Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Next Generation Pervaporation Process: Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamental Theories of Pervaporation
2.1. Parameters in Membrane Performance
2.2. Transport in PV
2.2.1. Preferential Sorption-Capillary Flow (PSCF) Mechanism
2.2.2. Solution-Diffusion (SD) Mechanism
Sorption of the Permeants
Diffusion through the Membrane
Transport Equation through the Membrane
2.3. Transport in Nanocomposite Membrane (NCM)
2.4. Effect of Process Conditions
2.4.1. FEED Concentration
2.4.2. Feed and Permeate Pressure
2.4.3. Effect of Temperature
2.4.4. Effect of Membrane Thickness
2.4.5. Concentration Polarization (CP) and Mass Transfer Coefficient (MTC)
3. Membranes for PV Applications
3.1. Dehydration of Organics
3.2. Removal of Organics from Aqueous Solution
3.3. Organic-Organic Separation
4. PV membranes Fabrication Techniques
4.1. Solution Casting Method
4.2. Solution Coating Method
4.3. Blending of Solutions
4.4. Hollow Fiber Spinning (HFS) Technique
4.5. Fabrication via Interfacial Polymerization (IP) Technique
4.6. Modifications of Composite Membranes via Physical and Chemical Treatment
5. Specific Applications of PV Membranes
5.1. Membrane Reactor
5.1.1. Roles of Membrane in Membrane Reactor
5.1.2. Use of Catalyst in Membrane Reactors
5.1.3. Membrane Chemical Reactors
Oxidative Coupling of Methane (OCM)
Water Gas Shift (WGS) Reaction
Membrane Reactors in the Petrochemical Industries
Esterification Reaction
5.2. Pervaporative Desalination
5.3. Pervaporative Desulfurization
6. Perceptions and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singha, N.R.; Karmakar, M.; Mahapatra, M.; Mondal, H.; Dutta, A.; Roy, C.; Chattopadhyay, P.K. Systematic synthesis of pectin-g-(sodium acrylate-co-N-isopropylacrylamide) interpenetrating polymer network for mere/synergistic superadsorption of dyes/M(II): Comprehensive determination of physicochemical changes in loaded hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 3211–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Das, P.; Ray, S.K. Recovery of pyridine from water by pervaporation using filled and crosslinked EPDM membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 2034–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, W.S.W.; Sirkar, K.K. (Eds.) Membrane Handbook; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bodzek, M.; Bohdziewicz, J.; Konieczny, K. Techniki Membranowe W Ochronie Srodowiska; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Slaskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, M.H.V. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Huang, R.Y.M. Liquid separation by membrane pervaporation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 1048–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, C.S. A review of: “Pervaporation membrane separation processes”. Sep. Purif. Methods 1991, 20, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, B.; Suhanya, D.; Sridhar, S.; Ramakrishna, M. Separation of organic–organic mixtures by pervaporation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Chung, T.S.; Qiao, X.Y.; Lai, J.Y. Polyimides membranes for pervaporation and biofuels separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1135–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ray, S.K.; Kuila, S.B.; Samanta, H.S.; Singha, N.R. Systematic choice of crosslinker and filler for pervaporation membrane: A case study with dehydration of isopropyl alcohol-water mixtures by polyvinyl alcohol membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujiburohman, M.; Feng, X. Permselectivity, solubility and diffusivity of propyl propionate/water mixtures in poly(ether block amide)membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Kuila, S.B.; Das, P.; Ray, S.K. Separation of toluene–methanol mixtures by pervaporation using crosslink IPN membranes. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2009, 48, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Ray, S.K. Removal of pyridine from water by pervaporation using crosslinked and filled natural rubber membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, E99–E107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Ray, S.; Ray, S.K.; Koner, B.B. Removal of pyridine from water by pervaporation using filled SBR membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.C.; Claudio, P.R.; Ronaldo, N.; Cristiano, P.B. Pervaporative recovery of volatile aroma compounds from fruit juices. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 274, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, M.; Karmakar, M.; Mondal, B.; Singha, N.R. Role of ZDC/S ratio for pervaporative separation of organic liquids through modified EPDM membranes: Rational mechanistic study of vulcanization. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 69387–69403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlenberg, L. On the nature of the process of osmosis and osmotic pressure with observation concerning dialysis. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 10, 141–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, P.A. Pervaporation, perstillation and percrystallization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1917, 39, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaluenga, J.P.G.; Tabe-Mohammadi, A. A review on the separation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures by pervaporation processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 169, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, L.M. A review of pervaporation for product recovery from biomass fermentation processes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 603–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptel, P.; Challard, N.; Cuny, J.; Neel, J. Application of the pervaporation process to separate azeotropic mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 1976, 1, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Pan, F.; Wang, M.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.; Gao, B.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Hybrid membranes for pervaporation separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Shi, G.M.; Le, N.L.; Tang, Y.P.; Zuo, J.; Nunes, S.P.; Chung, T. Recent membrane development for pervaporation processes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 57, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Kammermyer, K. Membranes in Separation; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Loeb, S.; Sourirajan, S. High Flow Porous Membranes for Separating Water from Saline Solutions. U.S. Patent 3,133,132, 12 May 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Binning, R.C.; James, F.E. Permeation. A new commercial separation tool. Perot. Eng. 1958, 30, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Binning, R.C.; Jennings, J.F.; Martin, E.C. Process for Removing Water from Organic Chemicals. U.S. Patent 3,035,060, 15 May 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Tusel, G.F.; Brüschke, H.E.A. Use of pervaporation systems in the chemical industry. Desalination 1985, 53, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.V. Membrane Technology: In the Chemical Industry, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jonquieres, A.; Clement, R.; Lochon, P.; Neel, J.; Dresch, M.; Chreticn, B. Industrial state-of-the-art of pervaporation and vapour permeation in the western countries. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 206, 87–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Shen, J.N.; Song, M.Y.; Chen, H.L. Preparation of poly(vinyl alcohol)-sodium alginate hollow fiber composite membranes and pervaporation dehydration characterization of aqueous alcohol mixtures. Desalination 2006, 193, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipnizki, F.; Field, R.W.; Ten, P.-K. Pervaporation-based hybrid process: A review of process design, applications and economics. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 153, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W. Research needs in the membrane separation industry: Looking back, looking forward. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 134–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kulprathipanja, S.; Hillock, A.M.W.; Husain, S.; Koros, W.J. Recent progress in mixed-matrix membranes. In Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 787–819. [Google Scholar]
- Michaels, A.S.; Baddour, R.F.; Bixler, H.J.; Choo, C.Y. Conditioned polyethylene as a permselective membrane separation of isomeric xylenes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process. Des. Dev. 1962, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrodt, V.N.; Sweeny, R.F.; Rose, A. Division of industrial and engineering chemistry Los Angeles, March. In Future Industrial Prospects of Membrane Processes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Long, R.B. Liquid permeation through plastic films. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1965, 4, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W.; Wijmans, J.G.; Huang, Y. Permeability, permeance and selectivity: A preferred way of reporting pervaporation performance data. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G. Process performance = Membrane properties + Operating conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 220, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampranpiboon, P.; Jiraratananon, R.; Uttapap, D.; Feng, X.; Huang, R.Y.M. Pervaporation separation of ethyl butyrate and isopropanol with polyether block amide (PEBA) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 173, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourirajan, S.; Shiyao, B.; Matsuura, T. An approach to membrane separation by pervaporation. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Pervaporation Processes in Chemical Industry, San Antonio, TX, USA, 8–11 March 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Sourirajan, S.; Shiyao, B.; Matsuura, T. Reverse Osmosis and UF/Process Principles; National Research Council of Canada: Ottawa, ON, USA, 1985; Chapter 4.
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasstone, S.; Laidler, K.J.; Eyring, H. The Theory of Rate Processes; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Peppas, N.A.; Reinhart, C.T. Solute diffusion in swollen membranes. Part I. A new theory. J. Membr. Sci. 1983, 15, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Hwang, S.-T. Modeling of multicomponent pervaporation for removal of volatile organic compounds from water. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 93, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, I.; Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. Separation of dissolved organics from water by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 49, 253–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, B.G.; Uribe, I.O. Mathematical modeling of the pervaporative separation of methanol−methylterbutyl ether mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Huang, R.Y.M. Polymeric membrane pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, C.; Urtiaga, A.; Gorri, D.; Ortiz, I. Pervaporative dehydration of organic mixtures using a commercial silica membrane: Determination of kinetic parameters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 42, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M.; Barrie, J.A.; Rogers, M.G. Heterogenous membranes: Diffusion in filled rubber. J. Polym. Sci. A 1963, 1, 2565–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, T.S.; Chan, S.S.; Wang, R.; Lu, Z.; He, C. Characterization of permeability and sorption in Matimid/C60 mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, Y.K.; Kulshrestha, V.; Awasthi, K.; Acharya, N.K.; Jain, A.; Singh, M.; Dolia, S.N.; Khan, S.A.; Avasthi, D.K. Characterization of nanocomposite polymeric membrane. J. Polym. Res. 2006, 13, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, T.C.; Freeman, B.D.; Spontak, R.J.; He, Z.; Pinnau, I.; Meakin, P.; Hill, A.J. Sorption, transport and structural evidence for enhanced free volume in poly(4-methyl-2-pentyne)/fumed silica NCMs. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, D.; Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.V. Membranes for gas separation based on poly (1-trimetylsilyl-1-propyne)-silica nanocomposites. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 246, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saga, S.; Matsumoto, H.; Saito, K.; Minagawa, M.; Tanioka, A. Polyelectrolyte membranes based on hydrocarbon polymer containing fullerene. J. Power Sources 2008, 176, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labille, J.; Masion, A.; Ziarelli, F.; Rose, J.; Brant, J.; Villieras, F.; Pelletier, M.; Borschneck, D.; Wiesner, M.R.; Bottero, J.Y. Hydration and dispersion of C-60 in aqueous systems: The nature of water-fullerene interactions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11232–11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamada, Y.; Sakai, J. Gas transport properties of ODPA-TAPOB hyperbranched polyimide-silica hybrid membranes. High Perform. Polym. 2006, 18, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, D.A.G. Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer Konstanten von heterogenen Substanzen. Ann. Phys. 1935, 24, 636–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, R.H.B.; Checchetti, A.; Chidichimo, G.; Drioli, E. Permeation through a heterogeneous membrane: The effect of the dispersed phase. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 128, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.Q.; Koros, W.J.; Miller, S.J. Mixed matrix membranes using carbon molecular sieves II. Modeling permeation behavior. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Omidkhah, M.; Pedram, M.Z. New permeation models for nanocomposite polymeric membranes filled with nonporous particles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, C.K.; Lee, K.