Numerical Reconstruction in Maritime Archaeology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. On Numerical Reconstruction
4. Numerical Reconstruction in Maritime Archaeology
- Strength of amphorae;
- Strength of wooden structures and structural details;
- Simulation of a ship sailing, capsizing and sinking;
- Shipwreck forensics;
- Variations in the shape of the ship’s hull.
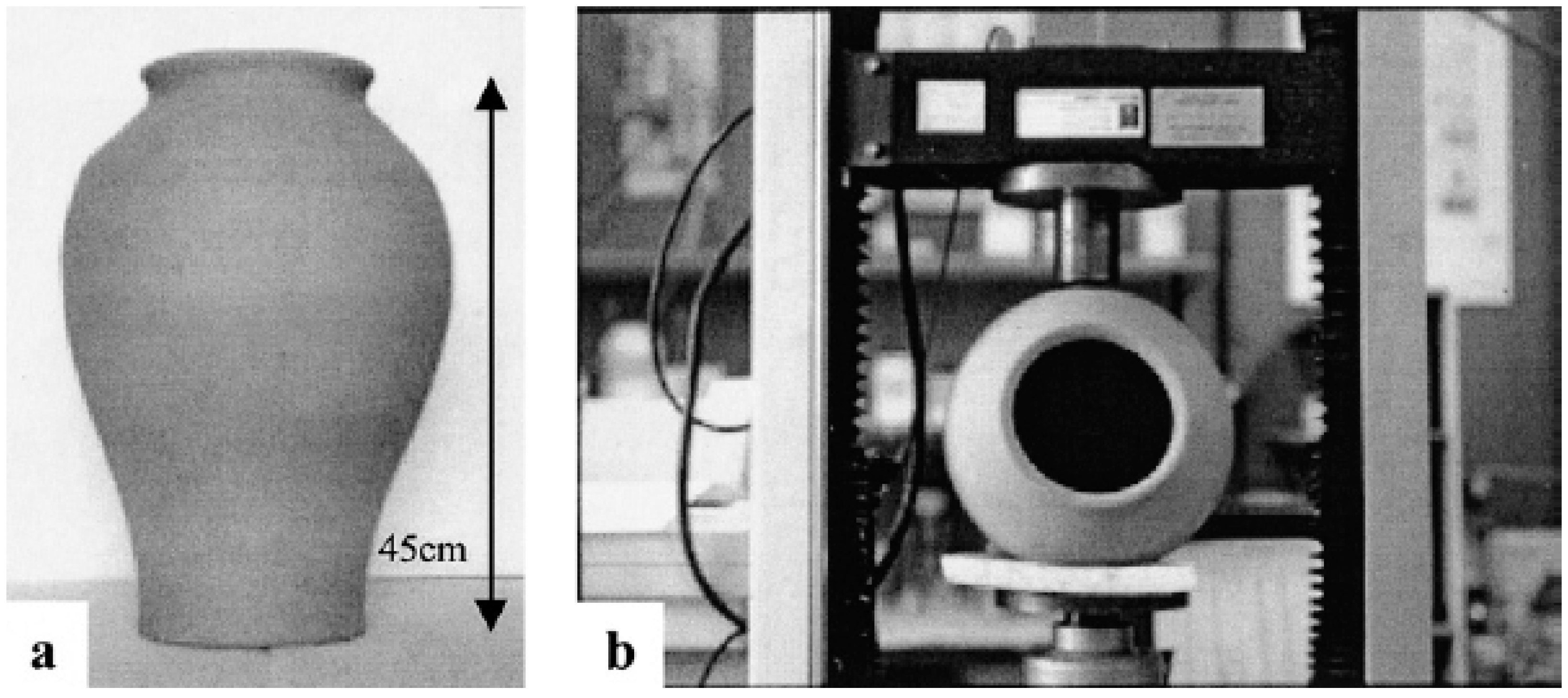
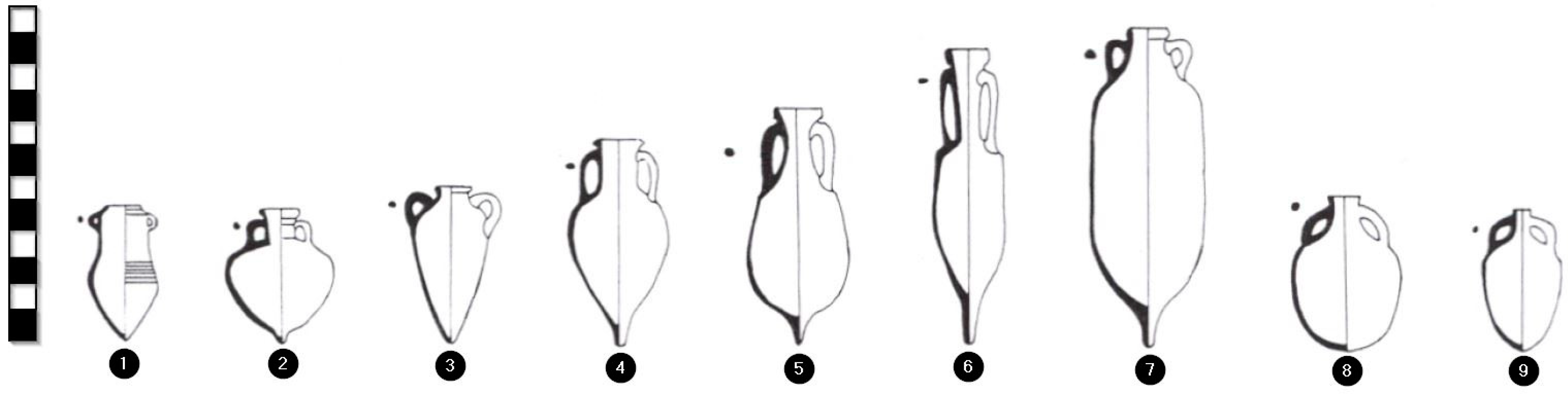
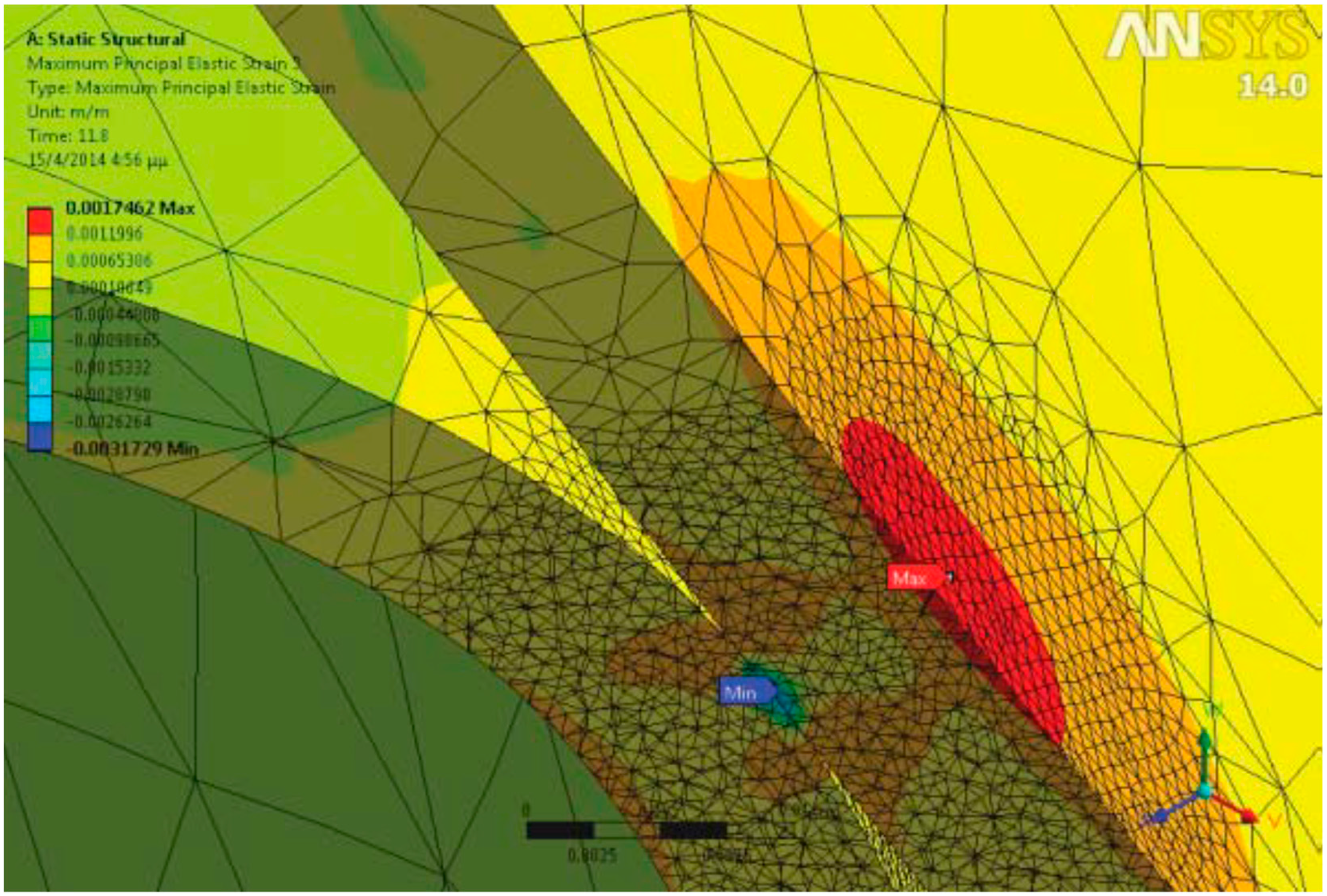
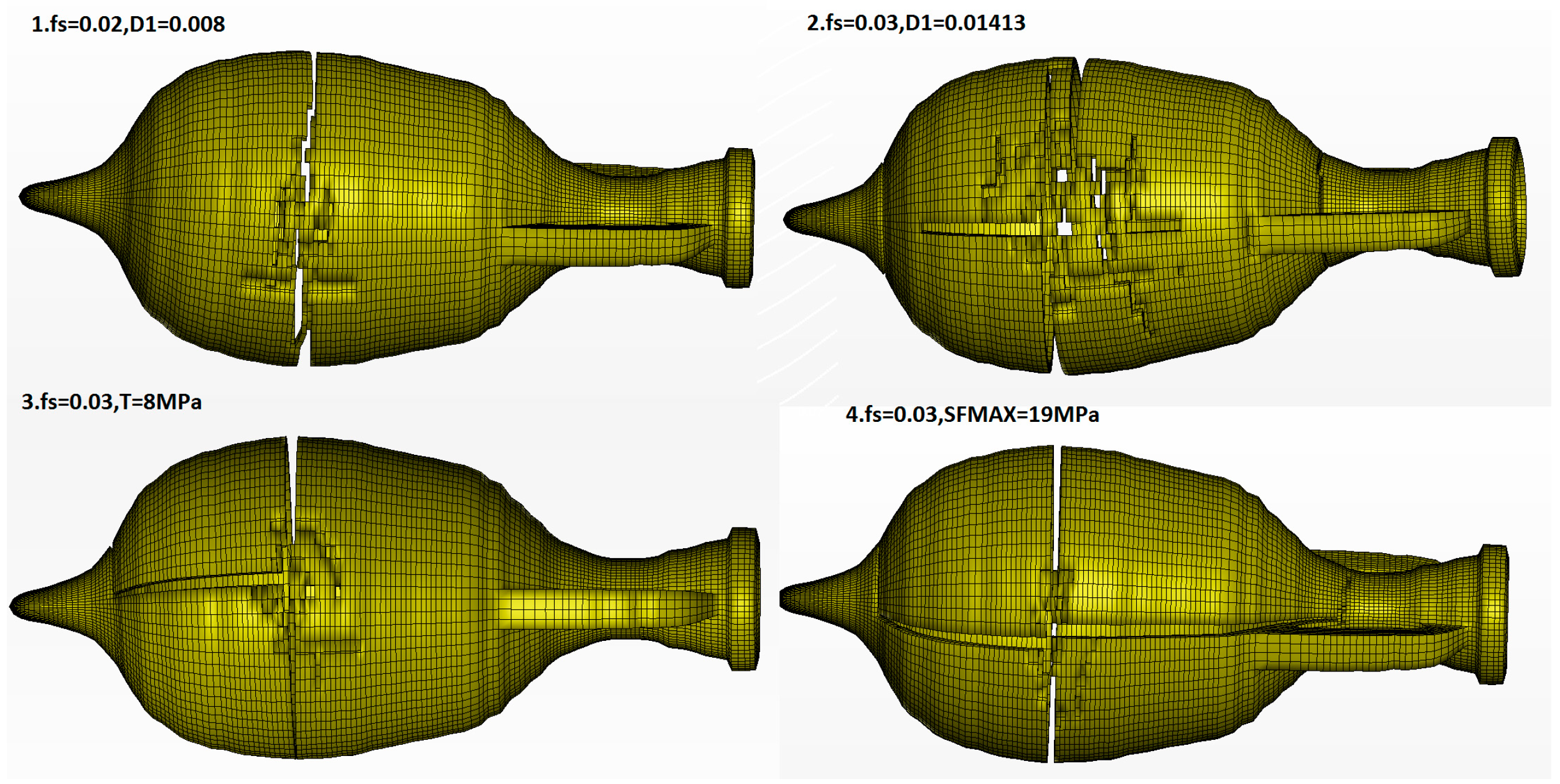
