A Sparse Bayesian Learning Method for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Underwater Maneuvering Platform Noise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Problem Description
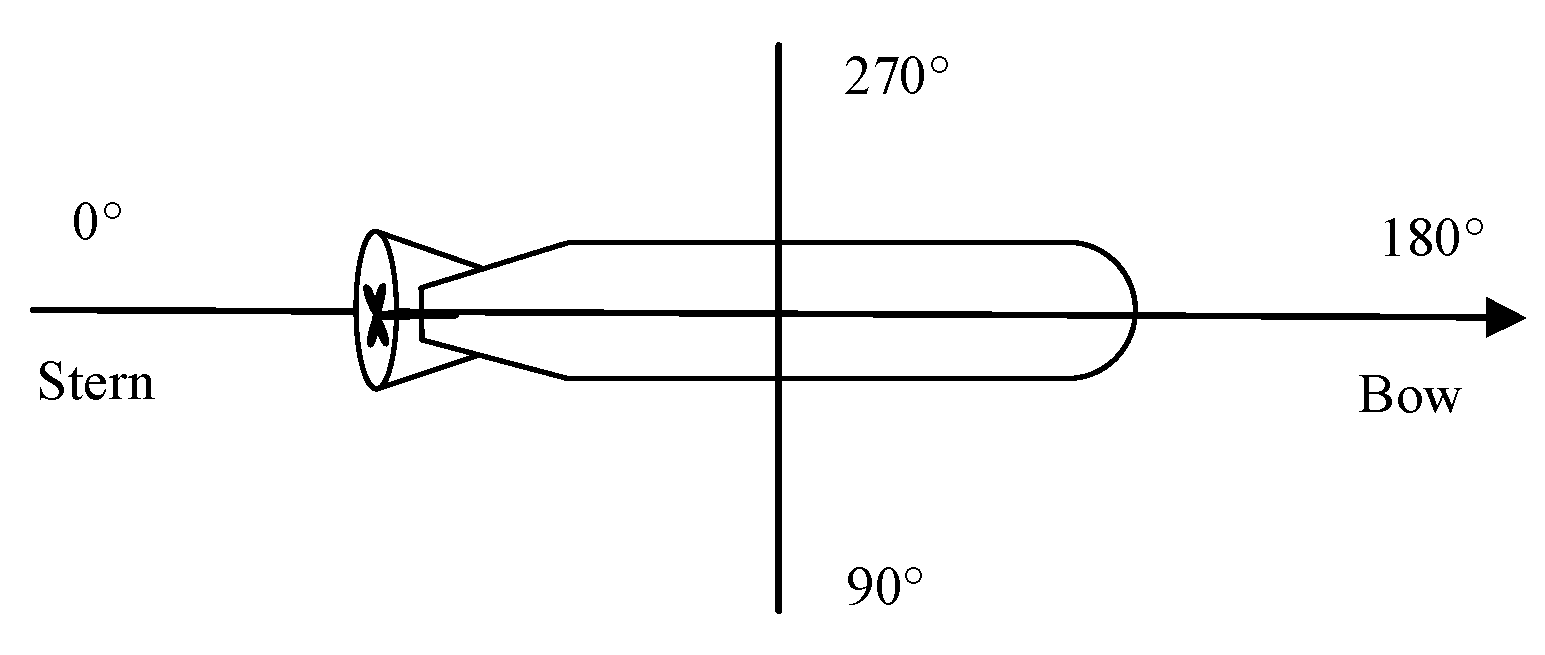
2.1. Spatial Distribution of Underwater Maneuvering Platform Noise
