Treatment of Synthetic Wastewater Containing Polystyrene (PS) Nanoplastics by Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Study of the Effects on Microbial Community and Membrane Fouling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Membranes
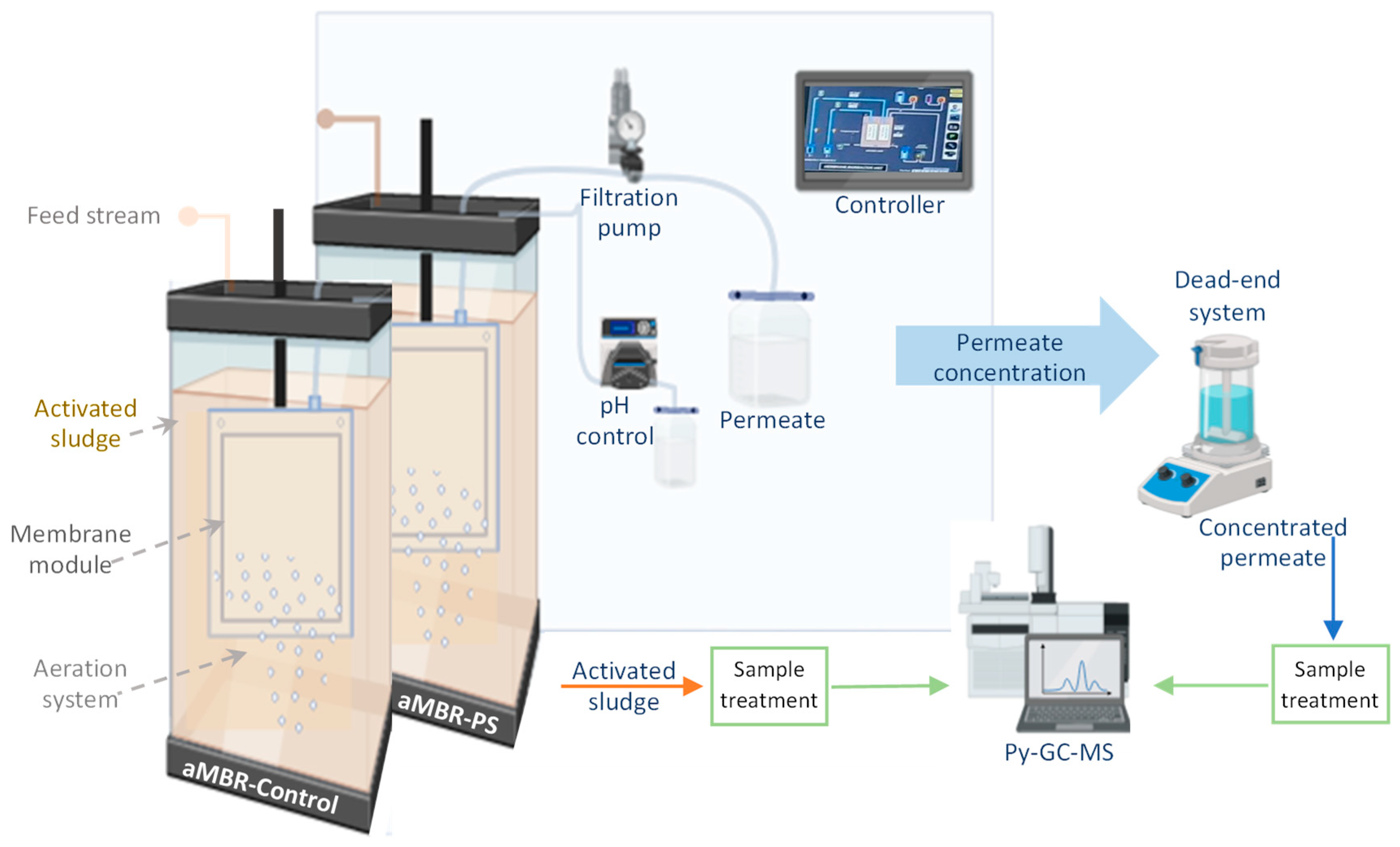
2.3. Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor (aMBR) System
2.4. Permeate and Sludge Characterization
2.4.1. Analytical Methods for Wastewater Parameters
2.4.2. Microbial Community Analysis and SMP
2.4.3. Semi-Quantification of PS Nanoplastics by Pyrolysis Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (Py-GC-MS)
Sampling and Sampling Treatment
Identification and Semi-Quantification
2.5. Membrane Characterization
2.5.1. RIS Analysis
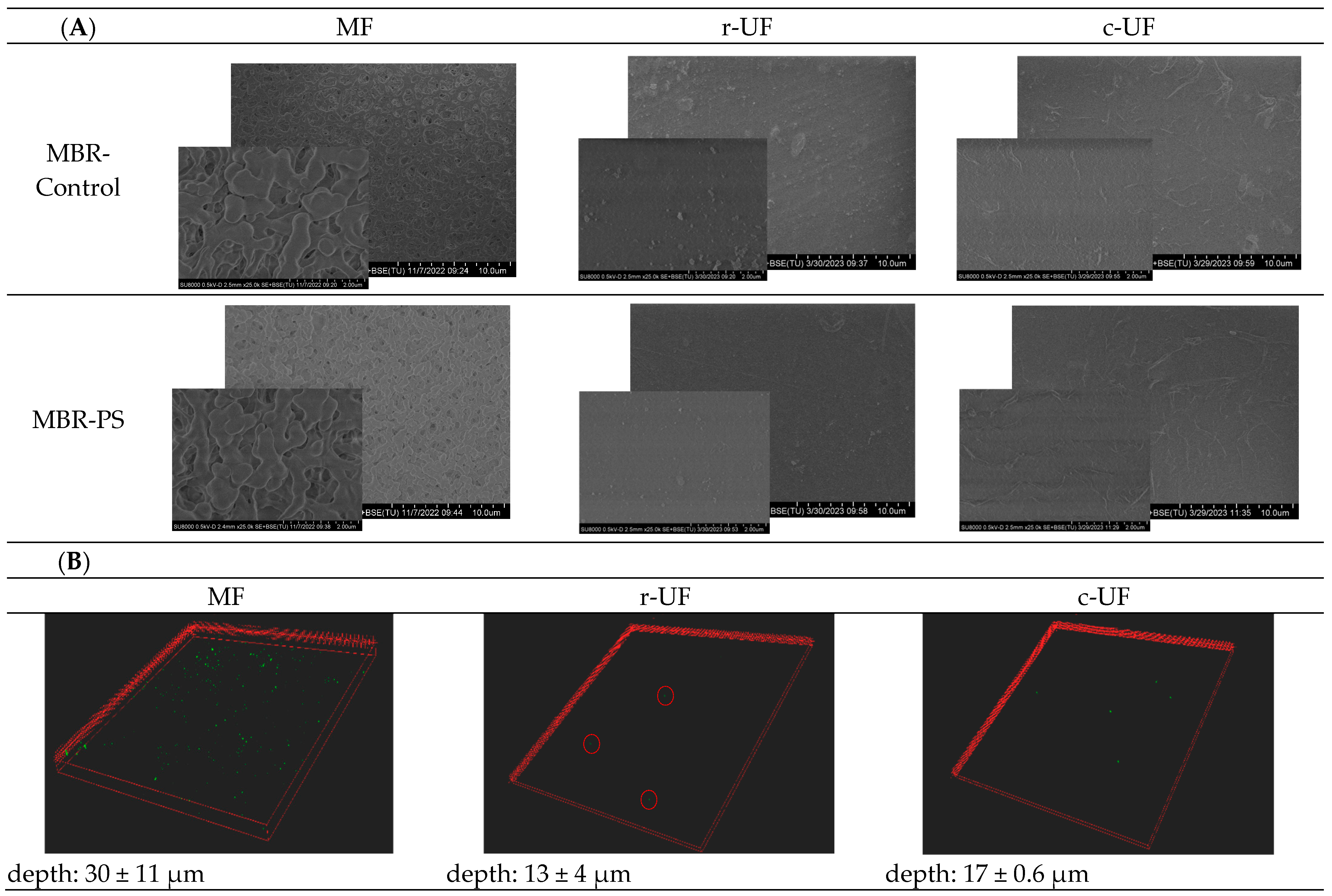
2.5.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5.3. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3. Results
3.1. Activated Sludge
3.1.1. Changes to Settleability of Sludge and SMP
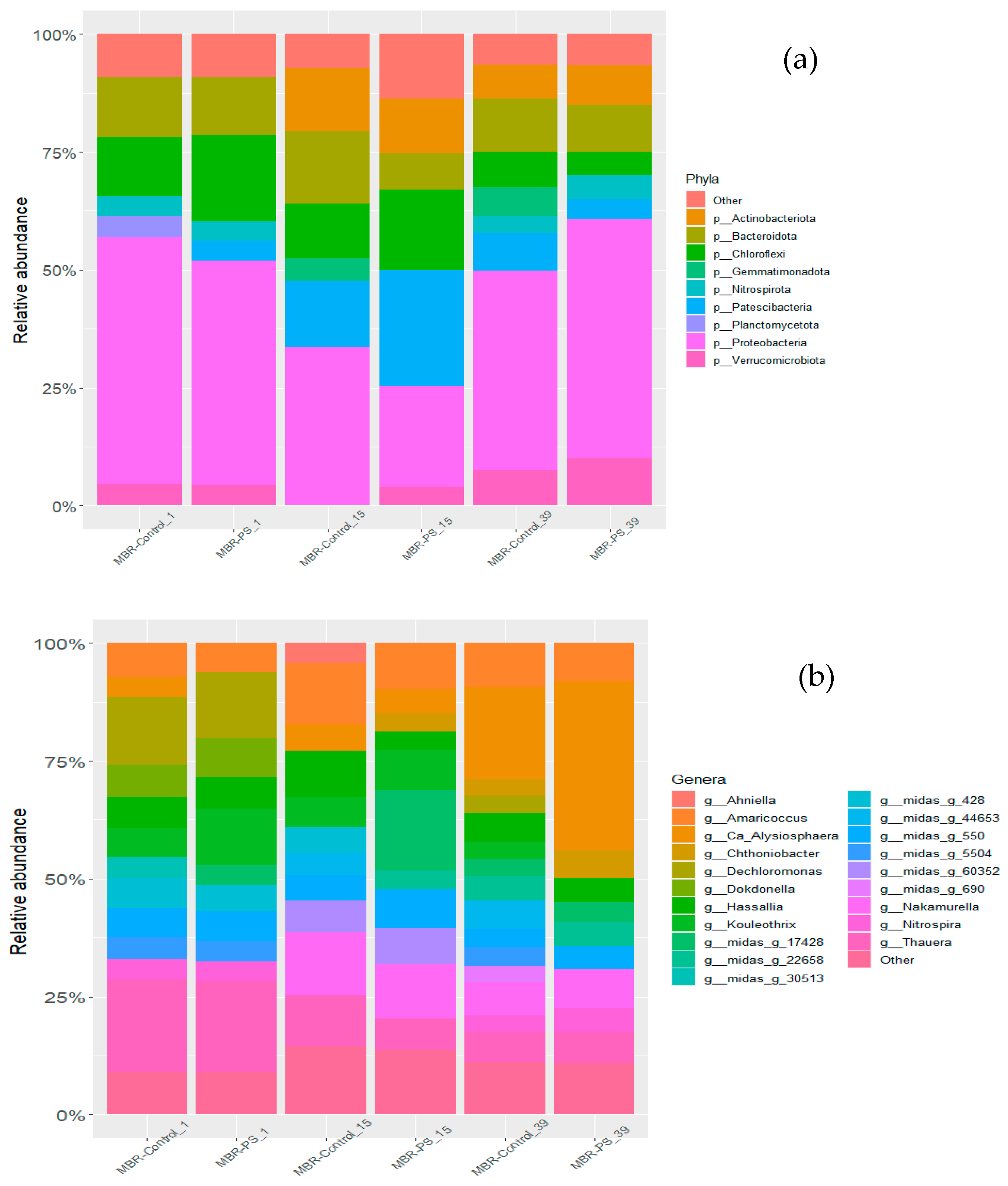
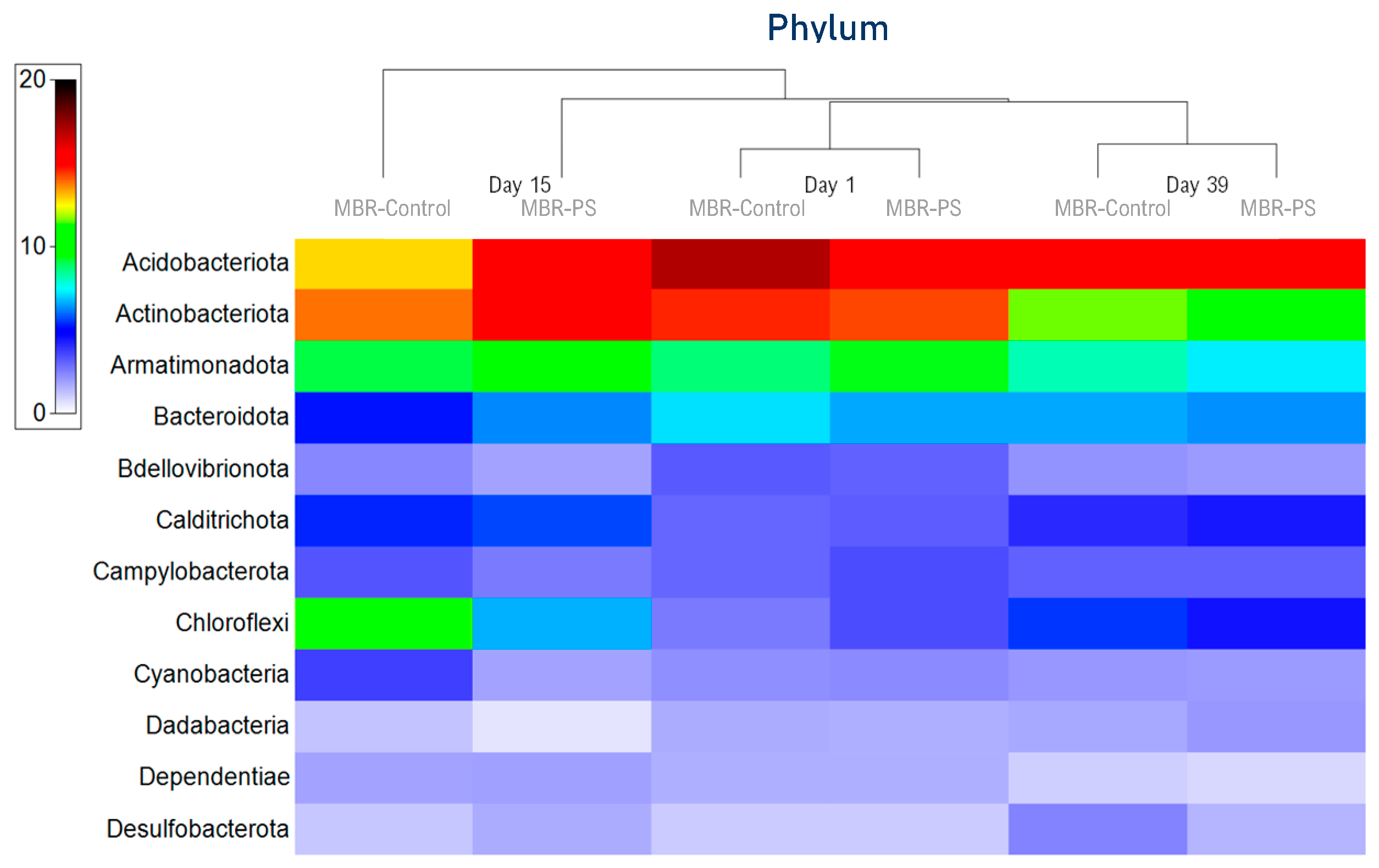
3.1.2. Microbial Community Analysis
3.2. Membrane Operation
3.2.1. Permeate Quality
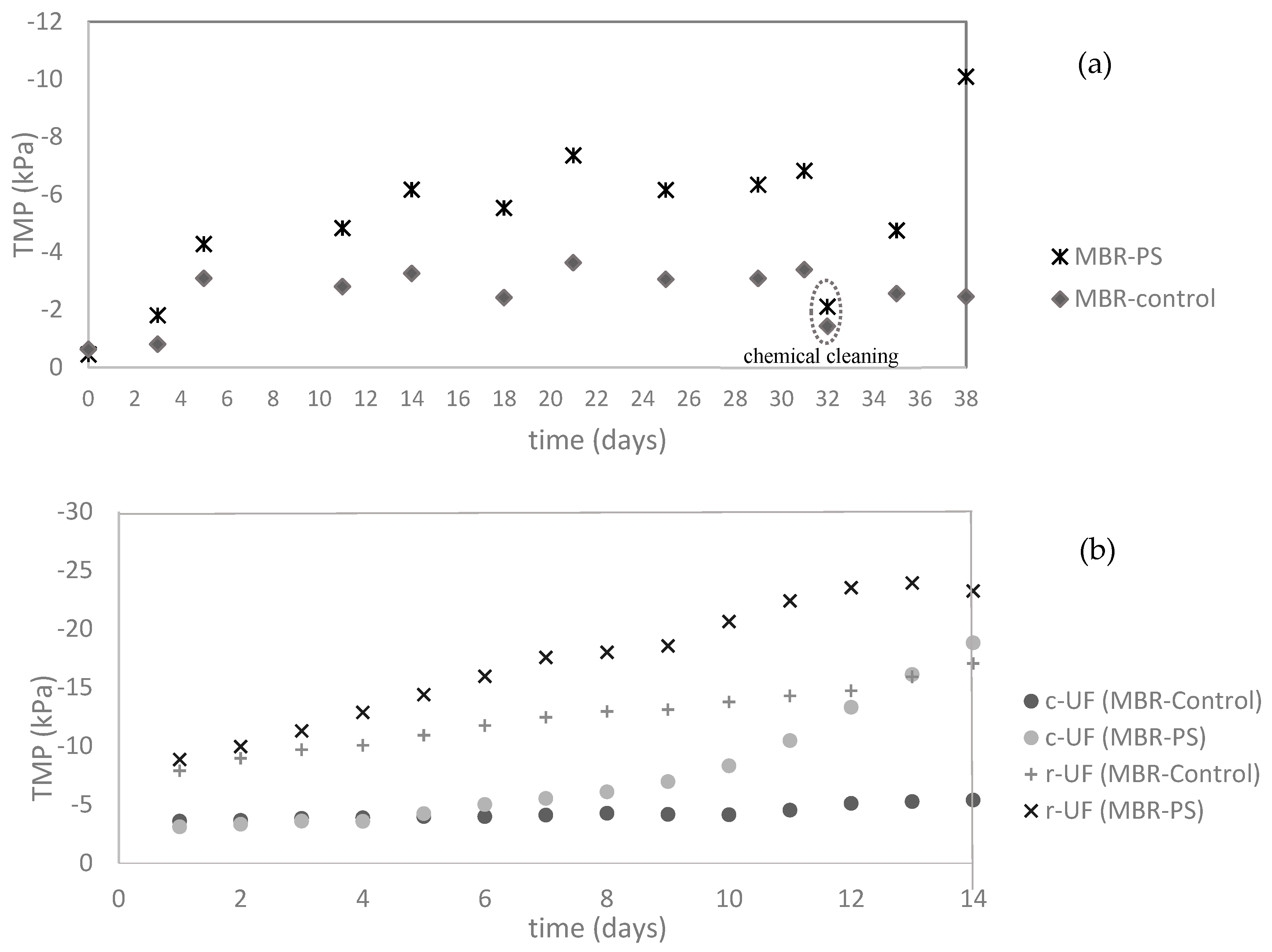
3.2.2. Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) Evolution
3.2.3. RIS Analysis and Surface Characterizations
3.2.4. Membrane Characterization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UF | Ultrafiltration | µ | Dynamic viscosity (Pa·s) |
| c-UF | Commercial ultrafiltration | J | Flux (L·m−2·h−1) |
| r-UF | Recycled ultrafiltration | Rt | Total resistance (m−1) |
| MF | Microfiltration | Rc | Cake layer resistance (m−1) |
