Performance Comparison of a Laterally-Fed Membrane Chromatography (LFMC) Device with a Commercial Resin Packed Column
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
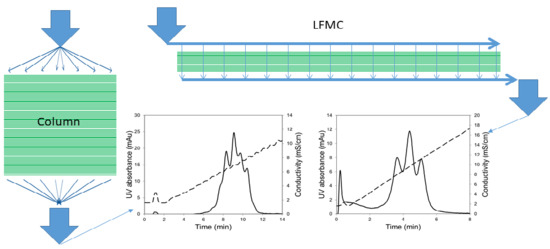
2.2. LFMC Device Design and Fabrication
2.3. Theoretical Plates Determination
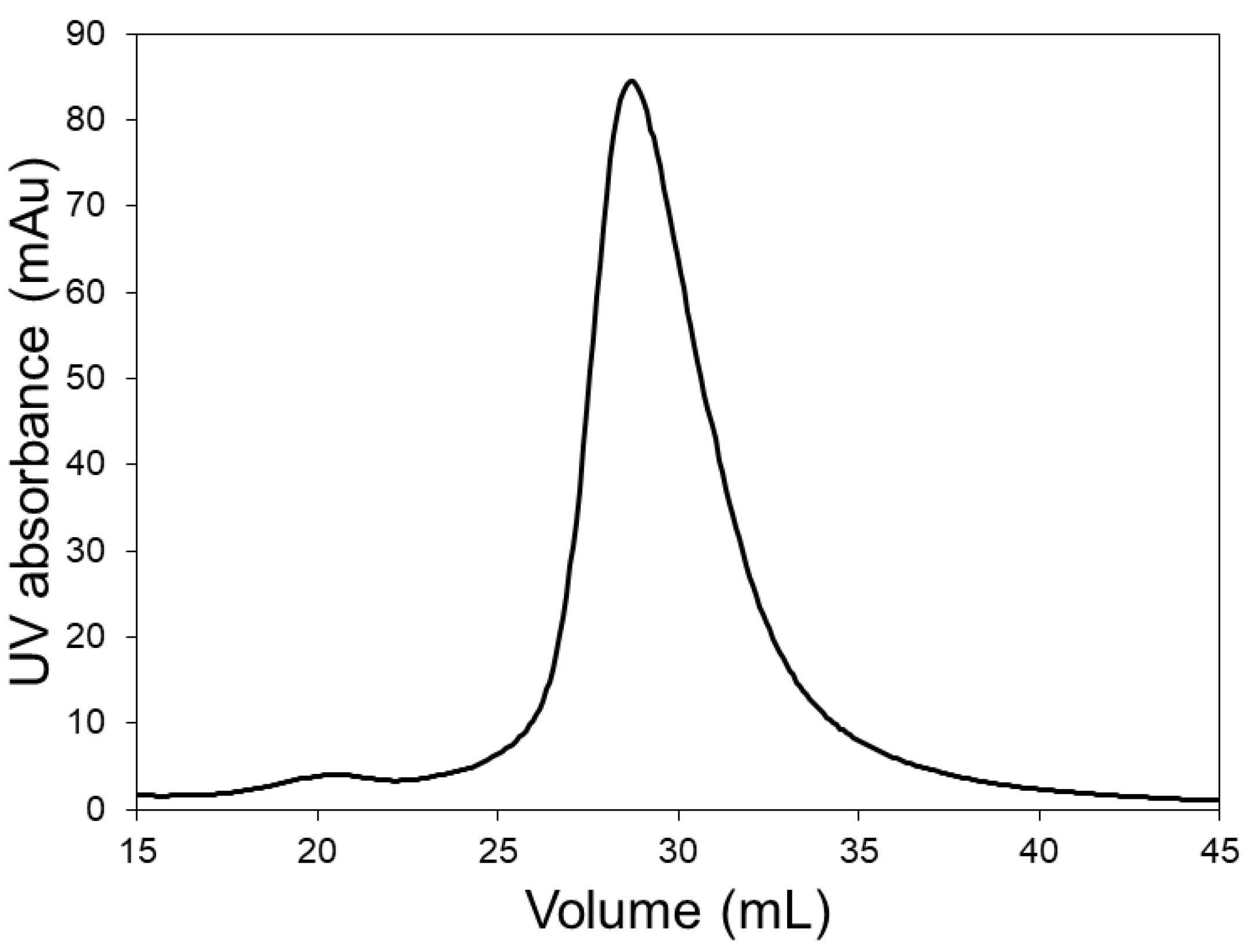
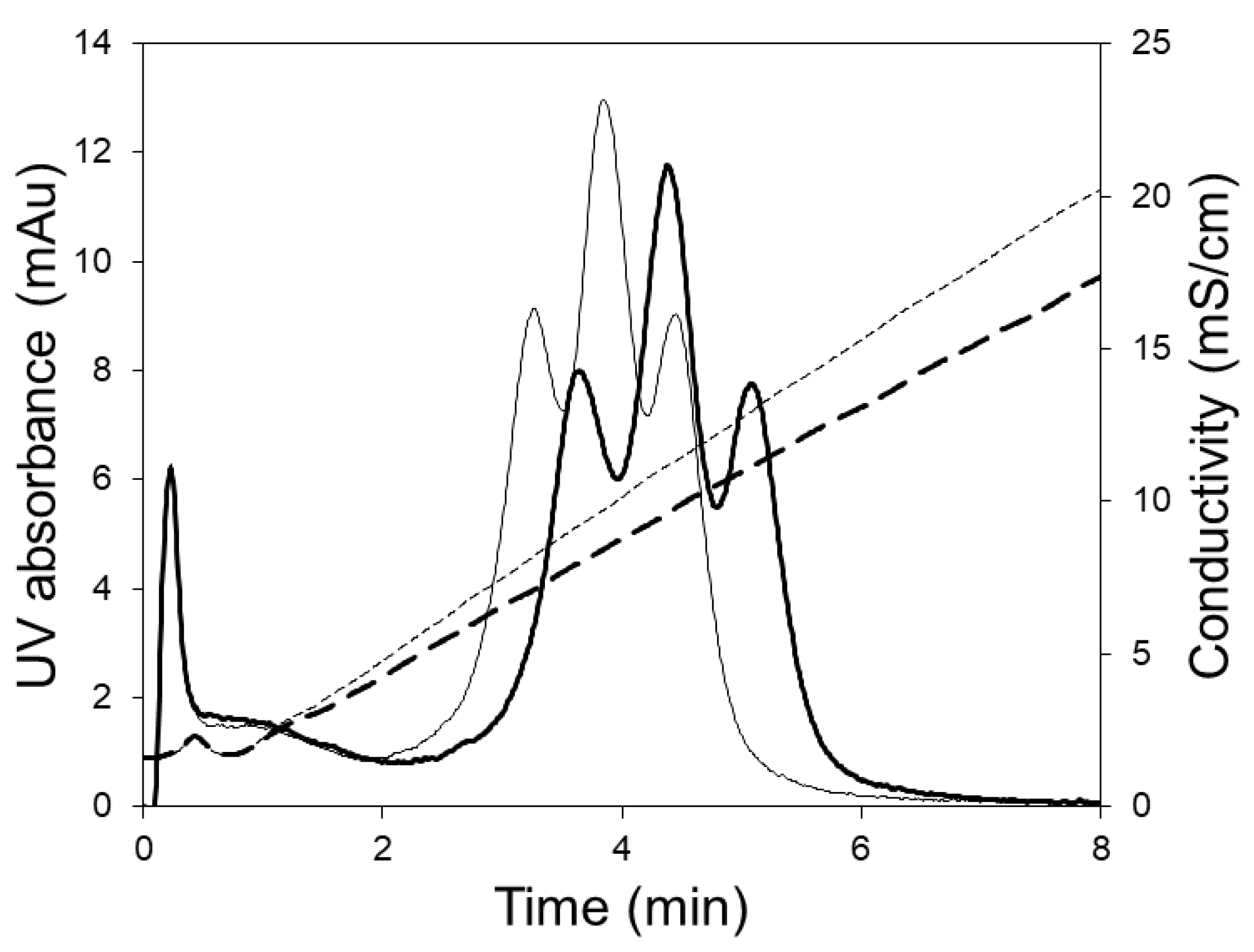
2.4. Model Protein Separation
2.5. Lysozyme Dimer Separation
2.6. Separation of mAb Charge Variants
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fekete, S.; Beck, A.; Veuthey, J.L.; Guillarme, D. Ion-exchange chromatography for the characterization of biopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 113, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinebach, F.; Müller-Späth, T.; Morbidelli, M. Continuous Counter-current Chromatography for the Capture and Polishing Steps in Biopharmaceuticals Production. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, A.T.; Ottens, M. Purifying biopharmaceuticals: Knowledge-based chromatographic process development. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zydney, A.L. Continuous downstream processing for high value biological products: A Review. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R. Protein separation using membrane chromatography: Opportunities and challenges. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 952, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boi, C. Membrane adsorbers as purification tools for monoclonal antibody purification. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 848, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Root, T.W.; Klingenberg, D.J.; Lightfoot, E.N. Flow distribution in chromatographic columns. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 831, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R. Using a box instead of a column for process chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1468, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybycien, T.M.; Pujar, N.S.; Steele, L.M. Alternative bioseparation operations: Life beyond packed-bed chromatography. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charcosset, C. Review Purification of Proteins b y Membrane Chromatography. J. Chem. Biotechnol. 1998, 71, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, D.K.; Lightfoot, E.N. Separation of biomolecules using adsorptive membranes. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 702, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, M.; Nordborg, A.; Gaspar, A.; Lacher, N.A.; Wang, Q.; He, X.Z.; Haddad, P.R.; Hilder, E.F. Charge heterogeneity profiling of monoclonal antibodies using low ionic strength ion-exchange chromatography and well-controlled pH gradients on monolithic columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1317, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svec, F.; Lv, Y. Advances and recent trends in the field of monolithic columns for chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 250–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.F.; Bin Don, B.; Zheng, M.J. Mixed-mode chromatography integrated with high-performance liquid chromatography for protein analysis and separation: Using bovine serum albumin and lysozyme as the model target. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, U.; Brorson, K.; Shukla, A.A. The need for innovation in biomanufacturing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Chenette, H.C.S.; Robinson, J.R.; Hobley, E.; Husson, S.M. Development of high-productivity, strong cation-exchange adsorbers for protein capture by graft polymerization from membranes with different pore sizes. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, J.H.; Nguyen, H.; Giovannini, R.; Ignowski, J.; Garger, S.; Salgotra, A.; Tom, J. A new large-scale manufacturing platform for complex biopharmaceuticals. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 3049–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, U. Disposables in Downstream Processing. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2010, 123, 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukumar, S.; Muralikrishnan, T.; Mendhe, R.; Rathore, A.S. Economic benefits of membrane chromatography versus packed bed column purification of therapeutic proteins expressed in microbial and mammalian hosts. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, V.; Zhong, L.; Moo-Young, M.; Chou, C.P. Recent advances in bioprocessing application of membrane chromatography. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.X.; Tressel, T. Basic concepts in Q membrane chromatography for large-scale antibody production. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.; Husson, S.M.; Murphy, L.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Anion exchange membrane adsorbers for flow-through polishing steps: Part II. Virus, host cell protein, DNA clearance, and antibody recovery. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madadkar, P.; Ghosh, R. High-resolution protein separation using a laterally-fed membrane chromatography device. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 499, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Madadkar, P. Laterally-Fed Membrane Chromatography Device. U.S. Patent 15/452,157, 4 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Madadkar, P.; Wu, Q.; Ghosh, R. A laterally-fed membrane chromatography module. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 487, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadkar, P.; Luna Nino, S.; Ghosh, R. High-resolution, preparative purification of PEGylated protein using a laterally-fed membrane chromatography device. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 1035, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Madadkar, P.; Wu, Q. On the workings of laterally-fed membrane chromatography. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 516, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madadkar, P.; Sadavarte, R.; Butler, M.; Durocher, Y.; Ghosh, R. Preparative separation of monoclonal antibody aggregates by cation exchange laterally-fed membrane chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1055–1056, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadavarte, R.; Madadkar, P.; Filipe, C.D.M.; Ghosh, R. Rapid preparative separation of monoclonal antibody charge variants using laterally-fed membrane chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1073, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, S.D.; Clark, M.R.; Routledge, E.G.; Cobbold, S.P.; Waldmann, H. Reshaping a therapeutic CD4 antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4181–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Vlasak, J.; Li, Y.; Pristatsky, P.; Fang, Y.; Pittman, T.; Roman, J.; Wang, Y.; Prueksaritanont, T.; Ionescu, R. Impact of methionine oxidation in human IgG1 Fc on serum half-life of monoclonal antibodies. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, S.; Beck, A.; Fekete, J.; Guillarme, D. Method development for the separation of monoclonal antibody charge variants in cation exchange chromatography, Part II: PH gradient approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 102, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponniah, G.; Kita, A.; Nowak, C.; Neill, A.; Kori, Y.; Rajendran, S.; Liu, H. Characterization of the Acidic Species of a Monoclonal Antibody Using Weak Cation Exchange Chromatography and LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9084–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorhouse, K.G.; Nashabeh, W.; Deveney, J.; Bjork, N.S.; Mulkerrin, M.G.; Ryskamp, T. Validation of an HPLC method for the analysis of the charge heterogeneity of the recombinant monoclonal antibody IDEC-C2B8 after papain digestion. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1997, 16, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozhkova, A. Quantitative analysis of monoclonal antibodies by cation-exchange chromatofocusing. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5989–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Bourret, J.; Cano, T. Isolation and characterization of therapeutic antibody charge variants using cation exchange displacement chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5079–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jones, L.; Taylor, L.; Kannan, G.; Jackson, F.; Lau, H.; Latypov, R.F.; Bailey, B. Characterization of a unique IgG1 mAb CEX profile by limited Lys-C proteolysis/CEX separation coupled with mass spectrometry and structural analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 1973–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, J.C.; Moreno, G.T.; Lou, Y.; Farnan, D. Validation of a pH gradient-based ion-exchange chromatography method for high-resolution monoclonal antibody charge variant separations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.; Pace, D.; Yan, B.; Mcgrath, T.; Smallwood, S.; Patel, K.; Park, J.; Park, S.S.; Latypov, R.F. Investigation of degradation processes in IgG1 monoclonal antibodies by limited proteolysis coupled with weak cation-exchange HPLC. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Anderson, D.J. Gradient Chromatofocusing. Versatile pH Gradient Separation of Proteins in Ion-Exchange HPLC: Characterization Studies Gradient Chromatofocusing. Versatile pH Gradient Separation of Proteins in Ion-Exchange HPLC: Characterization Studies, System. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5641–5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnan, D.; Moreno, G.T. Multiproduct high-resolution monoclonal antibody charge variant separations by pH gradient ion-exchange chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8846–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerontas, S.; Asplund, M.; Hjorth, R.; Bracewell, D.G. Integration of scale-down experimentation and general rate modelling to predict manufacturing scale chromatographic separations. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6917–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, A.S.; Kennedy, R.M.; O’Donnell, J.K.; Bemberis, I.; Kaltenbrunner, O. Qualification of a chromatographic column: Why and how to do it. BioPharm Int. 2003, 16, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, S.; Kira, A.; Imamura, M.; Masuda, T. Lysozyme dimer formation on lysozyme oxidation with as studied by fluorescence evolution. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 1982, 41, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, B.R.; Vekilov, P.G.; Rosenberger, F. Effects of microheterogeneity in hen egg-white lysozyme crystallization. Acta Crystallogr. D 1998, 54, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Cui, Z.F. Protein purification by ultrafiltration with pre-treated membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 167, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Cui, Z.F. Purification of lysozyme using ultrafiltration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 68, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Membrane Bed Volume (mL) | Number of Membrane Layers | Bed Height (mm) | Membrane Dimensions (mm × mm) | Pillar Array | Outer Dimension of Plate (mm × mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.7 | 12 | 3.3 | 70 × 20 | 28 × 7 | 150 × 40 |
| Device | Bed Volume (mL) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Number of Theoretical Plates Per Metre (m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HiTrap SP HP | 5 | 5.0 | 6500 |
| 10.0 | 4100 | ||
| 15.0 | 3600 | ||
| LFMC | 4.7 | 5.0 | 21,400 |
| 10.0 | 25,100 | ||
| 15.0 | 24,400 | ||
| 30.0 | 18,100 |
| Device | Bed Volume (mL) | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Pressure Drop (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HiTrap SP HP | 5 | 5 | 0.068 |
| 10 | 0.146 | ||
| 15 | 0.232 | ||
| LFMC | 4.7 | 5 | 0.037 |
| 10 | 0.083 | ||
| 15 | 0.134 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madadkar, P.; Sadavarte, R.; Ghosh, R. Performance Comparison of a Laterally-Fed Membrane Chromatography (LFMC) Device with a Commercial Resin Packed Column. Membranes 2019, 9, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110138
Madadkar P, Sadavarte R, Ghosh R. Performance Comparison of a Laterally-Fed Membrane Chromatography (LFMC) Device with a Commercial Resin Packed Column. Membranes. 2019; 9(11):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110138
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadadkar, Pedram, Rahul Sadavarte, and Raja Ghosh. 2019. "Performance Comparison of a Laterally-Fed Membrane Chromatography (LFMC) Device with a Commercial Resin Packed Column" Membranes 9, no. 11: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110138
APA StyleMadadkar, P., Sadavarte, R., & Ghosh, R. (2019). Performance Comparison of a Laterally-Fed Membrane Chromatography (LFMC) Device with a Commercial Resin Packed Column. Membranes, 9(11), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9110138