Spatiotemporal Nutrient Patterns, Stoichiometry, and Eutrophication Assessment in the Tieshan Bay Coastal Water, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Field Monitoring
2.2. Data Processing and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Method
2.3.1. Assessment of DIN and DIP Pollution Degrees in Tieshan Bay
2.3.2. EI Assessment in Tieshan Bay
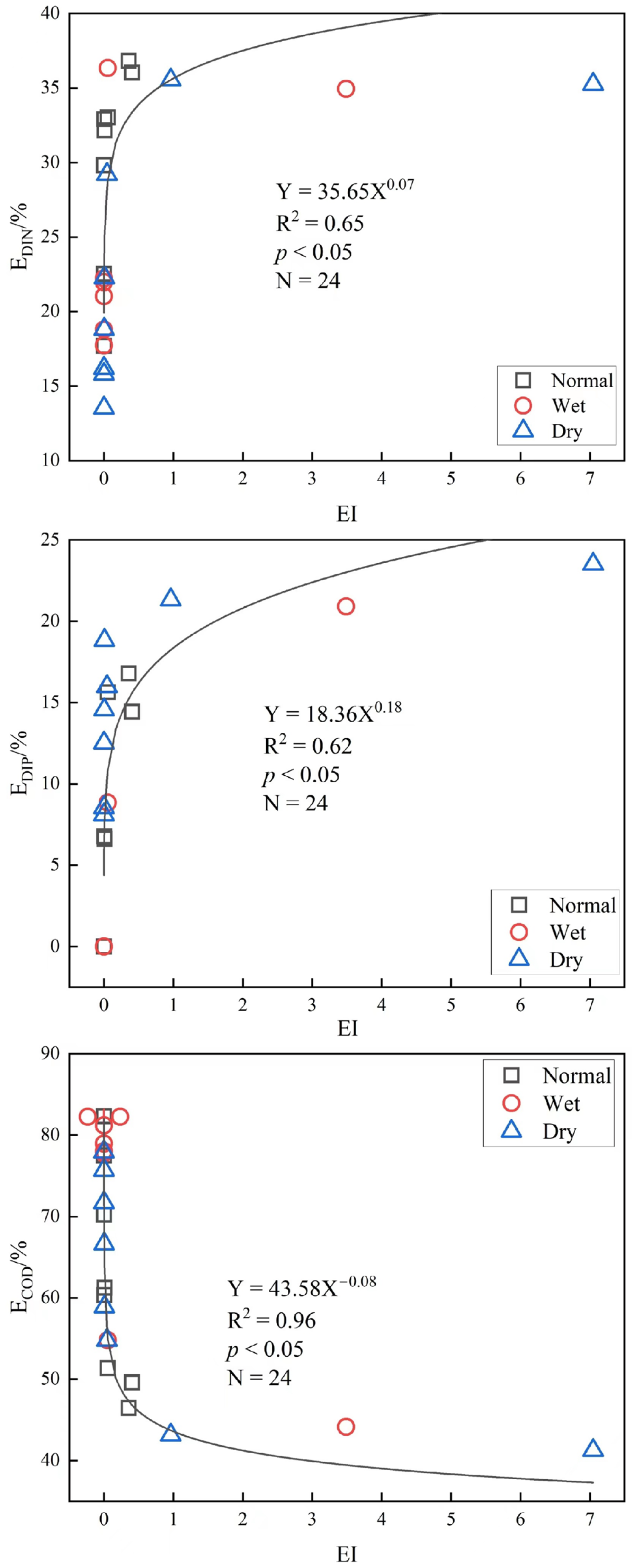
2.3.3. Contribution of COD and Nutrients to EI in Tieshan Bay
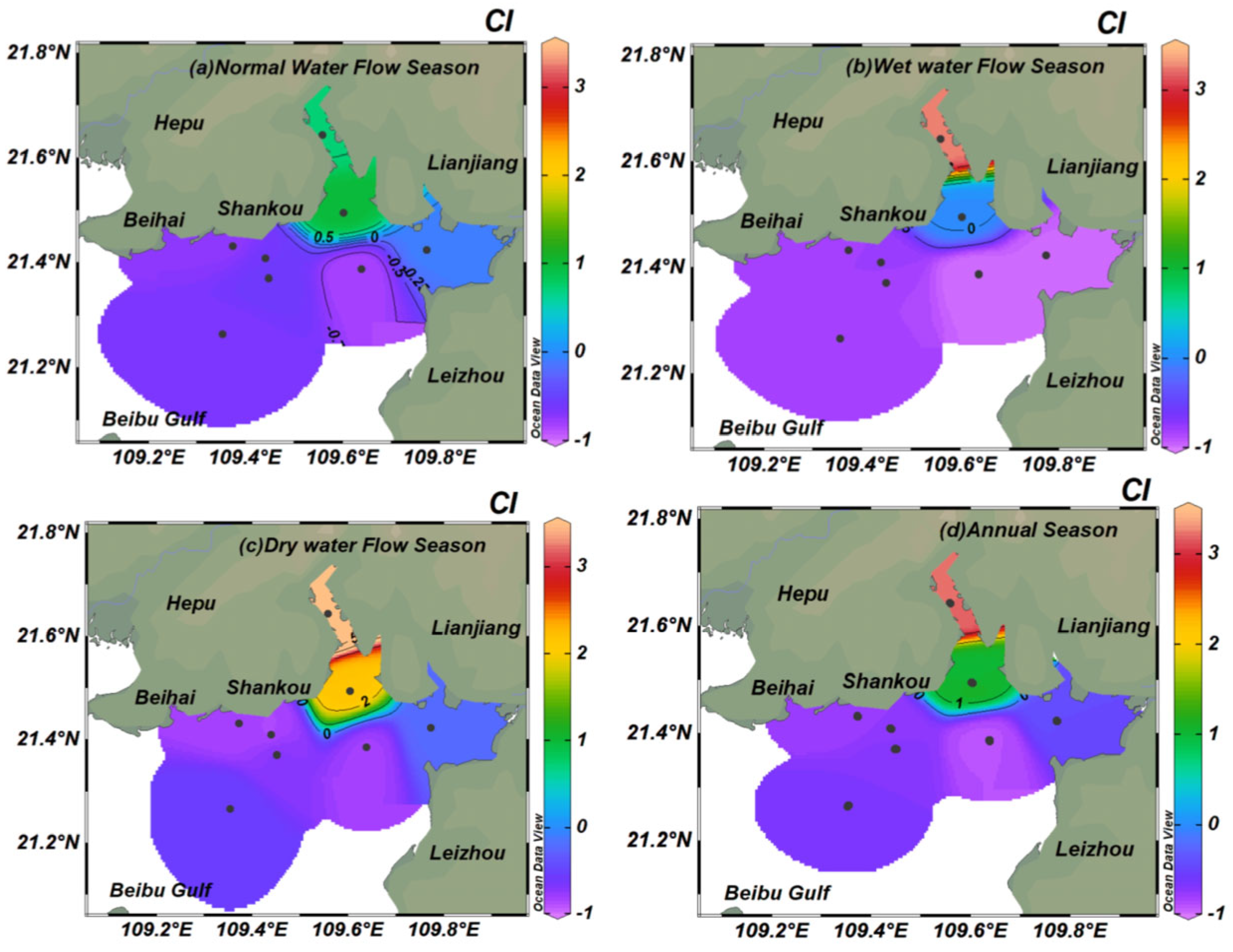
