Effect of Chemical Structure on the Performance of Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Nanofiltration Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials and Instrument
2.2. Solubilities of the Polymers
2.3. Membrane Preparation
2.4. Morphology and Structure
2.5. Water Flux and Salt Rejection
2.6. Thermal Stability and Chlorine Resistance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Solvents Used in the Coating Solutions
3.2. Separation Performance of Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Nanofiltration Membrane
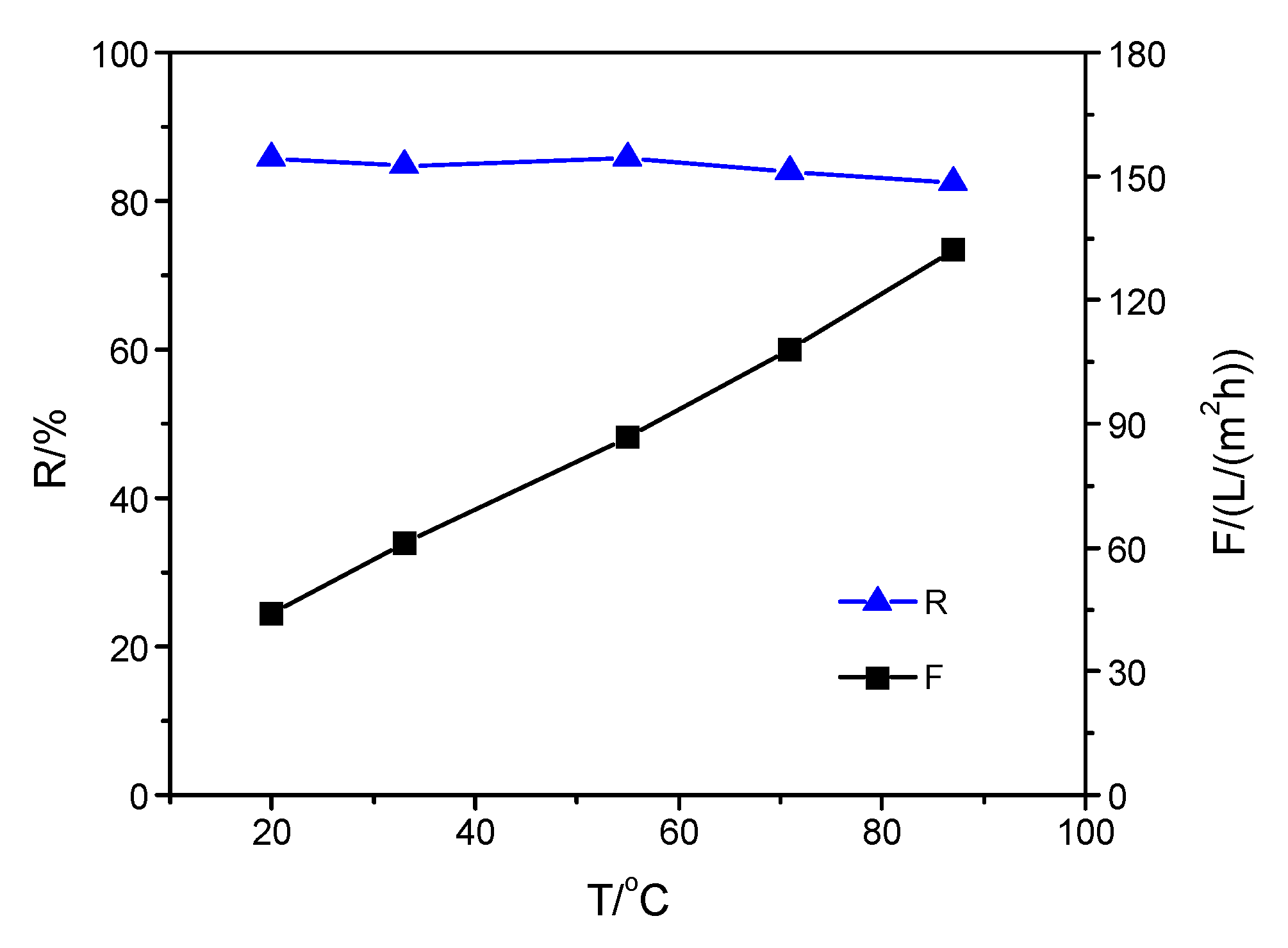
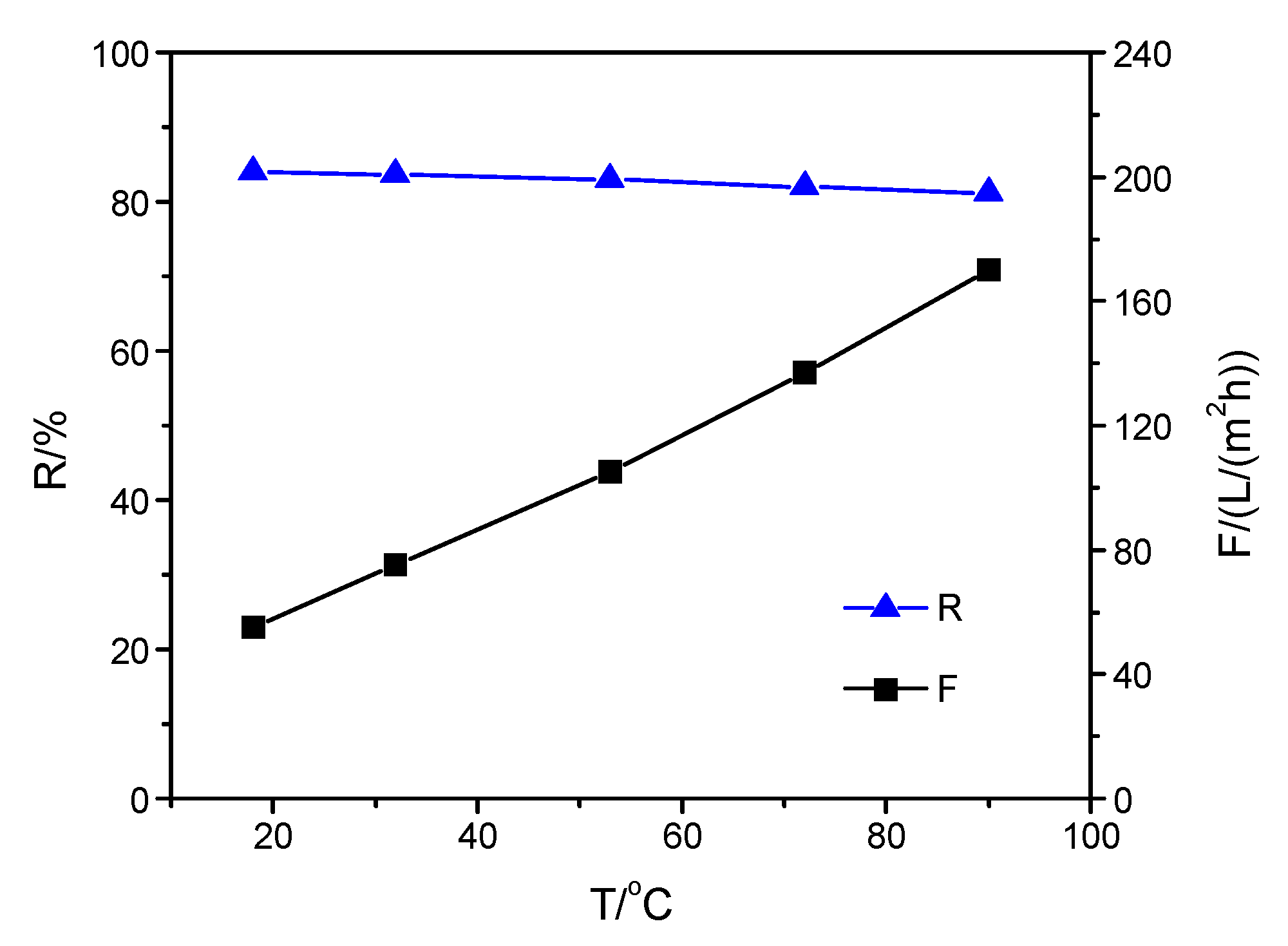
3.3. Performance of Composite Membranes with Different Selective Layers at Increasing Solution Temperature
3.4. Chlorine Resistance of Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Membranes
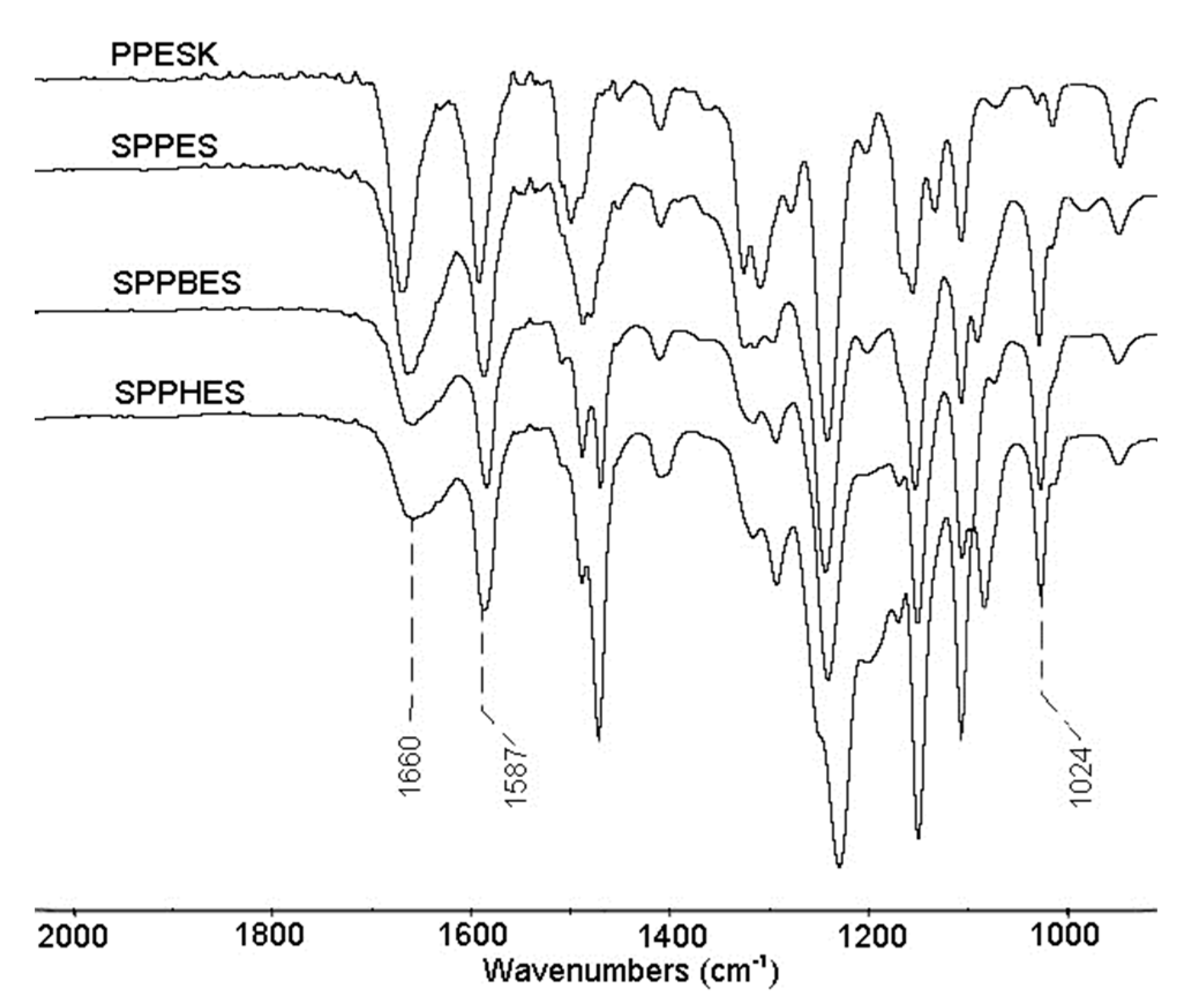
3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Membranes
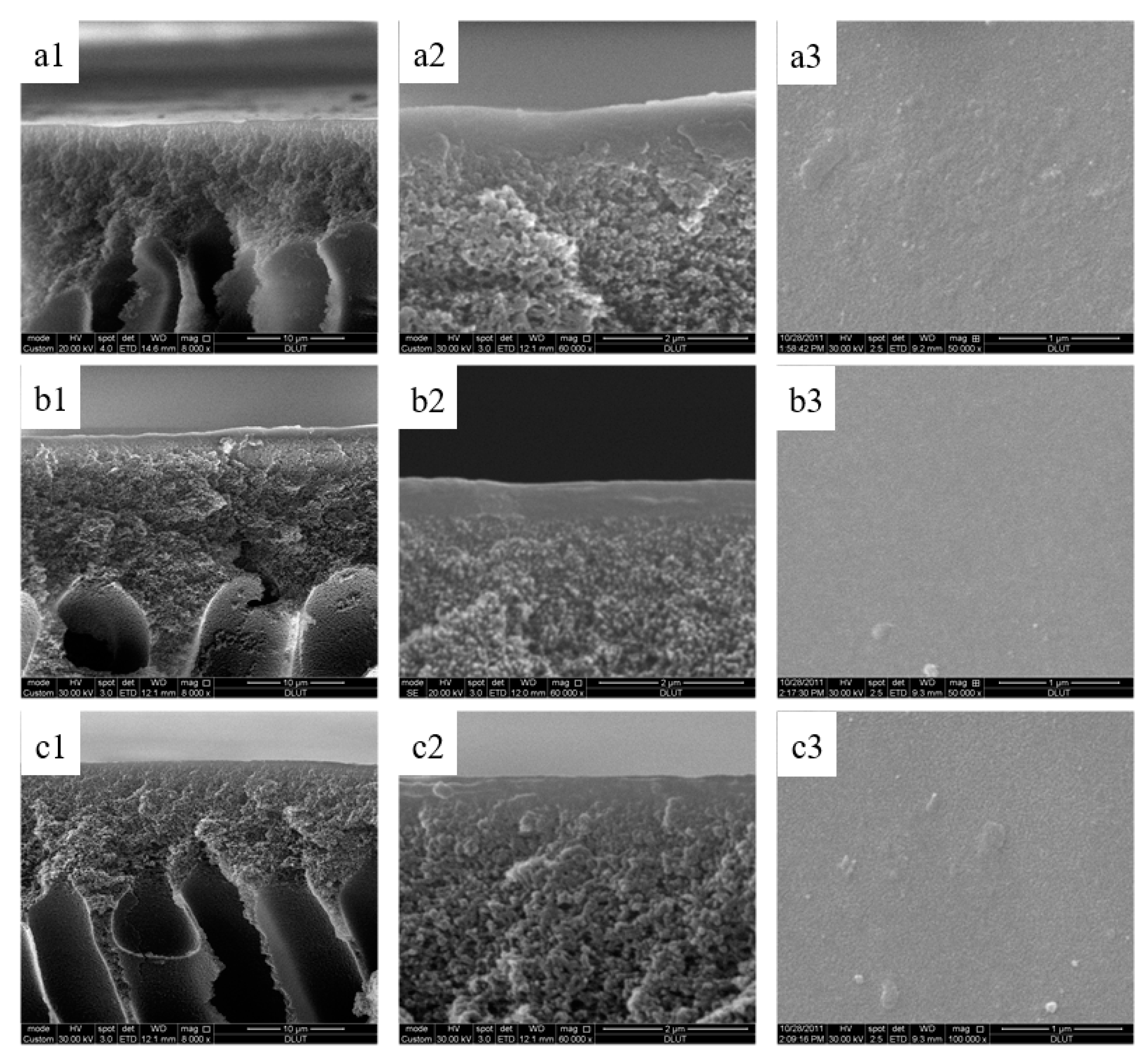
3.6. Morphological Structure of the Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Service, R.F. Desalination freshens up. Science 2006, 313, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyekwo, F.; Zhang, Q.G.; Gao, R.S.; Qu, Y.; Lin, C.X.; Huang, X.L.; Zhu, A.M.; Liu, Q.L. Cellulose nanofiber intermediary to fabricate highly-permeable ultrathin nanofiltration membranes for fast water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, S.M.C.; Bhattacharyya, D. Membrane based hybrid processes for high water recovery and selective inorganic pollutant separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Kale, A.; Khan, A.A. Reverse osmosis of edible vegetable oil industry effluent. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 205, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Moon, J.H.; Ma, X.X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, L.N.; Peng, R.Q.; Si, P.C.; Feng, J.K.; Li, Y.H.; et al. High performance graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane prepared by electrospraying for wastewater purification. Carbon 2018, 130, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, M.; Van Dyck, T.; Van Goethem, C.; Gebreyohannes, A.Y.