Optimized Screening Methods for Investigation of the Larval Settlement of Lanice conchilega on Artificial Substrates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
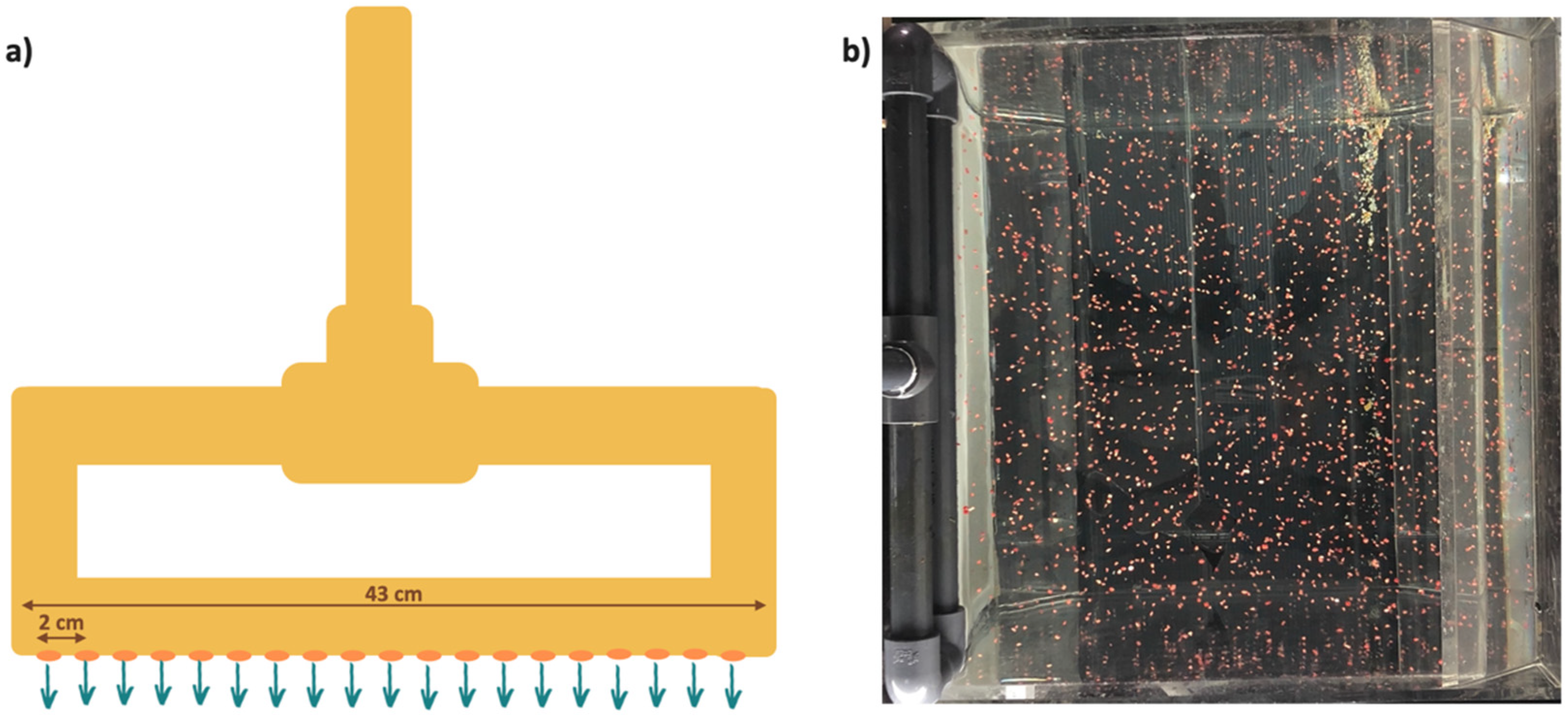
2.1. Experimental Setup Design
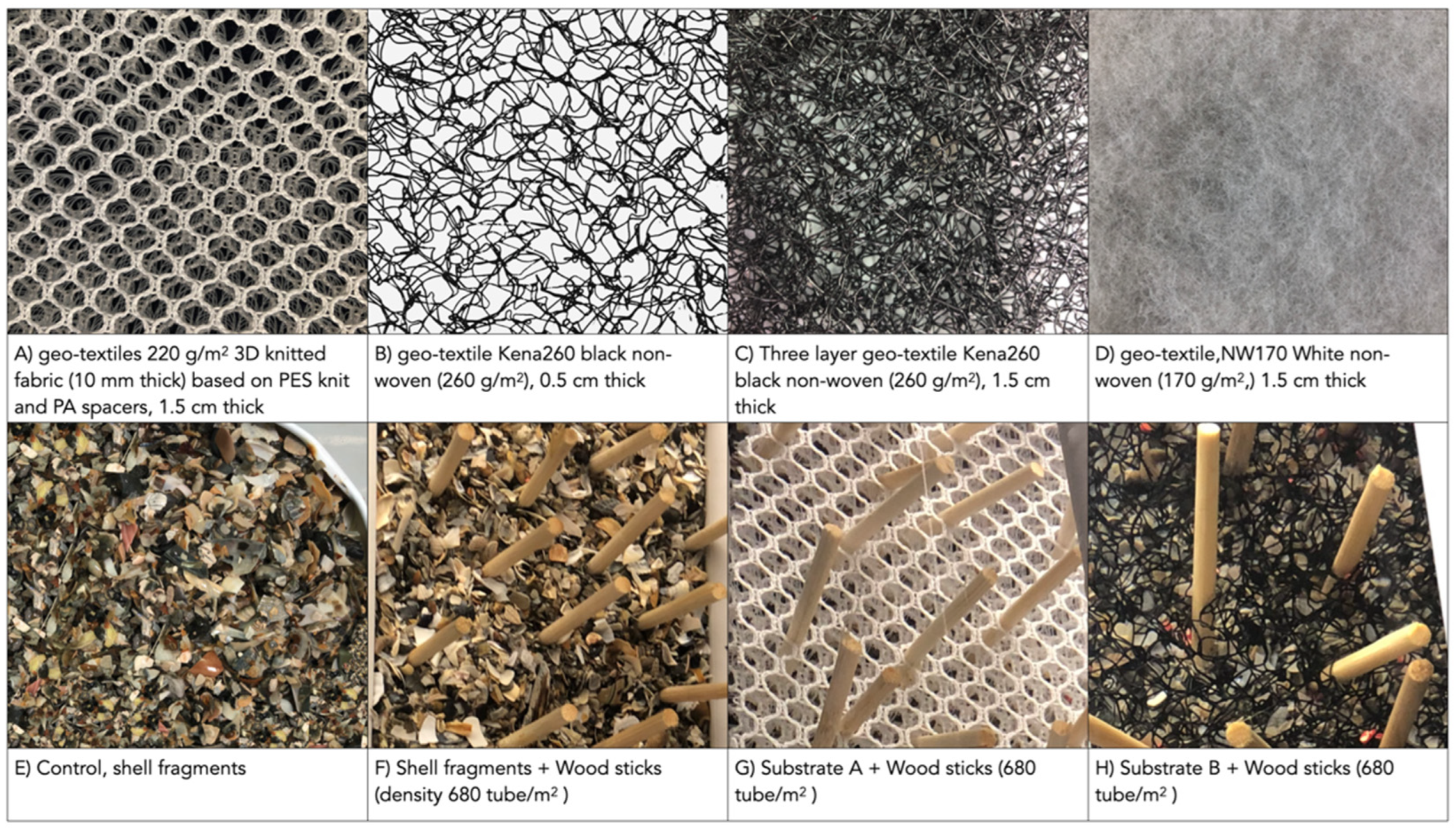
2.2. Artificially Screening Substrates Based on Capture Rate
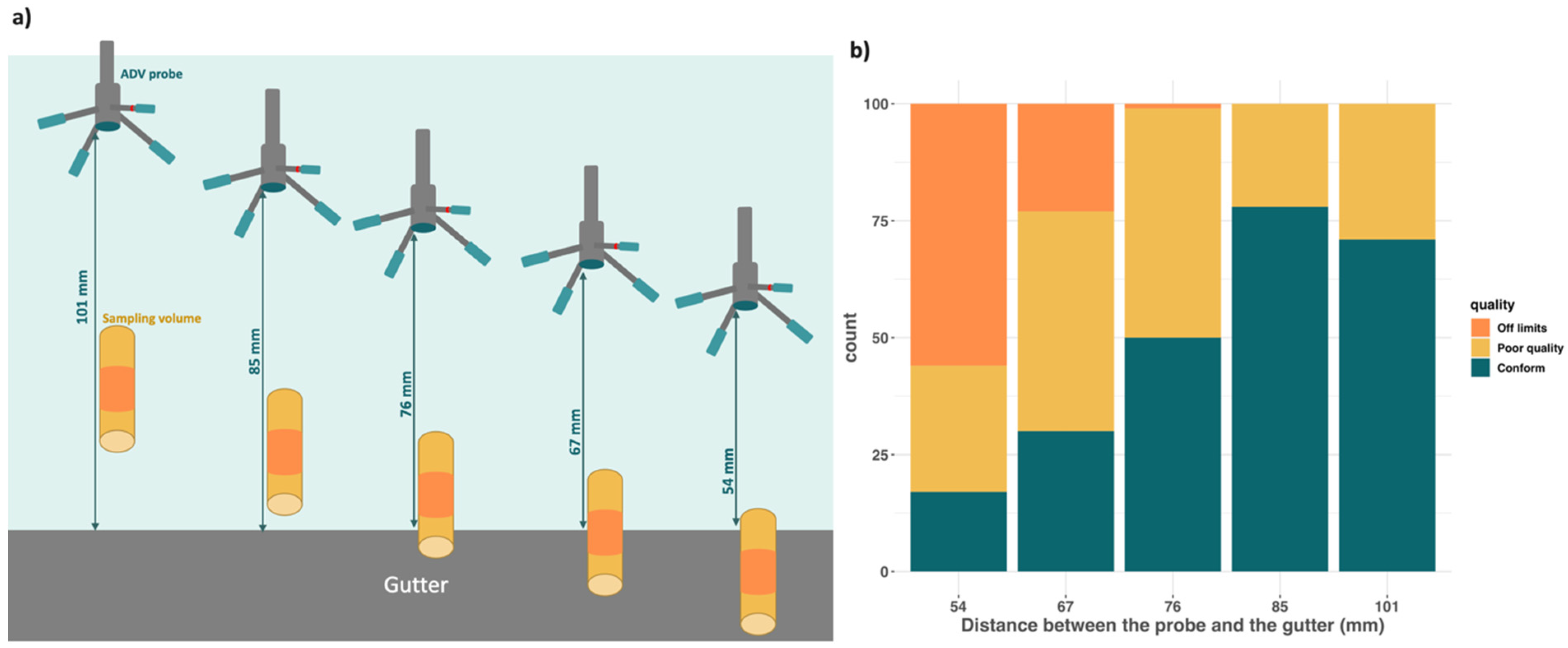
2.3. Screening Substrates Based on Their Ability to Affect Current Velocity
2.4. Screening Substrates Based on Larval Settlement
2.5. Statistical Tests
3. Results
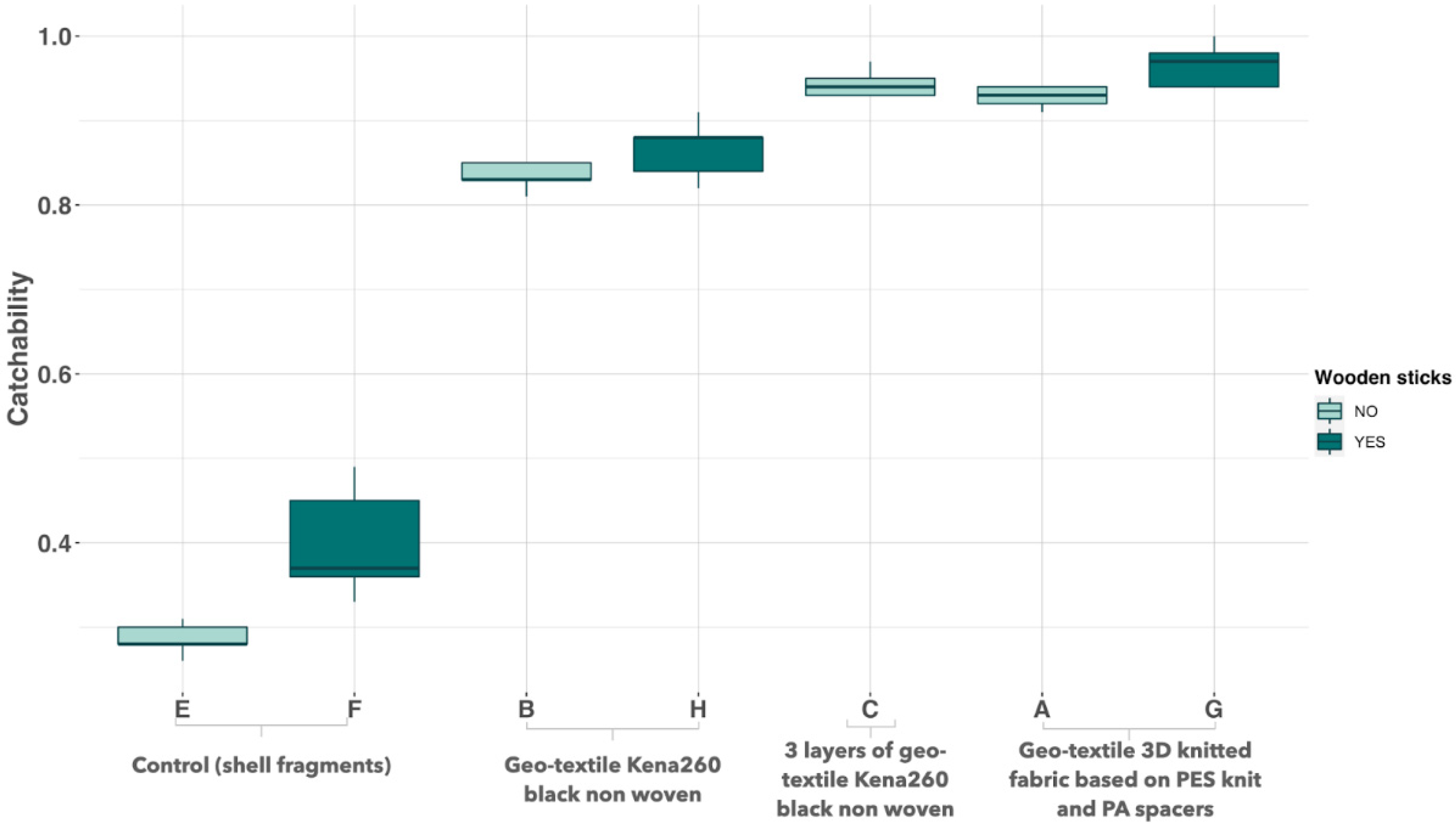
3.1. Screening of Substrate Based on Capture Rate
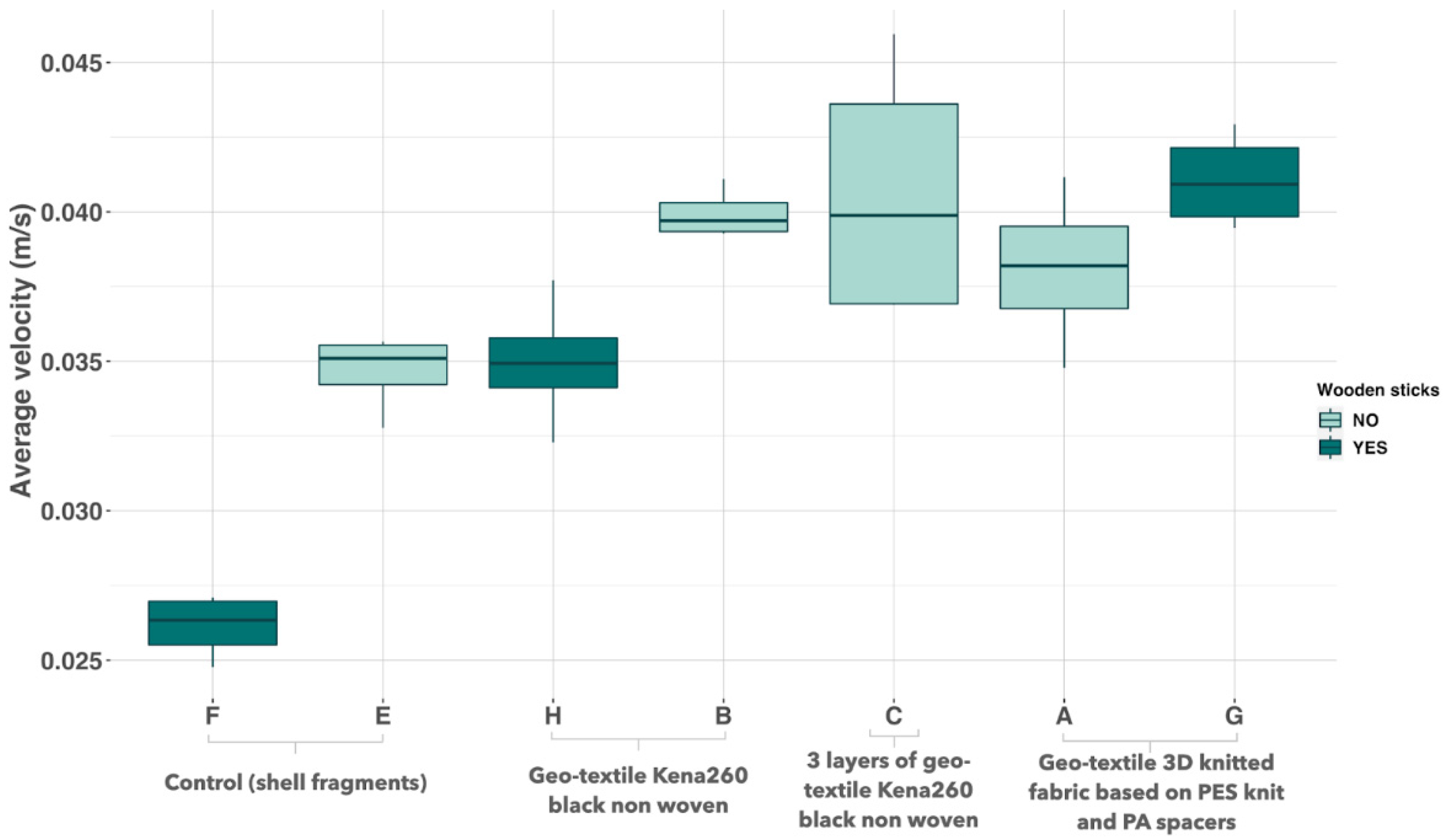
3.2. Screening of Substrates Based on Velocity
3.3. Screening of Substrates Based on Larval Settlement of L. Conchilega
4. Discussion
4.1. Methodological Development
4.2. Substrate Ranking
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- In, F.; Airoldi, L.; Gibson, R.; Atkinson, R.; Gordon, J. Loss, Status and Trends for Coastal Marine Habitats of Europe. Annu. Rev. 2007, 45, 345–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinochet, J.; Urbina, M.A.; Lagos, M.E. Marine invertebrate larvae love plastics: Habitat selection and settlement on artificial substrates. Environ. Pollut. Barking Essex. 2020, 257, 113571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.; Hagenaars, G.; Ranasinghe, R.; Baart, F.; Donchyts, G.; Aarninkhof, S. The State of the World’s Beaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annual Report 2009|UN-Habitat; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Available online: https://unhabitat.org/annual-report-2009 (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Gracia, A.