Enhanced Mixing Induced by Near-Inertial Waves Inferred by Glider Observation in the Northern South China Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
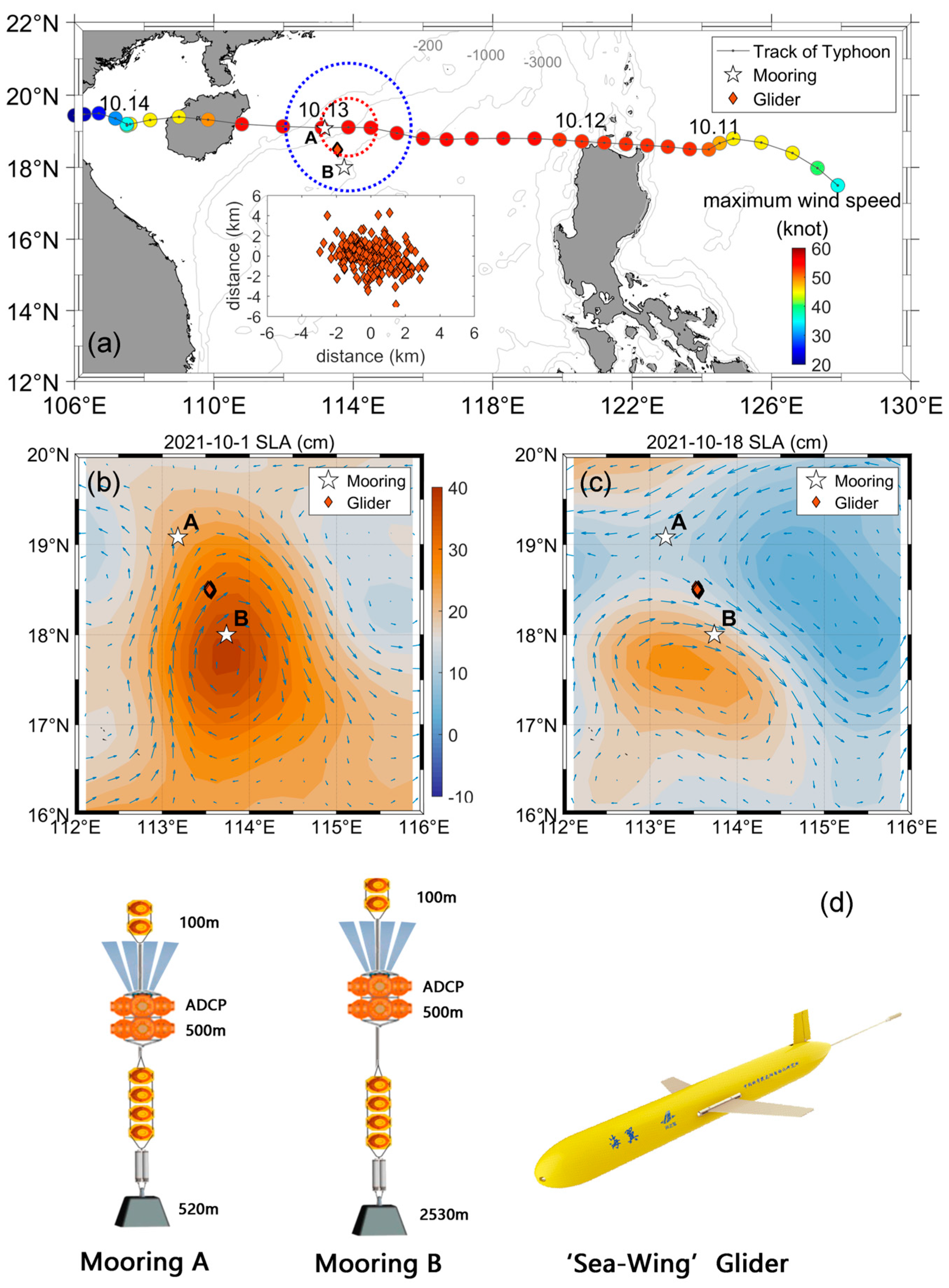
2.1. Mooring Observation
2.2. Glider Observations
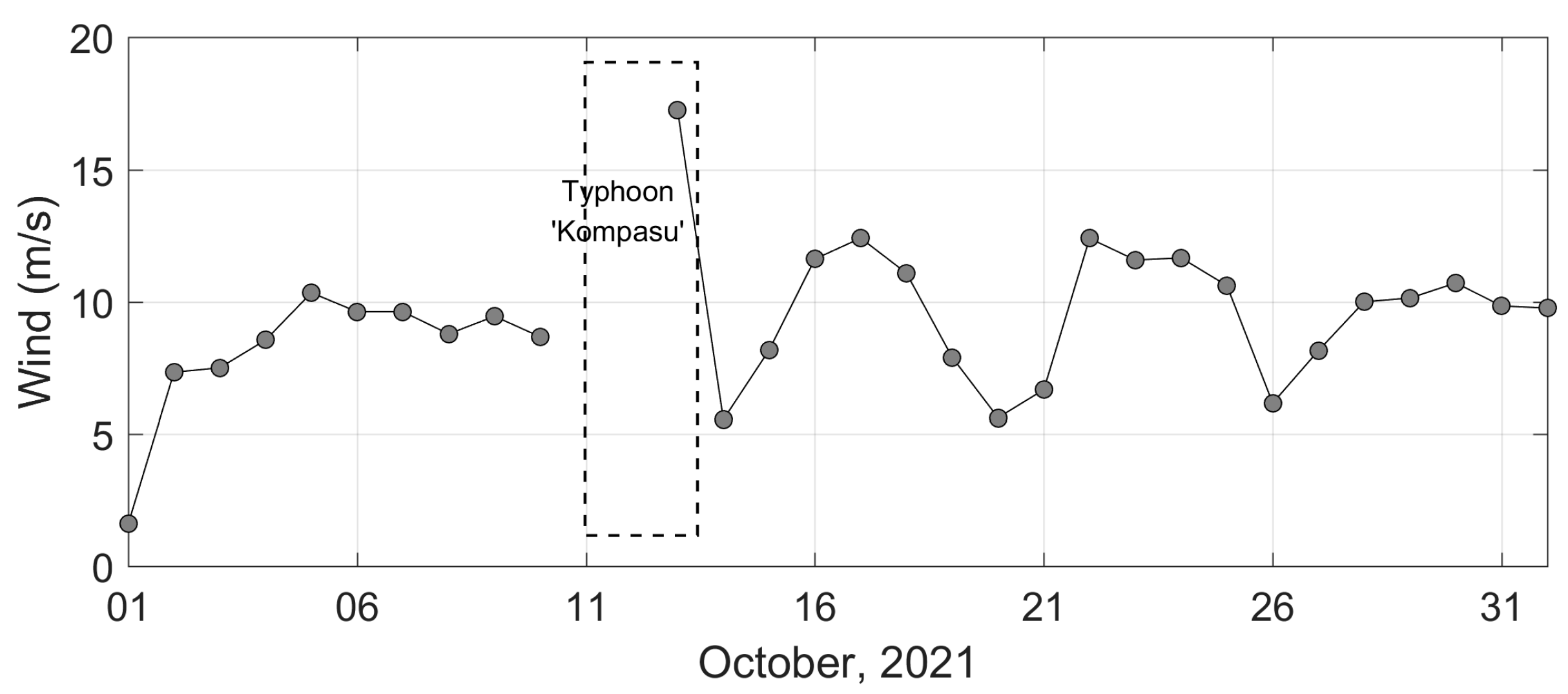
2.3. Typhoon and Wind Information
2.4. Mesoscale Eddy
2.5. Bandpass Filtering, Near-Inertial Kinetic Energy, and Near-Inertial Velocity Shears
2.6. Gregg–Henyey–Polzin Parameterization
3. Results
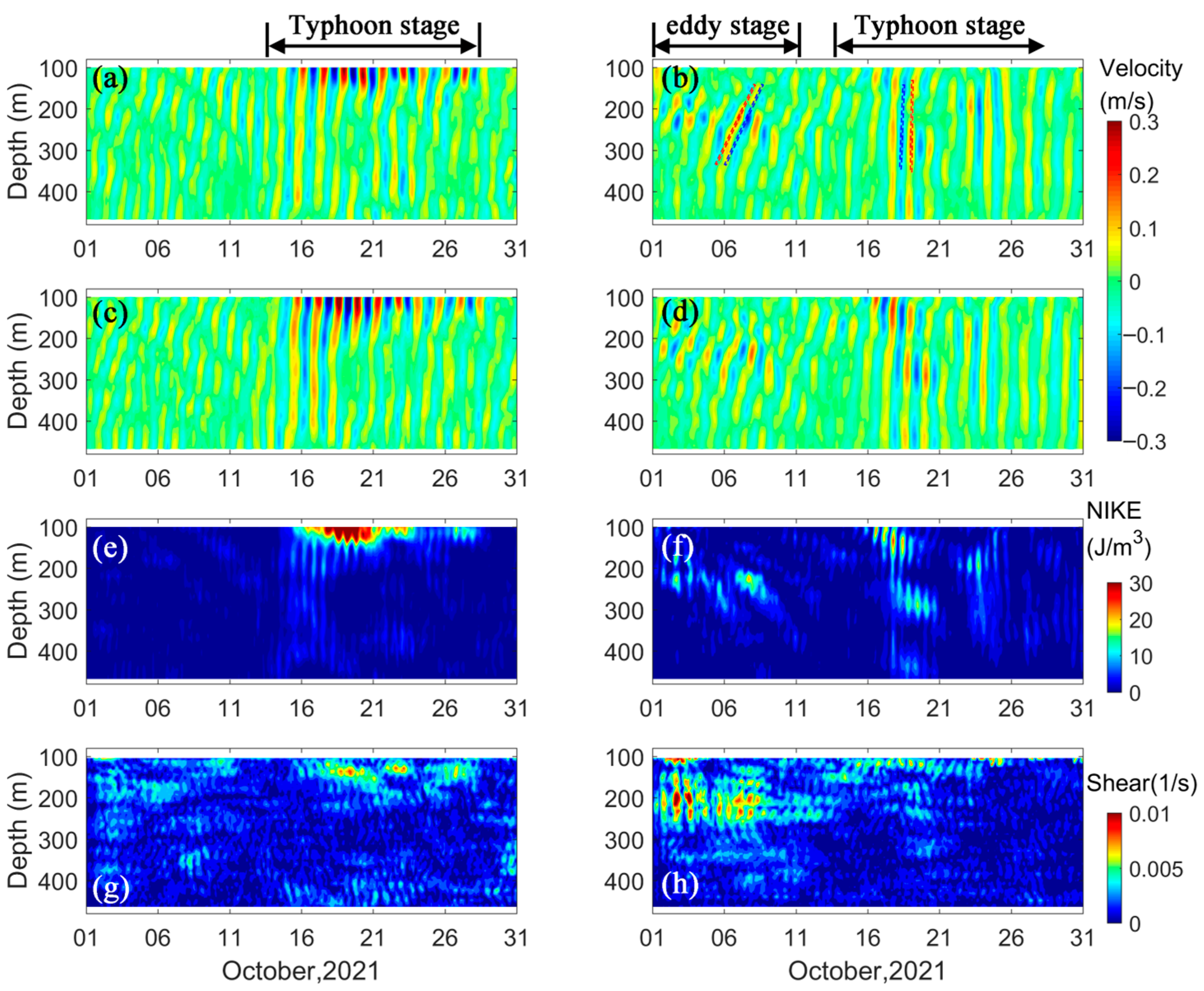
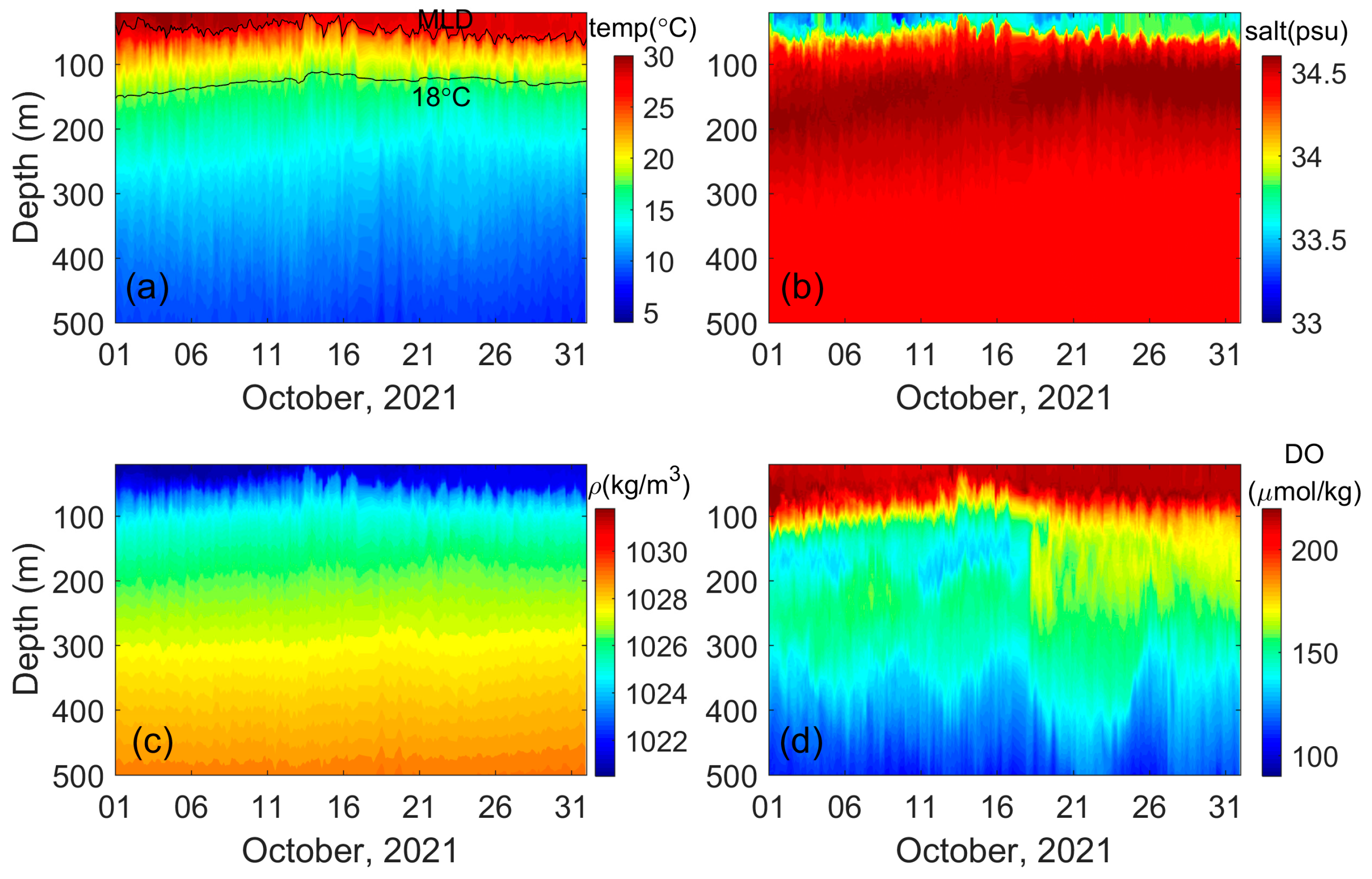
3.1. Characteristics of the Observed NIWs
3.2. Glider Observations
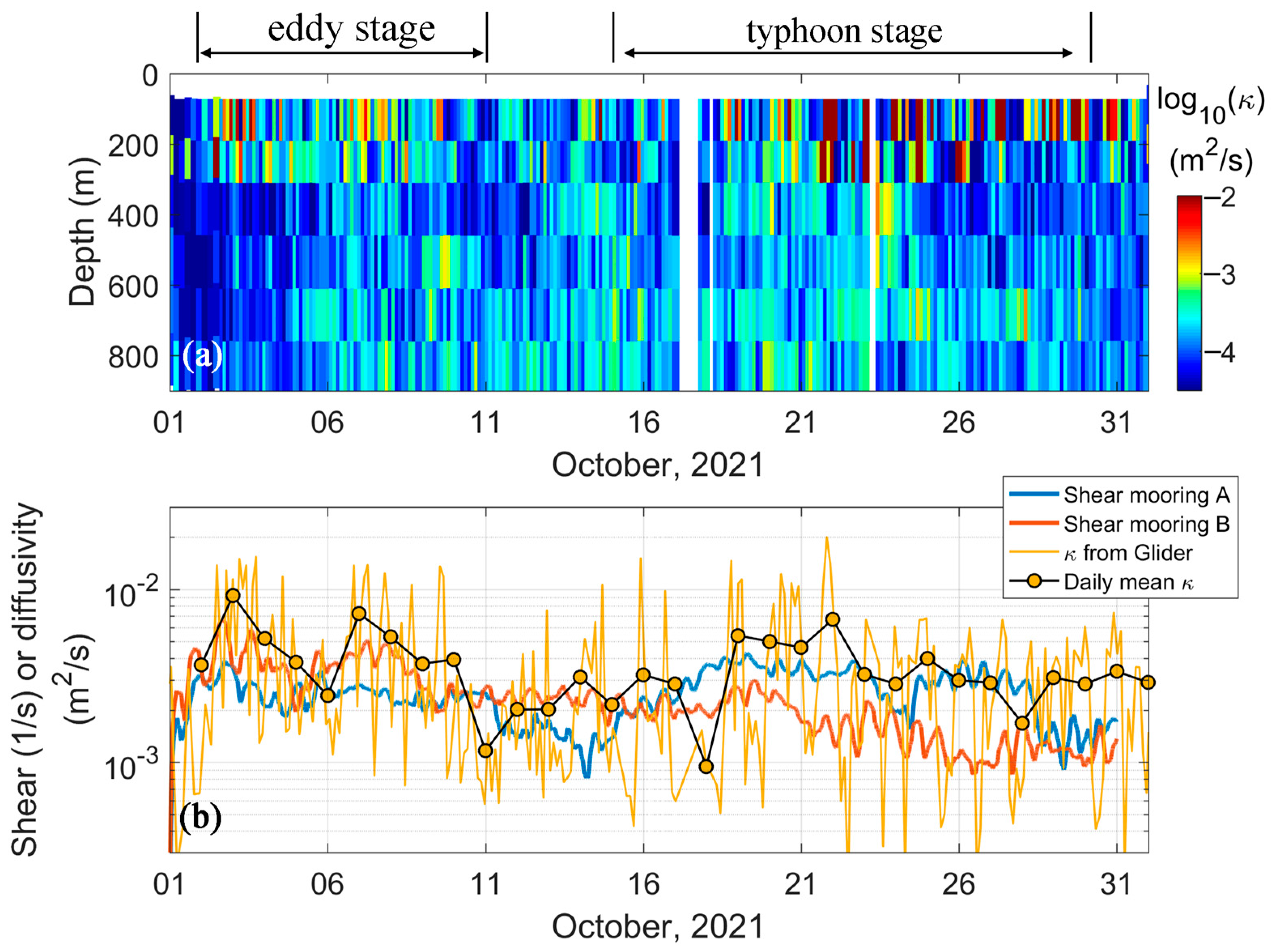
3.3. Enhanced Mixing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chelton, D.B.; Schlax, M.G.; Samelson, R.M. Global observations of nonlinear mesoscale eddies. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 91, 167–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W. Abyssal recipes. Deep-Sea Res. 1966, 13, 707–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Simmons, H.L.; Nash, J.D. Near-inertial internal gravity waves in the ocean. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.; Wunsch, C. Abyssal recipes II: Energetics of tidal and wind mixing. Deep-Sea Res. Pt I 1998, 45, 1977–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, K.; King, B.A. Global statistics of inertial motions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L14612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Kim, K.; Schmitt, R.W. Global distribution of the decay time scale of mixed layer inertial motions observed by satellite tracked drifters. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, C11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, C.; Ferrari, R. Vertical mixing, energy, and the general circulation of the oceans. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2004, 36, 281–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Marrero, A.; Barceló-Llull, B.; Pallàs-Sanz, E.; Aguiar-González, B.; Estrada-Allis, S.N.; Gordo, C.; Grisolía, D.; Rodríguez-Santana, A.; Arístegui, J. Near-inertial wave trapping near the base of an anticyclonic mesoscale eddy under normal atmospheric conditions. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2019, 124, 8455–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.S.; Park, J.J.; Chang, K.I.; Schmitt, R.W. Observation of near- inertial wave refections within the thermostad layer of an anticyclonic mesoscale eddy. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Xie, Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, W.T. Summer up welling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2003, 108, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T. Upper-layer circulation in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2000, 30, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xie, S.; Qu, T.; Huang, R.X. Deep South China Sea circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L05601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; Peacock, T.; Mackinnon, J.M.; Nash, J.D.; Buijsman, M.C.; Centurioni, L.R.; Chao, S.-Y.; Chang, M.-H.; Farmer, D.M.; Fringer, O.B.; et al. The formation and fate of internal waves in the South China Sea. Nature 2015, 521, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yang, Q.; Tian, J. An extreme internal solitary wave event observed in the northern South China Sea. Sci. Rep.-UK 2016, 6, 30041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, W. Enhanced diapycnal mixing in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2009, 39, 3191–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Chen, G.; Shang, X. Observa tions of the turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate in the upper central South China Sea. Ocean Dynam. 