Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Polyamide Membrane Structures and RO/FO Water Permeation Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Polyamide Model and Simulation Methods
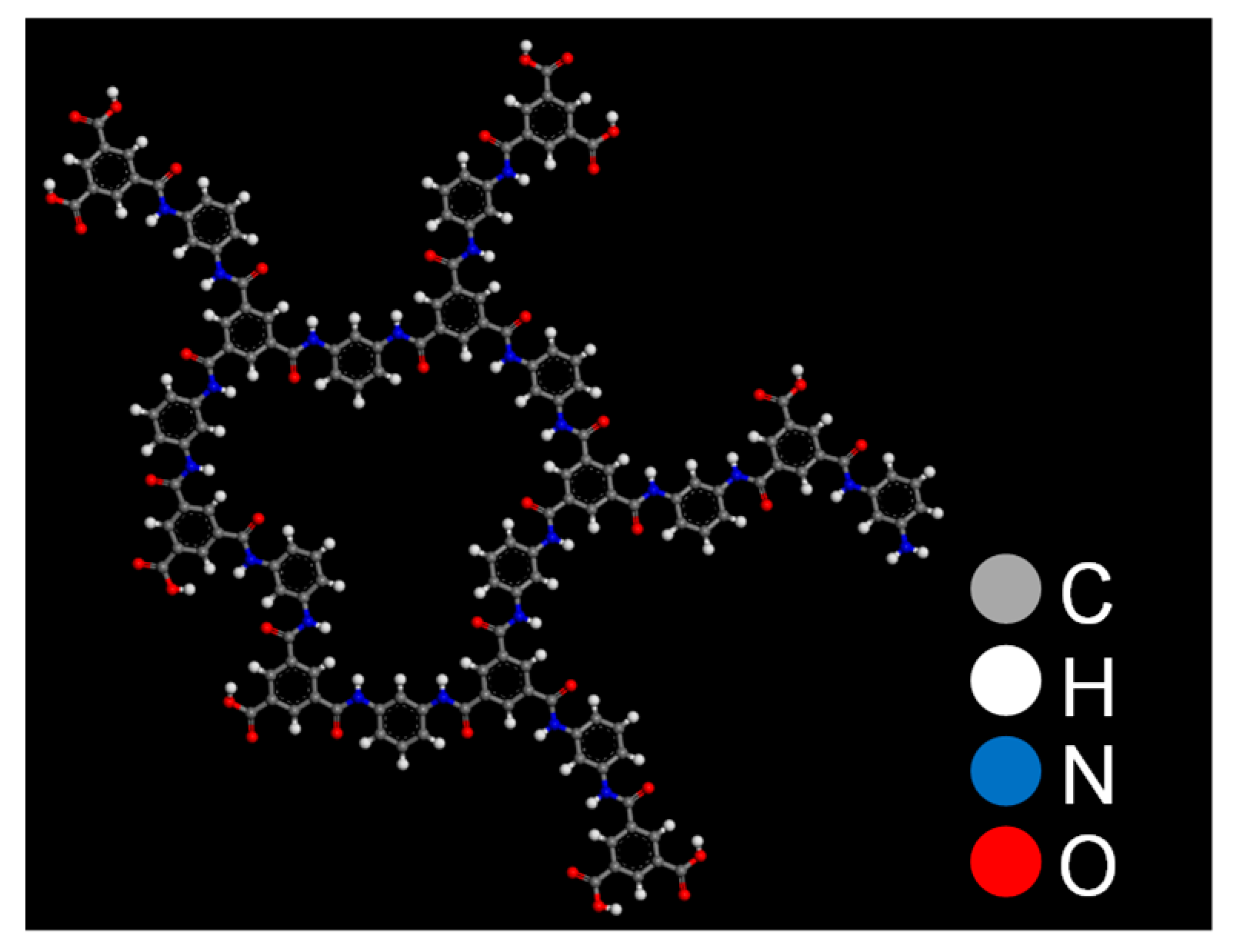
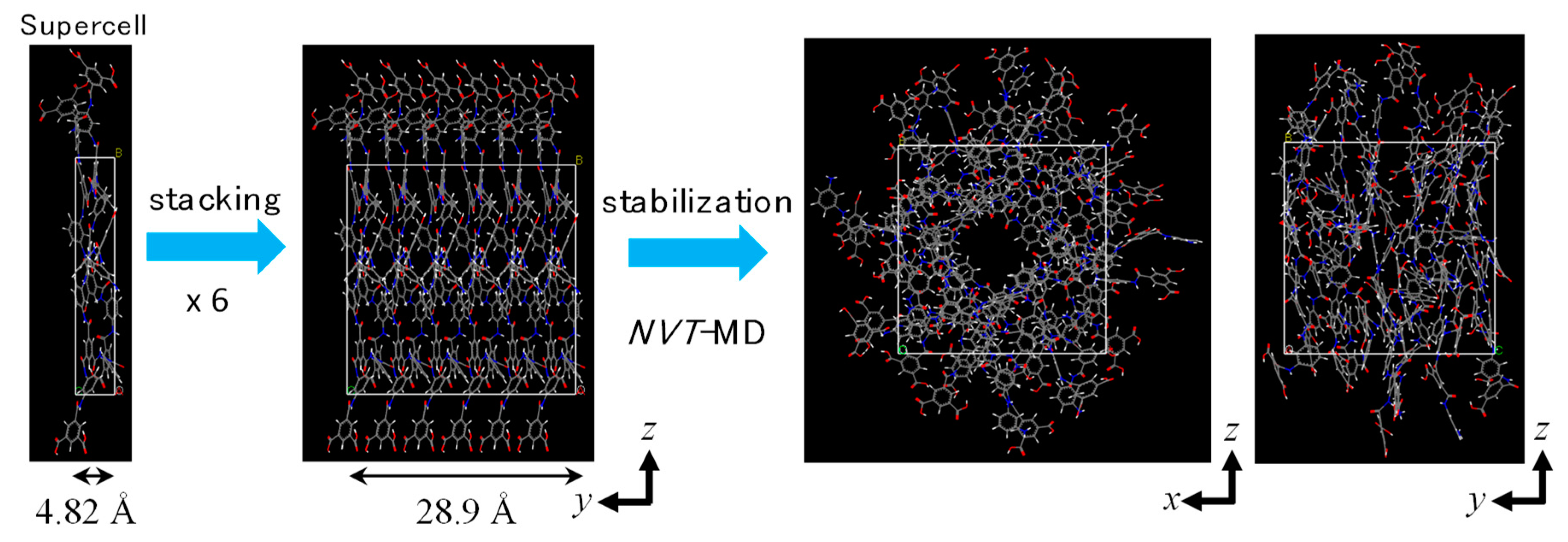
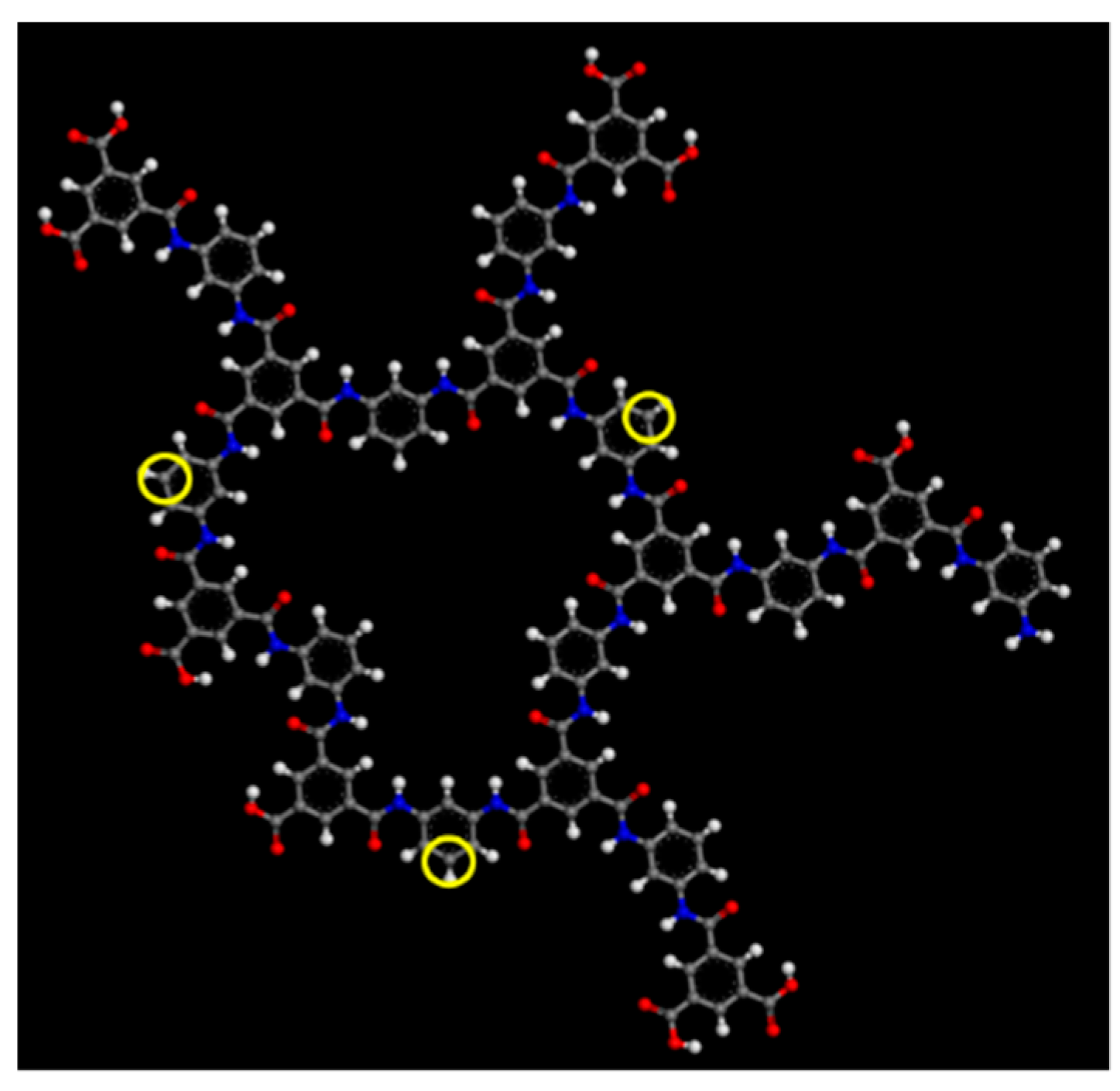
2.1. Polyamide Membrane Model
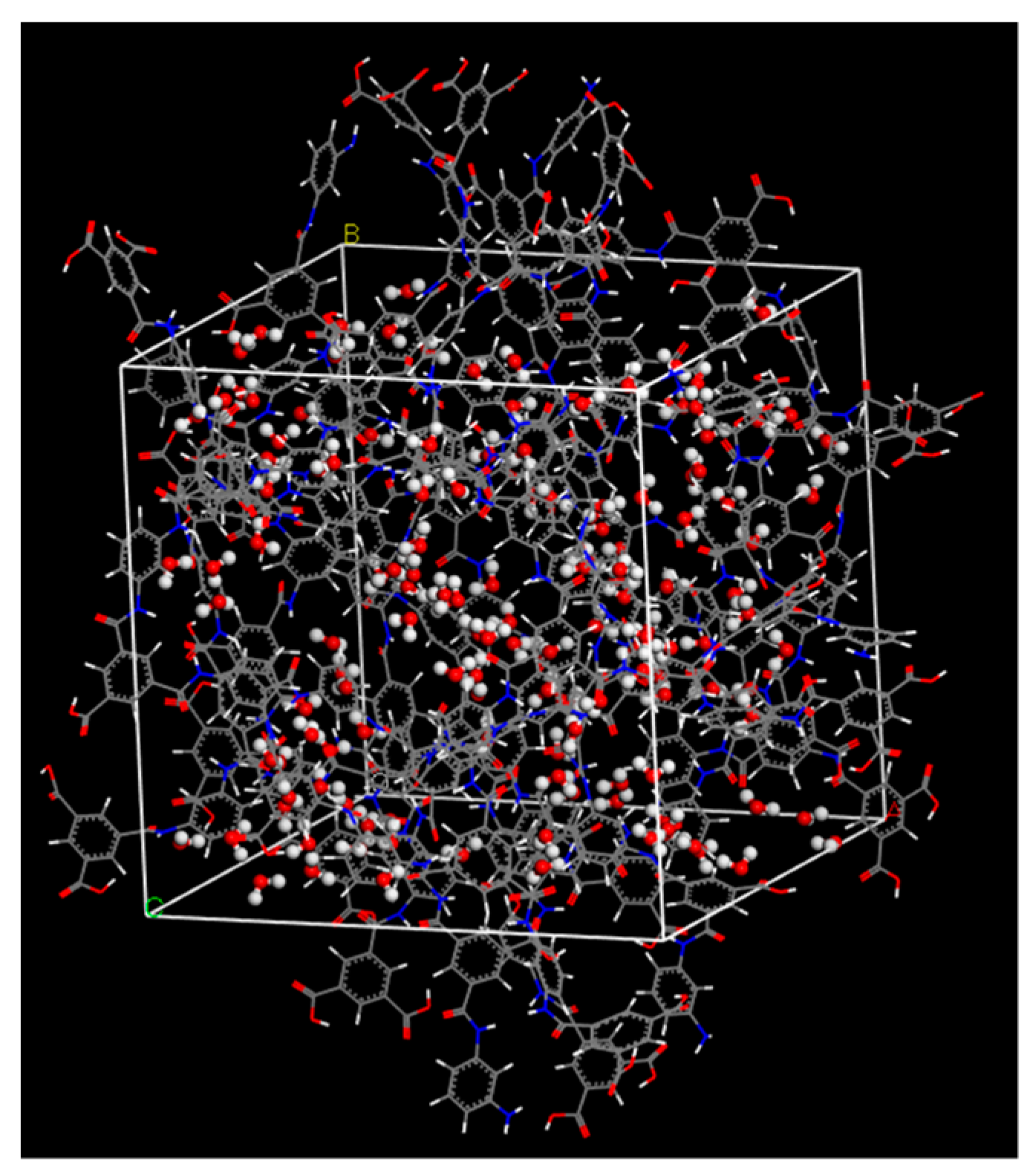
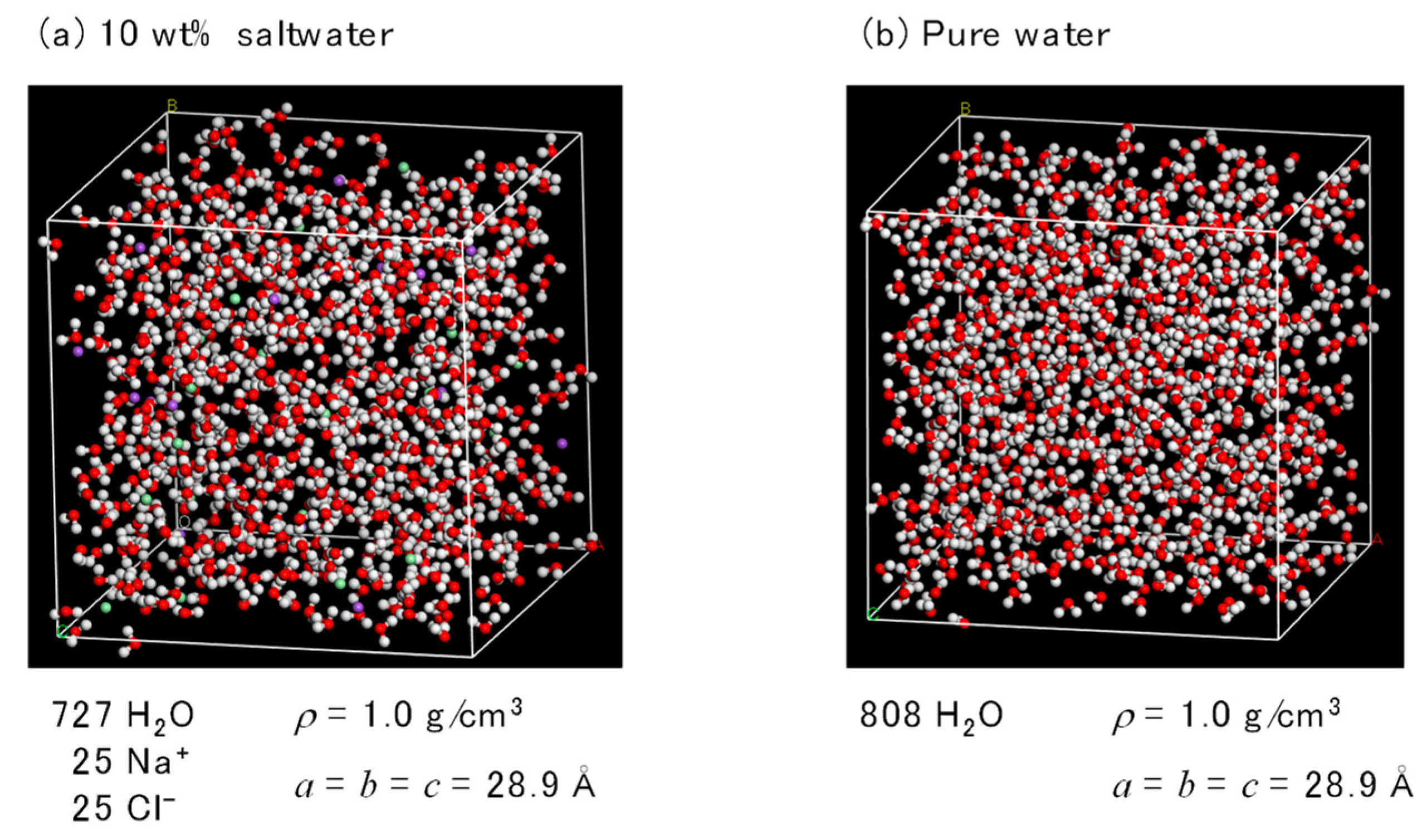
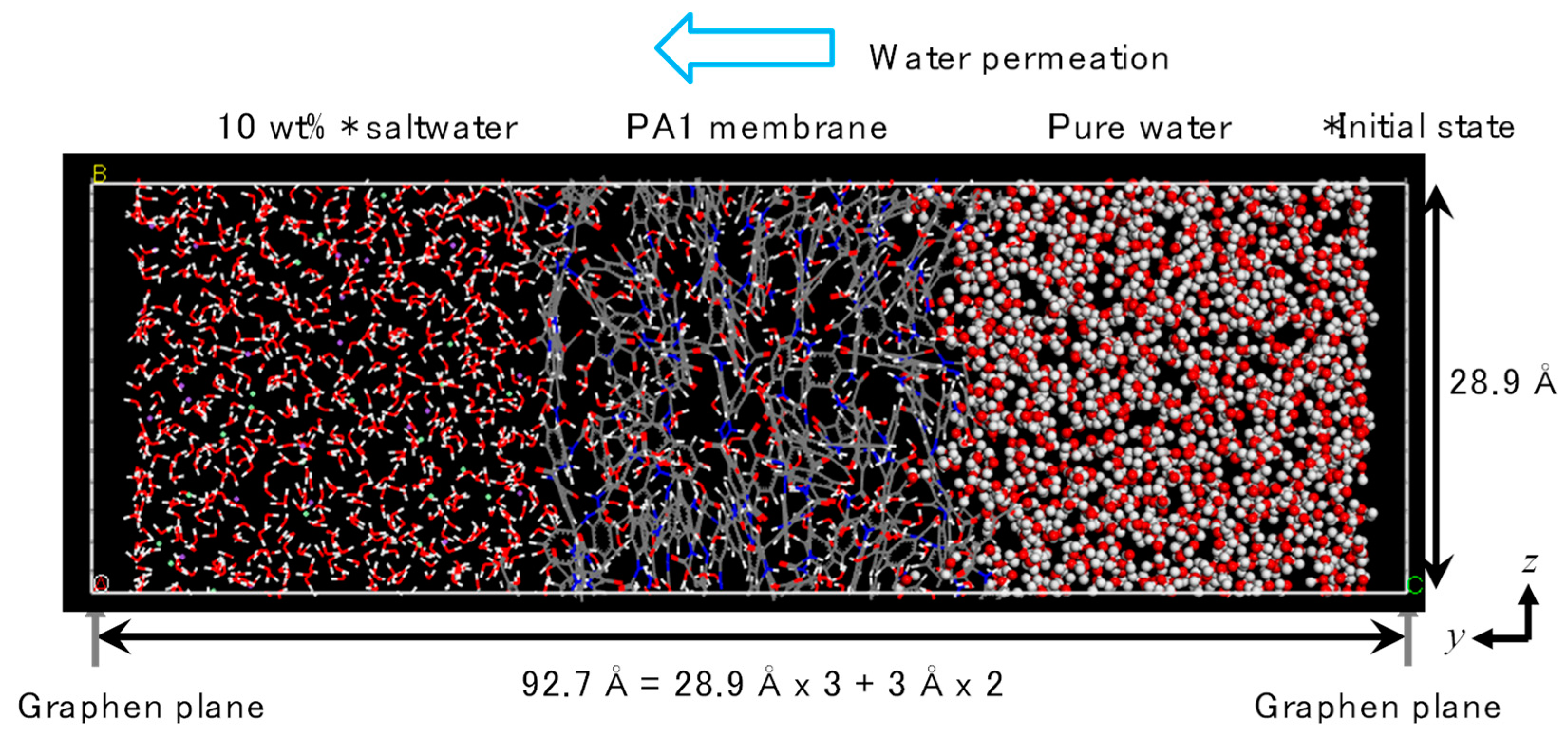
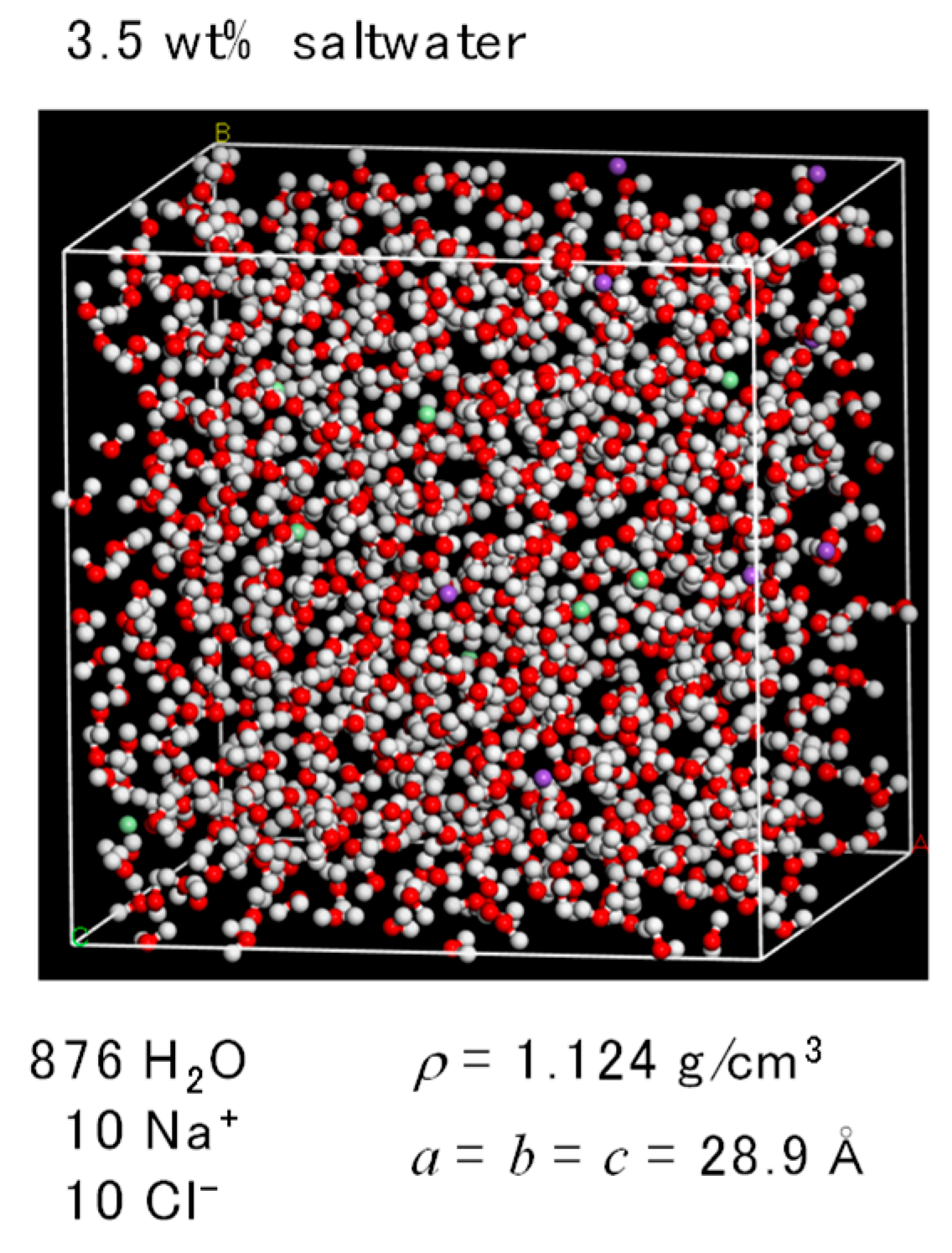
2.2. FO Simulation Cell
2.3. RO Simulation Cell
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polyamide Structure
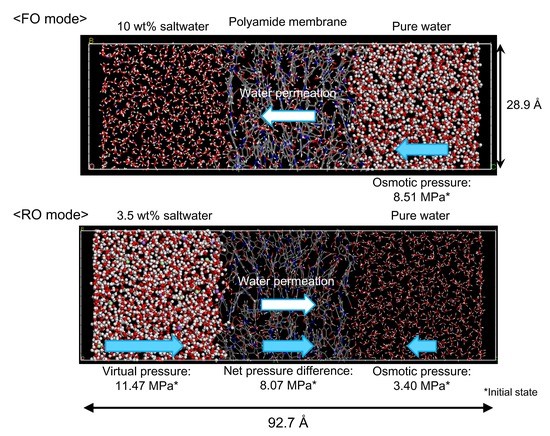
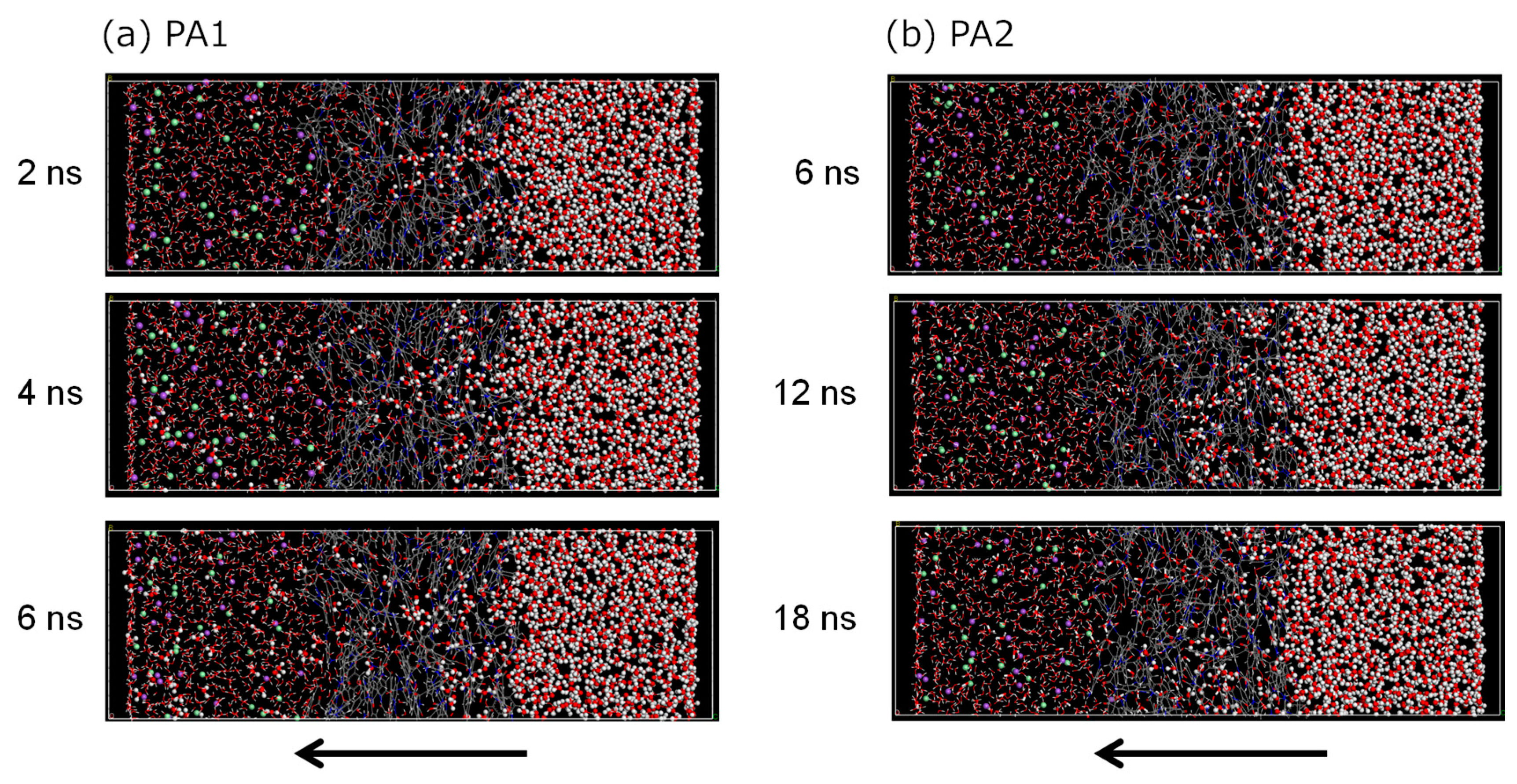
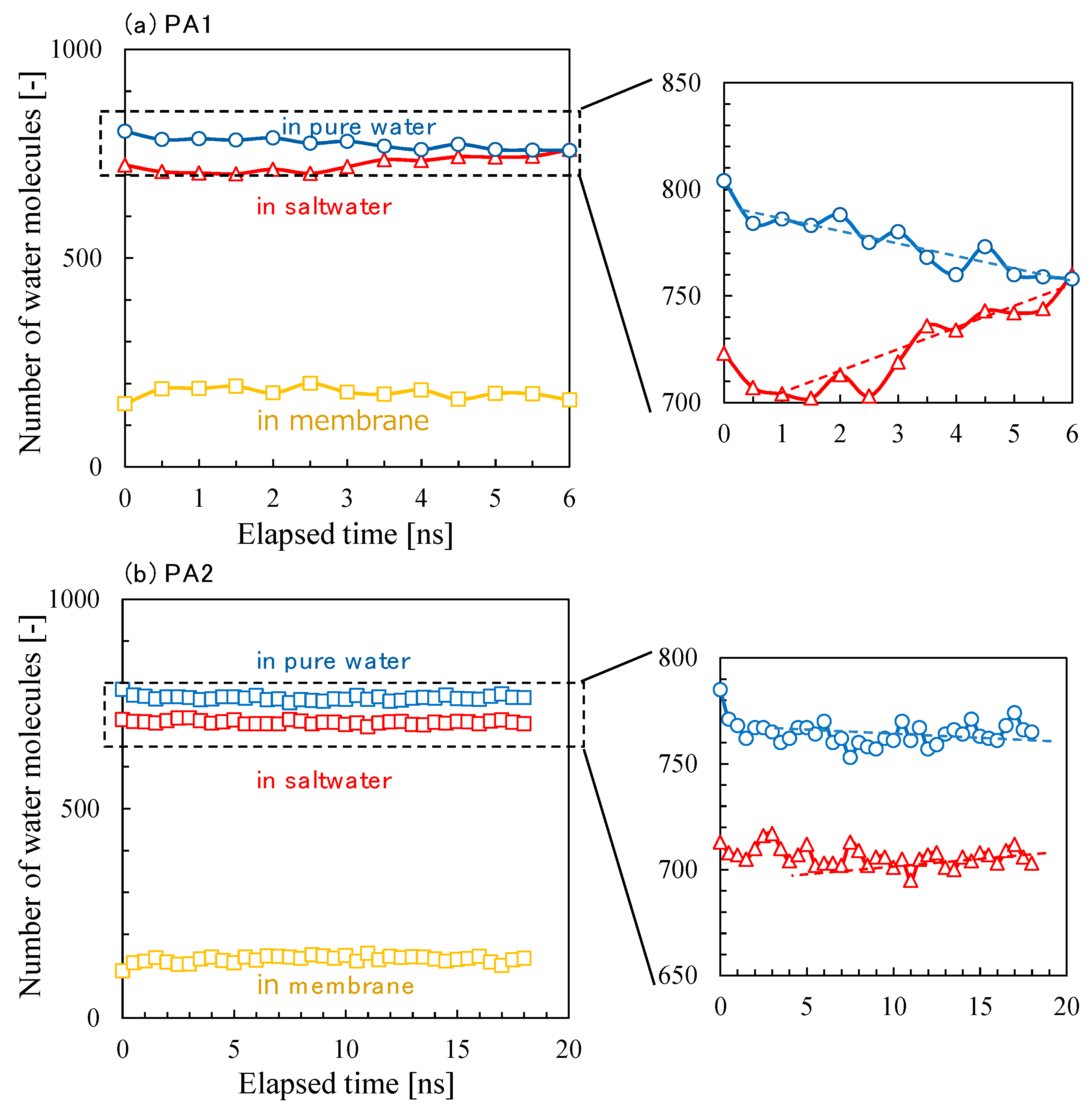
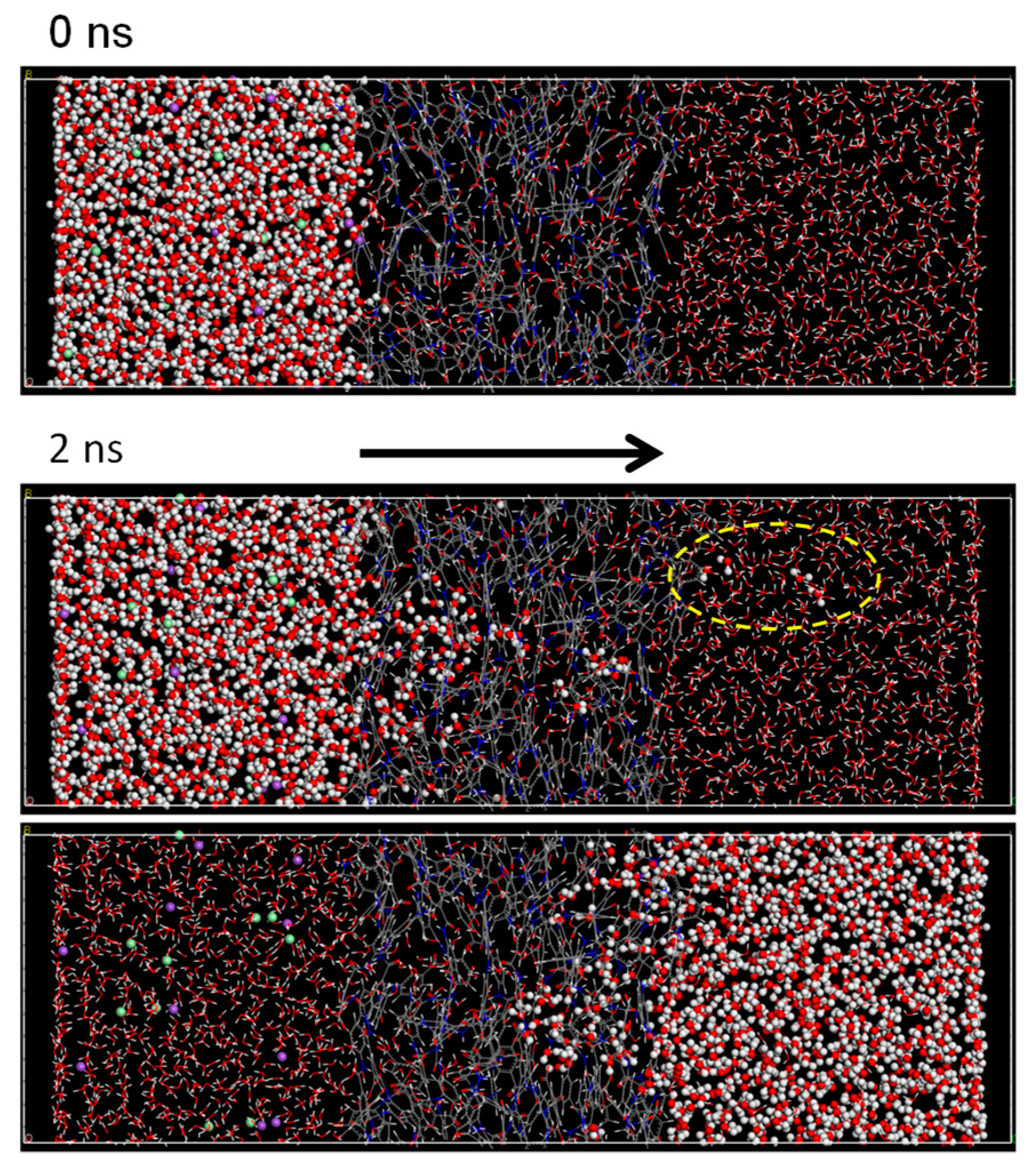
3.2. NVT-FO Simulation
3.3. NVT-RO Simulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltanieh, M.; Gill, W.N. Review of reverse-osmosis membranes and transport models. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1981, 12, 279–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution–diffusion model: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.R. Reformulation of the solution–diffusion theory of reverse osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 241, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegler, K.S.; El-Sayed, Y.M. The energetics of desalination