Modeling of Power Generation and Acid Recovery in an Analogous Process of Reverse Electrodialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experiments
2.3. Model Description
2.4. Governing Equations
2.5. Boundary Conditions
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
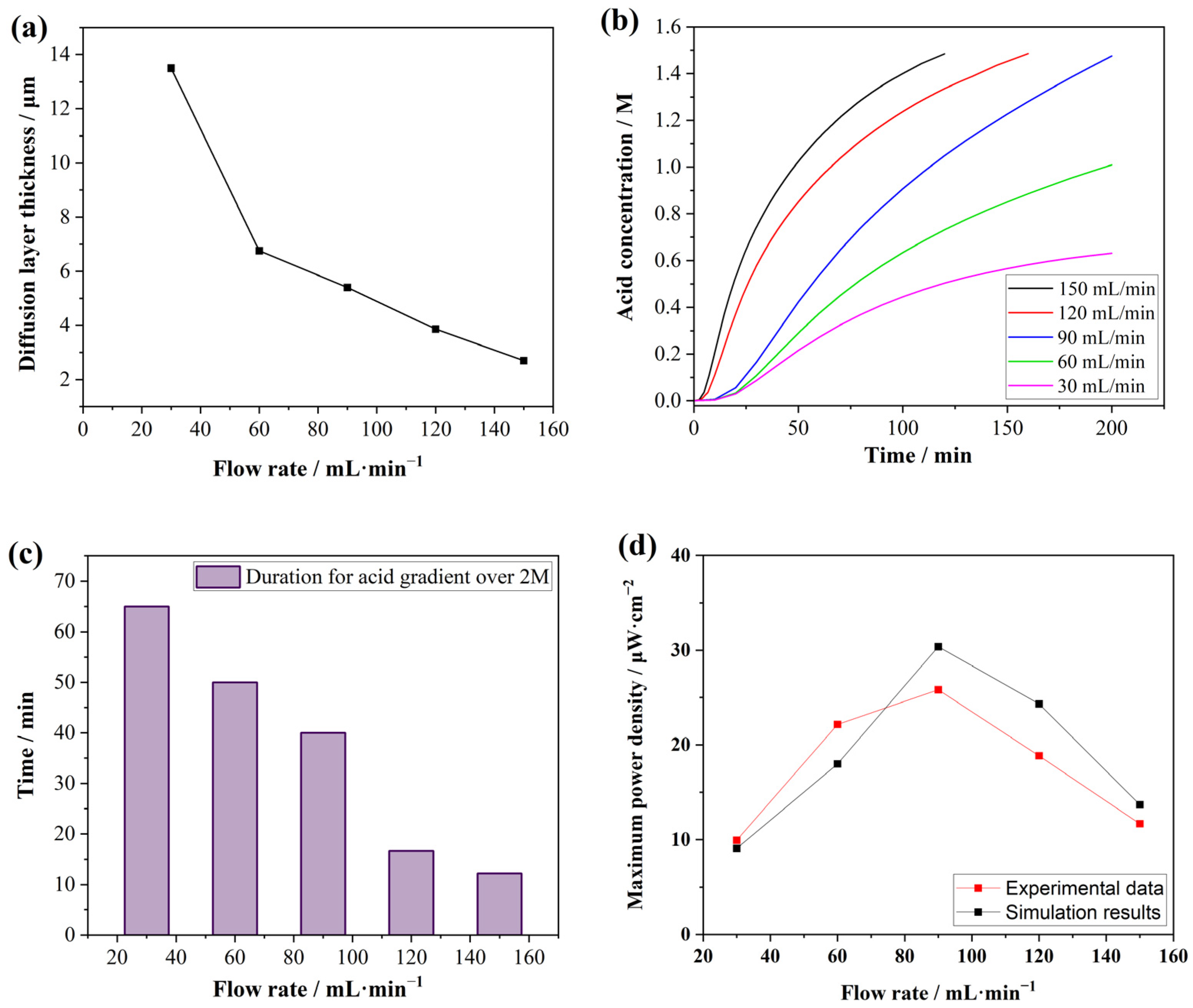
3.1. Distribution of Flow Rate and Pressure
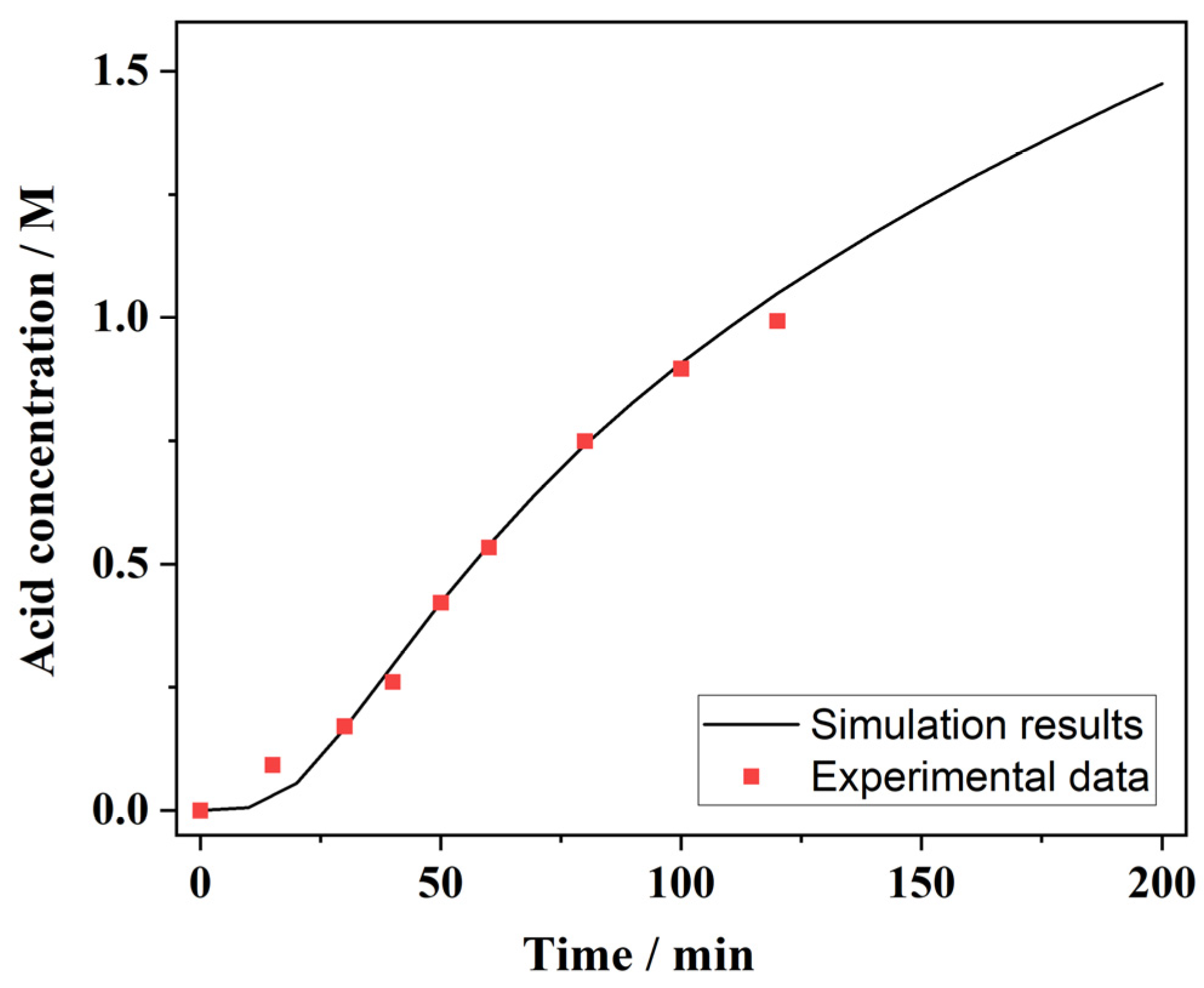
3.2. Acid Concentrations in the Receive Chamber
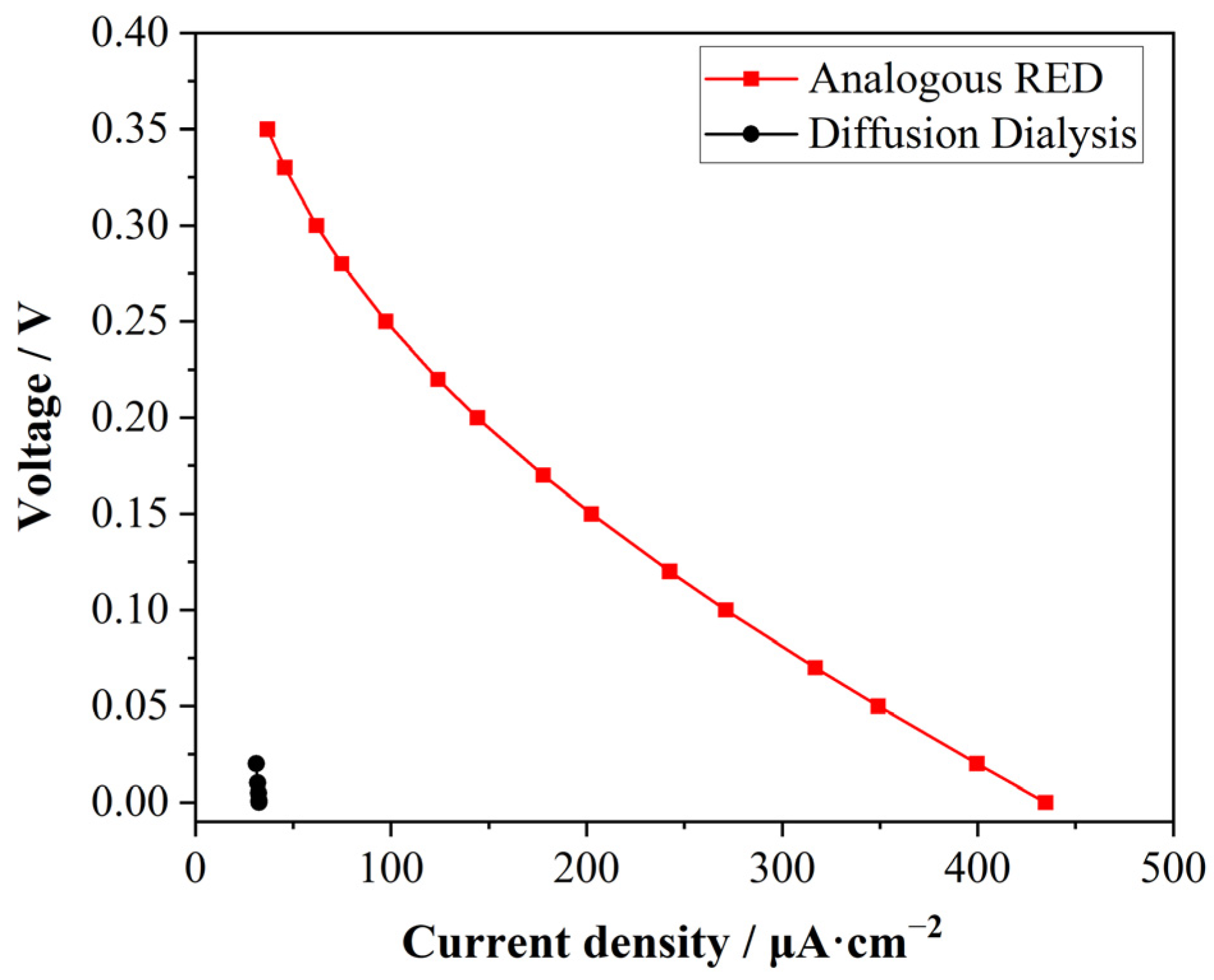
3.3. Output Voltages and Power Densities
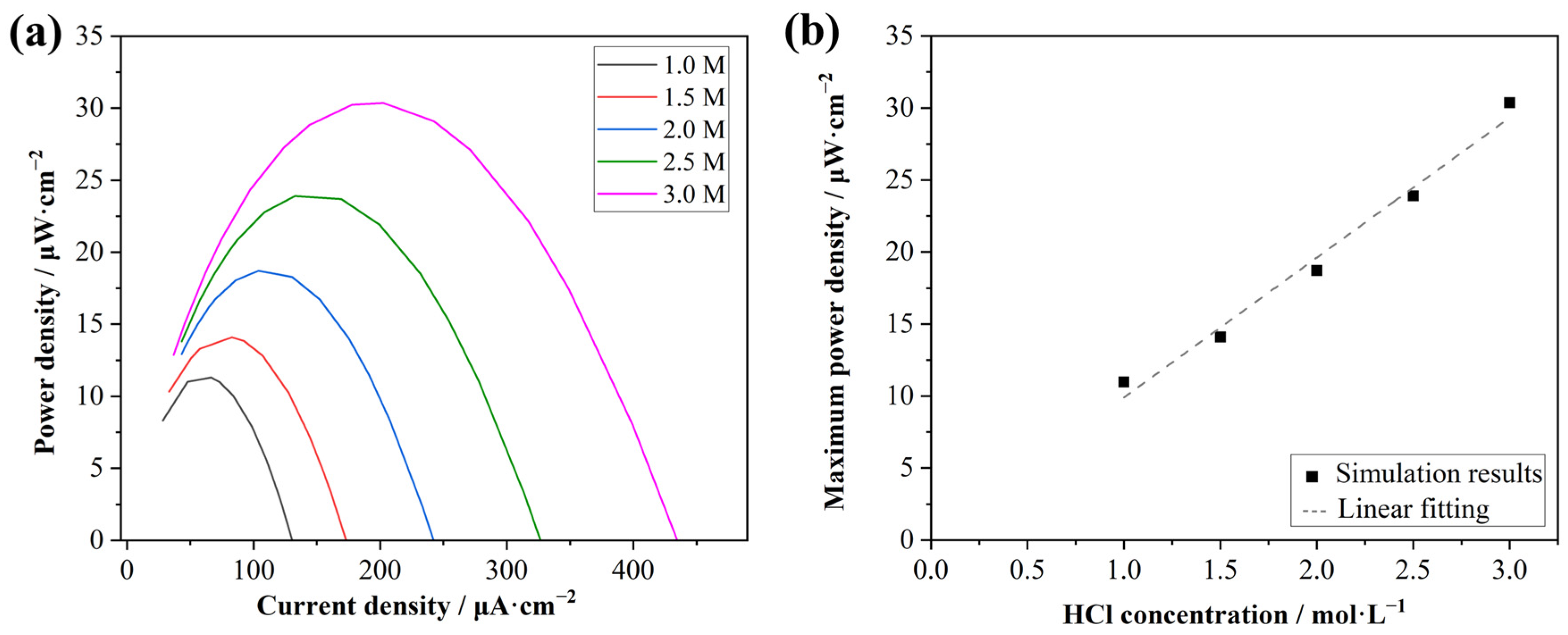
3.4. Output Power Densities with Different Acid Concentrations
3.5. Output Power Densities with Different Flow Rates
3.6. Comparison of Analogous RED with Diffusion Dialysis in Simulation
3.7. Challenges in Industrial Application of Analogous RED
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigerna, S.; Bollino, C.A.; Polinori, P. Convergence in renewable energy sources diffusion worldwide. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.D.; Ebong, A.U. A review of thin film solar cell technologies and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 1286–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Elimelech, M. Membrane-based processes for sustainable power generation using water. Nature 2012, 488, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Arnot, T.C.; Mattia, D. A review of reverse osmosis membrane materials for desalination—Development to date and future potential. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 370, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, J.; Saakes, M.; Metz, S.J.; Harmsen, G.J. Electrical Power from Sea and River Water by Reverse Electrodialysis: A First Step from the Laboratory to a Real Power Plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9207–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliev, I.K.; Filimonova, A.A.; Chichirov, A.A.; Akhmetzyanova, A.T.; Filimonov, A.A.; Beloev, I.H. Study of a Reverse Electrodialysis Plant Operation on Industrial Liquid Waste. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Communications, Information, Electronic and Energy Systems (CIEES), Veliko Tarnovo, Bulgaria, 20–22 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; He, M.; Calvani, D.; Qi, H.; Gupta, K.B.S.S.; de Groot, H.J.M.; Sevink, G.J.A.; Buda, F.; Kaiser, U.; Schneider, G.F. Power generation by reverse electrodialysis in a single-layer nanoporous membrane made from core–rim polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdizadeh, S.; Yasukawa, M.; Abo, T.; Kuno, M.; Noguchi, Y.; Higa, M. The Effect of Feed Solution Temperature on the Power Output Performance of a Pilot-Scale Reverse Electrodialysis (RED) System with Different Intermediate Distance. Membranes 2019, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontananova, E.; Messana, D.; Tufa, R.A.; Nicotera, I.; Kosma, V.; Curcio, E.; van Baak, W.; Drioli, E.; Di Profio, G. Effect of solution concentration and composition on the electrochemical properties of ion exchange membranes for energy conversion. J. Power Sources 2017, 340, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, G.Z.; Feinberg, B.J.; Hoek, E.M.V. Membrane-based production of salinity-gradient power. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4423–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Elizen, R.; Vermaas, D.A.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Performance-determining membrane properties in reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Chen, Y. Nanocomposite reverse electrodialysis (RED) ion-exchange membranes for salinity gradient power generation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 460, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shen, Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. Temperature dependence of water and salt transport in concentration gradient batteries: Insight from membrane properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 713, 123382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K.K. An overview of the recovery of acid from spent acidic solutions from steel and electroplating industries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Kumarl, S.; Ray, B.C.; Sahu, K.K. Extraction of acid and iron values from sulphate waste pickle liquor of a steel industry by solvent extraction route. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 88, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jin, X. Membrane disposition technology of steel pickling waste acid liquor resource utilization. Ind. Water Treat. 2006, 26, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, J.W.; Cheng, M.H. Steel-Industry Wastes. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1974, 46, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Helson, J. Apparatus and Method for Product Recovery and Electrical Energy Generation. WO2015028685A1, 4 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.X.; Xi, R.Y.; Xu, S.M.; Wang, P.; Wu, X. Numerical simulation of salinity gradient power generation using reverse electrodialysis. Desalination 2021, 512, 115132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Ryoo, W.; Chun, M.S.; Chung, G.Y. Simulation of enhanced power generation by reverse electrodialysis stack module in serial configuration. Desalination 2013, 318, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Xu, S.M.; Wu, X.; Wu, D.B.; Jin, D.X.; Wang, P.; Leng, Q. Theoretical simulation and evaluation for the performance of the hybrid multi-effect distillation-reverse electrodialysis power generation system. Desalination 2018, 443, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Nishimura, S. Process for Recovery of Waste H2SO4 and HCL. US19790020403, 1 July 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, E.J.F.; Ekström, H.; Fontes, E. COMSOL Multiphysics®: Finite element software for electrochemical analysis. A mini-review. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 40, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurreri, L.; Battaglia, G.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G.; Ciofalo, M. Multi-physical modelling of reverse electrodialysis. Desalination 2017, 423, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, Z.; Burheim, O.S.; Einarsrud, K.E. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of the Resistivity and Power Density in Reverse Electrodialysis: A Parametric Study. Membranes 2020, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zourmand, Z.; Faridirad, F.; Kasiri, N.; Mohammadi, T. Mass transfer modeling of desalination through an electrodialysis cell. Desalination 2015, 359, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrzadeh, M.; Kaviani, A.; Mohammadi, T. Mathematical modeling of desalination by electrodialysis. Desalination 2007, 206, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, C.-O.; Dahlkild, A.; Velin, A.; Behm, M. A model for the enhanced water dissociation on monopolar membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.J.F.; Wain, A.J. The Butler-Volmer equation in electrochemical theory: Origins, value, and practical application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 872, 114145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Nanoporous Membrane for Salinity Gradient Energy Harvesting. Joule 2020, 4, 2244–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Vasil’eva, V.I.; Akberova, E.M.; Uzdenova, A.M.; Urtenov, M.K.; Kovalenko, A.V.; Pismenskaya, N.P.; Mareev, S.A.; Pourcelly, G. Competition between diffusion and electroconvection at an ion-selective surface in intensive current regimes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 235, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryakov, M.; Gorobchenko, A.; Mareev, A.; Moroz, I.; Kislyi, A.; Anand, V.; Mareev, S. 3D simulation of the electrodialysis process. Unobvious spacer filaments placement to increase the limiting current. J. Membr. Sci. 2025, 721, 123829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Performance analysis of reverse electrodialysis stacks: Channel geometry and flow rate optimization. Energy 2018, 158, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; He, W.; Logan, B.E. Reducing pumping energy by using different flow rates of high and low concentration solutions in reverse