A Study on the Correlation between Ship Movement Characteristics and Ice Conditions in Polar Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
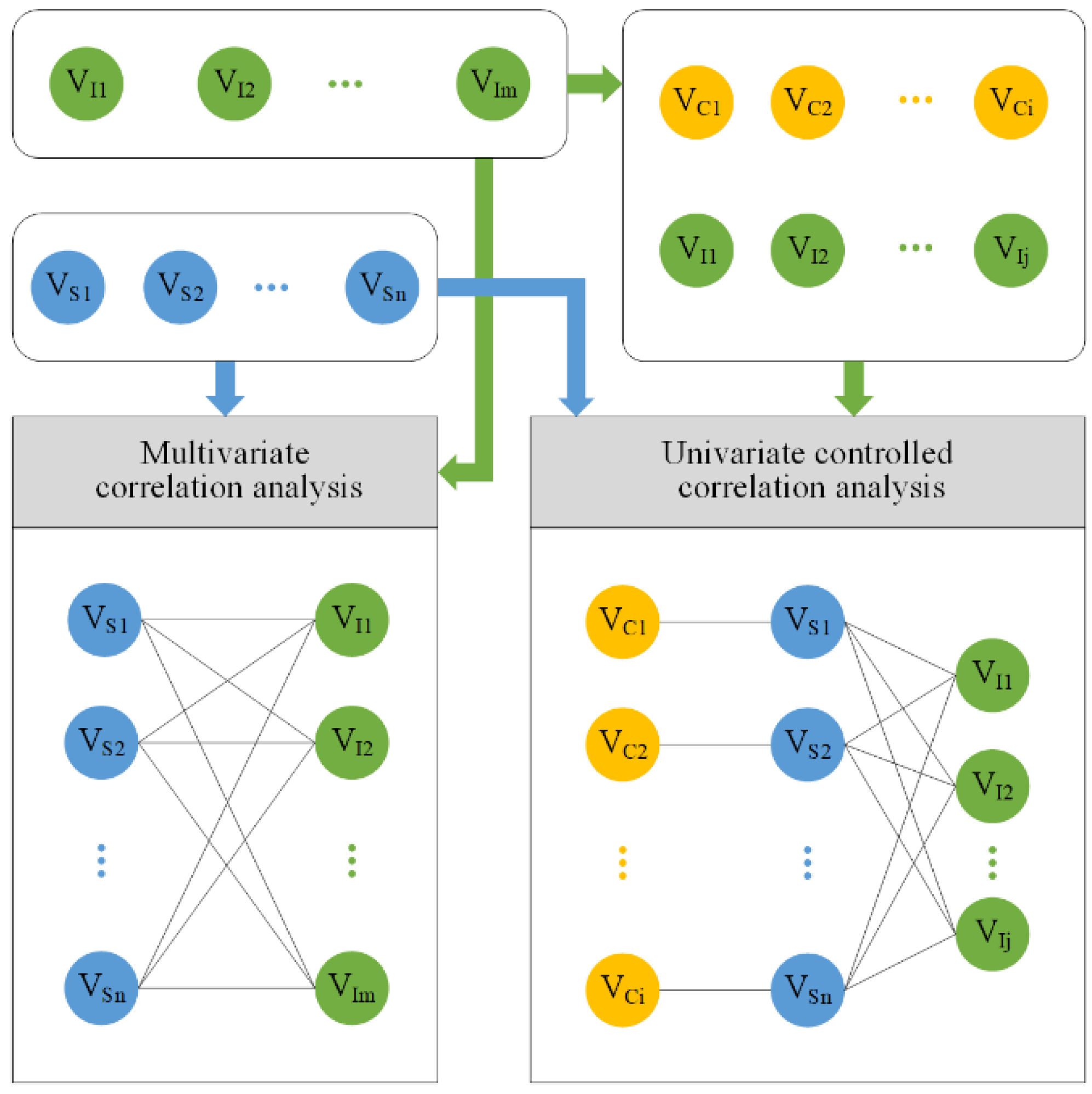
3.1. Correlation Analysis Framework
3.2. Data Collection
3.3. Data Preprocessing
3.4. Data General Characteristics and Visualization
3.5. Modeling
3.5.1. Multivariate Correlation Analysis
3.5.2. Univariate Controlled Correlation Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Analysis of Ship Movement Characteristics in Polar Waters
4.1.1. Characteristics of Ship Speed in Polar Waters
4.1.2. Characteristics of Variation of Ship Speed in Polar Waters
4.1.3. Characteristics of Ship Course in Polar Waters
4.1.4. Characteristics of the Ship’s Course Variations in Polar Waters
4.2. Correlation Analysis between Sea Ice Conditions and Ship Movement Characteristics
4.2.1. Correlation Analysis between Sea Ice Concentration and Ship Movement Characteristics
4.2.2. Correlation Analysis between Sea Ice Thickness and Ship Movement Characteristics
4.2.3. Correlation Analysis between Sea Ice Concentration and Sea Ice Thickness
4.2.4. Partial Correlation Analysis between Sea Ice Conditions and Ship Movement Characteristics
5. Discussion
5.1. Ship Movement Characteristics in Polar Waters
5.2. The Influence of Sea Ice Conditions on Ship Movement Characteristics
5.2.1. The Relationship between Sea Ice Concentration and Ship Movement Characteristics
5.2.2. The Relationship between Sea Ice Thickness and Ship Movement Characteristics
5.2.3. The Correlation between Sea Ice Concentration and Sea Ice Thickness
5.2.4. Partial Correlation Analysis between Sea Ice Conditions and Ship Movement Characteristics
5.3. Shortcomings and Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melia, N.; Haines, K.; Hawkins, E. Sea ice decline and 21st century trans-Arctic shipping routes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9720–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksenov, Y.; Popova, E.E.; Yool, A.; Nurser, A.J.G.; Williams, T.D.; Bertino, L.; Bergh, J. On the future navigability of Arctic sea routes: High-resolution projections of the Arctic Ocean and sea ice. Mar. Policy 2017, 75, 300–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, S.; Goerlandt, F.; Xi, Y. Arctic shipping risk