Role of Phospholipase D in G-Protein Coupled Receptor Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PLD Structure and Regulation of PLD Activity

3. GPCR Mediated PLD Signaling

4. PLD Influenced GPCR Functions
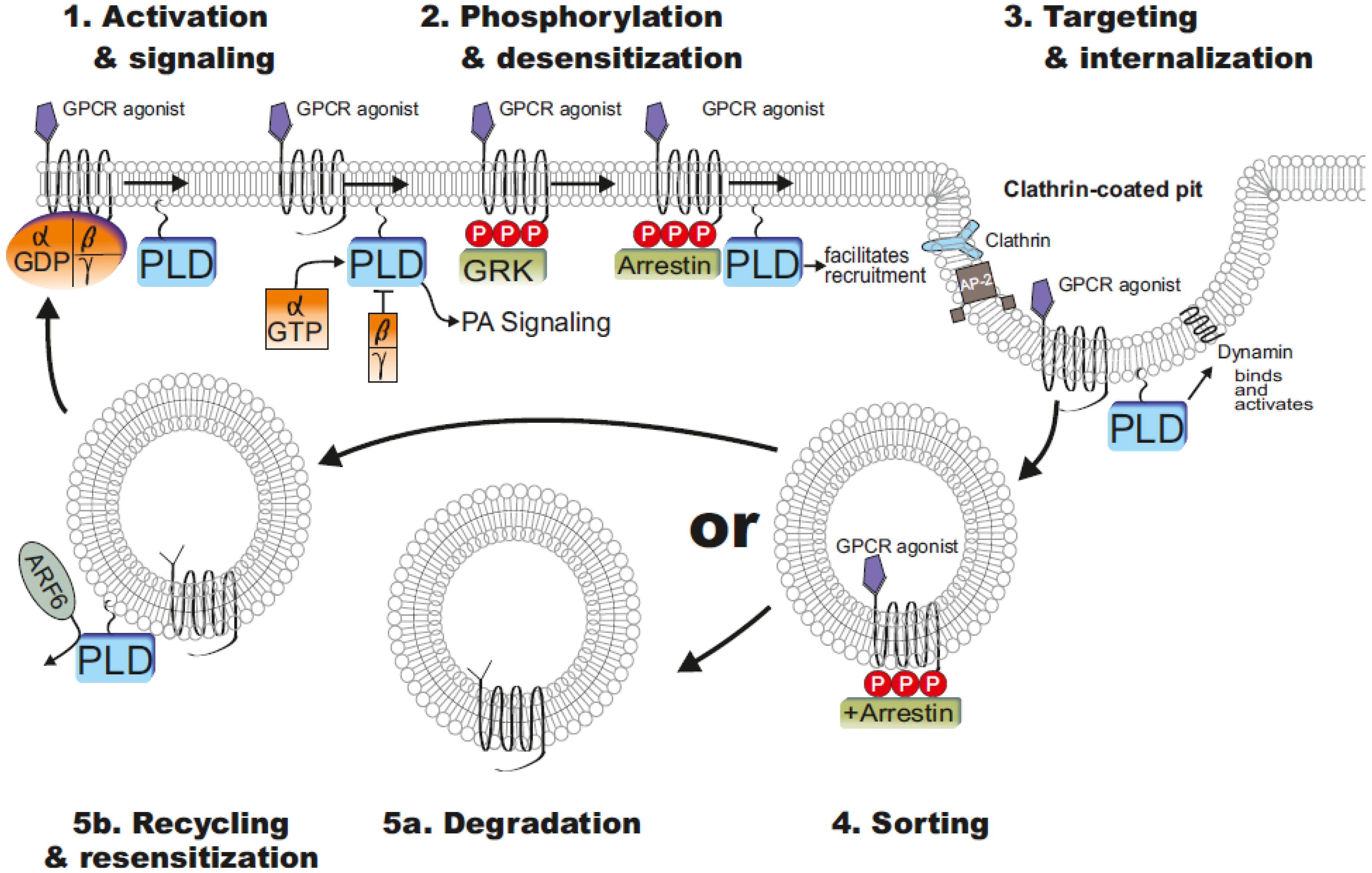
5. Pathophysiological Implications of PLD
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oude Weernink, P.A.; Han, L.; Jakobs, K.H.; Schmidt, M. Dynamic phospholipid signaling by G protein-coupled receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 888–900. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, M.; Kanfer, J. Solubilization and properties of a membrane-bound enzyme from rat brain catalyzing a base-exchange reaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1973, 53, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M.; Altshuller, Y.M.; Sung, T.C.; Rudge, S.A.; Rose, K.; Engebrecht, J.; Morris, A.J.; Frohman, M.A. Human adp-ribosylation factor-activated phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase d defines a new and highly conserved gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29640–29643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.M.; Jenco, J.M.; Nakashima, S.; Cadwallader, K.; Gu, Q.; Cook, S.; Nozawa, Y.; Prestwich, G.D.; Frohman, M.A.; Morris, A.J.; et al. Characterization of two alternately spliced forms of phospholipase d1. Activation of the purified enzymes by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, adp-ribosylation factor, and rho family monomeric gtp-binding proteins and protein kinase c-alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3860–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steed, P.M.; Clark, K.L.; Boyar, W.C.; Lasala, D.J. Characterization of human pld2 and the analysis of pld isoform splice variants. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, F.D.; Thompson, N.; Saqib, K.M.; Clark, J.M.; Powner, D.; Thompson, N.T.; Solari, R.; Wakelam, M.J. Phospholipase d1 localises to secretory granules and lysosomes and is plasma-membrane translocated on cellular stimulation. Curr. Biol. CB 1998, 8, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyberg, Z.; Sweeney, D.; Siddhanta, A.; Bourgoin, S.; Frohman, M.; Shields, D. Intracellular localization of phospholipase d1 in mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, W.E.; Parker, P.J. Endosomal localization of phospholipase d 1a and 1b is defined by the c-termini of the proteins, and is independent of activity. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarny, M.; Lavie, Y.; Fiucci, G.; Liscovitch, M. Localization of phospholipase d in detergent-insoluble, caveolin-rich membrane domains. Modulation by caveolin-1 expression and caveolin-182–101. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.K.; Her, Y.M.; Cho, M.L.; Oh, H.J.; Park, E.M.; Kwok, S.K.; Ju, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Min, D.S.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Il-15 promotes osteoclastogenesis via the pld pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 139, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvy, P.E.; Lavieri, R.R.; Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A. Phospholipase d: Enzymology, functionality, and chemical modulation. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6064–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conquer, J.A.; Jones, S.A.; Cruz, T.F. Effect of interleukin 1, lipopolysaccharide and phorbol esters on phospholipase d activity in chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. OARS Osteoarthr. Res. Soc. 1994, 2, 269–273. [Google Scholar]
- Ponting, C.P.; Kerr, I.D. A novel family of phospholipase d homologues that includes phospholipid synthases and putative endonucleases: Identification of duplicated repeats and potential active site residues. Protein Sci. 1996, 5, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, T.C.; Roper, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Rudge, S.A.; Temel, R.; Hammond, S.M.; Morris, A.J.; Moss, B.; Engebrecht, J.; Frohman, M.A.; et al. Mutagenesis of phospholipase d defines a superfamily including a trans-golgi viral protein required for poxvirus pathogenicity. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 4519–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciorra, V.A.; Rudge, S.A.; Wang, J.; McLaughlin, S.; Engebrecht, J.; Morris, A.J. Dual role for phosphoinositides in regulation of yeast and mammalian phospholipase d enzymes. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 159, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, T.C.; Altshuller, Y.M.; Morris, A.J.; Frohman, M.A. Molecular analysis of mammalian phospholipase d2. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, T.C.; Zhang, Y.; Morris, A.J.; Frohman, M.A. Structural analysis of human phospholipase d1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 3659–3666. [Google Scholar]