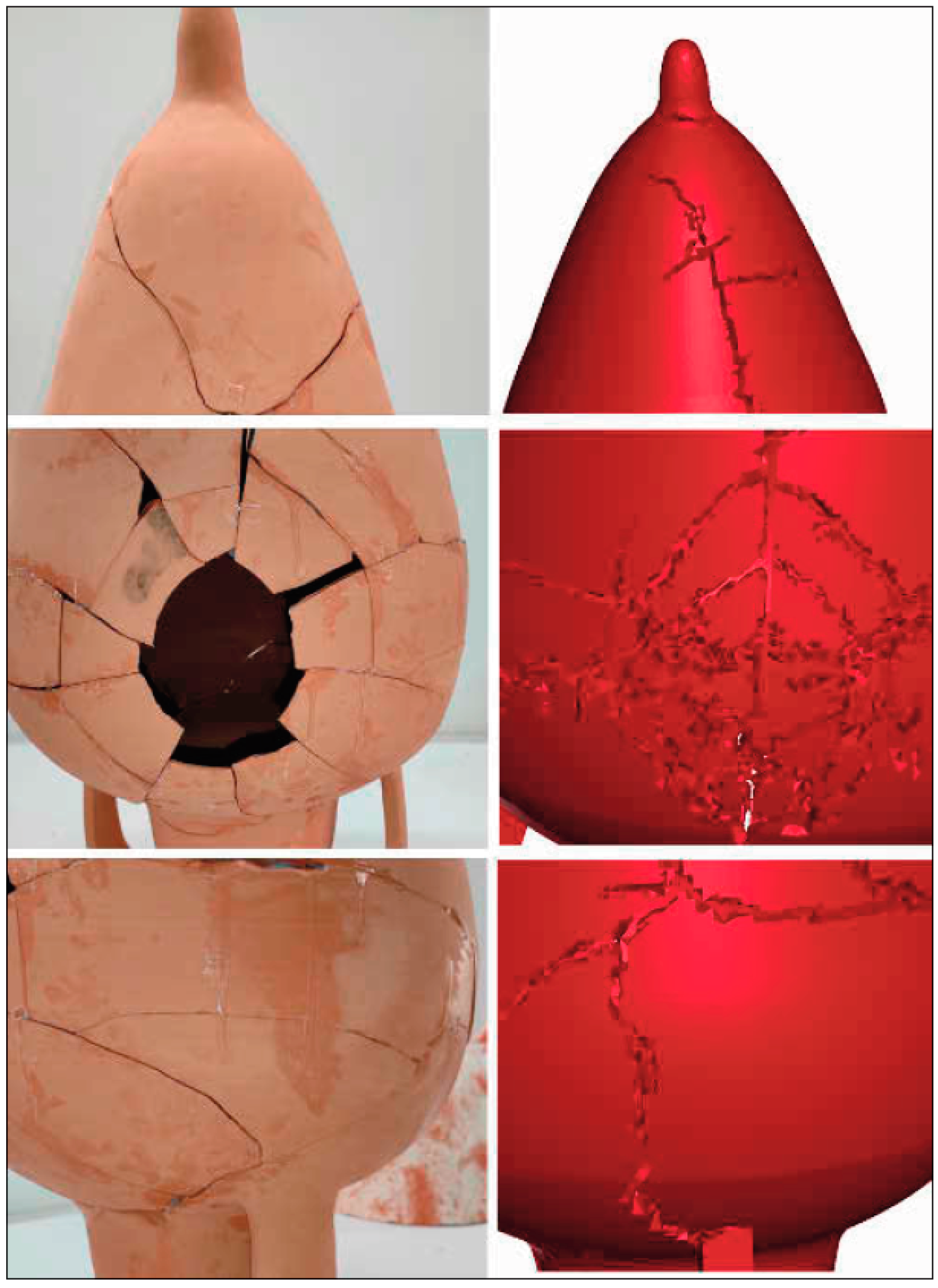
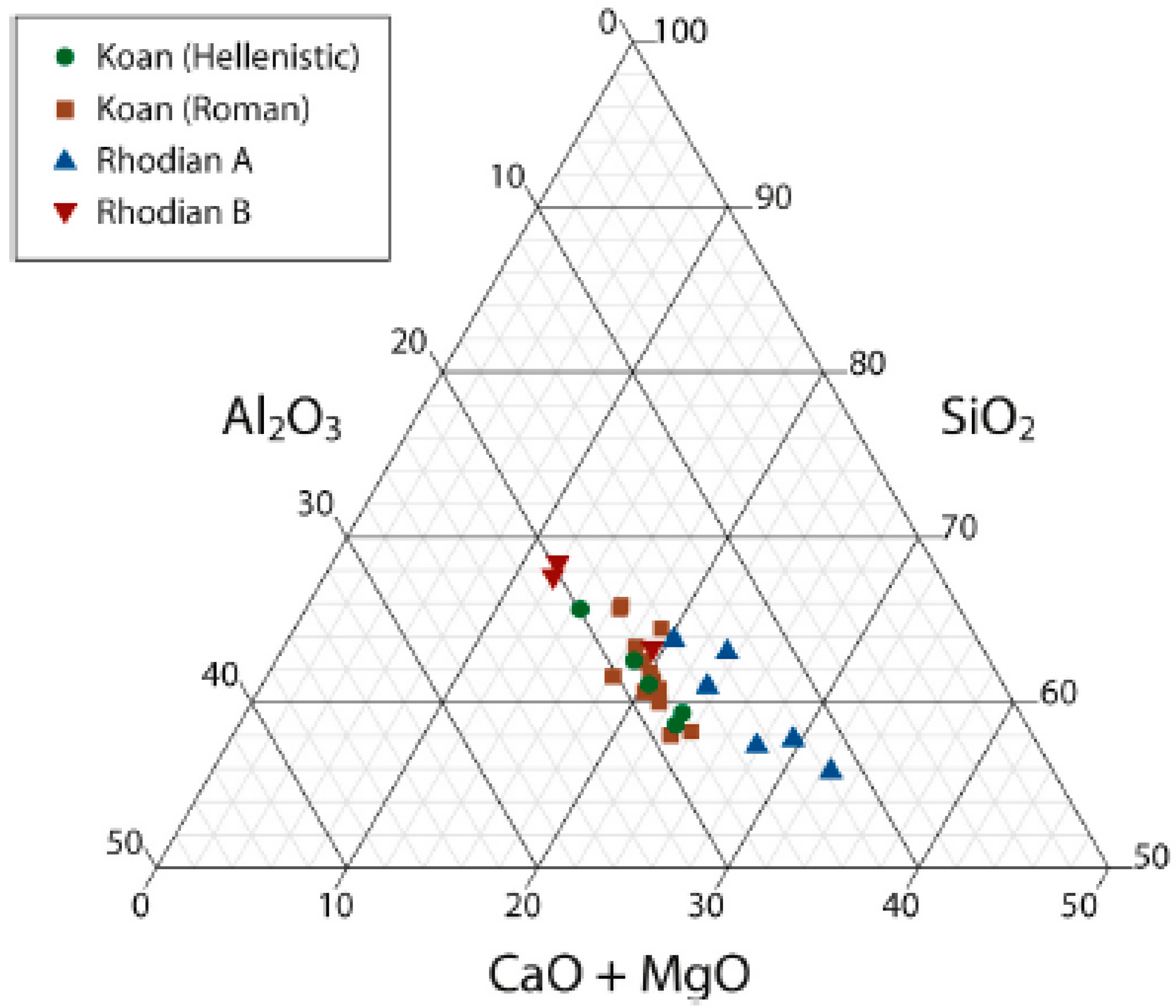
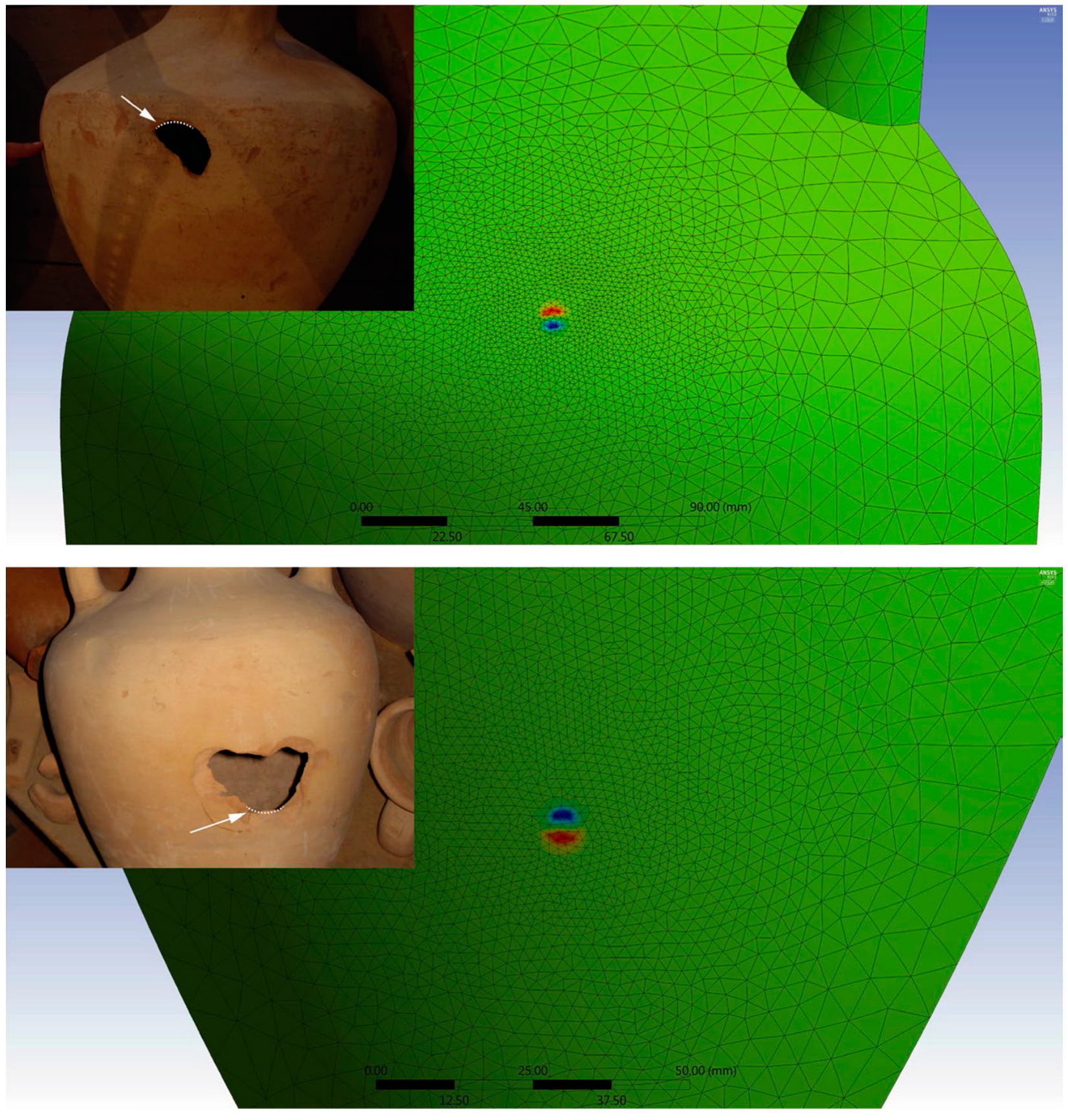
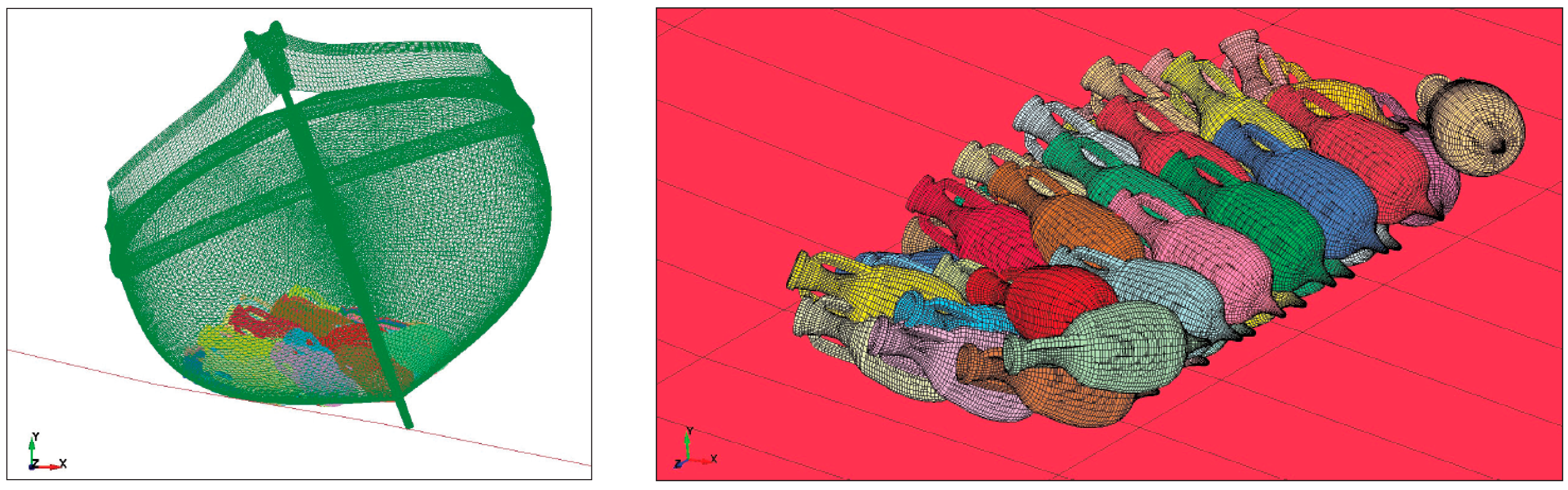
4.1. Strength of the Amphorae
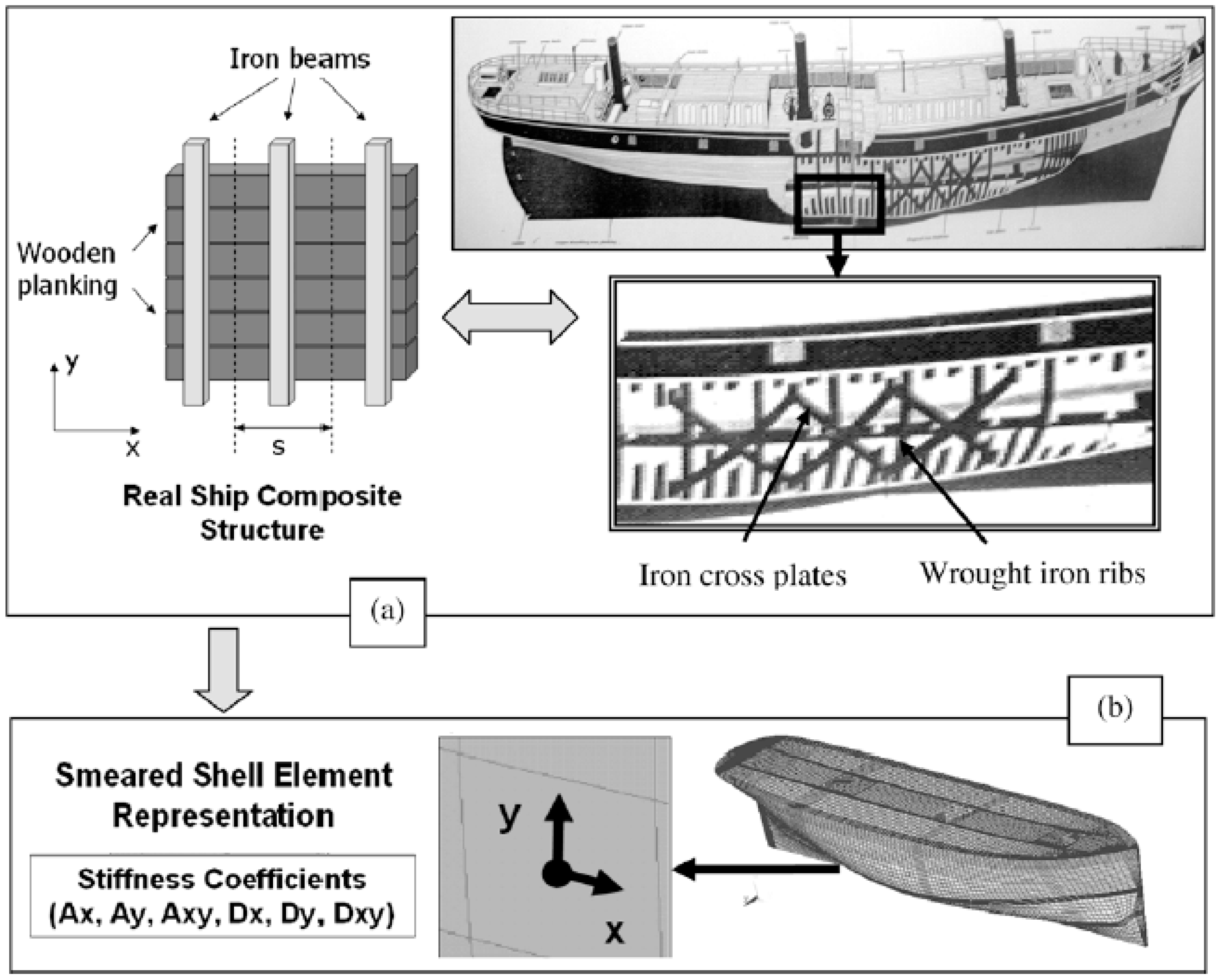
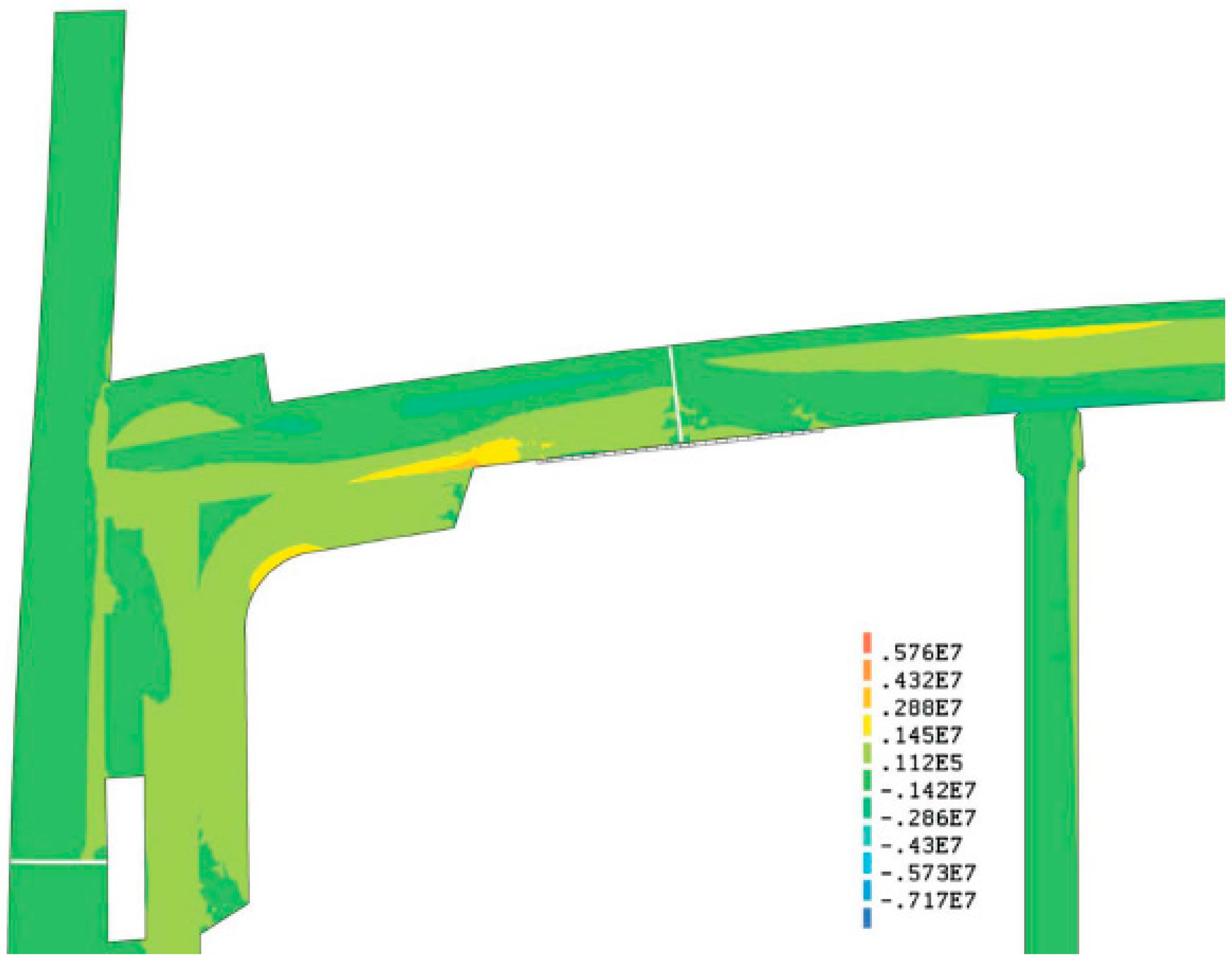