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Development of a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 557, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.Z.; Zhong, Q.Z.; Du, Y.; Lv, Y.; Xu, Z.K. Enzyme-triggered coatings of tea catechins/chitosan for nanofiltration membranes with high performance. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 6205–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Yang, H.C.; Wu, M.B.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Z.K. Nanofiltration membranes with cellulose nanocrystals as an interlayer for unprecedented performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16289–16295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Zoubi, H.A.; Darwish, N.A.; Mohammad, A.W.; Arabi, M.A. A comprehensive review of nanofiltration membranes: Treatment, pretreatment, modeling, and atomic force microscopy. Desalination 2004, 170, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Liu, F.; Wang, Y.; Lin, H.B.; Han, L. A tight nanofiltration membrane with multi-charged nanofilms for high rejection to concentrated salts. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.W.; Tang, C.Y.Y.; Li, P.; Adrian, P.; Hu, G.S. Perfluorooctane sulfonate removal by nanofiltration membrane-the effect and interaction of magnesium ion/humic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 503, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Everaert, K.; Wilms, D.; Vandecasteele, C. Application of nanofiltration for removal of pesticides, nitrate and hardness from ground water: Rejection properties and economic evaluation. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 193, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Al-Zoubi, H.; Darwish, N.A.; Mohammad, A.W. Nanofiltration of magnesium chloride, sodium carbonate, and calcium sulphate in salt solutions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 3299–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M.; Trägårdh, G.; Östergren, K. The influence of sodium chloride on mass transfer in a polyamide nanofiltration membrane at elevated temperatures. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F. Theoretical studies on the morphological and electrical properties of blended PES/SPEEK nanofiltration membranes using different sulfonation degree of SPEEK. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 334, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashvigh, A.A.; Luo, L.; Chung, T.S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C. Performance enhancement in organic solvent nanofiltration by double crosslinking technique using sulfonated polyphenylsulfone (sPPSU) and polybenzimidazole (PBI). J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.P.; Joshi, S.V.; Trivedi, J.J.; Devmurari, C.V.; Shah, V.J. Structure–performance correlation of polyamide thin film composite membranes: Effect of coating conditions on film formation. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 211, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, R.J. Composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 83, 81–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; He, G.; Gao, P.; Chen, G. Development and characterization of composite nanofiltration membranes and their application in concentration of antibiotics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 30, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Ma, T.Y.; Su, Y.L.; Wu, H.; You, X.D.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Kasher, R. Fabrication of composite nanofiltration membrane by incorporating attapulgite nanorods during interfacial polymerization for high water flux and antifouling property. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 544, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Ostadmoradi, N.; Rostami, S.M.M.; Homayoonfal, M. Role of Organic Acids in Flux Enhancement of Polyamide Nanofiltration Membranes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, X.G.; Chen, P.; Liao, G.X.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, J.Y. Synthesis and performance of novel poly (phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone)s. Acta Polym. Sin. 2003, 4, 469–475. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.Z.; Hay, A.S.; Jian, X.G.; Tjong, S. Synthesis and properties of poly (aryl ether sulfone)s containing the phthalazinone moiety. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 68, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Robertson, G.P.; Guiver, M.D.; Jian, X.G.; Mikhailenko, S.D.; Wang, K.P.; Kaliaguine, S. Sulfonation of poly(phthalazinones) with fuming sulfuric acid mixtures for proton exchange membrane materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 227, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.H.; Sao, C.; Zeng, S.D.; Jian, X.G. Sulfonation of copoly(ether sulfone) s containing phthalazinone moieties. J. Funct. Mater. 2010, 41, 874–877. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Zeng, S.D.; Jian, X.G. Heterogeneous sulfonation of copoly(phthalazinone ether sulfone). J. Funct. Polym. 2011, 24, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.H.; Jian, X.G.; Dai, Y. Preparation of sulfonated poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone) composite nanofiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 246, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.S.; Zhang, S.H.; Han, R.L.; Zhang, B.G.; Jian, X.G. Preparation and properties of novel sulfonated copoly (phthalazinone biphenyl ether sulfone) composite nanofiltration membrane. Desalination 2013, 318, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.K.; Kim, J.H.; Roh, I.J.; Kim, J.J. The changes of membrane performance with polyamide molecular structure in the reverse osmosis process. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, O.; Liu, C.; Chong, T.H.; Lienhard, J.H. Relating transport modeling to nanofiltration membrane fabrication: Navigating the permeability-selectivity trade-off in desalination pretreatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagley, E.B.; Nelson, T.P.; Seigliano, J.M. 3-dimensional solubility parameters and their relationship to internal pressure measurements in polar and hydrogen bonding solvents. J. Paint Technol. 