2.3.4. CI of Organic Pollution Assessment in Tieshan Bay
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Nutrient Concentration Variation in Tieshan Bay
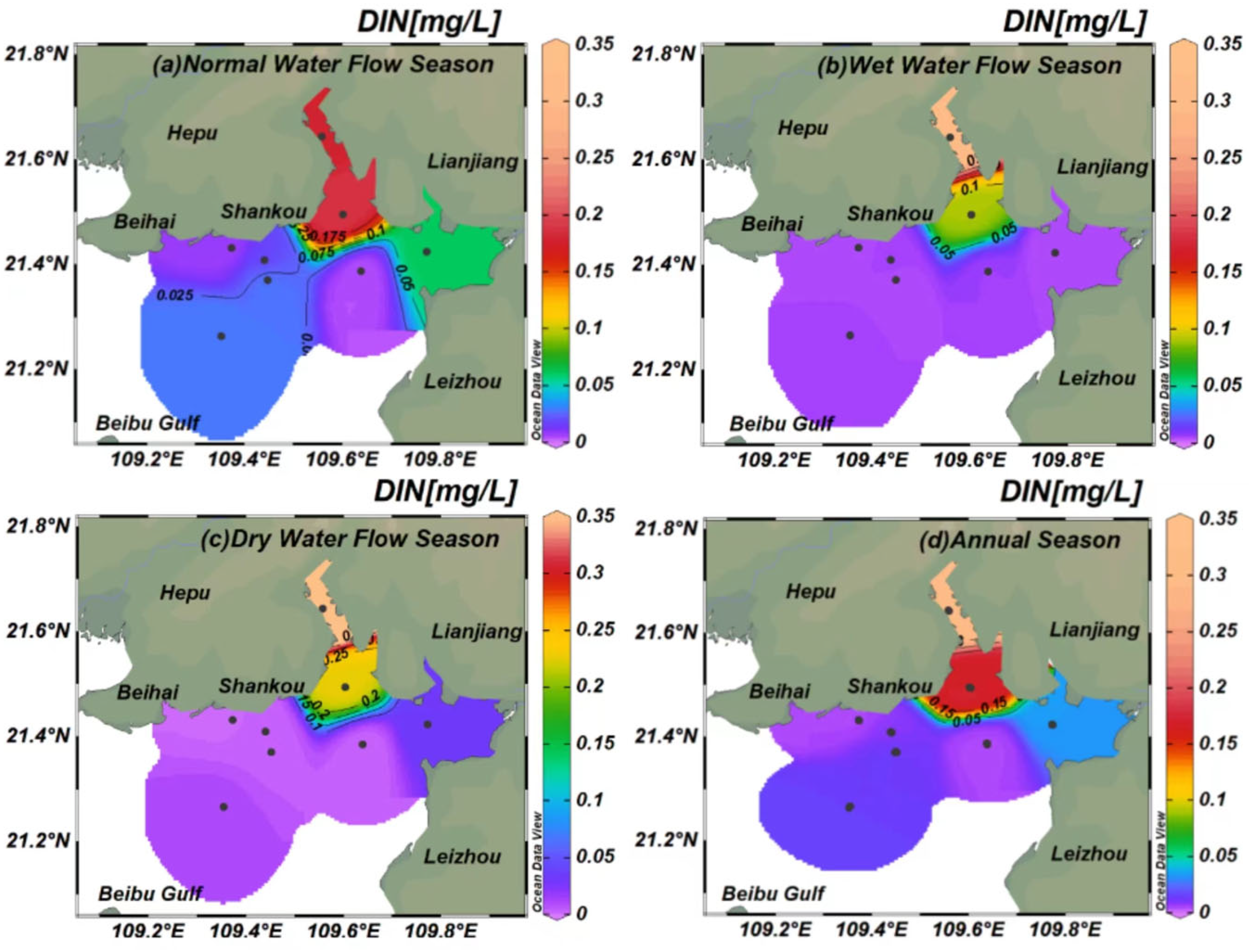
3.1.1. Spatiotemporal DIN Concentration Variation in Tieshan Bay