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Oakley, J.A.; Williams, A.T. Use of ecosystems in coastal erosion management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeteman, C.; de Lannoy, W.; Paepe, R.; van Cauwenberghe, C. Vulnerability of the Belgian Coastal Lowlands to Future Sea-level Rise. Impacts Sea-Level Rise Eur. Coast. Lowl. Inst. Br. Geogr. Spec. Publ. Ser. 1992, 27, 56–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lebbe, L.; van Meir, N.; Viaene, P. Potential Implications of Sea-Level Rise for Belgium. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 242, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Den Eynde, D.; Ponsar, S.; Luyten, P.; Ozer, J. Analysis of Climate Changes in the Time Series of Wind Speed, Significant Wave Height and Storm Surges at the Belgian Coast; Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, Operational Directorate Natural Environment: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; Available online: www.van-den-eynde-et-al-2019-crest-v6.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Charlier, R.H.; Meyer, D.; DeCroo, D. Beach protection and restoration part I: Hard structures and Beach erosion. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 1989, 33, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Biest, K.; Verwaest, T.; Vanneuville, W.; Reyns, J.; Mostaert, F. CLIMAR-Evaluation of Climate Change Impacts and Adaptation Responses for Marine Activities; Flanders Hydraulics Research: Antwerp, Belgium, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Temmerman, S.; Meire, P.; Bouma, T.