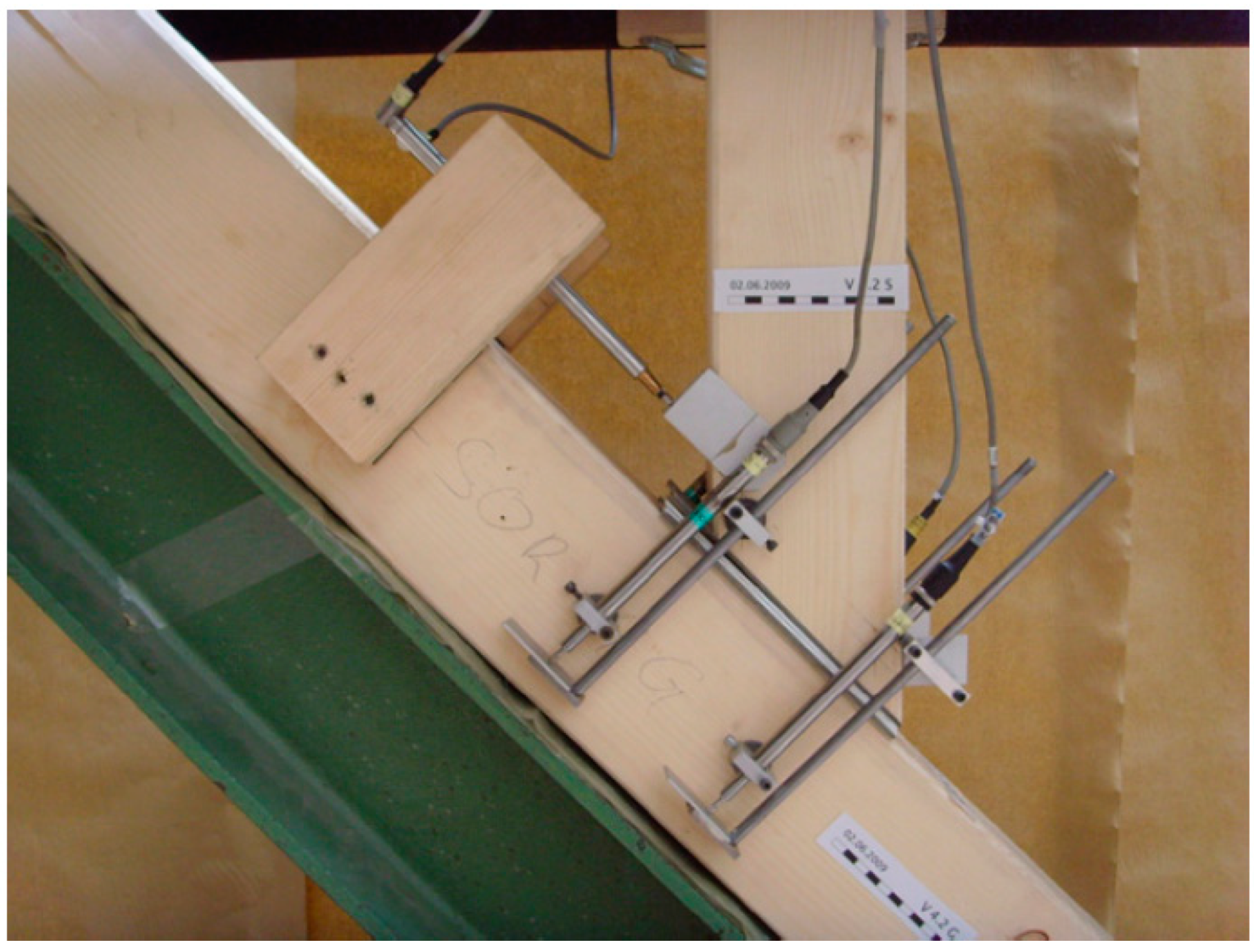
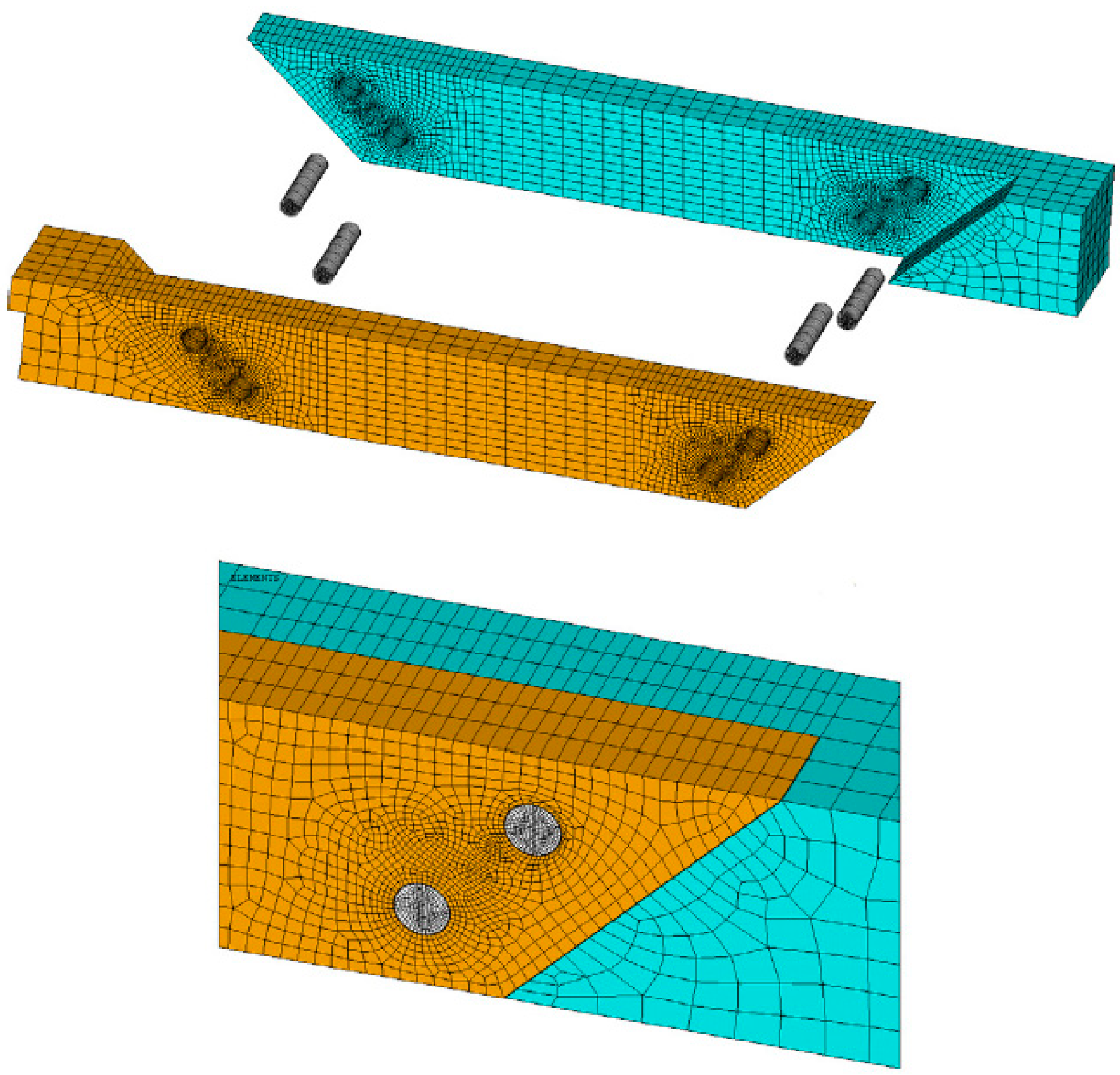
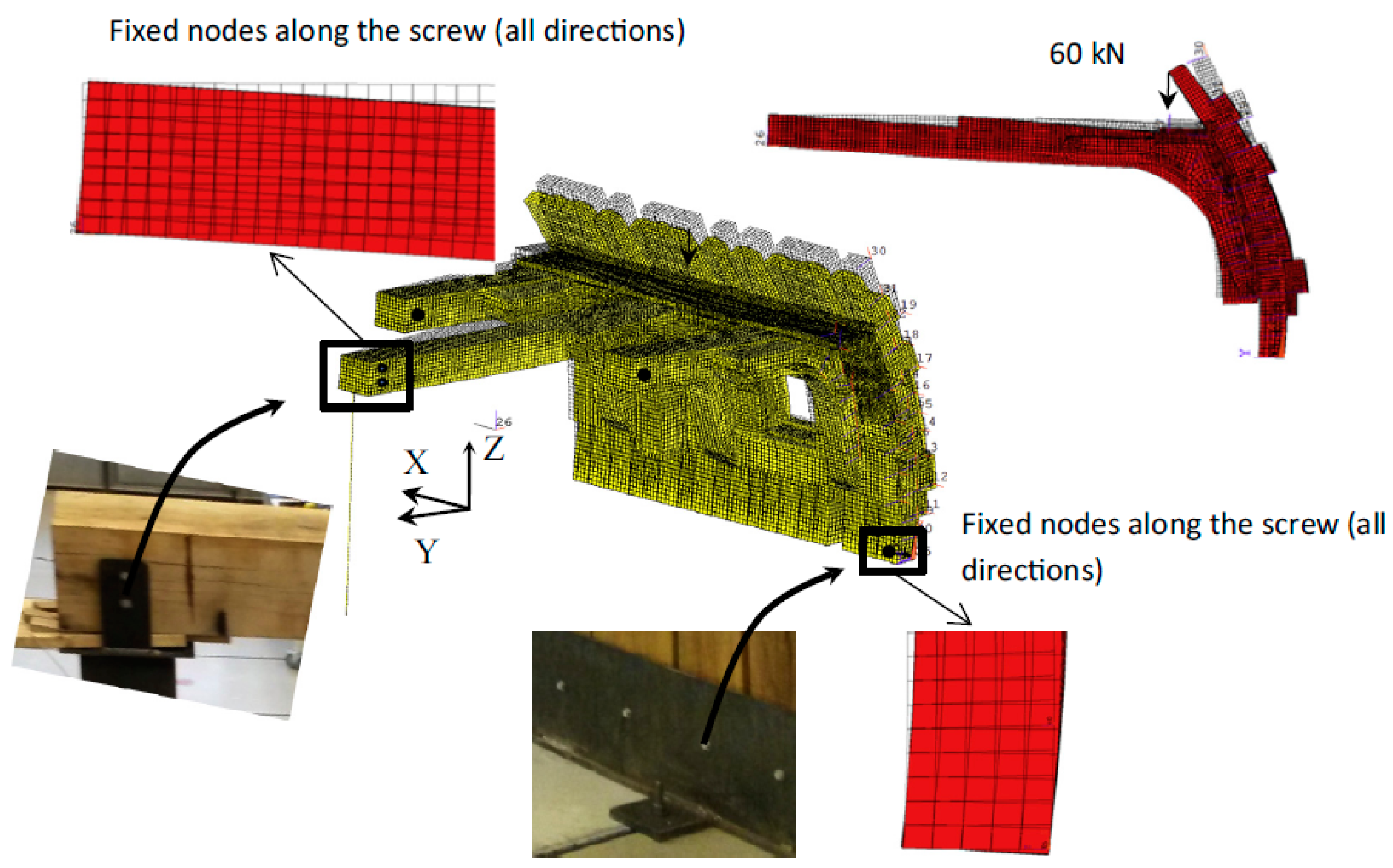
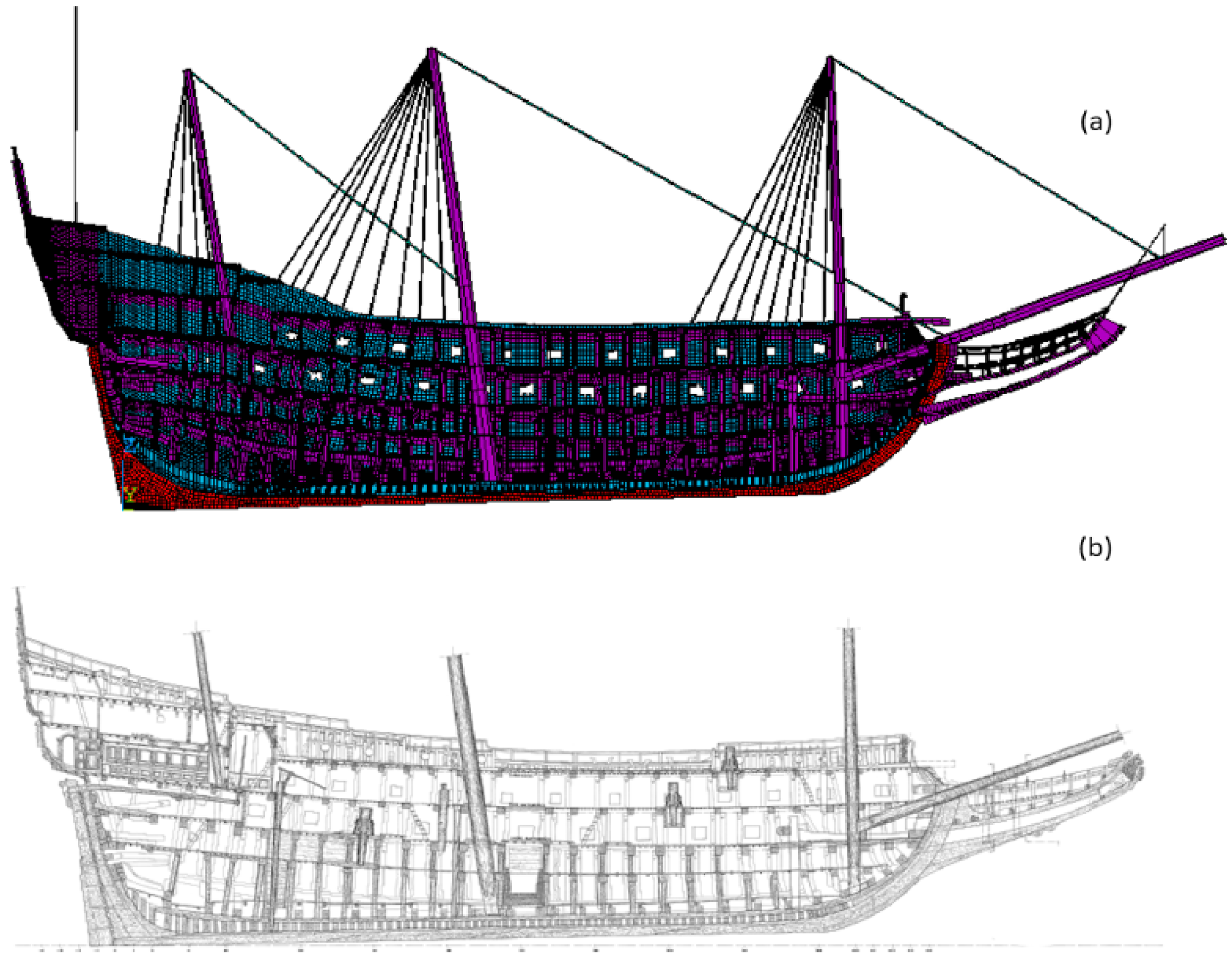
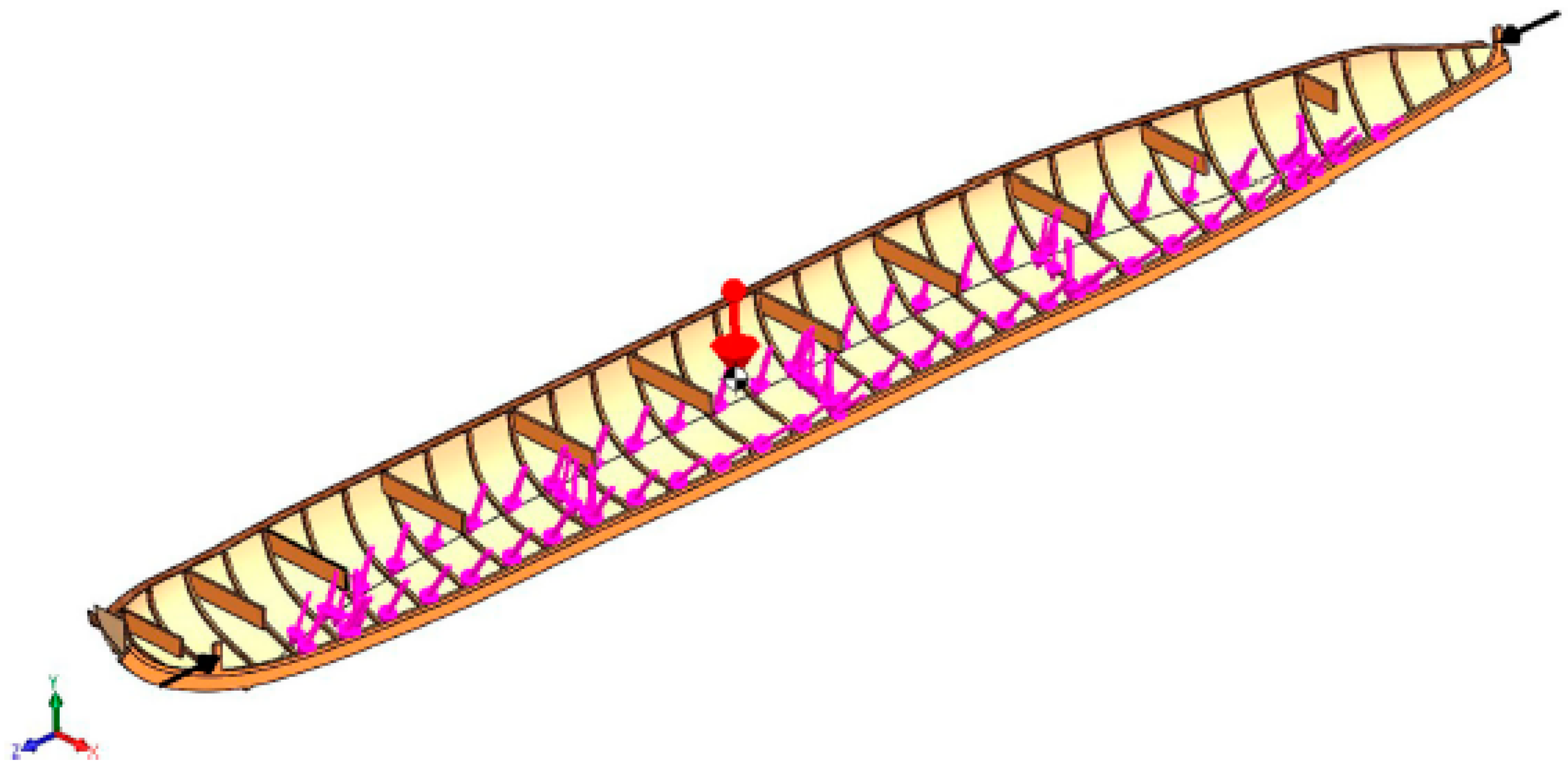
4.2. Strength of Wooden Structures and Structural Details
