A Numerical Investigation of Supercavitation Vehicle’s Hydrodynamic Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Method
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Acoustic Model
2.3. Calculation Approach
3. Numerical Simulation Set-Up
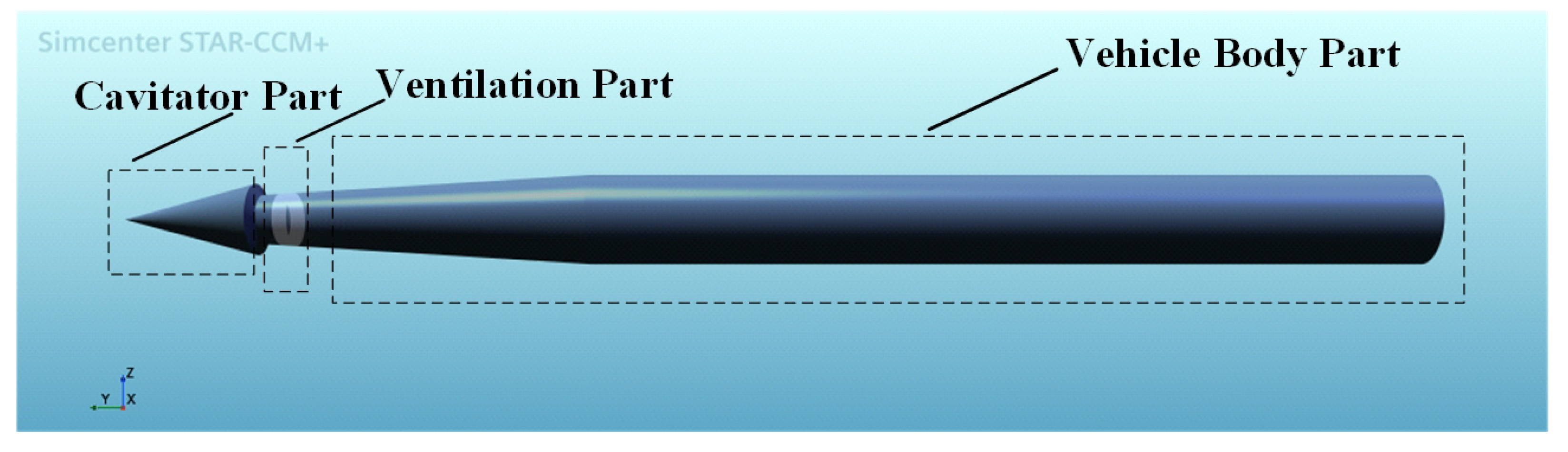
3.1. Vehicle Model
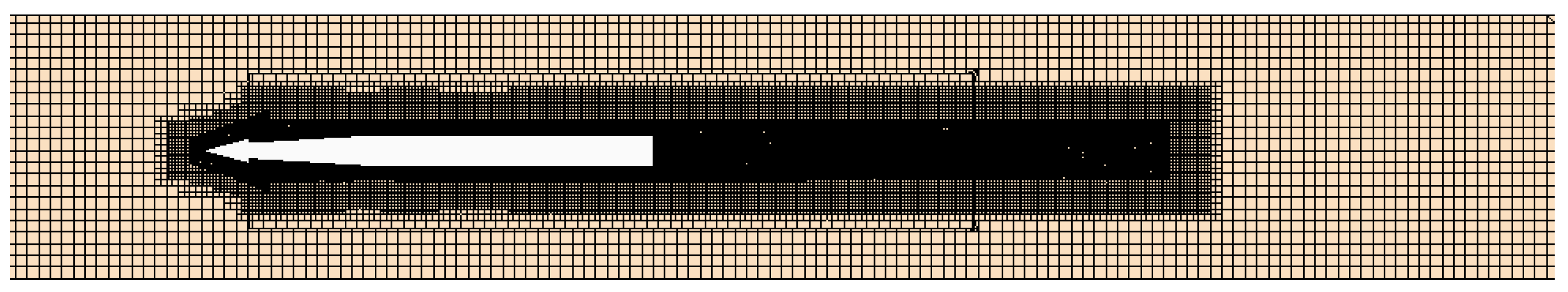
3.2. The Wall Boundary Setting and Mesh Partitioning
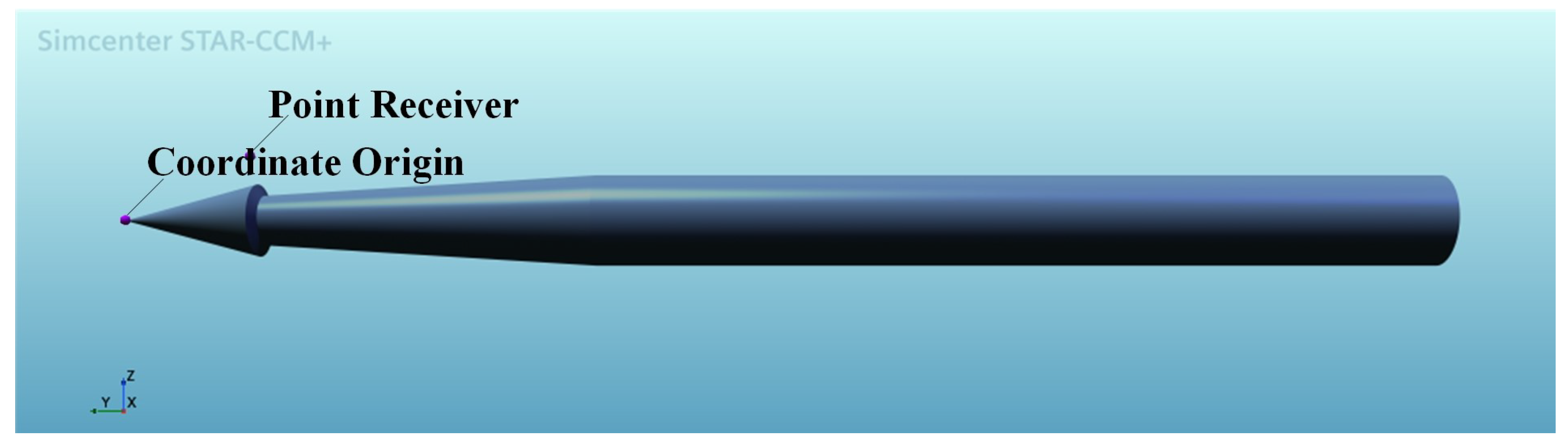
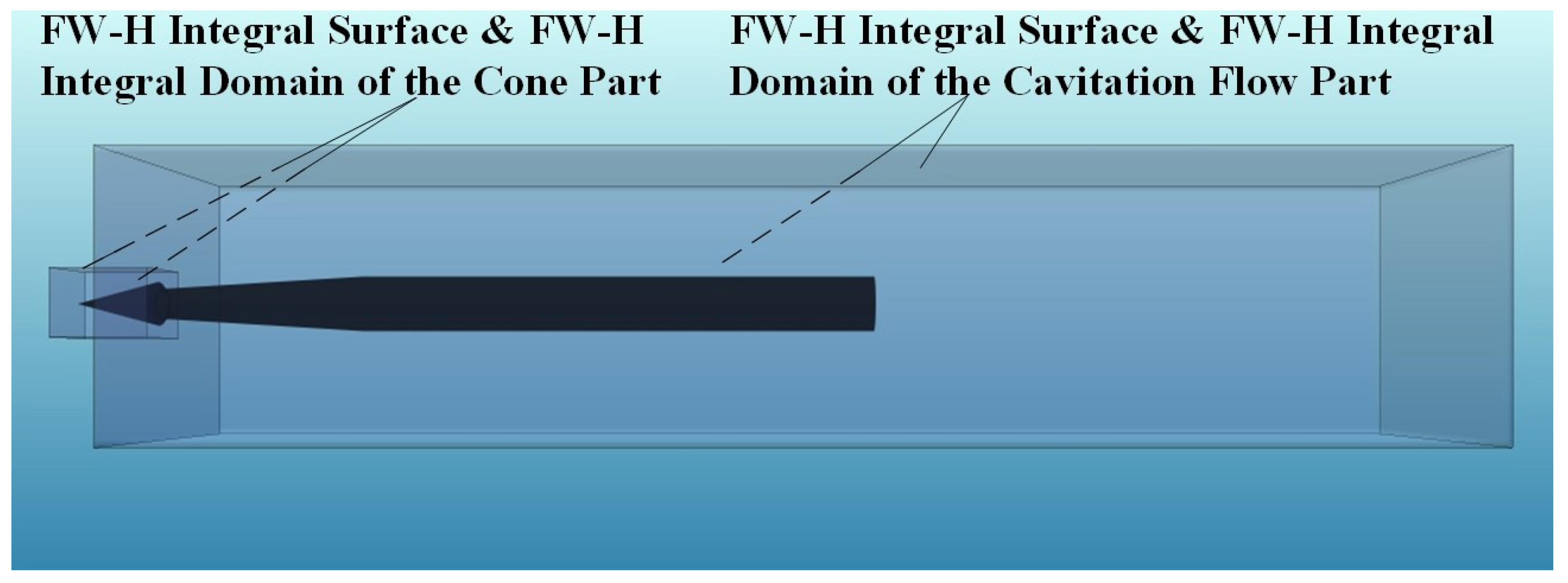
3.3. Noise Source and Point Receiver Setting
4. Results and Discussion
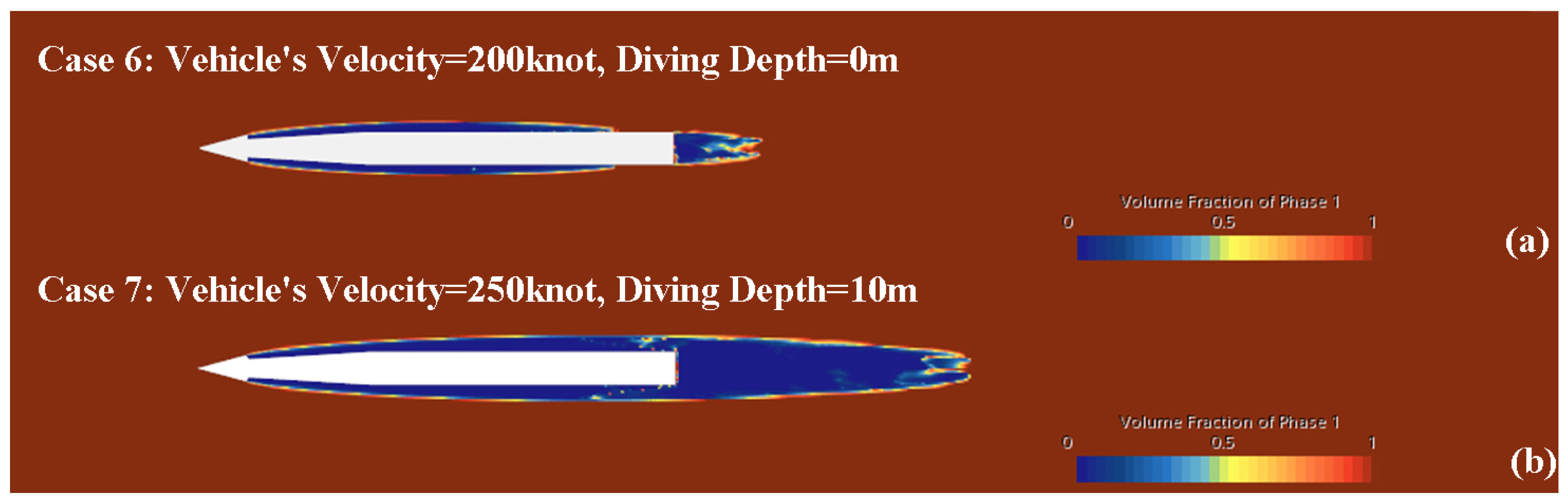
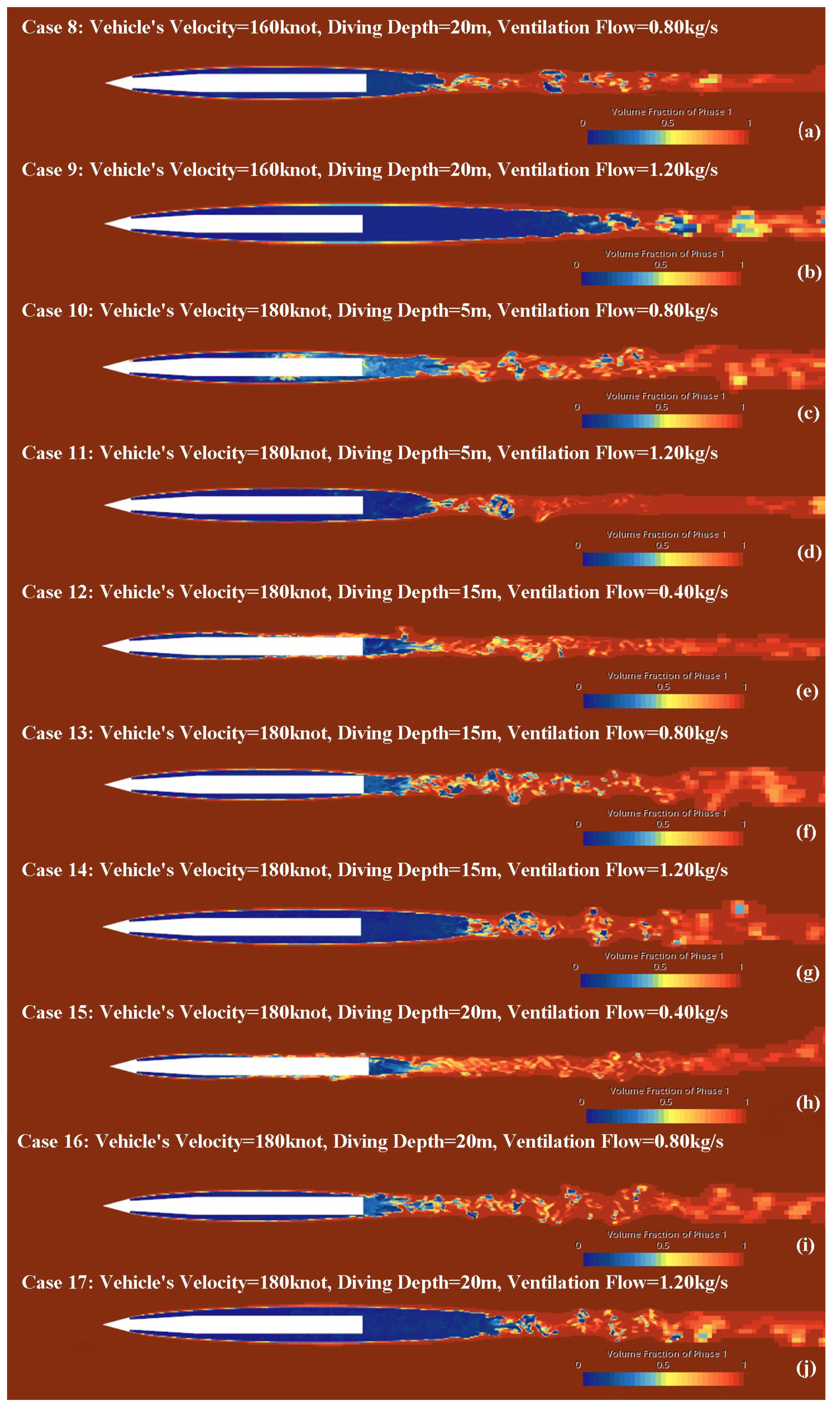
4.1. Cavitation Phenomenon under Different Operating Conditions
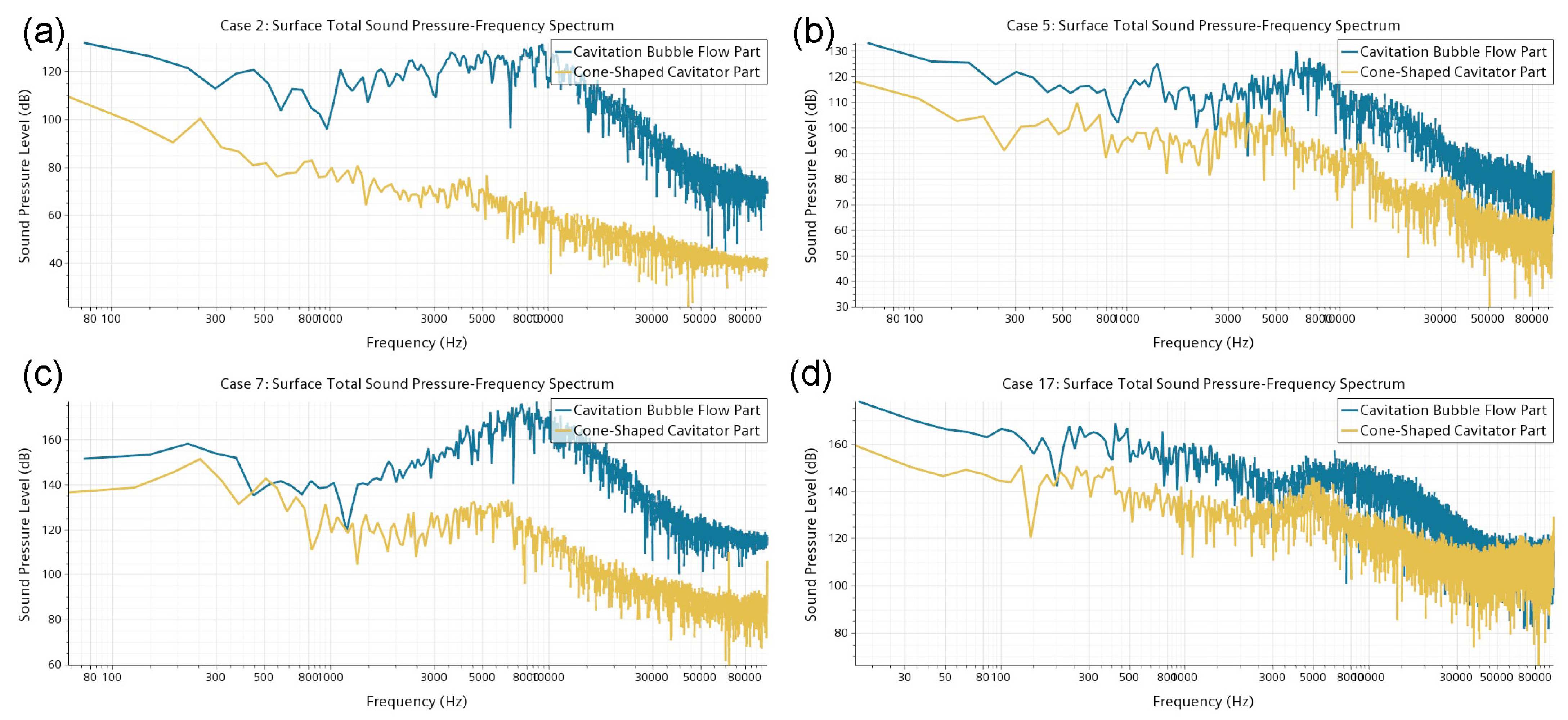
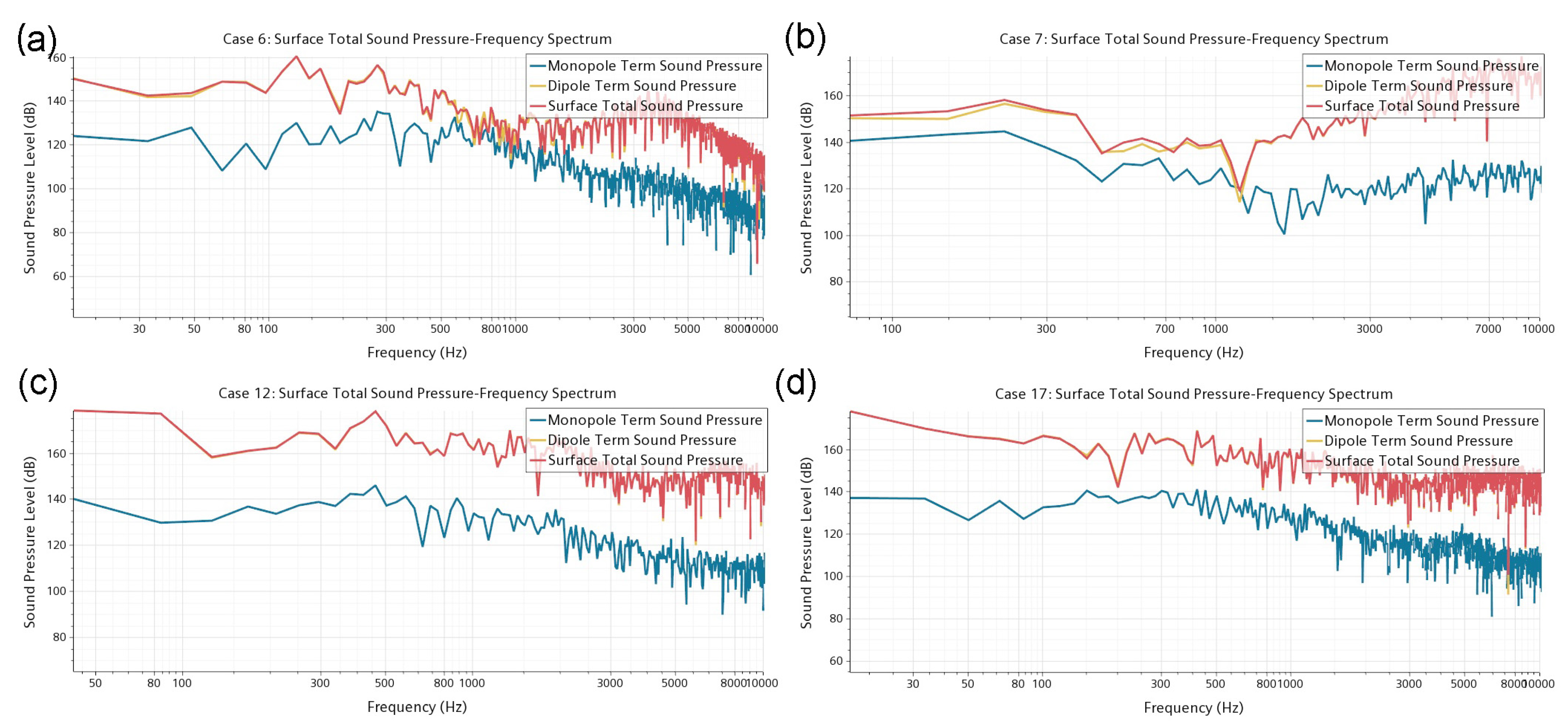
4.2. Noise Sources and Noise Order Characteristics
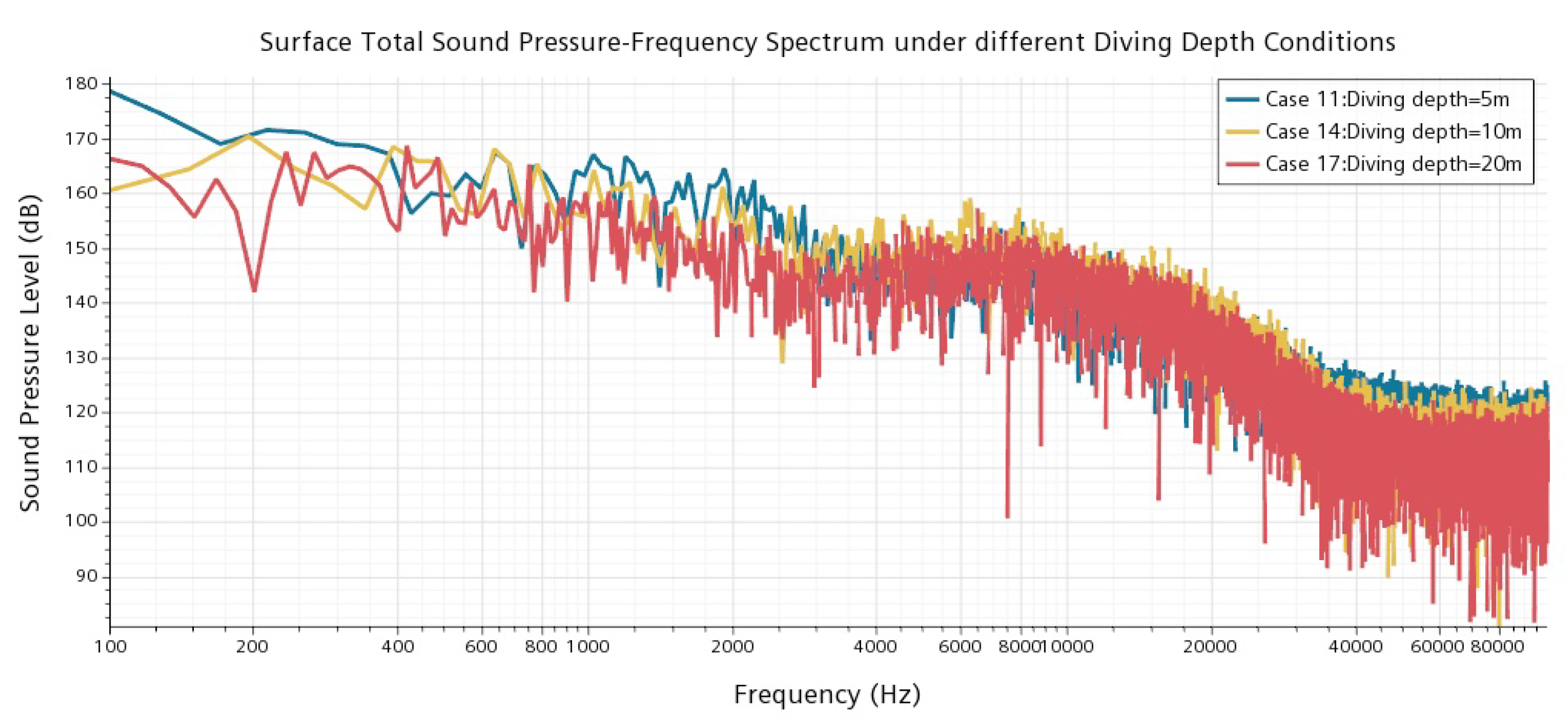
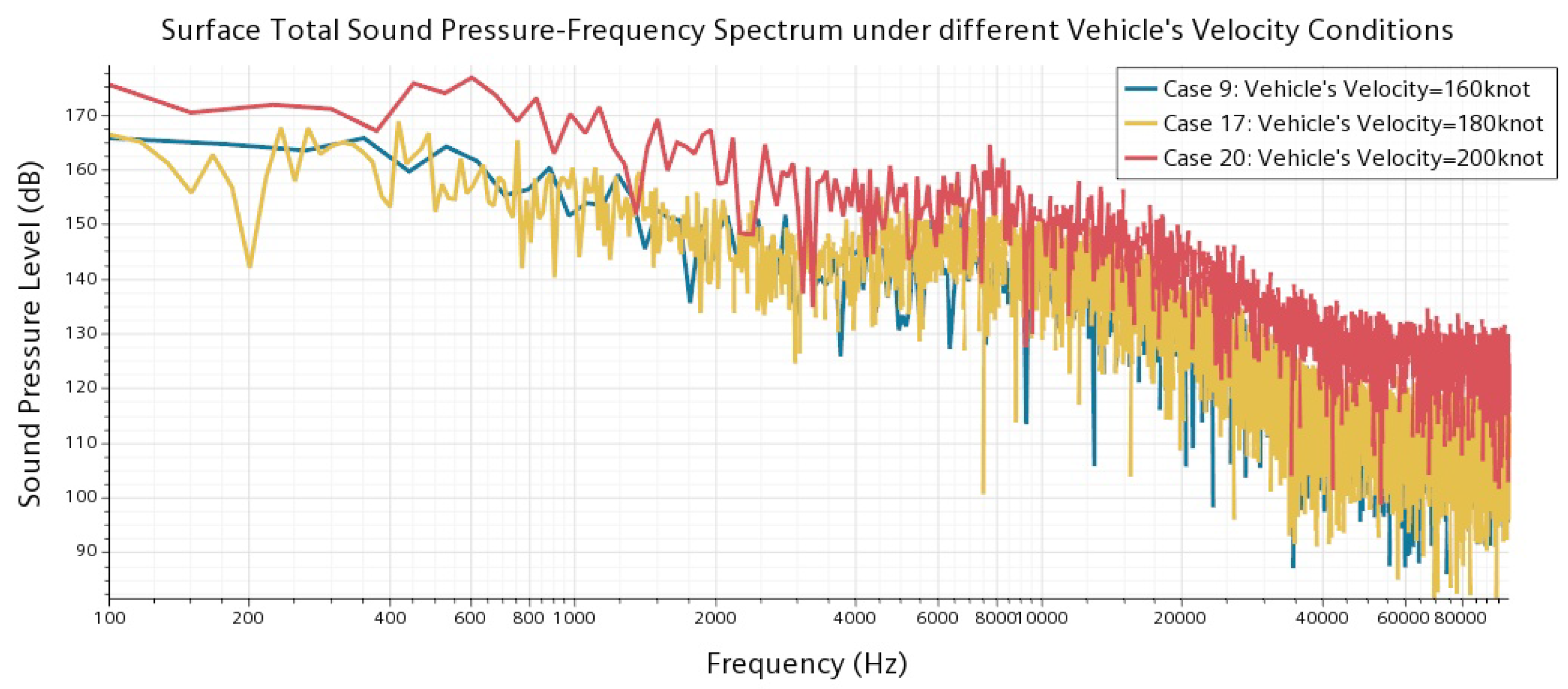
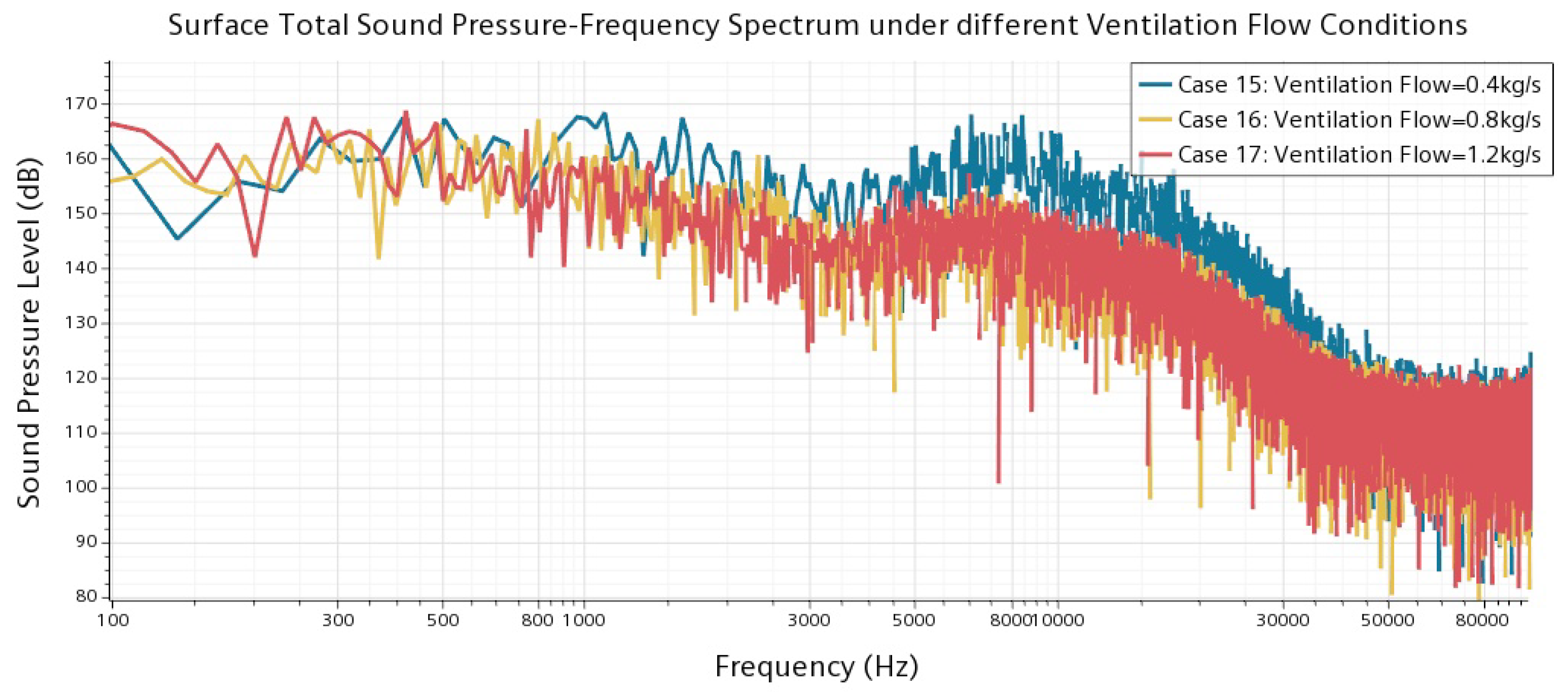
4.3. Hydrodynamic Noise under Different Operating Conditions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LES | Large Eddy Simulation |
| VOF | Volume of Fluid |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
References