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Ysebaert, T.; de Vriend, H.J. Ecosystem-based coastal defence in the face of global change. Nature 2013, 504, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsje, B.W.; van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Dekker, F.; Paalvast, P.; Bouma, T.J.; van Katwijk, M.M.; de Vries, M.B. How ecological engineering can serve in coastal protection. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 37, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.; Psuty, N.; Perez, B. The role of pulsing events in the functioning of coastal barriers and wetlands: Implications for human impact, management and the response to sea level rise. In Concepts and Controversies in Tidal Marsh Ecology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; pp. 633–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, R. Juveniles stick to adults: Recruitment of the tube-dwelling polychaete Lanice conchilega (Pallas, 1766). Hydrobiologia 2003, 503, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckx, T. Coastbusters: Investigation of ecosystem based coastal stabilisation solutions. In Proceedings of the 22nd World Dredging Congress, WODCON XXII, Shangai, China, 25–29 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ropert, M.; Dauvin, J.-C. Renewal and accumulation of a Lanice conchilega (Pallas) population in the baie des Veys, western Bay of Seine. Oceanol. Acta 2000, 23, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Hoey, G.; Guilini, K.; Rabaut, M.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. Ecological implications of the presence of the tube-building polychaete Lanice conchilega on soft-bottom benthic ecosystems. Mar. Biol. 2008, 154, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borsje, B.W.; Besio, G.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Blondeaux, P.; Vittori, G. Exploring Biological Influence on Offshore Sand Wave Length; SHOM: Leeds, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelmeir, E. Beobachtungen über den Röhrenbau von Lanice conchilega (Pallas) im Experiment und am natürlichen Standort. Helgoländer Wiss. Meeresunters. 1952, 4, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.E.; Jago, C.F. In situ assessment of modification of sediment properties by burrowing invertebrates. Mar. Biol. 1993, 115, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, D.A. Sedimentological effects and palaeoecological implications of the tube-building polychaete Lanice conchilega Pallas. Sedimentology 1987, 34, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Annelida, Borstenwürmer, Polychaeta. Bijdr. Tot De Dierkunde. 1992, 61, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buhr, K.-J.; Winter, J.E. Distribution and maintenance of a lanice conchilega association in the weser estuary (FRG), with special reference to the suspension—feeding behaviour of lanice conchilega. In Biology of Benthic Organisms: 11th European Symposium on Marine Biology, Galway, October 1976; Elsevier: Pergamon, Greece, 1977; pp. 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, D. Particle Resuspension in the Benthic Boundary Layer Induced by Flow around Polychaete Tubes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1983, 