management: A bibliometric analysis and a systematic review of risk influencing factors of navigational accidents. Saf. Sci. 2021, 139, 105254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowalski, S.; Hermanski, G. Ship resistance and propulsion in ice-covered waters: An experimental study. Trans. Soc. Nav. Archit. Mar. Eng. 2011, 119, 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, F.; Schoyen, H. Polar research and supply vessel capabilities—An exploratory study. Ocean Eng. 2021, 224, 108671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yao, R.; Yu, L.; Gan, X.; Wang, X. Line design and optimization for polar expedition cruise ships with transoceanic voyage characteristics. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2023, 28, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, K.; Li, X.; Xue, Y. Numerical Simulation of a Polar Ship Moving in Level Ice Based on a One-Way Coupling Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, C.; Feng, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, C. Predicting ship ramming performance in thick level ice via experiments. Ships Offshore Struct. 2022, 17, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, G. Numerical analysis of added resistance in head waves on a Polar Research Vessel and conventional ships. Ocean Eng. 2021, 233, 108888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leira, B.J.; Chai, W.; Radhakrishnan, G. On Characteristics of Ice Ridges and Icebergs for Design of Ship Hulls in Polar Regions Based on Environmental Design Contours. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, L.; Ding, S.; Liu, R.; Zheng, S. Experimental and numerical investigation on self-propulsion performance of polar merchant ship in brash ice channel. Ocean Eng. 2023, 269, 113424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, Y.; Pena-Castillo, L.; Soares, A. A Study on the Geometric and Kinematic Descriptors of Trajectories in the Classification of Ship Types. Sensors 2022, 22, 5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Zhou, W.; Guan, J.; Jin, J. A method for identifying marine targets based on mining of multi-characteristic movement patterns. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 95, 107434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yan, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Ma, Y.; Meng, F. An online identification approach for a nonlinear ship motion model based on a receding horizon. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2021, 43, 3000–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montewka, J.; Goerlandt, F.; Lensu, M.; Kuuliala, L.; Guinness, R. Toward a hybrid model of ship performance in ice suitable for route planning purpose. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2019, 233, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerlandt, F.; Montewka, J.; Zhang, W.B.; Kujala, P. An analysis of ship escort and convoy operations in ice conditions. Saf. Sci. 2017, 95, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, M.; Mao, W. Data-driven ship energy efficiency analysis and optimization model for route planning in ice-covered Arctic waters. Ocean Eng. 2019, 186, 106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yan, Y. Visual ship tracking via a hybrid kernelized correlation filter and anomaly cleansing framework. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 106, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ling, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Luo, L.; Yan, Y. Ship detection from coastal surveillance videos via an ensemble Canny-Gaussian-morphology framework. J. Navig. 2021, 74, 1252–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Wang, M. Real-Time Ship Tracking under Challenges of Scale Variation and Different Visibility Weather Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, L. Influences of solar energy on the energy efficiency design index for new; building ships. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 19389–19394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, X.; Shi, W.; Jia, T.; Li, W.; Chen, M. An empirical study on the intra-urban goods movement patterns using logistics big data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 1089–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagic, R.; Skuric, M.; Djukanovic, G.; Nikolic, D. Establishing Correlation between Cruise Ship Activities and Ambient PM Concentrations in the Kotor Bay Area Using a Low-Cost Sensor Network. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Liao, S.; Wu, B.; Yang, D. Exploring effects of ship traffic characteristics and environmental conditions on ship collision frequency. Marit. Policy Manag. 2020, 47, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, S.; Shi, C.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, P. Mining ship deficiency correlations from historical port state control (PSC) inspection data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zambon, A.; Moro, L.; Kennedy, A.; Oldford, D. Torsional vibrations of Polar-Class shaftlines: Correlating ice-propeller interaction torque to sea ice thickness. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 267, 113250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, P.C.; Sasa, K.; Kawahara, H.; Chen, C. Statistical estimation of container condensation in marine transportation between Far East Asia and Europe. J. Navig. 2022, 75, 176–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W. The research on floe ice force acting on the ”Xue Long” icebreaker based on synthetic ice test and virtual mass numerical method. J. Hydrodyn. 2021, 33, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulic, A.; Katalinic, M.; Corak, M.; Parunov, J. The effect of spatial correlation of sea states on extreme wave loads of ships. Ships Offshore Struct. 2021, 16, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennino, S.; Angrisano, A.; Della Corte, V.; Ferraioli, G.; Gaglione, S.; Innac, A.; Martellato, E.; Palumbo, P.; Piscopo, V.; Rotundi, A.; et al. Sea State Monitoring by Ship Motion Measurements Onboard a Research Ship in the Antarctic Waters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, W.; Xie, X.; Yang, S.; Hang, S.; Han, Y.; Hong, Z. Antarctic sea ice detection using a shipborne GPS reflectometry setup. Meas. Control. 2021, 54, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montewka, J.; Sinclair, H.; Kujala, P.; Haapala, J.; Lensu, M. Modelling ship performance in ice using Bayesian Networks. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering under Arctic Conditions, POAC 2013, Espoo, Finland, 9–13 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Alok, S.; Rajak, D.R.; Beg, J.; Bahuguna, I.M.; Talati, I. Investigating optimum ship route in the Antarctic in presence of sea ice and wind resistances—A case study between Bharati and