Behavioral Pattern of Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
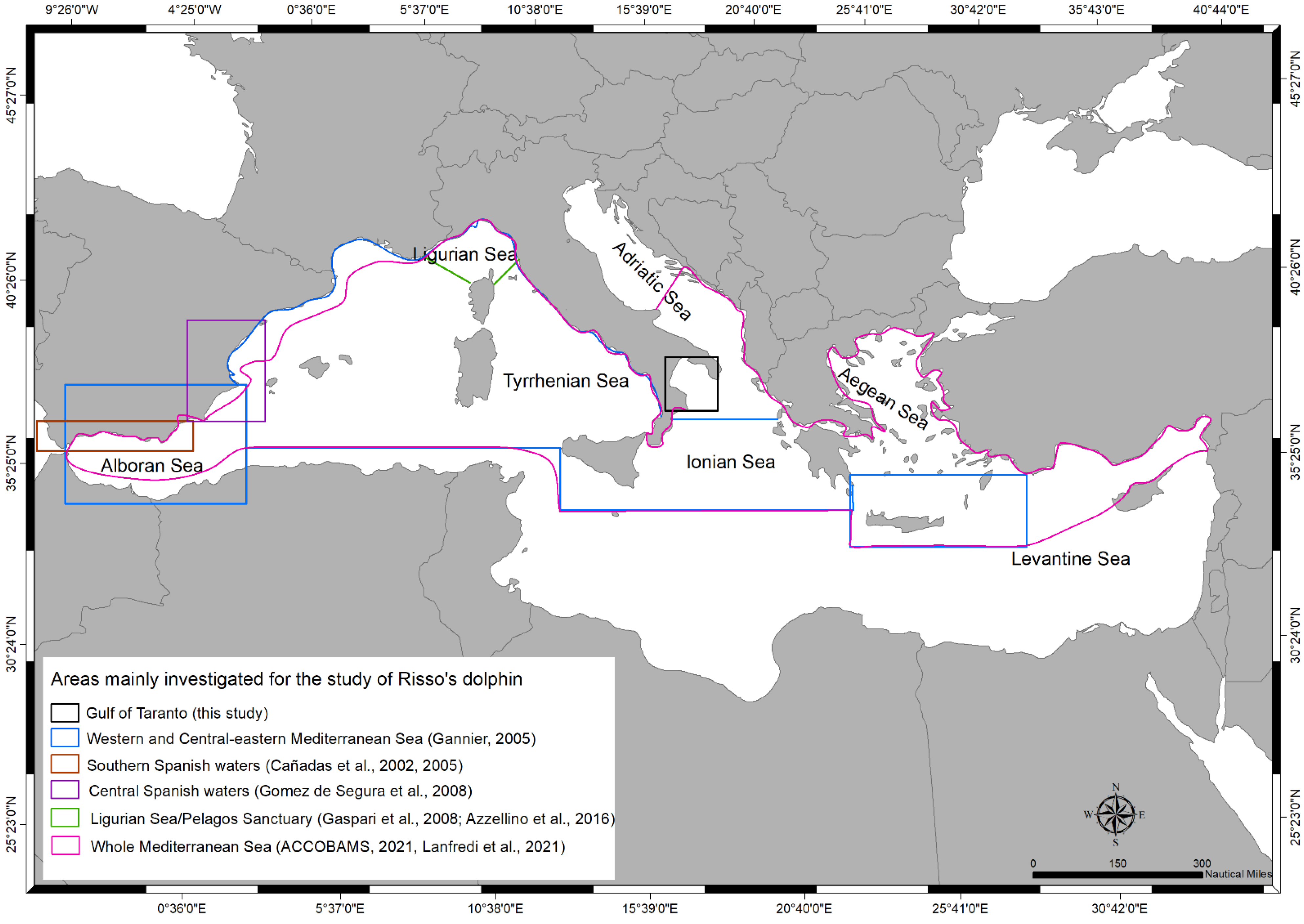
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of Single-Component Analysis
3.2. Behavioral Events and Occurrences
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brakes, P.; Dall, S.R. Marine mammal behavior: A review of conservation implications. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thode, A.; Mathias, D.; Straley, J.; O’Connell, V.; Behnken, L.; Falvey, D.; Wild, L.; Calambokidis, J.; Schorr, G.; Andrews, R.; et al. Cues, creaks, and decoys: Using passive acoustic monitoring as a tool for studying sperm whale depredation. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 1621–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, P.; Gasco, N.; Duhamel, G.; Guinet, C. Habituation to an acoustic harassment device (AHD) by killer whales depredating demersal longlines. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 72, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wade, P.R.; Reeves, R.R.; Mesnick, S.L. Social and behavioural factors in cetacean responses to overexploitation: Are odontocetes less “resilient” than mysticetes? J. Mar. Biol. 2012, 567276, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitehead, H. Conserving and managing animals that learn socially and share cultures. Learn. Behav. 2010, 38, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mann, J.; Connor, R.C.; Tyack, P.L.; Whitehead, H. Cetacean Societies: Field Studies of Dolphins and Whales; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gowans, S.; Würsig, B.; Karczmarski, L. The social structure and strategies of Delphinids: Predictions based on an ecological framework. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2007, 53, 195–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.D. Role of marine mammals in aquatic ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 158, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katona, S.; Whitehead, H. Are cetacean ecologically important? Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1988, 26, 553–568. [Google Scholar]
- Kiszka, J.J.; Heithaus, M.R.; Wirsing, A.J. Behavioural drivers of the ecological roles and importance of marine mammals. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 523, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, D.S.; Tizzi, R.; Mussi, B. Cetaceans value and conservation in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Biodivers. Endanger. Species 2015, S1, 004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergio, F.; Caro, T.; Brown, D.; Clucas, B.; Hunter, J.; Ketchum, J.; McHugh, K.; Hiraldo, F. Top predators as conservation tools: Ecological rationale, assumptions, and efficacy. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawkins, E.R.; Harcourt, R.; Bejder, L.; Brooks, L.O.; Grech, A.; Christiansen, F.; Marsh, H.; Harrison, P.L. Best practice framework and principles for monitoring the effect of coastal development on marine mammals. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Albouy, C.; Lasram, F.B.R.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Christensen, V.; Karpouzi, V.S.; Guilhaumon, F.; Mouillot, D.; Paleczny, M.; et al. The Mediterranean Sea under siege: Spatial overlap between marine biodiversity: Cumulative threats and marine reserves. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2012, 21, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasi, M.F.; Caserta, V.; Bruno, C.; Salzeri, P.; Di Paola, A.I.; Lucchetti, A. Behaviour and vocalizations of two sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) entangled in illegal driftnets in the Mediterranean Sea. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanizza, C.; Maglietta, R.; Buscaino, G.; Carlucci, R.; Ceraulo, M.; Cipriano, G.; Grammauta, R.; Renò, V.; Santacesaria, F.C.; Sion, L.; et al. Emission rate of acoustic signals for the common bottlenose and striped dolphins in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-eastern Mediterranean Sea). In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Bari, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Manna, G.; Rako-Gòspic, N.; Manghi, M.; Ceccherelli, G. Influence of environmental, social and behavioural variables on the whistling of the common bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2019, 73, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, B.D. Whistle characteristics in free-ranging bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in the Mediterranean Sea: Influence of behaviour. Mamm. Biol. 2011, 76, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papale, E.; Fanizza, C.; Buscaino, G.; Ceraulo, M.; Cipriano, G.; Crugliano, R.; Grammauta, R.; Gregorietti, M.; Renò, V.; Ricci, P.; et al. The social role of vocal complexity in striped dolphins. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 584301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintore, L.; Sciacca, V.; Viola, S.; Giacoma, C.; Papale, E.; Giorli, G. Fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus) in the Ligurian Sea: Preliminary study on acoustics demonstrates their regular occurrence in autumn. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, R.; Ricci, P.; Miccoli Sartori, S.; Cipriano, G.; Cosentino, A.; Lionetti, A.; Fanizza, C. Changes in behaviour and group size of Stenella coeruleoalba in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central Mediterranean Sea). Biol. Mar. Mediterr. 2015, 22, 266–270. [Google Scholar]
