Sustainable Cross-Linkers for the Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Aerogels: Research and Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Aerogels Synthesis Process
2.3. Investigation of Aerogel Properties
3. Results
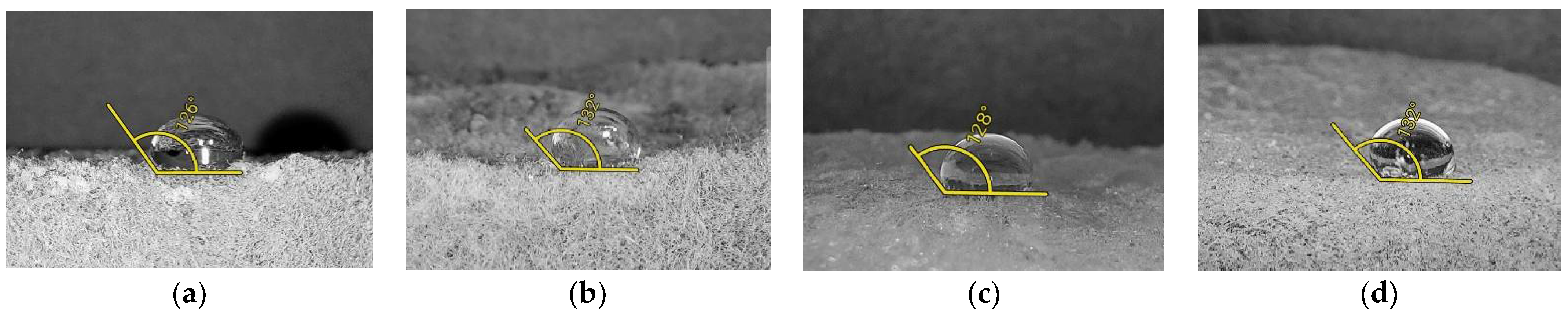
3.1. Hydrophobicity
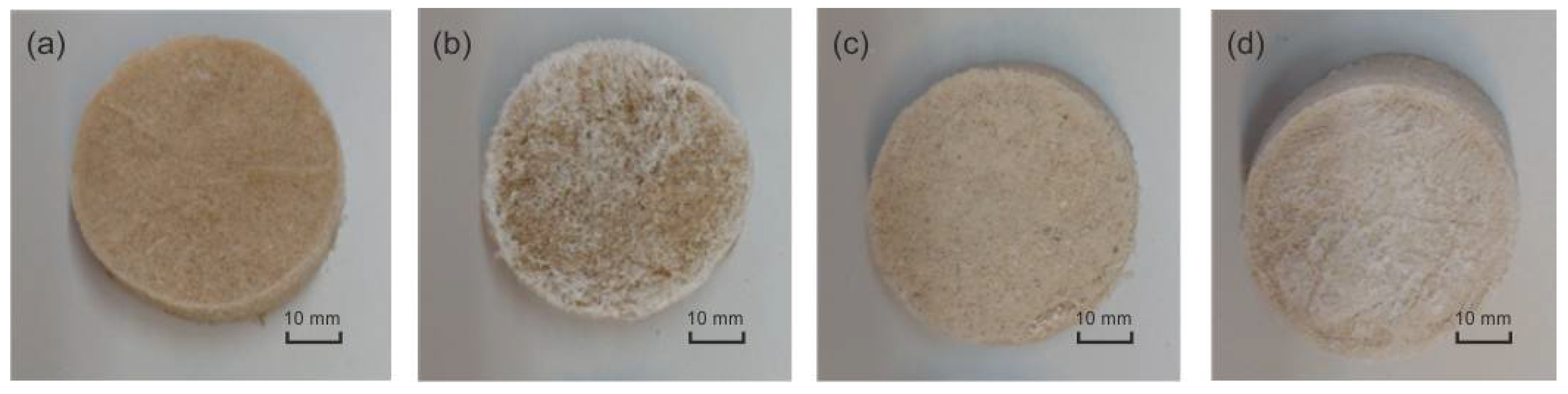
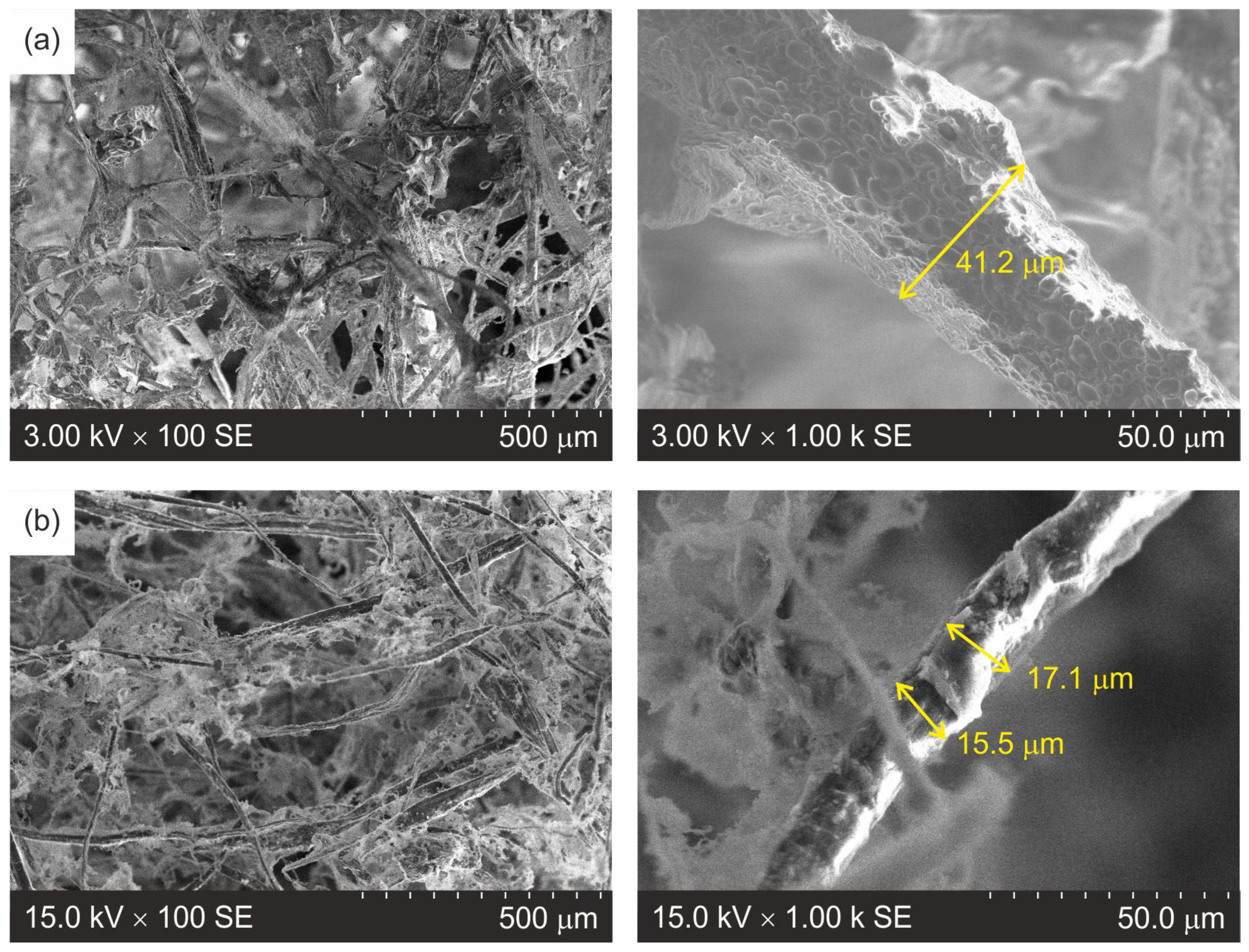
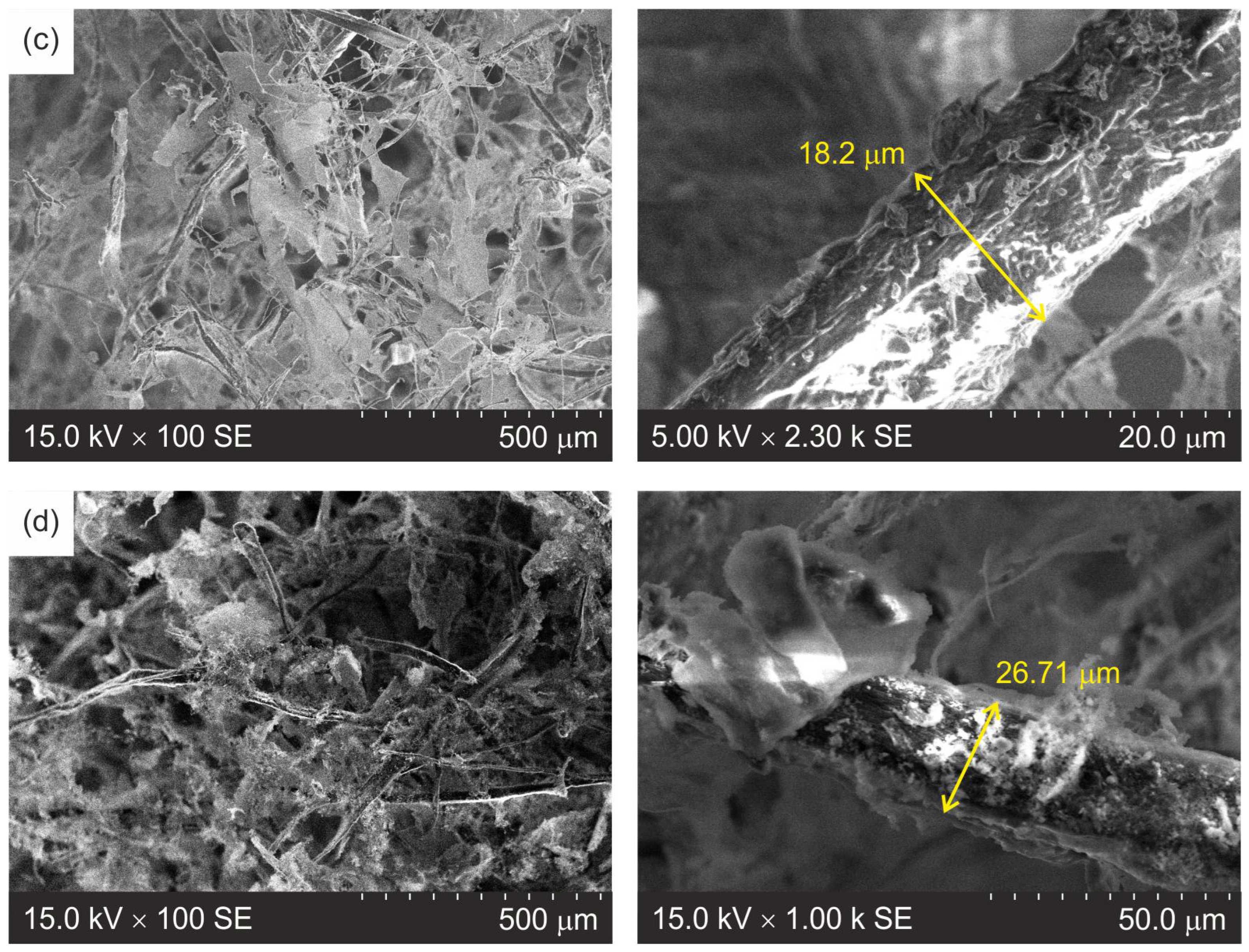
3.2. Morphology
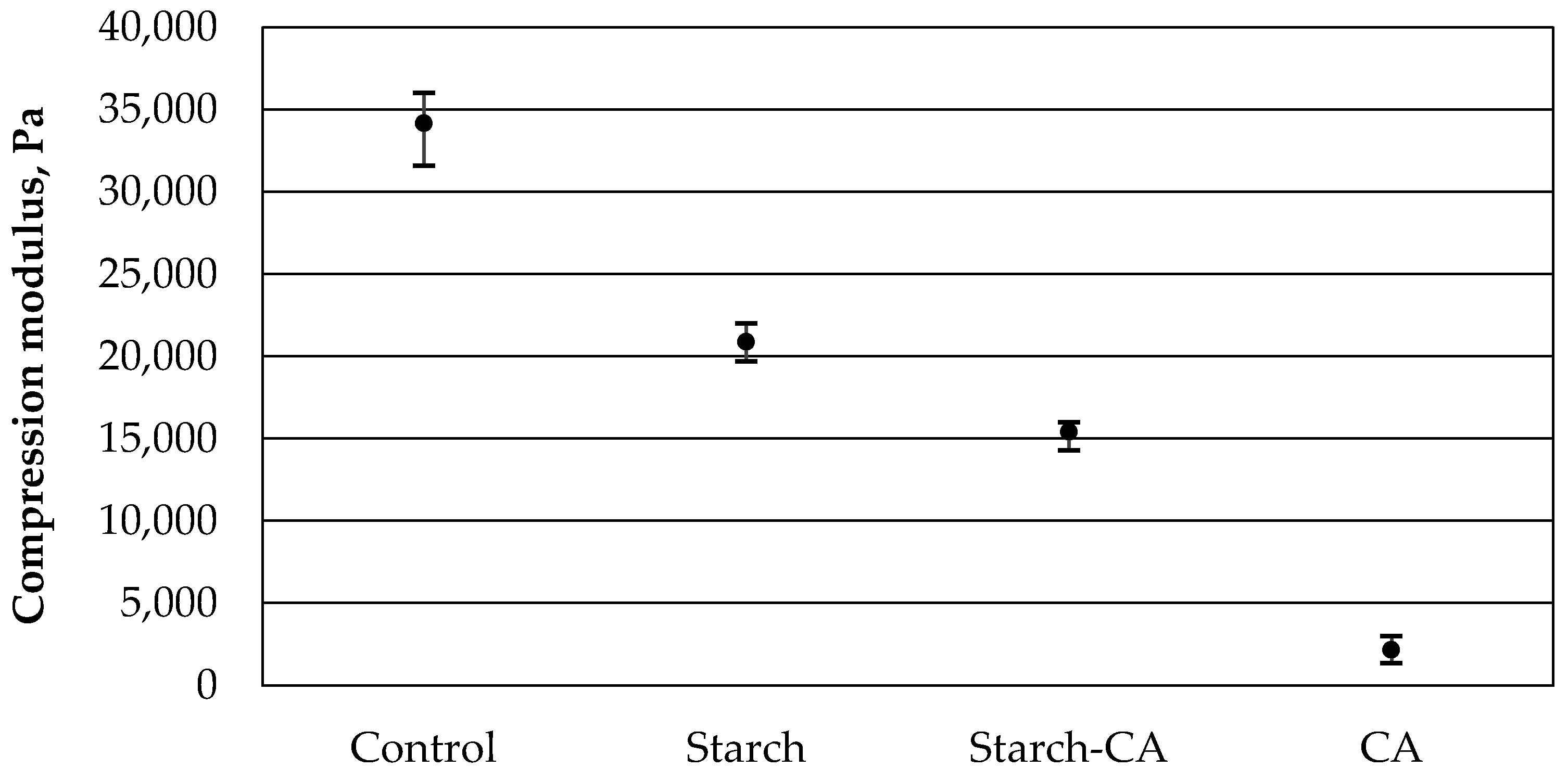
3.3. Results of the Compressive Mechanical Properties Test
3.4. Maximum Sorption Capacity
3.5. The Regeneration of the Aerogel Samples by Squeezing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Troisi, G.; Barton, S.; Bexton, S. Impacts of oil spills on seabirds: Unsustainable impacts of non-renewable energy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brussaard, C.; Peperzak, L.; Beggah, S. Immediate ecotoxicological effects of short-lived oil spills on marine biota. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langangena, O. The effects of oil spills on marine fish: Implications of spatial variation in natural mortality. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Understanding Oil Spills and Oil Spill Response; EPA 540-K-99-007; 1999. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-01/documents/ospguide99.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- Ibarra Torres, C.E.; Serrano Quezada, T.E.; Kharissova, O.V. Carbon-based aerogels and xerogels: Synthesis, properties, oil sorption capacities, and DFT simulations. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürtauer, S.; Hassan, M.; Elsherbiny, A.; Gabal, S.A.; Mehanny, S.; Abushammala, H. Current Status of Cellulosic and Nanocellulosic Materials for Oil Spill Cleanup. Polymers 2021, 13, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhajed, M.; Yadav, C.; Agrawal, A.K.; Maji, P.K. Esterified superhydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose based aerogel for oil spill treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 226, 115286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.; Huang, F.; Jiang, H.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Z. Preparation, Properties, and Applications of Natural Cellulosic Aerogels: A Review. Energy Built Environ. 2020, 1, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.Y.; Weng, Y.X.; Wang, Y.Z. Cellulose aerogels: Synthesis, applications, and prospects. Polymers 2018, 10, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Bao, W.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Porous Cellulose Aerogels with High Mechanical Performance and their absorption behaviors. Bioresources 2016, 11, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Chen, T.; Jiang, T.; Wang, C. Preparation and adsorption properties of magnetic hydrophobic cellulose aerogels based on refined fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Feng, J.; Le, N.T. Cellulose Aerogel from Paper Waste for Crude Oil Spill Cleaning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18386–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidgoli, H.; Mortazavi, Y.; Khodadadi, A.A. A functionalized nano-structured cellulosic sorbent aerogel for oil spill cleanup: Synthesis and characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitinen, O.; Suopajarvi, T.; Osterberg, M. Hydrophobic, superabsorbing aerogels from choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvent pretreated and silylated cellulose nanofibrils for selective oil removal. ACS Appl. Mater. 