1971, 43, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Van Krevelen, D.W.; Te Nijenhuis, K. Properties of Polymers, Their Correlation with Chemical Structure; Their Numerical Estimation and Prediction from Additive Group Contributions, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; p. 209. ISBN 978-0-08-054819-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, X.G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.H.; Yang, D.L. Solubility parameters poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone) and sulfonated poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone). J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2009, 49, 322–326. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, A.; Chowdhury, G.; Matsuura, T.; Sourirajan, S. Sulphonated poly (2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide)-polyethersulphone composite membranes. Effects of composition of solvent system, used for preparing casting solution, on membrane-surface structure and reverse-osmosis performance. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 129, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Jian, X.G.; Wu, C.R.; Zhang, S.H.; Yan, C. Influence of polymer structure on thermal stability of composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 256, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Polymer | δd/MPa1/2 | δp/MPa1/2 | δh/MPa1/2 | δv/MPa1/2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPESK | 20.4 | 5.7 | 7.8 | 21.2 |
| SPPES (DS = 0.87) | 20.0 | 7.3 | 11.9 | 21.3 |
| SPPBES (DS = 0.85) | 19.4 | 7.1 | 11.6 | 20.6 |
| SPPHES (DS = 0.82) | 19.1 | 7.8 | 12.1 | 20.6 |
| Solvent | δd/MPa1/2 | δp/MPa1/2 | δv/MPa1/2 | δh/MPa1/2 | Δδ/MPa1/2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPPES | SPPBES | SPPHES | PPESK | |||||
| EGME | 16.2 | 9.2 | 18.6 | 16.4 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 4.7 | 9.0 |