- Carlucci, R.; Ricci, P.; Cipriano, G.; Fanizza, C. Abundance, activity and critical habitat of the striped dolphin Stenella coeruleoalba in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central Mediterranean Sea). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2018, 28, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannier, A. Diel variations of the striped dolphin distribution off the French Riviera (Northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Aquat. Mamm. 1999, 25, 123–134. [Google Scholar]
- Gannier, A.; Laran, S. Summer activity patterns of the striped dolphin in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Eur. Res. Cetaceans 1999, 13, 312–316. [Google Scholar]
- Affinito, F.; Olaya Meza, C.; Akkaya Bas, A.; Brill, D.; Whittaker, G.; Capel, L. On the behaviour of an under-studied population of bottlenose dolphins in the Southern Adriatic Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2019, 99, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bearzi, G.; Notarbartolo Di Sciara, G.; Politi, E. Social ecology of bottlenose dolphins in the Kvarnerić (northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Mamm. Sci. 1997, 13, 650–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, G.; Politi, E.; Notarbartolo Di Sciara, G. Diurnal behavior of free-ranging bottlenose dolphins in the Kvarnerić (northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Mamm. Sci. 1999, 15, 1065–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genov, T.; Kotnjek, P.; Lesjak, J.; Hace, A.; Fortuna, C.M. Bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) in Slovenian and adjacent waters (northern Adriatic Sea). Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat. 2008, 18, 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Genov, T.; Centrih, T.; Kotnjek, P.; Hace, A. Behavioural and temporal partitioning of dolphin social groups in the northern Adriatic Sea. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canese, S.; Cardinali, A.; Fortuna, C.M.; Giusti, M.; Lauriano, G.; Salvati, E.; Greco, S. The first identified winter ground of fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus) in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2006, 86, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafortuna, C.L.; Jahoda, M.; Azzellino, A.; Saibene, F.; Colombini, A. Locomotor behaviours and respiratory pattern of the Mediterranean fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus). Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 90, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarbartolo Di Sciara, G.; Zanardelli, M.; Jahoda, M.; Panigada, S.; Airoldi, S. The fin whale Balaenoptera physalus (L. 1758) in the Mediterranean Sea. Mamm. Rev. 2003, 33, 105–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, K.L. Risso’s dolphin, Grampus griseus. In Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals, 3rd ed.; Würsig, B., Kovacs, K., Thewissen, J.G.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MD, USA, 2018; pp. 824–827. [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson, T.A.; Weir, C.R.; Anderson, R.C.; Ballance, L.T.; Kenney, R.D.; Kiszka, J.J. Global distribution of Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus: A review and critical evaluation. Mammal. Rev. 2014, 44, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicote, C.A.; Gazo, M.; Cañadas, A.; Pauner, O.; Sáiz, L.; Pastor, C.; Nuez, I. Grampus Project: Study and Monitoring of the Pilot Whale Population Associated with Submarine Canyons on the Catalan Coast; Technical Report; Fundacion Biodiversidad: Madrid, Spain, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, C.; Raduán, M.Á.; Raga, J.A. Diet of Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the western Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.R.; Pascoe, P.L. The stomach contents of a Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus stranded at Thurlestone, South Devon. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1985, 65, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockcroft, V.G.; Haschick, S.L.; Klages, N.W. The diet of Risso’s dolphin, Grampus griseus (Cuvier, 1812), from the east coast of South Africa. Z. Säugetierkunde 1993, 58, 286–293. [Google Scholar]
- Luna, A.; Sánchez, P.; Chicote, C.; Gazo, M. Cephalopods in the diet of Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) from the Mediterranean Sea: A review. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.B.; Vella, A.; Vidoris, P.; Christidis, A.; Koutrakis, E.; Frantzis, A.; Miliou, A.; Kallianiotis, A. Cetacean stranding and diet analyses in the North Aegean Sea (Greece). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2017, 98, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Dalsgaard, J.; Froese, R.; Torres, F. Fishing down marine food webs. Science 1998, 279, 860–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañadas, A.; Sagarminaga, R.; Garcıa-Tiscar, S. Cetacean distribution related with depth and slope in the Mediterranean waters off southern Spain. Deep Sea Res. Part. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 2053–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannier, A. Summer distribution and relative abundance of delphinids in the Mediterranean Sea. Rev. Ecol. Terre Vie 2005, 60, 223–238. [Google Scholar]