-H. A study on desorption resistance in pervaporation of single component through dense membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautenbach, R.; Hommerich, U. Experimental study of dynamic mass-transfer effects in pervaporation. AIChE J. 1998, 44, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Effect of copolymer type and composition on separation characteristics of pervaporation membranes-A case study with separation of acetone-water mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, H.; Radosz, M.; Towler, B.F.; Shen, Y. Polymer-inorganic NCMs for gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 55, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Separation of organic mixtures by pervaporation using crosslinked and filled rubber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 285, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M. Gas permeation properties of poly(amide-6-b-ethylene oxide)-silica hybrid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 193, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.Q.; Koros, W.J.; Miller, S.J. Mixed matrix membranes using carbon molecular sieves: I. Preparation and experimental results. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 311–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wen, R.; Guo, Y.; Su, J.; Matsuura, T. Multilayer poly(vinyl alcohol)-zeolite 4A composite membranes for ethanol dehydration by means of pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, G.; Gabriela, C.; Octavian, C. Structure of mixed matrix membranes made with SAPO-5 zeolite in polyurethane matrix. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 115, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Hagiwara, H.; Yanagishita, H.; Ito, K.; Tsuru, T. Structural characterization of thin-film PAm reverse osmosis membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Wang, J.; Tsuru, T. Gas transport properties of interfacially polymerized PAm composite membranes under different pre-treatments and temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 449, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Bourlinos, A.; Gournis, D.; Tsoufis, T.; Trapalis, C.; Mateo-Alonso, A.; Prato, M. Multipurpose organically modified carbon nanotubes: From functionalization to nanotube composites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8733–8740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Jegal, J.; Kim, W.N. Modification of performances of various membranes using MWNTs as a modifier. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 249–250, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, N.G.; Rana, S.; Cho, J.W.; Li, L.; Chan, S.H. Polymer nanocomposites based on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 837–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidas, A.I.; Ackerman, D.M.; Johnson, J.K.; Sholl, D.S. Rapid transport of gases in carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 185901-1–185901-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, M.; Chopra, N.; Andrews, R.; Hinds, B.J. Enhanced flow in carbon nanotubes. Nature 2005, 438, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, J.K.; Park, H.G.; Wang, Y.; Stadermann, M.; Artyukhin, A.B.; Grigoropoulos, C.P.; Noy, A.; Bakajin, O. Fast mass transport through sub-2-nanometer carbon nanotubes. Science 2006, 312, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Jinschek, J.R.; Chen, H.; Sholl, D.S.; Marand, E. Scalable fabrication of carbon nanotube/polymer NCMs for high flux gas transport. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2806–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, H.; Zhang, J.; Radosz, M.; Shen, Y. Carbon nanotube composite membranes of brominated poly(2,6-diphenyl-1,4-phenylene oxide) for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 294, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Jegal, J.; Kim, W.N.; Choi, H.S. Incorporation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes into poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes for use in the pervaporation of water/ethanol mixtures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, R.S.; Sridhar, S.; Sankarshana, T.; Ravikumar, Y.V.L. Gas permeation behavior of Pebax-1657 NCM incorporated with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 6530–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, Y.; Tofighy, M.A.; Mohammadi, T. Synthesis and characterization of carbon nanotubes/poly vinyl alcohol NCMs for dehydration of isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Samseth, J.; Hagg, M.B. Crosslinking and stabilization of NP filled PMP NCMs for gas separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 326, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancharernrat, T.; Rempel, G.L.; Prasassarakich, P. Preparation of styrene butadiene copolymer–silica nanocomposites via differential microemulsion polymerization and NR/SBR–SiO2 membranes for pervaporation of water–ethanol mixtures. Chem. Eng. 2014, 258, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, L.; Chen, X. Chitosan/TiO2 nanocomposite pervaporation membranes for ethanol dehydration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 3130–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.D.; Oliveira, T.; Livingston, A.G.; Li, K. Membranes for the dehydration of solvents by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 5–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtiaga, A.M.; Gorri, E.D.; Gómez, P.; Casado, C.; Ibáñez, R.; Ortiz, I. Pervaporation technology for the dehydration of solvents and raw materials in the process industry. Drying Technol. 2007, 25, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Choi, Y.; Moon, S. Water-swollen cation-exchange membranes prepared using poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA)/poly(styrene sulfonic acid-co-maleic acid) (PSSA-MA). J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 207, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.M.; Yeom, C.K. Pervaporation separation of aqueous mixtures using crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol membranes. III. Permeation of acetic acid-water mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 58, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.Y.; Hu, C.M. Separation of liquid mixtures by using polymer membranes. I. Water–alcohol separation by pervaporation through PVA-g-MMA/MA membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1991, 43, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.S.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, V.Y.; Shim, J.S. Pervaporation of water-ethanol mixtures through crosslinked and surface modified poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 51, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.G.; Zhu, C.-L.; Liu, M. Study of a new pervaporation membrane Part I. Preparation and characteristics of the new membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 90, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zou, Y.; Wei, T.; Mua, C.; Liu, X.; Tong, Z. Pervaporation dehydration of binary and ternary mixtures of n-butyl acetate, n-butanol and water using PVA-CS blended membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 173, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauclair, C.; Tarjus, H.; Schaetzel, P. Permselective properties of PVA-PAA blended membrane used for dehydration of fusel oil by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 125, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burshe, M.C.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Sorption and permeation of binary water-alcohol systems through PVA membranes crosslinked with multifunctional crosslinking agents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1997, 12, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-P. Modified alginate composite membranes for the dehydration of acetic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 170, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.-M.; Chung, T.-S.; Huang, Z.; Chng, M.L.; Kulprathipanja, S. Poly(vinyl alcohol) multilayer mixed matrix membranes for the dehydration of ethanol–water mixture. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 268, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.A.; Poeth, C.H.S.; Benes, N.E.; Buijs, H.C.W.M.; Vercauteren, F.F.; Keurentjes, J.T.F. Ceramic-supported thin PVA pervaporation membranes combining high flux and high selectivity; contradicting the flux-selectivity paradigm. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 276, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Facilitated transport of CO2 through polyvinylamine/polyethlene glycol blend membranes. Desalination 2006, 193, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bernstein, R. High-flux thin-film composite polyelectrolyte hydrogel membranes for ethanol dehydration by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 534, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.Y.M.; Moreira, H.; Nufarforizo, R.; Huang, Y.M. Pervaporation separation of acetic acid-water mixtures using modified membranes. I. Blended polyacrylic acid (PAA)-nylon 6 membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 35, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aptel, P.; Cuny, J.; Jozefonvicz, J.; Morel, G.; Neel, J. Liquid transport through membranes prepared by grafting of polar monomers onto poly(tetrafluoroethylene) films. III. Steady-state distribution in membrane during pervaporation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1974, 18, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotsu, T.; Isayama, M. Water-ethanol separation by pervaporation through plasma-graft-polymerized membranes of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate with acrylic acid or methacrylic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 1989, 45, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Dehydration of acetic acid by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 138, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Dehydration of acetic acid, alcohols, and acetone by pervaporation using acrylonitrile-maleic anhydride copolymer membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.D.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation separation using sodium alginate and its modified membranes-A review. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2007, 36, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulik, S.; Nazia, S.; Vani, B.; Sridhar, S. Pervaporation separation of acetic acid/water mixtures through sodium alginate/polyaniline polyion complex membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 170, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Nam, S.Y.; Ha, S.Y. Pervaporation of water/isopropanol mixtures through polyaniline membranes doped with poly(acrylic acid). J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 159, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. Network cross-linking of polyimide membranes for pervaporation dehydration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 185, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.L.; Hu, C.-C.; Lai, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L. Crosslinked polybenzoxazine based membrane exhibiting in-situ self-promoted separation performance for pervaporation dehydration on isopropanol aqueous solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 531, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurşuna, F.; Işıklan, N. Development of thermo-responsive poly(vinyl alcohol)-g-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) copolymeric membranes for separation of isopropyl alcohol/water mixtures via pervaporation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 41, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, D.A.; Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation separation of dimethylformamide/water mixtures through poly(vinyl alcohol)/poly(acrylic acid) blend membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Pervaporative dehydration of dimethyl formamide (DMF) by crosslinked copolymer membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 7210–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Thongsukmak, A.; Tang, J.; Sirkar, K.K. Concentration of aqueous hydrogen peroxide solution by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 389, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Oh, B.-K. Dehydration of water-pyridine mixture through poly(acrylonitrile-co-acryclic acid) membrane by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 98, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-Z.; Liu, X.-F.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.-Y. Membranes of crosslinked hyperbranch polymers and their pervaporation properties. Desalination 2009, 247, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chung, T.S.; Neo, B.W.; Gruender, M. Processing and engineering of pervaporation dehydration of ethylene glycol via dual-layer polybenzimidazole (PBI)/polyetherimide (PEI) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawski, J.K.; Kujawski, W.M.; Sondej, H.; Jarzynka, K.; Kujawska, A.; Bryjak, M.; Rynkowska, E.; Knozowska, K.; Kujawa, J. Dewatering of 2,2,3,3-tetrafluoropropan-1-ol by hydrophilic pervaporation with poly(vinyl alcohol) based PervapTM membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adoor, S.G.; Prathab, B.; Manjeshwar, L.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Mixed matrix membranes of sodium alginate and poly(vinyl alcohol) for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol at different temperatures. Polymer 2007, 48, 5417–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalad, V.T.; Gokavi, G.S.; Raju, K.V.S.