heat for desalination: A review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 221, 113105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Siebdrath, N.; Uhl, W.; Gitis, V.; Herzberg, M. New insights on early stages of RO membranes fouling during tertiary wastewater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tow, E.W.; Warsinger, D.M.; Trueworthy, A.M.; Swaminathan, J.; Thiel, G.P.; Zubair, S.M.; Myerson, A.S. Comparison of fouling propensity between reverse osmosis, forward osmosis, and membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Cho, H.; Shin, Y.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Koo, J. Comparison of fouling propensity and physical cleaning effect in forward osmosis, reverse osmosis, and membrane distillation. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 24532–24541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, F. Simultaneous anti-fouling and flux-enhanced membrane distillation via incorporating graphene oxide on PTFE membrane for coking wastewater treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 531, 147349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Kim, J.-O. Enhanced anti-wetting, slippery-surface membranes engineered for long-term operation with hypersaline synthetic and seawater feeds in membrane distillation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 96, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Zhao, L.; Li, N.; Smith, S.J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, J.; Ng, D.; Wu, C.; Martinez, M.R.; Batten, M.P. Aluminum fumarate MOF/PVDF hollow fiber membrane for enhancement of water flux and thermal efficiency in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, C.; Lu, X.; Ng, D.; Truong, Y.B.; Xie, Z. Activated carbon enhanced hydrophobic/hydrophilic dual-layer nanofiber composite membranes for high-performance direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 446, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, W.-U.; Muhammad, A.; Younas, M.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, J. Effect of membrane wetting on the performance of PVDF and PTFE membranes in the concentration of pomegranate juice through osmotic distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 584, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Song, P.; Xiao, C. Fabrication of super-hydrophobic polypropylene hollow fiber membrane and its application in membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 414, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoumick, M.C.; Paul, S.; Roy, S.; Harvey, B.G.; Mitra, S. Recovery of Isoamyl Alcohol by Graphene Oxide Immobilized Membrane and Air-Sparged Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2024, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Liu, M.; Fejjari, K.; Kang, W.; Liao, Y. Electrospun PTFE/PI bi-component membranes with robust 3D superhydrophobicity and high water permeability for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Chen, S.-S.; Chang, H.-M.; Thanh, C.N.D.; Le, H.Q.; Nguyen, N.C. Enhanced desalination using a three-layer OTMS based superhydrophobic membrane for a membrane distillation process. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 9640–9650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.-R.; Wang, S.-H.; Zhao, H.-L.; Wu, S.-B.; Xu, J.-M.; Li, L.; Liu, X.-Y. Layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly technology as promising strategy for tailoring pressure-driven desalination membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eykens, L.; De Sitter, K.; Dotremont, C.; Pinoy, L.; Van der Bruggen, B. Characterization and performance evaluation of commercially available hydrophobic membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 392, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Wang, M.-J.; Chung, T.-S. Zwitterionic poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate-co-acrylic acid) assisted simultaneous anti-wetting and anti-fouling membranes for membrane distillation. Desalination 2023, 555, 116527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Wang, M.J.; Chung, T.S. Development of multifunctional membranes via plasma-assisted nonsolvent induced phase separation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wu, F.; Qu, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, P. Advances in the research of carbon-, silicon-, and polymer-based superhydrophobic nanomaterials: Synthesis and potential application. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 318, 102932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkaew, N.; Simsek, M.; Griesche, C.; Baeumner, A.J. Functional nanomaterials and nanostructures enhancing electrochemical biosensors and lab-on-a-chip performances: Recent progress, applications, and future perspective. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 120–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Xiang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Zhong, W.; Li, M.; Yan, K.; Wang, D. Multistimulus responsive actuator with GO and carbon nanotube/PDMS bilayer structure for flexible and smart devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27215–27223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. A review on special wettability textiles: Theoretical models, fabrication technologies and multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Wei, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Cui, S.; Nie, Z. A novel strategy to enhance the desalination stability of FAS (fluoroalkylsilane)-modified ceramic membranes via constructing a porous SiO2@ PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) protective layer on their top. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y. Amphiphobic surface modification of electrospun nanofibrous membranes for anti-wetting performance in membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 432, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xue, Y.; Ding, J.; Feng, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Durable, self-healing superhydrophobic and superoleophobic surfaces from fluorinated-decyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane and hydrolyzed fluorinated alkyl silane. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, M.; Liu, L.; Yao, J.; Han, L. Beneficial CNT intermediate layer for membrane fluorination toward robust superhydrophobicity and wetting resistance in membrane distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 20942–20954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T.; Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Membrane modification. Nanotechnol. Membr. Process. 