- García-Polo, M.; Giménez, J.; Mons, J.; Castillo, J.; De Stephanis, R.; Santos, M.; Fernández-Maldonado, C. Stomach contents of cetaceans in the Alborán Sea and Gulf of Cádiz. Front. Mar. Sci. Conference Abstract. In Proceedings of the IMMR | International Meeting on Marine Research 2014, Peniche, Portugal, 10–11 July 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerem, D.; Hadar, N.; Goffman, O.; Scheinin, A.; Kent, R.; Boisseau, O.; Schattner, U. Update on the cetacean fauna of the Mediterranean Levantine Basin. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 6, 6–27. [Google Scholar]
- Azzellino, A.; Airoldi, S.; Gaspari, S.; Lanfredi, C.; Moulins, A.; Podestà, M.; Rosso, M.; Tepsich, P. Risso’s dolphin, Grampus griseus, in the western Ligurian Sea: Trends in population size and habitat use. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2016, 75, 205–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bearzi, G.; Reeves, R.R.; Remonato, E.; Pierantonio, N.; Airoldi, S. Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus in the Mediterranean Sea. Mamm. Biol. 2011, 76, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfredi, C.; Remonato, E.; Airoldi, S. Preliminary Report of the Mediterranean Grampus Project 2.0: Improving knowledge and Conservation of the Mediterranean Population of Risso’s Dolphins through Effective Partnerships; European Cetacean Society: La Spezia, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ACCOBAMS. Progress report regarding Risso’s dolphin conservation management plan (CMP) in ACCOBAMS area. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth Meeting of the Scientific Committee, Monaco, Monaco, 22–26 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gaspari, S. Social and population structure of striped and Risso’s dolphins in the Mediterranean Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gaspari, S.; Azzellino, A.; Airoldi, S.; Hoelzel, A.R. Social kin associations and genetic structuring of striped dolphin populations (Stenella coeruleoalba) in the Mediterranean Sea. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 2922–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, S.L. Aspects of the Biology, Ecology, and Behavior of Risso’s Dolphins (Grampus Griseus) off the California Coast. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Santa Cruz, CA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kruse, S.; Caldwell, D.K.; Caldwell, M.C. Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus (G. Cuvier, 1812). In Handbook of Marine Mammals; Ridgway, S., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 6, pp. 183–212. [Google Scholar]
- Shane, S.H. Behavior patterns of pilot whales and Risso’s dolphins off Santa Catalina Island, California. Aquat. Mamm. 1995, 21, 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Smultea, M.A.; Lomac-MacNair, K.; Nations, C.S.; McDonald, T.; Würsig, B. Behavior of Risso’s dolphins (Grampus griseus) in the Southern California Bight: An Aerial Perspective. Aquat. Mamm. 2018, 44, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevilla, M.S.; Wiggins, S.M.; Hildebrand, J.A. Spatial and temporal patterns of Risso’s dolphin echolocation in the Southern California Bight. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.N.D. Field notes on Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus) distribution, social ecology, behaviour, and occurrence in the Azores. Aquat. Mamm. 2008, 34, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, F.; Hartman, K.L.; Rood, E.J.; Hendriks, A.J.; Zult, D.B.; Wolff, W.J.; Huisman, J.; Pierce, G.J. Risso’s dolphins alter daily resting pattern in response to whale watching at the Azores. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2011, 27, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visser, F.; Keller, O.A.; Oudejans, M.G.; Nowacek, D.P.; Kok, A.C.M.; Huisman, J.; Sterck, E.H.M. Risso’s dolphins perform spin dives to target deep-dwelling prey. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 202320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, S.; Natoli, A. Grampus griseus (Mediterranean subpopulation). In IUCN 2012. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Version 2012 3.1. Available online: www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- ACCOBAMS. Conserving Whales, Dolphins and Porpoises in the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea and Adjacent Areas: An ACCOBAMS Status Report; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G., Tonay, A.M., Eds.; ACCOBAMS: Monaco, Monaco, 2021; pp. 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Lanfredi, C.; Arcangeli, A.; David, L.; Holčer, D.; Rosso, M.; Natoli, A. Risso’s dolphin, Grampus griseus, Mediterranean subpopulation. In The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species; Politecnico di Milano, University of Technology: Milano, Italy; Tethys Research Institute: Milano, Italy, 2021; In press. [Google Scholar]
