Process Simulation and Cost Evaluation of Carbon Membranes for CO2 Removal from High-Pressure Natural Gas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Process Design
2.2. Simulation Basis
2.3. Cost Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Feed Pressure Influence with 10% CO2 Feed
3.2. Permeate Pressure Influence with 50% CO2 Feed
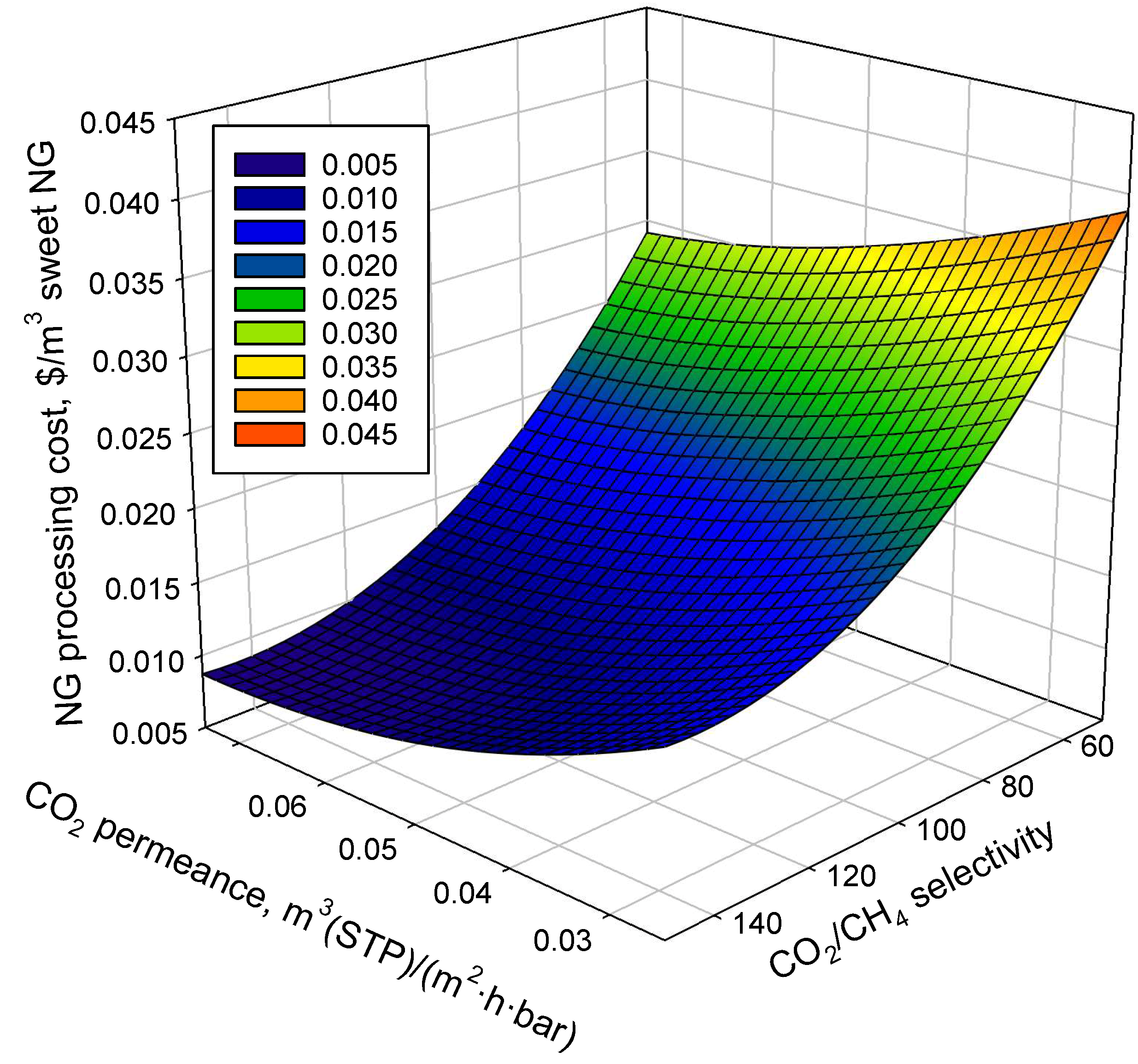
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Membrane Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leather, D.T.B.; Bahadori, A.; Nwaoha, C.; Wood, D.A. A review of Australia’s natural gas resources and their exploitation. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2013, 10, 68–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economides, M.J.; Wood, D.A. The state of natural gas. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2009, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidnay, A.J.; Parrish, W. Fundamentals of Natural Gas Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; p. 434. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue, M.; Rizzo, C.; Onorati, N.B.; Gambarotta, E.F.; Carati, A.; Bazzano, F. Regenerability of zeolites as adsorbents for natural gas sweetening: A case-study. Fuel 2012, 93, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, B.; Doman, D. Flow Regulated Pressure Swing Adsorption System. U.S. Patent 6063161, 16 May 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Molecular Gate® Adsorption Technology. Available online: http://www.moleculargate.com/ (accessed on 28 February 2018).