- Sciorra, V.A.; Rudge, S.A.; Prestwich, G.D.; Frohman, M.A.; Engebrecht, J.; Morris, A.J. Identification of a phosphoinositide binding motif that mediates activation of mammalian and yeast phospholipase d isoenzymes. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5911–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahelin, R.V.; Ananthanarayanan, B.; Blatner, N.R.; Singh, S.; Bruzik, K.S.; Murray, D.; Cho, W. Mechanism of membrane binding of the phospholipase d1 px domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 54918–54926. [Google Scholar]
- Di Fulvio, M.; Lehman, N.; Lin, X.; Lopez, I.; Gomez-Cambronero, J. The elucidation of novel SH2 binding sites on PLD2. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3032–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.H.; Ahn, B.H.; Namkoong, S.; Kim, Y.M.; Jin, J.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Min do, S. Differential regulation of apoptosis by caspase-mediated cleavage of phospholipase d isozymes. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 2198–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Gui, Y.; Du, G.; Frohman, M.A.; Zheng, X.L. Dependence of phospholipase d1 multi-monoubiquitination on its enzymatic activity and palmitoylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 13580–13588. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, G.M.; Frohman, M.A. Phospholipase d: A lipid centric review. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2005, 62, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanacev, N.Z.; Stuhne-Sekalec, L. On the mechanism of enzymatic phosphatidylation. Biosynthesis of cardiolipin catalyzed by phospholipase d. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1970, 210, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelam, M.J.; Hodgkin, M.; Martin, A. The measurement of phospholipase d-linked signaling in cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 1995, 41, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Frohman, M.A.; Sung, T.C.; Morris, A.J. Mammalian phospholipase d structure and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1439, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Henage, L.G.; Exton, J.H.; Brown, H.A. Kinetic analysis of a mammalian phospholipase d: Allosteric modulation by monomeric gtpases, protein kinase c, and polyphosphoinositides. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascher, C.; Balch, W.E. Dominant inhibitory mutants of arf1 block endoplasmic reticulum to golgi transport and trigger disassembly of the golgi apparatus. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Shome, K.; Nie, Y.; Romero, G. Adp-ribosylation factor proteins mediate agonist-induced activation of phospholipase d. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30836–30841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.J.; Henkels, K.M.; Mahankali, M.; Dinauer, M.C.; Gomez-Cambronero, J. Evidence for two crib domains in phospholipase d2 (pld2) that the enzyme uses to specifically bind to the small gtpase rac2. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 16308–16320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, K.C.; Elliott, C.M.; Exton, J.H. Evidence for rho-mediated agonist stimulation of phospholipase d in rat1 fibroblasts. Effects of clostridium botulinum c3 exoenzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13135–13139. [Google Scholar]
- Balboa, M.A.; Firestein, B.L.; Godson, C.; Bell, K.S.; Insel, P.A. Protein kinase c alpha mediates phospholipase d activation by nucleotides and phorbol ester in madin-darby canine kidney cells. Stimulation of phospholipase d is independent of activation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase c and phospholipase a2. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10511–10516. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, J.K.; Pachter, J.A.; Weinstein, I.B.; Bishop, W.R. Overexpression of protein kinase c beta 1 enhances phospholipase d activity and diacylglycerol formation in phorbol ester-stimulated rat fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 598–602. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.S.; Exton, J.H. Regulation of phospholipase d2 activity by protein kinase c alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22076–22083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Han, J.M.; Park, J.B.; Lee, S.D.; Oh, Y.S.; Chung, C.