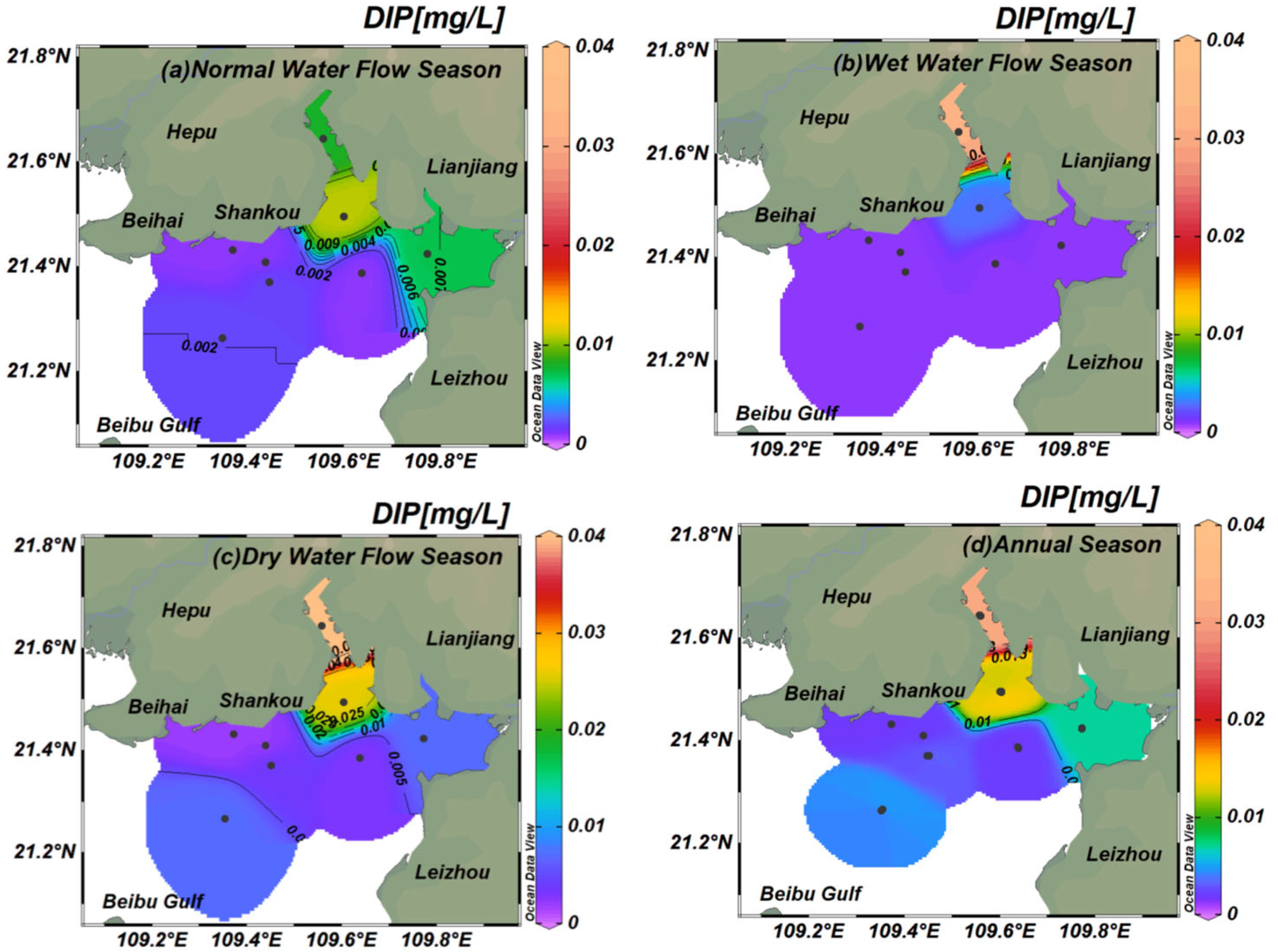
3.1.2. Spatiotemporal DIP Concentration Variation in Tieshan Bay
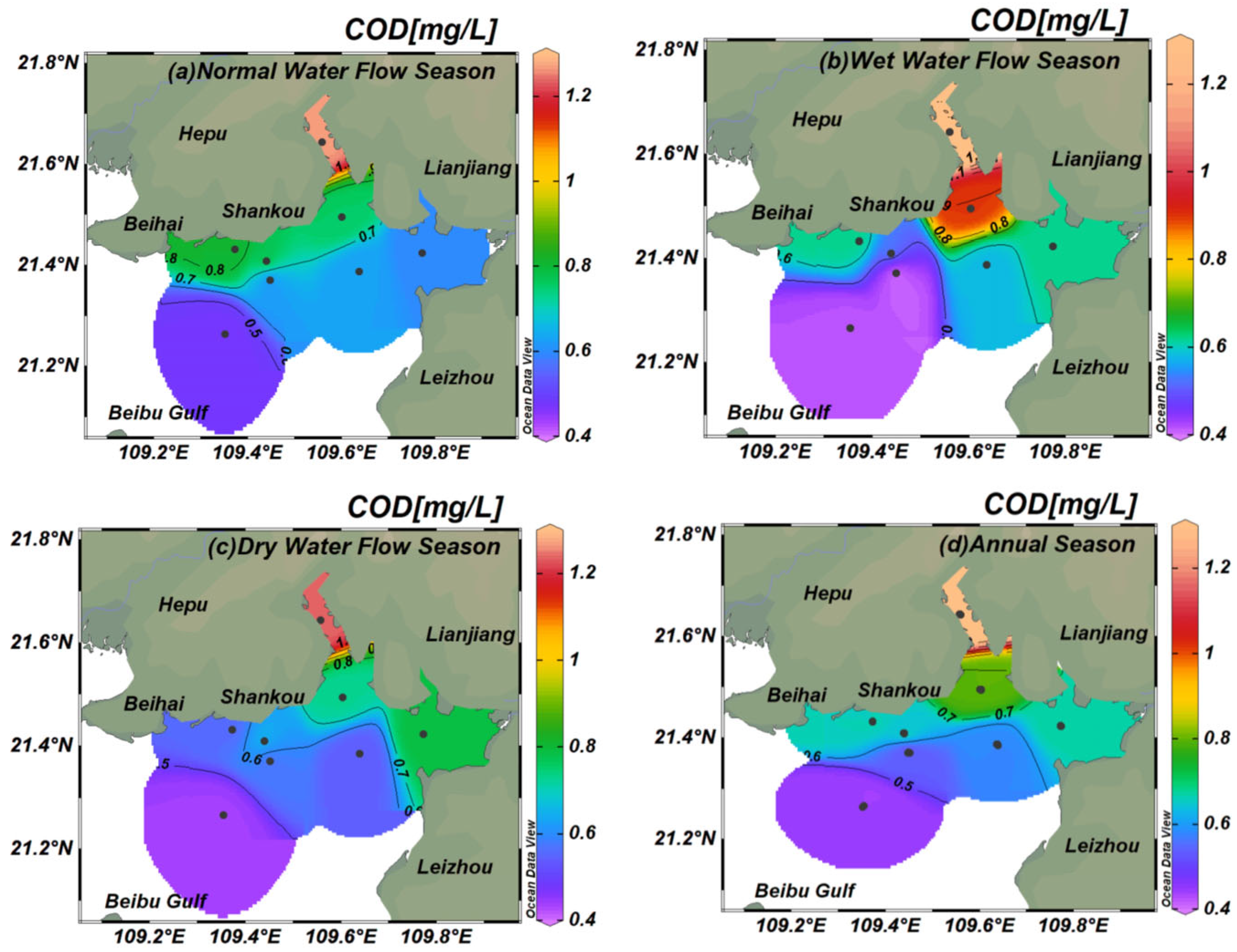
3.1.3. Spatiotemporal COD Concentration Variation in Tieshan Bay
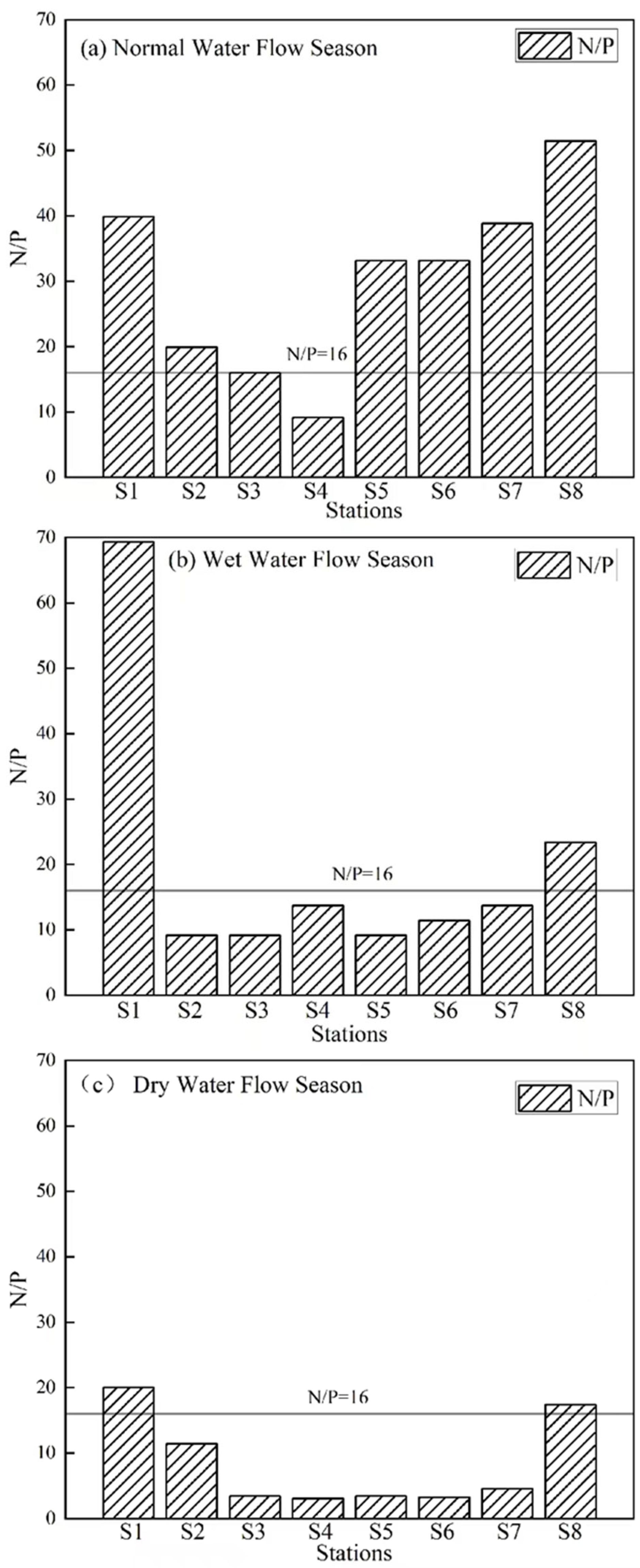