2.2. Establishment of Noise Model
- (1)
- Assume that there is a spherical surface on which Nw discrete points are randomly distributed.
- (2)
- Each discrete point is placed with independent narrow-band noise with the same power.
- (3)
- A receiving array is placed at the sphere center, and the sphere radius is significantly large compared to the array aperture. Therefore, the noise is approximated as a plane wave.
2.3. Received Data Model
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Sparse Bayesian Learning Framework under an Unknown SCN Covariance Matrix
3.2. SCN Covariance Matrix Estimation
3.3. Iterative Steps and Computational Complexity
| Algorithm 1: Underwater maneuvering platform noise sparse Bayesian learning (UNSBL) |
| Input: , ; Initialization: hyperparameters and ; maximum number of iterations ; iteration termination parameter ; While not converge do (1) Calculate and using Equations (15) and (16); (2) Update using Equation (18); (3) Update using Equation (21); (4) If or , break; (5) Else, go to step (1); (6) End if End while |
| Output: ; |
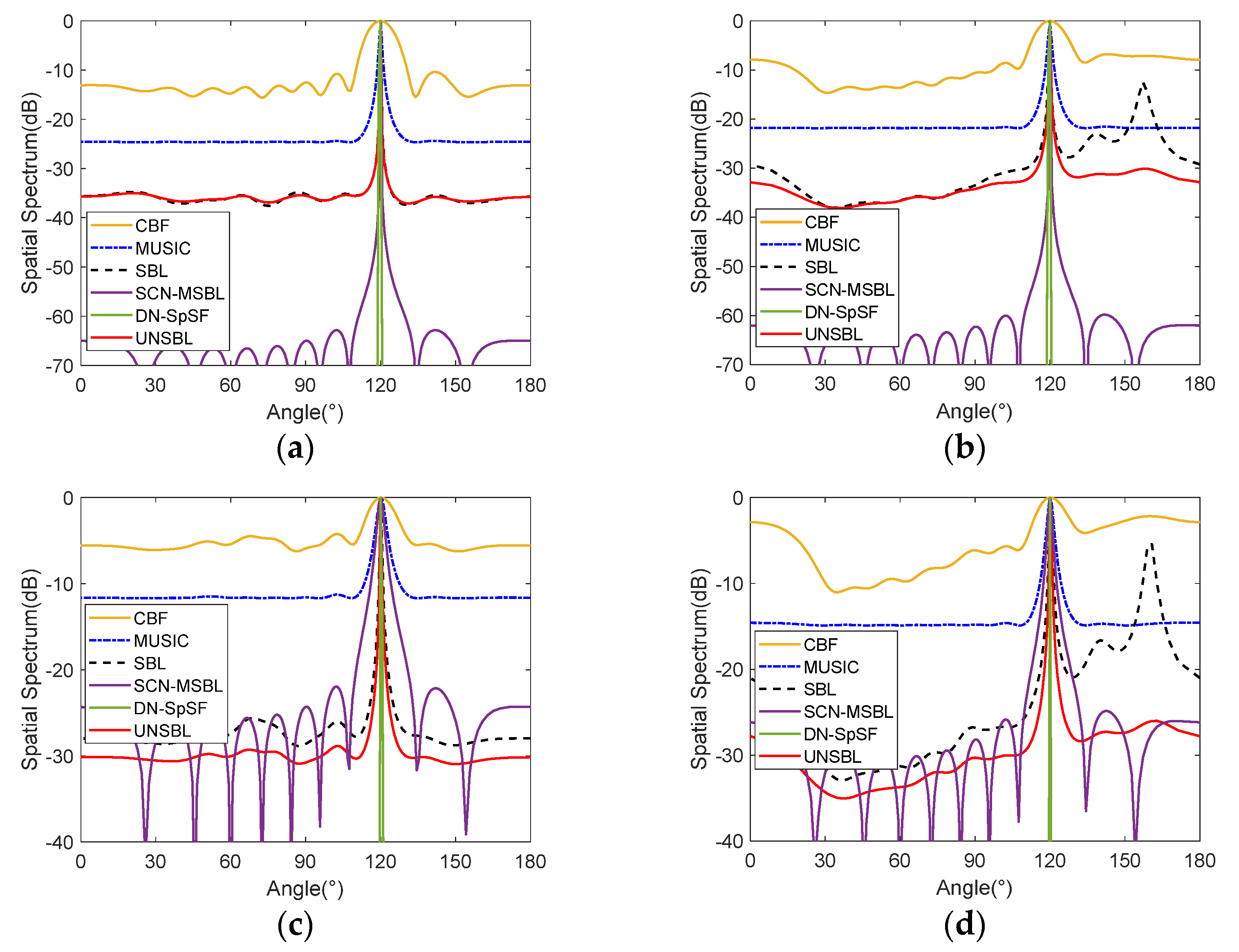
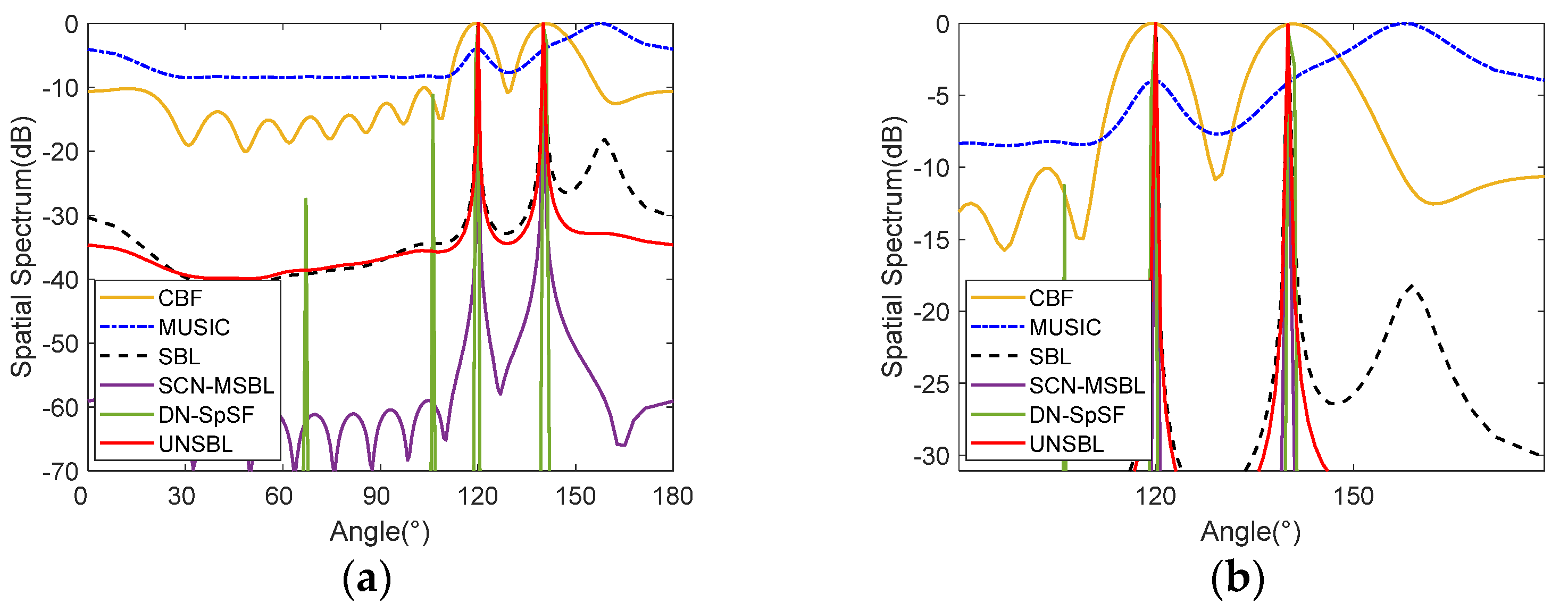
