Experimental Investigation on the Mechanism of Longshore Sediment Transport Using a Circular Wave Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
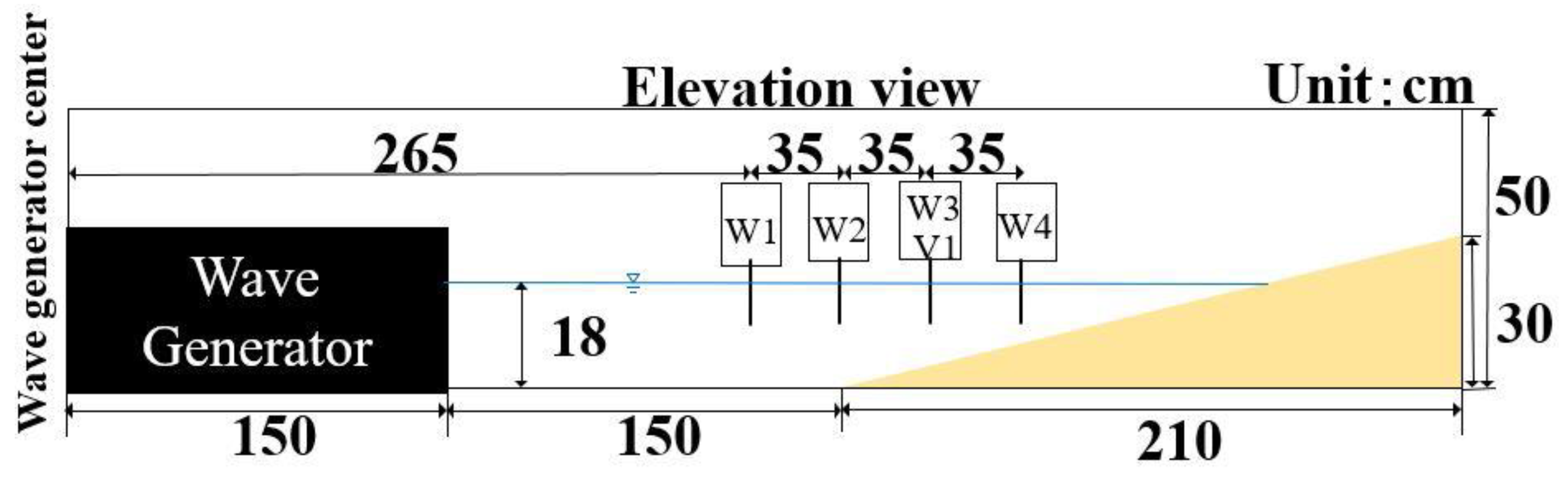
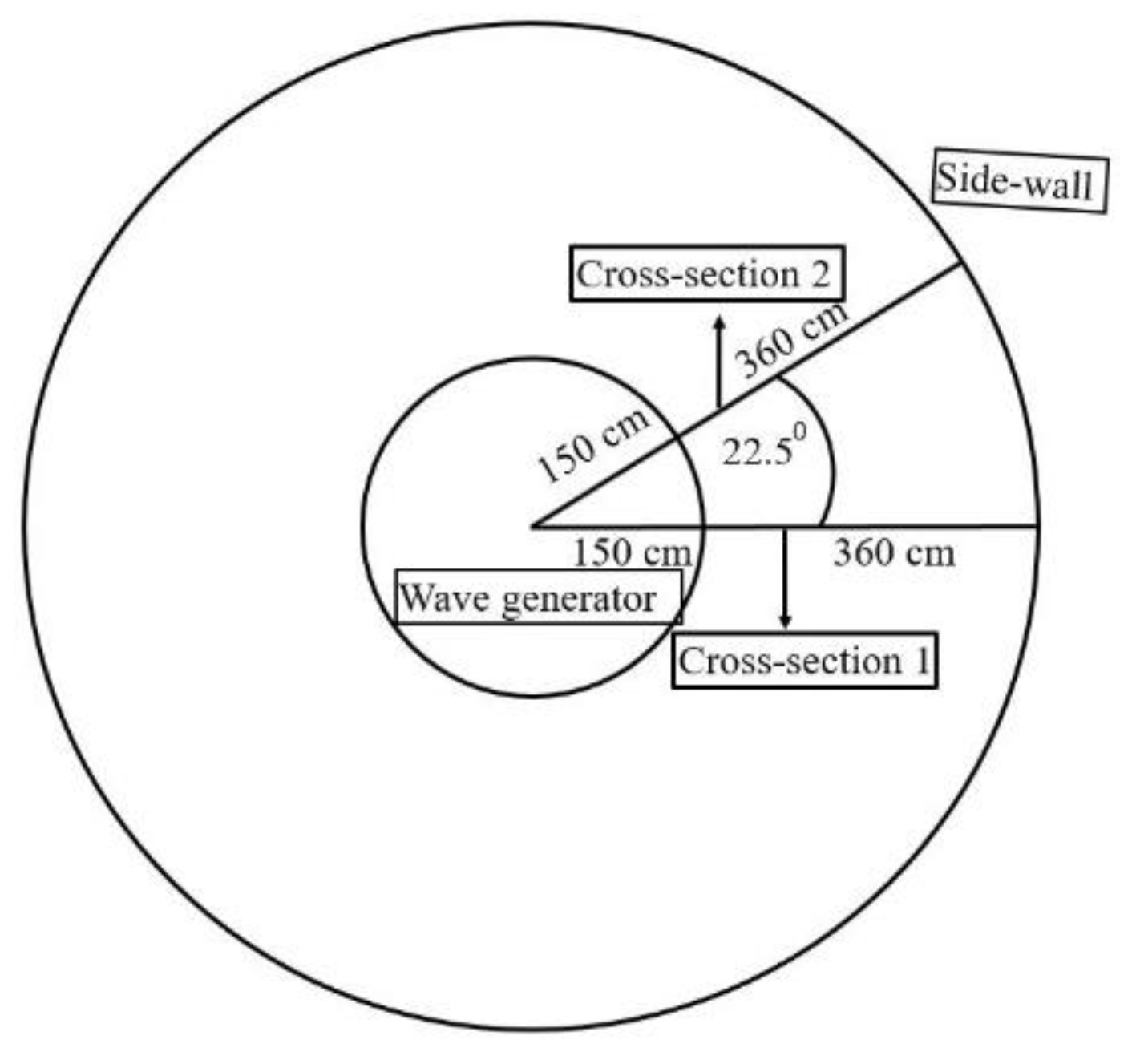
2. Experiment Model Set-Up and Wave Conditions
3. Results and Discussions
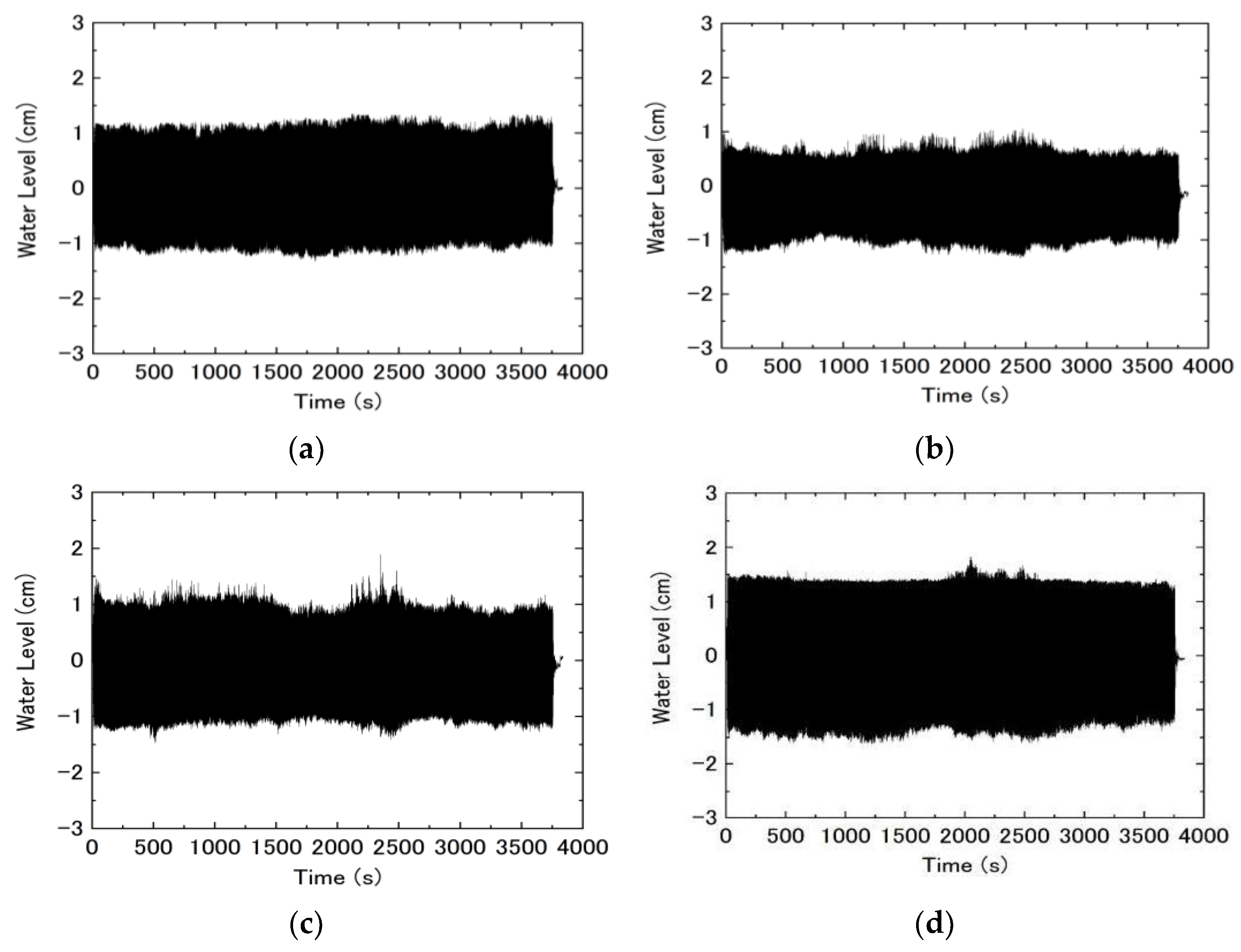
3.1. Wave Characteristics
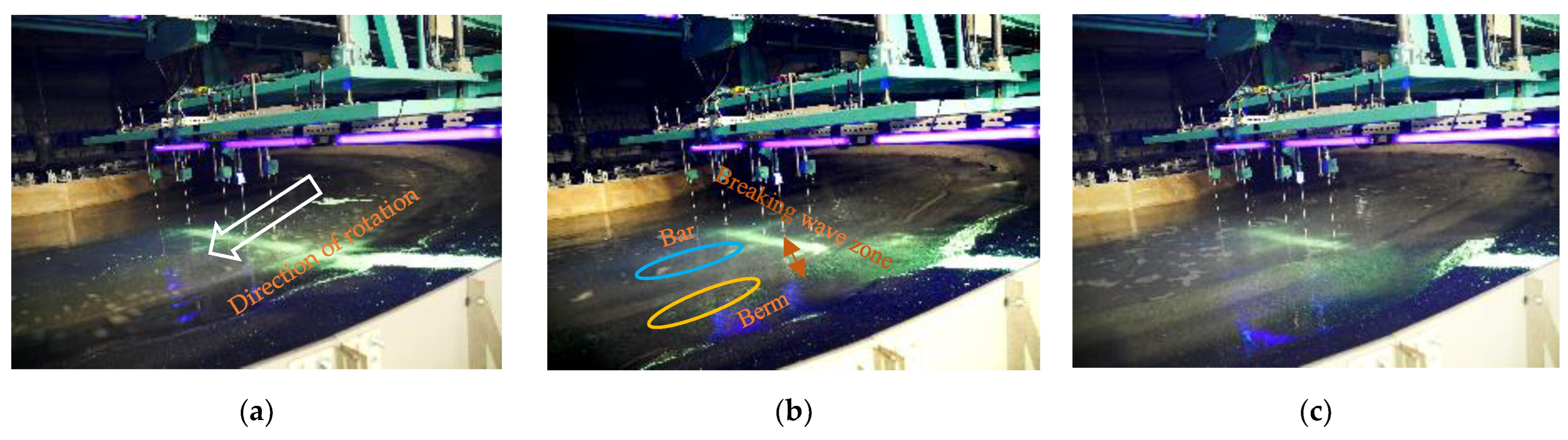
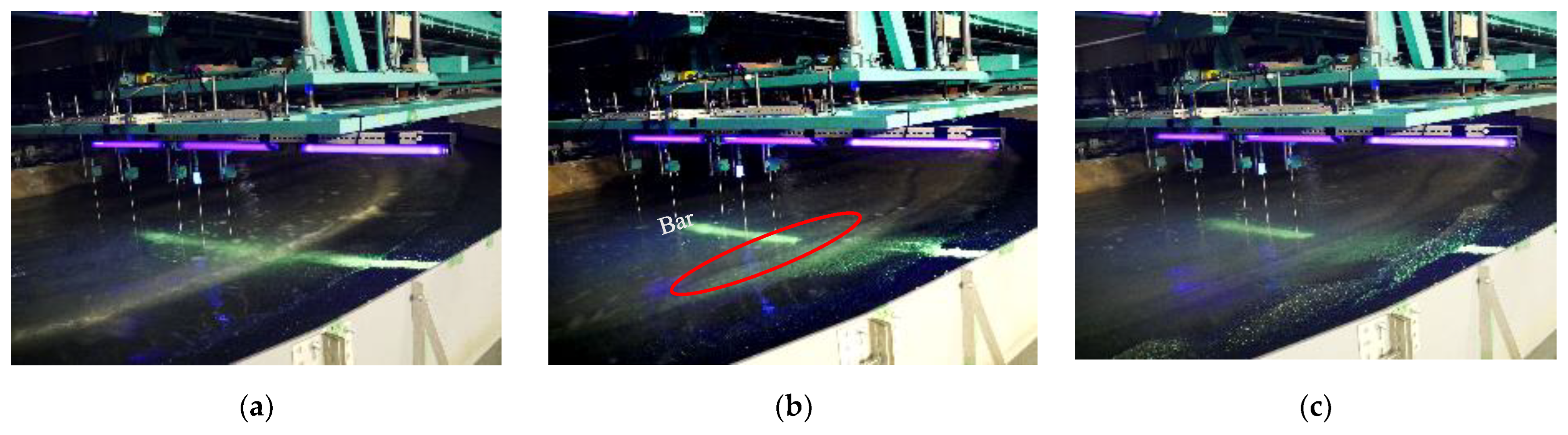
3.2. Topographical Changes before Equilibrium
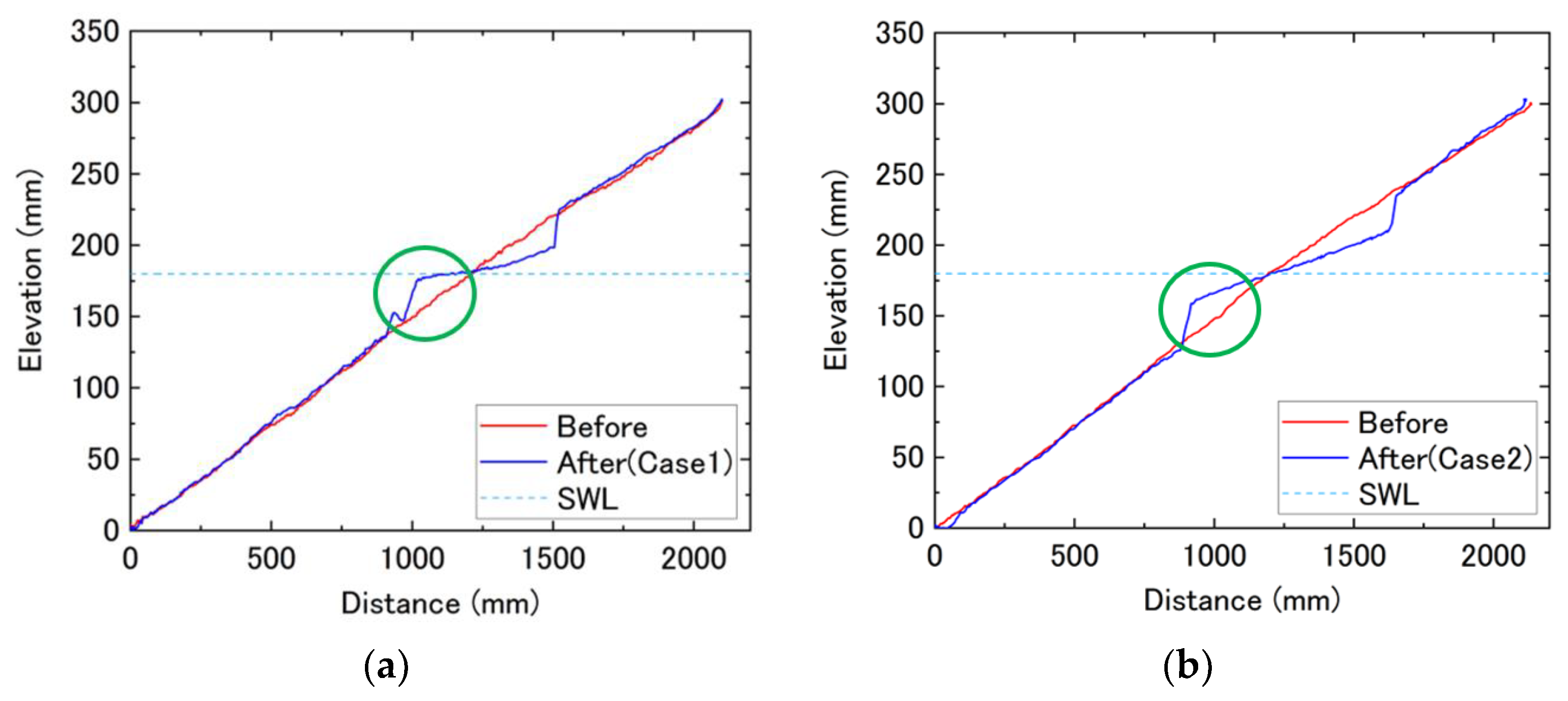
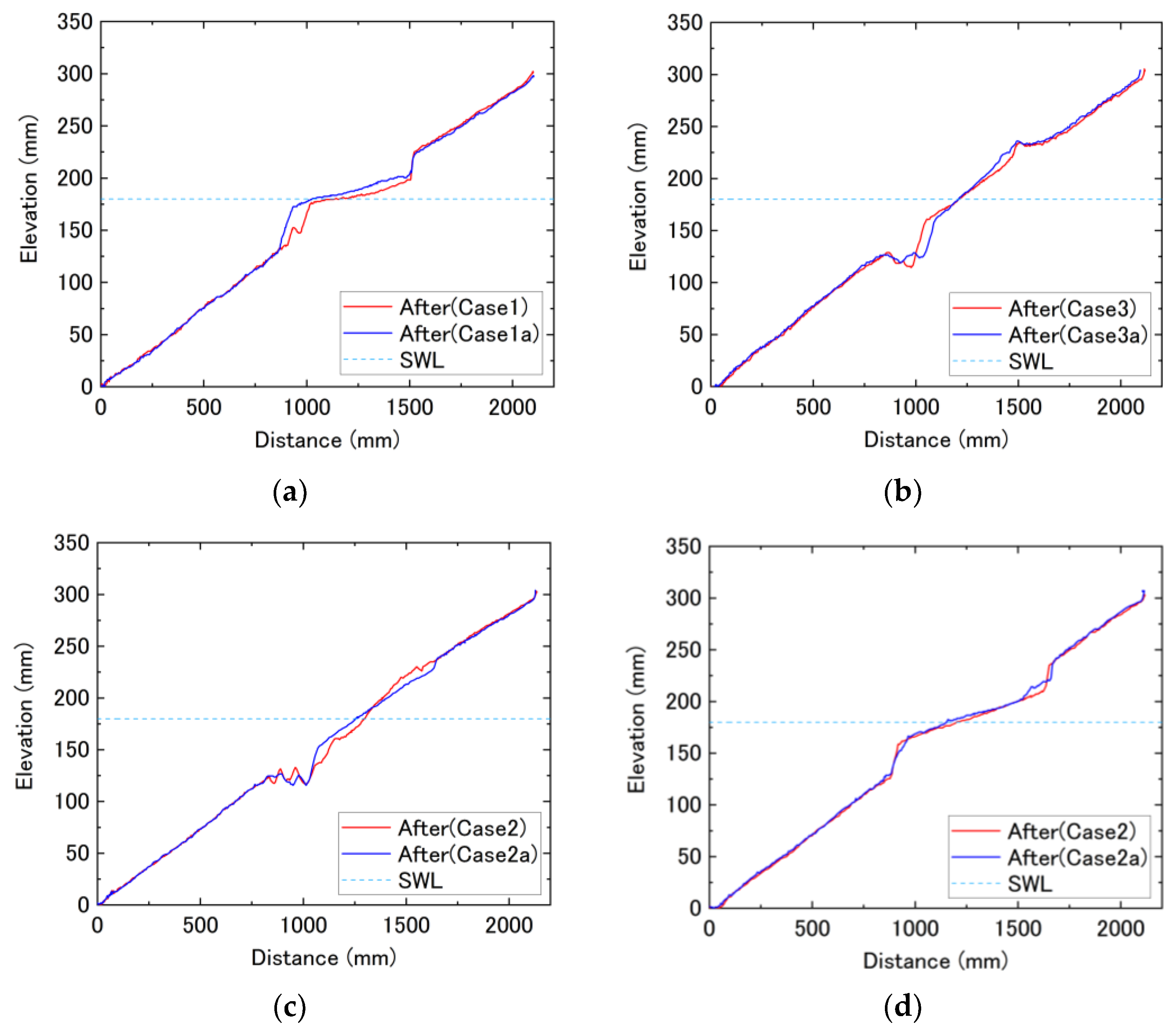
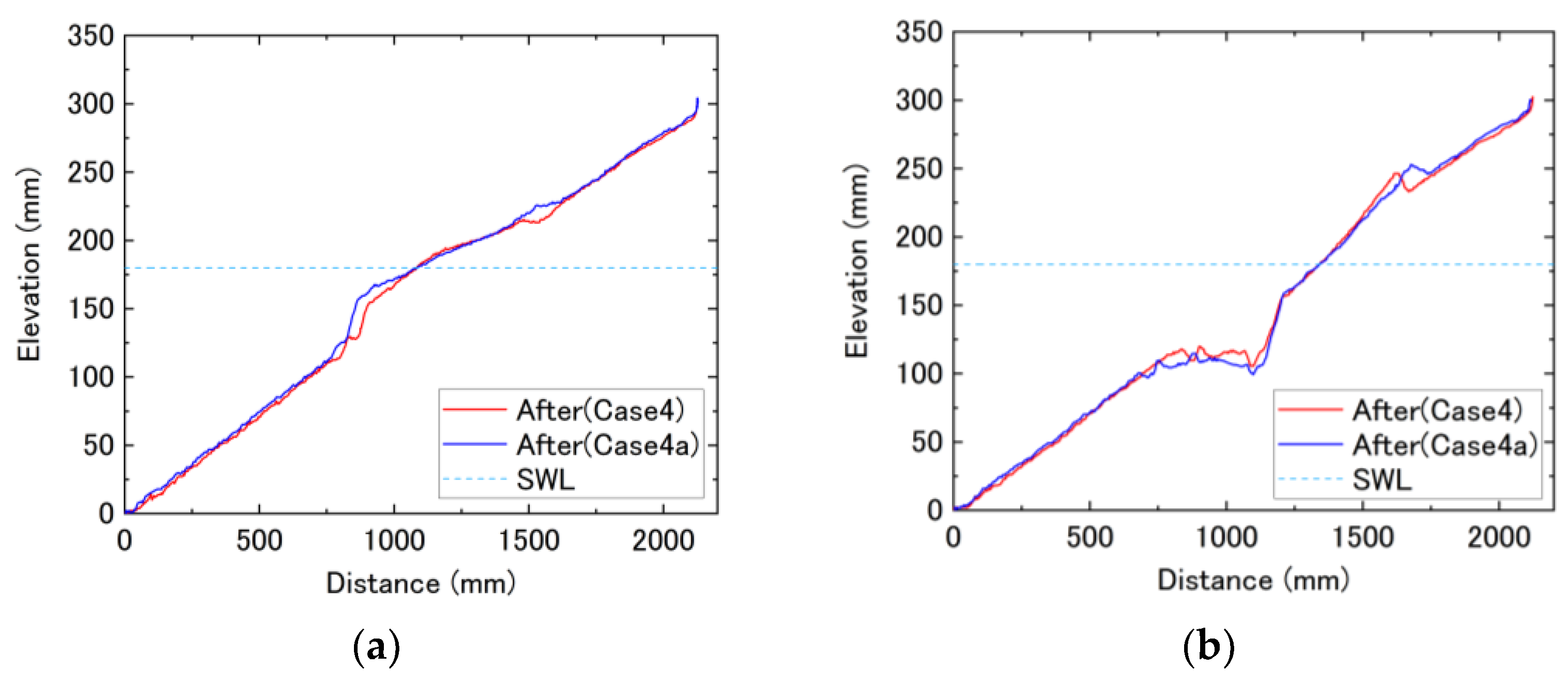
3.3. Topographical Changes after Equilibrium
3.4. Dynamic Characteristics of Sand Displacement before Equilibrium
3.5. Dynamic Characteristics of Sand Displacement after Equilibrium
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carter, C.H.; Guy, E.D., Jr. Coastal erosion: Processes, timing and magnitudes at the bluff toe. Mar. Geol. 1988, 84, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Coastal erosion and control. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 867–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, M.G.; Peel, D.; Duck, R.W. Towards a social-ecological resilience framework for coastal planning. Land Use Policy 2013, 30, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Pranzini, E.; Anfuso, G. The management of coastal erosion. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 156, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayakage, S.M.S.; Sasaki, J.; Suzuki, T.; Jayaratne, R.; Ranawaka, R.A.S.; Pathmasiri, S.D. On the status and mechanisms of coastal erosion in Marawila Beach, Sri Lanka. Nat. Hazards 2020, 103, 1261–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, T.; Black, K.P.; Greenwood, B. Cross-shore suspended sediment transport in the surf zone: A field-based parameterization. Mar. Geol. 2002, 185, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Smith, E.R.; Ebersole, B.A. Large-scale laboratory measurements of longshore sediment transport under spilling and plunging breakers. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 18, 118–135. [Google Scholar]
- Puleo, J.A.; Beach, R.A.; Holman, R.A.; Allen, J.S. Swash zone sediment suspension and transport and the importance of bore-generated turbulence. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2000, 105, 17021–17044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño-Tapia, I.J.; Russell, P.E.; O’Hare, T.J.; Davidson, M.A.; Huntley, D.A. Cross-shore sediment transport on natural beaches and its relation to sandbar migration patterns: 1. Field observations and derivation of a transport parameterization. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, C03001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günaydin, K.; Kabdaşli, M.S. Characteristics of coastal erosion geometry under regular and irregular waves. Ocean Eng. 2003, 30, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Lawrence, A.R. Cross-shore sediment transport under breaking solitary waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109, C03047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunamura, T.; Horikawa, K. Two-dimensional beach transformation due to waves. In Proceedings of the 14th ASCE Coastal Engineering. Conference, Copenhagen, Denmark, 24–28 June 1974; pp. 920–938. [Google Scholar]
- Ozolcer, I.H. An experimental study on geometric characteristics of beach erosion profiles. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N. Analytical Solution for Dune Erosion by Storms. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1987, 113, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, I.K.; Baldock, T.E.; Callaghan, D.P. Measurement and modelling of the influence of grain size and pressure gradient on swash uprush sediment