Maitri. Polar Sci. 2021, 30, 100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmritz, M.; Counillon, F.; Bitz, C.M.; Massonnet, F.; Bethke, I.; Gao, Y. Optimising assimilation of sea ice concentration in an Earth system; model with a multicategory sea ice model. Tellus Ser. A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2018, 70, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rong, H.; Teixeira, A.P.; Soares, C.G. Spatial correlation analysis of near ship collision hotspots with local maritime traffic characteristics. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2021, 209, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Z.; Wang, L. Spatial-Temporal Distribution Characteristics and Correlation Analysis of Air Pollutants from Ships in Inland Ports. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumiyama, K. Ship Performance in Ice; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]

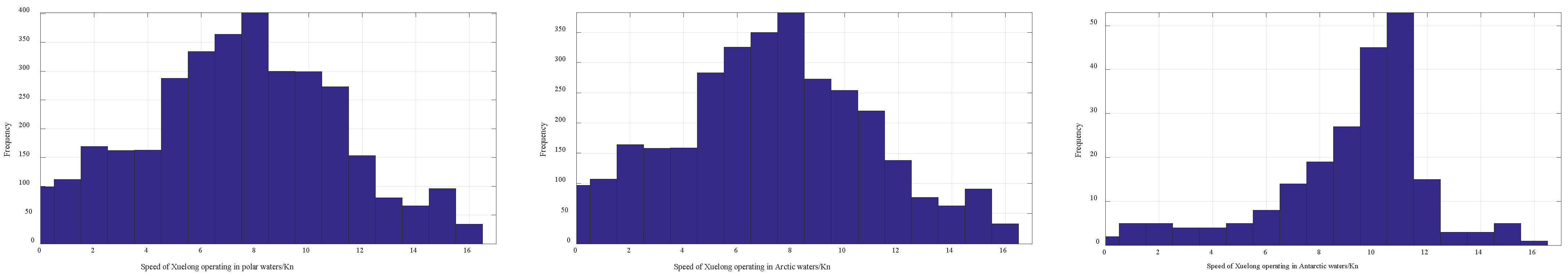

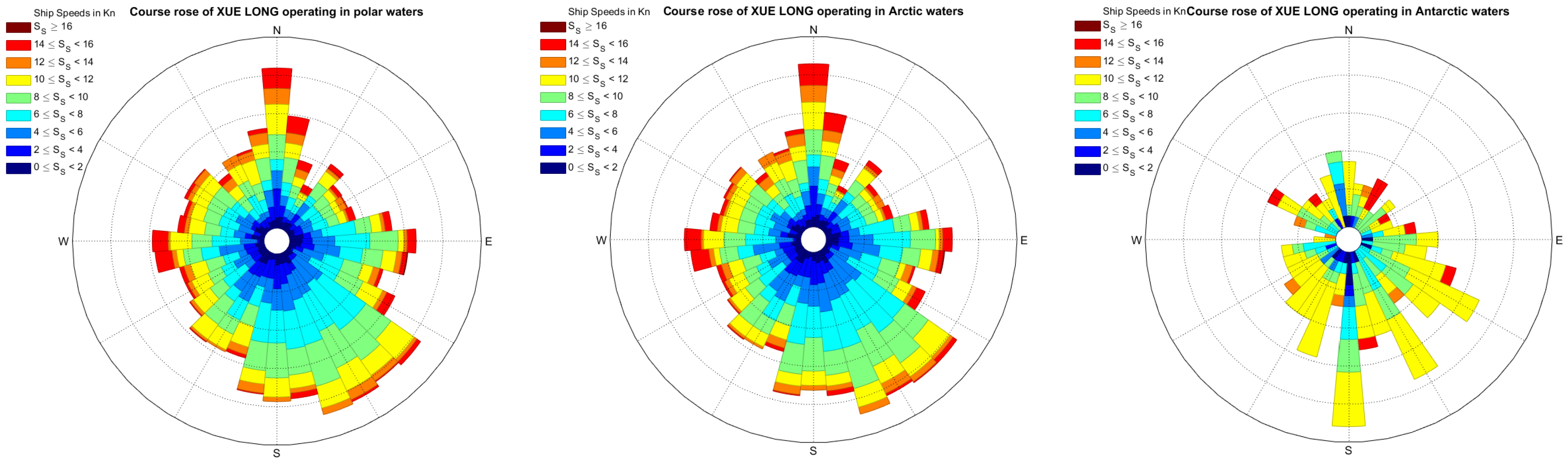
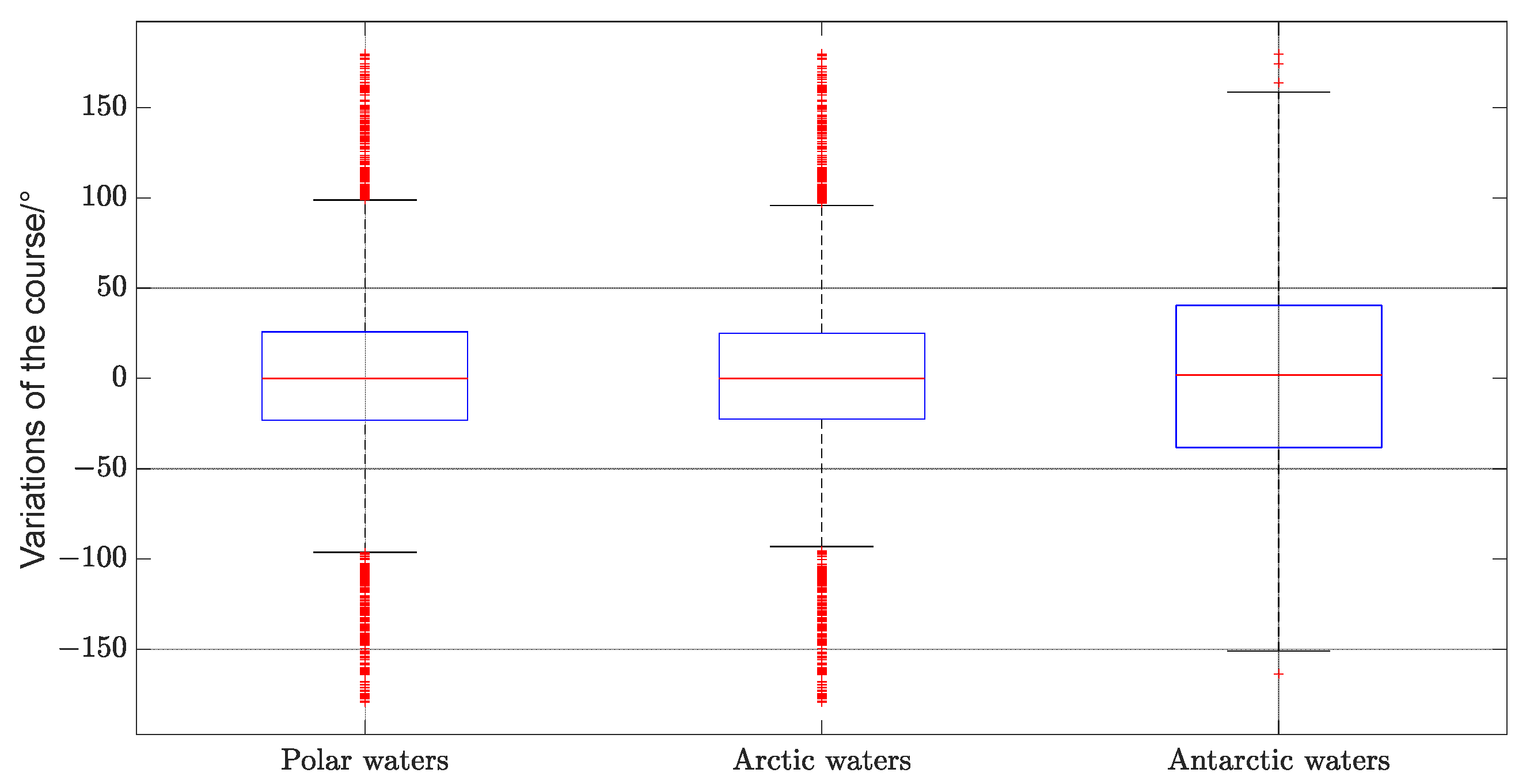

| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | S.D. | Median | Mode | Count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antarctic waters | 0.20 | 15.60 | 9.20 | 2.98 | 9.90 | 10.90 | 218 |
| Arctic waters | 0.00 | 16.00 | 7.38 | 3.65 | 7.40 | 8.30 | 3176 |
| Polar waters | 0.00 | 16.00 | 7.50 | 3.63 | 7.60 | 8.30 | 3394 |
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | S.D. | Median | Mode | Count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antarctic waters | −9.80 | 11.70 | −0.02 | 3.21 | 0.00 | −0.20 | 218 |
| Arctic waters | −14.90 | 13.80 | 0.00 | 2.91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3176 |
| Polar waters | −14.90 | 13.80 | 0.00 | 2.93 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3394 |
| Minimum | Maximum | Mean | S.D. | Median | Mode | Count | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antarctic waters | −163.60 | 179.70 | 2.95 | 68.52 | 1.95 | −20.00 | 218 |
| Arctic waters | −179.30 | 179.80 | −0.13 | 54.62 | 0.00 | −3.20 | 3176 |
| Polar waters | −179.30 | 179.80 | 0.07 | 55.61 | 0.00 | −3.20 | 3394 |
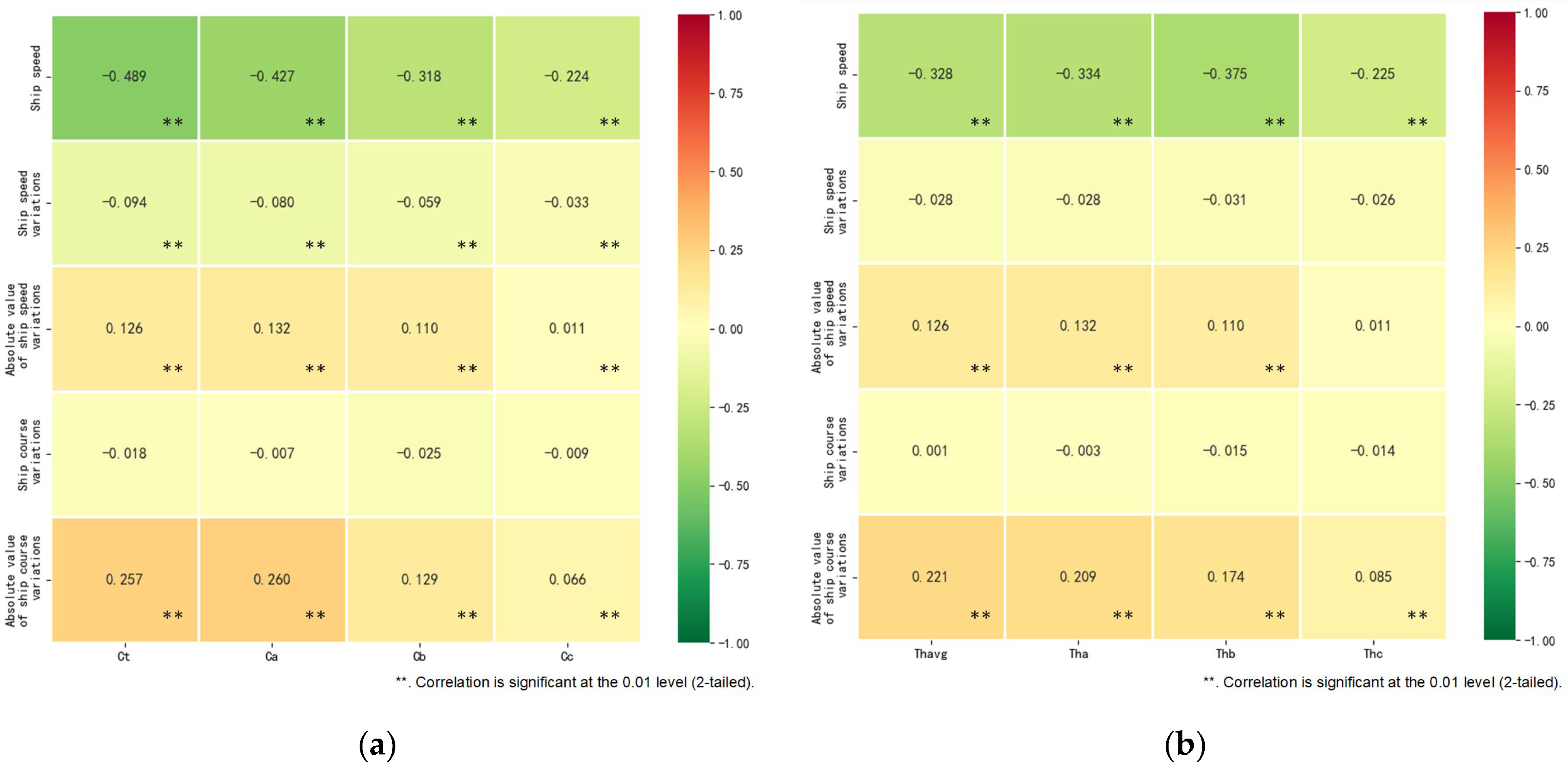
| Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ship speed | Correlation Coefficient | −0.489 ** | −0.427 ** | −0.318 ** | −0.224 ** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Ship speed variation | Correlation Coefficient | −0.094 ** | −0.080 ** | −0.059 ** | −0.033 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| The absolute value of ship speed variation | Correlation Coefficient | 0.126 ** | 0.132 ** | 0.110 ** | 0.011 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Ship course variations | Correlation Coefficient | −0.018 | −0.007 | −0.025 | −0.009 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.291 | 0.671 | 0.151 | 0.618 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| The absolute value of ship course variations | Correlation Coefficient | 0.257 ** | 0.260 ** | 0.129 ** | 0.066 ** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ship speed | Correlation Coefficient | −0.328 ** | −0.334 ** | −0.375 ** | −0.225 ** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Ship speed variation | Correlation Coefficient | −0.028 | −0.028 | −0.031 | −0.026 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.104 | 0.102 | 0.074 | 0.131 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| The absolute value of ship speed variation | Correlation Coefficient | 0.126 ** | 0.132 ** | 0.110 ** | 0.011 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.516 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Ship course variations | Correlation Coefficient | 0.001 | −0.003 | −0.015 | −0.014 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.976 | 0.858 | 0.391 | 0.407 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| The absolute value of ship course variations | Correlation Coefficient | 0.221 ** | 0.209 ** | 0.174 ** | 0.085 ** |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.597 ** | 0.602 ** | 0.609 ** | 0.356 ** | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.551 ** | 0.541 ** | 0.478 ** | 0.179 ** | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.493 ** | 0.527 ** | 0.693 ** | 0.330 ** | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.301 ** | 0.292 ** | 0.465 ** | 0.932 ** | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| N | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | 3394 | |
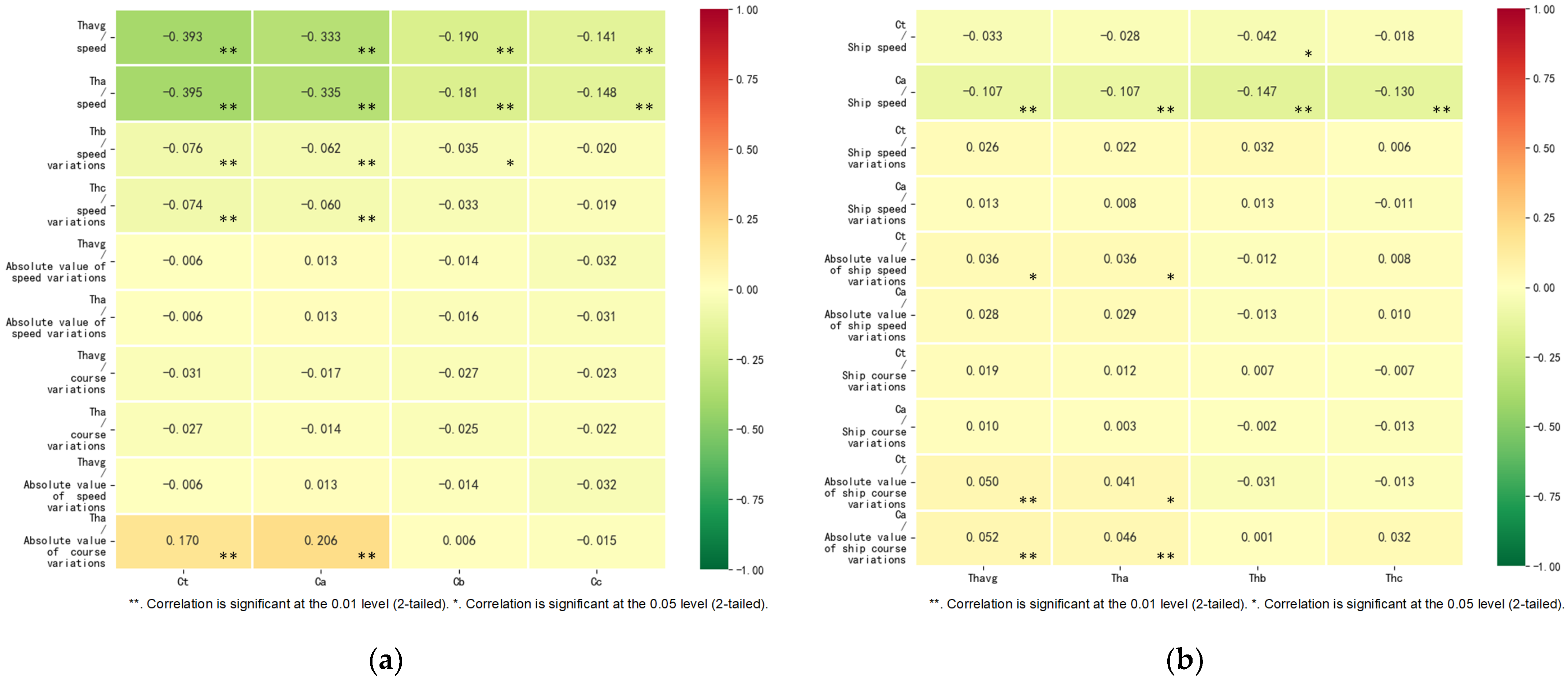