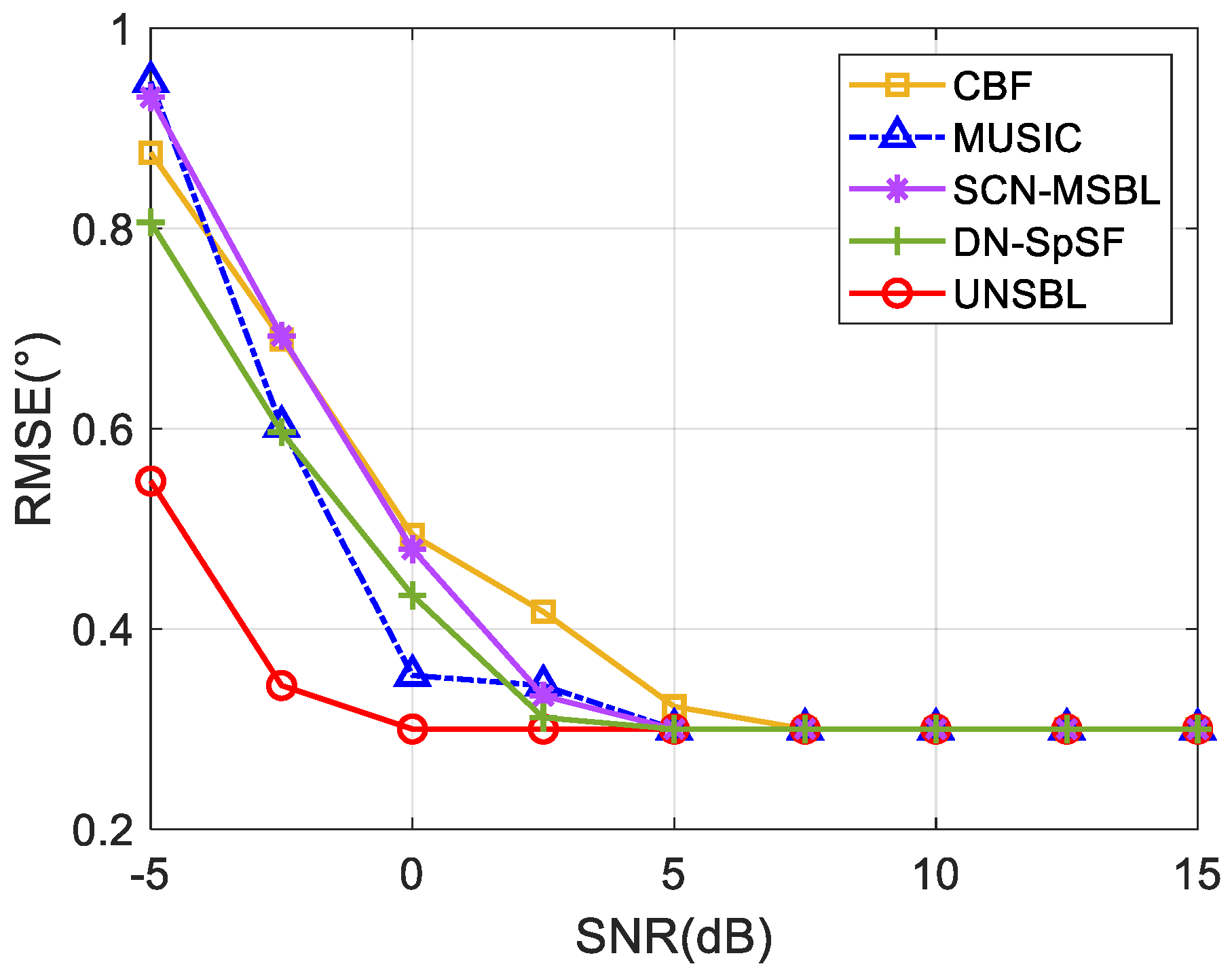
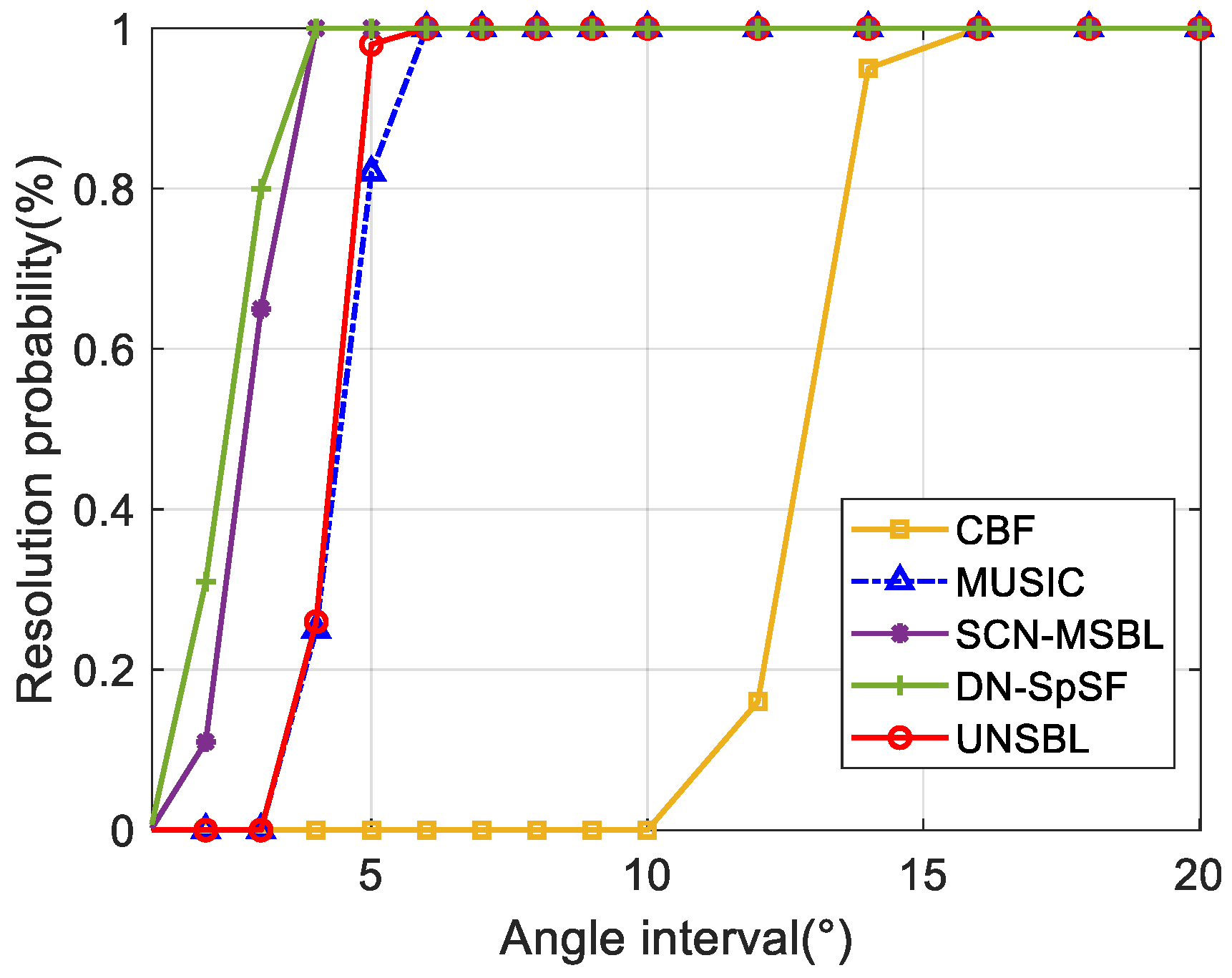
4. Simulation Analysis
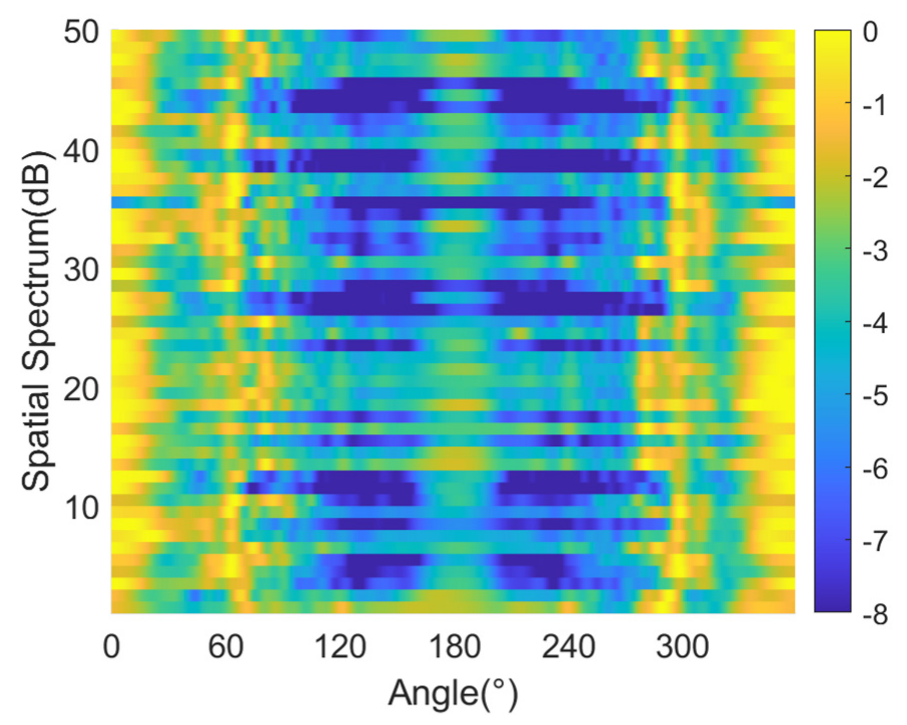
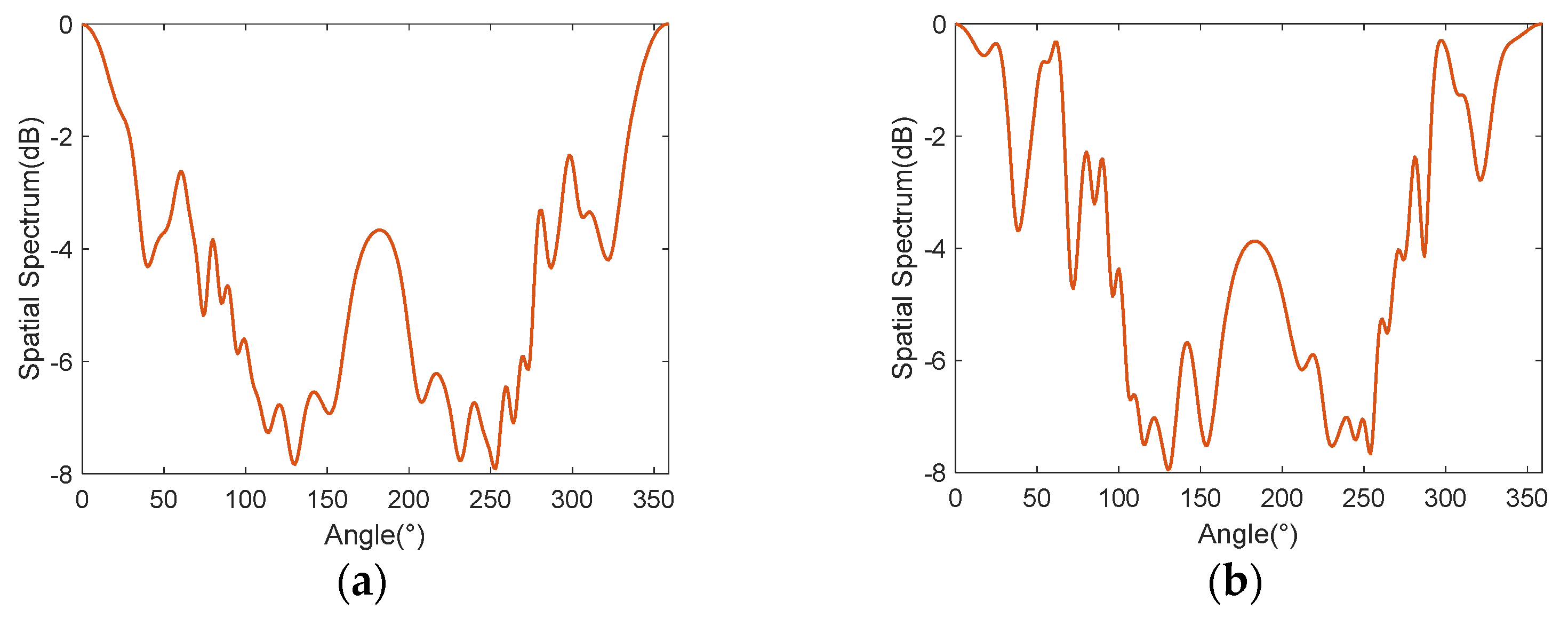
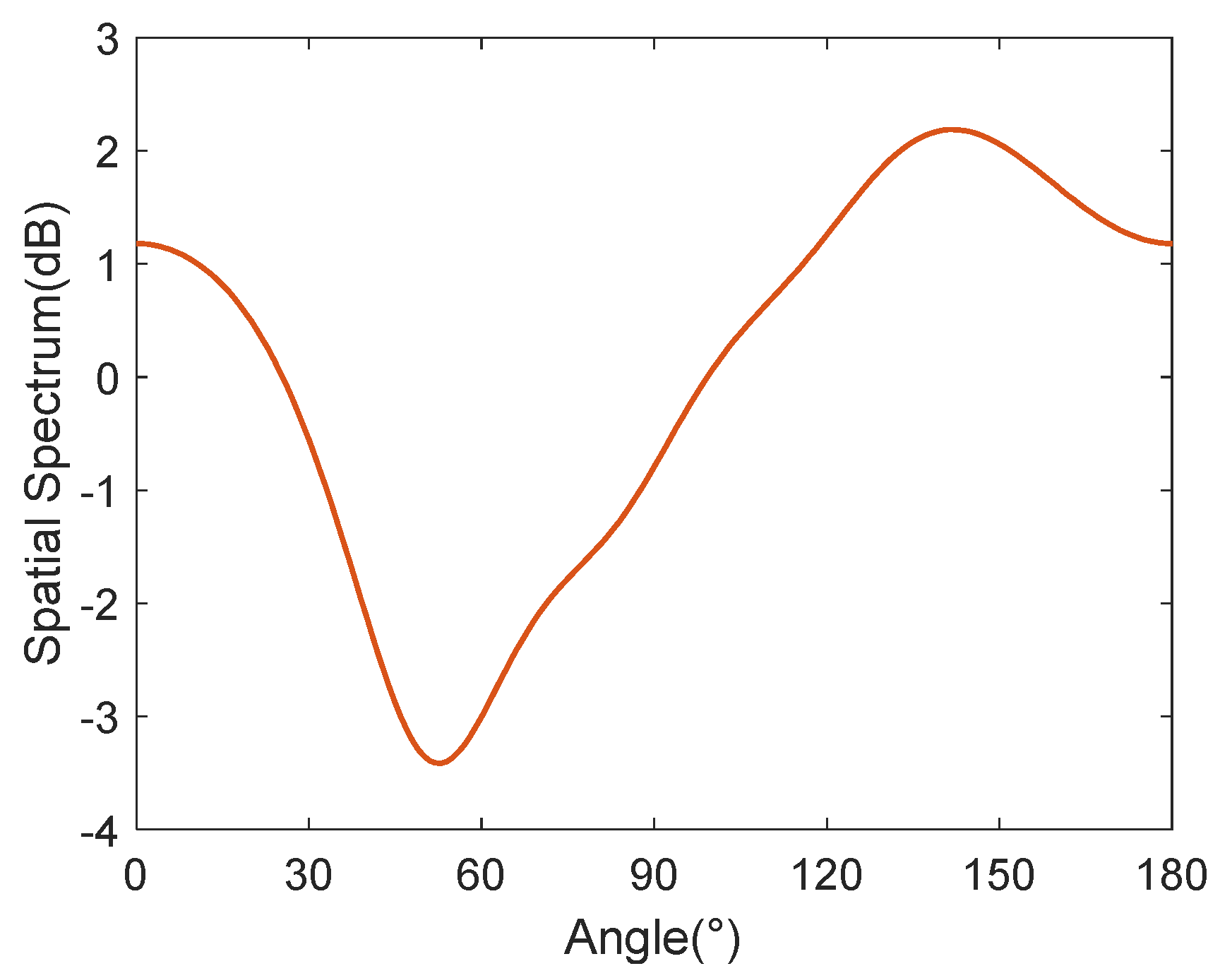
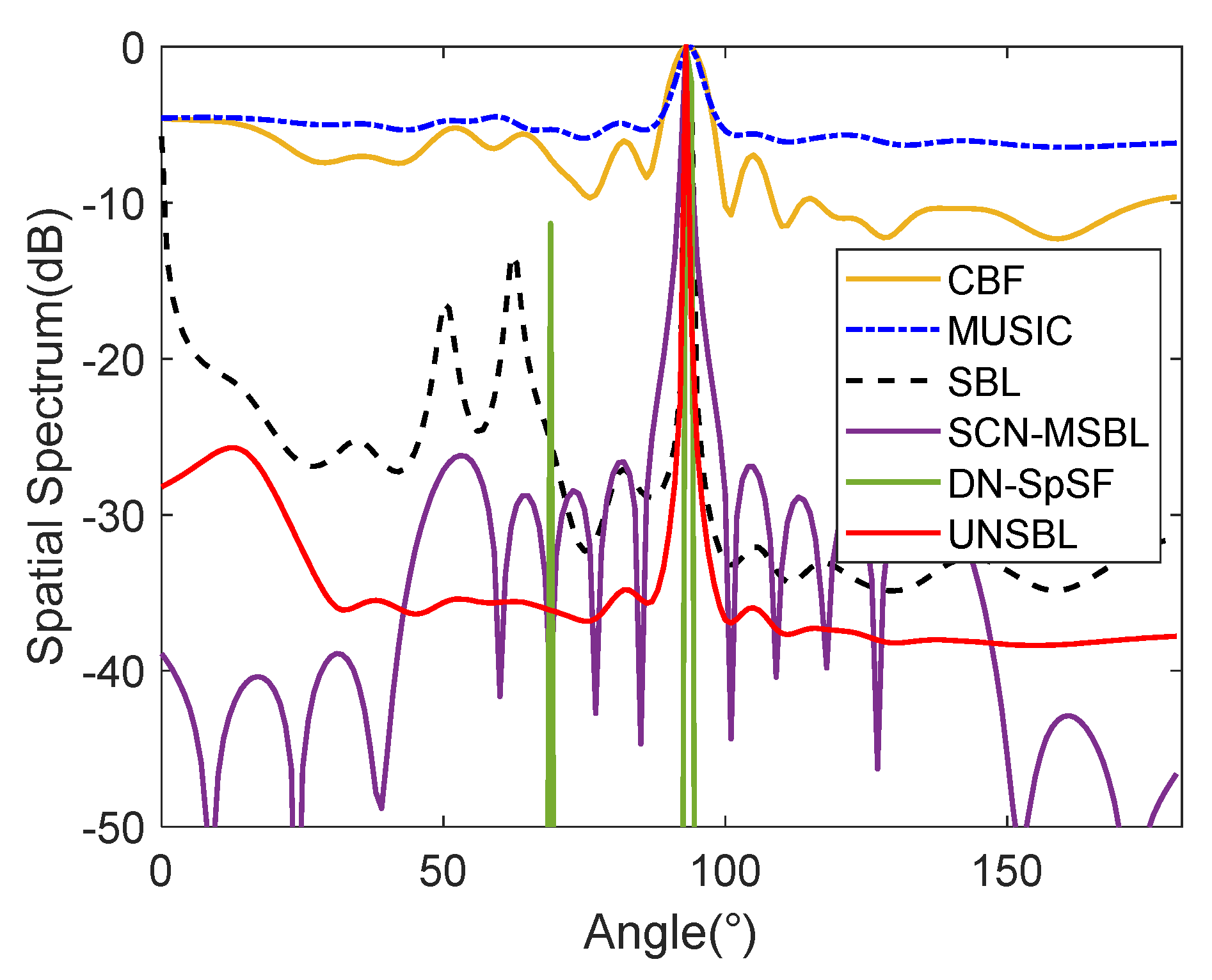
4.1. Spatial Spectra
4.2. Statistical Performance