2017, 9, 25029–25037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Dai, C.; Zhang, H. Regeneration of mesoporous silica aerogel for hydrocarbon adsorption and recovery. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Sun, Q.; Zheng, H. Green and facile fabrication of carbon aerogels from cellulose-based waste newspaper for solving organic pollution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Su, D.; Zhang, F.; Ji, H.; Liu, R. Superelastic and superhydrophobic bacterial cellulose/silica aerogels with hierarchical cellular structure for oil absorption and recovery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 346, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Utilising aerogel in effective oil spill cleanup and recovery. In Proceedings of the Annual Offshore Technology Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 5–8 May 2014; Volume 3, pp. 1929–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Gu, B.; Pennefather, M.P.; Nguyen, T.X.; Phan-Thien, N.; Duong, H.M. Cotton aerogels and cotton-cellulose aerogels from environmental waste for oil spillage cleanup. Mater. Des. 2007, 130, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Tian, Y.; Ye, F. Fabrication and application of starch-based aerogel: Technical strategies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qiu, J.; Shi, Y. Wettability-switchable bacterial cellulose/polyhemiaminal nanofiber aerogels for continuous and effective oil/water separation. Cellulose 2018, 25, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, H. Fabrication of hydrophobic cellulosic materials via gas–solid silylation reaction for oil/water separation. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4021–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.Y.; Jing, X.; Politowicz, A.L. Highly compressible ultra-light anisotropic cellulose/graphene aerogel fabricated by bidirectional freeze drying for selective oil absorption. Carbon 2018, 132, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Qian, Y.; Tan, F. Controllable synthesis of pomelo peel-based aerogel and its application in adsorption of oil/organic pollutants. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bastani, D.; Safekordi, A.A.; Alihosseini, A. Study of oil sorption by expanded perlite at 298.15 K. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 52, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, N.H.N.; Luu, T.P.; Thai, Q.B. Advanced fabrication and application of pineapple aerogels from agricultural waste. Mater. Technol. 2019, 35, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Fan, Z. Advanced fabrication and oil absorption properties of super-hydrophobic recycled cellulose aerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, S.H.; Mohd, N.H.; Suhaili, N. Preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulauskiene, T.; Uebe, J.; Karasu, A.U.; Anne, O. Investigation of Cellulose-Based Aerogels for Oil Spill Removal. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousinet, S.; Ghadban, A.; Fleury, E. Toward replacement of styrene by bio-based methacrylates in unsaturated polyester resins. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S. Remodeling of raw cotton fiber into flexible, squeezing-resistant macroporous cellulose aerogel with high oil retention capability for oil/water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, F.; Rigacci, A.; Pirard, A.; Berthon-Fabry, S.; Achard, P. Cellulose-based aerogels. Polymer 2006, 47, 7636–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puls, J.; Wilson, S.A.; Hölter, D. Degradation of Cellulose Acetate-Based Materials: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackay, J.; Eriksen, M.; Shafey, O. The Tobacco Atlas, 2nd ed.; The American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Uebe, J.; Paulauskiene, T.; Boikovych, K. Cost-effective and recyclable aerogels from cellulose acetate for oil spills clean-up. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 36551–36558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, H.W.; Kearney, R.L. Opportunities and Challenges for Starch in the Paper Industry. Starch/Stärke 1998, 50, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egharevba, H.M. Chemical Properties of Starch and Its Application in the Food Industry. In Chemical Properties of Starch; Emeje, M., Blumenberg, M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulauskiene, T.; Uebe, J.; Ziogas, Z. Cellulose aerogel composites as oil sorbents and their regeneration. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wang, R.