40, s301–s308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuers, J.; Jaklin, S.; Zuhlke, R.; Dittmann, S.; Gunther, C.P.; Hildenbrandt, H.; Grimm, V. A model on the distribution and abundance of the tube-building polychaete Lanice conchilega (Pallas, 1766) in the intertidal of the Wadden Sea. Verh. Ges. Für Ökol. 1998, 28, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Woodin, S.A. Refuges, Disturbance, and Community Structure: A Marine Soft-Bottom Example. Ecology 1978, 59, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, S.; Graf, G. Impact of irrigation on oxygen flux into the sediment: Intermittent pumping by Callianassa subterranea and “piston-pumping” by Lanice conchilega. Mar. Biol. 1995, 123, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.-Y. Larval settlement of polychaetes. Reprod. Strateg. Dev. Patterns Annelids 1999, 142, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zühlke, R.; Blome, D.; van Bernem, K.H.; Dittmann, S. Effects of the tube-building polychaeteLanice conchilega (Pallas) on benthic macrofauna and nematodes in an intertidal sandflat. Senckenberg. Marit. 1998, 29, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, D. A Comparative Study of Reproduction and Development in the Polychaete Family Terebellidae. Biol. Bull. 1993, 185, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keßler, M. Die Entwicklung von Lanice concbilega [Pallas} mit besonderer eriicksichtigung der Lebensweise. Helgoländer Wiss. Meeresunters. 1963, 8, 425–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, A.A.; Al-Sofyani, A.A.; Ba-Akdah, M.A.; Satheesh, S. Invertebrate recruitment on artificial substrates in the Red Sea: Role of substrate type and orientation. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2019, 99, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckman, J.E. Hydrodynamic processes affecting benthic recruitment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, M.; Bourget, E. Recruitment of marine invertebrates onto arborescent epibenthic structures: Active and passive processes acting at different spatial scales. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 153, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaklin, S. Recruitment dynamics of North Sea macrozoobenthos in intertidal soft bottoms: Larval availability, settlement and dispersal. Ph.D. Thesis, Staats-und Universitätsbibliothek Bremen, Bremen, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wyns, L.; Semeraro, A.; Sterckx, T.; Delbare, D.; van Hoey, G. Practical implementation of in vitro culture of Lanice conchilega (Polychaeta) in a coastal defence context. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 64, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeraro, A. Enhancing A Lanice Reef Report of Field Trials 2017–2020; Instituut voor Landbouwen Visserijonderzoek (ILVO): Oostende, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fingerut, J.; Hart, D.; Thomson, J. Larval settlement in benthic environments: The effects of velocity and bed element geometry. Freshw. Biol. 2011, 56, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, M.; Graf, G.; Springer, B. Skimming flow induced over a simulated polychaete tube lawn at low population densities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 192, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greve, W. The “planktonkreisel”, a new device for culturing zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 1968, 1, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakow, K.C.; Graham, W.M. Orientation and swimming mechanics by the scyphomedusa Aurelia sp. in shear flow. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arganda-Carreras, I.; Kaynig, V.; Rueden, C.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Schindelin, J.; Cardona, A.; Seung, H.S. Trainable Weka Segmentation: A machine learning tool for microscopy pixel classification. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2424–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swertz, O.C.; Colijn, F.; Hofstraat, H.W.; Althuis, B.A. Temperature, Salinity, and Fluorescence in Southern North Sea: High-Resolution Data Sampled from a Ferry. Environ. Manag. 1999, 23, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, R. Tube worms promote community change. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 308, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Hoey, G.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. Some recommendations for an accurate estimation of Lanice conchilega density based on tube counts. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2006, 60, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhaud, M.R.; Cazaux, C.P. Buoyancy characteristics of Lanice conchilega (Pallas) larvae (Terebellidae). Implications for settlement. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1990, 141, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Comprehensive Manual for Velocimeters-Vectrino Profiler; Nortek Manuals: Boston, MA, USA, 2018.