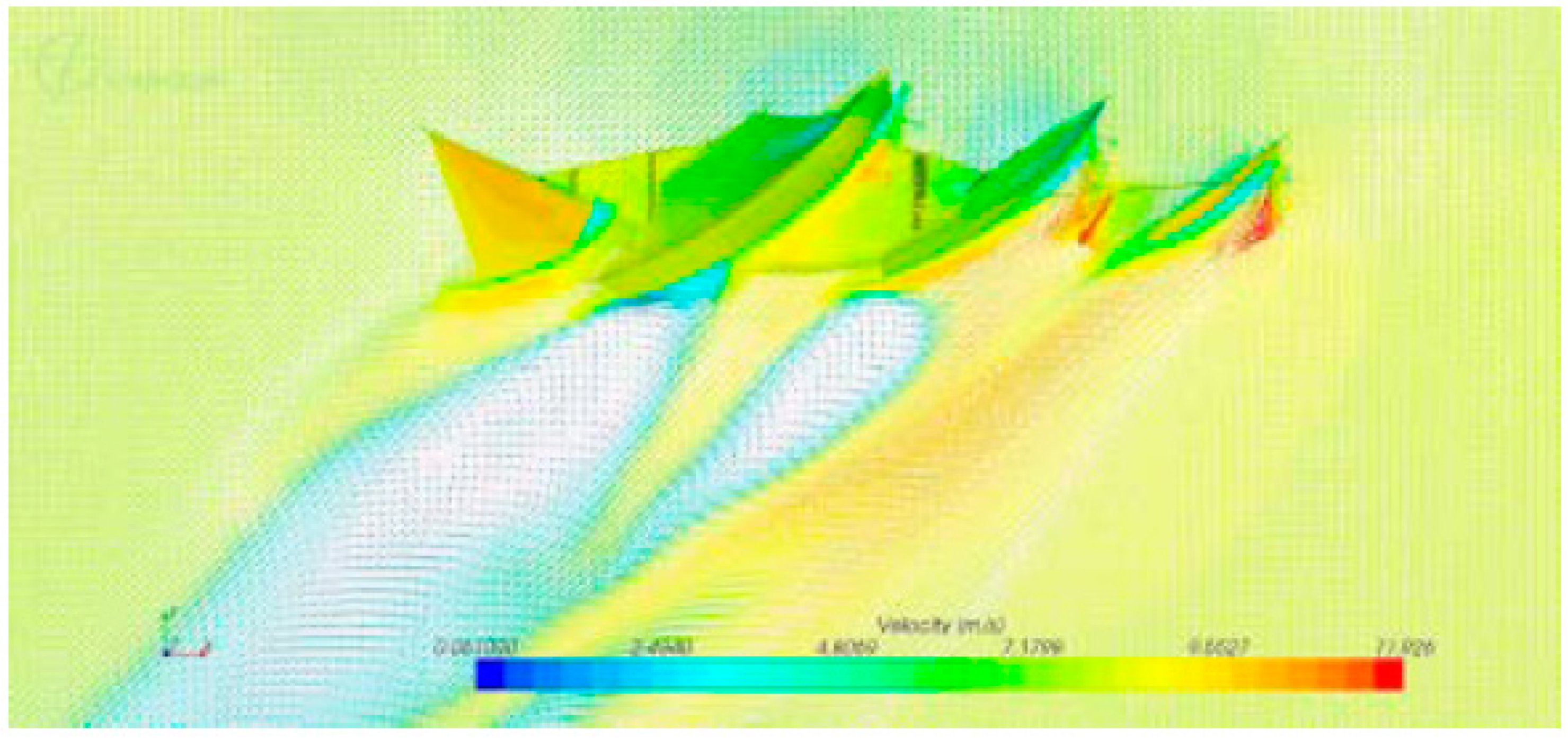
4.3. Simulation of Sailing, Capsizing and Sinking of the Ship
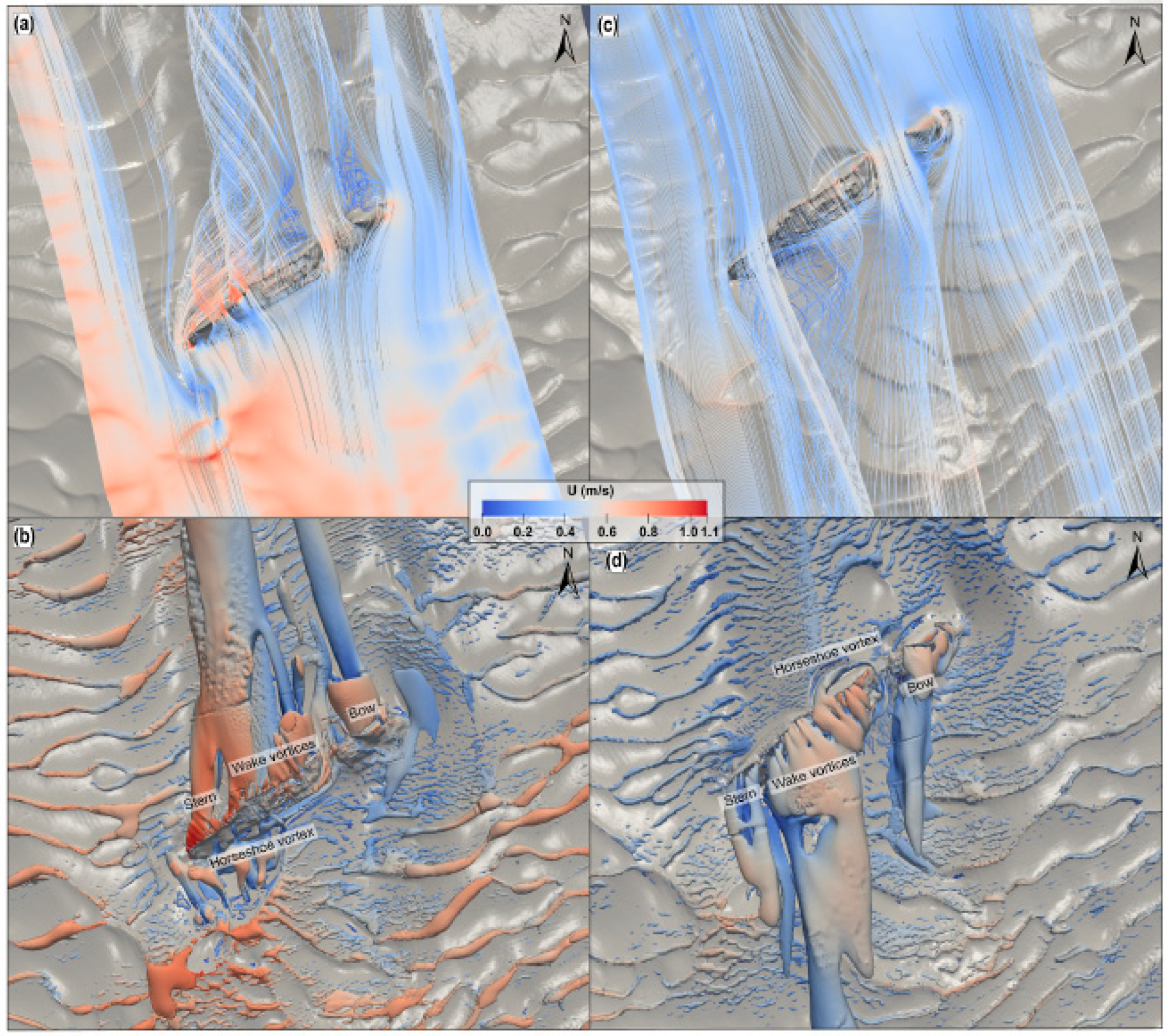
4.4. Shipwreck Forensics
- It is necessary to know the situation at the site in detail: status of the shipwreck, position and orientation, bathymetry, etc.;
- It is necessary to know environmental conditions, mainly sea currents;
- Validation of the results is difficult, since any change at the site that may confirm the results occurs only over time, and sometimes over extended periods.