| aMBR | Aerobic membrane bioreactor | Rf | Fouling resistance (m−1) |
| MNPs | Micronanoplastics | Rpb | Pore blocking resistance (m−1) |
| MPs | Microplastics | Rwt | Total resistance measured with clean water after physical cleaning (m−1) |
| NPs | Nanoplastics | Rm | Membrane resistance (m−1) |
| PS | polystyrene | NaOCl | Sodium hypochlorite |
| RO | Reverse osmosis | COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| PA | Polyamide | TSS | Total suspended solid |
| TMP | Transmembrane pressure (Pa) | D | Diameter |
| WWTPs | Wastewater treatment plants | PR | Permeability recovery |
| SBR | Sequencing batch reactor | ±SD | Standard deviations |
| SRT | Sludge retention time | EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| HRT | Hydraulic retention time | DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy | Pyr-GC-MS | Pyrolysis gas chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| CLSM | Confocal laser scanning microscopy | ||
| SEC | Size Exclusion Chromatography | ||
| MWCO | Molecular weight cut-off |
References
- Plastics-the Facts 2022 • Plastics Europe. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2022-2/ (accessed on 17 January 2024).
- Gigault, J.; ter Halle, A.; Baudrimont, M.; Pascal, P.Y.; Gauffre, F.; Phi, T.L.; El Hadri, H.; Grassl, B.; Reynaud, S. Current Opinion: What Is a Nanoplastic? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M.; Sillanpää, M. Occurrence, Identification and Removal of Microplastic Particles and Fibers in Conventional Activated Sludge Process and Advanced MBR Technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Setälä, O.; Heinonen, M.; Koistinen, A. How Well Is Microlitter Purified from Wastewater?