- Bellomo, S.; Cipriano, G.; Santacesaria, F.C.; Fanizza, C.; Crugliano, R.; Pollazzon, V.; Ricci, P.; Maglietta, R.; Carlucci, R. Impact of cetacean watching vessels on Risso’s dolphins behaviour in the Gulf of Taranto: Preliminary information to regulate dolphin watching. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Reggio Calabria, Italy, 4–6 October 2021; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, R.; Akkaya Bas, A.; Maglietta, R.; Renò, V.; Fanizza, C.; Rizzo, A.; Crugliano, R.; Cipriano, G. Site fidelity, residency pattern and habitat use of the Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-eastern Mediterranean Sea) by photo-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Bari, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Carlucci, R.; Baş, A.A.; Liebig, P.; Renò, V.; Santacesaria, F.C.; Bellomo, S.; Fanizza, C.; Maglietta, R.; Cipriano, G. Residency patterns and site fidelity of Grampus griseus (Cuvier, 1812) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Mammal. Res. 2020, 65, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crugliano, R.; Maglietta, R.; Bellomo, S.; Carlucci, R.; Cipriano, G.; Fanizza, C.; Pollazzon, V.; Santacesaria, F.C.; Ricci, P. Reliability of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for the groups size estimation of Grampus griseus (Cuvier, 1812) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-eastern Mediterranean Sea). In Proceedings of the 2021 International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Reggio Calabria, Italy, 4–6 October 2021; pp. 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglietta, R.; Renò, V.; Cipriano, G.; Fanizza, C.; Milella, A.; Stella, E.; Carlucci, R. DolFin: An innovative digital platform for studying Risso’s dolphins in the Northern Ionian Sea (North-eastern Central Mediterranean). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglietta, R.; Bruno, A.; Renò, V.; Dimauro, G.; Stella, E.; Fanizza, C.; Bellomo, S.; Cipriano, G.; Tursi, A.; Carlucci, R. The promise of machine learning in the Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus photo-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Bari, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Maglietta, R.; Renò, V.; Caccioppoli, R.; Seller, E.; Bellomo, S.; Santacesaria, F.C.; Colella, R.; Cipriano, G.; Stella, E.; Hartman, K.; et al. Convolutional Neural Networks for Risso’s dolphins identification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 80195–80206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renò, V.; Dimauro, G.; Labate, G.; Stella, E.; Fanizza, C.; Capezzuto, F.; Cipriano, G.; Carlucci, R.; Maglietta, R. Exploiting spe-cies distinctive visual cues towards the automated photo-identification of the Risso’s dolphin Grampus griseus. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Bari, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Renó, V.; Dimauro, G.; Labate, G.; Stella, E.; Fanizza, C.; Cipriano, G.; Carlucci, R.; Maglietta, R. A SIFT-based software system for the photo-identification of the Risso’s dolphin. Ecol. Inform. 2019, 50, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renò, V.; Losapio, G.; Forenza, F.; Politi, T.; Stella, E.; Fanizza, C.; Hartman, K.; Carlucci, R.; Dimauro, G.; Maglietta, R. Combined color semantics and deep learning for the automatic detection of dolphin dorsal fins. Electronics 2020, 9, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, R.; Battista, D.; Capezzuto, F.; Serena, F.; Sion, L. Occurrence of the basking shark Cetorhinus maximus (Gunnerus, 1765) in the Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Ital. J. Zool. 2014, 81, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Civitarese, G.; Gačić, M.; Lipizer, M.; Eusebi Borzelli, G.L. On the impact of the bimodal oscillating system (BiOS) on the biogeochemistry and biology of the Adriatic and Ionian seas (eastern Mediterranean). Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 3987–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matarrese, R.; Chiaradia, M.T.; Tijani, K.; Morea, A.; Carlucci, R. Chlorophyll a’multi-temporal analysis in coastal waters with MODIS data. Ital. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 43, 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pinardi, N.; Lyubartsev, V.; Cardellicchio, N.; Caporale, C.; Ciliberti, S.; Coppini, G.; Stefania, C.; Giovanni, C.; De Pascalis, F.; Zaggia, L. Marine rapid environmental assessment in the Gulf of Taranto: A multiscale approach. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 2623–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capezzuto, F.; Carlucci, R.; Maiorano, P.; Sion, L.; Battista, D.; Giove, A.; D’Onghia, G. The bathyal benthopelagic fauna in the Northwestern Ionian Sea: Structure, patterns and interactions. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, R.; Bandelj, V.; Ricci, P.; Capezzuto, F.; Sion, L.; Maiorano, P.; Libralato, S. Exploring spatio-temporal changes in the demersal and benthopelagic assemblages of the Northwestern Ionian Sea (Central Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 598, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorano, P.; Sion, L.; Carlucci, R.; Capezzuto, F.; Giove, A.; Costantino, G.; Tursi, A. The demersal faunal assemblage of the NW Ionian Sea (Central Mediterranean): Current knowledge and perspectives. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 219–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, P.; Libralato, S.; Capezzuto, F.; D’Onghia, G.; Maiorano, P.; Sion, L.; Carlucci, R. Ecosystem functioning of two marine food webs in the North-Western Ionian Sea (Central Mediterranean Sea). Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 10198–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlucci, R.; Maglietta, R.; Buscaino, G.; Cipriano, G.; Milella, A.; Pollazzon, V.; Fanizza, C. Review on research studies and monitoring system applied to cetaceans in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea). In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Lecce, Italy, 29 August–1 September 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Carlucci, R.; Capezzuto, F.; Cipriano, G.; D’Onghia, G.; Fanizza, C.; Libralato, S.; Ricci, P. Assessment of cetacean-fishery interactions in the marine food web of the Gulf of Taranto (northern Ionian Sea, central Mediterranean Sea). Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2021, 31, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, P.; Ingrosso, M.; Cipriano, G.; Fanizza, C.; Maglietta, R.; Renò, V.; Tursi, A.; Carlucci, R. Top-down cascading effects driven by the odontocetes in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central Mediterranean Sea). In Proceedings of the IMEKO Metrology for the Sea, Genova, Italy, 5–7 October 2020; pp. 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Carlucci, R.; Manea, E.; Ricci, P.; Cipriano, G.; Fanizza, C.; Maglietta, R.; Gissi, E. Managing multiple pressures for cetaceans’ conservation with an Ecosystem-Based Marine Spatial Planning approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, P.; Manea, E.; Cipriano, G.; Cascione, D.; D’Onghia, G.; Ingrosso, M.; Fanizza, C.; Maiorano, P.; Tursi, A.; Carlucci, R. Addressing Cetacean–Fishery Interactions to Inform a Deep-Sea Ecosystem-Based Management in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckland, S.T.; Anderson, D.R.; Burnham, K.P.; Laake, J.L.; Borchers, D.L.; Thomas, L. Advanced Distance Sampling; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, J. Behavioral sampling methods for cetaceans: A review and critique. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 1999, 15, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, D.R. Activity budget of free-ranging common dolphins (Delphinus delphis) in the northwestern Bay of Plenty, New Zealand. Aquat. Mamm. 2001, 27, 121–136. [Google Scholar]
- Altmann, J. Observational study of behavior: Sampling methods. Behaviour 1974, 49, 227–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irvine, A.B.; Scott, M.D.; Wells, R.S.; Kaufmann, J.H. Movements and activities of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops truncatus, near Sarasota, Florida. Fish. Bull. 1981, 79, 671–688. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, L.M.; Allen, S.J.; Harcourt, R.G. Group characteristics, site fidelity and seasonal abundance of bottlenose dolphins Tursiops aduncus in Jarvis bay and Port Stephens, south-eastern Australia. Aust. Mammal. 2002, 24, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shane, S.H. Behaviour and ecology of the bottlenose dolphins at Sanibel Island, Florida. In The Bottlenose Dolphin; Leatherwood, S., Reeves, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, A.C. An Ethogram of Naturally Occurring Behavior of Bottlenose Dolphins, Tursiops truncatus, in SOUTHERN California Waters. Master’s thesis, San Diego State University, San Diego, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Meissner, A.M.; Christiansen, F.; Martinez, E.; Pawley, M.D.M.; Orams, M.B.; Stockin, K.A. Behavioural effects of tourism on oceanic common dolphins, Delphinus sp., in New Zealand: The effects of Markov analysis variations and current tour operator compliance with regulations. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokal, R.R.; Rohlf, F.J. Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Azzolin, M.; Arcangeli, A.; Cipriano, G.; Crosti, R.; Maglietta, R.; Pietroluongo, G.; Carlucci, R. Spatial distribution modelling of striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) at different geographical scales within the EU Adriatic and Ionian Sea region, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2020, 30, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, S.; Santacesaria, F.C.; Fanizza, C.; Cipriano, G.; Renò, V.; Carlucci, R.; Maglietta, R. Photo-identification of Physeter macrocephalus in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-eastern Mediterranean Sea). In Proceedings of the IMEKO Metrology for the Sea, Genova, Italy, 3–5 October 2019; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Carlucci, R.; Fanizza, C.; Cipriano, G.; Paoli, C.; Russo, T.; Vassallo, P. Modeling the spatial distribution of the striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba) and common bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, R.; Cipriano, G.; Paoli, C.; Ricci, P.; Fanizza, C.; Capezzuto, F.; Vassallo, P. Random Forest population modelling of striped and common-bottlenose dolphins in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 204, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renò, V.; Dibari, P.; Fanizza, C.; Crugliano, R.; Dimauro, G.; Carlucci, R.; Coppini, G.; Lecci, R.; Maglietta, R.; Causio, S. Multimodal data fusion and analysis for cetaceans’ presence and abundance estimation in the Gulf of Taranto. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea; Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Reggio Calabria, Italy, 4–6 October 2021; pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santacesaria, F.C.; Bellomo, S.; Fanizza, C.; Maglietta, R.; Renò, V.; Cipriano, G.; Carlucci, R. Long term residency of Tursiops truncatus in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-eastern Mediterranean Sea. In Proceedings of the IMEKO Metrology for the Sea, Genova, Italy, 3–5 October 2019; pp. 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dede, A.; Saad, A.; Fakhri, M.; Öztürk, B. Cetacean sightings in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea during the cruise in summer 2008. J. Black Sea/Mediterr. Environ. 