transport. Coast. Eng. 2014, 83, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, M.; Aköz, M.S. An investigation on the formation of submerged bar under surges in sandy coastal region. China Ocean Eng. 2012, 26, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichentopf, S.; Cáceres, I.; Alsina, J.M. Breaker bar morpho dynamics under erosive and accretive wave conditions in large-scale experiments. Coast. Eng. 2018, 138, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, M.; Horikawa, K. Experimental Study on Longshore Current Velocity Distribution. Bull. Fac. Sci. Eng. 1978, 21, 123–149. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, P.J. Laboratory measurements of uniform longshore currents. Coast. Eng. 1991, 15, 563–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.G.; Ebersole, B.A. Establishing uniform longshore currents in a large-scale sediment transport facility. Coast. Eng. 2001, 42, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangduo, S.; Qinqin, G.; Zhili, Z.; Lulu, H.; Wei, C.; Mingtao, J. Experimental study and numerical simulation of mean longshore current for mild slope. Wave Motion 2020, 99, 102651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.; Jayaratne, R.; Tejada-Martinez, A.E.; Wang, P. Numerical investigation of beach profile evolution using a new sediment concentration model. Proc. Coast. Sediments 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Dong, G. A numerical investigation on nonlinear transformation of obliquely incident random waves on plane sloping bottoms. Coast. Eng. 2017, 130, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaoka, S.; Noguchi, K.; Suwa, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Watanabe, A.; Takagi, T. A beach profile change model including three transport processes. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference of Coastal Dynamics, Tokyo, Japan, 7–11 September 2009; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Long, T. Numerical modelling of wave-induced beach profile change with a two-phase SPH scheme. In Proceedings of the 8th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, IEMSs, Toulouse, France, 12 July 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, M. Model of Beach Profile Change under Random Waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1996, 122, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-J.; Zhang, E.C.; Lee, J.F. Numerical Simulation of Nonlinear Viscous Wavefields Generated by Piston-Type Wavemaker. J. Eng. Mech. 1998, 124, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabasi, M.; Soltanpour, M.; Suzuki, T.; Jayaratne, R. Modeling of berm formation and erosion at the southern coast of the Caspian Sea. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2020, 36, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, R.A.; Dean, R.G. The spiral wavemaker for littoral drift studies. In Proceedings of the 13th Coastal Engineering Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 July 1972; pp. 689–705. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, C.C. Shoaling of spiral waves in a circular basin. J. Geophys. Res. 1973, 78, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowbridge, J.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Suh, K. A simplified second-order solution for a spiral wave maker. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 1986, 91, 11783–11789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.N.; McDougal, W.G. Hydrodynamic analysis of variable draft spiral wavemaker. Ocean Eng. 1989, 16, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.; Dalrymple, R.A. Offshore Breakwaters in Laboratory and Field. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1987, 113, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F. Sample NEES Presentation Thomas Finholt School of Information University of Michigan. 2015. Available online: https://slideplayer.com/slide/5065618/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Katoh, K.; Yanagishima, S. Berm Formation and Berm Erosion. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Coastal Engineering, ASCE, Venice, Italy, 4–9 October 1992; pp. 2136–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Tomoda, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kuriyama, Y. Spatial distribution of cross-shore sediment transport rate for berm formation and erosion. In Proceedings of the Coastal Sediments ’07—6th International Symposium on Coastal Engineering and Science of Coastal Sediment Processes, ASCE, New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 May 2007; pp. 2037–2048. [Google Scholar]
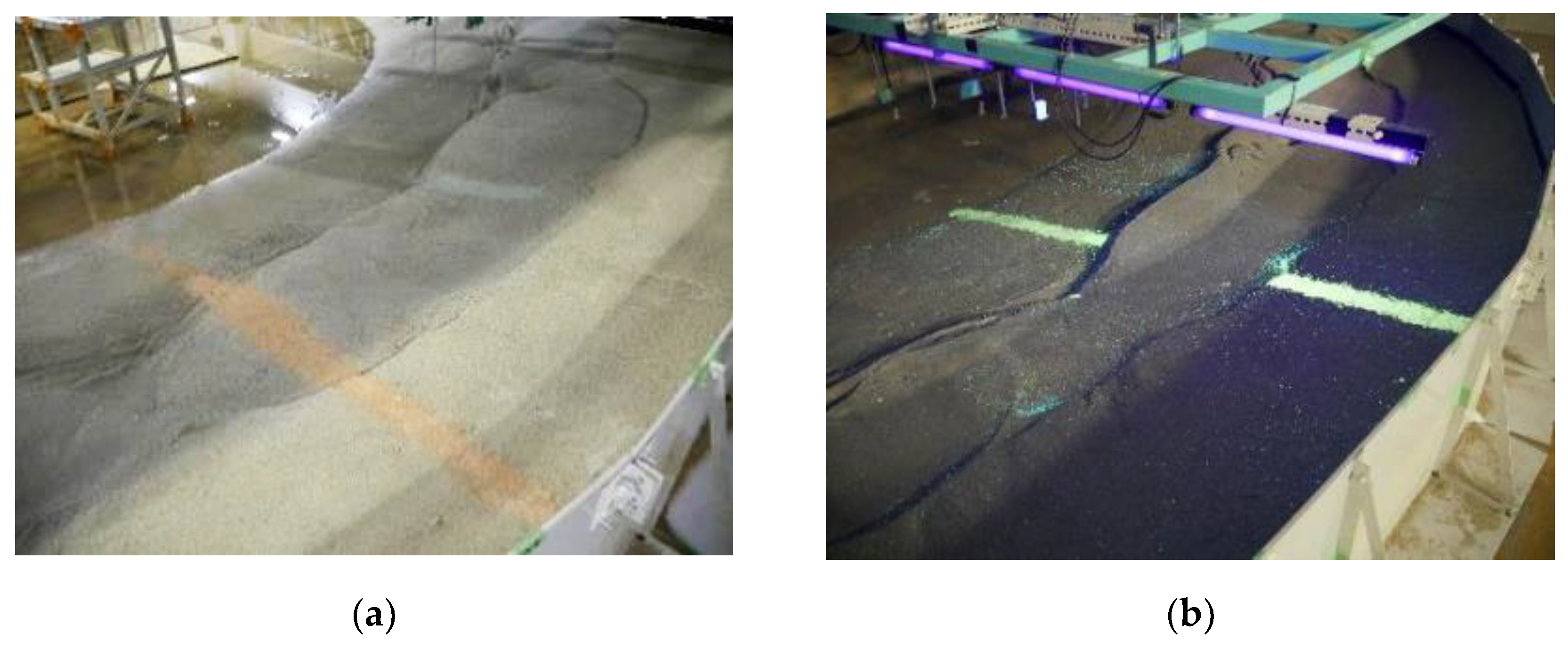



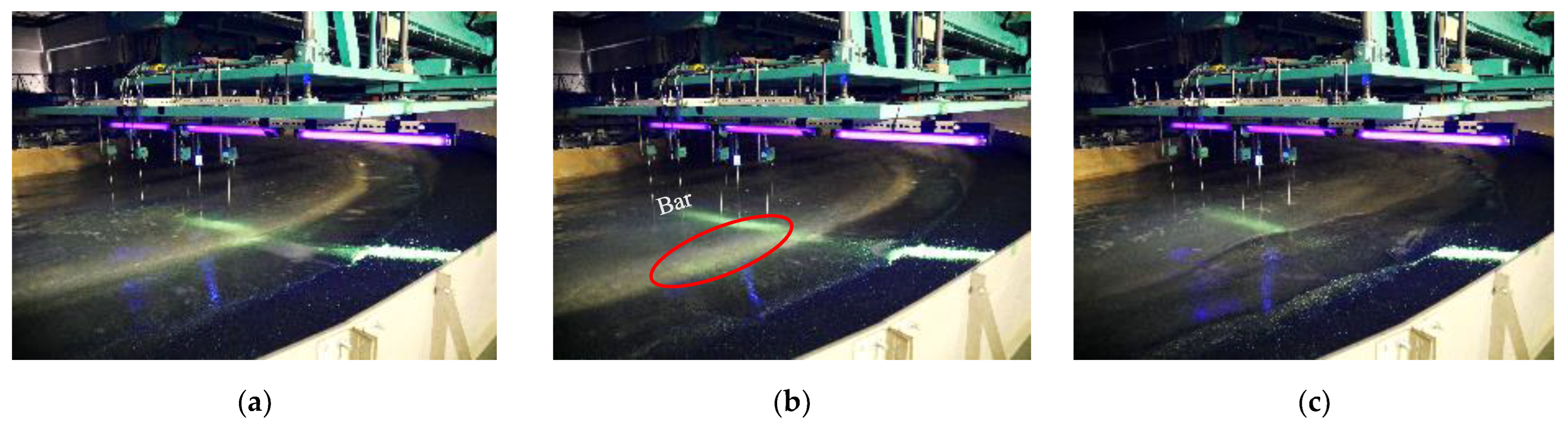

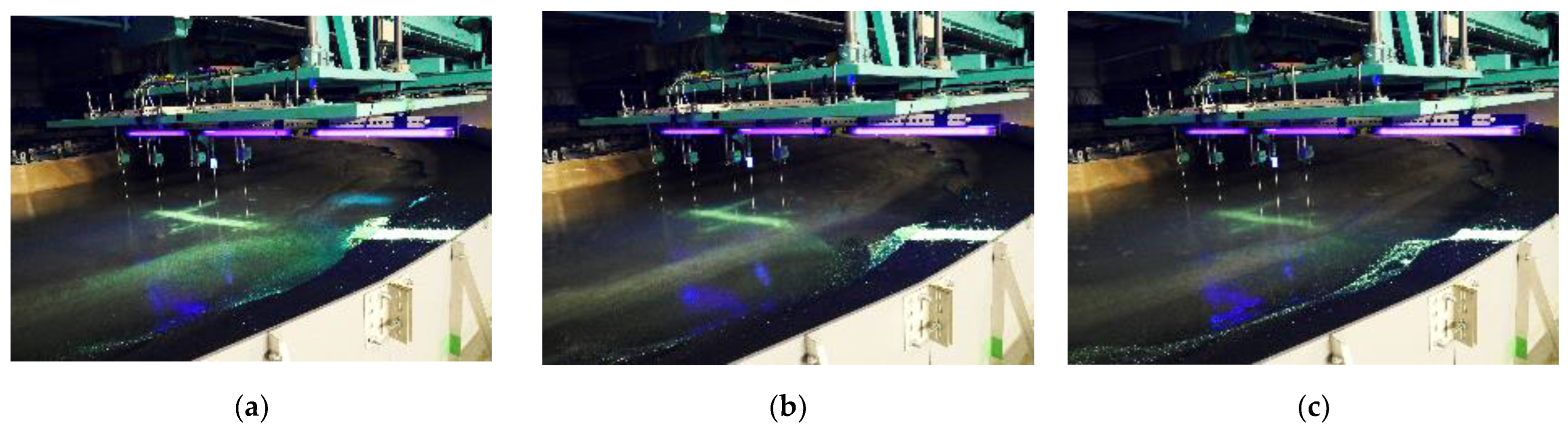
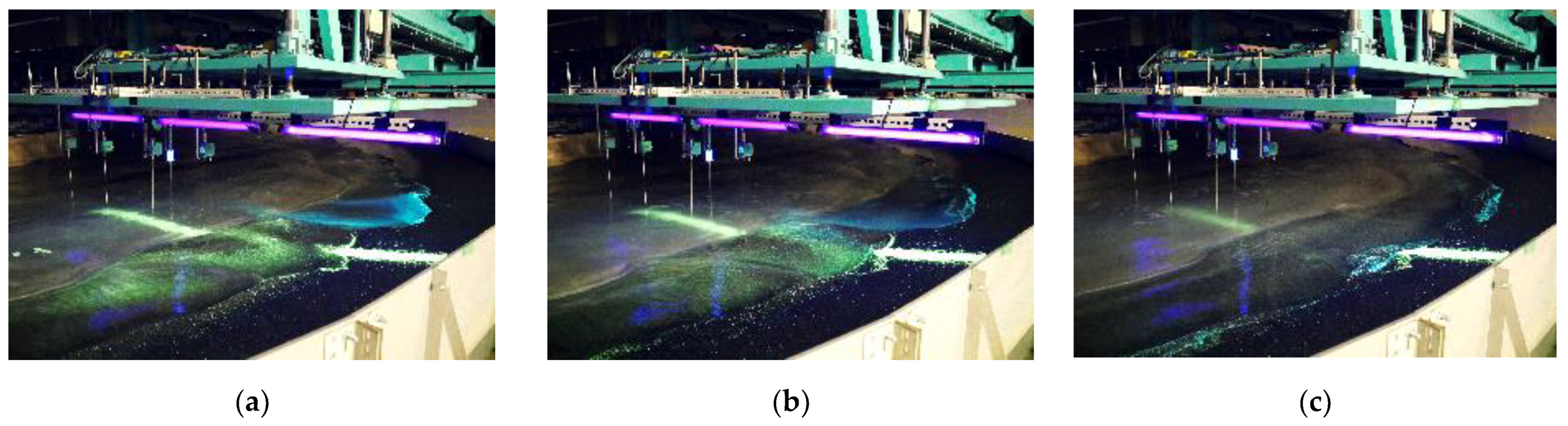
| Case | 1 | 1a | 2 | 2a | 3 | 3a | 4 | 4a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Terrain | 1: 7 Uniform Slope | Final terrain of Case 1 | 1: 7 Uniform Slope | Final terrain of Case 2 | 1: 7 Uniform Slope | Final terrain of Case 3 | 1: 7 Uniform Slope | Final terrain of Case 4 |
| Period | 2.50 s | 2.22 s | 2.0 s | 1.82 s | ||||
| Water depth | 18 cm | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.S.; Akita, N.; Nakamura, T.; Cho, Y.-H.; Mizutani, N. Experimental Investigation on the Mechanism of Longshore Sediment Transport Using a Circular Wave Basin. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091189
Islam MS, Akita N, Nakamura T, Cho Y-H, Mizutani N. Experimental Investigation on the Mechanism of Longshore Sediment Transport Using a Circular Wave Basin. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(9):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091189
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Mohammad Shaiful, Naoki Akita, Tomoaki Nakamura, Yong-Hwan Cho, and Norimi Mizutani. 2022. "Experimental Investigation on the Mechanism of Longshore Sediment Transport Using a Circular Wave Basin" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 9: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091189
APA StyleIslam, M. S., Akita, N., Nakamura, T., Cho, Y.-H., & Mizutani, N. (2022). Experimental Investigation on the Mechanism of Longshore Sediment Transport Using a Circular Wave Basin. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(9), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091189






