The Formulation, Development and Application of Oil Dispersants
Abstract
:1. Background
2. Brief History of Oil Dispersants
3. Regulations on Application of Oil Dispersants
4. Chemical Dispersants and Its Application
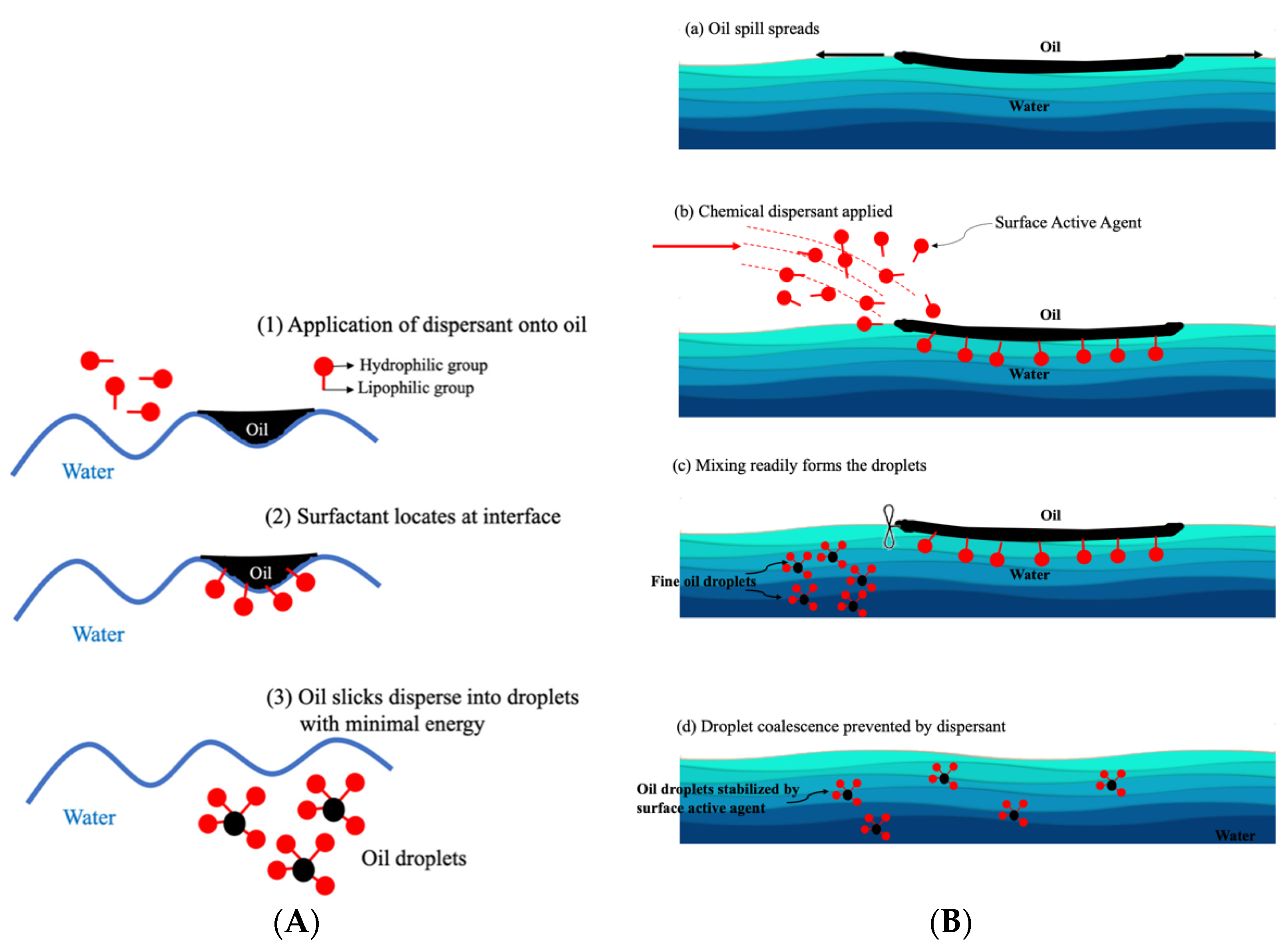
4.1. Mechanism of Oil Dispersion by Dispersant
4.2. Solvents
4.3. Surfactants
4.4. Factors to Affect Dispersion Effectiveness
4.5. Application of Dispersant
5. Factors to Determine the Effectiveness of Oil Dispersants
5.1. Emulsion
5.2. Hydrophilic–Lipophilic Balance
5.3. Hydrophilic–Lipophilic Difference (HLD)
6. Alternative Dispersants
6.1. Particle Stabilizers
Biomass-Derived Particles
6.2. Oil–Mineral Aggregates
6.3. Plant-Based Surfactants
6.4. Biosurfactants
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Wan, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, T.; Fei, Y. Oil Spills from Global Tankers: Status Review and Future Governance. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ITOPF. Oil Tanker Spill Statistics 2020; ITOPF: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lubchenco, J.; McNutt, M.K.; Dreyfus, G.; Murawski, S.A.; Kennedy, D.M.; Anastas, P.T.; Chu, S.; Hunter, T. Science in support of the Deepwater Horizon response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 20212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, J.R.; Payne, J.R.; Farlow, J.S.; Sarwar, C. Oil Spill Dispersants: Mechanisms of Action and Laboratory Tests; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, P.G. The Iconic Torrey Canyon Oil Spill of 1967—Marking Its Legacy. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 115, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Ghaly, A.E. Remediation Technologies for Marine Oil Spills: A Critical Review and Comparative Analysis. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 7, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prendergast, D.P.; Gschwend, P.M. Assessing the Performance and Cost of Oil Spill Remediation Technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 78, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.; Beegle-Krause, C.J.; Evers, K.-U.; Hughes, N.; Lewis, A.; Reed, M.; Wadhams, P. Oil Spill Response Capabilities and Technologies for Ice-Covered Arctic Marine Waters: A Review of Recent Developments and Established Practices. Ambio 2017, 46, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, H.; Purnell, K.; Law, R.J.; Kirby, M.F. The Use of Chemical Dispersants to Combat Oil Spills at Sea: A Review of Practice and Research Needs in Europe. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigg, A.; Farrington, J.W.; Gilbert, S.; Murawski, S.A.; John, V.T. A Decade of Gomri Dispersant Science. Oceanography 2021, 34, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiocco, R.J.; Lewis, A. Oil Spill Dispersants. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, A.; Findlay, A. Frequency of Dispersant Use Worldwide. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 2008, 2008, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, J.; Trannum, H.C.; Bakke, T.; Hodson, P.V.; Collier, T.K. Environmental Effects of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- 15 Dispersants Are Listed on the National Product Schedule. Available online: https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyNET.exe/P100W60V.txt?ZyActionD=ZyDocument&Client=EPA&Index=2016%20Thru%202020&Docs=&Query=&Time=&EndTime=&SearchMethod=1&TocRestrict=n&Toc=&TocEntry=&QField=&QFieldYear=&QFieldMonth=&QFieldDay=&UseQField=&IntQFieldOp=0&ExtQFieldOp=0&XmlQuery=&File=D%3A%5CZYFILES%5CINDEX%20DATA%5C16THRU20%5CTXT%5C00000011%5CP100W60V.txt&User=ANONYMOUS&Password=anonymous&SortMethod=h%7C-&MaximumDocuments=1&FuzzyDegree=0&ImageQuality=r75g8/r75g8/x150y150g16/i425&Display=hpfr&DefSeekPage=x&SearchBack=ZyActionL&Back=ZyActionS&BackDesc=Results%20page&MaximumPages=1&ZyEntry=2 (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Coolbaugh, T.; Varghese, G.; Li, L.S. Global Dispersant Approvals in Asia Pacific—Current Status and on Going Challenges. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 2017, 2017, 657–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canevari, G.P. Oil Spill Dispersants—Current Status and Future Outlook. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1971, 1971, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, R.R.; DeMarco, G. The Significance of Oil Spill Dispersants. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2000, 6, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.C.; Agrawal, N.R.; Aljirafi, F.O.; Bothun, G.D.; McCormick, A.V.; John, V.T.; Raghavan, S.R. Does the Solvent in a Dispersant Impact the Efficiency of Crude-Oil Dispersion? Langmuir 2019, 35, 16630–16639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, M.; Council, N.R. Using Oil Spill Dispersants on the Sea; National Academies Press: Washington, WA, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Place, B.J.; Perkins, M.J.; Sinclair, E.; Barsamian, A.L.; Blakemore, P.R.; Field, J.A. Trace Analysis of Surfactants in Corexit Oil Dispersant Formulations and Seawater. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2016, 129, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodbody-Gringley, G.; Wetzel, D.L.; Gillon, D.; Pulster, E.; Miller, A.; Ritchie, K.B. Toxicity of Deepwater Horizon Source Oil and the Chemical Dispersant, Corexit® 9500, to Coral Larvae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e45574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.K.; Lyons, S.L.; Harrison, S.J.; Findley, D.M.; Liu, Y.; Kujawinski, E.B. Long-Term Persistence of Dispersants Following the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadov, Z.H.; Rahimov, R.A.; Mammadova, K.A.; Gurbanov, A.V.; Ahmadova, G.A. Synthesis and Characteristics of Dodecyl Isopropylolamine and Derived Surfactants. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2016, 19, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.U.H.; Reddy, A.V.B.; Moniruzzaman, M. Chapter 16—Ionic Liquid–Based Surfactants for Oil Spill Remediation. In Ionic Liquid-Based Technologies for Environmental Sustainability; Jawaid, M., Ahmad, A., Reddy, A.V.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 257–268. [Google Scholar]
- National Reserach Counsil; Ocean Studies Board; Committee On Understanding Oil Spill Dispersants Efficacy And Effects. Oil Spill Dispersants: Efficacy and Effects; National Academies Press: Washington, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn, B.A.; Virkus, A.; Mukherjee, B.; Venosa, A.D. Dispersibility of Crude Oil in Fresh Water. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter-Groves, M. Global Dispersant Stockpile: Part of the Industry Solution to Worst Case Scenario Readiness. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 2014, 2014, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsor, P.A. Hydrotropy, Solubilisation and Related Emulsification Processes. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1948, 44, 376–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, M. Water-in-Oil Emulsion Formation: A Review of Physics and Mathematical Modelling. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 1995, 2, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.T. A Quantitative Kinetic Theory of Emulsion Type, I. Physical Chemistry of the Emulsifying Agent. In Gas/Liquid and Liquid/Liquid Interface, Proceedings of the International Congress of Surface Activity, London, UK, 8–13 January 1957; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1957; pp. 6–438. [Google Scholar]
