MXene/Carbon Nanocomposites for Water Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Properties and Synthesis of MXene
2.1. Common MXene Synthesis Procedure
2.2. In-Situ Synthesis of MXene
2.3. Hydrothermal Synthesis of MXene
2.4. Fluorine-Free Synthesis of MXene
3. Properties and Synthesis of MXene/Carbon Nanocomposite
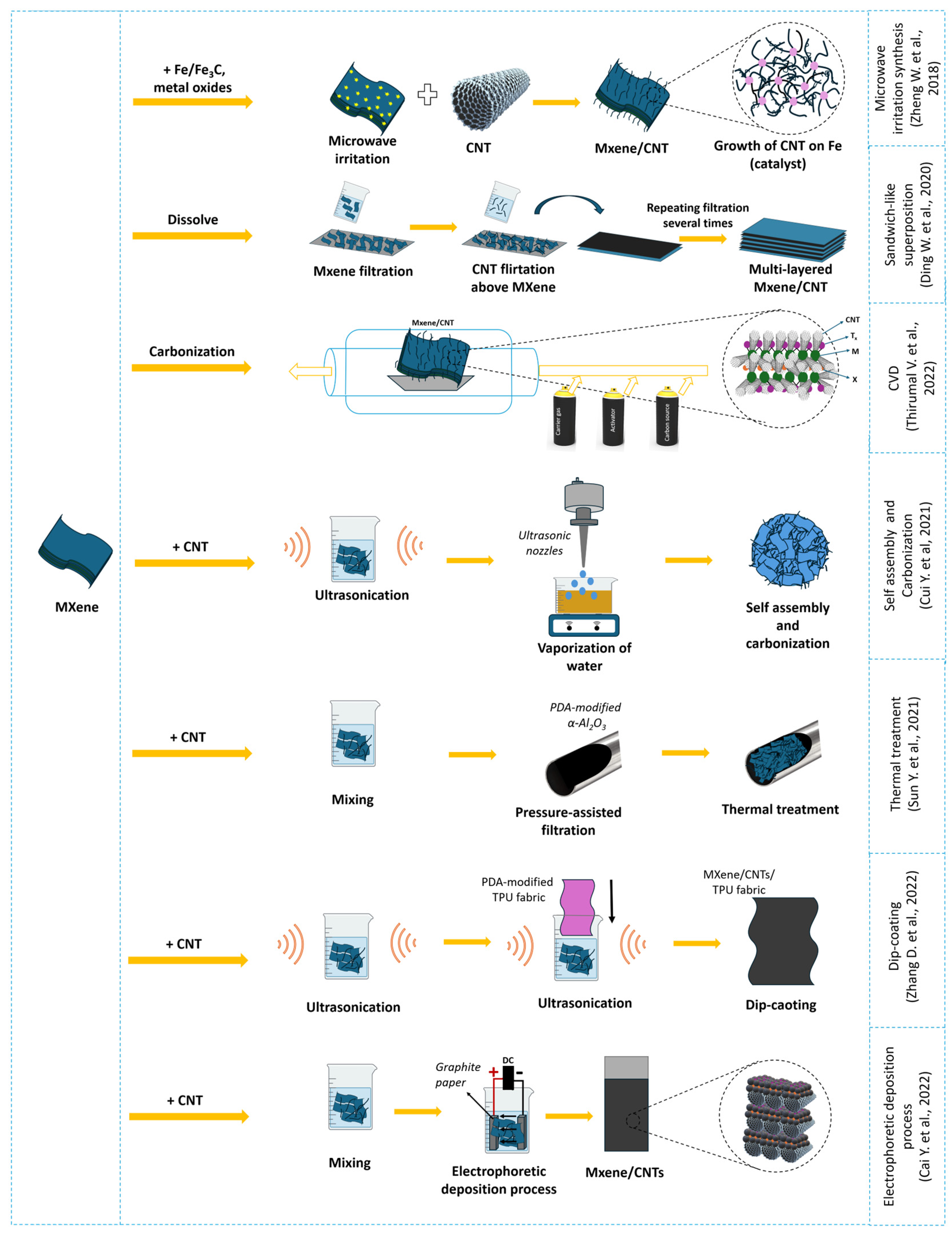
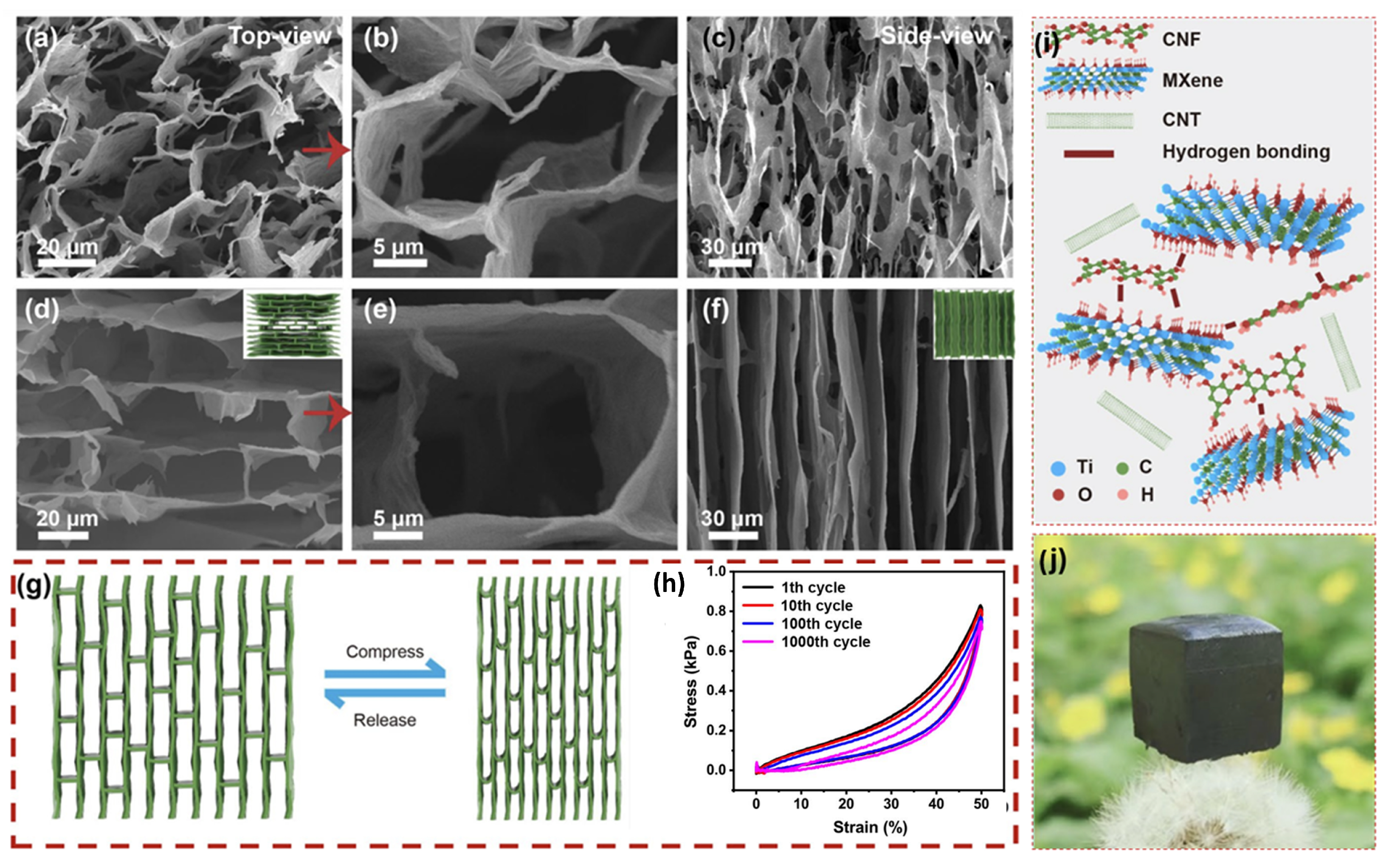
3.1. MXene/Carbon Nanotube Composite
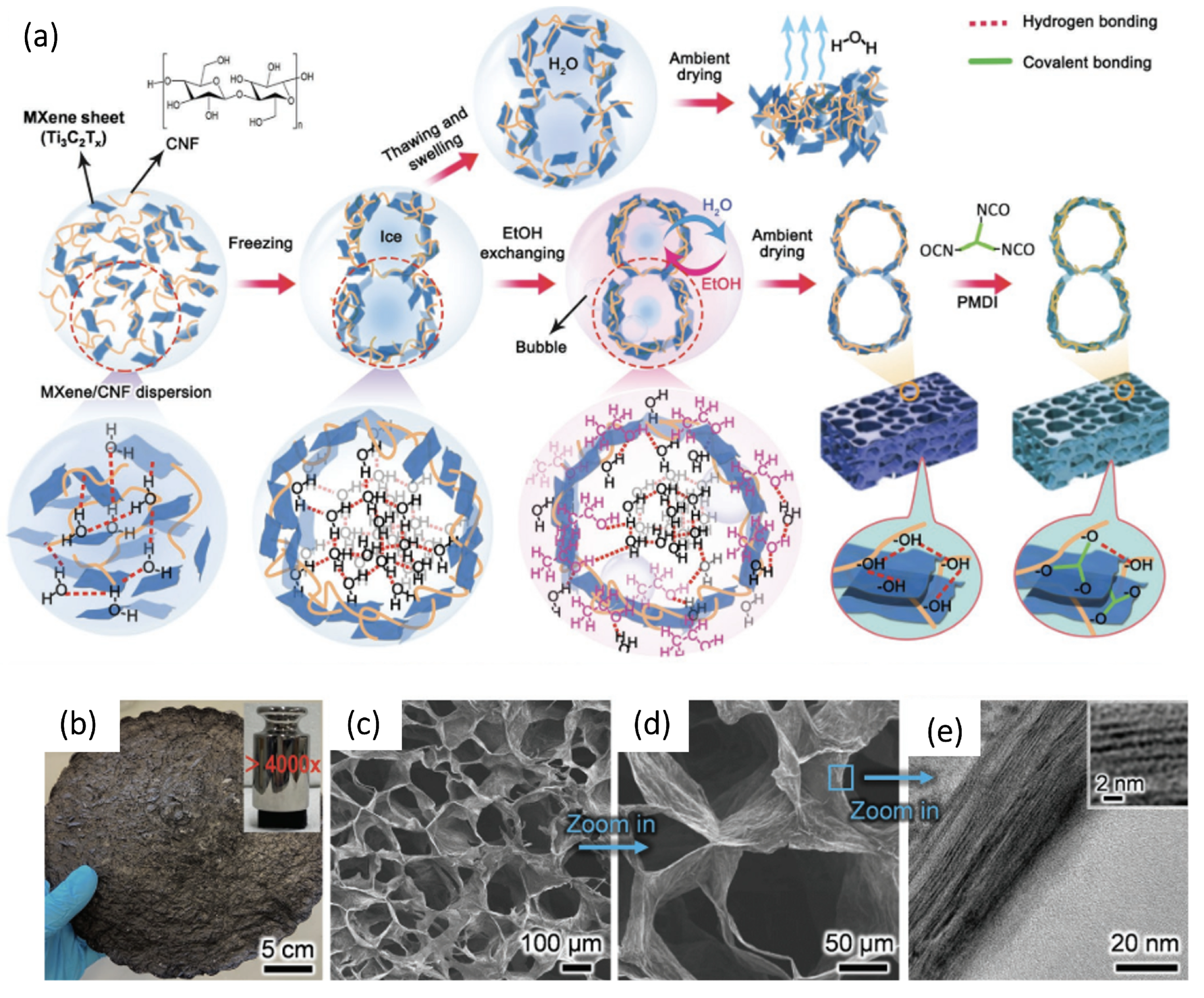
3.2. MXene/Carbon Nanofibers Composite

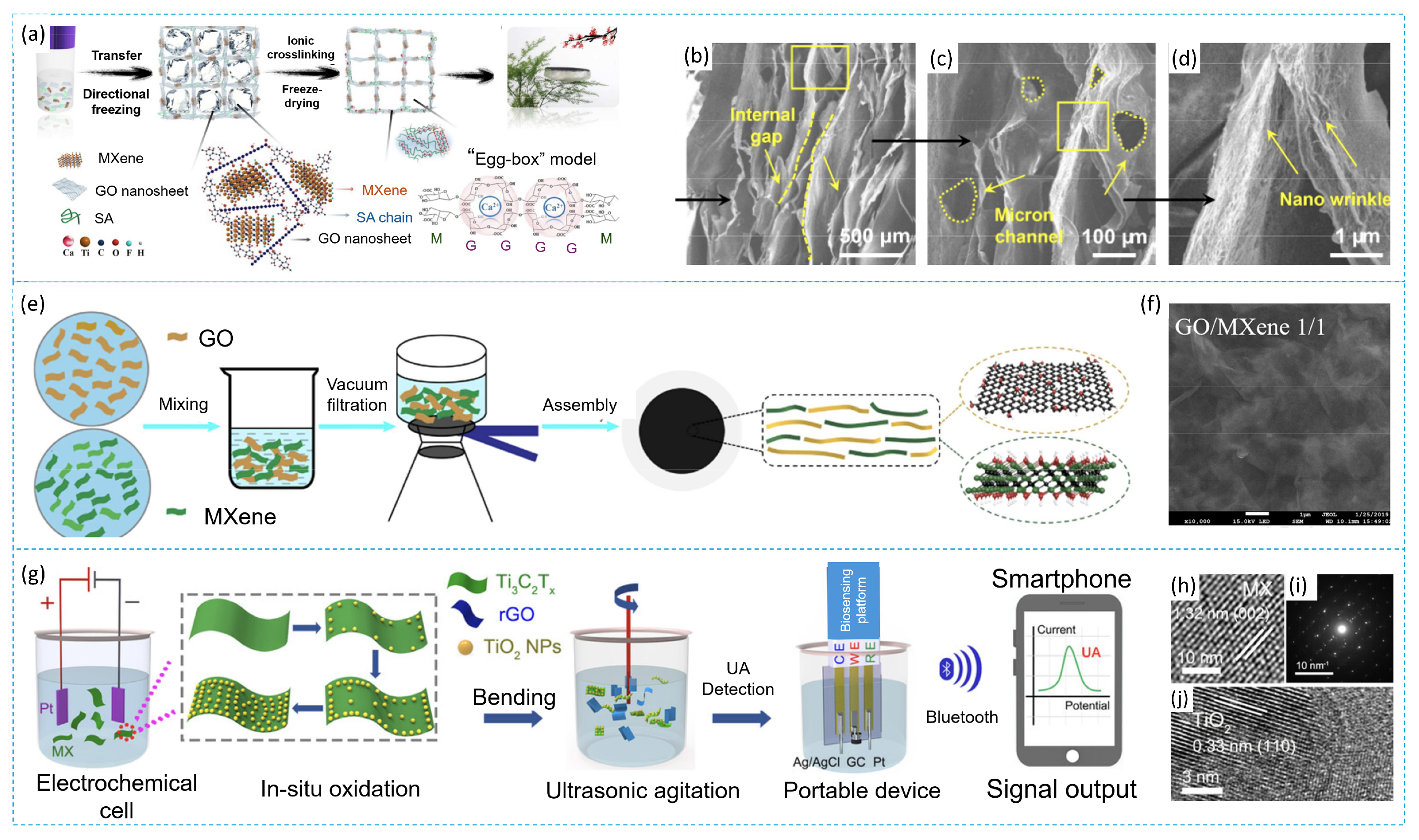
3.3. Composite MXene/Graphene Oxide
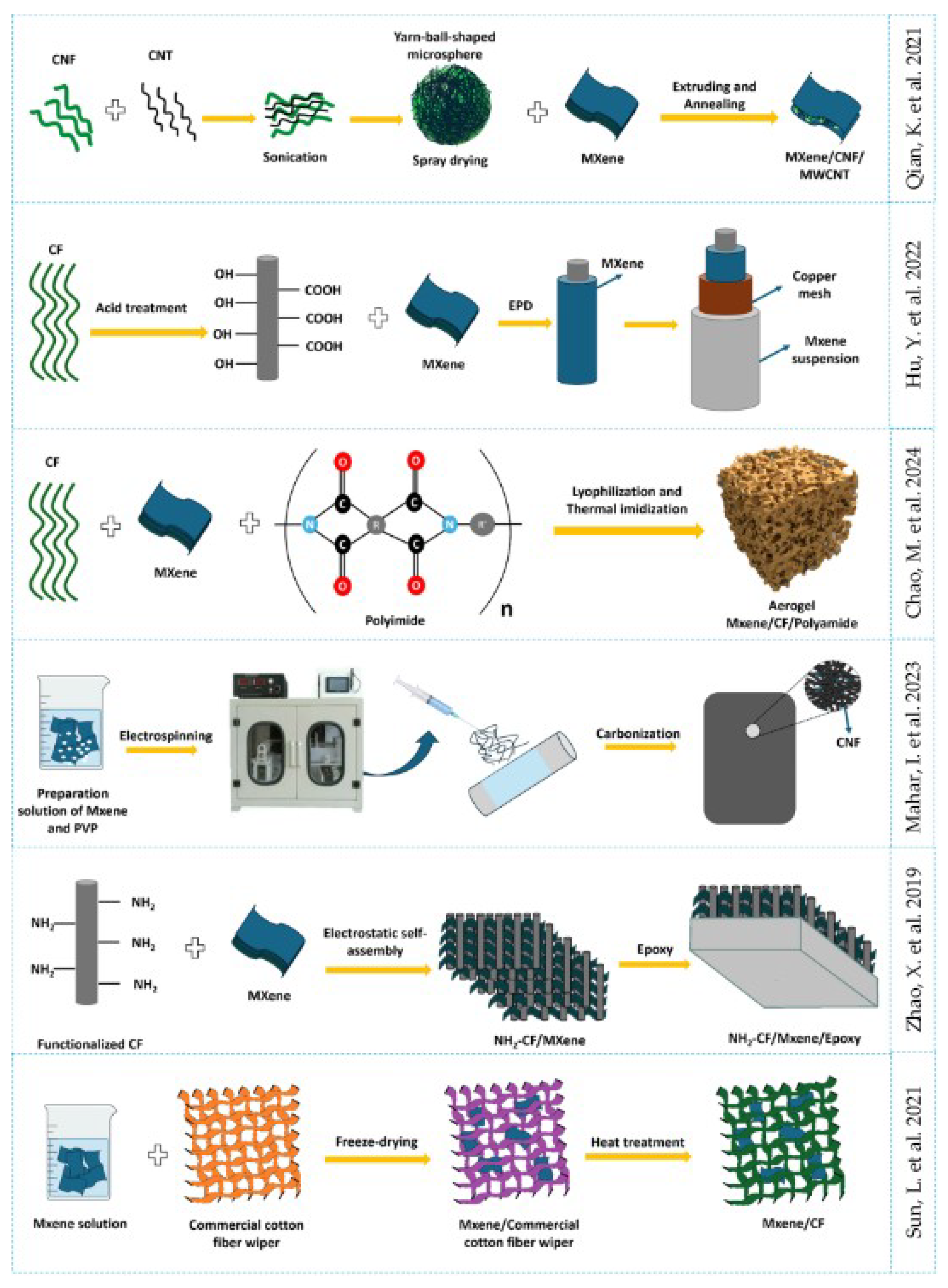
3.4. Composite MXene/Organic Based Material
4. Mechanism of Water Purification from Various Pollutants
4.1. Metals
4.2. Salts
4.3. Organic Contaminants
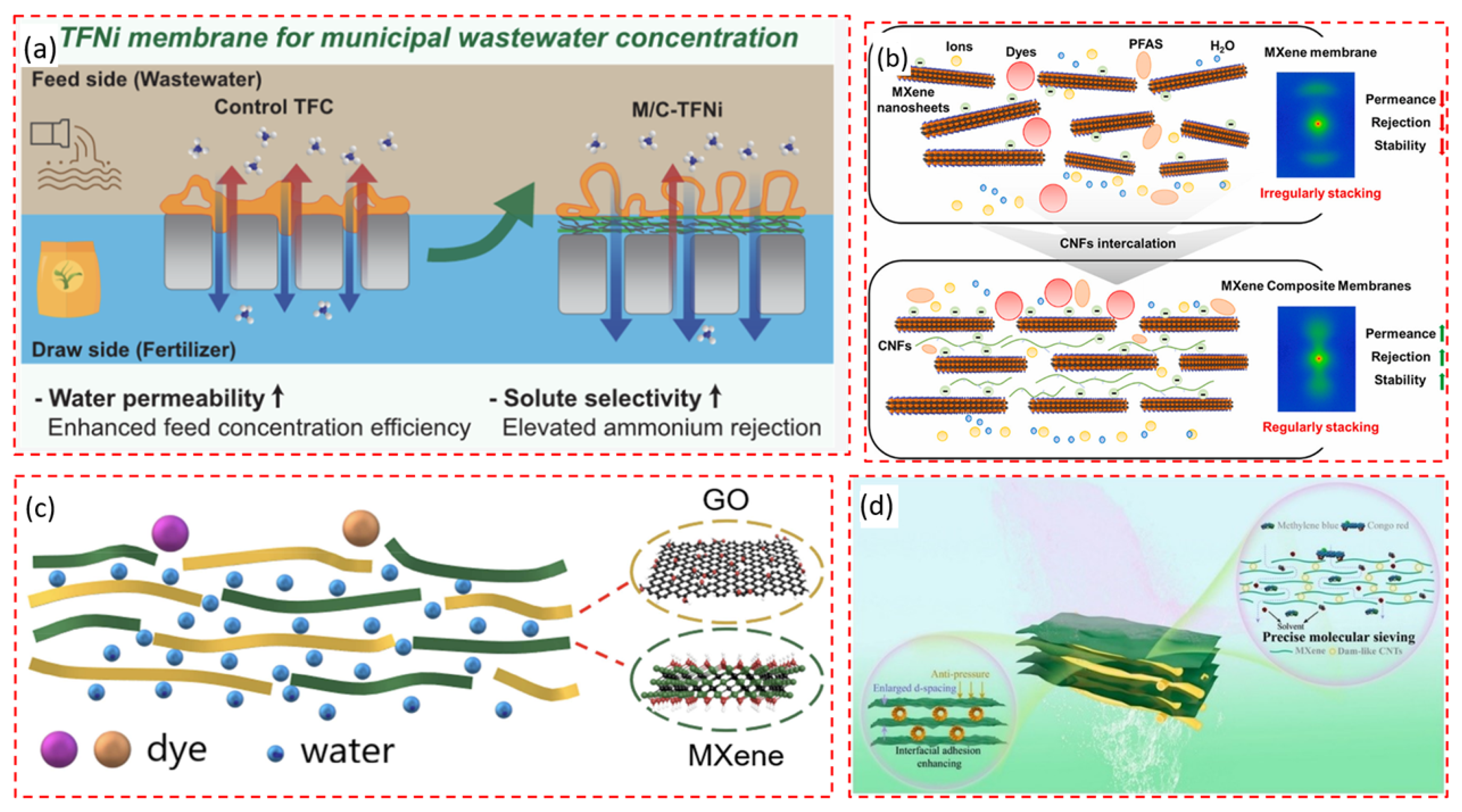
4.4. Dyes
| Composite | Pollutant | Tested Concentration | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Permeance (L/m2·h·bar) | Rejection (%) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Stability | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx/CNF based on polyvinylpyrrolid | Pb2+ | 10 ppb–10 ppm | n/a | n/a | n/a | 89 (in 20 min) | 12.7 | Removed 77% of Pb2+ and 60% of As3+ ions in the initial four cycles, but the efficiency notably declined after the fifth cycle | [151] |
| As3+ | 81 (in 30 min) | 3.3 | |||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/CeNF/FeOOH | Sb+3 | 2 mg/L, 12 mg/L | 34.15 | 0.17 (pore size is 6.62 nm) | Retention rate above 94.2% | n/a | 19.9 | Remained highly reusable after eight cycles, with a minor reduction in removal efficiency for Sb+3 and Sb+5 by 13.9% and 27.2%, respectively | [176] |
| Sb+5 | 18.1 | ||||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/CNT | Au+3 | 20 ppm | 230.6 | 0.942 | 437.6 | 99.8 | 2093 | The rejection rate remained consistent for the first three cycles but decreased to 51.6% over the subsequent six cycles | [179] |
| Ti3C2Tx/CNT in Nylon microfiltration membrane | Crystal violet (CV) | n/a | 45.3, membrane thickness is 820 nm) | n/a | 1214.3 | 99.8 | n/a | Rejection was 98.3% after 30 h Demonstrated stability in water for 30 h | [210] |
| Methyl orange (MO) | n/a | 1290.5 | 95.3 | ||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/CNT with polydopamine in α-Al2O3 substrates | Congo red (CR) | 10 mM | n/a | n/a | 10.8 | >99 | n/a | Maintained stability of >97% at pressures ranging from 1 to 5 bar, with a slight decrease in water permeability, and exhibited consistent performance during long-term continuous operation for up to 50 h | [127] |
| Rhodamine B (RhB) | 11.1 | 94.9 | |||||||
| MO | 13.2 | 92.4 | |||||||
| Na2SO4 | 10 ppm | 17.4 | 39.4 | ||||||
| MgSO4 | 20.9 | 31.7 | |||||||
| NaCl | 23.5 | 25.5 | |||||||
| MgCl2 | 25.9 | 20.8 | |||||||
| CNT/Ti3C2Tx/CNT | NaCl | 300–1000 mg/L | 25 | Pore size is 2–60 nm | rapid average desalination rate 3 mg/g min, 89% retention rate | n/a | 34.5 | Even after 40 cycles, the cell maintained high desalination capacity | [126] |
| Ti3C2Tx/GO on a mixed cellulose ester membrane | Na2SO4 | 5 mmol/L | Thickness is ~ 237 nm | n/a | 89.6 | 60.6 | 5.1–10.2% | Maintains high stability under high pressure, with rhodamine B rejection remaining over 98% even as the applied pressure increases | [184] |
| NaCl | ~39.5 | ||||||||
| MgSO4 | ~26 | ||||||||
| MgCl2 | 22.5 | ||||||||
| RhB | 10 ppm | ||||||||
| 99.3 | |||||||||
| Methylene blue (MB) | 97.6 | ||||||||
| CV | 99.1 | ||||||||