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.K.; Yoo, J.S.; et al. Phosphorylation and activation of phospholipase d1 by protein kinase c in vivo: Determination of multiple phosphorylation sites. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 10344–10351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kook, S.; Exton, J.H. Identification of interaction sites of protein kinase calpha on phospholipase d1. Cell. Signal. 2005, 17, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, M.; Wakelam, M.J.; Morris, A.J. Phospholipase d. Biochem. Cell biol. 2004, 82, 225–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, I.; Arnold, R.S.; Lambeth, J.D. Cloning and initial characterization of a human phospholipase d2 (HPLD2). Adp-ribosylation factor regulates HPLD2. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 12846–12852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Hongu, T.; Sato, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ali, W.; Cavallo, J.A.; van der Velden, A.; Tian, H.; di Paolo, G.; Nieswandt, B.; et al. Key roles for the lipid signaling enzyme phospholipase d1 in the tumor microenvironment during tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra79. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, T.; Hongu, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Funakoshi, Y.; Kanaho, Y. Molecular mechanisms of n-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced superoxide generation and degranulation in mouse neutrophils: Phospholipase d is dispensable. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciorra, V.A.; Hammond, S.M.; Morris, A.J. Potent direct inhibition of mammalian phospholipase d isoenzymes by calphostin-c. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 2640–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, H.; Planalp, R.; Cho, J.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V. Curcumin: From ancient medicine to current clinical trials. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 1631–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Selvy, P.E.; Buck, J.R.; Cho, H.P.; Criswell, T.L.; Thomas, A.L.; Armstrong, M.D.; Arteaga, C.L.; Lindsley, C.W.; Brown, H.A.; et al. Design of isoform-selective phospholipase d inhibitors that modulate cancer cell invasiveness. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Altshuller, Y.M.; Kim, Y.; Han, J.M.; Ryu, S.H.; Morris, A.J.; Frohman, M.A. Dual requirement for rho and protein kinase c in direct activation of phospholipase d1 through G protein-coupled receptor signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 4359–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cummings, R.; Zhao, Y.; Kazlauskas, A.; Sham, J.K.; Morris, A.; Georas, S.; Brindley, D.N.; Natarajan, V. Involvement of phospholipase d2 in lysophosphatidate-induced transactivation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta in human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39931–39940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Schulz, S.; Liang, Y.; Klein, J.; Hollt, V. Adp-ribosylation factor-dependent phospholipase d2 activation is required for agonist-induced mu-opioid receptor endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9979–9985. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Goschke, A.; Stumm, R.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Liang, Y.J.; Hollt, V.; Koch, T. Role of receptor internalization in the agonist-induced desensitization of cannabinoid type 1 receptors. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, L.O.; Koch, T.; Sievers, J.; Lucius, R. Internalization of PRP106–126 by the formyl-peptide-receptor-like-1 in glial cells. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senogles, S.E. The d2s dopamine receptor stimulates phospholipase d activity: A novel signaling pathway for dopamine. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 58, 455–462. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, R.J.; Parinandi, N.L.; Zaiman, A.; Wang, L.; Usatyuk, P.V.; Garcia, J.G.; Natarajan, V. Phospholipase d activation by sphingosine 1-phosphate regulates interleukin-8 secretion in human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30227–30235. [Google Scholar]