2021, 29, 135–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.C.; Lin, X.; Li, C. Structural design of the electrospun nanofibrous membrane for membrane distillation application: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 82632–82659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xie, B.; Mushtaq, N.; Xu, G.; Bar-Zeev, E.; Hu, Y. New insights into the role of carbon nanotubes spray-coated on both sides of the PTFE membrane in suppressing temperature polarization and enhancing water flux in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 689, 122184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontarek-Castro, E.; Castro-Muñoz, R. How to make membrane distillation greener: A review of environmentally friendly and sustainable aspects. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 164–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürklü-Kocaoğlu, S.; Güvensoy-Morkoyun, A.; Yıldırım, C.; Velioğlu, S.; Ahunbay, M.; Tantekin-Ersolmaz, Ş. Affinity-based engineering of carbon nanotube embedded polyamide membranes for simultaneous desalination and boron removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 699, 122636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhou, J. Finely tuned water structure and transport in functionalized carbon nanotube membranes during desalination. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 10560–10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humoud, M.S. Reduction in Salt Deposition on Carbon Nano-Tube Immobilized Membrane during Desalination via Membrane Distillation. Ph.D. Thesis, New Jersey Institute of Technology, Newark, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Humoud, M.S.; Intrchom, W.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Reduction of scaling in microwave induced membrane distillation on a carbon nanotube immobilized membrane. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humoud, M.S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Scaling Reduction in Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Membrane during Membrane Distillation. Water 2019, 11, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humoud, M.S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Enhanced performance of carbon nanotube immobilized membrane for the treatment of high salinity produced water via direct contact membrane distillation. Membranes 2020, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Bhoumick, M.C.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Carbon nanotube enhanced membrane filtration for trace level dewatering of hydrocarbons. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 121047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Carbon nanotube enhanced selective micro filtration of butanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Bhoumick, M.C.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Carbon Nanotube Enhanced Filtration and Dewatering of Kerosene. Membranes 2022, 12, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bhadra, M.; Mitra, S. Enhanced desalination via functionalized carbon nanotube immobilized membrane in direct contact membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 136, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoumick, M.C.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Synergistic effect of air sparging in direct contact membrane distillation to control membrane fouling and enhancing flux. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 272, 118681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoumick, M.C.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Reduction and Elimination of Humic Acid Fouling in Air Sparged Membrane Distillation Using Nanocarbon Immobilized Membrane. Molecules 2022, 27, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Omniphobic, Bilayer Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Fluorinated (FAS) Membranes for Bioethanol Recovery at High Concentrations via Membrane Distillation. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 4217–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra Bhoumick, M.; Paul, S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Selective Recovery of Ethyl Acetate by Air-Sparged Membrane Distillation Using Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Membranes and Process Optimization via a Response Surface Approach. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 3307–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoumick, M.C.; Li, C.; Roy, S.; Sundstrom, E.; Harvey, B.G.; Mitra, S. Enhanced Recovery of Aviation Biofuel Precursor Isoprenol Using Nanocarbon-Immobilized Membrane-Based Membrane Distillation. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 2875–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoumick, M.C.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Enrichment of 1, 4-dioxane from water by sweep gas membrane distillation on nano-carbon immobilized membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, O.; Roy, S.; Rao, L.; Mitra, S. Graphene oxide-carbon nanotube (GO-CNT) hybrid mixed matrix membrane for pervaporative dehydration of ethanol. Membranes 2022, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sae-Khow, O.; Mitra, S. Carbon nanotube immobilized composite hollow fiber membranes for pervaporative removal of volatile organics from water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16351–16356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Saridara, C.; Mitra, S. Microfluidic supported liquid membrane extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 543, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, C.M.; Saridara, C.; Mitra, S. Self-assembly of carbon nanotubes via ethanol chemical vapor deposition for the synthesis of gas chromatography columns. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5184–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Rao, L.; Stein, L.H.; Salemi, A.; Mitra, S. Development of a Carbon Nanotube-Enhanced FAS Bilayer Amphiphobic Coating for Biological Fluids. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Zheng, R.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Yuan, X.; Ji, Y.; Li, D.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.-M. Slippery for scaling resistance in membrane distillation: A novel porous micropillared superhydrophobic surface. Water Res. 2019, 155, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Guo, H.; He, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, H.; Volkov, A.V.; He, T. Unprecedented scaling/fouling resistance of omniphobic polyvinylidene fluoride membrane with silica nanoparticle coated micropillars in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoungjin An, A.; Lee, E.