| EGME + acetone (5:1) | 16.1 | 9.4 | 18.6 | 14.8 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 3.4 | 7.5 |
| EGME + DO (4:1) | 16.8 | 7.7 | 18.5 | 14.6 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 3.3 | 7.3 |
| EGME + ethanol (4:1) | 16.1 | 9.1 | 18.5 | 17.0 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 5.3 | 9.6 |
| Solvent | PPESK | SPPES (0.87) | SPPBES (0.85) | SPPHES (0.82) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGME | − | + | + | + |
| EGME + acetone (5:1) | − | + | + | + |
| EGME + DO (4:1) | − | + | + | + |
| EGME + ethanol (4:1) | − | + | + | + |
| Solvents | SPPES | SPPBES | SPPHES | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R/% | F/(L/(m2·h)) | R/% | F/(L/(m2·h)) | R/% | F/(L/(m2·h)) | |
| EGME + acetone (5:1) | 90 | 32 | 80 | 59 | 74 | 50 |
| EGME + DO (4:1) | 85 | 50 | 80 | 43 | 87 | 31 |
| EGME + ethanol (4:1) | 88 | 55 | 81 | 50 | 85 | 45 |
| EGME | 80 | 64 | 86 | 16 | 80 | 50 |
| Membrane | PWF/(L/(m2·h)) | R/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2SO4 | MgSO4 | NaCl | MgCl2 | ||
| SPPES | 70 | 85 | 53 | 47 | 14 |
| SPPBES | 69 | 77 | 31 | 20 | 10 |
| SPPHES | 60 | 80 | 38 | 35 | 14 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Guan, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Jian, X. Effect of Chemical Structure on the Performance of Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Nanofiltration Membranes. Membranes 2019, 9, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010006
Zhang S, Guan S, Liu C, Wang Z, Wang D, Jian X. Effect of Chemical Structure on the Performance of Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Nanofiltration Membranes. Membranes. 2019; 9(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shouhai, Shanshan Guan, Chengde Liu, Zhenlin Wang, Danhui Wang, and Xigao Jian. 2019. "Effect of Chemical Structure on the Performance of Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Composite Nanofiltration Membranes" Membranes 9, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9010006





