Colloidal Fouling of Nanofiltration Membranes: Development of a Standard Operating Procedure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
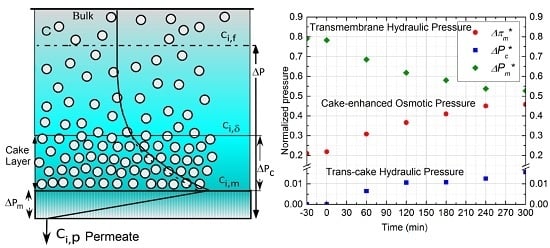
2. Theoretical Background and Development of Data Analysis Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Size and Zeta Potential of Silica Particles
3.2. Membrane Compaction Results
3.3. Critical Flux Measurement
3.4. Fouling Experiment Results
3.4.1. Effect of Silica Concentration
3.4.2. Effect of Cross-Flow Velocity
3.4.3. Effect of Operating Pressure
3.4.4. Effect of Salt Concentration
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Model Colloids, Membrane, and Reagents
4.2. Cross-Flow Membrane Filtration Setup
4.3. Experimental Protocol
4.4. Characterization of Silica Particles
4.5. Membrane Compaction
4.6. Critical Flux Measurement
4.7. Calculation of the Deposited Mass
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Tang, C.Y.; Chong, T.H.; Fane, A.G. Colloidal interactions and fouling of NF and RO membranes: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 164, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadrzadeh, M.; Hajinasiri, J.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Pernitsky, D. Nanofiltration of oil sands boiler feed water: Effect of pH on water flux and organic and dissolved solid rejection. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 141, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatbakhsh, M.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Pernitsky, D.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Hajinasiri, J. Treatment of an in situ oil sands produced water by polymeric membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 14869–14887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Fane, A.G.; Ho, W.S.; Matsuura, T. (Eds.) Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2008.
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A.D.; Munro, P.A.; Tragardh, G. The effect of protein fouling in microfiltration and ultrafiltration on permeate flux, protein retention and selectivity: A literature review. Desalination 1993, 91, 65–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfort, G.; Davis, R.H.; Zydney, A.L. The behavior of suspensions and macromolecular solutions in cross flow microfiltration: A Review. J. Memb. Sci. 1994, 96, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; De, S. Steady state modeling of concentration polarization including adsorption during nanofiltration of dye solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Kilduff, J.E.; Belfort, G. Modes of natural organic matter fouling during ultrafiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattaraj, S.; Jarusutthirak, C.; Charoensuk, C.; Jiraratananon, R. A combined pore blockage, osmotic pressure, and cake filtration model for crossflow nanofiltration of natural organic matter and inorganic salts. Desalination 2011, 274, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gouellec, Y.A.; Elimelech, M. Calcium sulfate (gypsum) scaling in nanofiltration of agricultural drainage water. J. Memb. Sci. 2002, 205, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Johnston, G.M. A model of membrane fouling by salt precipitation from multicomponent ionic mixtures in crossflow nanofiltration. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2002, 19, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Faibish, R.S.; Elimelech, M. Kinetics of permeate flux decline in crossflow membrane filtration of colloidal suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 196, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Elimelech, M. Cake-enhanced concentration polarization: A new fouling mechanism for salt-rejecting membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5581–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaun, Y.; Kilduff, J.E. Effect of colloids on salt transport in cross fow nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 346, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Bhattacharjee, S. Flux decline during cross flow membrane filtration of electrolytic solution in presence of charged nano-colloids: A simple electrokinetic model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 353, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, E.M.V.; Kim, A.S.; Elimelech, M. Influence of crossflow membrane filter geometry and shear rate on colloidal fouling in reverse osmosis and nanofiltration separations. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2002, 19, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffle, J.; Leppard, G.G. Characterization of aquatic colloids and macromolecules. 1. Structure and behavior of colloidal material. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Effect of solution chemistry on the surface charge of polymeric reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1996, 119, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussu, K.; Belpaire, A.; Volodin, A.; van Haesendonck, C.; van der Meeren, P.; Vandecasteele, C.; van der Bruggen, B. Influence of membrane and colloid characteristics on fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2007, 289, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.; Hong, S.; Elimelech, M. Influence of membrane surface properties on initial rate of colloidal fouling of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2001, 188, 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Masliyah, J.H.; Bhattacharjee, S. Electrokinetic and Colloid Transport Phenomena; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mamun, M.A.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Chatterjee, R.; Bhattacharjee, S.; De, S. Colloidal fouling of nanofiltration membranes: A novel transient electrokinetic model and experimental study. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 138, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.Y.; Elimelech, M. Influence of colloidal fouling on rejection of trace organic contaminants by reverse osmosis. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 244, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, K.L.; Li, Y.L.; Hwang, K.J.; Lu, W.M. Analysis and prediction of fouling layer structure in microfiltration. Desalination 2008, 234, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, T.; Bhattacharjee, S. Initial deposition of colloidal particles on a rough nanofiltration membrane. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2007, 85, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellona, C.; Drewes, J.E. The role of membrane surface charge and solute physico-chemical properties in the rejection of organic acids by NF membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2005, 249, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinasse, B.; Bacchin, P.; Aimar, P. On an experimental method to measure critical flux in ultrafiltration. Desalination 2002, 146, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinemann, K.V.; Nunes, S.P. Membranes for Water Treatment; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zydney, A.L. Stagnant film model for concentration polarization in membrane systems. J. Memb. Sci. 1997, 130, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Exp. No. | Operating Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔP (kPa) | Cp,f (ppm) | Ci,f (mM) | u (m/s) | |
| 1 | 965 | 300 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 965 | 500 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 3 | 965 | 500 | 10 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 689 | 300 | 10 | 0.1 |
| 5 | 1033 | 300 | 20 | 0.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Mamun, M.A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Pernitsky, D.; Sadrzadeh, M. Colloidal Fouling of Nanofiltration Membranes: Development of a Standard Operating Procedure. Membranes 2017, 7, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010004
Al Mamun MA, Bhattacharjee S, Pernitsky D, Sadrzadeh M. Colloidal Fouling of Nanofiltration Membranes: Development of a Standard Operating Procedure. Membranes. 2017; 7(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Mamun, Md Abdullaha, Subir Bhattacharjee, David Pernitsky, and Mohtada Sadrzadeh. 2017. "Colloidal Fouling of Nanofiltration Membranes: Development of a Standard Operating Procedure" Membranes 7, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010004
APA StyleAl Mamun, M. A., Bhattacharjee, S., Pernitsky, D., & Sadrzadeh, M. (2017). Colloidal Fouling of Nanofiltration Membranes: Development of a Standard Operating Procedure. Membranes, 7(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7010004