Impacts of Tidal Oscillations on Coastal Groundwater System in Reclaimed Land
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
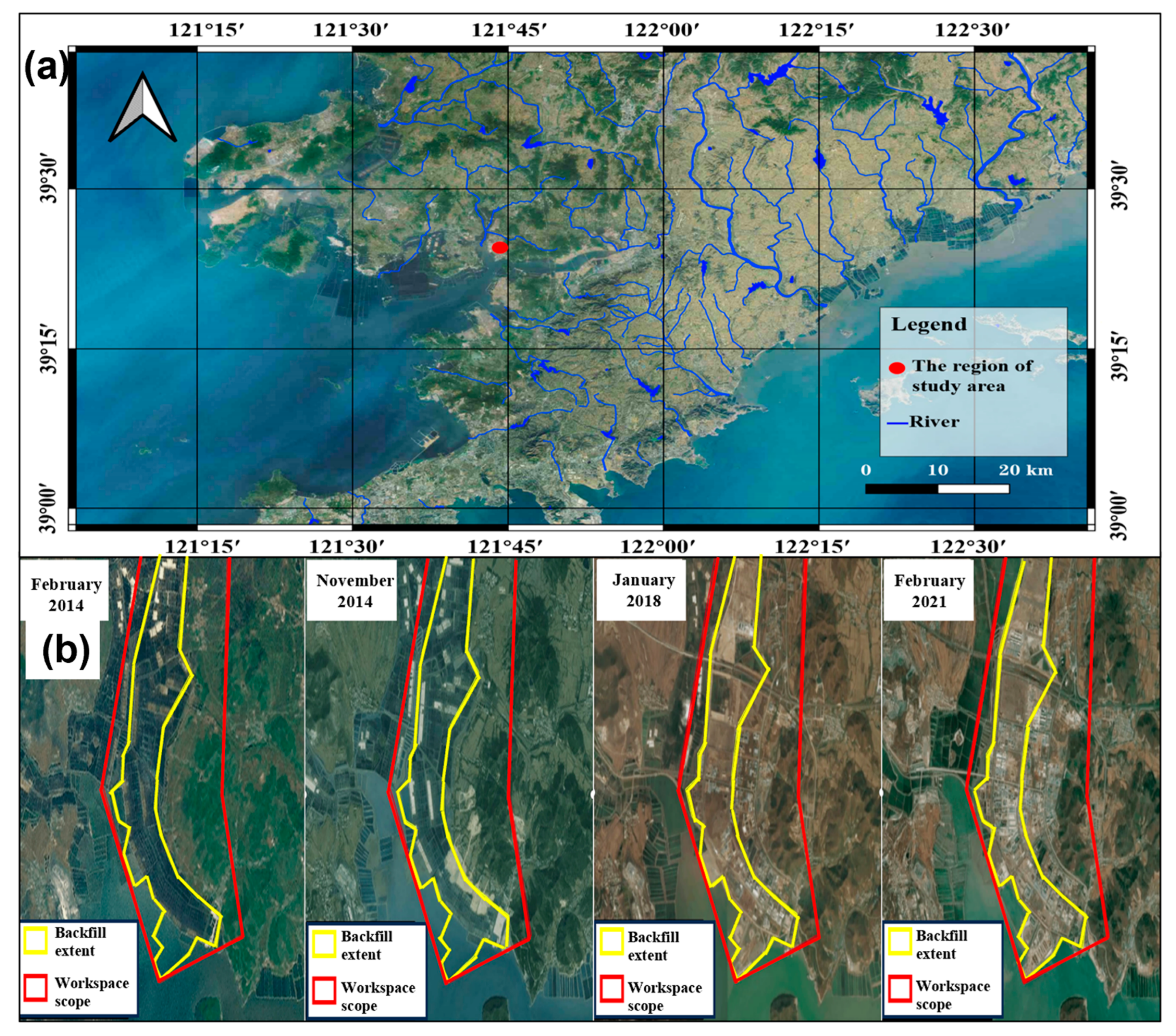
2.1. Study Area
2.2. The Lithology of the Field Site
2.3. Field Measurement
2.3.1. The Distribution of Groundwater Monitoring Wells
2.3.2. The Construction of the Groundwater Monitoring Wells and the Groundwater Measurement
2.3.3. The Measurement of the Groundwater Level and Salinity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Distribution of the Groundwater Level and Salinity
3.2. The Effect of Tide on the Groundwater Level
3.3. The Effect of Tide on the Groundwater Salinity
3.4. Harmonic Analysis for Tide Influence on Groundwater Level and Salinity
- is the value of the time series at time ;
- is the amplitude of the oscillation;
- is the frequency of the oscillation;
- is the phase angle or phase offset;
- is the time.