- Hrubes, J. High-speed imaging of supercavitating underwater projectiles. Exp. Fluids 2001, 30, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, R.; Daily, J.; Hammitt, F. Cavitation; Eng. Soc. Monographs; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1970; Volume 39, p. 213. [Google Scholar]
- Varga, J.; Sebestyen, G. Experimental investigation of cavitation noise. Houille Blanche 1966, 8, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, M.; Hammitt, F. New method for monitoring and correlating cavitation noise to erosion capability. J. Fluids Eng. 1982, 104, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, J.; Li, B.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, F. Experimental study on unsteady characteristics of the transient cavitation flow. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2021, 80, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, A.; Alishahi, M.; Emdad, H.; Saranjam, B. Part A: Experimental investigation of unsteady supercavitating flows. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2011, 104, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- May, A. Water entry and the cavity-running behavior of missiles. In Technical Report, Navsea Hydroballistics Advisory Committee Silver; Spring: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Savchenko, Y.N. Supercavitating Object Propulsion; Technical Report; Krainian Academy of Sciences Kiev Inst of Hydromechanics: Brussels, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Ahn, B.K.; Kim, H.T.; Jung, Y.R. Experimental investigation of drag characteristics of ventilated supercavitating vehicles with different body shapes. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 052106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadrahimi, A.; Negahdari, M.; Hosseini, S.A.; Parsaei, E. Investigation of the shape of the torpedo nose in supercavitation and numerical analysis of the effect of gas injection. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2021. Available online: https://jmst.kmsu.ac.ir/article_130211.html?lang=en (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Shao, S.; Balakrishna, A.; Yoon, K.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Hong, J. Effect of mounting strut and cavitator shape on the ventilation demand for ventilated supercavitation. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2020, 118, 110173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.D.; Hong, J.W.; Hilo, A.K.; Kim, K.; Ahn, B.K. Experimental investigation of ventilated supercavitation behind cone-shaped with different angles and disk-shaped cavitators. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2022, 14, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Gan, L.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H. Flow noise characteristics analysis of underwater high-speed vehicle based on LES/FW-H coupling model. Acoust. Aust. 2019, 47, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.S.; Lim, K.M.; Zheng, J.; Khoo, B.C. Numerical analysis of flow induced noise propagation in supercavitating vehicles at subsonic speeds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 1752–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.A.; Howe, M.; Salton, A. Low frequency sound produced by a ventilated supercavitating vehicle. J. Sound Vib. 2011, 330, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.; Howe, M.; Koch, R. On sound generated by gas-jet impingement on a bubbly gas–water interface, with application to supercavity self-noise. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 4438–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Deng, J. Numerical investigation on the collapse of a bubble cluster near a solid wall. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 043108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Deng, J. Numerical study of the collapse of multiple bubbles and the energy conversion during bubble collapse. Water 2019, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.Z.; Li, G.J.; Hu, W.S.; Mu, L. Modeling and Simulation of Cavitation Noise of Supercavitating Vehicle. Available online: https://dpi-journals.com/index.php/dtcse/article/view/23664 (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Skidmore, G.M.; Brungart, T.A.; Lindau, J.W.; Moeny, M.J. Noise generated by ventilated supercavities. Noise Control Eng. J. 2015, 63, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skidmore, G.M.; Brungart, T.A.; Lindau, J.W.; Moeny, M.J. The control of ventilated supercavity pulsation and noise. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2016, 85, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K. Origin of the broad-band noise in acoustic cavitation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 93, 106276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, N.M.; Riahi, M.; Valipour, A.; Raeyatpishe, M.M.; Molavi, E. Analytical and experimental study of hydrodynamic and hydroacoustic effects of air injection flow rate in ventilated supercavitation. Ocean Eng. 2015, 95, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, C.W.; Nichols, B.D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries. J. Comput. Phys. 1981, 39, 201–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, J. Instationaer Kavitierende Stroemungen-Ein Neues Modell, Basierend auf Front Capturing VOF und Blasendynamik. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universitaet Kalrsruhe, Karlsruhe, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Spurk, J. On the gas loss from ventilated supercavities. Acta Mech. 2002, 155, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



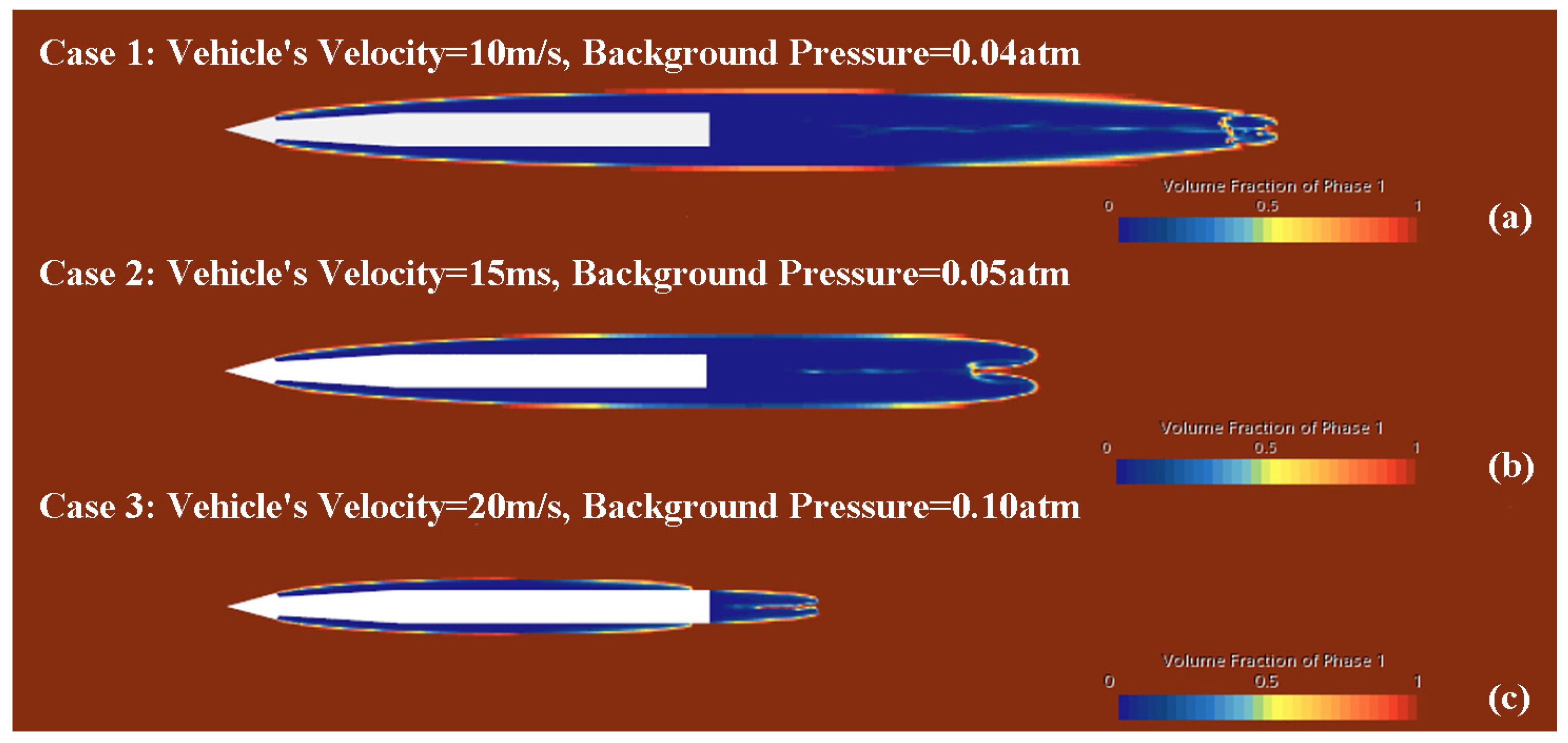





| Case | Vehicle Speed (m/s) | Background Pressure (atm) | Cavitation Number | Cavitation Flow’s Length (m) | Cavitation Flow’s Thickness (m) | Time Step (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.00 | 0.04 | 1.03 × 10 | 4.83 | 0.13 | 50 |
| 2 | 15.00 | 0.05 | 1.36 × 10 | 3.70 | 0.11 | 5 |
| 3 | 20.00 | 0.10 | 3.31 × 10 | 2.01 | 0.06 | 50 |
| Case | Vehicle’s Speed (m/s) | Background Pressure (atm) | Cavitation Number | Ventilation Flow (kg/s) | Ventilation Rate | Cavitation Flow’s Length (m) | Cavitation Flow’s Thickness (m) | Time Step (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 10.00 | 0.10 | 1.32 × 10 | 0.10 | 2.62 × 10 | 1.40 | 0.04 | 50 |