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Mixed matrix blend membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol)–poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) loaded with phosphomolybdic acid used in pervaporation dehydration of ethanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 354, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Alberto, M.; Gorgojo, P.; Szekely, G.; Budd, P.M. High-flux PIM-1/PVDF thin film composite membranes for 1-butanol/water pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qiu, S.; Yu, B.; Tang, G.; Xing, W.; Hu, Y. POSS-functionalized polyphosphazene nanotube: Preparation and effective reinforcement on UV-curable epoxy acrylate nanocomposite coatings. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, B.; Cao, R.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, S.; Liu, G.; Wu, H. Enhanced pervaporation performance of poly (dimethyl siloxane) membrane by incorporating titania microspheres with high silver ion loading. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalad, V.T.; Gokavi, G.S.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation separation of water-ethanol mixtures using organic-inorganic NCMs. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 14731–14744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Coterillo, C.; Andrés, F.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Irabien, Á. Synthesis and characterization of ETS-10/Chitosan NCMs for pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cruz, L.; Casado-Coterillo, C.; Iniesta, J.; Montiel, V.; Irabien, A. Preparation and characterization of novel chitosan-based mixed matrix membranes resistant in alkaline media. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42240–42249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adoor, S.G.; Manjeshwar, L.S.; Bhat, S.D.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Aluminum-rich zeolite beta incorporated sodium alginate mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration and esterification of ethanol and acetic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.; Zeng, Q.; Li, J. The influence of nano-sized TiO2 fillers on the morphologies and properties of PSF UF membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Li, J.; Ji, S.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G. In situ ultraviolet-light-induced TiO2 nanohybrid superhydrophilic membrane for pervaporation dehydration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, B.G.; Rao, K.S.V.K.; Reddy, K.M.; Rao, K.C.; Rao, P.S. Novel NCMs of sodium alginate filled with polyaniline-coated titanium dioxide for dehydration of 1,4-dioxane/water mixtures. Desalination 2008, 233, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminabhavi, T.M.; Patil, M.B.; Bhat, S.D.; Halgeri, A.B.; Vijayalakshmi, R.P.; Kumar, P. Activated charcoal-loaded composite membranes of sodium alginate in pervaporation separation of water-organic azeotropes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Parya, T.K.; Ray, S.K. Dehydration of 1,4-dioxane by perva-poration using filled and crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapur, R.S.; Patil, M.B.; Gudasi, K.B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Poly(vinylalcohol)-zeolite T mixed matrix composite membranes for pervaporation separation of water + 1,4-dioxane mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 58, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.P.; Kumar, M.; Saxena, A.; Shahi, V.K. Bifunctionalized organic–inorganic charged NCM for pervaporation dehydration of ethanol. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2010, 346, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Gong, L.; Fan, H.; Ji, S.; Zhang, G. Spray-assisted biomineralization of a superhydrophilic water uptake layer for enhanced pervaporation dehydration. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkkun, T.; Jenwiriyakula, W.; Amnuaypanich, S. Dehydration performance of double-network poly(vinyl alcohol) NCMs (PVAs-DN). J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z. Metal-organic frameworks based mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 235, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.L.; Yang, Z.X.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Xia, Y.D. Zeoliticimidazolate framework materials: Recent progress in synthesis and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16811–16831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhang, G.L.; Fan, Z.; Meng, Q.; Shen, C.; Gao, C.J. Stiff metal–organic framework–polyacrylonitrile hollow fiber composite membranes with high gas permeability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.J.; Tang, B.B.; Wu, P.Y. Metal–organic framework-graphene oxide composites: A facile method to highly improve the proton conductivity of PEMs operated under low humidity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15838–15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.H.; Lin, Y.F.; Huang, Y.S.; Tung, K.L.; Chang, K.S.; Chen, J.T.; Hung, W.S.; Lee, K.R.; Lai, J.Y. Synthesis of ZIF-7/chitosan mixed-matrix mem-branes with improved separation performance of water/ethanol mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 438, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.M.; Yang, T.X.; Chung, T.S. Polybenzimidazole (PBI)/zeoliticimidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8) mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration of alcohols. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 577–586. [Google Scholar]
- Ordonez, M.J.C.; Balkus, K.J.; Ferraris, J.P.; Musselman, I.H. Molecular sieving realized with ZIF-8/Matrimid mixed-matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Ong, Y.K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Chung, T.S. ZIF-90/P84 mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gupta, K.M.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Huang, A. Synthesis and seawater desalination of molecular sieving zeolitic imidazolate framework membranes. Desalination 2016, 385, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascón, J.; Freek, K.; Beatriz, Z.; Víctor, S.; Clara, C.; Joaquín, C. Practical approach to zeolitic membranes and coatings: State of the art, opportunities, barriers and future perspectives. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2829–2844. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Wang, H. Zeolitic imidazolate framework composite membranes and thin films: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4470–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amnuaypanich, S.; Patthana, J.; Phinyocheep, P. Mixed matrix membranes prepared from natural rubber/poly(vinyl alcohol) semi-interpenetrating polymer network (NR/PVA semi-IPN) incorporating with zeolite 4A for the pervaporation dehydration of water-ethanol mixtures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 4908–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Su, Y.H.; Lai, J.Y. Chitosan-silica complex membranes from sulfonic acid functionalized silica NPs for pervaporation dehydration of ethanol-water solutions. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunitha, K.; Rani, K.Y.; Moulik, S.; Satyanarayana, S.V.; Sridhar, S. Separation of NMP/water mixtures by nanocomposite PEBA membrane: Part I. Membrane synthesis, characterization and pervaporation performance. Desalination 2013, 330, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom, J.P.; Bargeman, D.; Strathmann, H. Zeolite filled membranes for gas separation and pervaporation. Zeolite and related microporous materials: State of art. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1994, 84, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, G.; Gnus, M.; Turczyn, R.; Strzelewicz, A.; Krasowska, M. Pervaporation with chitosan membranes containing iron oxide NPs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olukman, M.; Şanlı, O. A novel in situ synthesized magnetite containing acrylonitrile and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate grafted poly(vinyl alcohol) NCMs for pervaporation separation of acetone/water mixtures. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 98, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.M.; Chen, H.; Jean, Y.C.; Chung, T.S. Sorption, swelling, and free volume of polybenzimidazole (PBI) and PBI/zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) nano-composite membranes for PV. Polymer 2013, 54, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, K.; Nair, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, J.; Gomaa, H.; Wu, H.; Pan, F. PV performance comparison of hybrid membranes filled with two-dimensional ZIF-L nanosheets and zero-dimensional ZIF-8 NPs. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adoor, S.G.; Rajineekanth, V.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Rao, K.C.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Exploration of NCMs composed of phosphotungstic acid in sodium alginate for separation of aqueous–organic mixtures by PV. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 113, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L.; Funke, H.H. Organics/water separation by PV with a zeolite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Noble, R.D.; Falconer, J.L. Fundamentals and applications of PV through zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 245, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Loo, L.S.; Wang, K.A. PV performance of novelchitosan-POSS hybrid membranes: Effects of POSS and operatingconditions. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.L.; Tang, Y.P.; Chung, T.S. The development of high-performance6FDA NDA/DABA/POSS/Ultem® dual-layer hollow fibers for ethanol dehydration via PV. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 447, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.V.; Acquah, S.F.A.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Sokolova, M.P.; Mikhailova, M.E.; Polyakov, E.S.; Ermakov, S.S.; Markelov, D.A.; Roizard, D. Improvement of PV PVA membranes by the controlled incorporation of fullerenol NPs. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, S.; Geppert, B.; Steinbach, F.; Caro, J. Novel MOF UiO-66 layer: A Highly oriented membrane with good selectivity and hydrogen permeance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 12878–12885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Development of hybrid ultrafiltration membranes with improved water separation properties using modified super-hydrophilic metal-organic framework nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2017, 9, 21473–21484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.R.; Arredondo, K.Y.Y.; Liu, C.; Stevens, J.E.; Mayhob, A.; Shan, B.; Senthilnathan, S.; Balzer, C.J.; Mu, B. UiO-66 MOF and poly(vinyl cinnamate) nanofiber composite membranes synthesized by a facile three-stage process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 12386–12392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Qian, J.W.; Zhu, C.X.; An, Q.F.; Xu, T.Q.; Zheng, Q.; Song, Y. A novel method for fabricating polyelectrolyte complex/inorganic nanohybrid membranes with high isopropanol dehydration performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.T.; Ahmad, A.L.; Zein, S.H.S.; Sudesh, K.; Tan, S.H. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)-functionalised multi-walled carbon nanotubes/chitosan green NCMs and their application in pervaporation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 76, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeang, Q.Y.; Zein, S.H.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Tan, S.H. Comparison of the pervaporation performance of various types of carbon nanotube-based nanocomposites in the dehydration of acetone. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 107, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahian, S.; Raisi, A.; Aroujalian, A. Multilayer mixed matrix membranes containing modified-MWCNTs for dehydration of alcohol by pervaporation process. Desalination 2015, 355, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, L.; Shi, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Preparation and pervaporation property of chitosan membrane with functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11667–11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lawless, D.; Feng, X. Composite membranes comprising of polyvinylamine-poly(vinyl alcohol) incorporated with carbon nanotubes for dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417–418, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.W.; Piner, R.D.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Mechanical properties of monolayer graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6557–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, S.; Tyson, T.A.; Negusse, E. Investigation of the local structure of graphene oxide. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 3433–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F. Graphene-based nanomaterial: The state-of-the-art material for cutting edge desalination technology. Desalination 2015, 356, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, K.A.; Mansoor, B.; Mansour, A.; Khraisheh, M. Functional graphene nanosheets: The next generation membranes for water desalination. Desalination 2015, 356, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, H.K.; Nath, K. Graphene oxide incorporated novel polyvinyl alcohol composite membrane for pervaporative recovery of acetic acid from vinegar waste water. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 14, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehian, P.; Chung, T.S. Thermally treated ammonia functionalized graphene oxide/polyimide membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.; He, G.; Xing, R.; Pan, F.