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Cong, W. Cellulose/microalgae composite films prepared in ionic liquids. Algal Res. 2016, 20, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Feitosa, J.P.; Morais, J.P.S.; de Freitas Rosa, M. Bacterial cellulose aerogels: Influence of oxidation and silanization on mechanical and absorption properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, A.E.A.; dos Santos, F.V.; Freitas, K.M.; Santos Pimenta, L.P.; de Oliveira Andrate, L.; Marinho, T.A.; de Avelar, G.F.; de Silva, A.B.; Ferreira, R.V. Cellulose acetate nanofibers loaded with crude annatto extract: Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation for potential wound healing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.M.Z.; Ewais, E.M.M.; El-Sheikh, S.M. Potato starch consolidation of aqueous HA suspension. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2015, 3, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doshi, B.; Sillanpää, M.; Kalliola, S. A review of bio-based materials for oil spill treatment. Water Res. 2018, 135, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Kan, C. A review on development and applications of bio-inspired superhydrophobic textiles. Materials 2016, 9, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y. Dual Wet and Dry Resilient Cellulose II Fibrous Aerogel for Hydrocarbon–Water Separation and Energy Storage Applications. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 3530–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ifelebuegu, A.O.; Lale, E.E.; Mbanaso, F.U.; Theophilus, S.C. Facile Fabrication of Recyclable, Superhydrophobic, and Oleophilic Sorbent from Waste Cigarette Filters for the Sequestration of Oil Pollutants from an Aqueous Environment. Processes 2018, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pircher, N.; Veigel, S.; Aigner, N. Reinforcement