| Control Variable | Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ship speed | correlation coefficient | −0.393 ** | −0.333 ** | −0.190 ** | −0.141 ** | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship speed | correlation coefficient | −0.395 ** | −0.335 ** | −0.181 ** | −0.148 ** | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | −0.076 ** | −0.062 ** | −0.035 * | −0.02 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.254 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | −0.074 ** | −0.060 ** | −0.033 | −0.019 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0.051 | 0.263 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | −0.006 | 0.013 | −0.014 | −0.032 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.74 | 0.449 | 0.411 | 0.063 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | −0.006 | 0.013 | −0.016 | −0.031 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.742 | 0.436 | 0.346 | 0.073 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship course variation | correlation coefficient | −0.031 | −0.017 | −0.027 | −0.023 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.074 | 0.312 | 0.114 | 0.176 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship course variation | correlation coefficient | −0.027 | −0.014 | −0.025 | −0.022 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.118 | 0.409 | 0.146 | 0.204 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | −0.006 | 0.013 | −0.014 | −0.032 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.74 | 0.449 | 0.411 | 0.063 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship course variation | correlation coefficient | 0.170 ** | 0.206 ** | 0.006 | −0.015 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0.737 | 0.38 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Control Variable | Spearman’s Correlation Coefficient | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ship speed | correlation coefficient | −0.033 | −0.028 | −0.042 * | −0.018 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.057 | 0.103 | 0.015 | 0.298 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship speed | correlation coefficient | −0.107 ** | −0.107 ** | −0.147 ** | −0.130 ** | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | 0.026 | 0.022 | 0.032 | 0.006 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.131 | 0.2 | 