| Neutral red (NR) | 98.6 | ||||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/paper membrane | Oil (Sunflower oil, Diesel, Silicone oil, Petroleum oil, Hexane) | 1% v/v oil-in-water | (Effective membrane area is 1.77 cm2) | n/a | 450 | 99 | Separation efficiency over 99% | No signs of degradation were observed even after eight cycles of operation and washing (demonstrating the membrane’s anti-fouling properties through chemical-free cleaning) | [211] |
| Ti3C2Tx/GO | NaCl | 0.1 M | n/a | Pore size is 0.2 µm | 25, 6.62, 3.17, 2.14, and 0.79 for water, hexane, toluene, hexane, and IPA; for the NaCl, MgSO4, MR, MnB, RosB, and BB solutions were 2.25, 2.35, 2.1, 0.3, 0.67, and 0.23 | <1 | n/a | (High removal efficiency of organic dyes with hydrated radii exceeding 0.5 nm) | [212] |
| MgSO4 | 5 | ||||||||
| MR | 10 mg/L | 68 | |||||||
| MB | 99.5 | ||||||||
| Rose Bengal (RosB) | 93.5 | ||||||||
| Brilliant blue (BB) | 100 | ||||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/GO | Chrysoidine G | 10 mg/L | Thickness is ~550 nm | n/a | 6.5 | ~97 | n/a | Remain stable in water over one month (efficiency in >90% separation of dye molecules) | [161] |
| NR | 99.5 | ||||||||
| MB | 99.5 | ||||||||
| CV | ~99.5 | ||||||||
| BB | ~99.5 | ||||||||
| Humic acid | almost complete removal | ||||||||
| Bovine serum albumin | almost complete removal | ||||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/ GO/Nylon membrane | MO | 10 mg/L | Thickness is 140 nm | (Contact angle with water is 34.5°) | Acetone—48.32, Methanol—25.03, Ethanol—10.76, IPA—6.18 | 98.56 | n/a | Stable after 48 h filtration (Rejection: Acetone—1.9%, Methanol—0.5%, Ethanol—0.7%, IPA—1.9%) | [213] |
| MB | 99.1 | ||||||||
| Eosin | ~83 | ||||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/ CNT cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Acid orange 7 (AO7) | 100 mg/L; adsorbent dosage = 0.5 g/L | 56.19 | (Pore volume is 0.252 cm3/g, pore diameter is 13.77 nm) | n/a | n/a | 367.9 | The reduction in adsorption efficiency was minimal for AO7 after five cycles, followed by MO and CR. (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ and Cl−, NO3−, CO32−, SO42− had no significant effects on the removal of three dyes) | [214] |
| MO | 294.2 | ||||||||
| CR | 628.5 | ||||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/ carboxylated CeNF on polydopamine-nylon-66 substrate | NaCl | 1.0 g/L | Thicknesses is 129 nm, roughness is 61.6 nm | n/a | Highly permeable | 9.7 | No adsorption | Exhibited excellent stability, retaining its original morphology after 30 days of immersion in DI water (Separation factor for CR/NaCl: 512.0, for CR/Na2SO4: 517.2) | [196] |
| Na2SO4 | 30.7 | ||||||||
| MO | 100 mg/L | 82.4 | |||||||
| OG | 96.2 | ||||||||
| CR | 99.8 | ||||||||
| RB5 | 96.2 | ||||||||
| perfluoroalkyl substances | 1.0 mg/L | 94.7 | |||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/CNTs coated cotton fabrics (Solar driven interfacial water evaporation system) | Organic dyes (Reactive yellow K-3G, Acid red BG, Disperse navy blue S-2GL), Ions (Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+) | ~0.7–1030 mg/L for ions, ~200–262 mg/L | (Cotton a plane dimension is 0.5 m × 0.5 m) | n/a | Max wetted radius 30 mm, wetting time 0.324–0.362 s, spreading speed 22.88–24.94 mm/s | Organic dyes removal efficiency > 99%, ions concentration decreased to 0.16–1.12 mg/L | Water adsorption rate 51.14–51.59%/s, water evaporation rate of 1.35 kg m−2 h−1 | Remained almost unchanged after enduring 10 cycles (100 h) of solar evaporation tests in textile wastewater | [215] |
