Retrieval of Remotely Sensed Sediment Grain Size Evolution Characteristics along the Southwest Coast of Laizhou Bay Based on Support Vector Machine Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
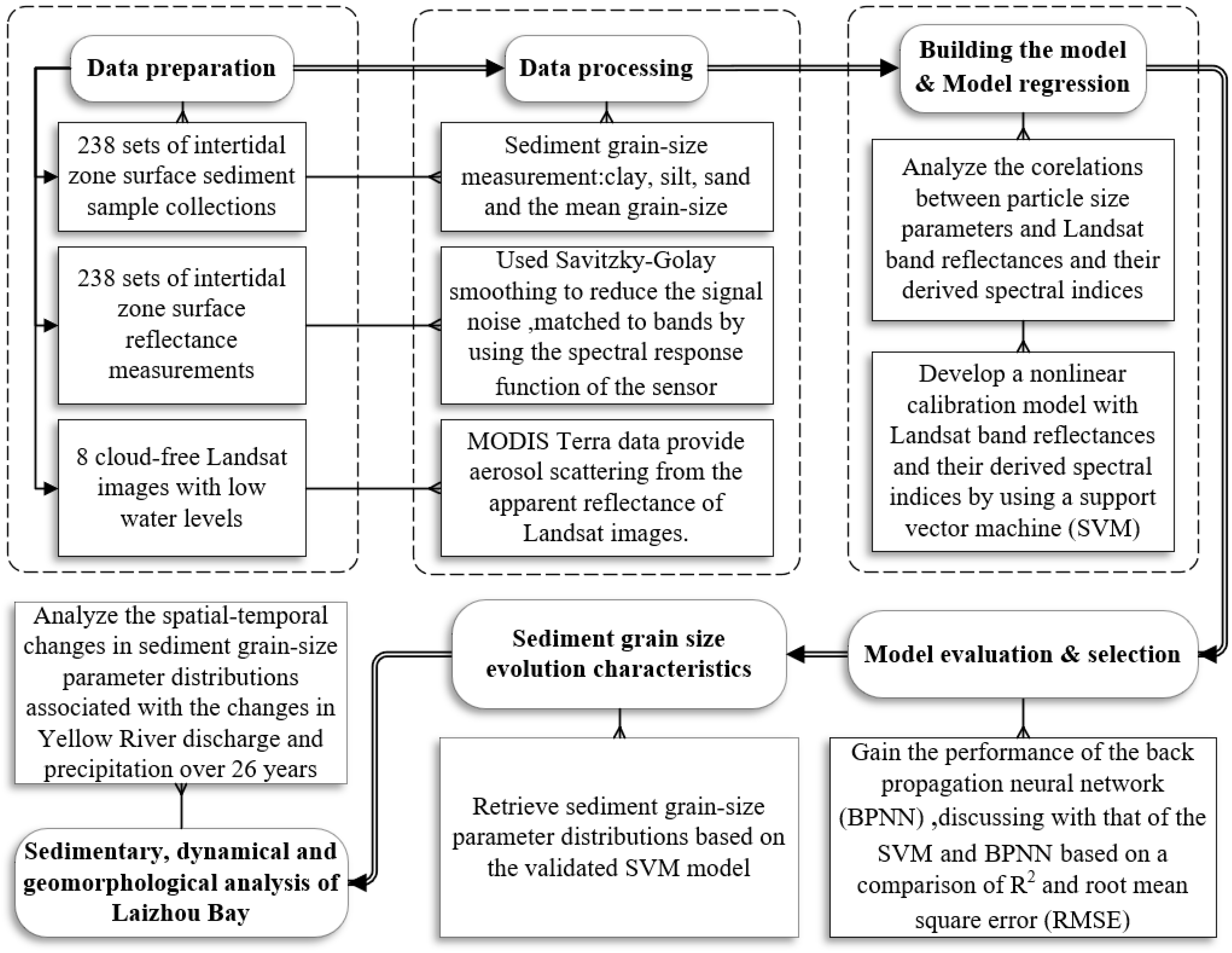
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Field Measurements and Laboratory Analysis
2.2.1. Sediment Grain-Size Measurement
2.2.2. Measurement and Preprocessing of the Sediment Reflectance Spectrum
2.2.3. Landsat Images and Preprocessing
2.3. Sediment Grain-Size Retrieval
2.3.1. Spectral Indices
2.3.2. Estimation Models
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Variation in Grain-Size Parameters
3.2. Temporal Variation in Grain Size
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, R.; Pan, H.; Xu, M. Recent Evolution of Coastal Tidal Flats and the Impacts of Intensified Human Activities in the Modern Radial Sand Ridges, East China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarella, D.; Longhitano, S.G.; Sabato, L.; Tropeano, M. Sedimentology and hydrodynamics of mixed (siliciclastic-bioclastic) shallow-marine deposits of Acerenza (Pliocene, Southern Apennines, Italy). Ital. J. Geosci. 2012, 131, 136–151. [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff, J.D.; Martini, A.P.; Elzidani, E.Z.H.; Naughton, T.J.; Kekacs, D.J.; Macdonald, D.G. Off-river waterbodies on tidal rivers: Human impact on rates of infilling and the accumulation of pollutants. Geomorphology 2013, 184, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedley, J.; Chambers, J.; Paice, R. Sediment Accumulation and Resuspension in the Vasse-Wonnerup Wetlands and Its Relationship to Internal Nutrient Cycling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, E.J.; Gardel, A.; Gratiot, N.; Proisy, C.; Allison, M.A.; Dolique, F.; Fromard, F. The Amazon-influenced muddy coast of South America: A review of mud-bank-shoreline interactions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 103, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodger, S.; Russell, P.; Davidson, M. Grain-size distributions on high energy sandy beaches and their relation to wave dissipation. Sedimentology 2017, 64, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngoc, N.T.; Tue, N.T. Correlating mass physical properties with ALOS reflectance spectra for;intertidal sediments from the Ba Lat Estuary (northern Vietnam): An exploratory laboratory study. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2013, 33, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, M.P.; Tyler, A.N.; Gilvear, D.J.; Bryant, R.G.; Mcdonald, P. Mapping intertidal estuarine sediment grain size distributions through airborne remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, E.; Pereda, R.; Luis, J.M.D.; Medina, R.; Viguri, J. Sediment grain size estimation using airborne remote sensing, field sampling, and robust statistic. Environ. Monit. Assessment 2011, 181, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deronde, B.; Kempeneers, P.; Forster, R.M. Imaging spectroscopy as a tool to study sediment characteristics on a tidal sandbank in the Westerschelde. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 69, 580–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, K. Supervised classification of continental shelf sediment off western Donegal, Ireland. In Agu Fall Meeting; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. OS31C-1414. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, E.; Adam, S.; Monbaliu, J.; Maktav, D. Assessment of unsupervised classification techniques for intertidal sediments. Environ. Manag. 2009, 45, 526–540. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, E.; Monbaliu, J. Suitability of spaceborne multispectral data for inter-tidal sediment characterization: A case study. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.W.; Jang, D.H.; Chi, K.H. Integration of IKONOS imagery for geostatistical mapping of sediment grain size at Baramarae beach, Korea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 5703–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Vitti, A. Grain size mapping in shallow rivers using spectral information: A lab spectroradiometry perspective. In Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jayson-Quashigah, P.N.; Addo, K.A.; Amisigo, B.; Wiafe, G. Assessment of short-term beach sediment change in the Volta Delta coast in Ghana using data from Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (Drone). Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 182, 104952–104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossel, R.A.V.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; Mcbratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.G.; Shaw, J.N.; Mask, P.L.; Rickman, D.; Luvall, J.; Wersinger, J.M. Remote sensing of near-surface soil properties with the airborne terrestrial applications sensor. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2004, 5544, 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, D.G.; Shaw, J.N.; Rickman, D.; Mask, P.L.; Luvall, J. Using Remote Sensing Data to Evaluate Surface Soil Properties in Alabama Ultisols. Soil Sci. 2005, 170, 954–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, J.; Yang, D. Experimental analysis of sand grain size mapping using UAV remote sensing. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonneau, P.E.; Lane, S.N.; Bergeron, N.E. Catchment-scale mapping of surface grain size in gravel bed rivers using airborne digital imagery. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, WO7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yates, M.G.; Jones, A.R.; Mcgrorty, S.; Goss-Custard, J.D. The Use of Satellite Imagery to Determine the Distribution of Intertidal Surface Sediments of the Wash, England. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1993, 36, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Wal, D.; Herman, P.M.J. Regression-bases synergy of optical, shorwave infrared and microwave remote sensing for monitoring the grain-size of intertidal sediments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerle, N.; Skidmore, A.K.; Van der Wal, D.; Herman, P.M.J. Quantifying the particle size of intertidal sediments with satellite remote sensing in the visible light, thermal infrared and microwave spectral domain. Bull. Geol. Soc. 2015, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhang, D.; Han, F. Remote Sensing Study on Sediment Grain Size Distribution and its Migration Trend Analysis in Tidal Flat Based on PCA and WNN Model. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2019, 6, 1168–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.N.; Wang, G.X.; Deng, W.; Hu, Y.M.; Hu, W.W. Influence of hydrology process on wetland landscape pattern: A case study in the yellow river delta. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hao, Z.; Cairang, L. The impacts of climate change and land cover/use transition on the hydrology in the upper yellow river basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 502, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Yan, W. Dispersal pattern of suspended sediment in the shear frontal zone off the Huanghe (Yellow River) mouth. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 854–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, N.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Hu, B.; Ji, Y. Sediment dispersion pattern off the present huanghe (yellow river) subdelta and its dynamic mechanism during normal river discharge period. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 86, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Shi, J. Comparability of Red/Near-Infrared Reflectance and NDVI Based on the Spectral Response Function between MODIS and 30 Other Satellite Sensors Using Rice Canopy Spectra. Sensors 2013, 13, 16023–16050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B. Revised Landsat-5 TM radiometric calibration procedures and postcalibration dynamic ranges. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2674–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, Q.; Cui, T.; Xue, C.; Zhang, S. Suspended sediment monitoring and assessment for Yellow River estuary from Landsat TM and ETM+ imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 146, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Andrefouet, S.; Carder, K.L. Atmospheric correction and cross-calibration of LANDSAT-7/ETM+ imagery over aquatic environments: A multiplatform approach using SeaWiFS/MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 78, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Castaño, D.J. Aerosol analysis with the Coastal Zone Color Scanner: A simple method for including multiple scattering effects. Appl. Opt. 1989, 28, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, H.R. Remote sensing of ocean color: A methodology for dealing with broad spectral bands and significant out-of-band response. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 8363–8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.W.; Tang, J.W.; Dong, Q.; Song, Q.T.; Ding, J. Retrieval of total suspended matter concentration in the Yellow and East China Seas from MODIS imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, W.W.; Carder, K.L. A Simple Spectral Solar Irradiance Model for Cloudless Maritime Atmospheres. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 1657–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsochantaridis, I.; Hofmann, T.; Joachims, T.; Altun, Y. Support vector machine learning for interdependent and structured output spaces. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Suykens, J.A.K.; Brabanter, J.D.; Lukas, L.; Vandewalle, J. Weighted least squares support vector machines: Robustness and sparse approximation. Neurocomputing 2002, 48, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Wang, Y.N.; Lu, X.F. A method to choose kernel function and its parameters for support vector machines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning & Cybernetics, Guangzhou, China, 18–21 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Korenjak, M.; Taylor-Harding, B.; Binné, U.L.; Satterlee, J.S.; Stevaux, O.; Aasland, R.; White-Cooper, H.; Dyson, N.; Brehm, A. Native E2F/RBF complexes contain Myb-interacting proteins and repress transcription of developmentally controlled E2F target genes. Cell 2005, 119, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qing, W.; Xiaolu, W.; Xueyan, L.; Xin, W.; Chao, Z. Grain size characteristics and corsening phenomenon of inter-tidal flat surficial sediment along the abandonded southern yellow river sub-delta. Quat. Sci. 2009, 37, 353–367. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, A.D.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, L. Study on the evolution of the tidal morphodynamic processes in south-western Laizhou Bay based on numerical simulation in the past 50 years. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 5, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Lee, S. Regional landslide susceptibility analysis using back-propagation neural network model at Cameron Highland, Malaysia. Landslides 2010, 7, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Park, S.C. Combination of modified BPNN algorithms and an efficient feature selection method for text categorization. Inf. Processing Manag. 