2017, 67, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Tian, J.; Liang, X. A mesoscale eddy pair southwest of Taiwan and its influence on deep circulation. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2013, 118, 6479–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Mao, H.; Liu, H.; Xie, Q.; Yu, J.; Su, D.; Ouyang, J.; Lian, S. Deformation of a warm eddy in the northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2019, 124, 5551–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Mao, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Lian, S.; Li, X.; Shang, X. Suppressed Thermocline Mixing in the Center of Anticyclonic Eddy in the North South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Mao, H.; Du, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Xu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Zhong, F.; Yu, L.; et al. A lens-shaped, cold core anticyclonic surface eddy in the northern South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 976273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, R.; Chen, D.; Zhang, D.; Shang, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Jin, W.; Yu, L.; et al. Sea surface current response patterns to tropical cyclones. J. Mar. Syst. 2020, 208, 103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Wu, R.; Liu, F.; Yu, L.; Shang, X.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Xie, X.; et al. Ocean Response to Successive Typhoons Sarika and Haima (2016) Based on Data Acquired via Multiple Satellites and Moored Array. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, M.C.; Sanford, T.B.; Winkel, D.P. Reduced mixing from the breaking of internal waves in equatorial waters. Nature 2003, 422, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, E.; Firing, E.; Hummon, J.M.; Chereskin, T.K.; Thurnherr, A.M. Global abyssal mixing inferred from lowered ADCP shear and CTD strain profiles. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 1553–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekera, H.; Padman, L.; Dillon, T.; Levine, M.; Paulson, C.; Pinkel, R. The application of internal-wave dissipation models to a region of strong forcing, J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1993, 23, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, C.; Munk, W. Space-time scales of internal waves: A progress report. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Liang, X.; Tian, J. Three-dimensional distribution of turbulent mixing in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2016, 46, 769–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wu, L. Low-frequency modulation of turbulent diapycnal mixing by anticyclonic eddies inferred from the HOT time series. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Shang, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, L. Variations of diurnal and inertial spectral peaks near the bi-diurnal critical latitude. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xie, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Qi, Y.; Yi, X. Tropical storm-induced turbulent mixing and chlorophyll-a enhancement in the continental shelf southeast of Hainan Island. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 129, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.K.; Beardsley, R.C. Evidence of a critical Richardson number in moored measurements during the upwelling season off Northern California. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 4855–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W. Internal waves and small-scale processes. In Evolution of Physical Oceanography; Warren, B.A., Wunsch, C., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1981; pp. 264–291. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, S.A. On the shape and breaking of finite amplitude internal gravity waves in a shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 85, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuto, V.M.; Howard, A.; Cheng, Y.; Dubovikov, M.S. Ocean turbulence. Part I: One-point closure model-momentum and heat vertical diffusivities. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, C. What is the “near-inertial” band and why is it different from the rest of the internal wave spectrum? J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Pinkel, R.; Klymak, J.M. Space-time scales of shear in the North Pacific. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2017, 47, 2455–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, R.A. The relation of near-inertial motions observed in the mixed layer during the JASIN (1978) Experiment to the local wind stress and to the quasi-geostrophic flow field. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1982, 12, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fer, I. Near-inertial mixing in the Central Arctic Ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2014, 44, 2031–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, D.; Moum, J.N. Decay of a near-inertial wave. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1994, 24, 2334–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; Gregg, M.C. Near-inertial mixing: Modulation of shear, strain and microstructure at low latitude. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2001, 106, 16947–16968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, C.B.; Talley, L.D.; MacKinnon, J.A. Spatial and temporal variability of global ocean mixing inferred from Argo profiles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L18612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, C.B.