Numerical Analysis of Flow Characteristics in Impeller-Guide Vane Hydraulic Coupling Zone of an Axial-Flow Pump as Turbine Device
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulation Methods
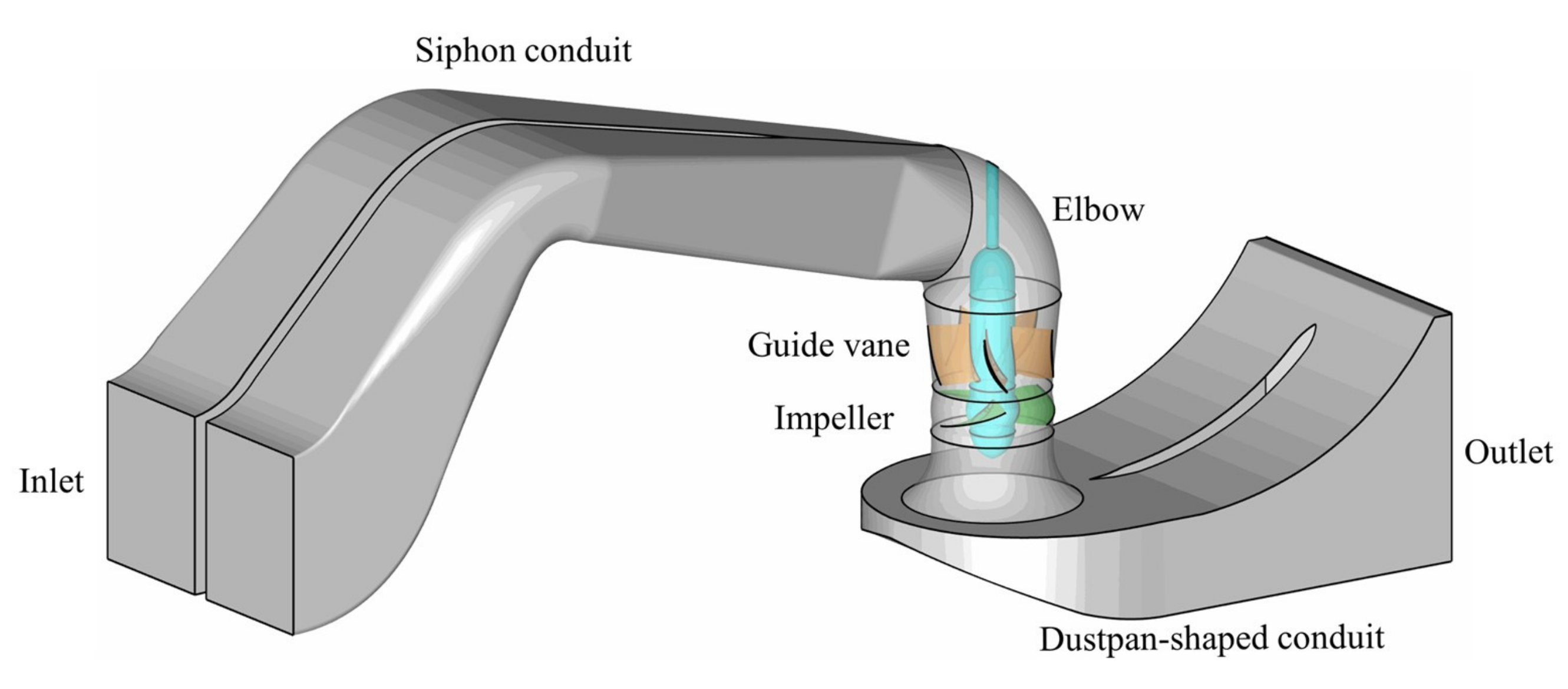
2.1. Geometric Model
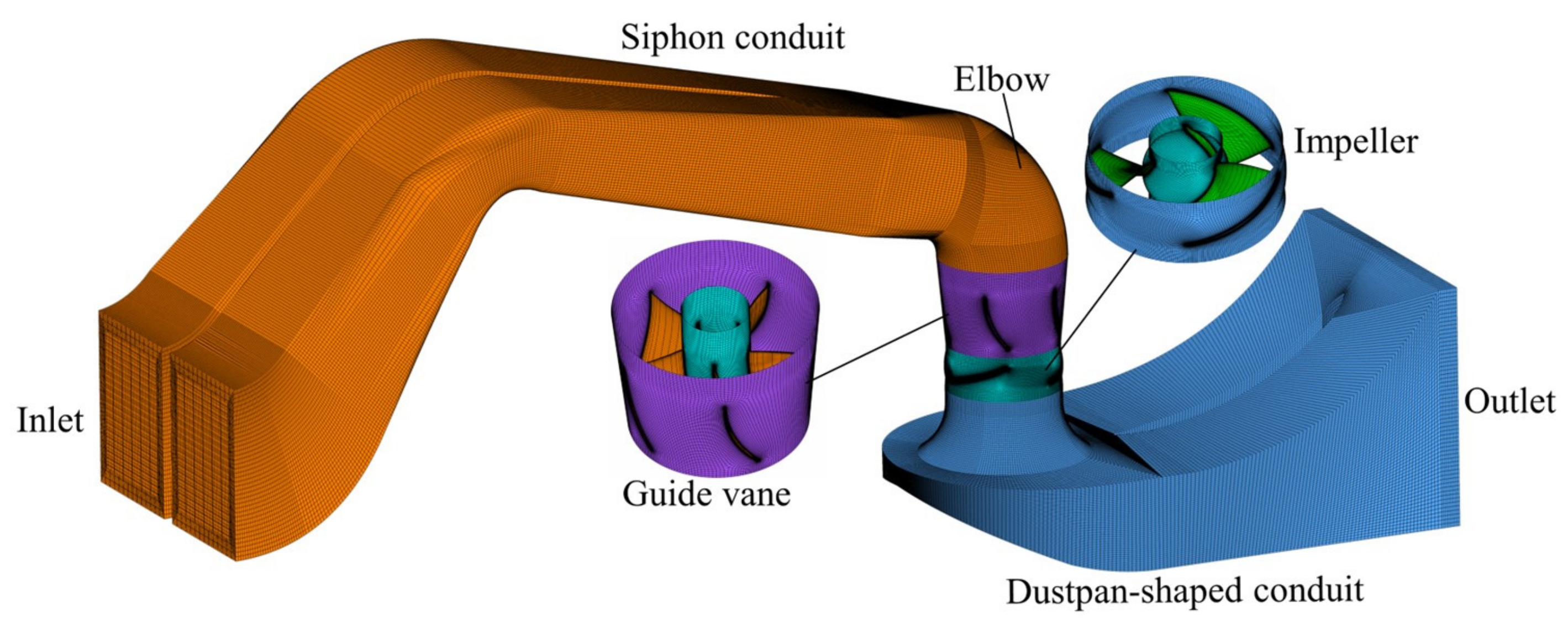
2.2. Mesh Generation and Validation
2.3. Turbulence Model and Boundary Conditions
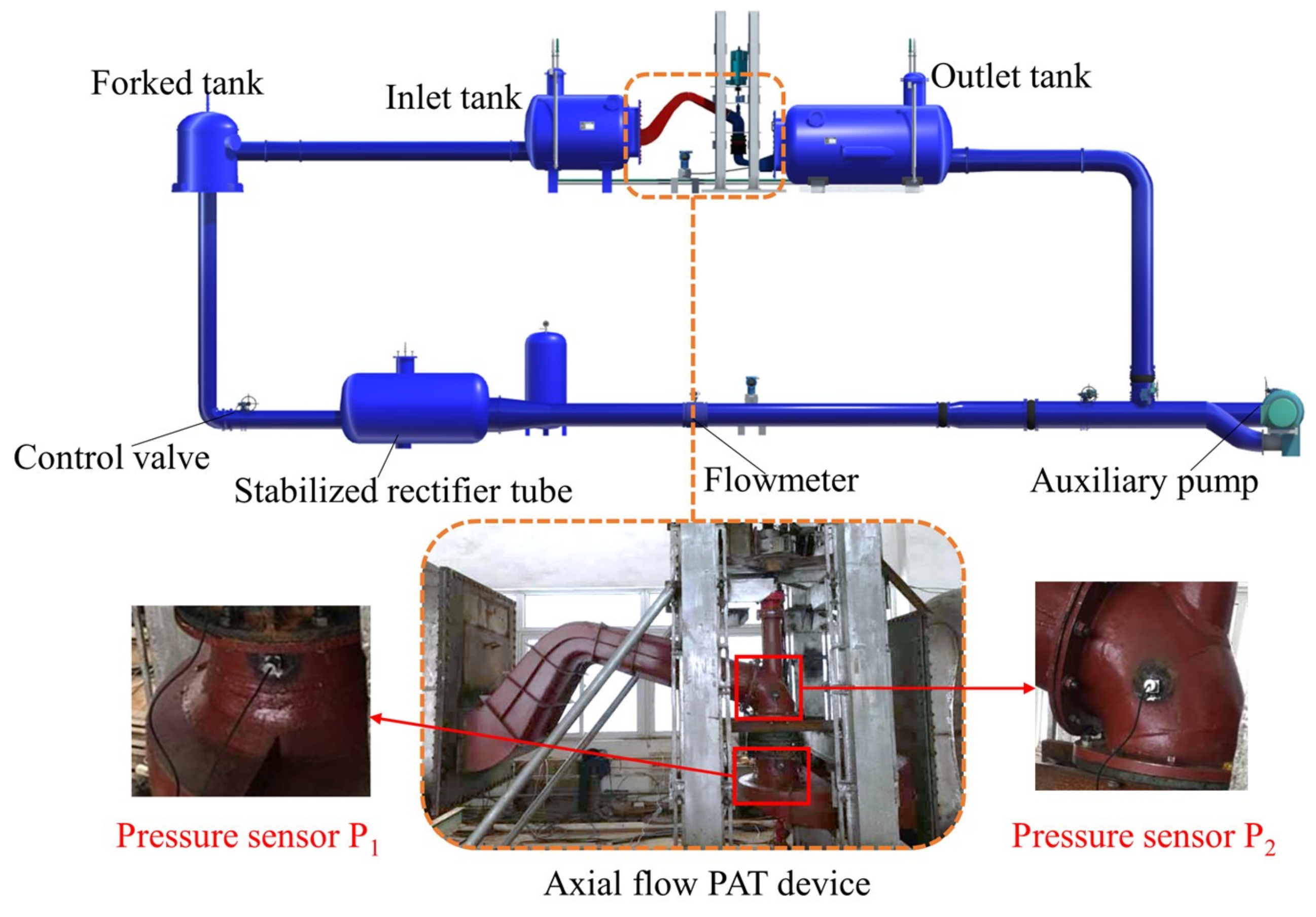
3. Experiment Equipment
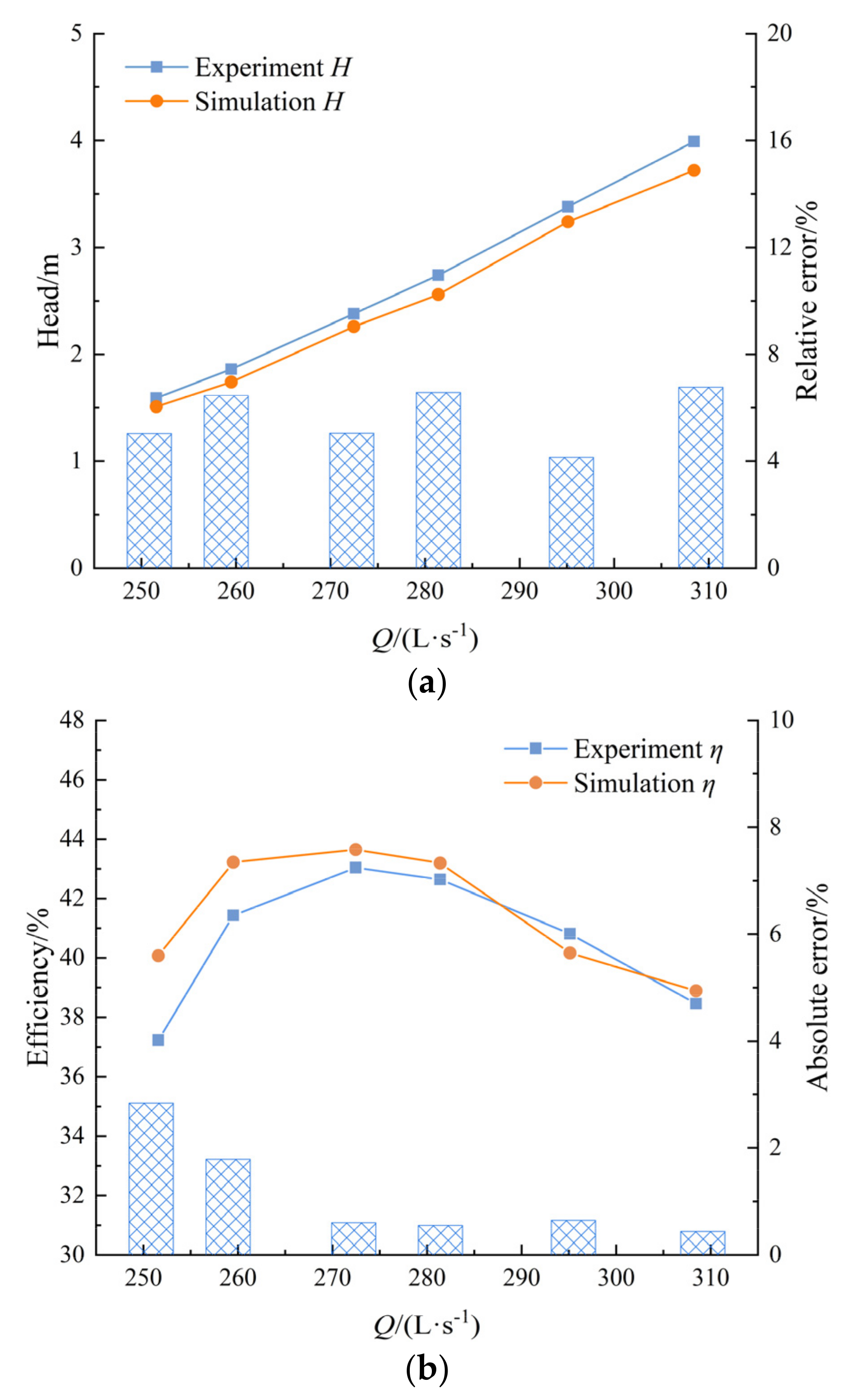
4. Results and Discussion
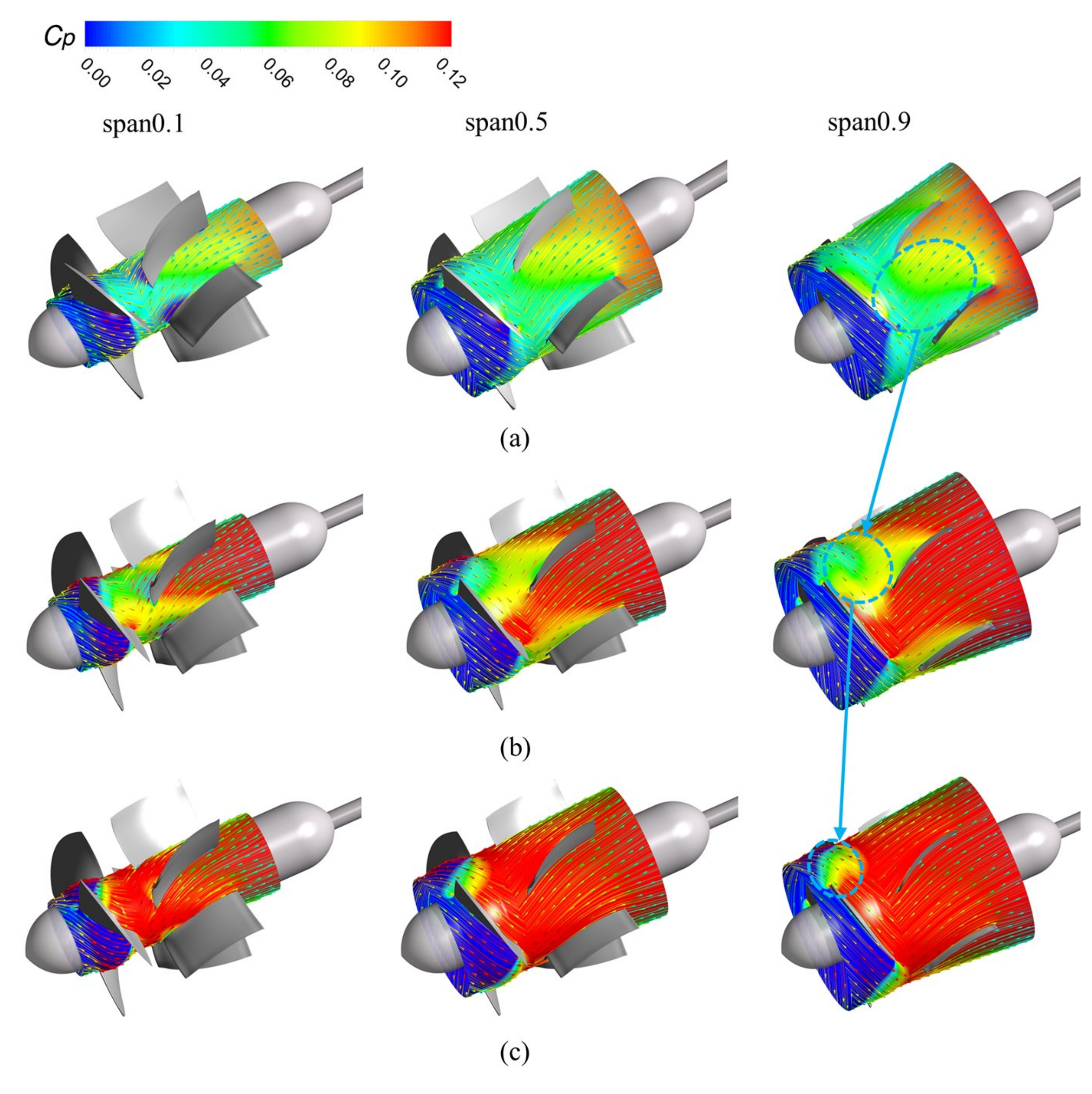
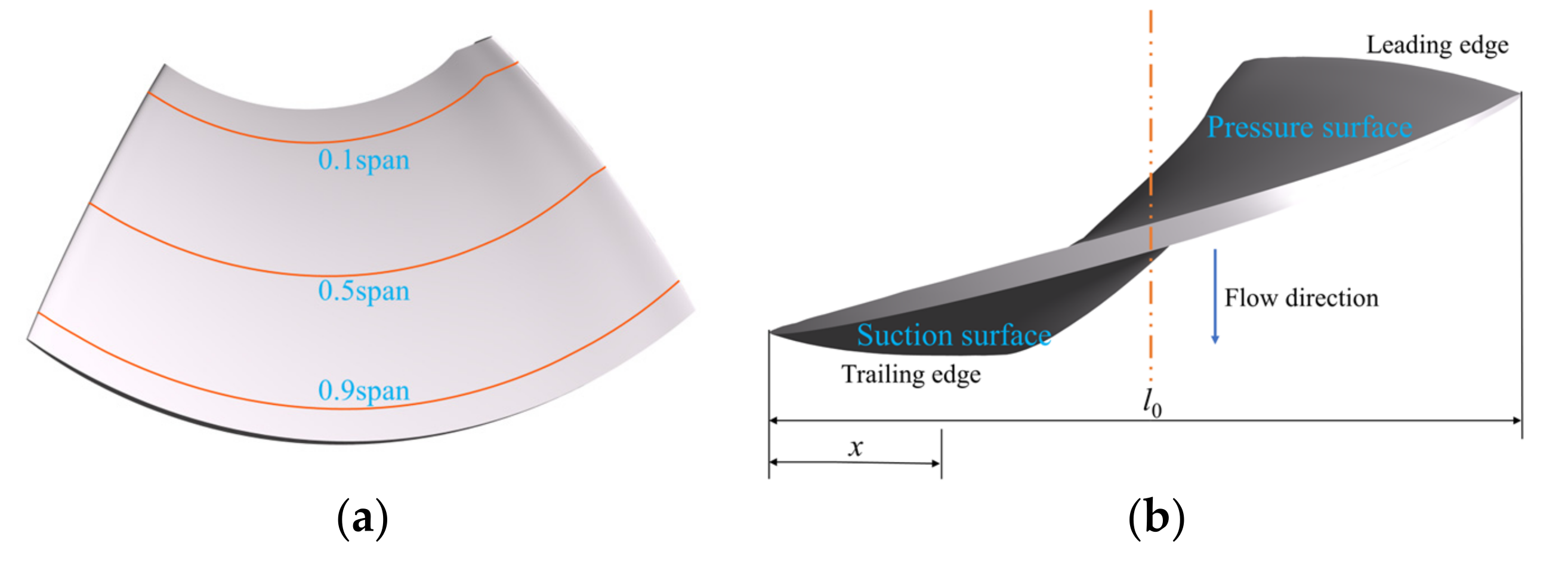
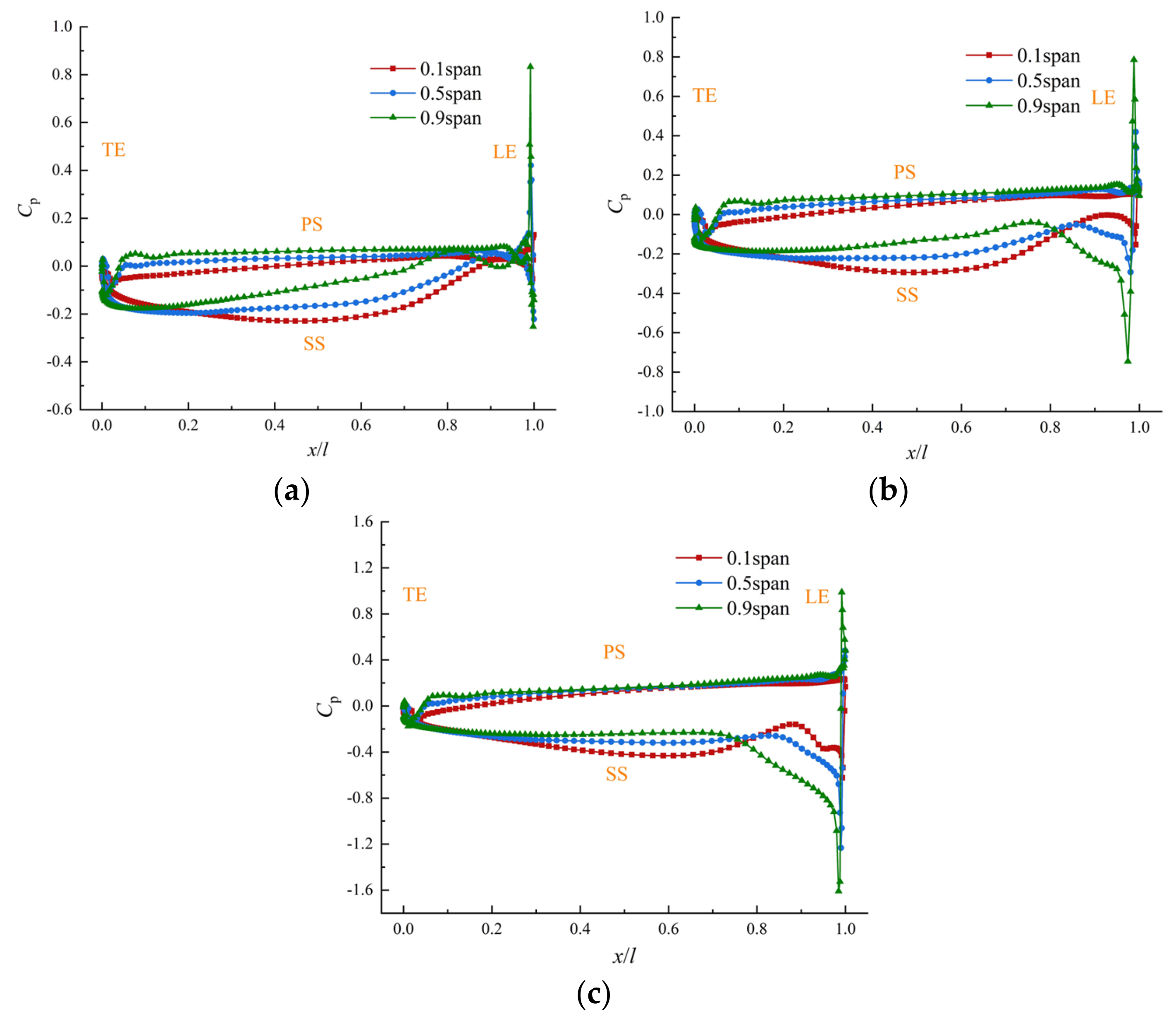
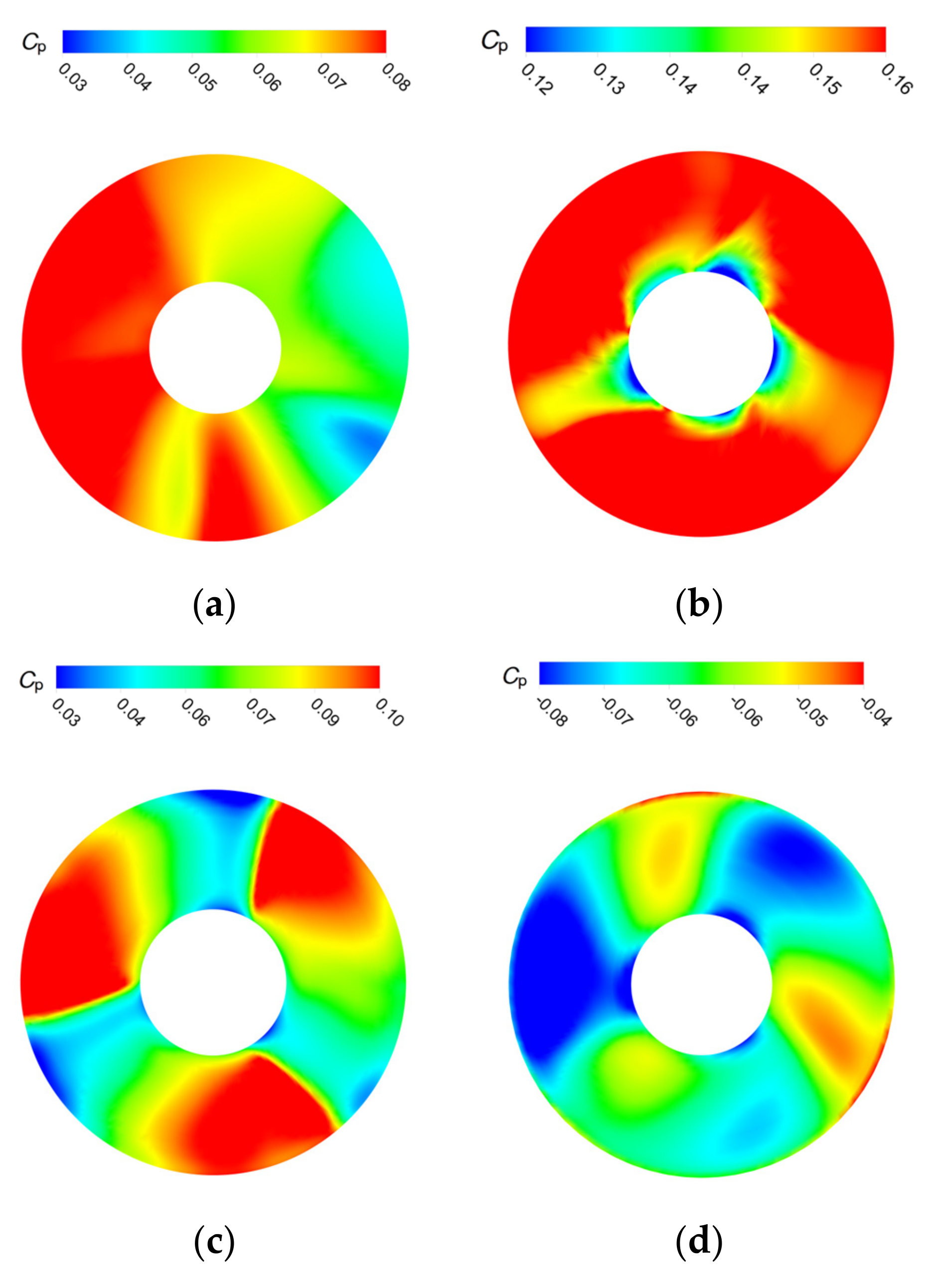
4.1. Internal Flow Characteristics in Impeller-Guide Vane Hydraulic Coupling Zone
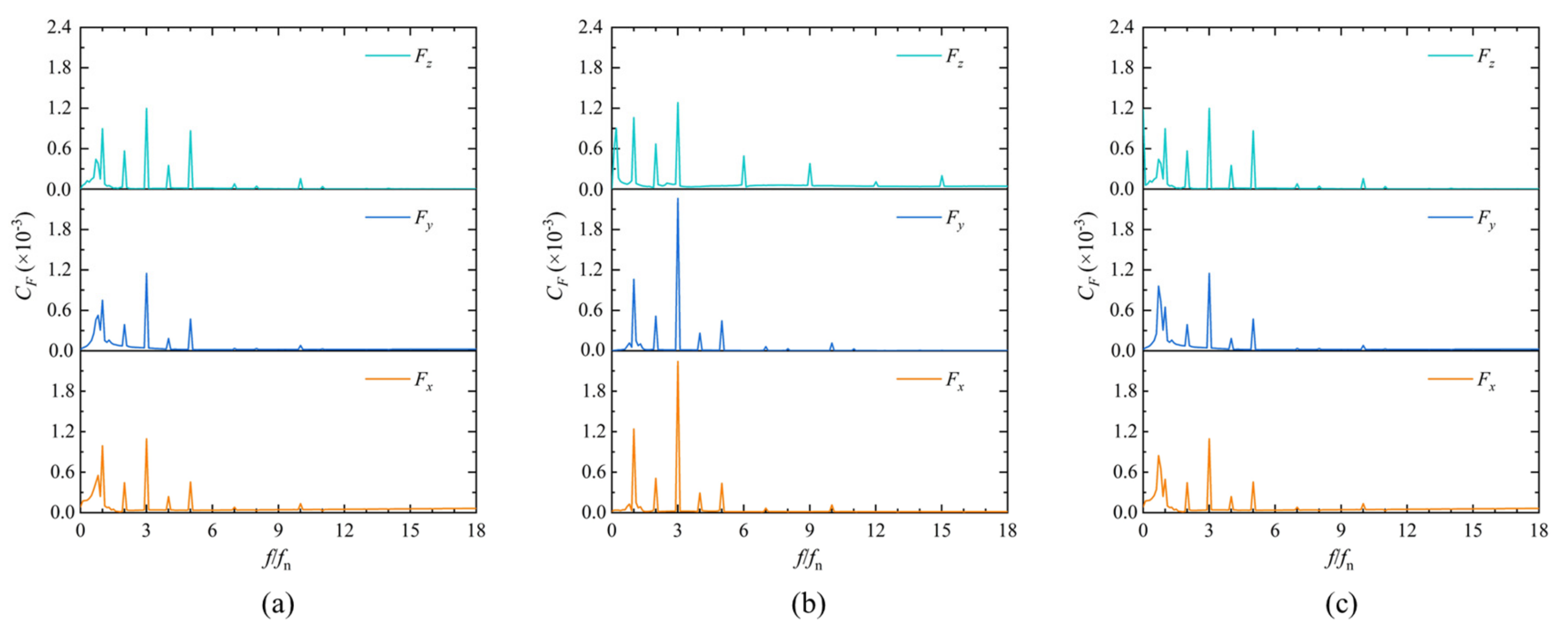
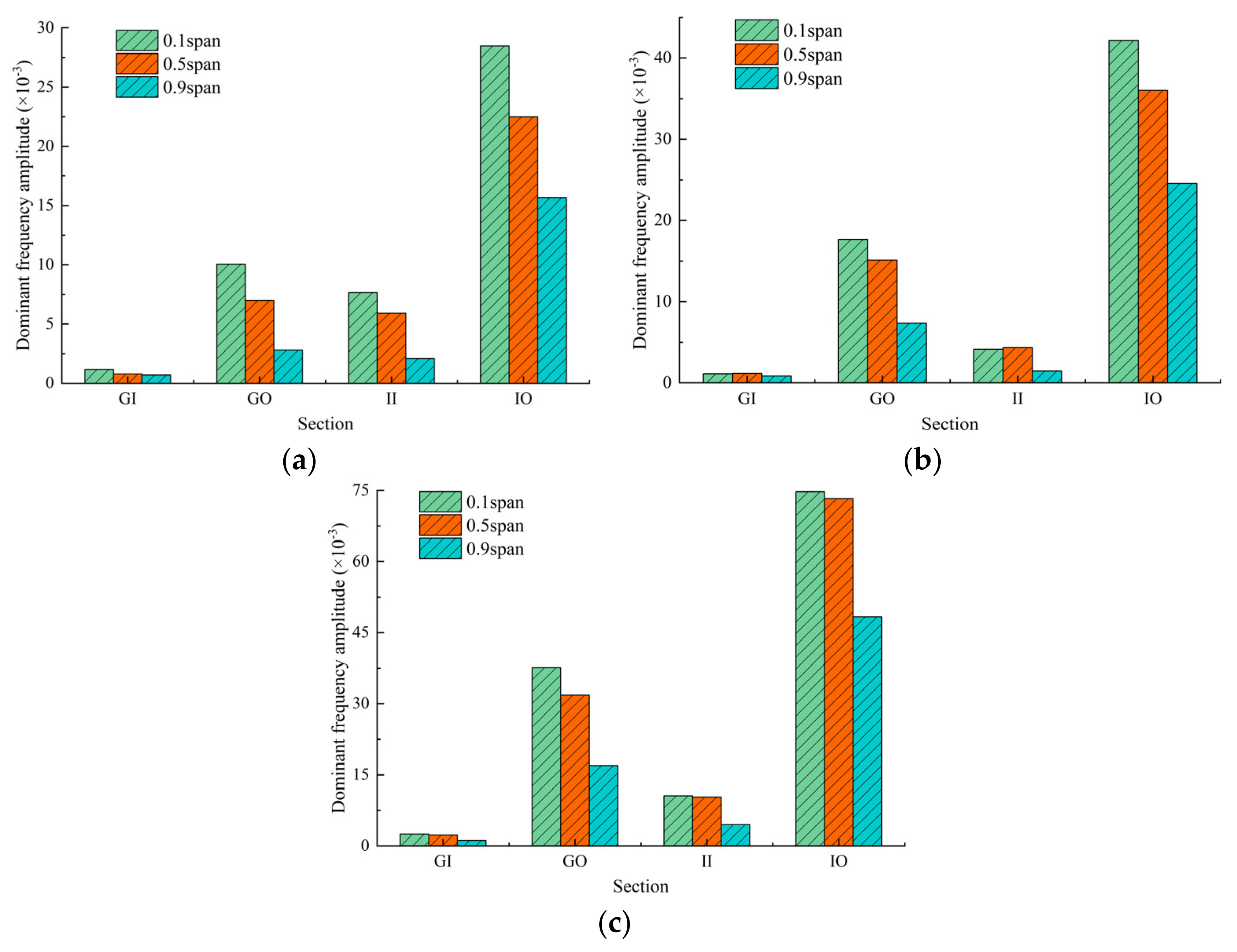
4.2. Fluid Force Pulsation Analysis of Impeller and Guide Vane
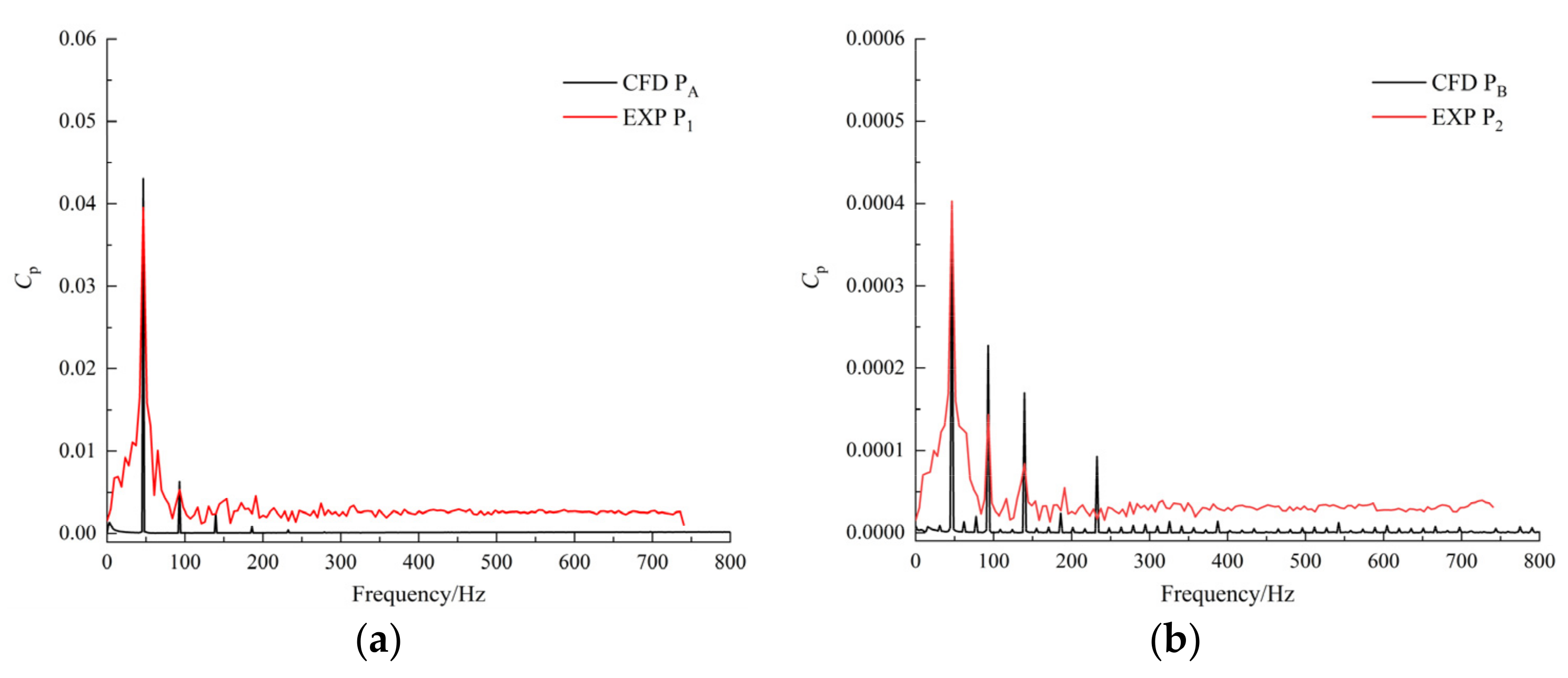
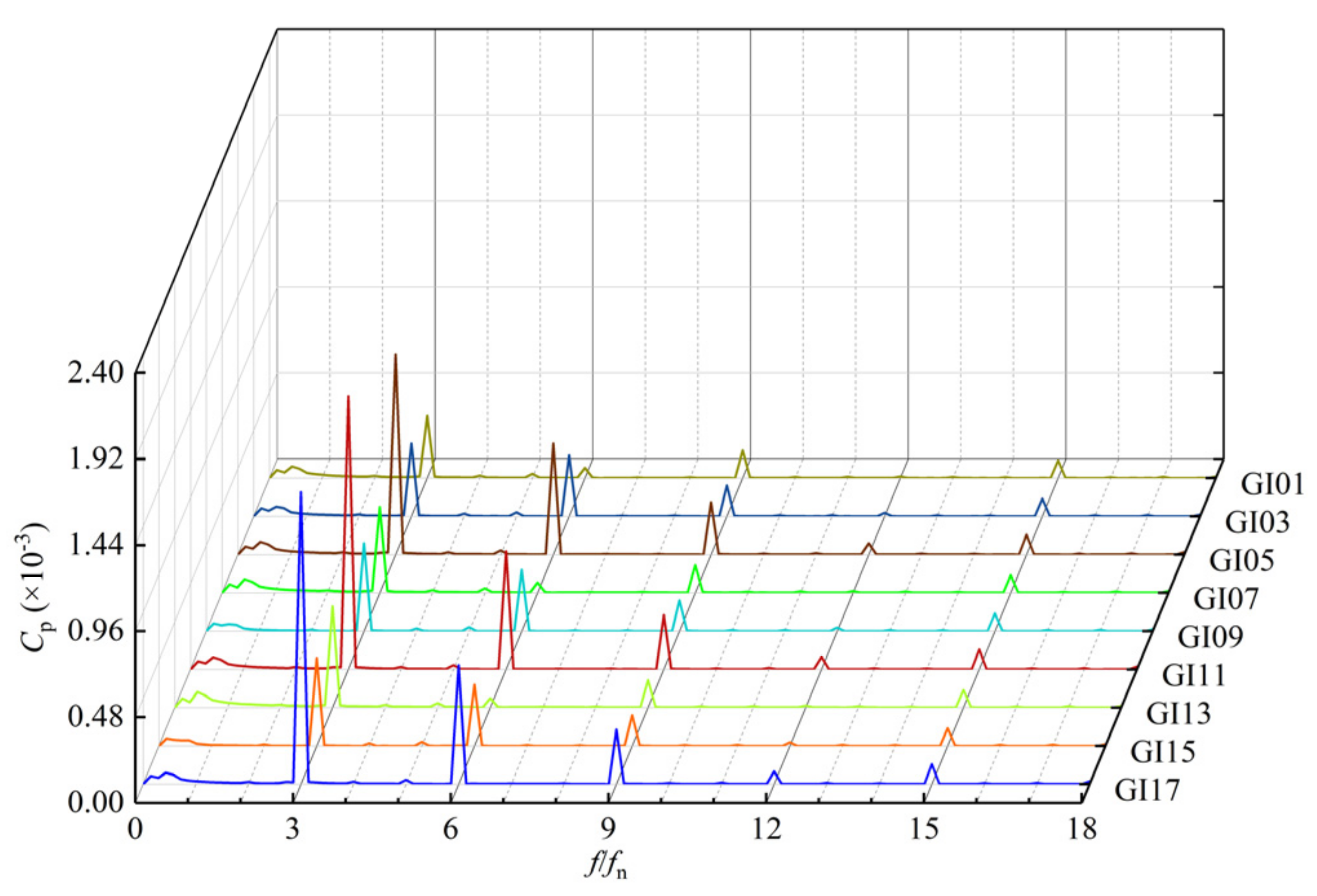
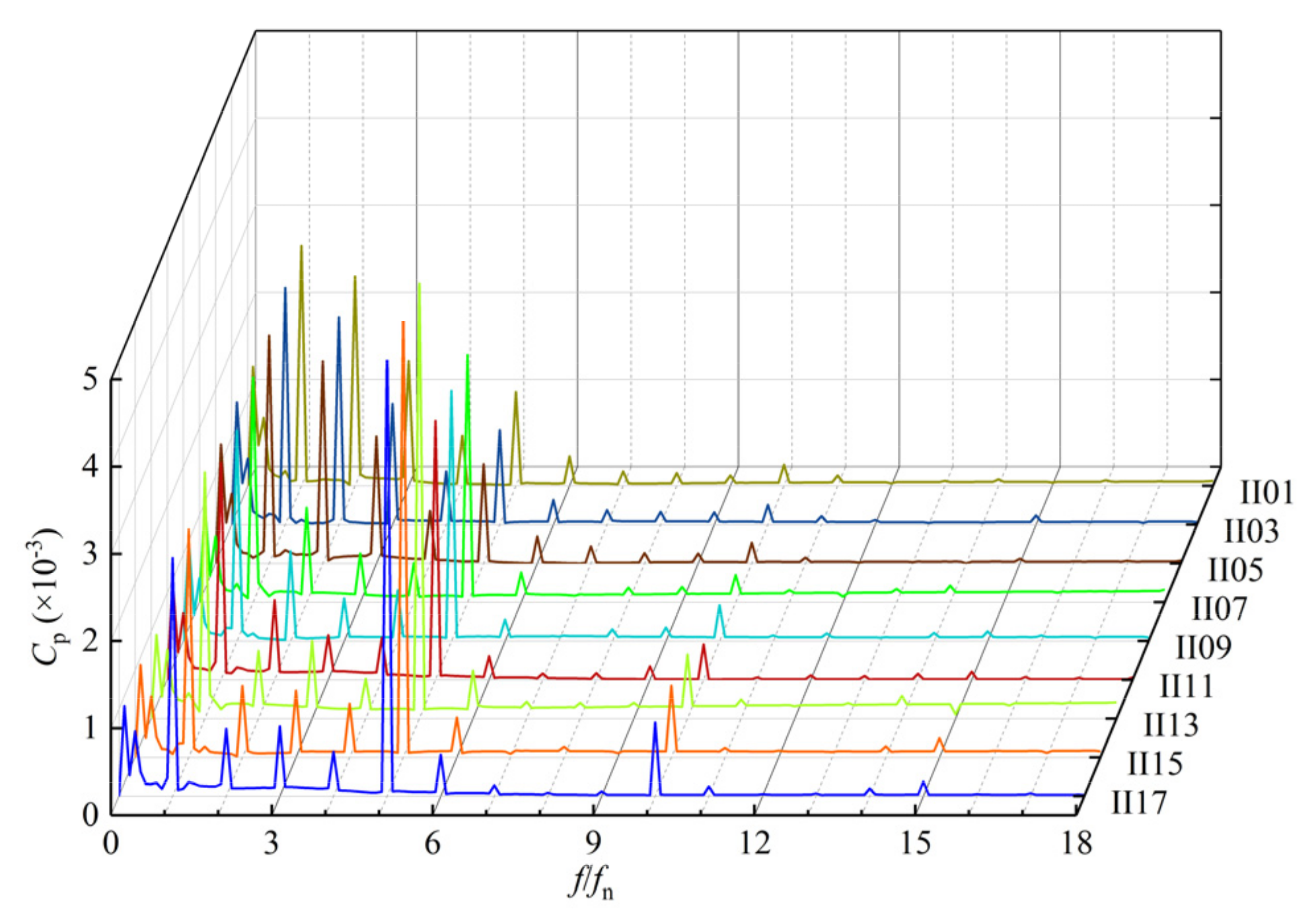
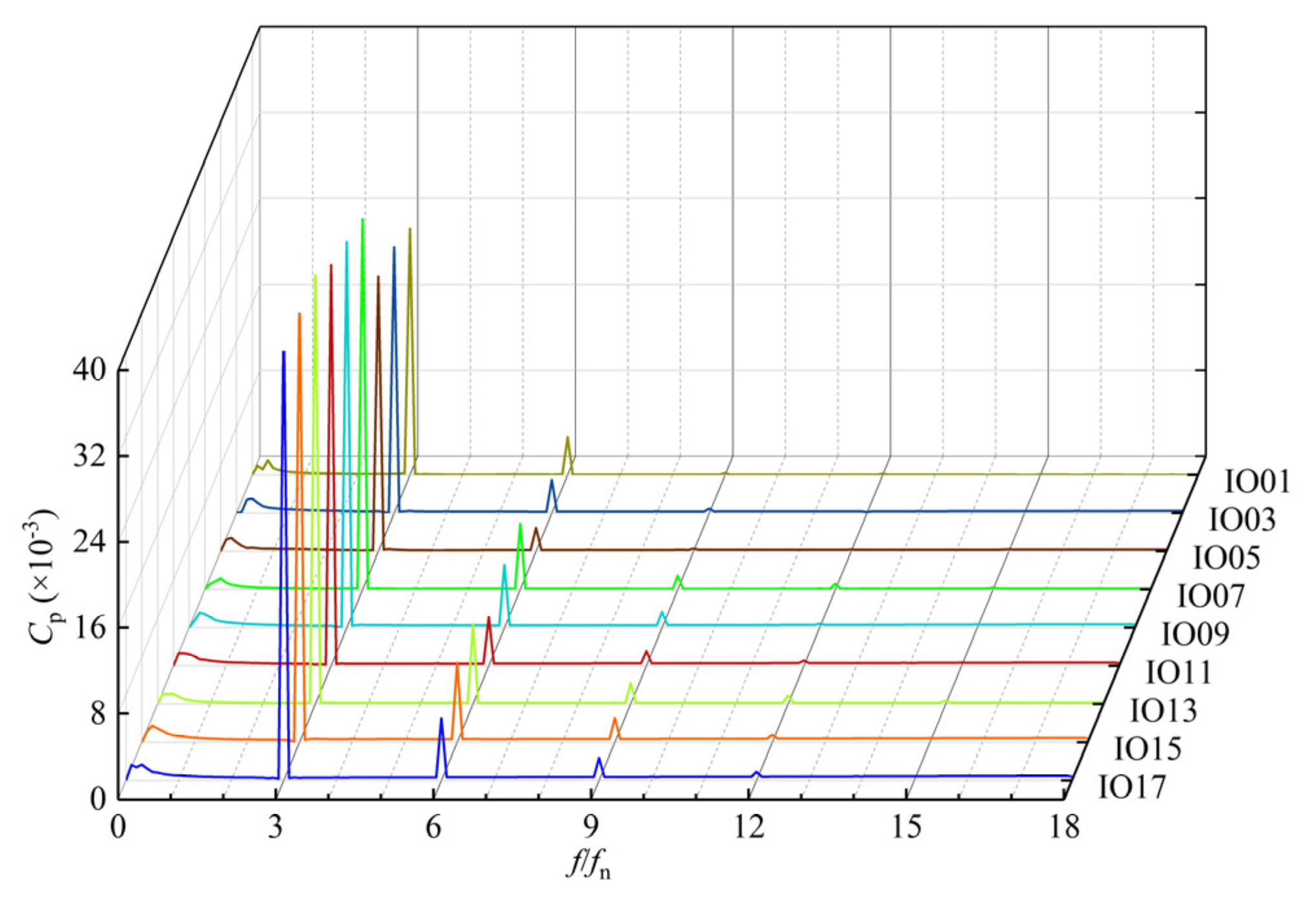
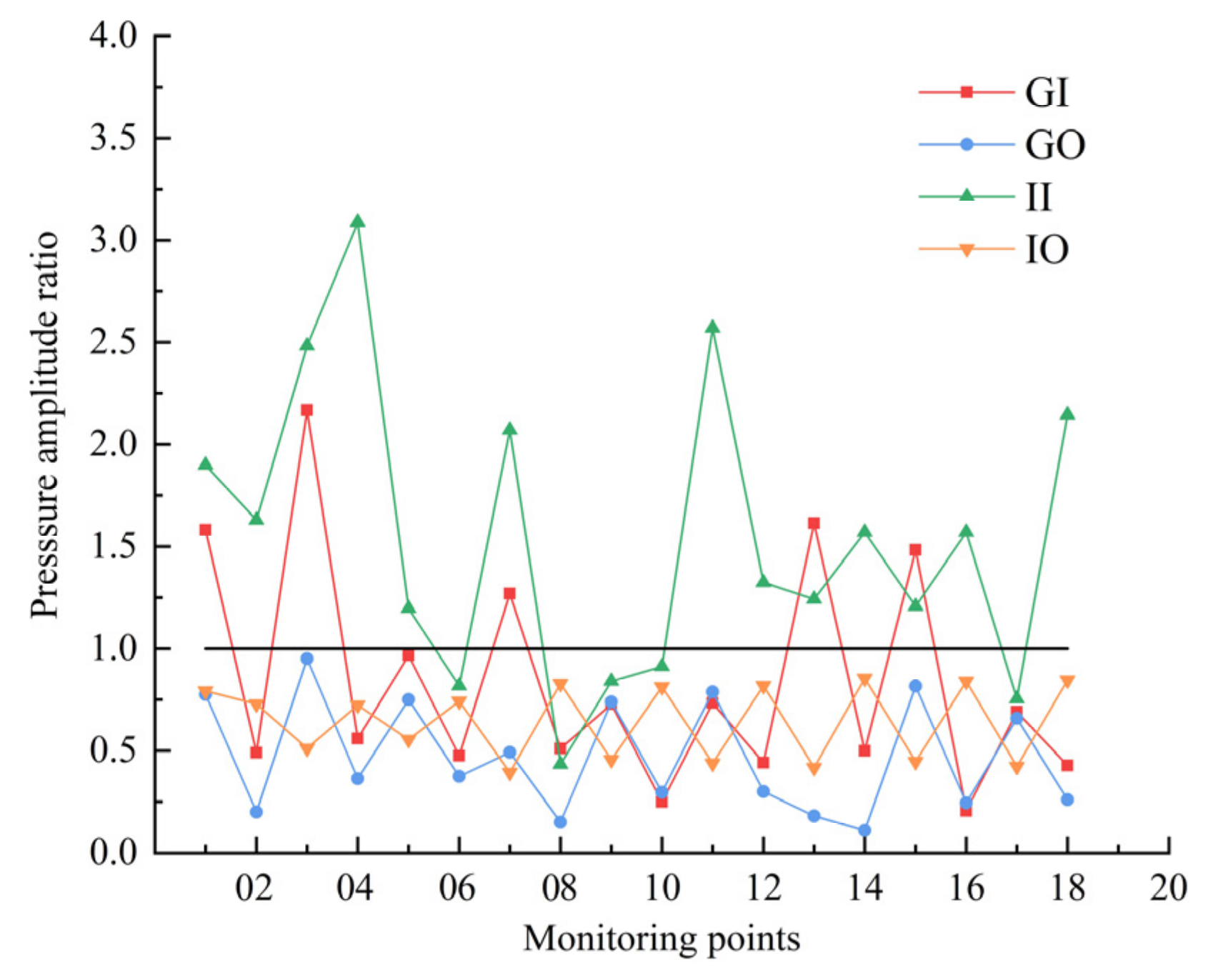
4.3. Analysis of Pressure Pulsation in Impeller-Guide Vane Hydraulic Coupling Zone
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ocko, I.B.; Hamburg, S.P. Climate impacts of hydropower: Enormous differences among facilities and over time. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14070–14082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qin, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, L. Potential assessment of photovoltaic power generation in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lakshminarayana, B.; Maddock, D. Steady and Unsteady Flow Field at Pump and Turbine Exits of a Torque Converter. J. Fluids Eng. 1998, 120, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pavesi, G.; Liu, X.; Xie, T.; Liu, J. Unsteady flow characteristics regarding hump instability in the first stage of a multistage pump-turbine in pump mode. Renew. Energy 2018, 127, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, B.; Xu, H. Numerical simulation of the unsteady flow in a high-head pump turbine and the runner improvement. In Proceedings of the Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting 2008, Jacksonville, FL, USA, 10–14 August 2008; Volume 48401, pp. 1115–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Numerical simulation of unsteady flow for a pump-turbine in transition cases with large-eddy simulation. Water Energy Int. 2019, 61, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Binama, M.; Kan, K.; Chen, H.X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Su, W.T.; Muhirwa, A.; Ntayomba, J. Flow instability transferability characteristics within a reversible pump turbine (RPT) under large guide vane opening (GVO). Renew. Energy 2021, 179, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Fan, H.; Liu, S.; Wu, Y. S-shaped characteristics on the performance curves of pump-turbines in turbine mode—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, S. Energy balance and local unsteady loss analysis of flows in a low specific speed model pump-turbine in the positive slope region on the pump performance curve. Energies 2019, 12, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Binama, M.; Su, W.T.; Li, X.B.; Li, F.C.; Wei, X.Z.; An, S. Investigation on pump as turbine (PAT) technical aspects for micro hydropower schemes: A state-of-the-art review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 148–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Kong, F.; Gou, Q.; Yang, S. Theoretical, experimental, and numerical study of special impeller used in turbine mode of centrifugal pump as turbine. Energy 2017, 130, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.J.; Luo, X.Q.; Guo, P.C.; Wu, Y.L. 3-D Simulation of a prototype pump-turbine during starting period in turbine model. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 52, 052028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S. Numerical research on unsteady flow rate characteristics of pump as turbine. Renew. Energy 2016, 94, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, F.; De Paola, F.; Fontana, N.; Giugni, M.; Marini, G. Experimental characterization of two pumps as turbines for hydropower generation. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wang, F.; Guo, Z.; Lu, J. Performance evaluation of an axial-flow pump with adjustable guide vanes in turbine mode. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tan, L. Dynamic mode decomposition and reconstruction of tip leakage vortex in a mixed flow pump as turbine at pump mode. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobeiri, A. Investigations of Time Dependent Flow Phenomena in a Turbine and a Pump-Turbine of Francis Type. Ph.D. Thesis, Laboratory for Hydraulic Machines, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, C. Compressible large eddy simulation of a Francis turbine during speed-no-load: Rotor stator interaction and inception of a vortical flow. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power 2018, 140, 112601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, W.D.; Bin, C.; Zhang, Q.H.; Cao, W.D. Experimental study of flow field in interference area between impeller and guide vane of axial flow pump. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2015, 26, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaidi, A.R. Influence of guide vanes on the flow fields and performance of axial pump under unsteady flow conditions: Numerical study. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 14, 6570–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Koutnik, J.; Seidel, U.; Hübner, B. Compressible simulation of rotor-stator interaction in pump-turbines. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2010, 3, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolet, C.; Ruchonnet, N.; Alligné, S.; Koutnik, J.; Avellan, F. Hydroacoustic simulation of rotor-stator interaction in resonance conditions in Francis pump-turbine. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2010, 12, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.G.; Mateos-Prieto, B.; Egusquiza, E. Monitoring of rotor-stator interaction in pump-turbine using vibrations measured with on-board sensors rotating with shaft. Shock. Vib. 2014, 2014, 276796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Okamoto, H. An experimental study on the fluid forces induced by rotor-stator interaction in a centrifugal pump. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2003, 9, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, L.; Shi, W.; Yang, Y.; Awais, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X. Correlation research of rotor–stator interaction and shafting vibration in a mixed-flow pump. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control. 2020, 39, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, H. Case study of pump failure due to rotor-stator interaction. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 1994, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santolaria Morros, C.; Fernández Oro, J.M.; Argüelles Díaz, K.M. Numerical modelling and flow analysis of a centrifugal pump running as a turbine: Unsteady flow structures and its effects on the global performance. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2011, 65, 542–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Gong, R.Z.; Wang, H.J.; Wei, X.Z.; Liu, Z.S.; Qin, D.Q. Analysis of rotor-stator interaction in turbine mode of a pump-turbine model. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2016, 9, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.X.; Sun, D.G.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhang, J.; Peng, G.Y. Numerical analysis of unsteady flow behaviour and pressure pulsation in pump turbine with misaligned guide vanes. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2012, 15, 032043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Appiah, D.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, S.; Gu, Y.; Asomani, S.N. Experimental and numerical investigations on pressure pulsation in a pump mode operation of a pump as turbine. Energy Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 1264–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roache, P.J. Quantification of uncertainty in computational fluid dynamics. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1997, 29, 123–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.S.M.; Doolan, C.J.; Wheatley, V. Grid convergence study for a two-dimensional simulation of flow around a square cylinder at a low Reynolds number. In Seventh International Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries; Witt, P.J., Schwarz, M.P., Eds.; CSIRO: Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, I.B.; Ghia, U.; Roache, P.J.; Freitas, C.J. Procedure for estimation and reporting of uncertainty due to discretization in CFD applications. J. Fluids Eng.-Trans. ASME 2008, 130, 078001. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ji, Q. Study on vortex flow and pressure fluctuation in dustpan-shaped conduit of a low head axial-flow pump as turbine. Renew. Energy 2022, 196, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, D.; Tang, F.; Sun, S. Numerical study for flow loss characteristic of an axial-flow pump as turbine via entropy production analysis. Processes 2022, 10, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Cheng, H. Numerical simulation for the tip leakage vortex cavitation. Ocean Eng. 2018, 151, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoran, Z.; Yexiang, X.; Zhengwei, W.; Hongying, L.; Soo-Hwang, A.; Yangyang, Y.; Honggang, F. Numerical analysis of non-axisymmetric flow characteristic for a pump-turbine impeller at pump off-design condition. Renew. Energy 2018, 115, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Lv, Y.; Jian, H.; Gao, H. Influence of rotation speed on flow field and hydraulic noise in the conduit of a vertical axial-flow pump under low flow rate condition. Machines 2022, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, S.; Wu, D.; Yang, S.; Wu, P. Effect of suction and discharge conditions on the unsteady flow phenomena of axial-flow reactor coolant pump. Energies 2020, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Design flow rate (L/s) | 272 |
| Design head (m) | 2.4 |
| Rated rotational speed (r/min) | 930 |
| Nominal impeller diameter (mm) | 300 |
| Impeller blades number | 3 |
| Guide vane body blades number | 5 |
