Meridionalization as a Possible Resource for Fisheries: The Case Study of Caranx rhonchus Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817, in Southern Italian Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Sampling Areas
2.2. Proximate Composition
2.3. Fatty Acid Profile Determination
2.4. Determination of Elements in Meat
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphometric Parameters
3.2. Proximate Composition and Fatty Acid Profile and Mineral Content
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianchi, C.N.; Morri, C. Global Sea warming and “tropicalization” of the Mediterranean Sea: Biogeographic and ecological aspects. Biogeographia 2003, 24, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boero, F.; Féral, J.P.; Azzurro, E.; Cardin, V.; Riedel, B.; Despalatović, M.; Munda, I.; Moschella, P.; Zaouali, J.; Fonda Umani, S.; et al. I—Executive Summary of CIESM workshop climate warming and related changes in Mediterranean marine biota. In CIESM Workshop Monographs; CIESM: Bd de Suisse, Monaco, 2008; Volume 35, pp. 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Azzurro, E. Commission Internationale pour l’Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Mediterranee—CIESM Monaco. The advance of thermophilic fishes in the Mediterranean Sea: Overview and methodological questions. In CIESM Workshop Monographs; CIESM: Bd de Suisse, Monaco, 2008; Volume 35, pp. 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, W.W.L.; Lam, V.W.Y.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Kearney, K.; Watson, R.; Pauly, D. Projecting global marine biodiversity im-pacts under climate change scenarios. Fish Fish. 2009, 10, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D.; Martin, J.L.; Genovesi, P.; Maris, V.; Wardle, D.A.; Aronson, J.; Courchamp, F.; Bella, G.; Garcìa-Berthou, E.; Pascal, M.; et al. Impacts of biological invasions: What’s what and the way forward. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fogarty, H.E.; Burrows, M.T.; Pecl, G.T.; Robinson, L.M.; Poloczanska, E.S. Are fish outsidetheir usual ranges early indicators of climate-driven range shifts? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2047–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galil, B.S.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A. Mare Nostrum, Mare Quod Invaditur—The History of Bioinvasions in the Mediterranean Sea, Histories of Bioinvasions in the Mediterranean; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 21–49. [Google Scholar]
- Galil, B.S.; Danovaro, R.; Rothman, S.B.S.; Gevili, R.; Goren, M. Invasive biota in the deep-sea Mediterranean: An emerging issue in marine conservation and management. Biol. Invasions 2019, 21, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shackleton, R.T.; Larson, B.M.; Novoa, A.; Richardson, D.M.; Kull, C.A. The human and social dimensions of invasion science and management. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 229, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, K.; De Young, C.; Soto, D.; Bahri, T. Climate change implications for fisheries and aquaculture. FAO Fish. Aquac. Tech. Paper 2009, 530, 212. [Google Scholar]
- Brander, K. Impacts of climate change on fisheries. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 79, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Sbragaglia, V.; Cerri, J.; Bariche, M.; Bolognini, L.; Ben Souissi, J.; Busoni, G.; Coco, S.; Chryssanthi, A.; Fanelli, E.; et al. Climate change, biological invasions, and the shifting distribution of Mediterranean fishes: A large-scale survey based on local ecological knowledge. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2779–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plagányi, É. Climate change impacts on fisheries. Science 2019, 363, 930–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinner, J.E.; Huchery, C.; Darling, E.S.; Humphries, A.T.; Graham, N.A.; Hicks, C.C.; Marshall, N.; McClanahan, T.R. Eval-uating social and ecological vulnerability of coral reef fisheries to climate change. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgueiro-Otero, D.; Ojea, E. A better understanding of social-ecological systems is needed for adapting fisheries to climate change. Mar. Policy 2020, 122, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleitou, P.; Crocetta, F.; Giakoumi, S.; Giovos, I.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Kalogirou, S.; Kletou, D.; Moutopoulos, D.K.; Rees, S. Fishery reforms for the management of non-indigenous species. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 280, 111690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimercati, G.; Kumschick, S.; Probert, A.F.; Volery, L.; Bacher, S. The importance of assessing positive and beneficial impacts of alien species. NeoBiota 2020, 62, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, N.; Corrales, X.; Karachle, P.K.; Chartosia, N.; Katsanevakis, S.; Sfenthourakis, S. Modelling the role of alien spe-cies and fisheries in an Eastern Mediterranean insular shelf ecosystem. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 175, 152–171. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rijn, I.; Kiflawi, M.; Belmaker, J. Alien species stabilize local fisheries catch in a highly invaded ecosystem. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 77, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saygu, I.; Heymans, J.J.; Fox, C.J.; Özbilgin, H.; Eryaşar, A.R.; Gökçe, G. The importance of alien species to the food web and bottom trawl fisheries of the Northeastern Mediterranean, a modelling approach. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 202, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, X.; Coll, M.; Ofir, E.; Heymans, J.J.; Steenbeek, J.; Goren, M.; Edelist, D.; Gal, G. Future scenarios of marine resources and ecosystem conditions in the Eastern Mediterranean under the impacts of fishing, alien species and sea warming. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Wallentinus, I.; Zenetos, A.; Leppäkoski, E.; Çinar, M.E.; Oztürk, B.; Grabowski, M.; Golani, D.; Cardoso, A.C. Impacts of invasive alien marine species on ecosystem services and biodiversity: A pan-European review. Aquat. Invasions 2014, 9, 391–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.M.; Suckling, D.M.; Byers, J.A.; Jang, E.B.; Wearing, C.H. Potential of “lure and kill” in long-term pest management and eradication of invasive species. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 815–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussellaa, W.; Neifar, L.; Goedknegt, A.; Thieltges, D.W. Lessepsian migration and parasitism: Richness, prevalence and intensity of parasites in the invasive fish Sphyraena chrysotaenia compared to its native congener Sphyraena sphyraena in Tunisian coastal waters. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connelly, N.A.; O’neill, C.R.; Knuth, B.A.; Brown, T.L. Economic Impacts of Zebra Mussels on Drinking Water Treatment and Electric Power Generation Facilities. Environ. Manag. 2007, 40, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ünal, V.; Göncüoğlu, H.; Durgun, D.; Tosunoğlu, Z.; Deval, M.C.; Turan, C. Silver-cheeked toadfish, Lagocephalus sceleratus (Actinopterygii: Tetraodontiformes: Tetraodontidae), causes a substantial economic losses in the Turkish Mediterranean coast: A call for decision makers. Acta Ichthyol. Piscat. 2015, 15, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medlock, J.M.; Hansford, K.M.; Schaffner, F.; Versteirt, V.; Hendrickx, G.; Zeller, H.; Van Bortel, W. A Review of the Invasive Mosquitoes in Europe: Ecology, Public Health Risks, and Control Options. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galil, B. Poisonous and venomous: Marine alien species in the Mediterranean Sea and human health. Invasive Species Hum. Health 2018, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bédry, R.; de Haro, L.; Bentur, Y.; Senechal, N.; Galil, B. Toxicological risks on the human health of populations living around the Mediterranean Sea linked to the invasion of non-indigenous marine species from the Red Sea: A review. Toxicon 2021, 191, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, M.A.; Kuebbing, S.; Domarco, R.D.; Simberloff, D. Invasive species: To eat or not to eat, that is the question. Conserv. Lett. 2012, 5, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, M.; Shlagman, A.; Lewinsohn, C. The benthic phase of the life cycle of Penaeus semisulcatus De Haan (Crustacea De-capoda) along the southeastern coast of the Mediterranean. Mar. Ecol. 1984, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.; Levitt, Y.; Galil, B.S.; Diamant, A.; Yokeş, M.B.; Goren, M. Distribution and population structure of the alien Indo-Pacific Randall’s threadfin bream Nemipterus randalli in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2014, 85, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogutu-Ohwayo, R. The decline of the native fishes of lakes Victoria and Kyoga (East Africa) and the impact of introduced species, especially the Nile perch, Lates niloticus, and the Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. J. Appl. Phycol. 1990, 27, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, C.; Farrugio, H. Fisheries in the Mediterranean. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2000, 1, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, S.; Filiz, H. Biological aspects of two coexisting native and non-native fish species in the Aegean Sea: Pagellus erythrinus vs Nempterus randalli. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F. Atlante dei Pesci dei Mari Italiani; Gruppo Ugo Mursia Editore; MURSIA: Milan, Italy, 1991; p. 438. [Google Scholar]
- Tiralongo, F.; Crocetta, F.; Riginella, E.; Lillo, A.O.; Tondo, E.; Macali, A.; Mancini, E.; Russo, F.; Coco, S.; Paolillo, G.; et al. Snapshot of rare, exotic and overlooked fish species in the Italian seas: A citizen science survey. J. Sea Res. 2020, 164, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. (Eds.) FishBase 2000: Concepts Designs and Data Sources; WorldFish: Penang, Malaysia, 2000; Volume 1594. [Google Scholar]
- Sley, A.; Jarboui, O.; Ghorbel, M.; Bouain, A. Diet composition and food habits of Caranx rhonchus (Carangidae) from the Gulf of Gabes (central Mediterranean). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2008, 88, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Bauchot, M.L.; Schneider, M. Fiches de la FAO d’identification des especes pour les besoins de la pêche (Révision 1) Méditerranée et Mer Noire. Zone Pêche 1987, 37, 761–11530. [Google Scholar]
- Philips, A.E. Feeding behavior of the European hake Merluccius merluccius Linnaeus, 1758 (Family: Gadidae) from Egyptian Mediterranean waters off Alexandria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Meat and meat products. In Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; Volume 2, pp. 931–948. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 60, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopherson, S.W.; Glass, R.L. Preparation of milk methyl esters by alcoholysis in an essentially non-alcoholic solution. J. Dairy Sci. 1969, 52, 1289–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felici, A.; Bilandžić, N.; Magi, G.E.; Iaffaldano, N.; Fiordelmondo, E.; Doti, G.; Roncarati, A. Evaluation of Long Sea Snail Hinia reticulata (Gastropod) from the Middle Adriatic Sea as a Possible Alternative for Human Consumption. Foods 2020, 9, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Released; Version 25.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khitouni, K.; Abdelmouleh, I.; Bouain, A.A.; Mihoubi, N.B. Variations of the chemical compositions of five coastal catch fish species of the Gulf of Gabes (Tunisia). Cybium 2010, 34, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Khitouni, I.K.; Mihoubi, N.B.; Bouain, A.; Rebah, F.B. Accumulation of Hg, Pb, Cr, and Fe in muscle and head of four fish species: Diplodus annularis, Zosterisessor ophiocephalus, Liza aurata and Caranx rhonchus. Int. J. Adv. Biol. 2014, 5, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Blakeway, R.D.; Jones, G.A.; Boekhoudt, B. Controlling lionfishes (Pterois spp.) with consumption: Survey data from Aruba demonstrate acceptance of non-native lionfishes on the menu and in seafood markets. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2019, 27, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulman, A.; Harris Holden, E.; Doumpas, N.; Deniz Akbora, H.; Al Mabruk Sara, A.A.; Azzurro, E.; Bariche, M.; Çiçek Burak, A.; Deidun, A.; Demirel, N.; et al. Low Pufferfish and Lionfish Predation in Their Native and Invad-ed Ranges Suggests Human Control Mechanisms May Be Necessary to Control Their Mediterranean Abundances. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 3, 868. [Google Scholar]
- Penca, J.; Said, A.; Cavallé, M.; Pita, C.; Libralato, S. Sustainable small-scale fisheries markets in the Mediterranean: Weak-nesses and opportunities. Marit. Stud. 2021, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Giakoumi, S.; Katsanevakis, S.; Albano, P.G.; Azzurro, E.; Cardoso, A.C.; Cebrian, E.; Deidun, A.; Edelist, D.; Francour, P.; Jimenez, C.; et al. Management priorities for marine invasive species. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleitou, P.; Savva, I.; Kletou, D.; Hall-Spencer, J.M.; Antoniou, C.; Christodoulides, Y.; Chartosia, N.; Hadjioannou, L.; Dimitriou, A.C.; Jimenez, C.; et al. Invasive lionfish in the Mediterranean: Low public awareness yet high stakeholder concerns. Mar. Policy 2019, 104, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

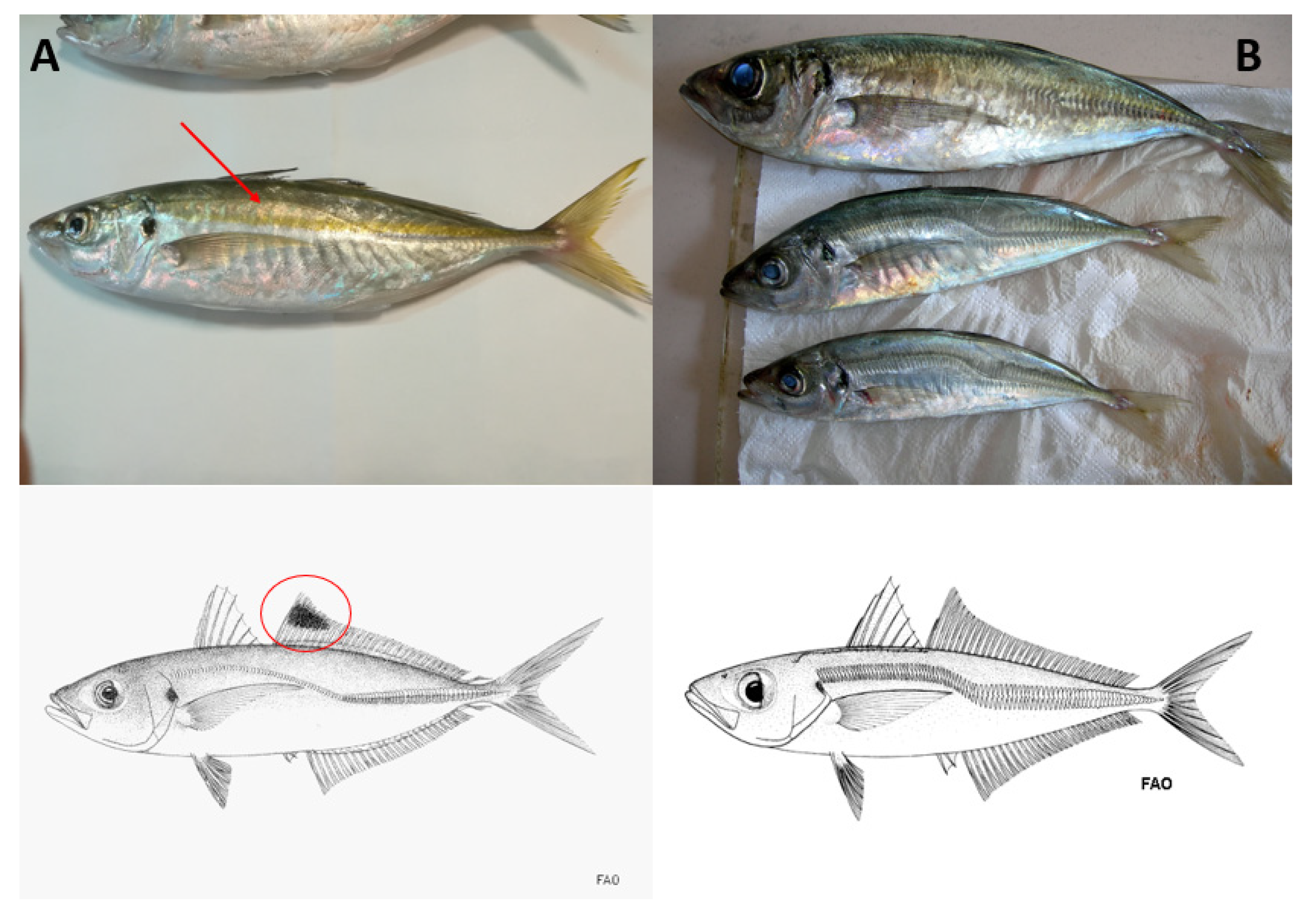

| Caranx rhonchus | Trachurus trachurus | |
|---|---|---|
| Total length (cm) | 35.08 ± 3.7 | 27.2 ± 2.4 |
| Standard length (cm) | 29.9 ± 3.69 | - |
| Total Body weight (g) | 372.25 ± 31.27 | 348.06 ± 8.97 |
| Moisture | Protein | Lipids | Ash | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caranx rhonchus | 74.99 ± 1.01 | 20.3 ± 0.93 | 2.34 ± 0.15 a | 1.2 ± 0.1 b |
| Trachurus trachurus | 78.09 ± 1.39 | 19.69 ± 0.11 | 1.09 ± 0.13 b | 1.59 ± 0.22 a |
| Caranx rhonchus | Trachurus trachurus | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Ca | 98 ± 7.86 b | 189.2 ± 4.38 a |
| Potassium | K | 537 ± 38.06 a | 413 ± 13.34 b |
| Magnesium | Mg | 41 ± 6.67 | 40.4 ± 1.52 |
| Sodium | Na | 49 ± 5.6 | 49.4 ± 2.41 |
| Iron | Fe | 1.01 ± 0.098 | 1.59 ± 0.04 |
| Selenium | Se | 0.066 ± 0.007 | 0.128 ± 0.08 |
| Zinc | Zn | 1.31± 0.07 | 1.11 ± 0.12 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 0.005 ± 0.003 | 0.011 ± 0.007 |
| Mercury | Hg | 0.03 ± 0.002 | 0.04 ± 0.001 |
| Lead | Pb | 0.017 ± 0.008 | 0.022 ± 0.004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coco, S.; Roncarati, A.; Tiralongo, F.; Felici, A. Meridionalization as a Possible Resource for Fisheries: The Case Study of Caranx rhonchus Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817, in Southern Italian Waters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020274
Coco S, Roncarati A, Tiralongo F, Felici A. Meridionalization as a Possible Resource for Fisheries: The Case Study of Caranx rhonchus Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817, in Southern Italian Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020274
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoco, Salvatore, Alessandra Roncarati, Francesco Tiralongo, and Alberto Felici. 2022. "Meridionalization as a Possible Resource for Fisheries: The Case Study of Caranx rhonchus Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817, in Southern Italian Waters" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020274
APA StyleCoco, S., Roncarati, A., Tiralongo, F., & Felici, A. (2022). Meridionalization as a Possible Resource for Fisheries: The Case Study of Caranx rhonchus Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, 1817, in Southern Italian Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10020274