- Kralova, I.; Sjöblom, J.; Øye, G.; Simon, S.; Grimes, B.A.; Paso, K. Heavy Crude Oils/Particle Stabilized Emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 169, 106–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyankson, E.; Demir, M.; Gonen, M.; Gupta, R.B. Interfacially Active Hydroxylated Soybean Lecithin Dispersant for Crude Oil Spill Remediation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2056–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinier, V.; le Goué, E.; Rondón-Gonzáles, M.; Passade-Boupat, N.; Bourrel, M. Optimization of Chemical Dispersants Effectiveness in Case of Subsurface Oil Spill. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 541, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandvik, P.J.; Daling, P. Optimisation of Oil Spill Dispersant Composition by Mixture Design and Response Surface Methods. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1998, 42, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Yan, L. Development of High Efficient and Low Toxic Oil Spill Dispersants Based on Sorbitol Derivants Nonionic Surfactants and Glycolipid Biosurfactants. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, J.-L.; Marquez, N.; Graciaa, A.; Lachaise, J. Partitioning of Ethoxylated Octylphenol Surfactants in Microemulsion−Oil−Water Systems: Influence of Temperature and Relation between Partitioning Coefficient and Physicochemical Formulation. Langmuir 2000, 16, 5534–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, L.G.; Almaraz, B.A.S.; Amen, K.Y.; Bothun, G.D.; Raghavan, S.R.; John, V.T.; McCormick, A.V.; Penn, R.L. Using Microemulsion Phase Behavior as a Predictive Model for Lecithin–Tween 80 Marine Oil Dispersant Effectiveness. Langmuir 2021, 37, 8115–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, W.H.; Morgan, J.C.; Jacobson, J.K.; Schechter, R.S. Low Interfacial Tensions Involving Mixtures of Surfactants. Soc. Pet. Eng. J. 1977, 17, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, E.J.; Yuan, J.S.; Bhakta, A.S. The Characteristic Curvature of Ionic Surfactants. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2008, 11, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.; Nouraei, M.; Latta, T.; Acosta, E. Hydrophilic-Lipophilic-Difference (Hld) Guided Formulation of Oil Spill Dispersants with Biobased Surfactants. Tenside Surfactants Deterg. 2019, 56, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongsayamanont, W.; Soonglerdsongpha, S.; Khondee, N.; Pinyakong, O.; Tongcumpou, C.; Sabatini, D.A.; Luepromchai, E. Formulation of Crude Oil Spill Dispersants Based on the Hld Concept and Using a Lipopeptide Biosurfactant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 334, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawavimarn, P.; Rongsayamanont, W.; Subsanguan, T.; Luepromchai, E. Bio-Based Dispersants for Fuel Oil Spill Remediation Based on the Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Deviation (Hld) Concept and Box-Behnken Design. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.K.; Acosta, E.J. Hld–Nac and the Formation and Stability of Emulsions near the Phase Inversion Point. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 6467–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, W.; Gotch, F. Separation of Solids in the Surface-Layers of Solutions and ‘Suspensions’ (Observations on Surface-Membranes, Bubbles, Emulsions, and Mechanical Coagulation).—Preliminary Account. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1904, 72, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, S.U. Cxcvi.—Emulsions. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1907, 91, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, A.; Nikova, A.; Venkataraman, P.; John, V.T.; Bose, A. Oil Emulsification Using Surface-Tunable Carbon Black Particles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Lee, K. Chemical Dispersion of Oil with Mineral Fines in a Low Temperature Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 72, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Worthen, A.J.; Foster, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Cornell, K.A.; Bryant, S.L.; Truskett, T.M.; Bielawski, C.W.; Johnston, K.P. Modified Montmorillonite Clay Microparticles for Stable