processes. Desalination 2001, 134, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, S.; Powels, J.G. Computer simulation of osmosis and reverse osmosis in solutions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1994, 225, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudan, R.; Lin, J.; Murad, S. Molecular simulations of electro-osmosis in fluid mixtures using semi-permeable membranes. Fluid Phase Equilib. 1998, 150, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, S.; Nitsche, L.C. The effect of thickness, pore size and structure of a nanomembrane on the flux and selectivity in reverse osmosis separations: A molecular dynamics study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 397, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Smitha, B.; Mayor, S.; Prathab, B.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Gas permeation properties of polyamide membrane prepared by interfacial polymerization. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 9392–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, E.; Walters, D.E.; Bodnar, Y.D.; Faibish, R.S.; Roux, B. Molecular dynamics study of a polymeric reverse osmosis membrane. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 10177–10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Harder, E.; Faibish, R.S.; Roux, B. Computer simulations of water flux and salt permeability of the reverse osmosis FT-30 aromatic polyamide membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, T.; Shimazu, A.; Yahagi, S.; Matsuyama, H. Characterization of methyl-substituted polyamides used for reverse osmosis membranes by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy and MD Simulation. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 2009, 113, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Szymczyk, A.; Goujon, F.; Soldera, A.; Ghoufi, A. Structure and dynamics of water confined in a polyamide reverse-osmosis membrane: A molecular-simulation study. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 458, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Szymczyk, A.; Ghoufi, A. On the structure and rejection of ions by a polyamide membrane in pressure-driven molecular dynamics simulations. Desalination 2015, 368, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Keten, S.; Lueptow, R.M. Dynamics of water and solute transportin polymeric reverse osmosis membranes via molecular dynamics simulations. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 506, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, M.E.; Raghunathan, A.V.; Alurua, N.R. Fast reverse osmosis using boron nitride and carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 133120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, Z.E.; Carrington, L.A.; Raiteri, P.; Gale, J.D. A computational investigation