- is a constant term;
- is the total number of harmonic components considered;
- is the amplitude of the harmonic component;
- is the frequency of the harmonic component;
- is the phase angle of the harmonic component.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Our research shows that there is an exponential reduction in the fluctuating amplitude of groundwater levels and the groundwater salinity as distance further inland from the coast;
- (2)
- The semi-diurnal tides M2 and S2 in the propagation process of groundwater system are faster than that of full-diurnal tides K1 and O1, and the amplitude attenuation rate is lower than that of K1 and O1.
- (3)
- The intrusion process in high-permeable zones can be remarkably fast, driven by tidal oscillations and facilitated by the backfill material. Tidal signals can influence groundwater levels and salinity up to a one-kilometer range of inland.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charette1, M.A.; Buesseler, K.O. Submarine groundwater discharge of nutrients and copper to an urban subestuary of Chesapeake Bay (Elizabeth River). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-C.; Hsu, H.-T.; Liao, C.B.; Chiueh, P.-T. Groundwater response to tidal fluctuation and rainfall in a coastal aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, W. The effect of submarine groundwater discharge on the ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 59–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Barry, D.; Stagnitti, F.; Parlange, J. Submarine groundwater discharge and associated chemical input to a coastal sea. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3253–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiao, J. Quantifying tidal contribution to submarine groundwater discharges: A review. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.L.; Intralawan, A.; Vázquez, G.; Pérez-Maqueo, O.; Sutton, P.; Landgrave, R. The coasts of our world: Ecological, economic and social importance. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 63, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.D.; Bakker, M.; Post, V.E.; Vandenbohede, A.; Lu, C.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Barry, D. Seawater intrusion processes, investigation and management: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 51, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuo, Y.; Jarsjö, J.; Destouni, G. Bathymetry-topography effects on saltwater–fresh groundwater interactions around the shrinking Aral Sea. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Engesgaard, P.; Sonnenborg, T.O. Origin and dynamics of saltwater intrusion in a regional aquifer: Combining 3-D saltwater modeling with geophysical and geochemical data. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 1792–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-H.; Zhuang, S.-Y. Experimental investigation of effect of tide on coastal groundwater table. J. Hydrodyn. 2010, 22, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanyon, J.; Eliot, I.; Clarke, D. Groundwater-level variation during semidiurnal spring tidal cycles on a sandy beach. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1982, 33, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, A.D. The effect of tidal fluctuation on a coastal aquifer in the UK. Groundwater 1991, 29, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastias Espejo, J.M.; Rau, G.C.; Blum, P. Groundwater responses to Earth tides: Evaluation of analytical solutions using numerical simulation. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2022JB024771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, G.; Lu, Y. Numerical modeling of tidal effects on groundwater dynamics in a multi-layered estuary aquifer system using equivalent tidal loading boundary condition: Case study in Zhanjiang, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, M.; Post, V.E.; Simmons, C.T. Effects of tidal fluctuations on mixing and spreading in coastal aquifers: Homogeneous case. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 6910–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Robinson, C.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A.; Bakhtyar, R. Effects of wave forcing on a subterranean estuary. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, W.K.; Jin, G.; Xin, P.; Robinson, C.; Gibbes, B.; Li, L. Tidal influence on seawater intrusion in unconfined coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W02502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xin, P.; Lu, C.; Robinson, C.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Effects of episodic rainfall on a subterranean estuary. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 5774–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie-Ashtiani, B.; Simmons, C.T.; Werner, A.D. Influence of Boundary Condition Types on Unstable Density-Dependent Flow. Groundwater 2014, 52, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenhoff, L.B.; Smit, Y.; Donker, J.J.; Ruessink, G. Tide-induced variability in beach surface moisture: Observations and modelling. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2019, 44, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Feng, X.; Yin, B. The impact of coastal reclamation on tidal and storm surge level in Sanmen Bay, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1971–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Cui, L.; Li, L.; He, L.; Ma, P. The Effects of Tidal Flat Reclamation on the Stability of the Coastal Area in the Jiangsu Province, China, from the Perspective of Landscape Structure. Land 2022, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Perrone, D.; Seybold, H.; Fan, Y.; Kirchner, J.W. Groundwater level observations in 250,000 coastal US wells reveal scope of potential seawater intrusion. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, P.; Wilson, A.; Shen, C.; Ge, Z.; Moffett, K.B.; Santos, I.R.