—A Detailed Study on the Stepwise Removal of Microlitter in a Tertiary Level Wastewater Treatment Plant. Water Res. 2017, 109, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, G.; Mishra, S. A Review on Emerging Micro and Nanoplastic Pollutants, Heavy Metals and Their Remediation Techniques. Nanofabrication 2023, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Corbacho, A.; Martín-García, A.P.; Franco, A.A.; Quiroga, J.M.; Røjgaard Andreasen, R.; Koustrup Jørgensen, M.; Morten Lykkegaard, C. Occurrence, Identification and Removal of Microplastics in a Wastewater Treatment Plant Compared to an Advanced MBR Technology: Full-Scale Pilot Plant. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimi, O.S.; Farner Budarz, J.; Hernandez, L.M.; Tufenkji, N. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Aquatic Environments: Aggregation, Deposition, and Enhanced Contaminant Transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1704–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, B.S.S.; Palanisamy, S. A Review on Occurrence, Characteristics, Toxicology and Treatment of Nanoplastic Waste in the Environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43258–43273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigault, J.; El Hadri, H.; Nguyen, B.; Grassl, B.; Rowenczyk, L.; Tufenkji, N.; Feng, S.; Wiesner, M. Nanoplastics Are Neither Microplastics nor Engineered Nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvitie, J.; Mikola, A.; Koistinen, A.; Setälä, O. Solutions to Microplastic Pollution–Removal of Microplastics from Wastewater