2009, 45, 329–340. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ruan, G. Bernoulli Neural Network with Weights Directly Determined and with the Number of Hidden–Layer Neurons Automatically Determined. In International Symposium on Neural Networks on Advances in Neural Networks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Garca, P.; Vidal, E. Inference of k-testable languages in the strict sense and application to syntacti.c pattern recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 12, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madgwick, S.O.H.; Harrison, A.J.L.; Vaidyanathan, R. Estimation of IMU and MARG orientation using a gradient descent algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rajath, K.M.P.; Keerthi, S.R.; Aishwarya, K.M. Artificial neural networks for face recognition using PCA and BPNN. In Proceedings of the Tencon IEEE Region 10 Conference, Marina Bay Sands, Singapore, 22–26 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, T. Back propagation neural network with adaptive differential evolution algorithm for time series forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suykens, J.A.K.; Vandewalle, J. Least Squares Support Vector Machine Classifiers. Neural Processing Lett. 1999, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Chang, E.Y. Support vector machine active learning for image retrieval. In Proceedings of the Ninth ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, September 30–October 5 2001; pp. 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Yoo, H.R.; Han, J.W.; Chang, H.K. Quantitative estimation of intertidal sediment characteristics using remote sensing and GIS. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.; Gornat, B.; Rimon, D. Drip Irrigation: Principles, Design and Agricultural Practices; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, M.H.; Vanclooster, M. Predicting the Soil Moisture Characteristic Curve from Particle Size Distribution with a Simple Conceptual Model. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, Y.; Ruessink, G.; Brakenhoff, L.B.; Donker, J.J.A. Measuring spatial and temporal variation in surface moisture on a coastal beach with a near-infrared terrestrial laser scanner. Aeolian Res. 2018, 31, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L.; Gege, P. Physics-based Bathymetry and Water Quality Retrieval Using PlanetScope Imagery: Impacts of 2020 COVID-19 Lockdown and 2019 Extreme Flood in the Venice Lagoon. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarah, C.; Laurence, S.; Leon, S.; Joseph, M. Tracking Dynamic Northern Surface Water Changes with High-Frequency Planet CubeSat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1306–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Wicaksono, P.; Lazuardi, W. Assessment of PlanetScope images for benthic habitat and seagrass species mapping in a complex optically shallow water environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5739–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Date | Sensor | Time (UTC) | Track/Path | Water Level (m NAP) | Tidal Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 February 1989 | TM | 02:14 | 121/34 | −1.60 | incoming |
| 26 March 1995 | TM | 01:51 | 121/34 | −1.35 | outgoing |
| 10 December 1999 | ETM+ | 02:34 | 121/34 | −1.77 | incoming |
| 12 October 2001 | ETM+ | 02:29 | 121/34 | −1.80 | outgoing |
| 11 November 2006 | ETM+ | 02:31 | 121/34 | −1.55 | incoming |
| 3 November 2009 | ETM+ | 02:32 | 121/34 | −1.85 | incoming |