| Tip clearance size (mm) | 0.2 |
| Parameter | = Efficiency |
|---|---|
| N1, N2, N3 | 6,143,640, 2,746,492, 721,326 |
| r21, r32 | 1.31, 1.56 |
| φ1, φ2, φ3 | 43.64%, 42.82%, 42.13% |
| p | 4.2 |
| , | 44.03%, 42.9% |
| , | 1.9%, 1.6% |
| , | 0.89%, 0.19% |
| GCI21, GCI32 | 1.13%, 0.37% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Nasr, A. Numerical Analysis of Flow Characteristics in Impeller-Guide Vane Hydraulic Coupling Zone of an Axial-Flow Pump as Turbine Device. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030661
Yang F, Li Z, Lv Y, Li J, Zhou G, Nasr A. Numerical Analysis of Flow Characteristics in Impeller-Guide Vane Hydraulic Coupling Zone of an Axial-Flow Pump as Turbine Device. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(3):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030661
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fan, Zhongbin Li, Yuting Lv, Jindong Li, Guangxin Zhou, and Ahmed Nasr. 2023. "Numerical Analysis of Flow Characteristics in Impeller-Guide Vane Hydraulic Coupling Zone of an Axial-Flow Pump as Turbine Device" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 3: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030661
APA StyleYang, F., Li, Z., Lv, Y., Li, J., Zhou, G., & Nasr, A. (2023). Numerical Analysis of Flow Characteristics in Impeller-Guide Vane Hydraulic Coupling Zone of an Axial-Flow Pump as Turbine Device. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(3), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11030661