Oil-in-Seawater Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11502–11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, G.; Mao, L.; Bao, M.; Li, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhang, J. Preparation of Oil-in-Seawater Emulsions Based on Environmentally Benign Nanoparticles and Biosurfactant for Oil Spill Remediation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthen, A.J.; Foster, L.M.; Dong, J.; Bollinger, J.A.; Peterman, A.H.; Pastora, L.E.; Bryant, S.L.; Truskett, T.M.; Bielawski, C.W.; Johnston, K.P. Synergistic Formation and Stabilization of Oil-in-Water Emulsions by a Weakly Interacting Mixture of Zwitterionic Surfactant and Silica Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.Y.; Joachim, E.; Choi, H.; Kim, K. Toxicity of Silica Nanoparticles Depends on Size, Dose, and Cell Type. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Huang, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances on Cellulose Nanocrystals for Pickering Emulsions: Development and Challenge. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Österberg, M.; Sipponen, M.H.; Mattos, B.D.; Rojas, O.J. Spherical Lignin Particles: A Review on Their Sustainability and Applications. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2712–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laitinen, O.; Ojala, J.; Sirviö, J.A.; Liimatainen, H. Sustainable Stabilization of Oil in Water Emulsions by Cellulose Nanocrystals Synthesized from Deep Eutectic Solvents. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherhal, F.; Cousin, F.; Capron, I. Structural Description of the Interface of Pickering Emulsions Stabilized by Cellulose Nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Greca, L.G.; Xiang, W.; Lehtonen, J.; Huan, S.; Nugroho, R.W.N.; Tardy, B.L.; Rojas, O.J. Adsorption and Assembly of Cellulosic and Lignin Colloids at Oil/Water Interfaces. Langmuir 2019, 35, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.; Stoffyn-Egli, P.; Wood, P.A.; Lunel, T. Formation and Structure of Oil-Mineral Fines Aggregates in Coastal Environments. In Proceedings of the twenty-first Arctic and marine oilspill program (AMOP) technical seminar, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 10–12 June 1998; p. 962. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, E.H.; Lee, K. Interaction of Oil and Mineral Fines on Shorelines: Review and Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, Z.; Lee, K.; Kepkay, P.; Mullin, J.V. Modelling the Transport of Oil–Mineral-Aggregates (Omas) in the Marine Environment and Assessment of Their Potential Risks. Environ. Model. Assess. 2011, 16, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delvigne, G.A.L.; van der Stel, J.A.; Sweeney, C.E.; Laboratorium, W.; Hydraulics, I.E.; Service, U.S.M.M. Measurement of Vertical Turbulent Dispersion and Diffusion of Oil Droplets and Oiled Particles: Final Report; Engineering Hydraulics: Redmond, WA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Delvigne, G.A.L.; Van der Stel, J.A.; Sweeney, C.E. Final Report: Ocs Study Mms 87-111; US Department of the Interior, Minerals Management Service: Anchorage, AK, USA, 1987; 501p. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Boufadel, M.; Chen, B.; Foght, J.; Hodson, P.; Swanson, S.; Venosa, A. Expert Panel Report on the Behaviour and Environmental Impacts of Crude Oil Released into Aqueous Environments; Royal Society of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stoffyn-Egli, P.; Lee, K. Formation and Characterization of Oil–Mineral Aggregates. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2002, 8, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajijolaiya, L.O.; Hill, P.S.; Khelifa, A.; Islam, R.M.; Lee, K. Laboratory Investigation of the Effects of Mineral Size and Concentration on the Formation of Oil–Mineral Aggregates. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Lee, K. Piv Investigation of Oil–Mineral Interaction for an Oil Spill Application. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 170, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zheng, X. A Review of Oil-Suspended Particulate Matter Aggregation—a Natural Process of Cleansing Spilled Oil in the Aquatic Environment. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khelifa, A.; Stoffyn-Egli, P.; Hill, P.S.; Lee, K. Characteristics of Oil Droplets Stabilized by Mineral Particles: Effects of Oil Type and Temperature. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 2002, 8, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyankson, E.; DeCuir, M.J.; Gupta, R.B. Soybean Lecithin as a Dispersant for Crude Oil Spills. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athas, J.C.; Jun, K.; McCafferty, C.; Owoseni, O.; John, V.T.; Raghavan, S.R. An Effective Dispersant for Oil Spills Based on Food-Grade Amphiphiles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 9285–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, B.; Brito, J.; Brasileiro, P.; Rufino, R.; Luna, J.; Santos, V.; Sarubbo, L. Formulation of a Commercial Biosurfactant for Application as a Dispersant of Petroleum and by-Products Spilled in Oceans. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, M.U.H.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Sivapragasam, M.; Talukder, M.M.R.; Yusup, S.B.; Goto, M. A Binary Mixture of a Biosurfactant and an Ionic Liquid Surfactant as a Green Dispersant for Oil Spill Remediation. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 280, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, B.; Chen, B. Env-624: A New High-Yielding Bio-Dispersant Producer Mutated from Rhodococcus Erythropolis Strain P6–4p. 2016. Available online: http://www.csce2016.ca/ (accessed on 30 January 2022).
- Cao, T. Generation of Biodispersants for Offshore Oil Spill Response. Master’s Thesis, Memorial University of Newfoundland, Newfoundland and Labrador, NL, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, B.; Lee, K.; Nedwed, T.J.; Greer, C.; Zhang, B. A Cross-Comparison of Biosurfactants as Marine Oil Spill Dispersants: Governing Factors, Synergetic Effects and Fates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Cai, Q.; Ling, J.; Lee, K.; Chen, B. Fish Waste Based Lipopeptide Production and the Potential Application as a Bio-Dispersant for Oil Spill Control. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, M.E.; Colonna, W.J.; Patra, P.; Zhang, H.; Green, C.; Reznik, G.; Pynn, M.; Jarrell, K.; Nyman, J.A.; Somasundaran, P.; et al. Production and Characterization of Microbial Biosurfactants for Potential Use in Oil-Spill Remediation. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2014, 55, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshtagh, B.; Hawboldt, K.; Zhang, B. Kinetic Modeling of Biosurfactant Production by Bacillus Subtilis N3–1p Using Brewery Waste. Chem. Prod. Process. Model. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, H.; Sasaki, M.; Komatsu, K.; Miura, A.; Matsuda, H. Oil Spill Remediation by Using the Remediation Agent Je1058bs That Contains a Biosurfactant Produced by Gordonia Sp. Strain Je-1058. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farahani, M.D.; Zheng, Y. The Formulation, Development and Application of Oil Dispersants. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030425
Farahani MD, Zheng Y. The Formulation, Development and Application of Oil Dispersants. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(3):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030425
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarahani, Majid D., and Ying Zheng. 2022. "The Formulation, Development and Application of Oil Dispersants" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 3: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030425
APA StyleFarahani, M. D., & Zheng, Y. (2022). The Formulation, Development and Application of Oil Dispersants. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(3), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10030425