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Wang, B. Incorporating zwitterionic graphene oxides into sodium alginate membrane for efficient water/alcohol separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2016, 8, 2097–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.P.; Chan, J.X.; Chung, T.S.; Weber, M.; Staudt, C.; Maletzko, C. Simultaneously covalent and ionic bridging towards antifouling of GO-imbedded nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 10573–10584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Rai, R.K.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, T.S. Aldehyde functionalized graphene oxide frameworks as robust membrane materials for pervaporative alcohol dehydration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 161, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.M.; Payne, P.A. A study of organic compound pervaporation through silicone rubber. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 49, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blume, J.; Schwering, F.J.F.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Smolders, C.A. Sorption and Permeation properties of poly(dimethyl siloxane) films. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Pervaporation Processes in the Chemical Industry, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 3–7 December 1989; Backish, R., Ed.; Bakish Materials Corporation: Engel Wood, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Netke, S.A.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Sorption and permeation of aqueous picolines in elastomeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 91, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Hennepe, H.J.C.; Bargeman, D.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Smolders, C.A. Zeolite -filled silicone rubber membranes. Part-I, Membrane preparation and pervaporation results. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 35, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.D.; Peinemann, K.V.; Behling, R.D. Preparation and characterization of thin film zeolite-PDMS composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 73, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netke, S.A.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Sorption and permeation of acetic acid through zeolite filled membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rom, A.; Friedl, A. Investigation of pervaporation performance of POMS membrane during separation of butanol from water and the effect of added acetone and ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Tang, B.; Ingashimura, T. Ethanol-water separation by pervaporation through substituted polyacetylene membranes. Polym. J. 1986, 7, 565–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, C.S.; Hickey, P.J.; Juricic, F.P. Pervaporation of aqueous ethanol mixtures through poly (dimethyl siloxane) membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1990, 25, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.V.; Khotimskii, V.S.; Plate, N. Organophilic polymers for pervaporation. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Pervaporation Processes in the Chemical Industry, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 3–7 December 1989; Backish, R., Ed.; Bakish Materials Corporation: Engel Wood, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Okabe, K.; Okita, K. Separation of ethanol from ethanol/water mixtures by plasma-polymerized membranes from silicone compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 1988, 36, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabra, M.M.; Netke, S.A.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Pervaporative separation of carboxylic acid-water mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 1995, 5, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.W.Y.; Finlayson, J.; Dickson, J.M.; Jiang, J.; Brook, M.A. Pervaporation performance of oligosilylstyrene-polydimethylsiloxane membrane for separation of organics from water. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 134, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Yanagishita, H.; Kitamoto, D.; Negishi, H.; Haraya, K.; Sano, T. Concentration of fermented ethanol by pervaporation using silicalite membranes coated with silicone rubber. Desalination 2002, 149, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddeeker, K.W.; Bengtson, G.; Pingel, H. Pervaporation of isomeric butanols. J. Membr. Sci. 1990, 54, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Kondo, M.; Fuzita, Y. Transport mechanism in PEBA membrane. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Pervaporation Processes in the Chemical Industry, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 27–30 September 1992; Backish, R., Ed.; Bakish Materials Corporation: Engel Wood, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, E.S.; Stone, M.L.; Baver, W.F.; Gianotto, A.K. The removal of organic chemicals from waste stream using polyphosphazene membranes. In Proceedings of the Euromembrane, 5–8 October 1992; Aimer, P., Aptel, P., Eds.; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, T.; Hoshi, M.; Higuchi, A. Separation of aqueous organic solvents through poly(acrylic acid ester-co-acrylic acid) membranes by pervaporation. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Pervaporation Processes in the Chemical Industry, Heidelberg, Germany, 11–15 March 1991; Backish, R., Ed.; Bakish Materials Corporation: Engel Wood, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Pithan, F.; Staudt-Bickel, C.; Lichtenthaler, R.N. Synthesis of highly fluorinated copolyimide membranes for the removal of high boiling organics from process water and wastewater by pervaporation. Desalination 2002, 148, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uragami, T.; Yamada, H.; Miyata, T. Removal of dilute volatile organic compounds in water through graft copolymer membranes consisting of poly(alkylmethacrylate) and poly(dimethylsiloxane) by pervaporation and their membrane morphology. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 187, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uragami, T.; Fukuyama, E.; Miyata, T. Selective removal of dilute benzene from water by poly(methyl methacrylate)-graft-poly(dimethyl siloxane) membranes containing hydrophobic ionic liquid by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, J.D.; Yoshida, W.; Cohen, Y. A novel ceramic-supported polymer membrane for pervaporation of dilute volatile organic compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 162, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, K.; Pintauro, P.N.; Ponangi, R. Separation of dilute organic/water mixtures with asymmetric poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-J.; Aranda, P.; Martin, C.R. Pervaporation separation of ethanol/water mixtures by polystyrenesulfonate/alumina composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.; Galiano, F.; Jansen, J.C.; Figoli, A. Strategy for scale-up of SBS pervaporation membranes for ethanol recovery from diluted aqueous solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 176, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Ameri, E. Pervaporation characteristics of a PDMS/PMHS membrane for removal of dimethyl sulfoxide from aqueous solutions. Vacuum 2017, 141, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Nie, L.; Liu, J.; Zheng, J. Separation of methanol from methanol/water mixtures with pervaporation hybrid membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, A.J.; Mizsey, P. Methanol removal from aqueous mixture with organophilic pervaporation: Experiments and modelling. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 98, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Wan, Y. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) recovery from aqueous solutions via pervaporation with vinyltriethoxysilane-grafted-silicalite-1/polydimethylsiloxane mixed matrix membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uragami, T.; Matsuoka, Y.; Miyata, T. Permeation and separation characteristics in removal of dilute volatile organic compounds from aqueous solutions through copolymer membranes consisted of poly(styrene) and poly(dimethylsiloxane) containing a hydrophobic ionic liquid by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 506, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, C.J.; Leak, D.; Patterson, D.A. Hybrid and mixed matrix membranes for separations from fermentations. Membranes 2016, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vane, L.M.; Namboodiri, V.V.; Meier, R.G. Factors affecting alcohol-water pervaporation performance of hydrophobic zeolite-silicone rubber mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, L.M.; Namboodiri, V.V.; Bowen, T.C. Hydrophobic zeolite-silicone rubber mixed matrix membranes for ethanol-water separation: Effect of zeolite and silicone component selection on pervaporation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Lu, J.; Tan, T.T.; Li, J.D. Mixed matrix membranes with HF acidetched ZSM-5 for ethanol/water separation: Preparation and pervaporation performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 259, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evcin, A.; Tutkun, O. Pervaporation separation of ethanol-water mixtures by zeolite-filled polymeric membranes. Ceramics-Silikaty 2009, 53, 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Shi, X.; Bai, Y.X.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H. Silicalite-filled polyether block-amides membranes for recovering ethanol from aqueous solution by pervaporation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2009, 32, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.L.; Su, Y.; Wan, Y.H. Preparation and characterization of vinyl triethoxysilane (VTES) modified silicalite-1/PDMS hybrid pervaporation membrane and its application in ethanol separation from dilute aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Li, Y.S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.S. Capillary sup-ported ultrathin homogeneous silicalite-poly(dimethyl siloxane)NCM for bio-butanol recovery. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Fu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Tang, X. Pervaporation of ethanol aqueous solution by polydimethylsiloxane/polyphosphazene nanotube NCMs. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 339, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, A.B.; Nisola, G.M.; Choi, S.S.; Kim, Y.; Chung, W.J. Surface-functionalized silica NPs as fillers in polydimethylsiloxane membrane for the pervaporative recovery of 1-butanol from aqueous solution. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 87, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, R.; Jin, W. Novel organic–inorganic pervaporation membrane with a superhydrophobic surface for the separation of ethanol from an aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 127, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.L.; Wang, Y.; Chung, T.S. Pebax/POSS mixed matrix membranesfor ethanol recovery from aqueous solutions via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, S.; Vandezande, P.; Mullens, S.; De Sitter, K.; Peeters, R.; VanBael, M.K. Preparation and benchmarking of thin film supported PTMSP-silica pervaporation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 389, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.N.; Liu, G.P.; Zhao, X.H.; Jin, W.Q. Hydrophobic-ZIF-71 filled PEBA mixed matrix membranes for recovery of biobutanol via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Lau, C.Y.; Rozowski, M.; Howard, C.; Xu, Y.; Lai, T.; Dose, M.E.; Lively, R.P.; Lind, M.L. Free-standing ZIF-71/PDMS NCMs for the recovery of ethanol and 1-butanol from water through pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.F.; Yang, L.; Bai, Y.X.; Gu, J.; Sun, Y.P. ZSM-5 filled polyurethane urea membranes for pervaporation separation isopropyl acetate from aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 85, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Jin, H.; Li, Y.S.; Bux, H.; Hu, Z.Y.; Ban, Y.J.; Yang, W. Metal-organic framework ZIF-8 NCM for efficient recovery of furfural via pervaporation and vapor permeation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 428, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessling, M.; Werner, U.; Huang, S.T. Pervaporation of aromatic C8–isomers. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 57, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCandless, F.P. Separation of aromatics and napthalenes by penneation through modified vinyledene fluoride films. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1973, 12, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabasso, I. Organic liquid mixtures separation by permselective polymer membranes. I. Selection and characteristics of dense isotropic membranes employed in the pervaporation process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev. 1983, 22, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Separation of organic mixtures by pervaporation using crosslinked rubber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschke, H.E.A.; Schneider, W.H.; Scholz, W.H.; Steinhauser, H. Removal of methanol from organic mixtures. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Pervaporation Process in the Chemical Industry, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 27–30 September 1992; Backish, R., Ed.; Bakish Materials Corporation: Engel Wood, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, S.K.; Sawant, S.B.; Joshi, J.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Methanol selective membranes for separation of methanol-ethylene glycol mixtures by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Sawant, S.B.; Pangarkar, V.G. Separation of Methyl-tert-butyl alcohol (MTBE)-Methanol by pervaporation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 2645–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.K.; Sikdar, S.K. Separation of azeotropic organic liquid mixtures by pervaporation. AICHE J. 1991, 37, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Synthesis of highly methanol selective membranes for separation of methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE)–methanol mixtures by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozzelino, G.; Malucelli, G. Permeation of methanol/methyl-t-butyl ether mixtures through poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) films. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 235, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J. Vapor permeation separation of MeOH/MTBE through polyimide/sulfonated poly(ether-sulfone) hollow-fiber membranes. Desalination 2004, 161, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Yoshioka, T.; Fujime, J.; Murakami, A. Pervaporation separation of MeOH/MTBE through agarose membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 178, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.M.; Bartels, C.R.; Pasternak, M.; Reale, J. Opportunities for membranes in the production of octane enhancers. AIChE Symp. Ser. 1989, 85, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Khayet, M.; Nasef, M.M.; Mengual, J.I. Radiation grafted poly(ethylene terephthalate)-graft-polystyrene pervaporation membranes for organic/organic separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 263, 77–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, A.V.; Volkov, V.V.; Khotimskii, V.S. Membranes Based on poly[(1-Trimethylsilyl)-1-Propyne] for Liquid-Liquid Separation. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2009, 51, 1367–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, M.; Ohi, K.; Yoshimi, Y.; Kanamori, T. Pervaporative separation of organic mixtures using dinitrophenyl group-containing cellulose acetate membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 253, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Dickson, J.M.; Jiang, J.; Brook, M.A. Effect of low flow rate on pervaporation of 1,2-dichloroethane with novel polydimethylsiloxane composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 231, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, V.S.; Paredes, M.L.L.; Borges, C.P.; Habert, A.C.; Nobrega, R. Removal of aromatics from multicomponent organic mixtures by pervaporation using polyurethane membranes: Experimental and modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 206, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Hinode, H.; Kajiuchi, T. Permeation and separation of styrene/ethylbenzene mixtures through cross-linked poly(hexamethylene sebacate) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 156, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Persin, M.; Sarrazin, J. Methanol removal from organic mixtures by pervaporation using polypyrrole membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 117, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, M.; Romero, A.I.; Parentis, M.L.; Vidaurre, E.F.C.; Gottifredi, J.C. Acrylic acid plasma polymerizedpoly(3-hydroxybutyrate) membranes formethanol/MTBE separation by pervaporation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 109, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, Z.V.P.; Shah, M.K. Separation of isopropyl alcohol–toluene mixtures by pervaporation using poly(vinyl alcohol) membrane. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S56–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.P.; Freeman, B.D.; Kalik, D.S.; Kalakkunnath, S. Aromatic polyimide and polybenzoxazole membranes for the fractionation of aromatic/aliphatic hydrocarbons by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390–391, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, T.C.; Meier, R.G.; Vane, L.M. Stability of MFI zeolite-filled PDMS membranes during pervaporative ethanol recovery from aqueous mixtures containing acetic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 298, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation separation of toluene/alcohol mixtures using silicalite zeolite embedded chitosan mixed matrix membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Kumar, A. Separation of 1-butanol/2,3-Butanediol using ZSM-5 zeolite-filled polydimethylsiloxane membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 339, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaddondar, M.; Pahlavanzadeh, H.; Hosseini, S.S.; Ruan, G.; Tan, N.R. Self-assembled polyelectrolyte surfactant NCMs for pervaporation separation of MeOH/MTBE. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouinti, L.; Roizard, D.; Belbachir, M. PVC–activated carbon based matrices: A promising combination for pervaporation membranes useful for aromatic–alkane separations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 147, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Pan, F.; Sun, H.; Lu, L.; Jiang, Z. Novel nanocomposite pervaporation membranes composed of poly(vinyl alcohol) and chitosan-wrapped carbon nanotube. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 300, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.N.; Chu, Y.X.; Ruan, H.M.; Wu, L.G.; Gao, C.J.; Bruggen, B.V. Pervaporation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures through mixed matrix membranes of chitosan and Ag+/carbon nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 462, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.V.; Polotskaya, G.A.; Gavrilova, V.A.; Toikka, A.M.; Liu, J.C.; Trchova, M.; Slouf, M.; Pientka, Z. PAm membranes modified by carbon nanotubes: Application for pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kang, Y.; Chin, C. Spectroscopic characterization of cellulose acetate polymer membranes containing Cu(1,3-butadiene)OTf as a facilitated olefin transport carrier. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wu, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, C. Separation cyclohexene/cyclohexane mixtures with facilitated transport membrane of poly(vinyl alcohol)-Co2+. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 45, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Z. Formation of AgCl nanoparticle in reverse micro-emulsion using polymerizable surfactant and the resulting copolymer hybrid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 429, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tor, A.; Arslan, G.; Muslu, H.; Celiktas, A.; Cengeloglu, Y.; Ersoz, M. Facilitated transport of Cr(III) through polymer inclusion membrane with di(2-ethyl-hexyl) phosphoric acid (DEHPA). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 329, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ji, S.; Li, J.-R. Co(HCOO)2-based hybrid membranes for the pervaporation separation of aromatic/aliphatic hydrocarbon mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, S.; Mun, S.; Kang, Y. Facile synthesis of copper nanoparticles by ionic liquids and its application to facilitated olefin transport membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 7437–7441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, F.; Jiang, Z. Novel graphite-filled PVA/CS hybrid membrane for pervaporation of benzene/cyclohexane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Qu, L.; Ren, J.; Li, Y. A novel atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma graft-filling technique to fabricate the composite membranes for pervaporation of aromatic/aliphatic hydrocarbons. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ji, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, G. Poly(vinyl alcohol)–graphene oxide nanohybrid “pore-filling” membrane for pervaporation of toluene/n-heptane mixtures. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.-Q.; Jiang, T.-Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, L.-G.; Yu, X.-Y.; Lin, J.-Z.; Shi, S.-X.-X. Enhanced performance of polyimide hybrid membranes for benzene separation by incorporating three-dimensional silver–graphene oxide. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2016, 478, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Yue, Y.; Li, W. Application of zeolite-filled pervaporation membrane. Zeolites 1996, 16, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, M.G.; Magalad, V.T.; Gokavi, G.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Raju, K.V.S.N. Pervaporation separation of isopropanol-water mixtures using mixed matrix blend membranes of poly(vinylalcohol)/poly(vinylpyrrolidone) loaded with phosphomolybdic acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 121, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Huang, S.H.; Hung, W.S.; Kao, S.T.; Wang, D.M.; Jean, Y.C.; Lee, K.R.; Lai, J.Y. Study on the influence of the free volume of hybrid membrane on PV performance by positron annihilation spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 313, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, C.V.; Yeriswamy, B.; Sudhakar, H.; Sudhakara, P.; Subha, M.C.S.; Rao, J.I.K.C. Preparation and characterization of NP-filled, mixed-matrix membranes for the PV dehydration of isopropyl alcohol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, T.; Tseng, H.; Wey, M. Preparation and characterization of multi-walled carbon nanotube/PBNPI nanocomposite membrane for H2/CH4 separation. Int J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 8707–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.; Kim, I.; Tak, T. Preparation and characterization of fouling-resistant TiO2 self-assembled nanocomposite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 275, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Madaeni, S.S.; Khataee, A.R.; Salehi, E.; Zinadini, S.; Monfared, H.A. TiO2 embedded mixed matrix PES nanocomposite membranes: Influence of different sizes and types of nanoparticles on antifouling and performance. Desalination 2012, 292, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solè, I.; Pey, C.M.; Maestro, A.; González, C.; Porras, M.; Solans, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Nano-emulsions prepared by the phase inversion composition method: Preparation variables and scale up. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2010, 344, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, H.Z.; Chung, T.S. The effects of substrate characteristics and pre wetting agents on PAN-PDMS composite hollow fiber membranes for CO2/N2 and O2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yave, W.; Car, A.; Funari, S.S.; Nunes, S.P.; Peinemann, K.V. CO2-Philic polymer membrane with extremely high separation performance. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, J. Enhancing the permselectivity of pervaporation membrane by constructing the active layer through alternative self-assembly and spin-coating. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390–391, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Cao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, F. High pervaporation Dehydration Performance of the Composite Membrane with an Ultrathin Alginate/Poly(acrylic acid)−Fe3O4 Active Layer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yoon, K.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. High flux filtration medium based on nanofibrous substrate with hydrophilic nanocomposite coating. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7684–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, A.; Bayer, I.; Loth, E. Inherently superoleophobic nanocomposite coatings by spray atomization. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genne, I.; Kuypers, S.; Leysen, R. Effect of the addition of ZrO2 to polysulfone based UF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 113, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wara, N.M.; Francis, L.F.; Velamakanni, B.V. Addition of alumina to cellulose acetate membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 104, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Polymer/silica nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 3893–3957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; He, R.; Jens, O.J.; Bjerrum, N.J. Approaches and recent development of polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cell operating above 100 °C. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 4896–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mascia, L.; Zhang, Z. Carbon fibre composites based on polyimide/siIica ceramers: Aspects of structure-properties relationship. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1996, 27, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, M.; Srivastava, S.K.; Samantaray, B.K.; Bhowmick, A.K. Rubber–clay nanocomposite by solution blending. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 2216–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, S.; Mameli, E.; Marazzato, C.; Magagnini, P. Comparison of solution-blending and melt-intercalation for the preparation of poly(ethylene-co-acrylic acid)/organoclay nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1645–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wilkie, C.A. Preparation of PVC-clay nanocomposites by solution blending. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2002, 8, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaleno, L.; Schjødt-Thomsen, J.; Pinto, J.C. Morphology, thermal and mechanical properties of PVC/MMT nanocomposites prepared by solution blending and solution blending + melt compounding. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2010, 70, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, M.; Srivastava, S.K.; Samantaray, B.K.; Bhowmick, A.K. EVA/clay nanocomposite by solution blending: Effect of aluminosilicate layers on mechanical and thermal properties. Macromol. Res. 2003, 11, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Pu, C.; Viswanathan, R.; Fan, Q.; Liu, R.; Smotkin, E.S. Carbon supported and unsupported Pt–Ru anodes for liquid feed direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 3657–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, E. The promotion of CO electro-oxidation on platinumbismuth as a model for surface mediated oxygen transfer. Catal. Today 1997, 38, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, T.; Johnson, R.; Hormes, J.; Noding, S.; Rambabu, B. A study of methanol electro-oxidation reactions in carbon membrane electrodes and structural properties of Pt alloy electro-catalysts by EXAFS. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2000, 485, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, H.I. Permeability Separatory Apparatus, Permeability Separatory Membrane Element, Method of Making the Same and Process Utilizing the Same. U.S. Patent 3,228,876, 19 September 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Sukitpaneenit, P.; Chung, T. PVDF/nanosilica dual-layer hollow fibers with enhanced selectivity and flux as novel membranes for ethanol recovery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 978–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Widjojo, N.; Sukitpaneenit, P.; Teoh, M.M.; Lipscomb, G.G.; Chung, T.S.; Lai, J.Y. Evolution of polymeric hollow fibers as sustainable technologies: Past, present, and future. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 1401–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Chung, T.S. Pushing the limits of high performance dual-layer hollow fiber fabricated via I2PS process in dehydration of ethanol. AICHE J. 2013, 59, 3006–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-H.; Ma, L.-C.; Lin, G.-C.; Tsai, H.-A.; Lai, J.-Y. The effects of surface modifications on preparation and pervaporation dehydration performance of chitosan/polysulfone composite hollow-fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Ong, Y.K.; Wang, P.; Chung, T.-S. Thin-film composite tri-bore hollow fiber (TFCTbHF) membranes for isopropanol dehydration by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Ho, W.S.W. Novel reverse osmosis membranes incorporated with a hydrophilic additive for seawater desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ntim, S.A.; Mitra, S.; Sirkar, K.K. Facile fabrication of superior nanofiltration membranes from interfacially polymerized CNT-polymer composites. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S. Positively charged nanofiltration membrane formed by interfacial polymerization of 3,3′,5,5′-biphenyl tetraacyl chloride and piperazine on a poly (acrylonitrile) (PAN) support. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.W. Condensation Polymers: By Interfacial and Solution Methods; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1965; p. 561. [Google Scholar]
- Cadotte, J.E.; Petersen, R.J.; Larson, R.E.; Erickson, E.E. A new thin-film composite seawater reverse osmosis membrane. Desalination 1980, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadotte, J.E. Evolution of Composite Reverse Osmosis Membranes. In Materials Science of Synthetic Membranes; Lloyd, D.R., Ed.; ACS Symposium Seriese American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1985; Volume 269, pp. 273–294. [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy, A.; Brumlik, C.J.; Martin, C.R.; Collins, G.E. Interfacial polymerization of thin polymer films onto the surface of a microporous hollow-fiber membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 94, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.Y. Pervaporation separation of water from ethanol through polyimide composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 169, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Yu, C.H.; Lai, J.Y. Poly (tetrafluoroethylene)/PAm thin-film composite membranes via interfacial polymerization for pervaporation dehydration on an isopropanol aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.P.; Chung, T.S. Molecular design of thin film composite (TFC) hollow fiber membranes for isopropanol dehydration via pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 405–406, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Wang, J.; Tsuru, T. Application of interfacially polymerized PAm composite membranes to isopropanol dehydration: Effect of membrane pre-treatment and temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 453, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, H.A.; Chae, S.; Lin, S.; Wiesner, M.R. Synthesis and characterization of a carbon nanotube/polymer NCM for water treatment. Desalination 2011, 272, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Hwang, G.; El-Din, M.G.; Liu, Y. Development of nanosilver and multi-walled carbon nanotubes thin-film NCM for enhanced water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394–395, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizadeh, M.; Aroujalian, A.; Raisi, A. Effect of added NaX nano-zeolite into PAm as a top thin layer of membrane on water flux and salt rejection in a reverse osmosis process. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Aswal, V.K. Characterization of physical structure of silica nanoparticles encapsulated in polymeric structure of PAm films. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2008, 326, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Patel, R.; Im, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Min, B.R. Silver nanoparticles immobilized on thin film composite PAm membrane: Characterization, nanofiltration, antifouling properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2007, 18, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liao, K.; Hu, C.; Lee, K.; Lai, J. Study on characterization and pervaporation performance of Interfacially polymerized PAm thin-film composite Membranes for dehydrating tetrahydrofuran. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.W.; Kwolek, S.L. Interfacial polycondensation. II. Fundamentals of polymer formation at liquid interfaces. J. Polym. Sci. 1959, 40, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, Y.; Sooriyakumaran, R.; Miller, D.C.; Fujiwara, M.; Terui, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; McCloskey, B.D.; Freeman, B.D.; Allen, R.D. Novel thin film composite membrane containing ionizable hydrophobes: PH dependent reverse osmosis behavior and improved chlorine resistance. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4615–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.H.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Yan, Y.; Subramani, A.; Huang, X.; Hurwitz, G.; Ghosh, A.K.; Jawor, A. Interfacial polymerization of thin film nanocomposites: A new concept for reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 294, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freger, V. Nanoscale heterogeneity of PAm membranes formed by interfacial polymerization. Langmuir 2003, 19, 4791–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Sun, P.; Henry, L.L.; Sun, B. Mechanisms of structure and performance controlled thin film composite membrane formation via interfacial polymerization process. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 251, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.H. Dehydration of isopropanol by novel poly(vinyl alcohol)-silicone hybrid membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, B.V.K.; Sairam, M.; Raju, K.V.S.N.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Pervaporation separation of water+ isopropanol mixtures using novel nanocomposite membranes of poly (vinyl alcohol) and polyaniline. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 260, 142–155. [Google Scholar]
- Varghese, J.G.; Kittur, A.A.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Dehydration of THF–water mixtures using zeolite-incorporated polymeric membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2408–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairam, M.; Naidua, B.V.K.; Nataraj, S.K.; Sreedhar, B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Poly(vinylalcohol)iron oxide nanocomposite membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol,1,4-dioxane and tetrahydrofuran. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 283, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urtiaga, A.; Gorri, E.D.; Casado, C.; Ortiz, I. Pervaporative dehydration of industrial solvents using azeolite NaA commercial membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 32, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, Y.; Ghadimi, A.; Mohammadi, T. Recovery of alcohols from water using polydimethylsiloxane-silica NCMs: Characterization and pervaporation performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2871–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Chen, Y. Anti-trade-off in dehydration of ethanol by novel PVA/APTEOS hybrid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 287, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Lizon, T.; Edwards, E.; Lobiundo, G.; Freitas dos Santos, L. Dehydration of water/t-butanol mixtures by pervaporation: Comparative study of commercially available polymeric microporous silica and zeolite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 197, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Kissich, K.; Ghorpade, A.; Hannah, R.; Bhattacharyya, D. Pervaporation of alcohol-water and dimethylformamide-water mixtures using hydrophilic zeolite NaA membranes: Mechanisms and experimental results. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 179, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, H.; Asamura, H.; Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, K. Preparation and pervaporation properties of X- and Y-type zeolite membranes. In Membrane Formation and Modification; Pinnau, I., Freeman, B.D., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kulprathipanja, S.; Neuzil, R.W.; Li, N.N. Separation by Means of Mixed Matrix Membranes. U.S. Patent 4,740,219, 26 April 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Te Hennepe, H.J.C.; Smolders, C.A.; Bargeman, D.; Mulder, M.H.V. Exclusion and tortuosity effects for alcohol/water separation by zeolite filled PDMS membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1991, 26, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Q.L.; Zhu, A.M.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.H. Characterization and permeation performance of novel organic-inorganic hybrid membranes of poly(vinyl alcohol)/1,2-bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 16559–16565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Shi, B.L.; Lan, Y.Q. Preparation of PDMS-silica NCMs with silane coupling for recovering ethanol by pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Rajagopalan, R. Matrimids/MgO mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation. AIChE J. 2007, 53, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Park, S.H.; So, W.W.; Moon, S.J. Pervaporation separation of aqueous organic mixtures through sulfated zirconia-poly(vinyl alcohol) membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2001, 79, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhas, D.P.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Raghu, A.V. Mixed matrix membranes of H-ZSM5-loaded poly(vinyl alcohol) used in pervaporation dehydration of alcohols: Influence of silica/alumina ratio. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 54, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Chung, T.S. Homogeneous polyimide/cyclodextrin composite membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, T.; Mosleh, S.; Bakhtiari, O.; Mohammadi, T. Mixed matrix membranes of Matrimid 5218 loaded with zeolite 4A for pervaporation separation of water-isopropanol mixtures. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorribas, S.; Kudasheva, A.; Almendro, E. Pervaporation and membrane reactor performance of polyimide based mixed matrix membranes containing MOF HKUST-1. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 124, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, J.; Fan, H.; Ji, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z. Sonication-enhanced in situ assembly of organic/inorganic hybrid membranes: Evolution of nanoparticle distribution and pervaporation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamizawa, S.; Kachi-Terajima, C.; Kohbara, M.; Akatsuka, T.; Jin, T. Alcohol-vapor inclusion in single-crystal adsorbents [MII2 (bza)4(pyz)]n (M=Rh, Cu): Structural study and application to separation membranes. Chemistry 2007, 2, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moermans, B.; Beuckelaer, W.D.; Vankelecom, I.F.J.; Ravishankar, R.; Martens, J.A.; Jacobs, P.A. Incorporation of nano-sized zeolites in membranes. Chem. Commun. 2000, 24, 2467–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Wang, K.H.; Lai, J.Y.; Liu, Y.L. Hydrophilic chitosan-modified polybenzoimidazole membranes for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol aqueous solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.; Doonan, C.J.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Knobler, C.B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Synthesis, structure, and carbondioxide capture properties of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 43, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albo, J.; Santos, E.; Neves, L.A.; Simeonov, S.P.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Crespo, J.G.; Irabien, A. Separation performance of CO2 through supported magnetic ionic liquid membranes (SMILMs). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Tsuru, T. Thin ionic liquid membranes based on inorganic supports with different pore sizes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 8045–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gou, C.; Liu, H. Magnetically rotational reactor for absorbing benzene emissions by ionic liquids. China Particuol. 2006, 5, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, Z.X.; Fu, S.; Wu, W.; Zhu, D. Polymers containing fullerene or carbon nanotube structures. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 1079–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayan, P.M. Nanotubes from carbon. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 1787–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekker, S.; Salvetat, J.P.; Jakab, E.; Bonard, J.M.; Forro, L. Hydrogenation of carbon nanotubes and graphite in liquid ammonia. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 7938–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.; Detrembleur, C.; Sciannamea, V.; Pagnoulle, C.; Jérôme, R. Grafting of alkoxyamine end-capped (co)polymers onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Polymer 2004, 45, 6097–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauter, M.S.; Wang, Y.; Okemgbo, K.C.; Osuji, C.O.; Giannelis, E.P.; Elimelech, M. Antifouling ultrafiltration membranes via post-fabrication grafting of biocidal nanomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2011, 3, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Kang, Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Giannelis, E.P.; Huang, X.; Elimelech, M. Highly hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) ultrafiltration membranes via postfabrication grafting of surface-tailored silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2013, 5, 6694–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shameli, A.; Ameri, E. Synthesis of cross-linked PVA membranes embedded with multi-wall carbon nanotubes and their application to esterification of acetic acid with methanol. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Singha, N.R.; Ray, S.K. Removal of tetrahydrofuran (THF) from water by pervaporation using homo and blend polymeric membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Ray, S.K. Separation of toluene-methanol mixtures by pervaporation using semi-IPN polymer membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Kar, S.; Ray, S.K. Synthesis of chemically modified polyvinyl alcohol membranes for dehydration of dioxane by pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 422–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Kar, S.; Ray, S.K. Synthesis of novel polymeric membrane for separation of MTBE-methanol by pervaporation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1970–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuila, S.B.; Ray, S.K.; Das, P.; Singha, N.R. Synthesis of full interpenetrating network membranes of poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) in the matrix of polyvinyl alcohol for dehydration of ethylene glycol by pervaporation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, H.S.; Ray, S.K.; Das, P.; Singha, N.R. Separation of acid–water mixtures by pervaporation using nanoparticle filled mixed matrix copolymer membranes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Dehydration of tetrahydrofuran (THF) by pervaporation using crosslinked copolymer membranes. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2008, 47, 1620–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, N.R.; Kar, S.; Ray, S.; Ray, S.K. Separation of isopropyl alcohol–water mixtures by pervaporation using crosslink IPN membranes. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2009, 48, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, M.; Mahapatra, M.; Dutta, A.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Singha, N.R. Fabrication of semisynthetic collagenic materials for mere/synergistic adsorption: A model approach of determining dye allocation by systematic characterization and optimization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 438–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, M.; Mahapatra, M.; Singha, N.R. Separation of tetrahydrofuran using RSM optimized accelerator-sulfur-filler of rubber membranes: Systematic optimization and comprehensive mechanistic study. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 1416–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Luis, P.; Irabien, A. Absorption of coal combustion flue gases in ionic liquids using different membrane contactors. Desalination Water Treat. 2011, 27, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Irabien, A. Non-dispersive absorption of CO2 in parallel and cross-flow membrane modules using EMISE. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Luis, P.; Irabien, A. Carbon dioxide capture from flue gases using a cross-flow membrane contactor and the ionic liquid 1-Ethyl-3-methylimidazolium ethylsulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 11045–11051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norkobilov, A.; Gorri, D.; Ortiz, I. Process flowsheet analysis of pervaporation-based hybrid processes in the production of ethyl tert-butyl ether. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkovich, A.L.Y.; Zilka, J.L.; Jimenez, D.M.; Roberts, G.L.; Cox, J.L. Experimental investigations of inorganic membrane reactors: A distributed feed approach for partial oxidation reactions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandra, A.M.; Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.H.; Moser, W.R.; Dixon, A.G. Oxidative coupling of methane in porous Vycor membrane reactors. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 116, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, T.; Fujimoto, K. Oxide ion transport for selective oxidative coupling of methane with new membrane reactor. AICHE J. 1994, 40, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hidajat, K.; Ching, C. Oxidative coupling of methane in a solid oxide membrane reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 3576–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Dixon, A.G.; Moser, W.R.; Ma, Y.; Balachandran, U. Oxygen permeable dense membrane reactor for the oxidative coupling of methane. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 170, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, Y.S.; Won, J. Silver polymer electrolyte membranes for facilitated olefint transport: Carrier properties, transport mechanism and separation performance. Macromol. Res. 2004, 12, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapteijn, F.; Bakker, W.J.W.; Zheng, G.; Poppe, J.; Moulijn, J.A. Permeation and separation of light hydrocarbons through a silicalite-1 membrane: Application of the generalized Maxwell-Stefan equations. Chem. Eng. J. BioChem. Eng. J. 1995, 57, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlhorn, R.J.R.; Keizer, K.; Burggraaf, A.J. Gas transport and separation with ceramic membranes. Part II. Synthesis and separation properties of microporous membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 66, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanchi, M.T.; Kaghazchi, T.; Kargari, A. Application of membrane separation processes in petrochemical industry: A review. Desalination 2009, 235, 199–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.J.; Boerrigter, M.; Koops, G.H. Polymeric hollow fiber gas separation embranes: Preparation and the suppression of plasticization in propane/propylene environments. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 184, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falbo, F.; Tasselli, F.; Brunetti, A.; Drioli, E.; Barbieri, G. Polyimide hollow fiber membranes for CO2 separation from wet gas mixtures. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 102–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esche, E.; Müller, D.; Song, S.; Wozny, G. Optimization during the process synthesis: Enabling the oxidative coupling of methane by minimizing the energy required for the carbon dioxide removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stünkel, S. Kohlendioxid-Abtrennung in der Gasaufbereitung des Prozesses der Oxidativen Kupplung von Methan. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Esche, E.; Stünkel, S.; Brinkmann, T.; Wind, J.; Shishatskiy, S.; Wozny, G. Energy, equipment and cost savings by using a membrane unit in an amine-based absorption process for CO2 removal. Chem. Ing. Technik 2013, 85, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B. Pervaporation membrane reactors. Compr. Membr. Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 135–163. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, A.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E.; Lee, K.; Sea, B.; Lee, D. WGS reaction in a membrane reactor using a porous stainless steel supported silica membrane. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2007, 46, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Drioli, E.; Santella, F.; Violante, V.; Capannelli, G.; Vitulli, G. A study on catalytic membrane reactors for water gas shift reaction. Gas Sep. Purif. 1996, 10, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, G.; Brunetti, A.; Granato, T.; Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E. Engineering evaluations of a catalytic membrane reactor for the water gas shift reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 7676–7683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, A.; Barbieri, G.; Drioli, E.; Granato, T.; Lee, K. A porous stainless steel supported silica membrane for WGS reaction in a catalytic membrane reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 5621–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcliffe, A.J.; Singh, R.P.; Berchtold, K.A.; Lima, F.V. Modeling and optimization of high-performance polymer membrane reactor systems for water–gas shift reaction applications. Processes 2016, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelo, C.A.; David, L.F.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar]
- Barbir, F. PEM electrolysis for production of hydrogen from renewable energy sources. Sol. Energy 2005, 78, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Van Wagner, E.; Freeman, B.D.; Toy, L.G.; Gupta, R.P. Plasticization-enhanced hydrogen purification using polymeric membranes. Science 2006, 311, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.L.; Ting, B.; Shung, T.; Greenberg, A.R. Polymeric membranes for the hydrogen economy: Contemporary approaches and prospects for the future. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, S.; Noruzi, A.; Babaluo, A.A.; Haghighi, M. Performance of Pd composite membrane prepared by organic–inorganic method in WGS membrane reactor. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Figoli, A.; Khayet, M. Pervaporation, Vapour Permeation and Membrane Distillation: Principles and Applications; Woodhead Publishing in Elsevier: Kidlington, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Nagase, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kiyozumi, Y.; Sato, K.; Nishioka, M.; Hamakawa, S.; Mizukami, F. Stoichiometric Ester Condensation Reaction Processes by PervaporativeWater Removal via Acid-Tolerant Zeolite Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 3743–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziobrowski, Z.; Kiss, K.; Rotkegel, A.; Nemest Othy, N.; Krupiczka, R.; Gubicza, L. Pervaporation aided enzymatic production of glycerol monostearate in organic solvents. Desalination 2009, 241, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, B.; Ameri, E. Methyl acetate production by coupled esterification-reaction process using synthesized cross-linked PVA/silica NCMs. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 288, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkova, A.; Polotskaya, G.; Toikka, A. Pervaporation composite membranes for ethyl acetate production. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2015, 87, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M.; Phillip, W.A. The future of seawater desalination: Energy, technology, and the environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.J. Worldwide water crisis. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 313, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korngold, E.; Korin, E.; Ladizhensky, I. Water desalination by pervaporation with hollow fiber membranes. Desalination 1996, 107, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwijnenberg, H.J.; Koops, G.H.; Wessling, M. Solar driven membrane pervaporation for desalination processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 250, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korin, E.; Ladizhensky, I.; Korngold, E. Hydrophilic hollow fiber membranes for water desalination by the pervaporation method. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 1996, 35, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.H.; Oh, K.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Yeo, J.G.; Sharma, P. Pervaporative seawater desalination using NaA zeolite membrane: Mechanisms of high water flux and high salt rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.P.; Kruchinina, E.V.; Baklagina, Y.G.; Khripunov, A.K.; Tulupova, O.A. Deep desalination of water by evaporation through polymeric membranes. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2007, 80, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.; Hoang, M.; Xie, Z. Pervaporation- a further low energy desalination option? Water AWA 2010, 37, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Hoang, M.; Duong, T.; Ng, D.; Dao, B.; Gray, S. Sol-gel derived poly(vinyl alcohol)/maleic acid/silica hybrid membrane for desalination by pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, B.; Pan, K.; Li, L.; Giannelis, E.P.; Cao, B. High performance hydrophilic pervaporation composite membranes for water desalination. Desalination 2014, 347, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Shen, L.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Robust construction of graphene oxide barrier layer on nanofibrous substrate assisted by flexible poly(vinylalcohol) for efficient pervaporation desalination. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3558–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, F.; Cote, L.J.; Huang, J.X. Graphene oxide: Surface activity and two-dimensional assembly. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1954–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, I.; Zor, E.; Bingol, H.; Ersoz, M. Green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline composite and its application for salt rejection by polysulfone-based composite membranes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 5707–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.P.; Paul, D.R.; Chung, T.S. Free-standing graphene oxide thin films assembled by a pressurized UF method for dehydration of ethanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 458, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhan, W.; Qi, G.; Lin, S.; Nan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cao, B.; Pan, K. High performance graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile composite pervaporation membranes for desalination applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5140–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhri, S.G.; Rajai, B.H.; Singh, P.S. Nanoscale homogeneity of silica-poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes by controlled cross-linking via sol-gel reaction in acidified and hydrated ethanol. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65862–65869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Xu, K.; Huang, A. Synthesis of graphene oxide/polyimide mixed matrix membranes for desalination. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Ng, D.; Hoang, M.; Duong, T.; Gray, S. Separation of aqueous salt solution by pervaporation through hybrid organic-inorganic membrane: Effect of operating conditions. Desalination 2011, 273, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, F.C.; Seip, H.M. Acid rain in Europe and the United States: An update. Environ. Sci. Policy 2004, 7, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Carmichael, G.R.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wei, C.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Tan, Q. Sulfur dioxide emissions in China and sulfur trends in East Asia since 2000. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6311–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia, Z.; Jalali, A.M.; Taromi, F.A. Molecular dynamics simulations on desulfurization of n-octane/thiophene mixture using silica filled polydimethylsiloxane NCMs. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 24, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Suzuki, T.; Takahashi, N.; Yokota, K.; Sugiura, M. Effect of the addition of transition metals to Pt/Ba/Al2O3 catalyst on the NOx storage-reduction catalysis under oxidizing conditions in the presence of SO2. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2001, 30, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, I.V.; Moulijn, J.A. Science and technology of novel processes for deep desulfurization of oil refinery streams: A review. Fuel 2003, 82, 607–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, S.; Mey, D.; Perot, G.; Bouchy, C.; Diehl, F. On the hydrodesulfurization of FCC gasoline: A review. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 278, 143–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fihri, A.; Mahfouz, R.; Shahrani, A.; Taie, I.; Alabedi, G. Pervaporative desulfurization of gasoline: A review. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 107, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.G.; Kong, Y.; Wang, G.; Qu, H.M.; Yang, E.R.; Shi, D.Q. Selection and crosslinking modification of membrane material for FCC gasoline desulfurization. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 285, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Lin, L.; Yang, J.; Shi, D.; Qu, H.; Xie, K.; Li, L. FCC gasoline desulfurization by pervaporation: Effects of gasoline components. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 293, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlewska, K.; Konieczny, K. Pervaporative desulfurization of gasoline—Separation of hydrocarbon/thiophene mixtures using polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based membranes. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 57, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, X.; Wua, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Z. Enhanced pervaporative desulfurization by polydimethylsiloxane membranes embedded with silver/silica core–shell microspheres. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, W.; Cao, R.; Wu, H. Efficient desulfurization by polymer–inorganic NCMs fabricated in reverse microemulsion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211–212, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J.; Pan, F.; Cao, X.; Wang, B.; Yang, J. Polydimethylsiloxane–graphene nanosheets hybrid membranes with enhanced pervaporative desulfurization performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
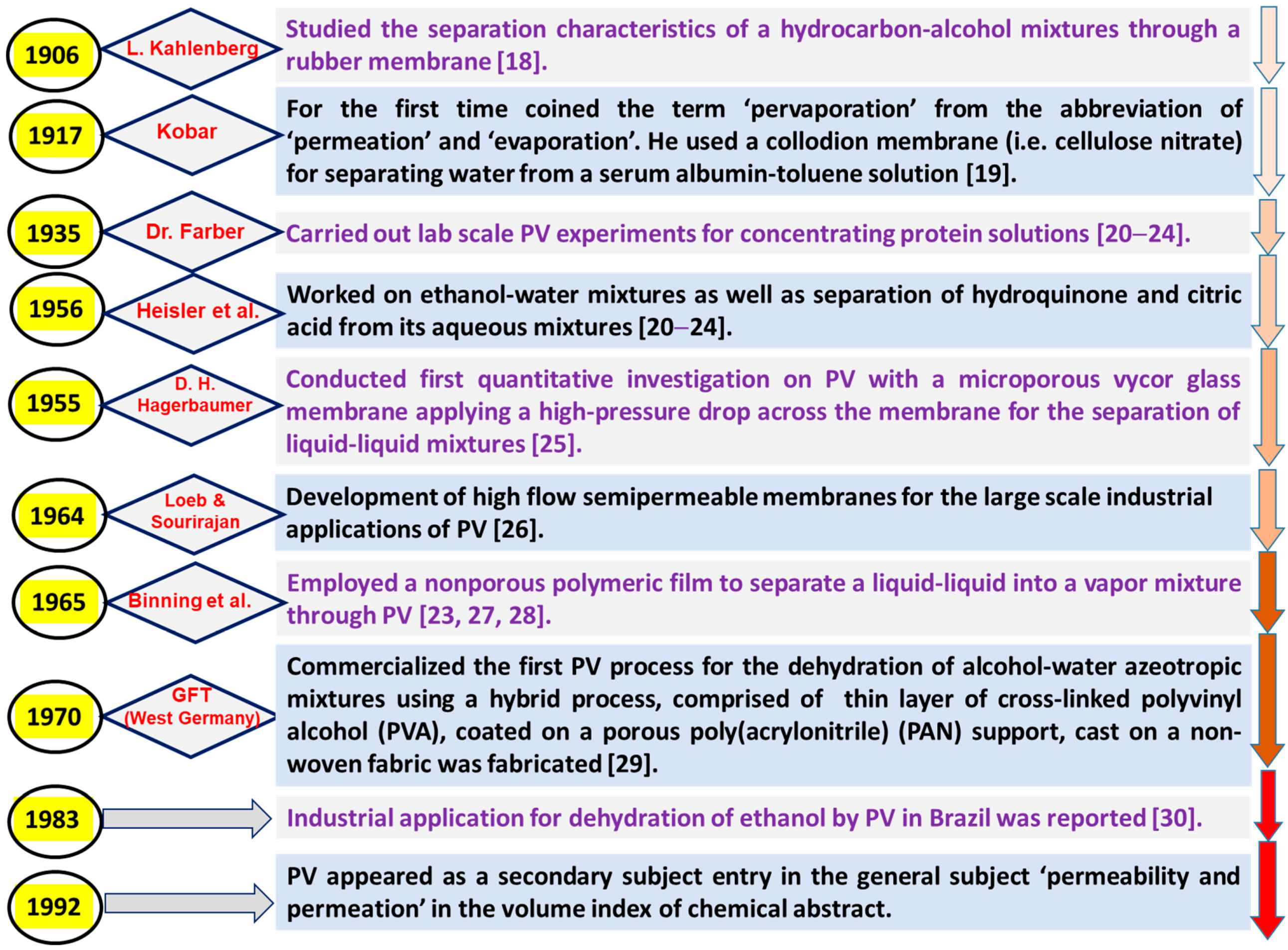








| Organic Polymers | Inorganic NPs/Mesh Size | Amount of Organic Polymer Used (wt %) | Amount of Inorganic Nanocomposite Used (wt %) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSf | ZrO2/~1.00 μm | 18 | 0–90 | [285] |
| Poly(amic acid) | TEOS/7–20 nm | 61–79 | 39–21 | [290] |
| EVA | 12Me-MMT | - | - | [291] |
| EAA | MMT | 5 g/200 mL | 2 | [292] |
| PVC | Na-MMT | 10 g | 0.2 g | [293] |
| PVC | OMMT | 10 g | 0.2 g | [293] |
| PVC | MMT | - | 1–25 phr | [294] |
| PVC | Na-MMT | - | 1–25 phr | [294] |
| PVC | OMMT | - | 1–25 phr | [294] |
| EVA | 12Me-MMT | - | 0–6 | [295] |
| CA | Alumina | 10 | 50 | [286] |
| Organic Polymer Used | NP Used | Thickness (μm) | Utility | TF (g m−2 h−1)/Temperature (K)/Feed (wt %) | SF/Permeability | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE a | PA b | – | PV c (IPA d/H2O) | 1720 ± 150/343/70:30 (IPA/H2O)/– | 177 (IPA/H2O)/– | [313] |
| PVA e | APTEOS hybrid f | 18 | PV (IPA/H2O) | 26.5/303/90:10 (IPA/H2O)/– | 1580 (H2O/IPA)/– | [327] |
| PVA | Zeolite | – | PV (IPA/H2O) | 3.2/303/90:10 (IPA/H2O)/– | 216 (H2O/IPA)/– | [328] |
| CS g | Zeolite | 40 | PV (THF h/H2O) | 170/303/95:5 (THF/H2O)/– | 2140 (THF/H2O)/– | [329] |
| PVA | 1.5 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (IPA/H2O) | 95/303/90:10 (IPA/H2O)/– | 122 (H2O/IPA)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 3.0 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (IPA/H2O) | 82/303/90:10 (IPA/H2O)/– | 143 (H2O/IPA)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 4.5 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (IPA/H2O) | 79/303/90:10 (IPA/H2O)/– | 470 (H2O/IPA)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 1.5 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (DO j/H2O) | 98/303/90:10 (DO/H2O)/– | 82 (H2O/DO)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 3.0 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (DO/H2O) | 91/303/90:10 (DO/H2O)/– | 104 (H2O/DO)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 4.5 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (DO/H2O) | 84/303/90:10 (DO/H2O)/– | 144 (H2O/DO)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 1.5 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (THF/H2O) | 180/303/90:10 (THF/H2O)/– | 342 (H2O/THF)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 3.0 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (THF/H2O) | 139/303/90:10 (THF/H2O)/– | 421 (H2O/THF)/– | [330] |
| PVA | 4.5 wt % FeO | 45 | PV (THF/H2O) | 95/303/90:10 (THF/H2O)/– | 519 (H2O/THF)/– | [330] |
| Ceramic | Zeolite NaA k | 8 | PV (THF/H2O) | 430/318/93:7 (THF/H2O)/– | 1240 (H2O/THF)/– | [331] |
| Ceramic | Zeolite NaA k | 8 | PV (AC l/H2O) | 130/313/97:3 (AC/H2O)/– | 50 (H2O/AC)/– | [331] |
| PVA | 0.5 wt % CNT(CS) m | 80 | PV (benzene/cyclohexane) | 53.0 ± 0.5/323/50/50 (wt/wt) (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | 23.1 ± 0.4 (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | [259] |
| PVA | 1.0 wt % CNT(CS) | 80 | PV (benzene/cyclohexane) | 60.8 ± 0.6/323/50/50 (wt/wt) (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | 30.4 ± 0.8 (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | [259] |
| PVA | 1.5 wt % CNT(CS) | 80 | PV (benzene/cyclohexane) | 67.3 ± 1.0/323/50/50 (wt/wt) (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | 37.6 ± 0.5 (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | [259] |
| PVA | 2.0 wt % CNT(CS) | 80 | PV (benzene/cyclohexane) | 65.9 ± 1.2/323/50/50 (wt/wt) (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | 53.4 ± 0.4 (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | [259] |
| PVA | 2.5 wt % CNT(CS) | 80 | PV (benzene/cyclohexane) | 58.9 ± 0.9/323/50/50 (wt/wt) (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | 46.4 ± 0.7 (benzene/cyclohexane)/– | [259] |
| Polymeric Network | Inorganic Nanocomposite | Flux (g m−2 h−1)/SF(–)(x/y)/Temperature (K) | Feed Composition (wt %/wt %) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDMS a | TMS-H-silica b | 135/33 (IPA c/H2O)/298 | IPA/H2O (4/96) | [332] |
| PDMS | TMS-H-silica | 405/32 (IPA/H2O)/323 | IPA/H2O (4/96) | [332] |
| PDMS | TMS-H-silica | 117/28 (EtOH/H2O)/303 | EtOH/H2O (4/96) | [332] |
| PDMS | TMS-H-silica | 329/26 (EtOH/H2O)/323 | EtOH/H2O (4/96) | [332] |
| CS e | 3 wt % Silica | 450/639 (EtOH/H2O)/343 | EtOH/H2O (90/10) | [153] |
| CS | 5 wt % Silica | 410/919 (EtOH/H2O)/343 | EtOH/H2O (90/10) | [153] |
| CS | 10 wt % Silica | 450/735 (EtOH/H2O)/343 | EtOH/H2O (90/10) | [153] |
| CS | 20 wt % Silica | 320/919 (EtOH/H2O)/343 | EtOH/H2O (90/10) | [153] |
| CS | 30 wt % Silica | 410/1102 (EtOH/H2O)/343 | EtOH/H2O (90/10) | [153] |
| PVA f | APTEOS g | 35.5/537/(H2O/EtOH)/323 | EtOH/H2O (85/15) | [333] |
| PVA | BTEE h | 227/70 (H2O/EtOH)/323 | EtOH/H2O (85/15) | [339] |
| P84 co-polyimide i | Zeolite-5A | 40/4200 (H2O/IPA c)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [123] |
| PVA f | KA zeolites j | 179/410 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [272] |
| PVA | NaA zeolites k | 140/1170 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [272] |
| PVA | CaA zeolites l | 157/1170 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [272] |
| PVA | NaX zeolites | 170/516 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [272] |
| PVA | KA zeolites j | 179/410 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (80/20) | [272] |
| PVA | NaA zeolites k | 183/328 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (80/20) | [272] |
| PVA | CaA zeolites l | 190/233 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (80/20) | [272] |
| PVA | NaX zeolites | 216/233 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (80/20) | [272] |
| P84 co-polyimide i | Zeolite-13X | 110/2700 (H2O/IPA)/333 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [274] |
| PBI m | ZIF-8 n | 103/1686 (H2O/IPA)/333 | IPA/H2O (85/15) | [146] |
| PBI | ZIF-8 | 81/341.7 (H2O/n-BuOH)/333 | n-BuOH/H2O (85/15) | [146] |
| PBI | ZIF-8 | 992/10 (H2O/EtOH)/333 | EtOH/H2O (85/15) | [146] |
| PVA f | 5 wt % ZIF-8 | 868/132 (H2O/IPA)/303 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [275] |
| PVA | 7.5 wt % ZIF-8 | 952/91 (H2O/IPA)/293 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [275] |
| PDMS a | Fumed silica (A200) | 200/19 (EtOH/H2O)/313 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [340] |
| PDMS | Fumed silica | –/7 (EtOH/H2O)/313 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [340] |
| PDMS | Carbon black | –/7 (EtOH/H2O)/308 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [340] |
| PDMS | Zeolite Y | 750/5 (EtOH/H2O)/308 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [340] |
| PDMS | Silicalite-1 o | 51/17 (EtOH/H2O)/295.5 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [340] |
| Matrimid p | MgO | 4500/1800 (H2O/IPA c)/373 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [341] |
| PVA | PMA q | 36/29991 (IPA/H2O)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [273] |
| PVA | Silicalite-1 o | 69/2241 (IPA/H2O)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [273] |
| PVA | Sulfated zirconia | 183/86 (H2O/EtOH)/323 | EtOH/H2O (80/20) | [342] |
| PVA | H-ZSM5 r | 182/46 (H2O/EtOH)/323 | EtOH/H2O (85/15) | [343] |
| Matrimid p | Cyclodextrin | 50/>5000 (H2O/IPA c)/323 | IPA/H2O (86/14) | [344] |
| Matrimid | Zeolite-4A | 21/>5000 (H2O/IPA)/303 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [345] |
| Matrimid | Cu3(BTC)2 s | 400/245 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [346] |
| Polyimide t | Zeolite-13X | 150/272 (H2O/IPA)/323 | IPA/H2O (90/10) | [276] |
| NaCMC u/PVA f | Zeolite-13X | 121/5118 (H2O/EtOH)/308 | EtOH/H2O (90/10) | [277] |
| PDMS a | SiO2 | 807/13 (H2O/EtOH)/333 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [347] |
| PDMS | ZIF-8 n | 1229/10 (H2O/EtOH)/333 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [347] |
| PDMS | SiO2 | 1693/9 (H2O/n-BuOH)/333 | n-BuOH/H2O (5/95) | [347] |
| PDMS | ZIF-8 n | 1743/30 (H2O/n-BuOH)/333 | n-BuOH/H2O (5/95) | [347] |
| PDMS | PZSNTs v | –/10 (EtOH/H2O)/313 | EtOH/H2O (10/90) | [222] |
| PDMS | [CuII2(bza)4(pyz)]n | 23/2 (EtOH/H2O)/308 | EtOH/H2O (5/95) | [348] |
| PDMS | Silicalite-1 o | –/16 (EtOH/H2O)/308 | EtOH/H2O (6/94) | [349] |
| CS e | IDD w | 184/125 (IPA/H2O)//298 | IPA/H2O (70/30) | [350] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roy, S.; Singha, N.R. Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Next Generation Pervaporation Process: Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects. Membranes 2017, 7, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7030053
Roy S, Singha NR. Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Next Generation Pervaporation Process: Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects. Membranes. 2017; 7(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoy, Sagar, and Nayan Ranjan Singha. 2017. "Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Next Generation Pervaporation Process: Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects" Membranes 7, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7030053
APA StyleRoy, S., & Singha, N. R. (2017). Polymeric Nanocomposite Membranes for Next Generation Pervaporation Process: Strategies, Challenges and Future Prospects. Membranes, 7(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes7030053