2012, 18, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, C.; Cucknell, A.C.; Romagosa, M.; Boisseau, O.; Moscrop, A.; Frantzis, A.; McLanaghan, R. Final Report of a Visual and Acoustic Survey for Marine Mammals in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea during Summer 2013; International Fund for Animal Welfare: Yarmouth, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Azzellino, A.; Airoldi, S.; Gaspari, S.; Nani, B. Habitat use of cetaceans along the continental slope and adjacent waters in the western Ligurian Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2008, 55, 296–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzellino, A.; Panigada, S.; Lanfredi, C.; Zanardelli, M.; Airoldi, S.; Notarbartolo di Sciara, G. Predictive habitat models for managing marine areas: Spatial and temporal distribution of marine mammals within the Pelagos sanctuary (Northwestern Mediterranean Sea). Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2012, 67, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadas, A.; Sagarminaga, R.; de Stephanis, R.; Urquiola, E.; Hammond, P.S. Habitat preference modelling as a conservation tool: Proposals for marine protected areas for cetaceans in southern Spanish waters. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2005, 15, 495–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laran, S.; Joiris, C.; Gannier, A.; Kenney, R.D. Seasonal estimates of densities and predation rates of cetaceans in the Ligurian Sea, northwestern Mediterranean Sea: An initial examination. J. Cetacean Res. Manag. 2010, 11, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, J.B.; Evans, P.G.; Northridge, S.P. Atlas of Cetacean Distribution in North-West European Waters; Joint Nature Conservation Committee: Peterborough, UK, 2003.
- Hartman, K.; Visser, F.; Hendriks, A. Social structure of Risso’s dolphins (Grampus griseus) at the Azores: A stratified community based on highly associated social units. Can. J. Zool. 2008, 86, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, K.; Fernandez, M.; Azevedo, J.M.N. Spatial segregation of calving and nursing Risso’s dolphins (Grampus griseus) in the Azores, and its conservation implications. Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorli, G.; Au, W.W.L.; Neuheimer, A. Differences in foraging activity of deep sea diving odontocetes in the Ligurian Sea as determined by passive acoustic recorders. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caruso, F.; Alonge, G.; Bellia, G.; de Domenico, E.; Grammauta, R.; Larosa, G.; Buscaino, G. Long-term monitoring of dolphin biosonar activity in deep pelagic waters of the Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, F.; Miller, P.J.O.; Antunes, R.N.; Oudejans, M.G.; Mackenzie, M.L.; Aoki, K.; Tyack, P.L. The social context of individual foraging behaviour in long-finned pilot whales (Globicephala melas). Behaviour 2014, 151, 1453–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, F.; Kok, A.C.; Oudejans, M.G.; Scott-Hayward, L.A.S.; DeRuiter, S.L.; Alves, A.C.; Miller, P.O.J. Vocal foragers and silent crowds: Context-dependent vocal variation in Northeast Atlantic long-finned pilot whales. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2017, 71, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartman, K.L.; Fernandez, M.; Wittich, A.; Azevedo, J.M.N. Sex differences in residency patterns of Risso’s dolphins (Grampus griseus) in the Azores: Causes and management implications. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2015, 31, 1153–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, K.L.; van der Harst, P.; Vilela, R. Continuous focal group follows operated by a drone enable analysis of the relation between sociality and position in a group of male Risso’s dolphins (Grampus griseus). Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearzi, M. Dolphin sympatric ecology. Mar. Biol. Res. 2005, 1, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quérouil, S.; Silva, M.A.; Cascão, I.; Magalhães, S.; Seabra, M.I.; Machete, M.A.; Santos, R.S. Why do dolphins form mixed-species associations in the Azores? Ethology 2008, 114, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensland, E.; Angerbjörn, A.; Berggren, P. Mixed species groups in mammals. Mamm. Rev. 2003, 33, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syme, J.; Kiszka, J.J.; Parra, G.J. Dynamics of cetacean Mixed-Species Groups: A review and conceptual framework for assessing their functional significance. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 678173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzis, A.; Herzing, D.L. Mixed species associations of striped dolphin (Stenella coeruleoalba), short-beaked common dolphin (Delphinus delphis) and Risso’s dolphin (Grampus griseus), in the Gulf of Corinth (Greece, Mediterranean Sea). Aquat. Mamm. 2002, 28, 188–197. [Google Scholar]
- Bacon, C.E.; Smultea, M.A.; Fertl, D.; Würsig, B.; Burgess, E.A.; Hawks-Johnson, S. Mixed-species associations of marine mammals in the Southern California Bight, with emphasis on Risso’s Dolphins (Grampus griseus). Aquat. Mamm. 2017, 43, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würtz, M.; Marrale, D. Food of striped dolphin, Stenella coeruleoalba, in the Ligurian Sea. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1993, 73, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.W.; Coe, J.M. Survey of marine debris ingestion by odontocete cetaceans. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Marine Debris; Honolulu, HI, USA, 2–7 April 1989, Shomura, R.S., Godfrey, H.L., Eds.; NOAA Technical Memorandum 1990; Volume 154, pp. 747–774. Available online: https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/6012 (accessed on 9 December 2021).