- Gosau, N.; Fahimi-Vahid, M.; Michalek, C.; Schmidt, M.; Wieland, T. Signalling components involved in the coupling of alpha 1-adrenoceptors to phospholipase d in neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2002, 365, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Stunff, H.; Dokhac, L.; Bourgoin, S.; Bader, M.F.; Harbon, S. Phospholipase D in rat myometrium: Occurrence of a membrane-bound ARF6 (ADP-ribosylation factor 6)-regulated activity controlled by betagamma subunits of heterotrimeric G-proteins. Biochem. J. 2000, 352, Pt 2. 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Preininger, A.M.; Henage, L.G.; Oldham, W.M.; Yoon, E.J.; Hamm, H.E.; Brown, H.A. Direct modulation of phospholipase d activity by gbetagamma. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 70, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Plonk, S.G.; Park, S.K.; Exton, J.H. The alpha-subunit of the heterotrimeric g protein g13 activates a phospholipase d isozyme by a pathway requiring rho family gtpases. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 4823–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haft, C.R.; de la Luz Sierra, M.; Barr, V.A.; Haft, D.H.; Taylor, S.I. Identification of a family of sorting nexin molecules and characterization of their association with receptors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 7278–7287. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, S.A.; Barr, V.A.; Haft, D.H.; Taylor, S.I.; Haft, C.R. Identification and characterization of snx15, a novel sorting nexin involved in protein trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5074–5084. [Google Scholar]
- Nilssen, L.S.; Dajani, O.; Christoffersen, T.; Sandnes, D. Sustained diacylglycerol accumulation resulting from prolonged g protein-coupled receptor agonist-induced phosphoinositide breakdown in hepatocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 94, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.A.; Shome, K.; Watkins, S.C.; Romero, G. The recruitment of raf-1 to membranes is mediated by direct interaction with phosphatidic acid and is independent of association with ras. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23911–23918. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, G.; Tarkowski, B.; Baccarini, M. Raf kinases in cancer-roles and therapeutic opportunities. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3477–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishikawa, K.; Chalfant, C.E.; Perry, D.K.; Bielawska, A.; Hannun, Y.A. Phosphatidic acid is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 and an inhibitor of ceramide-mediated responses. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21335–21341. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, N.; Sonenberg, N. Upstream and downstream of mtor. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1926–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.A. Phosphatidic acid and lipid-sensing by mtor. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.S.; Lincoln, H.C.; Kim, C.R.; Frey, J.W.; Goodman, C.A.; Zhong, X.P.; Hornberger, T.A. The role of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and phosphatidic acid in the mechanical activation of mammalian target of rapamycin (MTOR) signaling and skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1551–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G.H.; Fisette, P.L.; Anderson, R.A. Type I phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase isoforms are specifically stimulated by phosphatidic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 11547–11554. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Seifert, A.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Rankovic, V.; Schroder, H.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Hollt, V.; Koch, T. Role of phospholipase d2/phosphatidic acid signal transduction in micro- and delta-opioid receptor endocytosis. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, L.; Foster, D.A. Role for phospholipase d in receptor-mediated endocytosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Huang, P.; Liang, B.T.; Frohman, M.A. Phospholipase d2 localizes to the plasma membrane and regulates angiotensin II receptor endocytosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Brandenburg, L.O.; Seyferth, S.; Wruck, C.J.; Koch, T.; Rosenstiel, P.; Lucius, R.; Pufe, T. Involvement of phospholipase d 1 and 2 in the subcellular localization and activity of formyl-peptide-receptors in the human colonic cell line ht29. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2009, 26, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Kim, I.S.; Park, J.B.; Lee, M.N.; Lee, H.Y.; Suh, P.G.; Ryu, S.H. The phox homology domain of phospholipase d activates dynamin gtpase activity and accelerates egfr endocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.A.; Milano, S.K.; Benovic, J.L. Regulation of receptor trafficking by grks and arrestins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2007, 69, 451–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, S.A.; Miller, W.E.; Kim, K.M.; Caron, M.G. beta-Arrestin/AP-2 interaction in G protein-coupled receptor internalization: Identification of a beta-arrestin binging site in beta 2-adaptin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9247–9254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.R.; Sanjuan, M.A.; Merida, I. Type ialpha phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase is a putative target for increased intracellular phosphatidic acid. FEBS Lett. 2000, 476, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.; Doughman, R.L.; Firestone, A.J.; Bunce, M.W.; Anderson, R.A. Type I gamma phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase targets and regulates focal adhesions. Nature 2002, 420, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneson, L.S.; Kunz, J.; Anderson, R.A.; Traub, L.M. Coupled inositide phosphorylation and phospholipase d activation initiates clathrin-coat assembly on lysosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 17794–17805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Malerod, L.; Berg, T.; Kjeken, R. Clathrin-dependent endocytosis. Biochem. J. 2004, 377, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T.; Wu, D.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Hollt, V. Role of phospholipase d2 in the agonist-induced and constitutive endocytosis of g-protein coupled receptors. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.T.; Ingram, S.L.; Henderson, G.; Chavkin, C.; von Zastrow, M.; Schulz, S.; Koch, T.; Evans, C.J.; Christie, M.J. Regulation of mu-opioid receptors: Desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, B.L.; Trejo, J. Clathrin-dependent mechanisms of g protein-coupled receptor endocytosis. Traffic 2007, 8, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, F.D.; Rozelle, A.L.; Yin, H.L.; Balla, T.; Donaldson, J.G. Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and arf6-regulated membrane traffic. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankovic, M.; Jacob, L.; Rankovic, V.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Schroder, H.; Hollt, V.; Koch, T. Adp-ribosylation factor 6 regulates mu-opioid receptor trafficking and signaling via activation of phospholipase d2. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padron, D.; Tall, R.D.; Roth, M.G. Phospholipase d2 is required for efficient endocytic recycling of transferrin receptors. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begle, A.; Tryoen-Toth, P.; de Barry, J.; Bader, M.F.; Vitale, N. Arf6 regulates the synthesis of fusogenic lipids for calcium-regulated exocytosis in neuroendocrine cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4836–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttner, W.B.; Zimmerberg, J. Implications of lipid microdomains for membrane curvature, budding and fission. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, O.A.; Brown, F.D.; Donaldson, J.G. An effector domain mutant of arf6 implicates phospholipase d in endosomal membrane recycling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, T.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Liang, Y.; Schulz, S.; Beyer, A.; Schroder, H.; Hollt, V. Phospholipase d2 modulates agonist-induced mu-opioid receptor desensitization and resensitization. J. Neurochem. 2004, 88, 680–688. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, T.; Widera, A.; Bartzsch, K.; Schulz, S.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Wundrack, N.; Beyer, A.; Grecksch, G.; Hollt, V. Receptor endocytosis counteracts the development of opioid tolerance. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.S.; Zhang, J.; Barak, L.S.; Caron, M.G. Molecular mechanisms of g protein-coupled receptor desensitization and resensitization. Life Sci. 1998, 62, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; Mayer, D.; Pfeiffer, M.; Stumm, R.; Koch, T.; Hollt, V. Morphine induces terminal micro-opioid receptor desensitization by sustained phosphorylation of serine-375. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3282–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grecksch, G.; Bartzsch, K.; Widera, A.; Becker, A.; Hollt, V.; Koch, T. Development of tolerance and sensitization to different opioid agonists in rats. Psychopharmacology 2006, 186, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.; Konietzko, J.; Poll, F.; Koch, T.; Hollt, V.; Schulz, S. Agonist-selective patterns of micro-opioid receptor phosphorylation revealed by phosphosite-specific antibodies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.C.; Chieng, B.; Azriel, Y.; Christie, M.J. Cellular morphine tolerance produced by betaarrestin-2-dependent impairment of mu-opioid receptor resensitization. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7122–7130. [Google Scholar]