into the suitability of purely siliceous zeolites as reverse osmosis membranes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 4063–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X. High permeability and salt rejection reverse osmosis by a zeolite nano-membrane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 6817–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanugi, D.C.; Grossman, J.C. Water Desalination across Nanoporous Graphene. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3602–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelle, S.; Yoshida, H.; Joly, L.; Ybert, C.; Bocquet, L. Carbon membranes for efficient water-ethanol separation. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 145, 124708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilder, T.A.; Yang, R.; Gordon, D.; Rendell, A.P.; Chung, S.H. Silicon carbide nanotube as a chloride-selective channel. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 4465–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, L.K.; Madarshahian, R.; Yoon, Y.; Caicedo, J.M.; Flora, J.R.V. A probabilistic approach for estimating water permeability in pressure-driven membranes. J. Mol. Model. 2016, 22, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, M.; Wu, L.; Hu, Y. Carbon nanotube: Possible candidate for forward osmosis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xu, Z. Ultimate osmosis engineered by the pore geometry and functionalization of carbon nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, B.L.; Grubmuller, H. Water permeation across biological membranes: Mechanism and dynamics of Aquaporin-1 and GlpF. Science 2001, 294, 2353–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.G.; Guliaev, A.B.; Walian, P.J.; Jap, B.K. Water transport in AQP0 Aquaporin: Molecular dynamics studies. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 360, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya-Secchi, R.; Garate, J.A.; Holmes, D.S.; Perez-Acle, T. Molecular dynamics study of the archaeal aquaporin AqpM. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binesh, A.R.; Kamali, R. Molecular dynamics insights into human aquaporin 2 water channel. Biophys. Chem. 2015, 207, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Lawa, A.W.; Zhou, K. Strained single-layer C2N membrane for efficient seawater desalination via forward osmosis: A molecular dynamics study. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yoshioka, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Shintani, T.; Tsuru, T.; Saeki, D.; Chen, Y.; Tung, K.; Matsuyama, H. Water transport and ion rejection investigation for application of cyclic peptide nanotubes to forward osmosis process: A simulation study. Desalination 2017, 424, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Ma, H.; Saji, M.S.; Murad, S. Aromatic