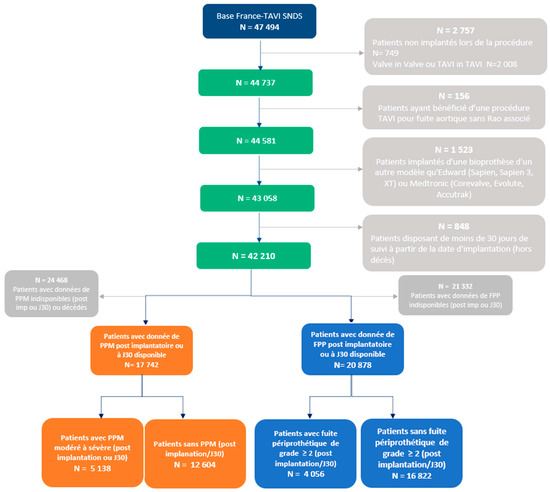
J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11(20), 6121; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11206121 - 17 Oct 2022
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 2150
Abstract
Background. Evidence has shown a close association between COVID-19 infection and renal complications in both individuals with previously normal renal function and those with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Methods. The aim of this study is to evaluate the in-hospital mortality of SARS-CoV-2 patients
[...] Read more.
Background. Evidence has shown a close association between COVID-19 infection and renal complications in both individuals with previously normal renal function and those with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Methods. The aim of this study is to evaluate the in-hospital mortality of SARS-CoV-2 patients according to their clinical history of CKD or estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). This is a prospective multicenter observational cohort study which involved adult patients (≥18 years old) who tested positive with SARS-CoV-2 infection and completed their hospitalization in the period between November 2020 and June 2021. Results. 1246 patients were included in the study, with a mean age of 64 years (SD 14.6) and a median duration of hospitalization of 15 days (IQR 9–22 days). Cox’s multivariable regression model revealed that mortality risk was strongly associated with the stage of renal impairment and the Kaplan–Meier survival analysis showed a progressive and statistically significant difference (p < 0.0001) in mortality according to the stage of CKD. Conclusion. This study further validates the association between CKD stage at admission and mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. The risk stratification based on eGFR allows clinicians to identify the subjects with the highest risk of intra-hospital mortality despite the duration of hospitalization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Challenges in the Management of Renal Patients in the COVID-19 Era)
►
Show Figures