of bacterial cellulose aerogels with bio-compatible polymers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sescousse, R.; Gavillon, R.; Budtova, T. Aerocellulose from cellulose–ionic liquid solutions: Preparation, properties and comparison with cellulose–NaOH and cellulose–NMMO routes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamparas, M.; Tzivras, D.; Dracopoulos, V.; Ioannides, T. Application of Sorbents for Oil Spill Cleanup Focusing on Natural-Based Modified Materials: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


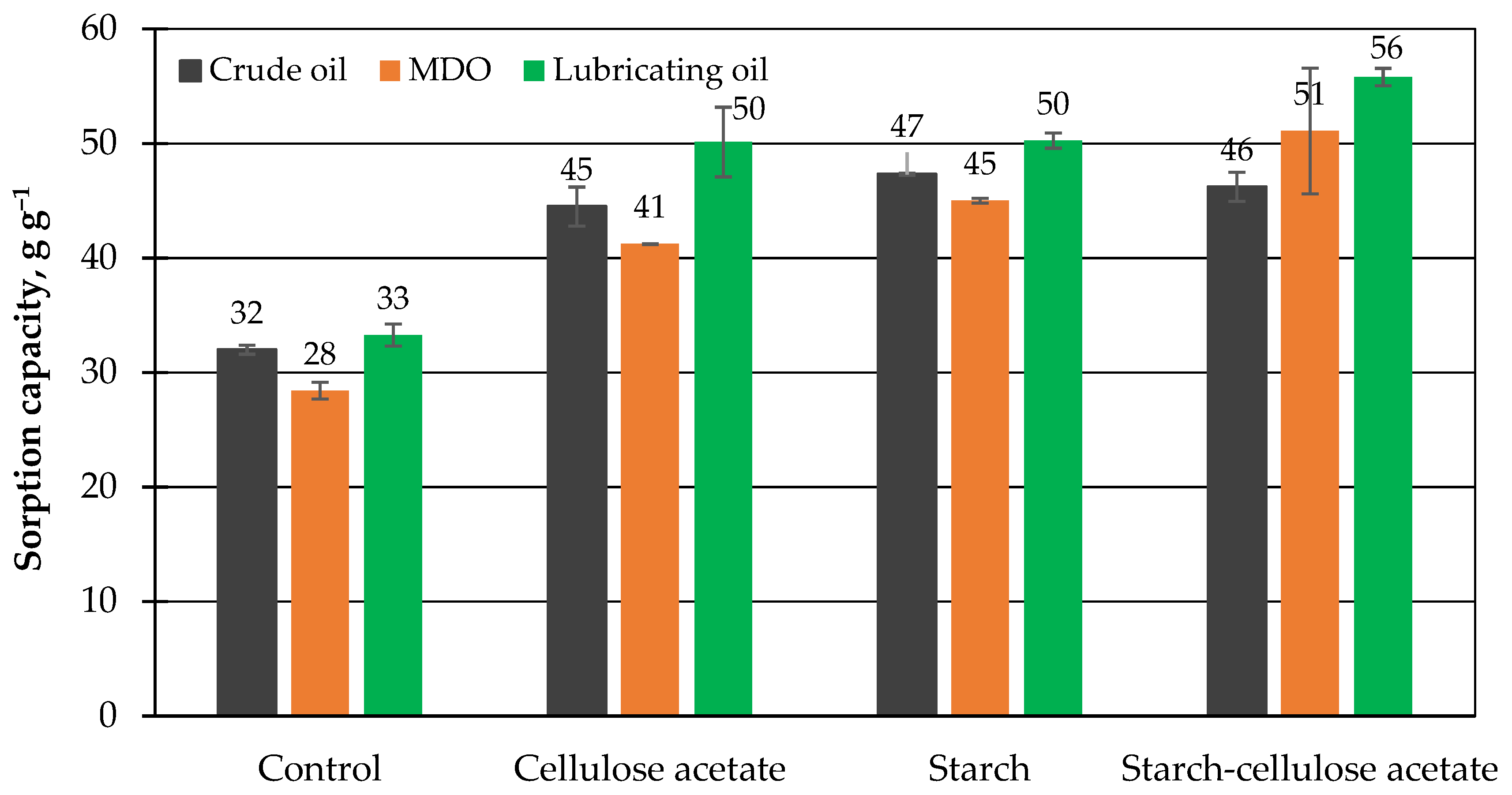
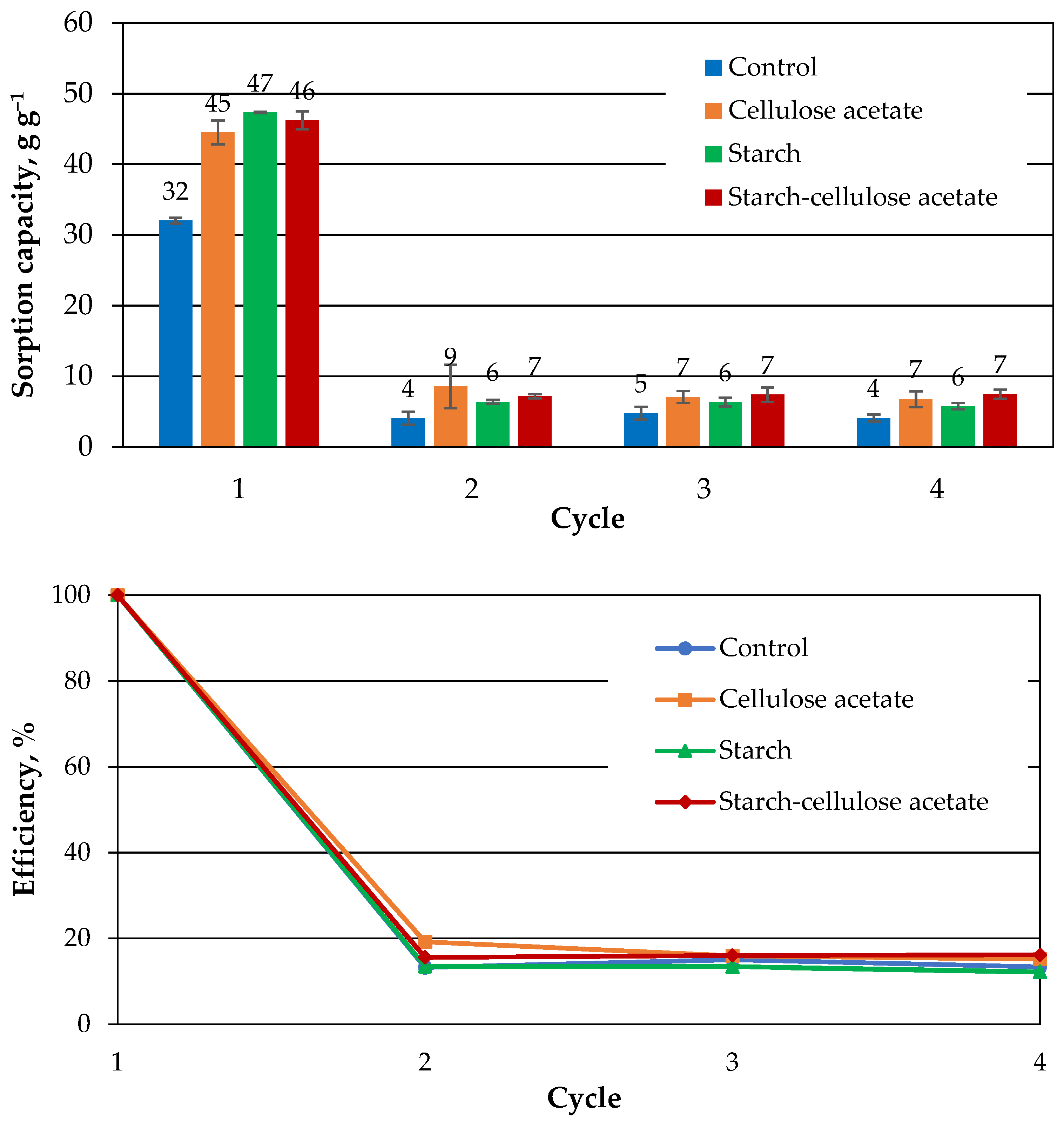


| Cross-Linking Agent | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester Resin (Control Samples) | Cellulose Acetate | Starch | Starch–Cellulose Acetate | |
| Contact angles of water droplets, ° | 124 ± 2 | 128 ± 4 | 127 ± 2 | 129 ± 2 |
| Aerogel Sample | Density in g cm−3 | Porosity in % |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 96.74 |
| Starch | 0.018 ± 0.001 | 98.68 |
| Starch–cellulose acetate | 0.014 ± 0.001 | 98.84 |
| Cellulose acetate | 0.011 ± 0.001 | 99.18 |
| Cross-Linking Agent | Modification with MTMS | Dimension | Chemical Element | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Si | Other | |||
| Control samples with polyester resin | No | wt% | 42.24 | 54.78 | 0.45 | 2.53 |
| at% | 50.07 | 48.75 | 0.23 | 0.95 | ||
| Yes | wt% | 38.28 | 56.52 | 0.82 | 4.38 | |
| at% | 46.38 | 51.41 | 0.42 | 1.79 | ||
| Cellulose acetate | No | wt% | 33.53 | 57.38 | 0.91 | 8.18 |
| at% | 41.98 | 53.93 | 0.48 | 3.61 | ||
| Yes | wt% | 33.86 | 58.82 | 0.95 | 6.37 | |