Effluent with Advanced Wastewater Treatment Technologies. Water Res. 2017, 123, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohana, A.A.; Rahman, M.; Sarker, S.K.; Haque, N.; Gao, L.; Pramanik, B.K. Nano/Microplastics: Fragmentation, Interaction with Co-Existing Pollutants and Their Removal from Wastewater Using Membrane Processes. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrano, D.M.; Beltzung, A.; Frehland, S.; Schmiedgruber, M.; Cingolani, A.; Schmidt, F. Synthesis of Metal-Doped Nanoplastics and Their Utility to Investigate Fate and Behaviour in Complex Environmental Systems. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doddy Sutrisna, P.; Riadi, L.; Cipta Buana, P.W.; Khoiruddin, K.; Boopathy, R.; Gede Wenten, I.; Siagian, U.W. Membrane and Membrane-Integrated Processes for Nanoplastics Removal and Remediation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 220, 110635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodzek, M.; Pohl, A.; Bodzek, M. Possibilities of Removing Microplastics from the Aquatic Environment Using Membrane Processes. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 288, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Zhou, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Liao, W. The Current State and Future Opportunities of Micro- and Nano-Plastics Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, C.B.; Ferrer-Polonio, E.; Bes-Piá, M.A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Fernández-Navarro, J.; Alonso-Molina, J.L.; Amorós-Muñoz, I. Effect of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on the Activated Sludge Process Performance