electrodialysis cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 486, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, B.; Nikonenko, V.; Larchet, C.; Métayer, M.; Dammak, L. Correlation between transport parameters of ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 195, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Auclair, B.; Parchikov, S.; Nikonenko, V. A simplified procedure for ion-exchange membrane characterisation. New J. Chem. 2004, 28, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.P.; Liu, B.T. Current efficiency of ion-selective membranes: Effects of local electroneutrality and Donnan equilibrium. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 7928–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janotta, B.; Schalenbach, M.; Tempel, H.; Eichel, R.-A. An assessment of electroneutrality implementations for accurate electrochemical ion transport models. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 508, 145280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, G.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y. Modeling of Power Generation and Acid Recovery in an Analogous Process of Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes 2025, 15, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15040126
Lang Q, Liu Y, Guo G, Liu F, Zhang Y. Modeling of Power Generation and Acid Recovery in an Analogous Process of Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes. 2025; 15(4):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15040126
Chicago/Turabian StyleLang, Qiaolin, Yang Liu, Gaojuan Guo, Fei Liu, and Yang Zhang. 2025. "Modeling of Power Generation and Acid Recovery in an Analogous Process of Reverse Electrodialysis" Membranes 15, no. 4: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15040126
APA StyleLang, Q., Liu, Y., Guo, G., Liu, F., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Modeling of Power Generation and Acid Recovery in an Analogous Process of Reverse Electrodialysis. Membranes, 15(4), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15040126