- George, G.; Bhoria, N.; AlHallaq, S.; Abdala, A.; Mittal, V. Polymer membranes for acid gas removal from natural gas. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 158, 333–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favvas, E.P.; Katsaros, F.K.; Papageorgiou, S.K.; Sapalidis, A.A.; Mitropoulos, A.C. A review of the latest development of polyimide based membranes for CO2 separations. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 120, 104–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, P.; Drioli, E. Membrane gas separation progresses for process intensification strategy in the petrochemical industry. Pet. Chem. 2010, 50, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Kim, T.-J.; Hägg, M.-B. Hybrid fixed-site-carrier membranes for CO2 removal from high pressure natural gas: Membrane optimization and process condition investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yu, Q.; Hägg, M.-B. CO2 Capture. In Encyclopedia of Membrane Science and Technology; Hoek, E.M.V., Tarabara, V.V., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Favvas, E.P.; Romanos, G.E.; Papageorgiou, S.K.; Katsaros, F.K.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. A methodology for the morphological and physicochemical characterisation of asymmetric carbon hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favvas, E.P.; Kapantaidakis, G.C.; Nolan, J.W.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Preparation, characterization and gas permeation properties of carbon hollow fiber membranes based on Matrimid(R) 5218 precursor. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 186, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Lindbråthen, A.; Lie, J.A.; Andersen, I.C.T.; Hägg, M.-B. CO2 separation with carbon membranes in high pressure and elevated temperature applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungta, M.; Wenz, G.B.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Qiu, W.; Adams, J.S.; Koros, W.J. Carbon molecular sieve structure development and membrane performance relationships. Carbon 2017, 115, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lie, J.A.; Sheridan, E.; Hagg, M.-B. Preparation and characterization of hollow fiber carbon membranes from cellulose acetate precursors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chu, Y.; Lindbråthen, A.; Hillestad, M.; Hägg, M.-B. Carbon molecular sieve membranes for biogas upgrading: Techno-economic feasibility analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, Y.; Chung, T.-S.; Kawi, S. Facilitated transport by hybrid POSS®–Matrimid®–Zn2+ nanocomposite membranes for the separation of natural gas. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 356, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, B.D.; Stern, S.A. Membrane processes for the removal of acid gases from natural gas. I. Process configurations and optimization of operating conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 81, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, B.D.; Stern, S.A. Membrane processes for the removal of acid gases from natural gas. II. Effects of operating conditions, economic parameters, and membrane properties. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 81, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, L.; Hussain, A.; Follmann, M.; Melin, T.; Hägg, M.B. CO2 removal from natural gas by employing amine absorption and membrane technology—A technical and economical analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Rice, P.A.; Stern, S.A. Upgrading low-quality natural gas with H2S- and CO2-selective polymer membranes: Part I. Process design and economics of membrane stages without recycle streams. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 209, 177–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Lau, K.K.; Shariff, A.M.; Murshid, G. Process simulation and optimal design of membrane separation system for CO2 capture from natural gas. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 36, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hägg, M.-B.; Kim, T.-J. Hybrid FSC membrane for CO2 removal from natural gas: Experimental, process simulation, and economic feasibility analysis. AlChE J. 2014, 60, 4174–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, D. Development of Carbon Membranes for Hydrogen Recovery; Norwegian University of Science and Technology: Trondheim, Norway, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Turton, R.; Bailie, R.C.; Whiting, W.B.; Shaeiwitz, J.A.; Bhattacharyya, D. Analysis, Synthesis, and Design of Chemical Processes, 4th ed.; Pearson Education: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- He, X. Techno-economic feasibility analysis on carbon membranes for hydrogen purification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Feed flow, m3(STP)/h | 50,000 |
| Feed gas composition | Table 2 |
| Feed/permeate pressure, bar | Table 2 |
| Feed temperature, °C | 30 |
| CO2 permeance, m3(STP)/(m2·h·bar) * | |
| CO2/CH4 selectivity * | |
| CH4 purity, vol.% | >98 |
| CH4 loss, % | <2 |
| Membrane area, m2 | Adjusted |
| Scenario | Feed Gas Composition, vol.% | Feed Pressure (pF), bar | Permeate Pressure (pP), bar | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | Methane | First Stage | Second Stage | ||
| Case 1 | 10 | 90 | 50–90 | 1 | 1 |
| Case 2 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 1 | 1–5 |
| Feed Pressure, Bar | Membrane Area, m2 | Power Demand, kW | CRC, $ | OPEX, $ | CS, $/m3 Sweet NG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 1.19 × 105 | 1109 | 4.00 × 106 | 3.55 × 105 | 1.278 × 10−2 |
| 60 | 1.06 × 105 | 1154 | 3.78 × 106 | 3.69 × 105 | 1.219 × 10−2 |
| 70 | 9.46 × 104 | 1180 | 3.58 × 106 | 3.78 × 105 | 1.162 × 10−2 |
| 80 | 8.94 × 104 | 1238 | 3.54 × 106 | 3.96 × 105 | 1.156 × 10−2 |
| 90 | 8.27 × 104 | 1256 | 3.42 × 106 | 4.02 × 105 | 1.122 × 10−2 |
| Parameters | Carbon Membrane in this Work | FSC Membranes [24] |
|---|---|---|
| Feed pressure, bar | 50 | 20 |
| Second-stage permeate pressure, bar | 1–5 | 1 |
| CH4 purity in sweet NG, vol.% | 98 | 96.08 |
| CH4 loss, % | 2 | 0.35 |
| Specific power consumption, kWh/Nm3 sweet NG | 0.1 | 2.43 × 10−2 |
| Specific membrane area, m2/Nm3 sweet NG | 9.90 | 0.56 |
| CS, $/Nm3 sweet NG | 4.33 × 10−2 * | 4.22 × 10−3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, Y.; He, X. Process Simulation and Cost Evaluation of Carbon Membranes for CO2 Removal from High-Pressure Natural Gas. Membranes 2018, 8, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040118
Chu Y, He X. Process Simulation and Cost Evaluation of Carbon Membranes for CO2 Removal from High-Pressure Natural Gas. Membranes. 2018; 8(4):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040118
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Yunhan, and Xuezhong He. 2018. "Process Simulation and Cost Evaluation of Carbon Membranes for CO2 Removal from High-Pressure Natural Gas" Membranes 8, no. 4: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040118
APA StyleChu, Y., & He, X. (2018). Process Simulation and Cost Evaluation of Carbon Membranes for CO2 Removal from High-Pressure Natural Gas. Membranes, 8(4), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040118