and Biomass Characteristics. A Laboratory Study with a Sequencing Batch Reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, B.; Xing, D.; Yang, S.; Cao, G. Responses of Nitrogen Removal under Microplastics versus Nanoplastics Stress in SBR: Toxicity, Microbial Community and Functional Genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, S.; Tijani, J.O.; Elabor, R.; Salau, R.B.; Egbosiuba, T.C.; Amigun, A.T.; Shuaib, D.T.; Sumaila, A.; Fiola, T.; Abubakar, Y.K.; et al. Technological Approaches for Removal of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in the Environment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Thomas, K.V.; Luo, Z.; Gowen, A.A. FTIR and Raman Imaging for Microplastics Analysis: State of the Art, Challenges and Prospects. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, G.L.; Gallardo, J.D.; Jones, E.W.; Hollliman, P.J.; Watson, T.M.; Sarp, S. Detection of Trace Sub-Micron (Nano) Plastics in Water Samples Using Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (PY-GCToF). Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Dekiff, J.H.; Willmeyer, J.; Nuelle, M.T.; Ebert, M.; Remy, D. Identification of Polymer Types and Additives in Marine Microplastic Particles Using Pyrolysis-GC/MS and Scanning Electron Microscopy. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.; Ocaña-Biedma, H.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J. Experimental Evaluation of the Process Performance of MF and UF Membranes for the Removal of Nanoplastics. Membranes 2023, 13, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, S.; Carretero, P.; Teli, S.B.; De la