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Yau, Y.Y.; Moore, W. Surface water and groundwater interactions in salt marshes and their impact on plant ecology and coastal biogeochemistry. Rev. Geophys. 2022, 60, e2021RG000740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.-F.; Yu, S.-E.; Wu, Y.-B.; Pan, D.-F.; She, D.-L.; Ji, J. Seasonal variations in groundwater level and salinity in coastal plain of eastern China influenced by climate. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 905190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hak, D.; Nadaoka, K.; Bernado, L.P.; Le Phu, V.; Quan, N.H.; Toan, T.Q.; Trung, N.H.; Van Ni, D.; Van, P.D.T. Spatio-temporal variations of sea level around the Mekong Delta: Their causes and consequences on the coastal environment. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2016, 10, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, T.; Dulai, H.; Fuleky, P. Traditional and novel time-series approaches reveal submarine groundwater discharge dynamics under baseline and extreme event conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, H. Numerical study of hydrodynamic and solute transport with discontinuous flows in coastal water. Environ. Model. Assess. 2018, 23, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yan, G.; Ma, Y.; Scheuermann, A. Measurement of In-Situ Flow Rate in Borehole by Heat Pulse Flowmeter: Field-Case Study and Reflection. Geosciences 2023, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.J., Jr.; Zhan, X. Hydraulic tests in highly permeable aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, W12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Ma, Y.; Scheuermann, A.; Li, L. The Hydraulic Properties of Aquabeads Considering Forchheimer Flow and Local Heterogeneity. Geotech. Test. J. 2022, 45, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Shi, H.; Ma, Y.; Scheuermann, A.; Li, L. Intrinsic permeabilities of transparent soil under various aqueous environmental conditions. Géotechnique Lett. 2022, 12, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, H. The Bouwer and Rice Slug Test—An Update a. Groundwater 1989, 27, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briciu, A.-E. Diurnal, semidiurnal, and fortnightly tidal components in orthotidal proglacial rivers. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Úbeda, J.P.; Calvache, M.L.; Duque, C.; López-Chicano, M. Filtering methods in tidal-affected groundwater head measurements: Application of harmonic analysis and continuous wavelet transform. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 97, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Mao, X.; Lv, X.; Jiang, W. The m2 cotidal chart in the bohai, yellow, and east china seas from dynamically constrained interpolation. J. Atmospheric Ocean. Technol. 2020, 37, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, L.; Cai, S.; Wang, G. Tidal harmonic analysis and prediction with least-squares estimation and inaction method. Estuarine, Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 220, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Pan, H.; Cao, A.; Lv, X. A harmonic analysis method adapted to capturing slow variations of tidal amplitudes and phases. Cont. Shelf Res. 2018, 164, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.A. Use of harmonic analysis to study tidal fluctuations in aquifers near the sea. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirahata, K.; Yoshimoto, S.; Tsuchihara, T.; Ishida, S. Improvements in a simple harmonic analysis of groundwater time series based on error analysis on simulated data of specified lengths. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slooten, L.J.; Carrera, J.; Castro, E.; Fernandez-Garcia, D. A sensitivity analysis of tide-induced head fluctuations in coastal aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Enot, P.; Barry, D.; Li, L.; Binley, A.; Jeng, D.-S. Tidal influence on behaviour of a coastal aquifer adjacent to a low-relief estuary. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanon, E.; Yechieli, Y.; Gvirtzman, H.; Shalev, E. Tide-induced fluctuations of salinity and groundwater level in unconfined aquifers–Field measurements and numerical model. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Yang, Y.; Chui, T.F.M. Tidal responses of groundwater level and salinity in a silty mangrove swamp of different topographic characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Phase Lag: (h) | Constituents of Tide | Well (100 m to Coastline) | Well (550 m to Coastline) | Well (1070 m to Coastline) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water level | M2 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 16.4 |
| S2 | 7.1 | 8.7 | 12.2 | |
| K1 | 11.9 | 12.0 | 12.9 | |
| O1 | 12.7 | 13.3 | 26.9 | |
| Salinity | M2 | 14.1 | 13.4 | 15.6 |
| S2 | 13.1 | 16.5 | 12.7 | |
| K1 | 25.2 | 47.7 | 39.1 | |
| O1 | 27.3 | 35.3 | 45.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Ma, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, Z.; Yan, G.; You, Z. Impacts of Tidal Oscillations on Coastal Groundwater System in Reclaimed Land. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102019
Guo J, Ma Y, Ding C, Zhao H, Cheng Z, Yan G, You Z. Impacts of Tidal Oscillations on Coastal Groundwater System in Reclaimed Land. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(10):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102019
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jing, Ye Ma, Chao Ding, Huawen Zhao, Zhixin Cheng, Guanxi Yan, and Zaijin You. 2023. "Impacts of Tidal Oscillations on Coastal Groundwater System in Reclaimed Land" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 10: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102019
APA StyleGuo, J., Ma, Y., Ding, C., Zhao, H., Cheng, Z., Yan, G., & You, Z. (2023). Impacts of Tidal Oscillations on Coastal Groundwater System in Reclaimed Land. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(10), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102019