| 5 | 10.00 | 0.10 | 1.32 × 10 | 0.30 | 7.85 × 10 | 2.65 | 0.07 | 5 |
| Case | Vehicle’s Speed (knot) | Diving Depth (m) | Cavitation Number | Cavitation Flow’s Length (m) | Cavitation Flow’s Thickness (m) | Time Step (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 200.00 | 0.00 | 1.85 × 10 | 1.81 | 0.05 | 10 |
| 7 | 250.00 | 10.00 | 2.37 × 10 | 3.51 | 0.10 | 5 |
| Case | Vehicle’s Speed (m/s) | Diving Depth (m) | Cavitation Number | Ventilation Flow (kg/s) | Ventilation Rate | Cavitation Flow’s Length (m) | Cavitation Flow’s Thickness (m) | Time Step (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 160.00 | 20 | 8.68 × 10 | 0.80 | 2.54 × 10 | 2.78 | 0.07 | 5 |
| 9 | 160 | 20 | 8.68 × 10 | 1.20 | 3.81 × 10 | 4.49 | 0.12 | 5 |
| 10 | 180 | 5 | 3.43 × 10 | 0.80 | 2.26 × 10 | 2.81 | 0.07 | 5 |
| 11 | 180 | 5 | 3.43 × 10 | 1.20 | 3.39 × 10 | 2.74 | 0.07 | 5 |
| 12 | 180 | 15 | 5.72 × 10 | 0.40 | 1.13 × 10 | 1.58 | 0.04 | 10 |
| 13 | 180 | 15 | 5.72 × 10 | 0.80 | 2.26 × | 2.58 | 0.07 | 5 |
| 14 | 180 | 15 | 5.72 × 10 | 1.20 | 3.39 × 10 | 3.07 | 0.08 | 5 |
| 15 | 180 | 20 | 6.86 × 10 | 0.40 | 1.13 × 10 | 1.06 | 0.04 | 5 |
| 16 | 180 | 20 | 6.86 × 10 | 0.80 | 2.26 × 10 | 2.46 | 0.07 | 5 |
| 17 | 180 | 20 | 6.86 × 10 | 1.20 | 3.39 × 10 | 3.41 | 0.10 | 5 |
| 18 | 200 | 0 | 1.85 × 10 | 0.60 | 1.53 × 10 | 20 | ||
| 19 | 200 | 20 | 5.56 × 10 | 0.80 | 2.03 × 10 | 1.24 | 0.04 | 5 |
| 20 | 200 | 20 | 5.56 × 10 | 1.20 | 3.05 × 10 | 2.73 | 0.07 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P. A Numerical Investigation of Supercavitation Vehicle’s Hydrodynamic Noise. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051004
Ye J, Zhang J, Wang Y, Zhao P. A Numerical Investigation of Supercavitation Vehicle’s Hydrodynamic Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(5):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051004
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jiacheng, Jing Zhang, Yuebing Wang, and Peng Zhao. 2023. "A Numerical Investigation of Supercavitation Vehicle’s Hydrodynamic Noise" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 5: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051004
APA StyleYe, J., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., & Zhao, P. (2023). A Numerical Investigation of Supercavitation Vehicle’s Hydrodynamic Noise. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(5), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11051004