polyamide reverse-osmosis membrane: An atomistic molecular dynamics simulation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 10311–10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y. Water flow inside polamide reverse osmosis membranes: A non-equilibrium molecular dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H. COMPASS: An ab Initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications—Overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7338–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronell, O.; Marinas, B.J.; Cahill, D.G. Depth Heterogeneity of fully aromatic polyamide active layers in reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4513–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cahill, D.G.; Coronell, O.; Marinas, B.J. Absorption of water in the active layer of reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 331, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, V.; Freger, V. Hydration, porosity and water dynamics in the polyamide layer of reverse osmosis membranes: A molecular dynamics study. Polymer 2014, 55, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, T.; Kanezashi, M.; Tsuru, T. Micropore size estimation on gas separation membranes: A study in experimental and molecular dynamics. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 2179–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albo, J.; Hagiwara, H.; Yanagishita, H.; Ito, K.; Tsuru, T. Structural characterization of thin-film polyamide reverse osmosis membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 1442–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kook, S.; O’Rourke, B.E.; Lee, J.; Hwang, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Kim, I.S. Characterization of pore size distribution (PSD) in cellulose triacetate (CTA) and polyamide (PA) thin active layers by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) and fractional rejection (FR) method. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Park, H.B.; Sagle, A.C.; Freeman, B.D.; McGrath, J.E. Water permeability and water/salt selectivity tradeoff in polymers for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humplik, T.; Lee, J.; CO’Hern, S.; Fellman, B.A.; Baig, M.A.; Hassan, S.F.; Atieh, M.A.; Rahman, F.; Laoui, T.; Karnik, R.; et al. Nanostructured materials for water desalination. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 292001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

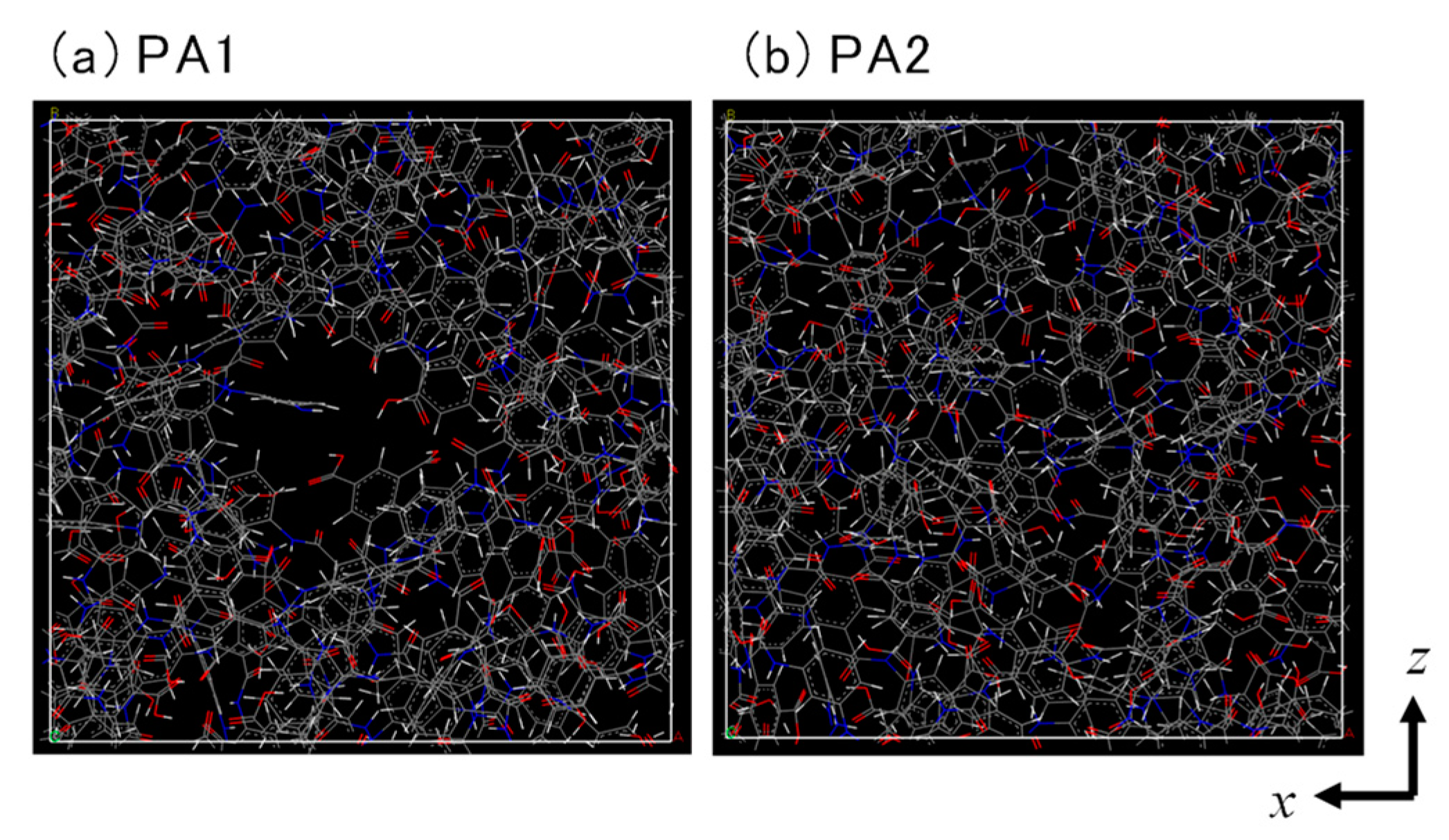








| Major Void Size (nm) | Porosity (%) | PFO (LMH/bar) | PRO (LMH/bar) | Salt Leakage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA1 | 0.65–0.85 | 19.5 | 350–400 | 550–600 | Not detected |