| Ti3C2Tx/CNTs for photocatalytic degradation | RhB | 0.01 M dye into 100 mL DI water | n/a | n/a | (Composite is used as catalyst) | Degradation efficiency 75% | n/a | (Enhanced the photo absorption capability and decreased the presence of organic toxic pollutants in wastewater) | [123] |
| Ti3C2Tx/O-multiwalled CNT@polyacrylonitrile | RosB | 11 mg/mL | Surface roughness is 14.95 nm | n/a | n/a | 99% | n/a | After 21 h rejection was 99% | [216] |
| MB | 98% | ||||||||
| CV | 100% | ||||||||
| Janus green (JG) B | 99% | After 21 h rejection was 97% | |||||||
| air compressor lubricating oil | 98% | ||||||||
| p- Ti3C2Tx/Single-walled CNT | MB | 30–1000 mg/L | 1.91 | n/a | n/a | 97.8% | n/a | Rejection was 95.2% in the fifth cycle of electrosorption | [217] |
| Ti3C2Tx/cellulose acetate | NaCl | 2000–4000 ppm | n/a | n/a | 256.85\269.02 | 28.14% | n/a | 1.7% weight loss of pristine CA | [218] |
| MgCl2 | 40.35% | ||||||||
| MgSO4 | 56.08% | ||||||||
| RhB | 92.34% | ||||||||
| MG | 98.27% | ||||||||
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | 100% | ||||||||
| Ti3C2Tx/GO | NaCl | 0.2M | Rq is 143 nm Ra is 116 nm | n/a | 0.688 | 99.3% | n/a | Due to dense bonding between nanosheets due to functional groups of components, membrane swelling is suppressed and the permeation rate of ions (K+, Na+, Li+, Al3+) is reduced, while the ion sieving characteristics of the membranes were improved by 7–40 times compared to the untreated membrane | [219] |
| Ti3C2Tx/Cellulose Acetate Mixed-Matrix CCAM-10% | Methyl green (MG) | 100 mg/L | 44.27 m2/g | 12.83 nm | 348.5 | 96.60% | n/a | There are good antifouling properties: the flux recovery ratio is 67.30% and irreversible fouling ratio at 32.70, as well as improved performance and durability of the membrane for water filtration in cross-flow mode compared to dead-end flow mode. | [135] |
| BSA | 99.51% |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.E. Urban Water Pollution by Heavy Metals, Microplastics, and Organic Contaminants. In Current Directions in Water Scarcity Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 6, pp. 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, K.K.; AbdulkadhimAl-Ghaban, A.M.H.; Rdewi, E.H. Synthesis of a Novel ZnO/TiO2-Nanorod MXene Heterostructured Nanophotocatalyst for the Removal Pharmaceutical Ceftriaxone Sodium from Aqueous Solution under Simulated Sunlight. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, S.; Husnain, S.M.; Kazmi, S.A.R.; Abbas, Y.; Jeon, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Shahzad, F. MXene/AgNW Composite Material for Selective and Efficient Removal of Radioactive Cesium and Iodine from Water. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoto-Martínez, T.; Hernández-Brito, J.J.; Gelado-Caballero, M.D. Pump-Underway Ship Intake: An Unexploited Opportunity for Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) Microplastic Monitoring Needs on Coastal and Oceanic Waters. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.S.S.; Billah, M.M.; Ali, M.M.; Bhuiyan, M.K.A.; Guo, L.; Mohinuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.B.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Yan, M.; et al. Microplastics in Aquatic Environments: A Comprehensive Review of Toxicity, Removal, and Remediation Strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Resources Institute. Available online: https://www.wri.org/data/aqueduct-projected-water-stress-country-rankings# (accessed on 8 April 2024).