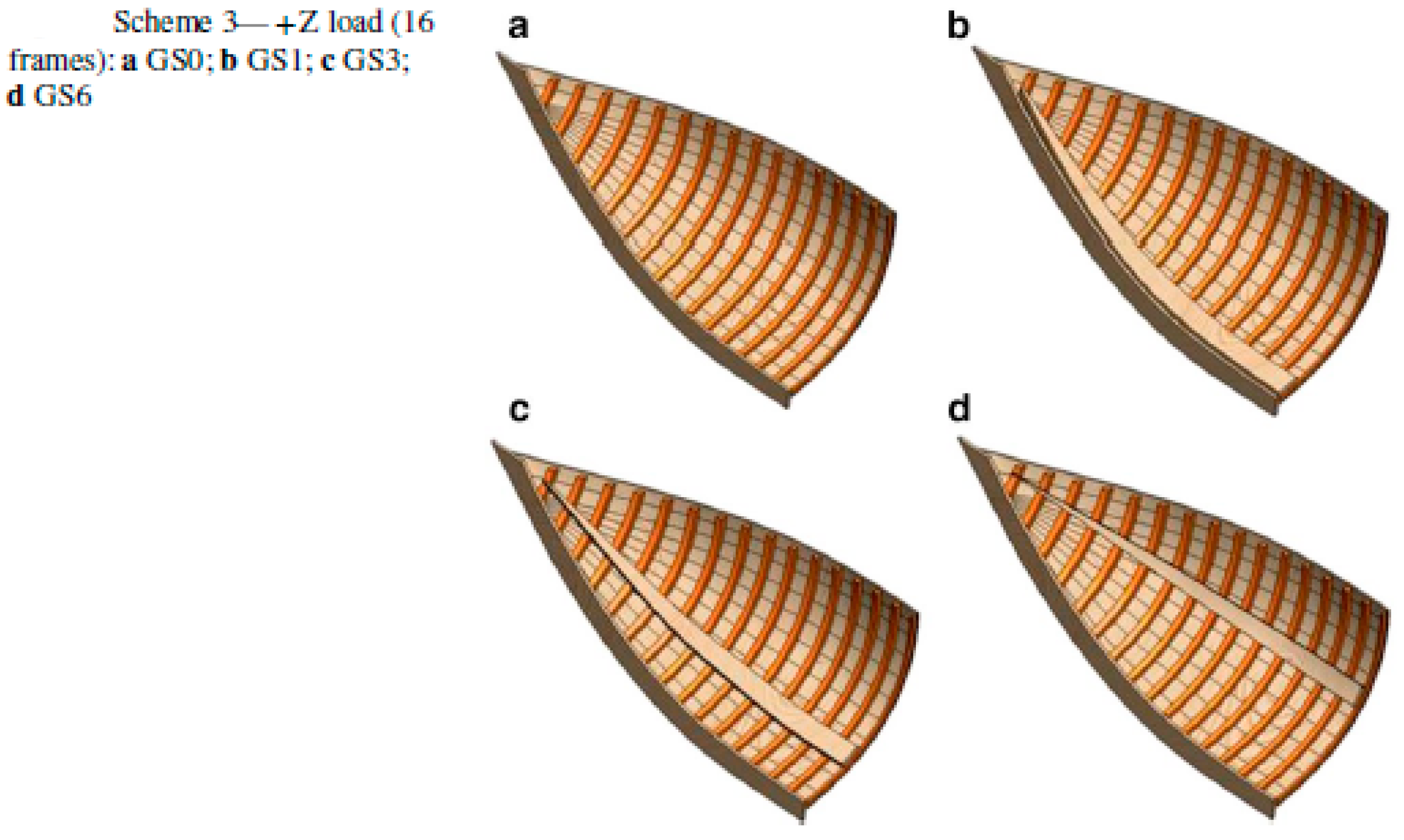
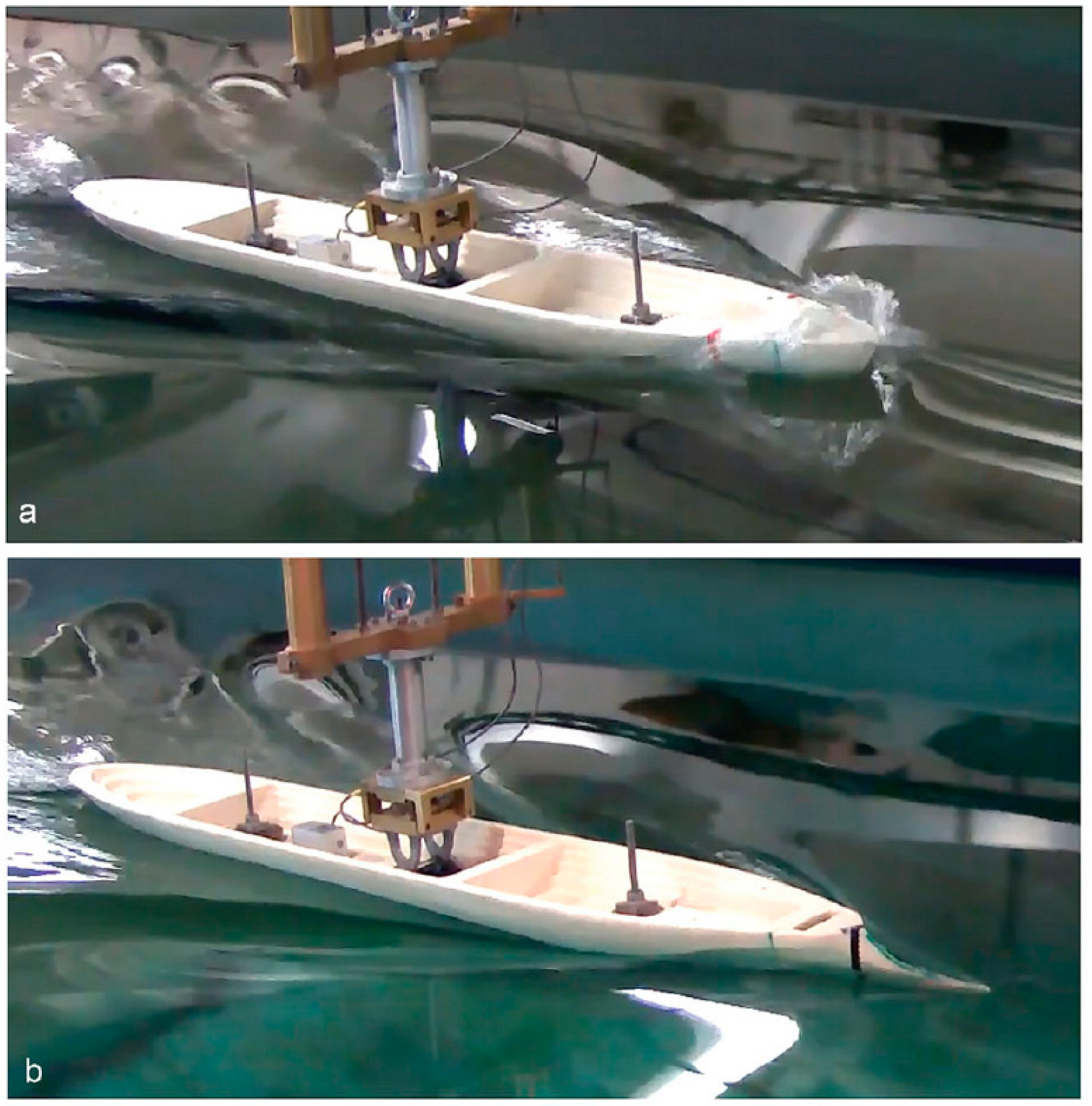
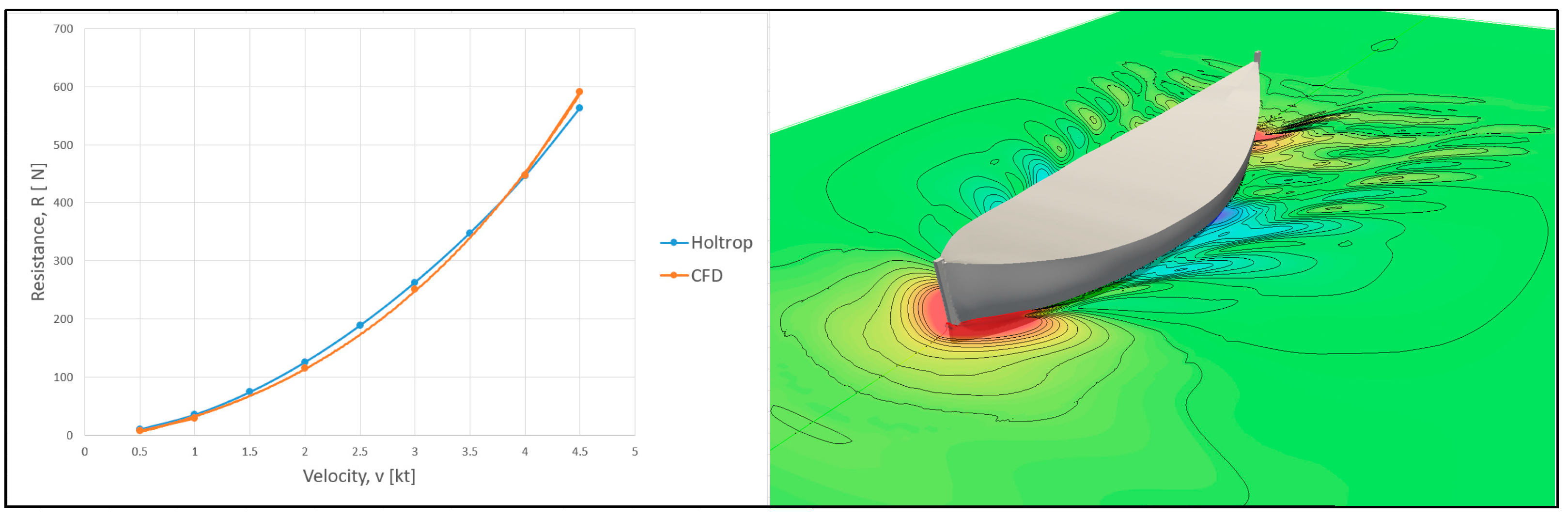
4.5. Ship Hull Form Variation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKinnon, J.F. Archaeology and the Emergence of Fields: Maritime. In Encyclopedia of Global Archaeology; Smith, C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 414–420. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbins, D.; Adams, J. Shipwrecks and Maritime Archaeology. World Archaeol. 2001, 32, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Li, S.; Park, H.S. Eighty Years of the Finite Element Method: Birth, Evolution, and Future. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2022, 29, 4431–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwick, D. Conceptual Evolution in Ancient Shipbuilding: An Attempt to Reinvigorate a Shunned Theoretical Framework. In Interpreting Shipwrecks: Maritime Archaeology Approaches; Adams, J., Johan, R., Eds.; The Highfield Press: Southampton, UK, 2014; pp. 46–71. ISBN 978-0-9926336-3-9. [Google Scholar]
- Twede, D. The Packaging Technology and Science of Ancient Transport Amphoras. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2002, 15, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molland, A.F. The Maritime Engineering Reference Book: A Guide to Ship Design, Construction and Operation; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2008; ISBN 978-0-7506-8987-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zienkiewicz, O.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Zhu, J.L. Finite Element Method: Its Basis and Fundamentals, 7th ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 978-1-85617-633-0. [Google Scholar]
- Budynas, R.; Sadegh, A. Roark’s Formulas for Stress and Strain, 9th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-260-45375-1. [Google Scholar]
- Versteeg, H.; Malalasekera, W. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite Volume Method, 2nd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-13-127498-3. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.; Huang, S.; Guedes Soares, C. Viscous Fluid–Flexible Structure Interaction Analysis on Ship Springing and Whipping Responses in Regular Waves. J. Fluids Struct. 2021, 106, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, A.B.; Demesticha, S. Mediterranean Connections Maritime Transport Containers and Seaborne Trade in the Bronze and Early Iron Ages, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-62958-354-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kilikoglou, V.; Vekinis, G. Failure Prediction and Function Determination of Archaeological Pottery by Finite Element Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2002, 29, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T. A Course of Lectures on Natural Philosophy and the Mechanical Arts; Joseph Johnson: London, UK, 1807; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.R.H.; Ashby, M.F. Elastic Moduli. In Engineering Materials 1; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 31–47. ISBN 978-0-08-102051-7. [Google Scholar]
- Tsantini, E.; Jiménez-Piqué, E.; Montana, G.; Randazzo, L. Strength of Pre-Roman Amphorae: Comparison of the Different Types. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2015, 2, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, N.S.; Vekinis, G.; Kilikoglou, V. Impact Resistance of Archaeological Ceramics: The Influence of Firing and Temper. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 7, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić Rossi, I.; Senjanović, I.; Rudan, S.; Indof, J. Podrijetlo i Funkcija Šiljatoga Dna Amfora. Pril. Inst. Arheol. Zagreb. 2004, 21, 91–105. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, A.; Georgopoulou, V.; Nodarou, E.; Kilikoglou, V. Koan Amphorae from Halasarna—Investigations in a Hellenistic Amphora Production Centre. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, A.M.; Graziano, T.; Andaloro, E.; La Marca, A.; Colelli, C.; Crisci, G.M.; Barrese, E.; Bocci, M. Archaeometric Characterization of Amphorae and Bricks of Imperial Age Found in a Roman Villa near the Luzzi Town (Cosenza, Calabria, Italy). Period. Mineral. 2011, 80, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, A.; Kilikoglou, V. Breaking Pots—Simulating Design Failures of Transport Amphorae by Using the Finite Element Method (FEM). In Proceedings of the 1st CAA GR Conference, Rethymno, Crete, Greece, 6 March 2014; pp. 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Sviličić, Š.; Rudan, S.; Radić Rossi, I. Analysis of Amphorae Resistance to Ruptures and Cracks. Archaeol. Maritima Mediterr. Int. J. Underw. Archaeol. 2022, 19, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, A.; Vekinis, G.; Kilikoglou, V. Modeling of Biaxial Flexure Tests of Transport Amphorae with the Finite Element Method: Fracture Strength, Deformation and Stress Distribution. Results Eng. 2022, 15, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, A.; Kilikoglou, V. Digital Modeling of Function and Performance of Transport Amphorae. Int. J. Ceramic. Eng. Sci. 2020, 2, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uršić, J. Čvrstoća Broda, I. Dio; Sveučilišna Naklada d.o.o.: Zagreb, Croatia, 1991; ISBN 86-7819-001-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner, R.; Lambert, A. Steam, Steel and Shellfire: The Steam Warship 1815–1905; Conway Maritime Press: London, UK, 1992; ISBN 0851775640. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, Y.; Fujimoto, R.; Hagiwara, T. Shell Strength Tests and Structural Analysis of Large Wooden Ships. J. Soc. Nav. Archit. Jpn. 1990, 167, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, K. Documentation and Analysis of Ancient Ships. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Lyngby, Denmark, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mackerle, J. Finite Element Analyses in Wood Research: A Bibliography. Wood Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 579–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.; Dawson, P. Using Finite Element Methods to Analyze Ancient Architecture: An Example from the North American Arctic. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.W.; Zhu, E.C. Finite Element Modelling of Anisotropic Elasto-Plastic Timber Composite Beams with Openings. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyanov, S.; Mason, P.; Bailey, C. Smeared Shell Modelling Approach for Structural Analysis of Heritage Composite Structures—An Application to the Cutty Sark Conservation. Comput. Struct. 2010, 88, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, C.; Dabbagh, A. Finite Element Analysis of the Vasa’s Bottom Structure. Master’s Thesis, University of Skovde, Skovde, Sweeden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- del Coz Díaz, J.J.; García Nieto, P.J.; Lozano Martínez-Luengas, A.; Suarez Domínguez, F.J.; Domínguez Hernández, J. Non-Linear Numerical Analysis of Plywood Board Timber Connections by DOE-FEM and Full-Scale Experimental Validation. Eng. Struct. 2013, 49, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, S.; Bertolini-Cestari, C.; Fioravanti, M.; Chiabrera, E. Numerical Modeling and Assessment of the Ebe Schooner-Brig. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2012, 6, 453–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melisan, J. Strength Analysis of Traditional Ships in Efforts To Improve Sea Transportations Safety in Indonesia. Int. J. Eng. 2012, 12, 878–883. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, H.; Eisenhut, L.; Seim, W. Multi-Mode Failure of Form-Fitting Timber Connections—Experimental and Numerical Studies on the Tapered Tenon Joint. Eng. Struct. 2013, 48, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z. Traditional Chinese Wood Structure Joints with an Experiment Considering Regional Differences. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2014, 8, 224–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciszewska-Kędzior, A.; Kunecký, J.; Hasníková, H.; Sebera, V. Lapped Scarf Joint with Inclined Faces and Wooden Dowels: Experimental and Numerical Analysis. Eng. Struct. 2015, 94, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Qiu, H.; Lu, Y. Flexural Behaviour of Timber Dovetail Mortise–Tenon Joints. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milch, J.; Tippner, J.; Sebera, V.; Kunecký, J.; Kloiber, M.; Navrátil, M. The Numerical Assessment of a Full-Scale Historical Truss Structure Reconstructed with Use of Traditional All-Wooden Joints. J. Cult. Herit. 2016, 21, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajman, P.; Máca, J. Stiffness of Scarf Joints with Dowels. Comput. Struct. 2018, 207, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, R.; van Dijk, N.P.; Bjurhager, I.; Gamstedt, E.K. Comparison of Experimental Testing and Finite Element Modelling of a Replica of a Section of the Vasa Warship to Identify the Behaviour of Structural Joints. Eng. Struct. 2017, 147, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, R.; Alavyoon, N.; Ahlgren, A.; Gamstedt, E.K. Full Scale Finite Element Modelling and Analysis of the 17th-Century Warship Vasa: A Methodological Approach and Preliminary Results. Eng. Struct. 2021, 231, 111765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfman, N.; Cvikel, D.; Nishri, B. A Comparative Structural Analysis of Shell-First and Frame-Based Ship Hulls of the 1st Millennium AD. Nav. Eng. J. 2018, 130, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Helfman, N.; Nishri, B.; Cvikel, D. Finite Element Analysis of Shell-First and Longitudinally Reinforced Frame-Based Wooden Ships. J. Marit. Archaeol. 2019, 14, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliav, J.; Helfman, N. Lightweight Construction of an Athenian Trireme: A Feasibility Study. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2022, 51, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1995-1-1:2004; Eurocode 5: Design of Timber Structures—Part 1-1: General-Common Rules and Rules for Buildings. CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- Foecke, T.; Ma, L.; Russel, M.A.; Conlin, D.L.; Murphy, L.E. Investigating Archaeological Site Formation Processes on the Battleship USS Arizona Using Finite Element Analysis. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C. Windward Sailing Capabilities of Ancient Vessels. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2009, 38, 314–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasher, W.C.; Flaherty, L.S. CFD Analysis of the Survivability of a Square-Rigged Sailing Vessel. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2009, 3, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciortan, C.; Fonseca, N. Numerical Simulations of the Sails of a Xvith Century Portuguese Nau Marine 201. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering, Lisbon, Portugak, 28 September 2011; pp. 278–289. [Google Scholar]
- Stettler, J.W.; Thomas, B.S. Flooding and Structural Forensic Analysis of the Sinking of the RMS Titanic. Ships Offshore Struct. 2013, 8, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kery, S. Marine Forensics: The Art and Science of Simulating Ships In Storm Conditions. In Proceedings of the Interservice/Industry Training, Simulation, and Education Conference (I/ITSEC) 2017, Orlando, FL, USA, 27 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah, B.V.; Thampi, S.G.; Rambabu, N.; Mustafa, V.; Akbar, M.A. Characterization and CFD Analysis of Traditional Vessels of Kerala. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2020, 9, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudan, S.; Radić Rossi, I. Numerička Simulacija Potonuća Broda na Temelju Arheoloških Zapisa. Archaeol. Adriat. 2020, 14, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawsitt, S.; Hobberstad, L.C. Computational Fluid Dynamics: Floating a Digital Barcode 02. Archaeonautica 2021, 21, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, T.A.G.; Quinn, R. The Role of Computational Fluid Dynamics in Understanding Shipwreck Site Formation Processes. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 45, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R.; Smyth, T.A.G. Processes and Patterns of Flow, Erosion, and Deposition at Shipwreck Sites: A Computational Fluid Dynamic Simulation. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2018, 10, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Montblanc, T.; Izquierdo, A.; Quinn, R.; Bethencourt, M. Waves and Wrecks: A Computational Fluid Dynamic Study in an Underwater Archaeological Site. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majcher, J.; Quinn, R.; Smyth, T.; Plets, R.; McGonigle, C.; Westley, K.; Sacchetti, F.; Coughlan, M. Using Difference Modelling and Computational Fluid Dynamics to Investigate the Evolution of Complex, Tidally Influenced Shipwreck Sites. Ocean Eng. 2022, 246, 110625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, W.M.; Ferreiro, L.D.; Vardalas, J.; Royal, J.G. Cutwaters Before Rams: An Experimental Investigation into the Origins and Development of the Waterline Ram: An Experiment in Ancient Cutwater Hydrographics. Int. J. Naut. Archaeol. 2017, 46, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerat, G.; Rudan, S.; Zamarin, A.; Rossi, I.R. Uncertainty in the Reconstruction of the Ancient Ship Hull and Its Impact on Sailing Characteristics. In Proceedings of the 16th International Symposium on Boat and Ship Archeology, Zadar, Croatia, 26 September–1 October 2021. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rudan, S.; Sviličić, Š.; Bolf, D.; Rossi, I.R. Numerical Reconstruction in Maritime Archaeology. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061184
Rudan S, Sviličić Š, Bolf D, Rossi IR. Numerical Reconstruction in Maritime Archaeology. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(6):1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061184
Chicago/Turabian StyleRudan, Smiljko, Šimun Sviličić, Davor Bolf, and Irena Radić Rossi. 2023. "Numerical Reconstruction in Maritime Archaeology" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 6: 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061184
APA StyleRudan, S., Sviličić, Š., Bolf, D., & Rossi, I. R. (2023). Numerical Reconstruction in Maritime Archaeology. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(6), 1184. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11061184