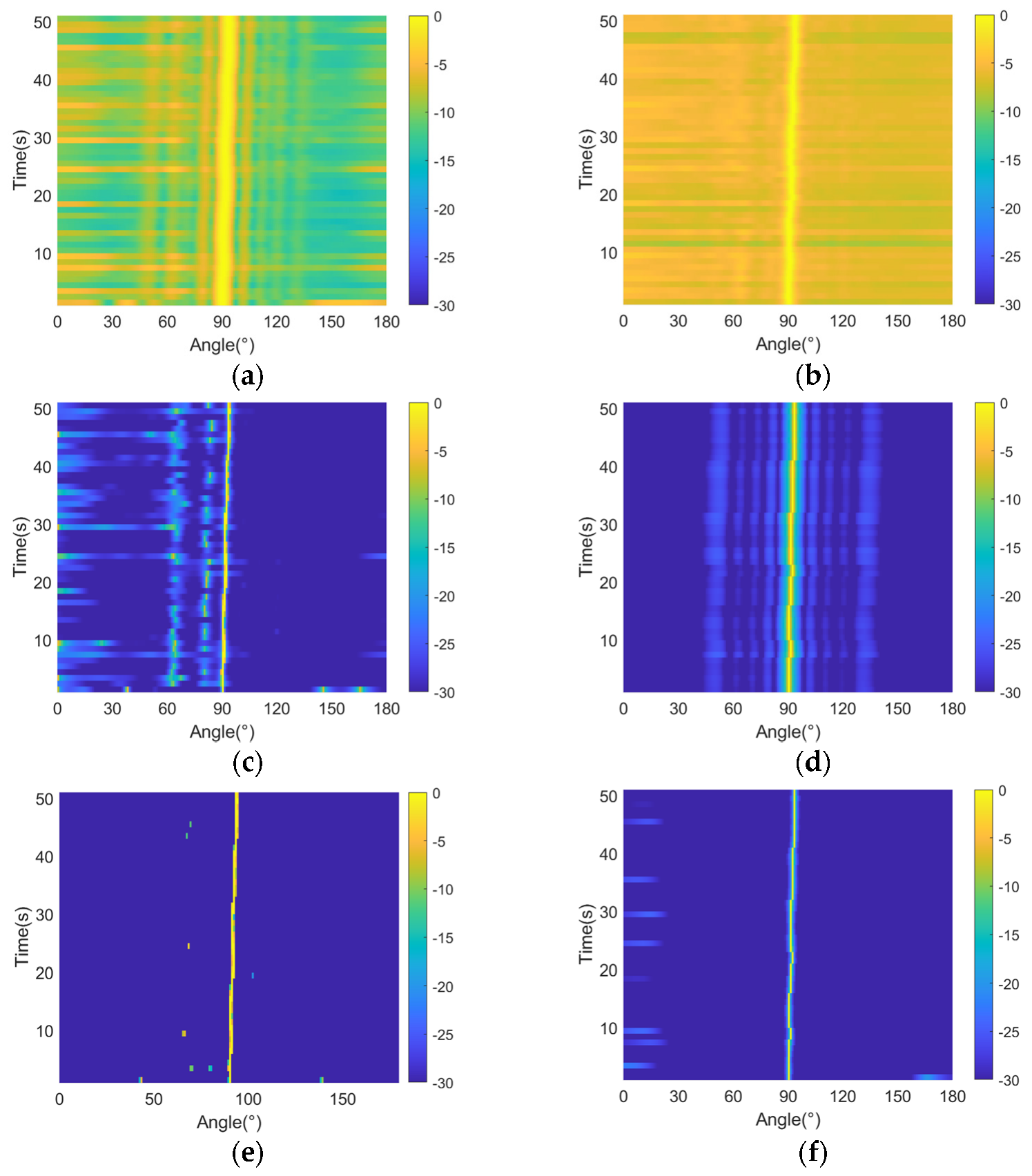
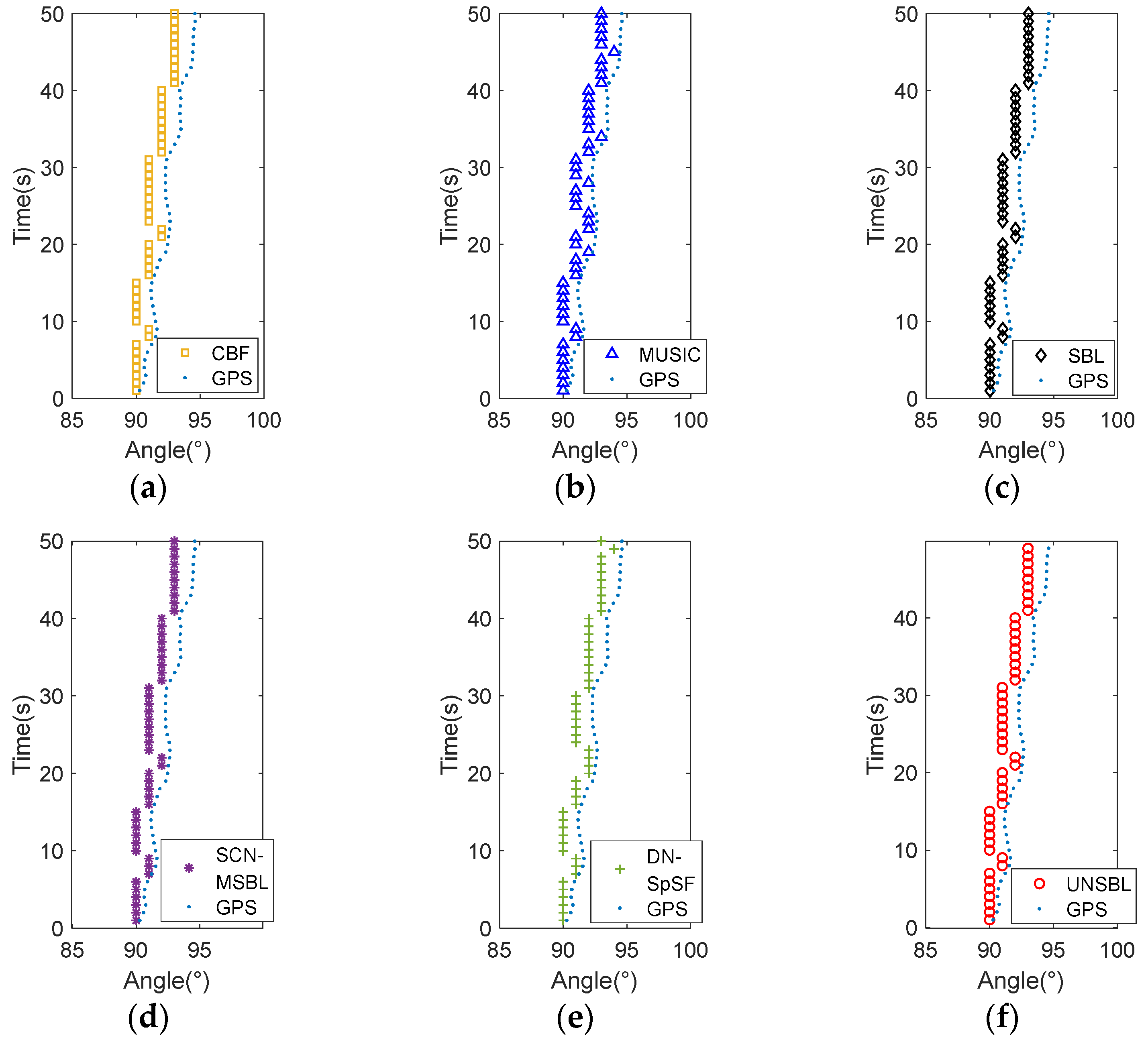
5. Sea Trial
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- UNSBL avoids spurious peaks and yields good and robust performance with various SNRs and coherent signals through spatial spectrum analysis.