- Masaló, I.; Reig, L.; Oca, J. Study of fish swimming activity using acoustical Doppler velocimetry (ADV) techniques. Aquac. Eng. 2008, 38, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanson, H. Acoustic Doppler velocimetry (ADV) in the field and in laboratory: Practical experiences. In Proceedings of the International Meeting on Measurements and Hydraulics of Sewers IMMHS’08, Summer School GEMCEA/LCPC, Bouguenais, France, 19–21 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, D.; Mazurkiewicz, M. Methods of culturing polychaetes. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Kimura, S.; Kawamura, T.; Horii, T.; Kurogi, H.; Kitagawa, T. Simulating larval dispersal processes for abalone using a coupled particle-tracking and hydrodynamic model: Implications for refugium design. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 387, 205–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLelland, S.J.; Nicholas, A.P. A new method for evaluating errors in high-frequency ADV measurements. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanckaert, K.; Lemmin, U. Means of noise reduction in acoustic turbulence measurement. J. Hydraul. Res. 2006, 44, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgaris, G.; Trowbridge, J.H. Evaluation of the Acoustic Doppler Velocimeter (ADV) for Turbulence Measurements*. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoey, G.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. Chapter 5: Population—dynamics of subtidal Lanice conchilega (Pallas, 1766) populations at the Belgian Continental Shelf. In Spatio-Temporal Variability within the Macrobenthicy Abra Alba Community, with Emphasis on the Structuring Role of Lanice Conchilega; Universiteit Gent: Ghent, Belgium, 2006; pp. 93–116. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, K. Algal blooms in the North Sea: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Dana. Charlottenlund. 1989, 8, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Toonen, R.; Pawlik, J. Settlement of the gregarious tube worm Hydroides dianthus (Polychaeta: Serpulidae). II. Testing the desperate larva hypothesis. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 2001, 224, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabaut, M.; Guilini, K.; van Hoey, G.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. A bio-engineered soft-bottom environment: The impact of Lanice conchilega on the benthic species-specific densities and community structure. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Degraer, S.; Moerkerke, G.; Rabaut, M.; Van Hoey, G.; Du Four, I.; Vincx, M.; Henriet, J.-P.; Van Lancker, V. Very-high resolution side-scan sonar mapping of biogenic reefs of the tube-worm Lanice conchilega. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3323–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashefipour, S.M.; Daryaee, M.; Ghomeshi, M. Effect of bed roughness on velocity profile and water entrainment in a sedimentary density current. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 45, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostaschuk, R. A field study of turbulence and sediment dynamics over subaqueous dunes with flow separation. Sedimentology 2000, 47, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Bilal, M. Chapter 15-Research progress of biodegradable materials in reducing environmental pollution. In Abatement of Environmental Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidenbach, M.A.; Koseff, J.R.; Koehl, M.a.R. Hydrodynamic forces on larvae affect their settlement on coral reefs in turbulent, wave-driven flow. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bashevkin, S.M.; Dibble, C.D.; Dunn, R.P.; Hollarsmith, J.A.; Ng, G.; Satterthwaite, E.V.; Morgan, S.G. Larval dispersal in a changing ocean with an emphasis on upwelling regions. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e03015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, T.P.; Aleynik, D.; Burrows, M. Larval dispersal of intertidal organisms and the influence of coastline geography. Ecography 2013, 37, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Hurlaborde, A.; Semeraro, A.; Sterckx, T.; Van Hoey, G. Optimized Screening Methods for Investigation of the Larval Settlement of Lanice conchilega on Artificial Substrates. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101443
D’Hurlaborde A, Semeraro A, Sterckx T, Van Hoey G. Optimized Screening Methods for Investigation of the Larval Settlement of Lanice conchilega on Artificial Substrates. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(10):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101443
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Hurlaborde, Alice, Alexia Semeraro, Thomas Sterckx, and Gert Van Hoey. 2022. "Optimized Screening Methods for Investigation of the Larval Settlement of Lanice conchilega on Artificial Substrates" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 10: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101443
APA StyleD’Hurlaborde, A., Semeraro, A., Sterckx, T., & Van Hoey, G. (2022). Optimized Screening Methods for Investigation of the Larval Settlement of Lanice conchilega on Artificial Substrates. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(10), 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101443