| at% | 42.05 | 54.84 | 0.51 | 2.60 | ||
| Starch | No | wt% | 33.82 | 60.92 | 0.25 | 5.01 |
| at% | 41.61 | 56.26 | 0.13 | 2.00 | ||
| Yes | wt% | 33.11 | 61.33 | 0.67 | 4.89 | |
| at% | 40.86 | 56.82 | 0.35 | 1.97 | ||
| Starch–cellulose acetate | No | wt% | 35.19 | 58.77 | 0.62 | 5.42 |
| at% | 43.20 | 54.16 | 0.33 | 2.31 | ||
| Yes | wt% | 34.42 | 58.09 | 1.13 | 6.36 | |
| at% | 42.57 | 53.93 | 0.60 | 2.90 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paulauskiene, T.; Teresiute, A.; Uebe, J.; Tadzijevas, A. Sustainable Cross-Linkers for the Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Aerogels: Research and Application. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040491
Paulauskiene T, Teresiute A, Uebe J, Tadzijevas A. Sustainable Cross-Linkers for the Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Aerogels: Research and Application. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(4):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040491
Chicago/Turabian StylePaulauskiene, Tatjana, Audrone Teresiute, Jochen Uebe, and Arturas Tadzijevas. 2022. "Sustainable Cross-Linkers for the Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Aerogels: Research and Application" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 4: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040491
APA StylePaulauskiene, T., Teresiute, A., Uebe, J., & Tadzijevas, A. (2022). Sustainable Cross-Linkers for the Synthesis of Cellulose-Based Aerogels: Research and Application. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(4), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10040491