| 23 August 2012 | ETM+ | 02:36 | 121/34 | −1.93 | incoming |
| 5 February 2015 | ETM+ | 02:40 | 121/34 | −2.05 | incoming |
| Spectral Indices | Expressions | Correlation Coefficients(r) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Grain-Size | Sand | Silt | Clay | ||||||
| rmax | rmin | rmax | rmin | rmax | rmin | rmax | rmin | ||
| R | original reflectance | 0.55 * | 0.02 | 0.58 * | 0.07 | 0.58 * | 0.07 | 0.52 * | 0.07 |
| SI | Ri + Rj | 0.48 * | 0.08 | 0.49 * | 0.09 | 0.48 * | 0.09 | 0.43 * | 0.04 |
| DI | Ri − Rj | 0.65 * | 0 | 0.71 * | 0.04 | 0.70 * | 0.04 | 0.64 * | 0.01 |
| PI | Ri × Rj | 0.43 * | 0.08 | 0.44 * | 0.08 | 0.43 * | 0.08 | 0.40 * | 0.04 |
| RI | Ri/Rj | 0.52 * | 0.01 | 0.59 * | 0 | 0.59 * | 0.01 | 0.50 * | 0.01 |
| NDI | (Ri − Rj)/(Ri + Rj) | 0.14 | 0 | 0.15 * | 0 | 0.16 * | 0 | 0.10 | 0 |
| Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | Mean Grain-Size (φ) | Discharge (109 m3) | Precipitation (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | Max | Min | Mean | |||
| 1989 | 9.65 | 1.35 | 5.32 | 93.02 | 9.25 | 59.62 | 93.51 | 3.19 | 48.78 | 6.79 | 3.25 | 4.05 | 568.80 | 369 |
| 1995 | 5.47 | 4.40 | 5.03 | 76.52 | 30.82 | 54.18 | 72.18 | 20.40 | 45.65 | 5.40 | 2.48 | 4.11 | 567.90 | 728 |
| 1999 | 5.47 | 4.86 | 5.01 | 85.15 | 30.09 | 59.03 | 70.80 | 12.35 | 38.99 | 5.86 | 2.30 | 4.10 | 61.69 | 373 |
| 2001 | 5.62 | 3.85 | 5.02 | 78.49 | 19.98 | 55.46 | 76.82 | 15.23 | 41.45 | 5.54 | 2.48 | 4.14 | 40.89 | 414 |
| 2006 | 5.96 | 3.18 | 5.03 | 84.54 | 18.88 | 54.13 | 80.25 | 9.48 | 43.23 | 5.51 | 1.40 | 4.01 | 186.70 | 452 |
| 2009 | 6.25 | 2.62 | 4.89 | 83.76 | 21.75 | 51.12 | 75.72 | 7.89 | 45.57 | 5.91 | 2.54 | 4.27 | 132.90 | 653 |
| 2012 | 6.57 | 1.61 | 4.89 | 75.76 | 9.51 | 52.03 | 92.93 | 19.64 | 44.27 | 5.65 | 2.37 | 4.11 | 282.50 | 534 |
| 2015 | 5.07 | 2.89 | 4.64 | 75.65 | 5.60 | 37.42 | 94.19 | 16.86 | 58.46 | 5.47 | 1.94 | 4.10 | 133.60 | 595 |
| Grain-Size Parameters | Hidden Layer Number | Node Number | R2 | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | ||||
| clay content | 2 | 6 | 11 | 0.67 | 1.95 |
| silt content | 2 | 16 | 16 | 0.78 | 101.27 |
| sand content | 2 | 11 | 16 | 0.79 | 120.53 |
| mean grain-size | 2 | 17 | 18 | 0.77 | 0.13 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Zhan, C.; Liu, Y.; Bi, J.; Li, G.; Cui, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q. Retrieval of Remotely Sensed Sediment Grain Size Evolution Characteristics along the Southwest Coast of Laizhou Bay Based on Support Vector Machine Learning. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070968
Yu X, Zhan C, Liu Y, Bi J, Li G, Cui B, Wang L, Liu X, Wang Q. Retrieval of Remotely Sensed Sediment Grain Size Evolution Characteristics along the Southwest Coast of Laizhou Bay Based on Support Vector Machine Learning. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(7):968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070968
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xiang, Chao Zhan, Yan Liu, Jialin Bi, Guoqing Li, Buli Cui, Longsheng Wang, Xianbin Liu, and Qing Wang. 2022. "Retrieval of Remotely Sensed Sediment Grain Size Evolution Characteristics along the Southwest Coast of Laizhou Bay Based on Support Vector Machine Learning" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 7: 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070968
APA StyleYu, X., Zhan, C., Liu, Y., Bi, J., Li, G., Cui, B., Wang, L., Liu, X., & Wang, Q. (2022). Retrieval of Remotely Sensed Sediment Grain Size Evolution Characteristics along the Southwest Coast of Laizhou Bay Based on Support Vector Machine Learning. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(7), 968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10070968