- (2)
- UNSBL achieves a higher accuracy in the case of low SNRs and small snapshot numbers through statistical analysis, compared to the existing methods. In other words, UNSBL is more robust to such cases than the other methods.
- (3)
- The feasibility and stability of UNSBL are validated through sea trial data processing. UNSBL provides a lower and flatter noise spectrum level without spurious peaks in the real underwater maneuvering platform noise.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffiths, L.; Jim, C. An Alternative Approach to Linearly Constrained Adaptive Beamforming. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1982, 30, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, J. High-Resolution Frequency-Wavenumber Spectrum Analysis. Proc. IEEE 1969, 57, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zou, N.; Liang, G. Robust Capon Beamforming against Steering Vector Error Dominated by Large Direction-of-Arrival Mismatch for Passive Sonar. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglass, A.S.; Song, H.C.; Dowling, D.R. Performance Comparisons of Frequency-Difference and Conventional Beamforming. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mañosas-Caballú, M.; Swindlehurst, A.L.; Seco-Granados, G. Power-Based Capon Beamforming: Avoiding the Cancellation Effects of GNSS Multipath. Signal Process. 2021, 180, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Park, Y.; Gerstoft, P. Gridless DOA Estimation and Root-MUSIC for Non-Uniform Linear Arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple Emitter Location and Signal Parameter Estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Yang, D.; Shi, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, Y. Augmented Subspace MUSIC Method for DOA Estimation Using Acoustic Vector Sensor Array. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2019, 13, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; Sharman, K.C. Maximum Likelihood Methods for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1990, 38, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipping, M.E. Sparse Bayesian Learning and the Relevance Vector Machine. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2001, 1, 211–244. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-M.; Huang, Z.-T.; Zhou, Y.-Y. An Efficient Maximum Likelihood Method for Direction-of-Arrival Estimation via Sparse Bayesian Learning. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2012, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wipf, D.P.; Rao, B.D. An Empirical Bayesian Strategy for Solving the Simultaneous Sparse Approximation Problem. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 3704–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstoft, P.; Mecklenbrauker, C.F.; Xenaki, A.; Nannuru, S. Multisnapshot Sparse Bayesian Learning for DOA. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1469–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; So, H.C. Real-Valued Sparse Bayesian Learning for DOA Estimation with Arbitrary Linear Arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 4977–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shoukairi, M.; Schniter, P.; Rao, B.D. A GAMP-Based Low Complexity Sparse Bayesian Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.-G.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Shi, J. Real-Valued Robust DOA Estimation Method for Uniform Circular Acoustic Vector Sensor Arrays Based on Worst-Case Performance Optimization. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 148, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo Marques, E.; Maciel, N.; Naviner, L.; Cai, H.; Yang, J. A Review of Sparse Recovery Algorithms. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 1300–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, B.; Weiss, A.J. Direction Finding Using Noise Covariance Modeling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, Y. Maximum Likelihood DOA Estimation in Unknown Colored Noise Fields. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2008, 44, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, M.; Prasad, S. A Modified Likelihood Function Approach to DOA Estimation in the Presence of Unknown Spatially Correlated Gaussian Noise Using a Uniform Linear Array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Sparse Spatial Spectral Estimation in Directional Noise Environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, EL263–EL268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Yang, L. Iterative Methods for DOA Estimation of Correlated Sources in Spatially Colored Noise Fields. Signal Process. 2021, 185, 108100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Shi, Z.; Qiu, L.; Sun, S.; Lan, T. Sparse Bayesian Learning Based Direction-of-Arrival Estimation under Spatially Colored Noise Using Acoustic Hydrophone Arrays. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hou, C.; Liao, G.; Guo, Q. Direction-of-Arrival Estimation in the Presence of Unknown Nonuniform Noise Fields. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2006, 31, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cron, B.F.; Sherman, C.H. Spatial-Correlation Functions for Various Noise Models. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 1732–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, C. A Sparse Bayesian Learning Method for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Underwater Maneuvering Platform Noise. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101879
Wang Y, Zhao L, Qiu L, Wang J, Li C. A Sparse Bayesian Learning Method for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Underwater Maneuvering Platform Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(10):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101879
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yan, Lei Zhao, Longhao Qiu, Jinjin Wang, and Chenmu Li. 2023. "A Sparse Bayesian Learning Method for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Underwater Maneuvering Platform Noise" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 10: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101879
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhao, L., Qiu, L., Wang, J., & Li, C. (2023). A Sparse Bayesian Learning Method for Direction of Arrival Estimation in Underwater Maneuvering Platform Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(10), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11101879