- Quillinan, N.; Lau, E.K.; Virk, M.; von Zastrow, M.; Williams, J.T. Recovery from mu-opioid receptor desensitization after chronic treatment with morphine and methadone. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 4434–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.G.; Chan, R.B.; Tian, H.; Laredo, M.; Shui, G.; Staniszewski, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Kim, T.W.; Duff, K.E.; et al. Phospholipase d2 ablation ameliorates alzheimer’s disease-linked synaptic dysfunction and cognitive deficits. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16419–16428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, J.K.; Ahn, B.H.; Na, Y.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.K.; Ko, Y.G.; Chung, K.C.; Kozlowski, P.B.; Min do, S.; et al. Phospholipase d1 is associated with amyloid precursor protein in alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, L.O.; Konrad, M.; Wruck, C.; Koch, T.; Pufe, T.; Lucius, R. Involvement of formyl-peptide-receptor-like-1 and phospholipase d in the internalization and signal transduction of amyloid beta 1–42 in glial cells. Neuroscience 2008, 156, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvers, M.; Pozgaj, R.; Pleines, I.; May, F.; Kuijpers, M.J.; Heemskerk, J.M.; Yu, P.; Nieswandt, B. Platelet hyperreactivity and a prothrombotic phenotype in mice with a gain-of-function mutation in phospholipase Cgamma2. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan, F.G.; McReynolds, M.; Couvillon, A.; Kam, Y.; Holla, V.R.; Dubois, R.N.; Exton, J.H. Requirement of phospholipase d1 activity in h-rasv12-induced transformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.; Stanton, M.L.; Feng, W.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Ramondetta, L.; Chen, L.; Brown, R.E.; Duan, X. Morphoproteomic analysis reveals an overexpressed and constitutively activated phospholipase D1-mTORC2 pathway in endometrial carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 4, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kanfer, J.N.; Singh, I.N.; Pettegrew, J.W.; McCartney, D.G.; Sorrentino, G. Phospholipid metabolism in alzheimer's disease and in a human cholinergic cell. J. Lipid Mediat. Cell Signal. 1996, 14, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.A.; Cohen, M.L. Amyloid beta-induced neurotoxicity is associated with phospholipase d activation in cultured rat hippocampal cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 229, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, Y.; Gong, W.; Tiffany, H.L.; Tumanov, A.; Nedospasov, S.; Shen, W.; Dunlop, N.M.; Gao, J.L.; Murphy, P.M.; Oppenheim, J.J.; et al. Amyloid (beta)42 activates a g-protein-coupled chemoattractant receptor, fpr-like-1. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, RC123. [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa, H.; Yu, Z.X.; Takeda; Le, Y.; Gong, W.; Ferrans, V.J.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Li, C.C.; Wang, J.M. Beta amyloid peptide (Abeta42) is internalized via the G-protein-coupled receptor FPRL1 and forms fibrillar aggregates in macrophages. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2454–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heurtaux, T.; Michelucci, A.; Losciuto, S.; Gallotti, C.; Felten, P.; Dorban, G.; Grandbarbe, L.; Morga, E.; Heuschling, P. Microglial activation depends on beta-amyloid conformation: Role of the formylpeptide receptor 2. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandenburg, L.-O.; Pufe, T.; Koch, T. Role of Phospholipase D in G-Protein Coupled Receptor Function. Membranes 2014, 4, 302-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030302
Brandenburg L-O, Pufe T, Koch T. Role of Phospholipase D in G-Protein Coupled Receptor Function. Membranes. 2014; 4(3):302-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030302
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandenburg, Lars-Ove, Thomas Pufe, and Thomas Koch. 2014. "Role of Phospholipase D in G-Protein Coupled Receptor Function" Membranes 4, no. 3: 302-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030302
APA StyleBrandenburg, L.-O., Pufe, T., & Koch, T. (2014). Role of Phospholipase D in G-Protein Coupled Receptor Function. Membranes, 4(3), 302-318. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes4030302