- Fossi, M.C.; Panti, C.; Baini, M.; Baulch, S. Impacts of marine litter on cetaceans: A focus on plastic pollution. In Marine Mammal Ecotoxicology: Impacts of Multiple Stressors on Population Health; Fossi, M.C., Panti, C., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 147–184. [Google Scholar]
- Fossi, M.C.; Romeo, T.; Baini, M.; Panti, C.; Marsili, L.; Campani, T.; Canese, S.; Galgani, F.; Druon, J.; Airoldi, S.; et al. Plastic debris occurrence, convergence areas and fin whales feeding ground in the Mediterranean marine protected area Pelagos sanctuary: A modeling approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossi, M.C.; Panti, C.; Baini, M.; Lavers, J.L. A review of plastic-associated pressures: Cetaceans of the Mediterranean Sea and Eastern Australian shearwaters as case studies. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deudero, S.; Alomar, C. Mediterranean marine biodiversity under threat: Reviewing influence of marine litter on species. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. Marine Litter Assessment in the Mediterranean; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, R.W.; Hooker, S.K. Ingestion of plastic and unusual prey by a juvenile harbour porpoise. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczaj, S.A.; Eskelinen, H.C. Why do dolphins play? Animal Behav. Con. 2014, 1, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger-Tal, O.; Polak, T.; Oron, A.; Lubin, Y.; Kotler, B.P.; Saltz, D. Integrating animal behavior and conservation biology: A conceptual framework. Behav. Ecol. 2011, 22, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Variables | Definition |
|---|---|
| Activity state | Description of observed behaviors [92] |
| Feeding (F) | Dolphin involved in chasing or capture of prey items close to the surface or showing erratic movements at the surface, multidirectional diving and rapid circle swimming. |
| Resting (R) | Dolphins observed in a tight group staying close to the surface, emerging at regular intervals and moving very slowly. Events of logging can be observed. |
| Socializing (S) | Physical interactions ranging from chasing to body contact, such as rubbing and touching or copulation between dolphins. Aerial behavior such as breaching frequently observed. |
| Traveling (T) | Dolphins moving steadily in a directional path, at normal to high speed. |
| Group formation (gf) | Description (this study) |
| Very tight formation (gf1) | Distance between individuals of approximately 0–2 m (less than one adult body length). |
| Tight formation (gf2) | Distance between individuals ranging from 2 to 15 m. |
| Loose formation (gf3) | Distance between individuals ranging from 15 to 50 m. |
| Spread formation (gf4) | Distance between individuals greater than 50 m and individuals weakly coordinated. |
| Cruising speed (sp) | Description (this study) |
| Low (sp1) | Individuals moving at a speed lower than 3 knots. |
| Normal (sp2) | Individuals moving at a speed ranging from 3 to 6 knots. |
| High (sp3) | Individuals moving at a speed higher than 6 knots. |
| Dive duration (dd) | Description (this study) |
| Regular surfacing intervals (dd1) | Dolphins surface quite regularly at 10–15 sec intervals. |
| Little time at surface (dd2) | Most of observation time spent underwater, mostly diving. |
| Mostly at surface (dd3) | Most of observation time spent on the surface, mostly floating. |
| Interaction among individuals (ai) | Description (this study) |
| Active inter-animal contact (ai1) | Two or more dolphins actively in contact with one another; splashes may obscure the details of their interaction. |
| Minimum contact (ai2) | Minimum and slight contact between individuals. |
| No contact (ai3) | No contact between individuals. |
| Events (e) | Description |
|---|---|
| Tail slap (e1) | Flukes raised above the surface and ventral side slapped downward, usually making a loud, percussive sound [92]. |
| Tail slap on back (e2) | Flukes raised above the surface and dorsal side slapped downward, usually making a loud, percussive sound [92]. |
| Flipper slap (e3) | Pectoral flipper slapping the surface [92]. |
| Small breach/leap (e4) | Body clears the water (not entire body) [92]. |
| Full breach/leap (e5) | Body clears the water (entire body) [92]. |
| Spyhopping (e6) | Brief vertical or near-vertical elevation of body and head-up exposure, followed by sinking return to water [93]. |