Campa, J.G.; Lozano, Á.E.; De Abajo, J. Hydrophilic Porous Asymmetric Ultrafiltration Membranes of Aramid-g-PEO Copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; García-Pacheco, R.; de la Campa, J.G.; García-Calvo, E. Effect of Sodium Hypochlorite Exposure on Polysulfone Recycled UF Membranes and Their Surface Characterization. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Patsios, S.I.; Senán-Salinas, J.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Molina, S.; García-Calvo, E. A Novel Application of Recycled Ultrafiltration Membranes in an Aerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AMBR): A Proof-of-Concept Study. Membranes 2022, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Pacheco, R.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Teli, S.B.; García-Calvo, E. Transformation of End-of-Life RO Membranes into NF and UF Membranes: Evaluation of Membrane Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. EUR-Lex-52019DC0640-EN-EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?qid=1576150542719&uri=COM%3A2019%3A640%3AFIN (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Morón-López, J.; Nieto-Reyes, L.; Senán-Salinas, J.; Molina, S.; El-Shehawy, R. Recycled Desalination Membranes as a Support Material for Biofilm Development: A New Approach for Microcystin Removal during Water Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, M. Nanoplastics Pose a Greater Effect than Microplastics in Enhancing Mercury Toxicity to Marine Copepods. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, E.W.; Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 23rd Edition, ISBN 9780875532875.