-J.; Guo, J.; Jeong, S.; Lee, J.-G.; Ghaffour, N. Enhanced vapor transport in membrane distillation via functionalized carbon nanotubes anchored into electrospun nanofibres. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Warsinger, D.M.; Samhaber, W.M. Wetting prevention in membrane distillation through superhydrophobicity and recharging an air layer on the membrane surface. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.J.; Chen, Y.; Chung, T.-S. Design of omniphobic interfaces for membrane distillation—A review. Water Res. 2019, 162, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Saheed, M.S.; Norani, M.M.; Burhanudin, Z.A. Optimization of the production of aligned CNTs array as the gas sensing element. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hodkiewicz, J. Rapid Quality Screening of Carbon Nanotubes with Raman Spectroscopy; Application Note; Thermal Fischer Scientific: Waltham, MA, USA, 2010; p. 51947. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Lu, C.; Wang, F.; Dong, X. Piezoelectric property of PVDF/graphene composite films using 1H, 1H, 2H, 2H-Perfluorooctyltriethoxysilane as a modifying agent. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, M.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Ge, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, M.; Shen, L.; He, J. Construction of underwater-superaerophilic Pd-CNTs/fluorosilane composite for enhancing heterogeneous catalytic hydrogenation reactions. Surf. Interface Anal. 2023, 55, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Cheng, J.; Du, X.; Guo, Q.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Q. Amphiphobic electrospun PTFE nanofibrous membranes for robust membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.Y.; Shen, H.M.; Xu, Z.L. PVDF–TiO2 composite hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes prepared by TiO2 sol–gel method and blending method. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 1763–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Khraisheh, M.; Esteves, R.J.; McLeskey, J.T., Jr.; AlGhouti, M.; Gad-el-Hak, M.; Tafreshi, H.V. Energy efficiency of direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2018, 433, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.; Abdelgaied, M.; El-Said, E.M. Study of a solar-driven membrane distillation system: Evaporative cooling effect on performance enhancement. Renew. Energy 2017, 106, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubev, G.; Eremeev, I.; Makaev, S.; Shalygin, M.; Vasilevsky, V.; He, T.; Drioli, E.; Volkov, A. Thin-film distillation coupled with membrane condenser for brine solutions concentration. Desalination 2021, 503, 114956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Sirkar, K.K.; Gilron, J. Studies on scaling of membranes in desalination by direct contact membrane distillation: CaCO3 and mixed CaCO3/CaSO4 systems. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 1844–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, G.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Hwang, T.-M.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-H. A review on fouling of membrane distillation. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 57, 10052–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmarghany, M.R.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Salem, M.S.; Sabry, M.N.; Nady, N. Thermal analysis evaluation of direct contact membrane distillation system. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 13, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Du, X.; Vahabi, H.; Zhao, S.; Yin, Y.; Kota, A.K.; Tong, T. Trade-off in membrane distillation with monolithic omniphobic membranes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, R.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Han, L. Desalinating Real Shale Gas Wastewater by Membrane Distillation: Performance and Potentials. Water 2023, 15, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambikkattu, J.; Kaleekkal, N.J. Fluoroalkylsilane grafted FeOOH nanorods impregnated PVDF-co-HFP membranes with enhanced wetting and fouling resistance for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, M.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Desalination across a graphene oxide membrane via direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 378, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| System | Relative Flux Reduction %, PTFE | Relative Flux Reduction %, CNIM | Relative Flux Reduction %, FAS-CNIM | Deposition of Salt PTFE (mg) | Deposition of Salt CNIM (mg) | Deposition of Salt FAS-CNIM (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3 | 58 ± 2 | 47 ± 2.5 | 38 ± 1 | 17.20 ± 2 | 13.35 ± 1 | 10.1 ± 1 |
| CaCO3 + CaSO4 | 69 ± 3 | 54 ± 2 | 43 ± 2 | 28.12 ± 1 | 21.2 ± 1 | 18.53 ± 1.5 |
| Salt Mixture | Parameter | PTFE | CNIM | FAS-CNIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaCO3 | TE (%) | 66.2 | 74.5 | 82.7 |
| SEC (kwh/m3) | 341 | 320 | 303 | |
| GOR | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.51 | |
| CaCO3 + CaSO4 | TE (%) | 62 | 70.3 | 78.6 |
| SEC (kwh/m3) | 354 | 330.5 | 311 | |
| GOR | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, S.; Bhoumick, M.C.; Mitra, S. Fouling Reduction and Thermal Efficiency Enhancement in Membrane Distillation Using a Bilayer-Fluorinated Alkyl Silane–Carbon Nanotube Membrane. Membranes 2024, 14, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070152
Paul S, Bhoumick MC, Mitra S. Fouling Reduction and Thermal Efficiency Enhancement in Membrane Distillation Using a Bilayer-Fluorinated Alkyl Silane–Carbon Nanotube Membrane. Membranes. 2024; 14(7):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070152
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Sumona, Mitun Chandra Bhoumick, and Somenath Mitra. 2024. "Fouling Reduction and Thermal Efficiency Enhancement in Membrane Distillation Using a Bilayer-Fluorinated Alkyl Silane–Carbon Nanotube Membrane" Membranes 14, no. 7: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070152
APA StylePaul, S., Bhoumick, M. C., & Mitra, S. (2024). Fouling Reduction and Thermal Efficiency Enhancement in Membrane Distillation Using a Bilayer-Fluorinated Alkyl Silane–Carbon Nanotube Membrane. Membranes, 14(7), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14070152