- Wang, S.; Dang, C.; Li, M.; Gu, L.; Wu, J.; Cao, X. Boosting Clean Water Evaporation and Sustainable Water Treatment by Photothermally Induced Artificial System. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 16105–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebron, Y.A.R.; Moreira, V.R.; Santos, L.V.D.S.; Amaral, M.C.S. Membrane Distillation and Ion Exchange Combined Process for Mining Wastewater Treatment, Water Reuse, and Byproducts Recovery. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, Z. Sedimentation of Nanoplastics from Water with Ca/Al Dual Flocculants: Characterization, Interface Reaction, Effects of pH and Ion Ratios. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Li, L.; Bhatia, M.; Ryu, H.; Santo Domingo, J.W.; Brown, J.; Goetz, J.; Seo, Y. Impact of Harmful Algal Bloom Severity on Bacterial Communities in a Full-Scale Biological Filtration System for Drinking Water Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J. Novel Insight into Prior Induced Crystallization on Brackish Water Nanofiltration. Desalination 2023, 568, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, E.; Fernandes, E.; Gomes, J.; Castro-Silva, S.; Martins, R.C. Olive Oil Extraction Industry Wastewater Treatment by Coagulation and Fenton’s Process. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Y. Electrochemical Treatments of Coking Wastewater and Coal Gasification Wastewater with Ti/Ti4O7 and Ti/RuO2–IrO2 Anodes. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narbaitz, R.M.; Chartrand, Z.G.; Sartaj, M.; Downey, J. Ammonia-Ca-K Competitive Ion-Exchange on Zeolites in Mining Wastewater Treatment: Batch Regeneration and Column Performance. J. Sustain. Min. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.M.; Li, Z.; Zayed, A.M. Carbon Nanotube Impregnated Anthracite (An/CNT) as a Superior Sorbent for Azo Dye Removal. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 25586–25601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, S.; Stapf, M.; Miehe, U.; Ekblad, M.; Cimbritz, M.; Falås, P.; Nilsson, J.; Sehlén, R.; Bester, K. Ozone Dose Dependent Formation and Removal of Ozonation Products of Pharmaceuticals in Pilot and Full-Scale Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Deng, S.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Removal of Micropollutants by an Electrochemically Driven UV/Chlorine Process for Decentralized Water Treatment. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, B.; Zhao, C.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; He, Y. A Novel NiO/BaTiO3 Heterojunction for Piezocatalytic Water Purification under Ultrasonic Vibration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowriboy, N.; Kalaivizhi, R.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Ganesh, M.R.; Aswathy, K.A. Fabrication and Characterization of Polymer Nanocomposites Membrane (Cu-MOF@CA/PES) for Water Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, S.; Bilad, M.R.; Man, Z.B.; Suleman, H.; Hadi Nordin, N.A.; Jaafar, J.; Dzarfan Othman, M.H.; Elma, M. An Energy-Efficient Membrane Rotating Biological Contactor for Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 124544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.M.; Adam, M.R.; Mohamad Kamal, S.N.E.A.; Jaafar, J.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Aziz, F.; Yusof, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Mohamud, R.; et al. A Review of the Potential of Conventional and Advanced Membrane Technology in the Removal of Pathogens from Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 286, 120454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.S.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Abdullah, M.S.; Mohd Ghazali, N.H.; Yahaya, N.K.E.M.; Hashim, N.; Othman, A.R.; Mohammed, A.; et al. Removal of Emerging Organic Micropollutants via Modified-Reverse Osmosis/Nanofiltration Membranes: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, F.; Gray, S. Cost and Efficiency Perspectives of Ceramic Membranes for Water Treatment. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, U. Comprehensive Review of Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes Application for Water Treatment. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 72, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevallos-Mendoza, J.; Amorim, C.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.; Montenegro, M. Removal of Contaminants from Water by Membrane Filtration: A Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, T.S.; Hossain, M.M.; Jeong, H.M.; Kim, K. Heavy Metal Removal Applications Using Adsorptive Membranes. Nano Converg. 2020, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and Application of Granular Activated Carbon from Biomass Waste Materials for Water Treatment: A Review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 292–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of Adsorption Process for Effective Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water and Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Lee, D.-J.; Park, S.-S. Estimation of Number of Graphene Layers Using Different Methods: A Focused Review. Materials 2021, 14, 4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.-K.; Gong, J.-L.; Fang, S.-Y.; Li, J.; Cao, W.-C.; Chen, Z.-P. Outstanding Anti-Bacterial Thin-Film Composite Membrane Prepared by Incorporating Silver-Based Metal–Organic Framework (Ag-MOF) for Water Treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 153059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Peydayesh, M.; Ying, Y.; Mezzenga, R.; Ping, J. Transition Metal Dichalcogenide–Silk Nanofibril Membrane for One-Step Water Purification and Precious Metal Recovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24521–24530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Avtar, R.; Xu, P.; Othman, M.H.D. Recovering Heavy Metals from Electroplating Wastewater and Their Conversion into Zn2Cr-Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) for Pyrophosphate Removal from Industrial Wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tony, M.A. Zeolite-Based Adsorbent from Alum Sludge Residue for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 2485–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Deng, J.; Wei, Y.; Caro, J.; Wang, H. Effective Ion Sieving with Ti3C2Tx MXene Membranes for Production of Drinking Water from Seawater. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchik, F.; Maldybayev, K.; Kan, T.; Kokhmetova, S.; Chae, M.S.; Kurbatov, A.; Galeyeva, A.; Kaupbay, O.; Nimkar, A.; Bergman, G.; et al. Boosting the Capacity of MXene Electrodes in Neutral Aqueous Electrolytes. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Sall, D.; Loupias, L.; Célérier, S.; Aouine, M.; Bargiela, P.; Prévot, M.; Morfin, F.; Piccolo, L. MXene-Supported Single-Atom and Nano Catalysts for Effective Gas-Phase Hydrogenation Reactions. Mater. Today Catal. 2023, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hui, Z.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, G.; Huang, W. Ti3C2Tx MXene for Sensing Applications: Recent Progress, Design Principles, and Future Perspectives. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3996–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, K.; Peng, M.; Tan, Y. Highly Stable 3D Ti3C2Tx MXene-Based Foam Architectures toward High-Performance Terahertz Radiation Shielding. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C. Efficient Water Purification Using Stabilized MXene Nanofiltration Membrane with Controlled Interlayer Spacings. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, X.; Lin, C.; Gao, H.; Cao, S.; Ni, Y.; Ma, X. Modified Ti3C2Tx (MXene) Nanosheet-Catalyzed Self-Assembled, Anti-Aggregated, Ultra-Stretchable, Conductive Hydrogels for Wearable Bioelectronics. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakunkov, A.; Nordenström, A.; Boulanger, N.; Hennig, C.; Baburin, I.; Talyzin, A.V. Temperature-Dependent Swelling Transitions in MXene Ti3C2Tx. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 10940–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, A.; Zhang, B.; Taufik, A.; Asakura, Y.; Hasegawa, T.; Zhu, J.; Shi, P.; Yin, S. CuO Nanoparticles/Ti3C2Tx MXene Hybrid Nanocomposites for Detection of Toluene Gas. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 4755–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Hamidinejad, M.; Liang, C.; Zhao, B.; Habibpour, S.; Yu, A.; Filleter, T.; Park, C.B. Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance of Polymer/SiC-Nanowire/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) Composites. Carbon 2021, 179, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Ou, K.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lv, Y.; Miao, Y.-E.; Wang, Y.; Lan, Q.; et al. Dual-Layered Covalent Organic Framework/MXene Membranes with Short Paths for Fast Water Treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 658, 120761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, S.; Sirajudheen, P.; Vignesh, R.B.; Kim, D.-G.; Ko, S.-O. Efficient Interfacial Charge Transfer of Hierarchical Crinkled (2D/2D) Ti3C2Tx MXene Assembled on Perforated GO Heterojunction for Enhanced Degradation of Organic Dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhitomirsky, I. MXene–Carbon Nanotube Composite Electrodes for High Active Mass Asymmetric Supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10335–10344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yan, X. Realizing High-Performance Lithium Ion Hybrid Capacitor with a 3D MXene-Carbon Nanotube Composite Anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Guo, D.; Li, Z.; Su, Y. Ti3C2Tx MXene/Graphene Nanocomposites: Synthesis and Application in Electrochemical Energy Storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Kumar, N.; Ray, S.S. Recent Advances in Carbon Nanomaterial-Based Adsorbents for Water Purification. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 405, 213111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Sundaram, B. Efficacy and Challenges of Carbon Nanotube in Wastewater and Water Treatment. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2023, 19, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, G.; Vecitis, C.D. Prospects of an Electroactive Carbon Nanotube Membrane toward Environmental Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 2892–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, L.; Koh, K.Y.; Chen, J.P. Modification of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane by Silver Nanoparticles-Graphene Oxide Hybrid Nanosheet for Effective Membrane Biofouling Mitigation. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anayee, M.; Shuck, C.E.; Shekhirev, M.; Goad, A.; Wang, R.; Gogotsi, Y. Kinetics of Ti3AlC2 Etching for Ti3C2Tx MXene Synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 9589–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, K.; Nan, X.; Zhu, C.; Fan, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J. Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of Ti3C2 MXene via a Copper and Silver Nitrate Mixed Solution Etching Process with Minimal Fluorine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 947, 117789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarycheva, A.; Gogotsi, Y. Raman Spectroscopy Analysis of the Structure and Surface Chemistry of Ti3C2Tx MXene. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhirev, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Shuck, C.E.; Anayee, M.; Torita, T.; Gogotsi, Y. Delamination of Ti3C2Tx Nanosheets with NaCl and KCl for Improved Environmental Stability of MXene Films. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 16027–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Orbay, M.; Luo, S.; Duluard, S.; Shao, H.; Harmel, J.; Rozier, P.; Taberna, P.-L.; Simon, P. Exfoliation and Delamination of Ti3C2Tx MXene Prepared via Molten Salt Etching Route. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahian, M.S.; Jayan, R.; Kaewmaraya, T.; Hussain, T.; Islam, M.M. Elucidating Synergistic Mechanisms of Adsorption and Electrocatalysis of Polysulfides on Double-Transition Metal MXenes for Na–S Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10298–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, P.; Soomro, R.A.