| PA2 | 0.58–0.72 | 16.8 | 15–25 | 4–5 | Not detected |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshioka, T.; Kotaka, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Shintani, T.; Wu, H.-C.; Matsuyama, H.; Fujimura, Y.; Kawakatsu, T. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Polyamide Membrane Structures and RO/FO Water Permeation Properties. Membranes 2018, 8, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040127
Yoshioka T, Kotaka K, Nakagawa K, Shintani T, Wu H-C, Matsuyama H, Fujimura Y, Kawakatsu T. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Polyamide Membrane Structures and RO/FO Water Permeation Properties. Membranes. 2018; 8(4):127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040127
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshioka, Tomohisa, Keisuke Kotaka, Keizo Nakagawa, Takuji Shintani, Hao-Chen Wu, Hideto Matsuyama, Yu Fujimura, and Takahiro Kawakatsu. 2018. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Polyamide Membrane Structures and RO/FO Water Permeation Properties" Membranes 8, no. 4: 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040127
APA StyleYoshioka, T., Kotaka, K., Nakagawa, K., Shintani, T., Wu, H.-C., Matsuyama, H., Fujimura, Y., & Kawakatsu, T. (2018). Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Polyamide Membrane Structures and RO/FO Water Permeation Properties. Membranes, 8(4), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8040127