0.064 | 0.732 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | 0.013 | 0.008 | 0.013 | −0.011 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.461 | 0.634 | 0.448 | 0.528 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | 0.036 * | 0.036 * | −0.012 | 0.008 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.034 | 0.035 | 0.49 | 0.625 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship speed variation | correlation coefficient | 0.028 | 0.029 | −0.013 | 0.01 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.097 | 0.097 | 0.454 | 0.559 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship course variation | correlation coefficient | 0.019 | 0.012 | 0.007 | −0.007 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.277 | 0.485 | 0.701 | 0.672 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| Ship course variation | correlation coefficient | 0.01 | 0.003 | −0.002 | −0.013 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.563 | 0.841 | 0.918 | 0.445 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship course variation | correlation coefficient | 0.050 ** | 0.041 * | −0.031 | −0.013 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.073 | 0.443 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
| The absolute value of ship course variation | correlation coefficient | 0.052 ** | 0.046 ** | 0.001 | 0.032 | |
| Sig. (2-tailed) | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.962 | 0.059 | ||
| N | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | 3391 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y. A Study on the Correlation between Ship Movement Characteristics and Ice Conditions in Polar Waters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11040729
Chen L, Huang C, Wang Y. A Study on the Correlation between Ship Movement Characteristics and Ice Conditions in Polar Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(4):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11040729
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Liang, Changhai Huang, and Yanhao Wang. 2023. "A Study on the Correlation between Ship Movement Characteristics and Ice Conditions in Polar Waters" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 4: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11040729