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, B. Advances in the Synthesis of 2D MXenes. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Guan, L.; Yang, X.; Zvyagin, A.V.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, C.; Yang, B.; Lin, Q. Muscle-Inspired MXene Conductive Hydrogels with Anisotropy and Low-Temperature Tolerance for Wearable Flexible Sensors and Arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Shpigel, N.; Rosy; Leifer, N.; Taragin, S.; Sharabani, T.; Aviv, H.; Perelshtein, I.; Nessim, G.D.; Noked, M.; et al. Enhancing the Energy Storage Capabilities of Ti3C2Tx MXene Electrodes by Atomic Surface Reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Patole, S.; Anwer, S.; Li, B.; Delclos, T.; Gogotsi, O.; Zahorodna, V.; Balitskyi, V.; Liao, K. Tensile Behaviors of Ti3C2Tx (MXene) Films. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 395704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Schwingenschlögl, U. Structure Prototype Outperforming MXenes in Stability and Performance in Metal-Ion Batteries: A High Throughput Study. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, B.; Miao, N.; Jiang, C.; Lu, H.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, M. Tuning the Magnetic Properties of Zr2N MXene by Biaxial Strain. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jia, X.; Liu, Y.; Wuliu, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X. A Synergetic Strategy of Well Dispersing Hydrophilic Ti3C2Tx MXene into Hydrophobic Polybenzoxazine Composites for Improved Comprehensive Performances. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 219, 109248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Bilal, M. Recent Advances in the Development of MXene-Based Membranes for Oil/Water Separation: A Critical Review. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 29, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Ling Zhao, D.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Xu, Y.; Li, B.; Teng, J.; Han, L.; Chung, T.-S. Mxenes for Membrane Separation: From Fabrication Strategies to Advanced Applications. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, T.; Gu, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z. Elucidating the Electronic Metal-Support Interaction Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution Activity on Ti3C2Tx MXene Basal Plane by Scanning Electrochemical Microscopy. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 8902–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, O.-S.; Madjet, M.E.; Mahmoud, K.A. Antibacterial Mechanism of Multifunctional MXene Nanosheets: Domain Formation and Phase Transition in Lipid Bilayer. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 8510–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Lim, M.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, J.S.; Yuk, J.M.; Lee, S.-M. Drastically Increased Electrical and Thermal Conductivities of Pt-Infiltrated MXenes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10739–10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sang, D.; He, C.; Sheng, X.; Lei, L. Mxene/Alginate Composites for Lead and Copper Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29015–29022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; He, H. Molecular Simulation Study of 2D MXene Membranes for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 677, 121623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarshenas, K.; Dou, H.; Habibpour, S.; Yu, A.; Chen, Z. Thin Film Polyamide Nanocomposite Membrane Decorated by Polyphenol-Assisted Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanosheets for Reverse Osmosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 1838–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabie, M.; Ali, A.Y.M.; Abo-Zahhad, E.M.; Elkady, M.F.; El-Shazly, A.H.; Salem, M.S.; Radwan, A.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Matsuyama, H.; Shon, H.K. New Hybrid Concentrated Photovoltaic/Membrane Distillation Unit for Simultaneous Freshwater and Electricity Production. Desalination 2023, 559, 116630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibah, N.A.; Zaine, S.N.A.; Shukur, M.F.A. Synthesis of Ti3C2 Mxene through In Situ HF and Direct HF Etching Procedures as Electrolyte Fillers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. MSF 2021, 1023, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sha, X.; Liang, J.; Yang, G.; Hu, X.; He, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Rapid Synthesis of Polyimidazole Functionalized MXene via Microwave-Irradiation Assisted Multi-Component Reaction and Its Iodine Adsorption Performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Pan, L.; Tang, H.; Du, F.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, T.; Yang, J. Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene Using HCl+LiF Etchant: Enhanced Exfoliation and Delamination. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, H. Electrochemical Performance of Ti3C2Tx MXenes Obtained via Ultrasound Assisted LiF-HCl Method. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, L.; Lee, D.; Yun, J.M.; Ryu, B.K.; Kim, K.H. Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of Ti3C2T MXene Film Based Supercapacitors in H2SO4/KI Redox Additive Electrolyte. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockreham, C.B.; Goncharov, V.G.; Hammond-Pereira, E.; Reece, M.E.; Strzelecki, A.C.; Xu, W.; Saunders, S.R.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Wu, D. Energetic Stability and Interfacial Complexity of Ti3C2Tx MXenes Synthesized with HF/HCl and CoF2/HCl as Etching Agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 41542–41554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, D.; Chae, Y.; Anayee, M.; Lee, Y.; Gogotsi, Y.; Ahn, C.W.; Jung, H.-T. Etching Mechanism of Monoatomic Aluminum Layers during MXene Synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 6346–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-Y.; Chiou, Y.-R.; Cheng, C.-S.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kongvarhodom, C.; Chen, H.-M.; Yougbaré, S.; Husain, S.; Ho, K.-C.; Kuo, T.-R.; et al. Incorporating Self-Assembled MXene to Improve Electrical Conductivity of Novel ZIF67 Derivatives Induced by NH4BF4 and NH4HF2 for Energy Storage. J. Energy Storage 2024, 82, 110589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wei, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Peng, F. A Hydrothermal Etching Route to Synthesis of 2D MXene (Ti3C2, Nb2C): Enhanced Exfoliation and Improved Adsorption Performance. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 18886–18893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Ahmad, S.; Nazir, F.; Dastan, D.; Shi, Z.; Garmestani, H.; Iqbal, M. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Water Splitting Application of D-Ti3C2 MXene/V2O5 Hybrid Nanostructures as an Efficient Bifunctional Catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 27383–27396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, L.; He, P.; Hu, Q.; Fan, L.-Z.; Zhou, A. Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Carbide Mo2CTx MXene by Hydrothermal Etching with Fluorides and Its Thermal Stability. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 19550–19556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Sahu, R.K.; Mishra, T.; Bhattacharya, P. Microwave-Assisted Rapid Synthesis of Titanium Phosphate Free Phosphorus Doped Ti3C2 MXene with Boosted Pseudocapacitance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 15794–15810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zschiesche, H.; Antonietti, M.; Gibilaro, M.; Chamelot, P.; Massot, L.; Rozier, P.; Taberna, P.; Simon, P. In Situ Synthesis of MXene with Tunable Morphology by Electrochemical Etching of MAX Phase Prepared in Molten Salt. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazaly, A.E.; Ahmed, H.; Rezk, A.R.; Halim, J.; Persson, P.O.Å.; Yeo, L.Y.; Rosen, J. Ultrafast, One-Step, Salt-Solution-Based Acoustic Synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 4287–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, C.; Filatov, A.S.; Cho, W.; Lagunas, F.; Wang, M.; Vaikuntanathan, S.; Liu, C.; Klie, R.F.; Talapin, D.V. Direct Synthesis and Chemical Vapor Deposition of 2D Carbide and Nitride MXenes. Science 2023, 379, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, J.; Ge, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, W.; Huang, W.; Shao, J.; Yang, J.; Dong, X. Stretchable Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanotube Composite Based Strain Sensor with Ultrahigh Sensitivity and Tunable Sensing Range. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Ricciardulli, A.G.; Lohe, M.R.; Blom, P.W.M.; Feng, X. Fluoride-Free Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide (MXene) Using A Binary Aqueous System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15491–15495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Xie, C.; Wang, Y. Preparation and Characterization of the Forward Osmosis Membrane Modified by MXene Nano-Sheets. Membranes 2022, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Gu, J.; Li, M.; Chao, M.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Yan, L.; Wang, X. Column-to-Beam Structure House Inspired MXene-Based Integrated Membrane with Stable Interlayer Spacing for Water Purification. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Gao, Q.; Xing, H.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, D.; Fan, B.; Zhao, B. Lightweight, Multifunctional MXene/Polymer Composites with Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and High-Performance Thermal Conductivity. Carbon 2021, 183, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, S.; Qarni, A.A.; Ul Haq, Y.; Ul Haq, Z.; Murtaza, I. Promising PVC/MXene Based Flexible Thin Film Nanocomposites with Excellent Dielectric, Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 12593–12605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, T.; Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, R. Construction of 3D MXene/Silver Nanowires Aerogels Reinforced Polymer Composites for Extraordinary Electromagnetic Interference Shielding and Thermal Conductivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, M.S.; Sokol, M.; Palmese, G.R.; Barsoum, M.W. Water Transport and Thermomechanical Properties of Ti3C2Tz MXene Epoxy Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39143–39149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Murali, G.; Patel, M.; Park, S.; In, I.; Kim, J. MXene-Integrated Metal Oxide Transparent Photovoltaics and Self-Powered Photodetectors. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 7134–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajavel, K.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Sun, R.; Wong, C. MXene/Metal Oxides-Ag Ternary Nanostructures for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsi, A.-Z.; Aziz, F.; Zulfiqar, S.; Haider, S.; Shakir, I.; Agboola, P.O. Synthesis, Characterization, Photocatalysis, and Antibacterial Study of WO3, MXene and WO3/MXene Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethinasabapathy, M.; Bhaskaran, G.; Park, B.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, W.-S.; Ryu, J.; Huh, Y.S. Iron Oxide (Fe3O4)-Laden Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2Tx) MXene Stacks for the Efficient Sequestration of Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Meng, J.; Bao, X.; Huang, Y.; Yan, X.; Qian, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T. Direct-Ink-Write 3D Printing of Programmable Micro-Supercapacitors from MXene-Regulating Conducting Polymer Inks. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2203683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbosiuba, T.C.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Kovo, A.S.; Afolabi, E.A.; Tijani, J.O.; Roos, W.D. Enhanced Adsorption of As(V) and Mn(VII) from Industrial Wastewater Using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Carboxylated Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabet, M.; Jahangiri, H.; Ghashghaei, E. Improving Microwave Absorption of the Polyaniline by Carbon Nanotube and Needle-like Magnetic Nanostructures. Synth. Met. 2017, 224, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, H.; Schnitzler, M.C.; Da Silva, W.M.; Santos, A.P. Purification of Carbon Nanotubes Produced by the Electric Arc-Discharge Method. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, N.; Srivastava, D.; Kumar Shukla, R.; Srivastava, A. Spectroscopic Study of Large-Scale Synthesized, Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotubes Using Spray Pyrolysis Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 12, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazhipkyzy, M.; Harris, P.J.F.; Nurgain, A.; Nemkayeva, R.R. Carbon Nanotubes Synthesized by CCVD Method Using Diatomite and Shungite Minerals. Eurasian Chem. Technol. J. 2022, 24, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; McLaughlan, J.; Zhang, L.; Falzon, B.G.; Mariotti, D.; Maguire, P.; Sun, D. Atmospheric Pressure Plasma-Synthesized Gold Nanoparticle/Carbon Nanotube Hybrids for Photothermal Conversion. Langmuir 2019, 35, 4577–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Merino, J.A.; Villarroel, R.; Chávez-Ángel, E.; Hevia, S.A. Laser Ablation Fingerprint in Low Crystalline Carbon Nanotubes: A Structural and Photothermal Analysis. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 178, 111255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Chen, Y.W.; Shi, Q.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, R.W.; Wang, J.N. Highly Aligned and Densified Carbon Nanotube Films with Superior Thermal Conductivity and Mechanical Strength. Carbon 2022, 186, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.P.; Lakkad, S.C. Effect of CNTs Growth on Carbon Fibers on the Tensile Strength of CNTs Grown Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, W.; He, J.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, W.; Li, A. Superwetting Monolithic Hollow-Carbon-Nanotubes Aerogels with Hierarchically Nanoporous Structure for Efficient Solar Steam Generation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Gong, J.; Sun, Y.; Yan, W.; Jin, R.; Li, J. High Permeability PEG/MXene@MOF Membrane with Stable Interlayer Spacing and Efficient Fouling Resistance for Continuous Oily Wastewater Purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 691, 122247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachina, E.V.; Ivanova, N.V.; Zakharov, Y.A.; Simenyuk, G.Y.; Ismagilov, Z.R.; Lomakin, M.V. Electrochemical Properties of the Composites Based on Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Modified with Nanoparticles of Mixed Cobalt and Nickel Hydroxides. Eurasian Chem. Technol. J. 2022, 24, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, Y.; Shin, J.; Yang, M.; Shin, N.; Shekhar, S.; Hong, S. Nanoscale Mapping of Carrier Mobilities in the Ballistic Transports of Carbon Nanotube Networks. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 21626–21635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhong, J.; Ou, J. Superdurable Fiber-Reinforced Composite Enabled by Synergistic Bridging Effects of MXene and Carbon Nanotubes. Carbon 2022, 190, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.-D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Jing, Y.-X.; Cao, X.-L.; Zhang, F.; Sun, S.-P. Enhancing Interfacial Adhesion of MXene Nanofiltration Membranes via Pillaring Carbon Nanotubes for Pressure and Solvent Stable Molecular Sieving. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 119033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hu, W.; Qiu, J.; Geng, B.; Du, M.; Zheng, Q. Solvent-Assisted Self-Assembly to Fabricate a Ternary Flexible Free-Standing polyaniline@MXene-CNTs Electrode for High-Performance Supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 921, 166062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liu, P.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Q.; Jiang, F.; Liu, P.; Liu, C.; Xu, J. Constructing Layered MXene/CNTs Composite Film with 2D–3D Sandwich Structure for High Thermoelectric Performance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2001340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Du, X.; Mathis, T.S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Shui, J.; Gogotsi, Y.; Xu, M. Maximizing Ion Accessibility in MXene-Knotted Carbon Nanotube Composite Electrodes for High-Rate Electrochemical Energy Storage. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumal, V.; Yuvakkumar, R.; Kumar, P.S.; Ravi, G.; Keerthana, S.P.; Velauthapillai, D. Facile Single-Step Synthesis of MXene@CNTs Hybrid Nanocomposite by CVD Method to Remove Hazardous Pollutants. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, P.; Chen, J.; Tian, W.B.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, Z.M. In Situ Synthesis of CNTs@Ti3C2 Hybrid Structures by Microwave Irradiation for High-Performance Anodes in Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3543–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shah, T.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B. Three Dimensional Porous MXene/CNTs Microspheres: Preparation, Characterization and Microwave Absorbing Properties. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 145, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Maximized Ion Accessibility in the Binder-Free Layer-by-Layer MXene/CNT Film Prepared by the Electrophoretic Deposition for Rapid Hybrid Capacitive Deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 121019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, S.; Cui, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Xing, W.; Jing, W. Assembly of Multidimensional MXene-Carbon Nanotube Ultrathin Membranes with an Enhanced Anti-Swelling Property for Water Purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 119075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yin, R.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Multifunctional MXene/CNTs Based Flexible Electronic Textile with Excellent Strain Sensing, Electromagnetic Interference Shielding and Joule Heating Performances. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 438, 135587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Fu, Y.; Liu, M.; Yue, H.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Li, H.; Yao, F. Dual-Phase MoS2/MXene/CNT Ternary Nanohybrids for Efficient Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. NPJ 2D Mater. Appl. 2022, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Nguyen, Q.-D.; Min, B.K.; Yi, Y.; Choi, C.-G. Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanotubes/Waterborne Polyurethane Based Composite Ink for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding and Sheet Heater Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, A.A.; Kazakova, M.A. Use of Carbon Materials of Different Nature in Determining Metal Concentrations in Carbon Nanotubes by X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 75, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinberg, P.; Methven, B.A.J.; Swider, K.; Mester, Z. Determination of Metallic Impurities in Carbon Nanotubes by Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 22717–22725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, H.; Graham, N.; Lian, Y.; Yu, W.; Sun, K. The Antifouling Performance of an Ultrafiltration Membrane with Pre-Deposited Carbon Nanofiber Layers for Water Treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 557, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Zhao, B.; Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Shen, A.; Ye, M. Novel CNT/MXene Composite Membranes with Superior Electrocatalytic Efficiency and Durability for Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, R.S.; Almasri, D.A.; Alfahel, R.; Hawari, A.H.; Hassan, M.K.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Mahmoud, K.A. MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/cellulose acetate mixed-matrix membrane enhances fouling resistance and rejection in the crossflow filtration process. Membranes 2022, 12, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Preparation and Characterization of a Thin-Film Composite Membrane Modified by MXene Nano-Sheets. Membranes 2022, 12, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Q.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, X.; Luo, C.; Ren, H.; Wu, D.; Liang, H. Secondary Wastewater Treatment Using Peroxymonosulfate Activated by a Carbon Nanofiber Supported Co3O4 (Co3O4@CNF) Catalyst Combined with Ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolowski, K.; Blazewicz, S.; Nocun, M.; Fraczek-Szczypta, A. Carbon Micro- and Nanofibrous Materials with High Adsorption Capacity for Water Desalination. Desalination 2021, 503, 114936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Amini, F.; Ehrmann, A. Recent Advances in Carbon Nanofibers and Their Applications—A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 138, 109963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, J. Preparation and Adsorption Application of Carbon Nanofibers with Large Specific Surface Area. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 16466–16475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, F.; Feng, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, J.; Shi, J.; Huang, M.; Shi, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Dong, L. Oxygen Engineering Enables N-Doped Porous Carbon Nanofibers as Oxygen Reduction/Evolution Reaction Electrocatalysts for Flexible Zinc–Air Batteries. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4002–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Byun, S.; Yuk, S.; Kim, S.; Song, S.H.; Lee, D. High-Rate Electrospun Ti3C2Tx MXene/Carbon Nanofiber Electrodes for Flexible Supercapacitors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 556, 149710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Han, P.; Meng, C.; Yu, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, H.; Wei, G.; Gu, Z. Comparative Study of Different Bonding Interactions on the Interfacial Adhesion and Mechanical Properties of MXene-Decorated Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Resin Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 245, 110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Pang, S.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Papageorgiou, D.G. Enhanced Interfacial Properties of Hierarchical MXene/CF Composites via Low Content Electrophoretic Deposition. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 237, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qi, S.; Liu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, F. Preparation and Mechanical Performances of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites by Mxene Nanosheets Coating. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 10516–10523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Fu, Q.; Pan, C. Hierarchical Porous “Skin/Skeleton”-like MXene/Biomass Derived Carbon Fibers Heterostructure for Self-Supporting, Flexible All Solid-State Supercapacitors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.; Chu, N.; Zhang, B.; Luo, C.; Yan, L. MXene/Carbon Fiber/Polyimide Composite Aerogel for Multifunctional Microwave Absorption. Compos. Commun. 2024, 46, 101837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, D.; Yang, K.; Luo, M.; Yang, P.; Zhou, X. Mxene (Ti3C2Tx)/Cellulose Nanofiber/Porous Carbon Film as Free-Standing Electrode for Ultrathin and Flexible Supercapacitors. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhao, D.L.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Kong, N.; Han, L.; Chen, C.; Teng, J.; Tang, C.; Chung, T.-S. Titanium Oxide Nanotubes Intercalated Two-Dimensional MXene Composite Membrane with Exceptional Antifouling and Self-Cleaning Properties for Oil/Water Separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Wu, H.; Fang, J.; Yang, Y.; Miao, M.; Cao, S.; Shi, L.; Feng, X. Yarn-Ball-Shaped CNF/MWCNT Microspheres Intercalating Ti3C2Tx MXene for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar, I.; Mahar, F.K.; Mahar, N.; Memon, A.A.; Pirzado, A.A.A.; Khatri, Z.; Thebo, K.H.; Ali, A. Fabrication and Characterization of MXene/Carbon Composite-Based Nanofibers (MXene/CNFs) Membrane: An Efficient Adsorbent Material for Removal of Pb+2 and As+3 Ions from Water. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 191, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Luo, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Rational Design of Hierarchically Sulfide and MXene-Reinforced Porous Carbon Nanofibers as Advanced Electrode for High Energy Density Flexible Supercapacitors. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 224, 109246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; He, Y.; Yan, S.; Yu, H.; Ma, J.; Hou, R.; Fan, Y.; Yin, X. Controlled Reduction and Fabrication of Graphene Oxide Membrane for Improved Permeance and Water Purification Performance. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 15130–15139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, P.; Tripathi, A.; Tiwari, A. Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 150, 111752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Li, Z.; Duan, J.; He, X. Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation Mechanism of Magnetic Graphene Oxide/ZnO Nanocomposites for Tetracycline Contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, H.; Xie, F.; Ma, X.; Niu, B.; Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Long, D. General Synthesis of Ultrafine Metal Oxide/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites for Ultrahigh-Flux Nanofiltration Membrane. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Youssry, S.M.; Soe, H.M.; Abdel-Galeil, M.M.; Kawamura, G.; Matsuda, A. Honeycomb-like Open-Edged Reduced-Graphene-Oxide-Enclosed Transition Metal Oxides (NiO/Co3O4) as Improved Electrode Materials for High-Performance Supercapacitor. J. Energy Storage 2020, 30, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, G.; Krishnaiah, K.V.; Ravi, N.; Padma Suvarna, R. FTIR, Raman and XRD Analysis of Graphene Oxide Films Prepared by Modified Hummers Method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1495, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; He, Y.; Xiao, G.; Fan, Y.; Ma, J.; Gao, Y.; Hou, R.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Mei, X. The Roles of Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups in Modulating Water Purification Performance of Graphene Oxide-Based Membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, X.; Guo, A.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Z.; Yu, F.; Hou, B.; Wang, Y.; Homewood, K.P.; Wang, X. 3D Macroscopic Graphene Oxide/MXene Architectures for Multifunctional Water Purification. Carbon 2020, 167, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Graham, N.; Yu, W.; Sun, K. Two-Dimensional MXene Incorporated Graphene Oxide Composite Membrane with Enhanced Water Purification Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 593, 117431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, W.; Shi, M.; Wu, M.; Shi, P.; Zhao, N.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; et al. An “On-Site Transformation” Strategy for Electrochemical Formation of TiO2 Nanoparticles/Ti3C2Tx MXene/Reduced Graphene Oxide Heterojunction Electrode Controllably toward Ultrasensitive Detection of Uric Acid. Small Struct. 2024, 5, 2400034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlamadi, G.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Liimatainen, H. Ultrahigh Fluid Sorption Capacity of Superhydrophobic and Tough Cryogels of Cross-Linked Cellulose Nanofibers, Cellulose Nanocrystals, and Ti3C2Tx MXene Nanosheets. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 24746–24760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, Q.; Yan, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.-B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Xie, X. Multifunctional Magnetic Ti3C2Tx MXene/Graphene Aerogel with Superior Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 6622–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, R.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hong, M.; Gao, J.; et al. Hyperelastic, Robust, Fire-Safe Multifunctional MXene Aerogels with Unprecedented Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Efficiency. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2306884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quero, F.; Rosenkranz, A. Mechanical Performance of Binary and Ternary Hybrid MXene/Nanocellulose Hydro- and Aerogels—A Critical Review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supian, M.A.F.; Amin, K.N.M.; Jamari, S.S.; Mohamad, S. Production of Cellulose Nanofiber (CNF) from Empty Fruit Bunch (EFB) via Mechanical Method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Pan, F.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Ultrathin Cellulose Nanofiber Assisted Ambient-Pressure-Dried, Ultralight, Mechanically Robust, Multifunctional MXene Aerogels. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Song, Q.; Liu, K.; Liu, H.; Pan, J.; Liu, W.; Dai, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Si, C.; et al. Nanocellulose-Assisted Construction of Multifunctional MXene-Based Aerogels with Engineering Biomimetic Texture for Pressure Sensor and Compressible Electrode. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Hu, P.; Hu, F.; Tian, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhang, P.; Pan, L.; Barsoum, M.W.; Cai, L.; Sun, Z. Multifunctional MXene/C Aerogels for Enhanced Microwave Absorption and Thermal Insulation. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Graham, N.; Yu, W.; Shi, Y.; Sun, K.; Liu, T. Preparation and Evaluation of a High Performance Ti3C2Tx-MXene Membrane for Drinking Water Treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 654, 120469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yu, Z.; Long, R.; Li, X.; Shao, L.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, G.; Zuo, Y. Self-Assembling 2D/2D (MXene/LDH) Materials Achieve Ultra-High Adsorption of Heavy Metals Ni2+ through Terminal Group Modification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, M.; Lu, H.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Tan, S.C. MXene Functionalized, Highly Breathable and Sensitive Pressure Sensors with Multi-Layered Porous Structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2214880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Z.-R.; Jiang, J.; Xu, Y.-J. Microstructure and Surface Control of MXene Films for Water Purification. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lou, Z.; Fu, R.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J.; Baig, S.A.; Xu, X. Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Incorporated with or without Amino Groups for Aqueous Pb(II) Removal: Comparison and Mechanism Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
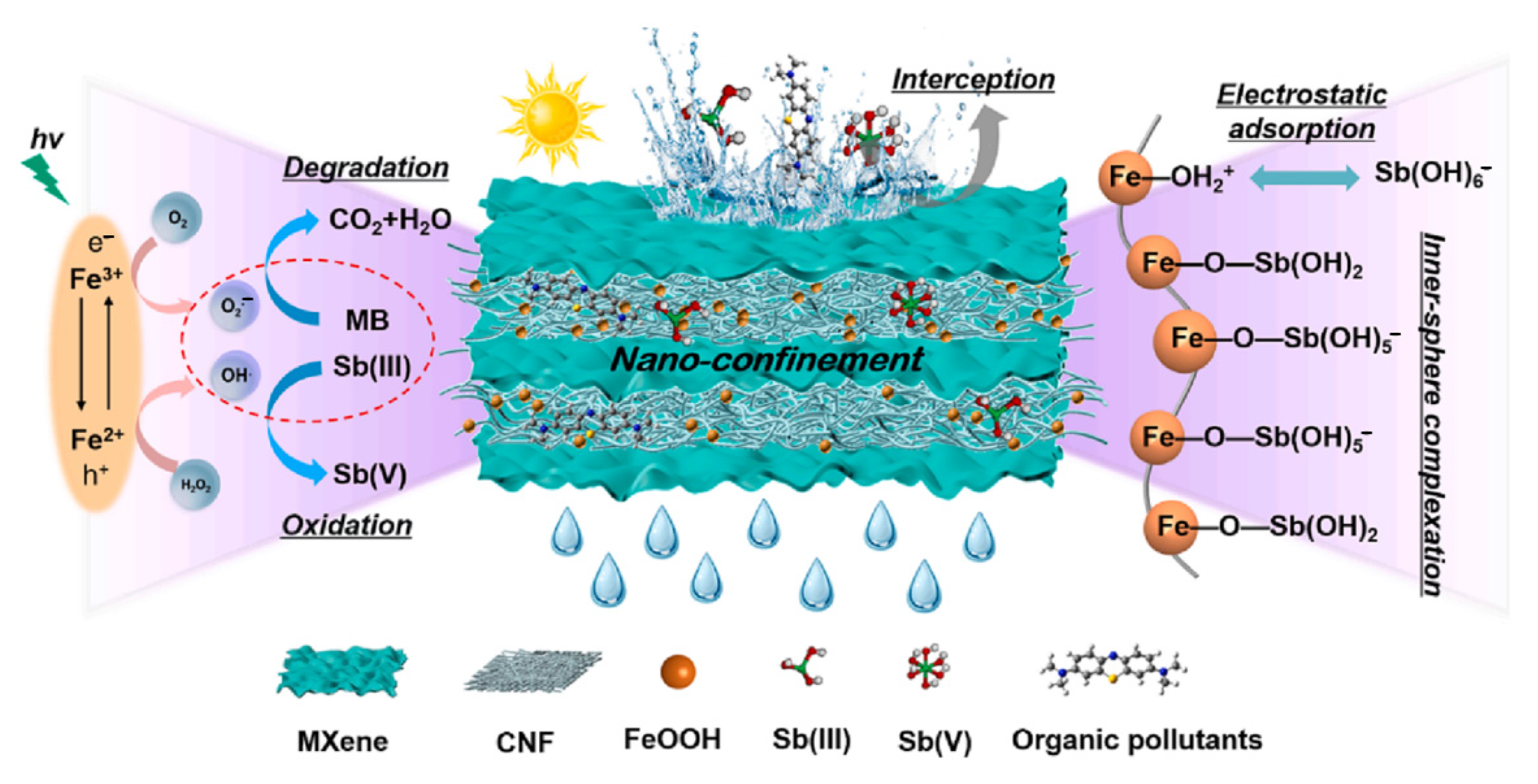
- Wan, K.; Fang, T.; Zhang, W.; Ren, G.; Tang, X.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Y.; Qi, P.; Liu, X. Enhanced Antimony Removal within Lamellar Nanoconfined Interspaces through a Self-Cleaning MXene@CNF@FeOOH Water Purification Membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 143018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, G.; Yi, Y. Innovative Strategy Based on Novel Ti3C2Tx MXenes Nanoribbons/Carbon Nanotubes Hybrids for Anodic Stripping Voltammetry Sensing of Mercury Ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 355, 131247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, M.A.; Salimi-Kenari, H.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Huynh, N.; Rashid, K.T.; Salih, I.K. Novel MXene-Modified Polyphenyl Sulfone Membranes for Functional Nanofiltration of Heavy Metals-Containing Wastewater. Membranes 2023, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, R.; Hou, P.-X.; Ma, Y.; Majeed, A.; Wang, X.; Liu, C. MXene-Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Membrane for Robust Recovery of Au from Trace-Level Solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43032–43041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.; Hu, T.; Hu, M.; Li, C.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; et al. MXenes Induce Epitaxial Growth of Size-Controlled Noble Nanometals: A Case Study for Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS). J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.-F.; Yang, Z.; Song, X.; Lee, J.H.; Tang, C.Y.; Park, H.-D. Interlayered Forward Osmosis Membranes with Ti3C2Tx MXene and Carbon Nanotubes for Enhanced Municipal Wastewater Concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13219–13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wu, N.; Yang, Y.; Pan, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Xiao, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Graphene Oxide-Assisted Multiple Cross-Linking of MXene for Large-Area, High-Strength, Oxidation-Resistant, and Multifunctional Films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, Y.; Wu, N.; Zhao, S.; Jin, H.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Bicontinuous, High-Strength, and Multifunctional Chemical-Cross-Linked MXene/Superaligned Carbon Nanotube Film. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 19293–19304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Wu, P. High-Performance Graphene Oxide Nanofiltration Membrane with Continuous Nanochannels Prepared by the In Situ Oxidation of MXene. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A. Non-Steric Mechanisms of Nanofiltration: Superposition of Donnan and Dielectric Exclusion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 22–23, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, Q.; Lou, M.; Bai, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, F.; Van Der Bruggen, B. GO-Based Membranes with Enhanced Stability and Permeability by Implanting Etched-MXene Nanosheets: The Role of Binding Energy in Stabilizing 2D Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 707, 122983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aher, A.; Nickerson, T.; Jordan, C.; Thorpe, F.; Hatakeyama, E.; Ormsbee, L.; Majumder, M.; Bhattacharyya, D. Ion and Organic Transport in Graphene Oxide Membranes: Model Development to Difficult Water Remediation Applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 604, 118024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, K. The Preparation of High-Performance and Stable MXene Nanofiltration Membranes with MXene Embedded in the Organic Phase. Membranes 2021, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitonov, A.A.; Ryzhkov, I.I. Modelling the Performance of Electrically Conductive Nanofiltration Membranes. Membranes 2023, 13, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliç, Z. Water Pollution: Causes, Negative Effects and Prevention Methods. İstanbul Sabahattin Zaim Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü Derg. 2021, 3, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Dai, Y.; Hou, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cui, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Shen, J. MXene Based Immobilized Microorganism for Chemical Oxygen Demand Reduction of Oilfield Wastewater and Heavy Oil Viscosity Reduction to Enhance Recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, M.; Xu, H.; Yang, W.; Zhang, K.; Tian, H.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z. Scalable Ti3C2Tx MXene Interlayered Forward Osmosis Membranes for Enhanced Water Purification and Organic Solvent Recovery. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9125–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wu, Z.; Feng, G.; Wei, L.; Weng, J.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E.; Wang, X. Multifunctional Sandwich-like Composite Film Based on Superhydrophobic MXene for Self-Cleaning, Photodynamic and Antimicrobial Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Dai, X.; Zhao, Y.; Han, D.; Zuo, Q.; Song, Z. Carbon Nanotubes as a Scaffold in the Ti3C2Tx(MXene)-Derivatized Membrane for Oil/Water Emulsion Separation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zhou, X.; Shen, L.; Zhao, D.L.; Kong, N.; Li, Y.; Qiu, X.; Chen, C.; Teng, J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Exceptional Self-Cleaning MXene-Based Membrane for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 700, 122691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Han, M.; Zhang, W.; Yi, M.; Xia, L.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S. High Performance Mixed-Dimensional Assembled MXene Composite Membranes for Molecular Sieving. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 698, 122606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Seredych, M.; Chen, C.; Gura, V.; Mikhalovsky, S.; Sandeman, S.; Ingavle, G.; Ozulumba, T.; Miao, L.; Anasori, B.; et al. MXene Sorbents for Removal of Urea from Dialysate: A Step toward the Wearable Artificial Kidney. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10518–10528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-M.; Liu, Z.-H.; Lü, Q.-F. Lignin Modified Ti3C2Tx Assisted Construction of Functionalized Interface for Separation of Oil/Water Mixture and Dye Wastewater. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 656, 130371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Mu, P.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Ultrathin 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene Membrane for Effective Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions in Acidic, Alkaline, and Salty Environment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 561, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezazi, M.; Quazi, M.M. Recent Developments in Two-Dimensional Materials-Based Membranes for Oil–Water Separation. Membranes 2023, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Shen, L.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, C.; Teng, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lin, H. Transversal Nanochannel-Enabled MXene Laminated Membranes for Superior Oil-Water Separation: A Fluid Mosaic Cytomembrane Inspired Approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 680, 121735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yi, M.; Chai, C.; Li, W.; Qi, P.; Wang, J.; Hao, J. Oxidation Stability Enhanced MXene-Based Porous Materials Derived from Water-in-Ionic Liquid Pickering Emulsions for Wearable Piezoresistive Sensor and Oil/Water Separation Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 618, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imsong, R.; Dhar Purkayastha, D. Dual-Functional Superhydrophilic/Underwater Superoleophobic 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene-PAN Membrane for Efficient Oil-Water Separation and Adsorption of Organic Dyes in Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Zhan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Yang, W.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y. Assembly of MXene/ZnO Heterojunction onto Electrospun Poly(Arylene Ether Nitrile) Fibrous Membrane for Favorable Oil/Water Separation with High Permeability and Synergetic Antifouling Performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 663, 120933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Feng, Q.; Yang, W.; Chiao, Y.-H.; Zhang, S.; Sun, A. Durable and Super-Hydrophilic/Underwater Super-Oleophobic Two-Dimensional MXene Composite Lamellar Membrane with Photocatalytic Self-Cleaning Property for Efficient Oil/Water Separation in Harsh Environments. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 637, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, W.; Matsumoto, R.A.; Thompson, M.W.; Liu, Y.-H.; Bootwala, Y.; Dixit, M.B.; Nemsak, S.; Crumlin, E.; Hatzell, M.C.; Cummings, P.T.; et al. In Situ Investigation of Water on MXene Interfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2108325118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Pei, L.; Xue, H.; Li, Z. Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Congo Red from Aqueous Solution on 3D MXene/Carbon Foam Hybrid Aerogels: A Study by Experimental and Statistical Physics Modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Guo, S.; Graham, N.; Yu, W.; Sun, K.; Liu, T. R-HGO/MXene Composite Membrane with Enhanced Permeability and Rejection Performance for Water Treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 691, 122216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Chen, W.; Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Tong, X.; Chen, Y. Two-Dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene/GO Hybrid Membranes for Highly Efficient Osmotic Power Generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2931–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, W.; Kong, Q.; Lin, T.; Tao, H.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, K.; Xie, Z. Construction of a Hierarchical Carbon Nanotube/MXene Membrane with Distinct Fusiform Channels for Efficient Molecular Separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 22666–22673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saththasivam, J.; Wang, K.; Yiming, W.; Liu, Z.; Mahmoud, K.A. A Flexible Ti3C2Tx (MXene)/Paper Membrane for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 16296–16304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.M.; Kim, D.W.; Ren, C.E.; Cho, K.M.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.H.; Nam, Y.T.; Gogotsi, Y.; Jung, H.-T. Selective Molecular Separation on Ti3C2Tx–Graphene Oxide Membranes during Pressure-Driven Filtration: Comparison with Graphene Oxide and MXenes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44687–44694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xie, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wang, L.; Ye, H.; Xiong, X.; Wang, S.; Han, K. Two-Dimensional Graphene Oxide/MXene Composite Lamellar Membranes for Efficient Solvent Permeation and Molecular Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Fan, W.; Zhang, J.; Xue, T.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. Adsorption of Anionic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions by a Novel CTAB/MXene/Carbon Nanotube Composite: Characterization, Experiments, and Theoretical Analysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 661, 160036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Fan, J.; Wang, W.; Yu, D. Simple and Robust MXene/Carbon Nanotubes/Cotton Fabrics for Textile Wastewater Purification via Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibade, T.F.; Tian, H.; Hassan Lasisi, K.; Xue, Q.; Yao, W.; Zhang, K. Multifunctional PAN UF Membrane Modified with 3D-MXene/O-MWCNT Nanostructures for the Removal of Complex Oil and Dyes from Industrial Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Cheng, M.; Su, Y.; Xue, J.; Liu, J.; Hou, S. A Facile Synthesis of Porous MXene-Based Freestanding Film and Its Spectacular Electrosorption Performance for Organic Dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 263, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.P.; Rasheed, P.A.; Gomez, T.; Azam, R.S.; Mahmoud, K.A. A Fouling-Resistant Mixed-Matrix Nanofiltration Membrane Based on Covalently Cross-Linked Ti3C2Tx (MXene)/Cellulose Acetate. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 607, 118139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Li, P.; Xiong, L.; Ding, L.; Wei, Y.; Wang, H. Supported MXene/GO Composite Membranes with Suppressed Swelling for Metal Ion Sieving. Membranes 2021, 11, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zeng, G.; Yan, G.; Luo, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H. Self-Cleaning Photocatalytic MXene Composite Membrane for Synergistically Enhanced Water Treatment: Oil/Water Separation and Dyes Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zeng, G.; Pu, S.; Yan, G.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, Z. A Dual Regulation Strategy for MXene-Based Composite Membrane to Achieve Photocatalytic Self-Cleaning Properties and Multi-Functional Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Composite | Synthesis Method | Additive | Morphological Features | Adsorption Capabilities | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx/CNTs | Electrostatic self-assembly | basalt fiber-reinforced polymer, epoxy | Uniform thickness; Basalt fibers tightly embedded in matrix composites | Synergistic effect of MXene/CNT/epoxy composite; High stability in alkaline environments | [118] |
| Ti3C2Tx/CNTs | CVD | - | Uniform growth CNTs with a diameter from 40 to 90 nm; Ti3C2Tx layered particles, a common network of Ti3C2Tx/CNTs | n/a | [123] |
| Ti3C2Tx/CNTs-cetyltrimethylammonium bromide on nanofiltration membrane | Vacuum-assisted filtration | cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Membranes with a layered structure had a larger gap between them; The interfacial adhesion force was increased by 6 times compared to the MXene membrane | Membrane has excellent mechanical strength and solvent resistance during molecular sieving; The permeability of pure water increased up to 5 times, with 20.09 L/m2·h·bar to 100.89 L/m2·h·bar | [119] |
| Ti3C2Tx/CNTs | Electrophoretic deposition | - | CNT provides maximum ion access to ion intercalation sites by increasing the distance between the layers of the MXene nanolayer. | Efficient and fast hybrid capacitive deionization; High fiber hydrophilicity; Specific capacity (178 F/g); Low degreasing resistance; High electrochemical stability (90%); After 1500 cycles and maximum Na+ diffusion coefficient; It can provide an energy-efficient desalination process and outstanding desalination stability with a retention rate of 89% after 40 cycles | [126] |
| Ti3C2Tx/functionalized CNTs | Thermal treatment | PDA-modified α-Al2O3 | 1D CNTs are well dispersed and embedded in two-dimensional MXene nanoliths; The formation of a homogeneous network and continuous three-dimensional (3D) labyrinthine short mass transfer channels | Improved permeability; Pronounced ability to suppress swelling; Stability | [127] |
| Dual-phase MoS2/Ti3C2Tx/CNT | One-step bisolvent solvothermal synthesis technique | 1 T enriched-MoS2 | Triple hybrid structure; Two-phase MoS2 (DP-MoS2) is formed directly on MXene, while CNTs act as crosslinking between 2D islands; MoO2 suppresses oxidation of MXene and rearrangement of 2D layers | Increasing the surface area to 32 m2/g | [129] |
| Ti3C2/knotted CNTs | CVD | the catalyst Ni–Mn–Al–O | Formation of a three-dimensional network architecture; CNT nodules with a size of 200 ± 20 nm; The average Ti3C2 flake size is ~250 nm; Ti3C2/CNT in the form of a sponge | n/a | [122] |
| Ti3C2Tx/CNT/waterborne polyurethane | Sonication | waterborne polyurethane | Free and uniform film with a thickness of 90 µm; | n/a | [130] |
| Ti3C2Tx/ Carboxylated-CNTs microspheres | Self-assembly | - | Layered structure of Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets with thickness 1.32 nm; Spherical hierarchical 3D structure of composite with typical shrinkage morphology | BET Surface Area 48.64 m2/g; Pore Volume 0.1462 cm3/g; Pore Size 24.19 nm | [125] |
| Ti3C2Tx/CNTs | Dip-coating | thermoplastic polyurethane nonwoven fabric | Hypersensitive microcrack structure; Porous fibrous mesh structure | Stability at high temperatures; The synergistic effect of the MXene/CNTs conductive coating | [128] |
| MXene/sodium lignosulfonate CNT | Self-assembly | sodium lignosulfonate, polyethersulfone substrate pretreated with dopamine | Uniform distribution; Structural integrity | The MB and CR dyes retention efficiency was more than 99% with a permeation flux of 51.6 L/m2·h·bar; This membrane shows electrocatalytic efficiency, whereby it degrades various organic dyes (MO, MB, MG, RhB) within 1 h; It has 80% recovery capacity | [134] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keneshbekova, A.; Smagulova, G.; Kaidar, B.; Imash, A.; Ilyanov, A.; Kazhdanbekov, R.; Yensep, E.; Lesbayev, A. MXene/Carbon Nanocomposites for Water Treatment. Membranes 2024, 14, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090184
Keneshbekova A, Smagulova G, Kaidar B, Imash A, Ilyanov A, Kazhdanbekov R, Yensep E, Lesbayev A. MXene/Carbon Nanocomposites for Water Treatment. Membranes. 2024; 14(9):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090184
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeneshbekova, Aruzhan, Gaukhar Smagulova, Bayan Kaidar, Aigerim Imash, Akram Ilyanov, Ramazan Kazhdanbekov, Eleonora Yensep, and Aidos Lesbayev. 2024. "MXene/Carbon Nanocomposites for Water Treatment" Membranes 14, no. 9: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090184
APA StyleKeneshbekova, A., Smagulova, G., Kaidar, B., Imash, A., Ilyanov, A., Kazhdanbekov, R., Yensep, E., & Lesbayev, A. (2024). MXene/Carbon Nanocomposites for Water Treatment. Membranes, 14(9), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes14090184