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Talley, L.D.; Waterhouse, A.F. Estimating the mean diapycnal mixing using a finescale strain parameterization. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meurs, P. Interactions between near-inertial mixed layer currents and the mesoscale: The importance of spatial variabilities in the vorticity field. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1998, 28, 1363–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, E.; Schmitt, R.W.; Toole, J.M. The energy balance in a warm-core ring’s near-inertial critical layer. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1995, 25, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, T.M.; Toole, J.M.; Klein, P.; Thomas, L.N. A near-inertial mode observed within a Gulf Stream warm-core ring. J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans 2013, 118, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, E. Near-inertial wave propagation in geostrophic shear. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1985, 15, 544–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.K.; Niiler, P.P. The inertial chimney: The near inertial energy drainage from the ocean surface to the deep layer. J. Geophys. Res. 1998, 103, 7579–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochum, M.; Briegleb, B.P.; Danabasoglu, G.; Large, W.G.; Jayne, S.R.; Alford, M.H.; Bryan, F.O. On the impact of oceanic nearinertial waves on climate. J. Clim. 2012, 26, 2833–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, D. Eddy-feature phytoplankton bloom induced by a tropical cyclone in the South China Sea. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 7444–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; DiMarco, S.F.; Jackson, G.A. Relative role of wind forcing and riverine nu trient input on the extent of hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Tang, D.; Alpers, W.; Wang, S. Response of dissolved oxygen and related ma rine ecological parameters to a tropical cyclone in the South China Sea. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Jin, H.; Li, H.; Huang, D.; Cai, W.J. Diatom bloom-derived bottom water hypoxia off the Changjiang estuary, with and without typhoon influence. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1552–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.B.; Tang, D.L.; Sheng, J.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Sui, Y. Study of dissolved oxygen responses to tropical cyclones in the Bay of Bengal based on Argo and satellite observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, H.; Qi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, J. Enhanced Mixing Induced by Near-Inertial Waves Inferred by Glider Observation in the Northern South China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112141
Mao H, Qi Y, Chen Y, Yu J. Enhanced Mixing Induced by Near-Inertial Waves Inferred by Glider Observation in the Northern South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(11):2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112141
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Huabin, Yongfeng Qi, Ying Chen, and Jiancheng Yu. 2023. "Enhanced Mixing Induced by Near-Inertial Waves Inferred by Glider Observation in the Northern South China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 11: 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112141
APA StyleMao, H., Qi, Y., Chen, Y., & Yu, J. (2023). Enhanced Mixing Induced by Near-Inertial Waves Inferred by Glider Observation in the Northern South China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(11), 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11112141