- FastDNATM Spin Kit for Soil DNA Extraction|MP Biomedicals. Available online: https://www.mpbio.com/eu/116560000-fastdna-spin-kit-for-soil-samp-cf (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of Extracellular Polymers from Activated Sludge Using a Cation Exchange Resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuriaga-Agustí, E.; Bes-Piá, A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Alonso-Molina, J.L. Influence of Extraction Methods on Proteins and Carbohydrates Analysis from MBR Activated Sludge Flocs in View of Improving EPS Determination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretas Alvim, C.; Bes-Piá, M.A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A. Separation and Identification of Microplastics from Primary and Secondary Effluents and Activated Sludge from Wastewater Treatment Plants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 126293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Di Trapani, D.; Judd, S. Fouling Mechanism Elucidation in Membrane Bioreactors by Bespoke Physical Cleaning. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Chronic Exposure to Different Sizes and Polymers of Microplastics on the Characteristics of Activated Sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Yan, P.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Fang, F. New Insight into the Effect of Short-Term Exposure to Polystyrene Nanoparticles on Activated Sludge Performance. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Xia, S.; Wu, Y. Biofouling and Control Approaches in Membrane Bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkotsis, P.K.; Zouboulis, A.I. Biomass Characteristics and Their Effect on Membrane Bioreactor Fouling. Molecules 2019, 24, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunacheva, C.; Stuckey, D.C. Analytical Methods for Soluble Microbial Products (SMP) and Extracellular Polymers (ECP) in Wastewater Treatment Systems: A Review. Water Res. 2014, 61, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; She, Z.; Chang, Q.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Yang, N. Effect of Salinity on Extracellular Polymeric Substances of Activated Sludge from an Anoxic–Aerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2789–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, F.; Meng, F.; Liao, B.Q.; Hong, H.; Chen, J.; Gao, W. A Critical Review of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPSs) in Membrane Bioreactors: Characteristics, Roles in Membrane Fouling and Control Strategies. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Fernández, C.; Tallec, K.; Le Goïc, N.; Lambert, C.; Soudant, P.; Huvet, A.; Suquet, M.; Berchel, M.; Paul-Pont, I. Cellular Responses of Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) Gametes Exposed in Vitro to Polystyrene Nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, T.; Sun, M.; Xu, M.; Che, S.; Pan, Z.; Wu, C.; Shen, L. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Lead to Ferroptosis in the Lungs. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 56, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Qian, J.; Wang, P.; Lu, B.; He, Y.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, Y. Exposure to Nanoplastic Induces Cell Damage and Nitrogen Inhibition of Activated Sludge: Evidence from Bacterial Individuals and Groups. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, W.J.; Lin, L.F.; Wu, Z.C. Effects of Microplastics Accumulation on Performance of Membrane Bioreactor for Wastewater Treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 131968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; He, X.; Wang, P.; Xu, B.; Li, K.; Lu, B.; Jin, W.; Tang, S. Effects of Polystyrene Nanoplastics on Extracellular Polymeric Substance Composition of Activated Sludge: The Role of Surface Functional Groups. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, Z.; Fortunato, L.; Cheng, T.; Leiknes, T. Metagenomic Analysis of Sludge and Early-Stage Biofilm Communities of a Submerged Membrane Bioreactor. Sci. Total Environ. J. 2020, 701, 134682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Structure and Function of the Microbial Consortia of Activated Sludge in Typical Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in Winter. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonsen Dueholm, M.; Nierychlo, M.; Skytte Andersen, K.; Rudkjøbing, V.; Knutsson, S.; MiDAS Global Consortium; Albertsen, M.; Halkjaer Nielsen, P. MiDAS 4: A Global Catalogue of Full-Length 16S RRNA Gene Sequences and Taxonomy for Studies of Bacterial Communities in Wastewater Treatment Plants. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, O.; Ng, K.K.; Tang, K.Y.; Ng, H.Y. Membrane Biological Reactors: Theory, Modeling, Design, Management and Applications to Wastewater Reuse. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/277565753_Membrane_Biological_Reactors_Theory_Modeling_Design_Management_and_Applications_to_Wastewater_Reuse (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Maliwan, T.; Pungrasmi, W.; Lohwacharin, J. Effects of Microplastic Accumulation on Floc Characteristics and Fouling Behavior in a Membrane Bioreactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 411, 124991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bretas Alvim, C.; Castelluccio, S.; Ferrer-Polonio, E.; Bes-Piá, M.A.; Mendoza-Roca, J.A.; Fernández-Navarro, J.; Alonso, J.L.; Amorós, I. Effect of Polyethylene Microplastics on Activated Sludge Process-Accumulation in the Sludge and Influence on the Process and on Biomass Characteristics. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morón -López, J.; Nieto-Reyes, L.; Aguado, S.; El-Shehawy, R.; Molina, S. Recycling of End-of-Life Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Membrane Biofilms Reactors (MBfRs). Effect of Chlorination on the Membrane Surface and Gas Permeability. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrasoul, A.; Doan, H.; Lohi, A. A Mechanistic Model for Ultrafiltration Membrane Fouling by Latex. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 433, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Manufacturer | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Membranes | Material | Nominal Pore Size | Nominal MWCO (Da) | Nominal MWCO (Da) |
| MF | Chlorinated polyethylene | 0.4 µm | --- | --- |
| r-UF | Polyethersulfone | 12 nm [25] | --- | 30,000 |
| c-UF | Polyethersulfone | <30 nm | 150,000 | 90,000 |
| Polymer | Pyrolytic Products | Indicator Ions (m/z) |
|---|---|---|
| PS | Styrene * | 104, 78, 51 |
| 3-Butene-1,3-diyldibenzene (Styrene dimer) | 91, 104, 130 | |
| 5-Hexene-1,3,5-triyltribenzene (Styrene trimer) | 91, 117, 194 |
| pH | CE (µS/cm) | COD (mg/L) | %R (COD) | TOC (mg/L) | %R (TOC) | Total N (mg/L) | %R (TN) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MF | ||||||||
| MBR- Control | 7.90 ± 0.20 | 564.92 ± 0.17 | 10.28 ± 2.30 | 97.44 ± 1.82 | 2.28 ± 0.65 | 97.88 ± 2.00 | 15.63 ± 4.50 | 49.60 ± 14.52 |
| MBR-PS | 7.91 ± 0.12 | 518.08 ± 0.17 | 8.84 ± 3.05 | 97.80 ± 0.76 | 1.83 ± 0.61 | 98.38 ± 0.84 | 18.75 ± 3.45 | 39.52 ± 11.14 |
| c-UF | ||||||||
| MBR- Control | 7.91 ± 0.10 | 482.60 ± 0.10 | 8.48 ± 1.39 | 97.89 ± 0.35 | 2.05 ± 0.82 | 98.46 ± 0.62 | 12.75 ± 2.50 | 50.96 ± 9.62 |
| MBR-PS | 7.93 ± 0.12 | 452.80 ± 0.08 | 9.18 ± 0.59 | 97.71 ± 0.15 | 1.98 ± 0.33 | 98.51 ± 0.25 | 18.00 ± 2.65 | 30.77 ± 10.18 |
| r-UF | ||||||||
| MBR- Control | 7.80 ± 0.08 | 440.75 ± 0.02 | 5.33 ± 0.67 | 98.61 ± 0.17 | 1.19 ± 0.12 | 99.09 ± 0.10 | 14.55 ± 1.67 | 46.18 ± 4.64 |
| MBR-PS | 7.92 ± 0.08 | 516.25 ± 0.09 | 5.88 ± 1.17 | 98.47 ± 0.34 | 1.07 ± 0.27 | 99.18 ± 0.21 | 18.25 ± 4.11 | 32.01 ± 17.18 |
| c-UF Membrane | r-UF Membrane | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Point | Second Week | Third Week | Fourth Week | |
| Conc. PS (mg L−1) | 52.86 | 52.31 | 55.03 | 55.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pompa-Pernía, A.; Molina, S.; Cherta, L.; Martínez-García, L.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J. Treatment of Synthetic Wastewater Containing Polystyrene (PS) Nanoplastics by Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Study of the Effects on Microbial Community and Membrane Fouling. Membranes 2024, 14, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080174
Pompa-Pernía A, Molina S, Cherta L, Martínez-García L, Landaburu-Aguirre J. Treatment of Synthetic Wastewater Containing Polystyrene (PS) Nanoplastics by Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Study of the Effects on Microbial Community and Membrane Fouling. Membranes. 2024; 14(8):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080174
Chicago/Turabian StylePompa-Pernía, Anamary, Serena Molina, Laura Cherta, Lorena Martínez-García, and Junkal Landaburu-Aguirre. 2024. "Treatment of Synthetic Wastewater Containing Polystyrene (PS) Nanoplastics by Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Study of the Effects on Microbial Community and Membrane Fouling" Membranes 14, no. 8: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080174
APA StylePompa-Pernía, A., Molina, S., Cherta, L., Martínez-García, L., & Landaburu-Aguirre, J. (2024). Treatment of Synthetic Wastewater Containing Polystyrene (PS) Nanoplastics by Membrane Bioreactor (MBR): Study of the Effects on Microbial Community and Membrane Fouling. Membranes, 14(8), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14080174