| Fluking (e7) | Dolphin arches back and exposes flukes [92]. |
| Chase (e8) | Single rapid forward movement on surface played by single individuals that produces a linear splash and directed towards another individual, not followed by any immersion (this study). |
| Torpedo (e9) | Single rapid forward movement on surface played by a single individual that produces a linear splash, followed by the immersion of the animal [33]. |
| Logging (e10) | Floating at or just below the water surface moving slowly in one direction [58]. |
| FEEDING vs. SOCIALIZING | SOCIALIZING vs. RESTING | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gf1 | gf2 | gf3 | gf4 | gf1 | gf2 | gf3 | gf4 | |
| p-value | 0.303 | 0.091 | 0.101 | 0.318 | 0.447 | 0.774 | 0.316 | NaN |
| U-value | 38.500 | 35.000 | 55.500 | 53.000 | 60.000 | 77.500 | 85.000 | 72.500 |
| sp1 | sp2 | sp3 | sp1 | sp2 | sp3 | |||
| p-value | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.001 ** | 0.005 ** | 0.040 * | ||
| U-value | 45.500 | 45.000 | 46.500 | 20.000 | 114.000 | 84.000 | ||
| dd1 | dd2 | dd3 | dd1 | dd2 | dd3 | |||
| p-value | 0.162 | 0.003 ** | 0.091 | 0.702 | 0.003 ** | 0.527 | ||
| U-value | 37.000 | 63.000 | 35.000 | 79.000 | 95.500 | 62.000 | ||
| ai1 | ai2 | ai3 | ai1 | ai2 | ai3 | |||
| p-value | 0.020 * | 0.303 | 0.003 ** | 0.005 ** | 0.407 | 0.003 ** | ||
| U-value | 31.500 | 38.500 | 63.000 | 114.000 | 84.000 | 23.500 | ||
| FEEDING vs. RESTING | SOCIALIZING vs. TRAVELING | |||||||
| gf1 | gf2 | gf3 | gf4 | gf1 | gf2 | gf3 | gf4 | |
| p-value | 0.009 ** | 0.021 * | 0.000 *** | 0.001 ** | 0.910 | 0.828 | 0.857 | 0.800 |
| U-value | 59.500 | 66.500 | 169.500 | 143.000 | 136.000 | 147.500 | 134.000 | 137.500 |
| sp1 | sp2 | sp3 | sp1 | sp2 | sp3 | |||
| p-value | 0.000 *** | 0.006 ** | 0.011 * | 0.062 | 0.350 | 0.900 | ||
| U-value | 35.000 | 159.000 | 131.500 | 82.500 | 171.000 | 143.500 | ||
| dd1 | dd2 | dd3 | dd1 | dd2 | dd3 | |||
| p-value | 0.094 | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.003 ** | 0.016 * | 0.070 | ||
| U-value | 77.500 | 189.000 | 38.500 | 47.500 | 181.500 | 191.000 | ||
| ai1 | ai2 | ai3 | ai1 | ai2 | ai3 | |||
| p-value | 0.111 | 0.150 | 0.005 ** | 0.049 * | 0.641 | 0.028 * | ||
| U-value | 84.000 | 87.500 | 163.000 | 202.000 | 153.500 | 67.500 | ||
| FEEDING vs. TRAVELING | RESTING vs. TRAVELING | |||||||
| gf1 | gf2 | gf3 | gf4 | gf1 | gf2 | gf3 | gf4 | |
| p-value | 0.033 * | 0.013 * | 0.013 * | 0.000 *** | 0.133 | 0.820 | 0.041 * | 0.517 |
| U-value | 126.000 | 108.500 | 297.500 | 273.500 | 969.000 | 832.500 | 705.500 | 839.000 |
| sp1 | sp2 | sp3 | sp1 | sp2 | sp3 | |||
| p-value | 0.028 * | 0.347 | 0.505 | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.023 * | ||
| U-value | 122.500 | 240.500 | 223.000 | 1186.000 | 527.500 | 736.000 | ||
| dd1 | dd2 | dd3 | dd1 | dd2 | dd3 | |||
| p-value | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.118 | 0.000 *** | 0.240 | 0.000 *** | ||
| U-value | 49.000 | 377.500 | 154.000 | 420.500 | 816.500 | 1271.500 | ||
| ai1 | ai2 | ai3 | ai1 | ai2 | ai3 | |||
| p-value | 0.033 * | 0.102 | 0.012 * | 0.079 | 0.457 | 0.351 | ||
| U-value | 126.000 | 150.500 | 301.000 | 720.500 | 800.500 | 927.500 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cipriano, G.; Carlucci, R.; Bellomo, S.; Santacesaria, F.C.; Fanizza, C.; Ricci, P.; Maglietta, R. Behavioral Pattern of Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020175
Cipriano G, Carlucci R, Bellomo S, Santacesaria FC, Fanizza C, Ricci P, Maglietta R. Behavioral Pattern of Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(2):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020175
Chicago/Turabian StyleCipriano, Giulia, Roberto Carlucci, Stefano Bellomo, Francesca Cornelia Santacesaria, Carmelo Fanizza, Pasquale Ricci, and Rosalia Maglietta. 2022. "Behavioral Pattern of Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 2: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020175
APA StyleCipriano, G., Carlucci, R., Bellomo, S., Santacesaria, F. C., Fanizza, C., Ricci, P., & Maglietta, R. (2022). Behavioral Pattern of Risso’s Dolphin (Grampus griseus) in the Gulf of Taranto (Northern Ionian Sea, Central-Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(2), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020175