3.2. Spatiotemporal DIN/DIP Variation in Tieshan Bay
3.3. Spatiotemporal EI Variation in Tieshan Bay
3.4. Contribution of Nutrients to EI
3.5. Spatiotemporal CI Variation in Tieshan Bay
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of DIN, DIP, and COD in Tieshan Bay with Those of Other Chinese and World
4.2. Effects of the Riverine Freshwater Input on DIN, DIP, and COD in Tieshan Bay
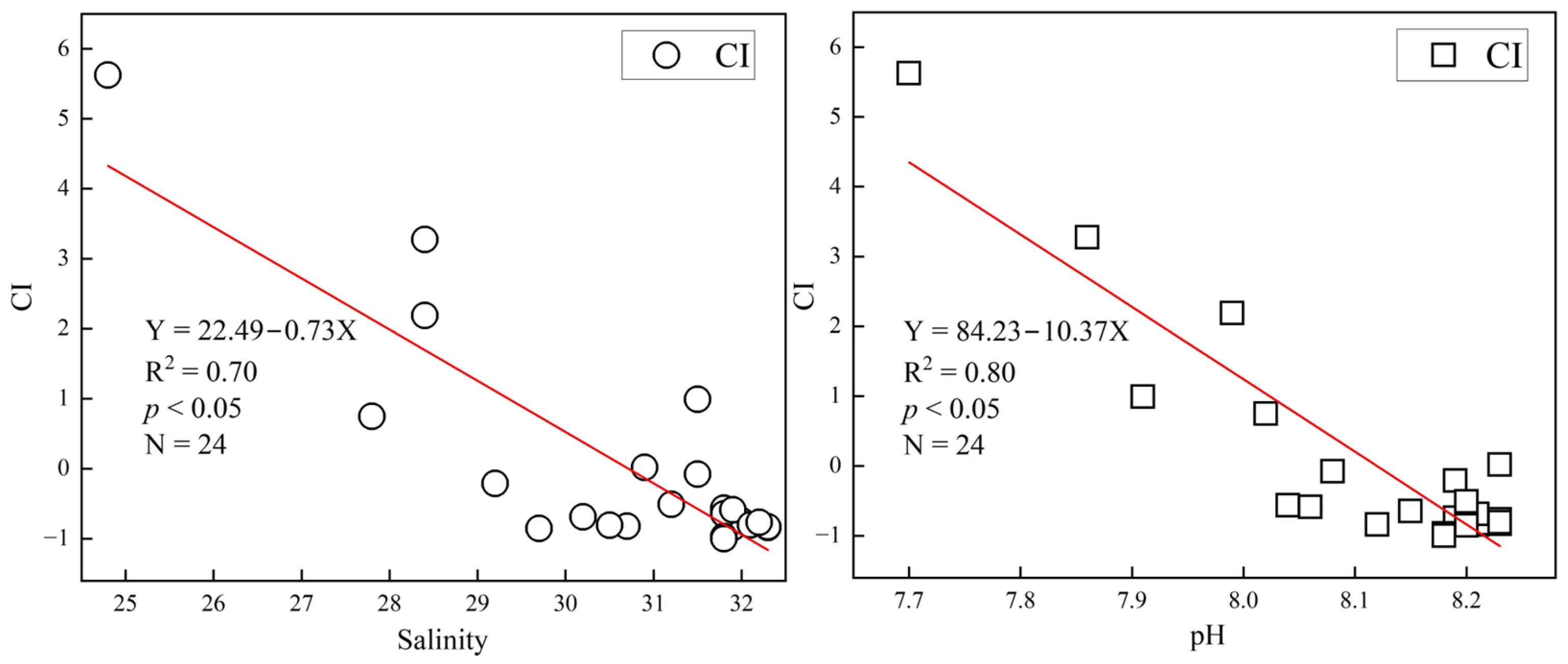
4.3. Seawater Acidification and the Effect of Stream Input on Organic Pollution
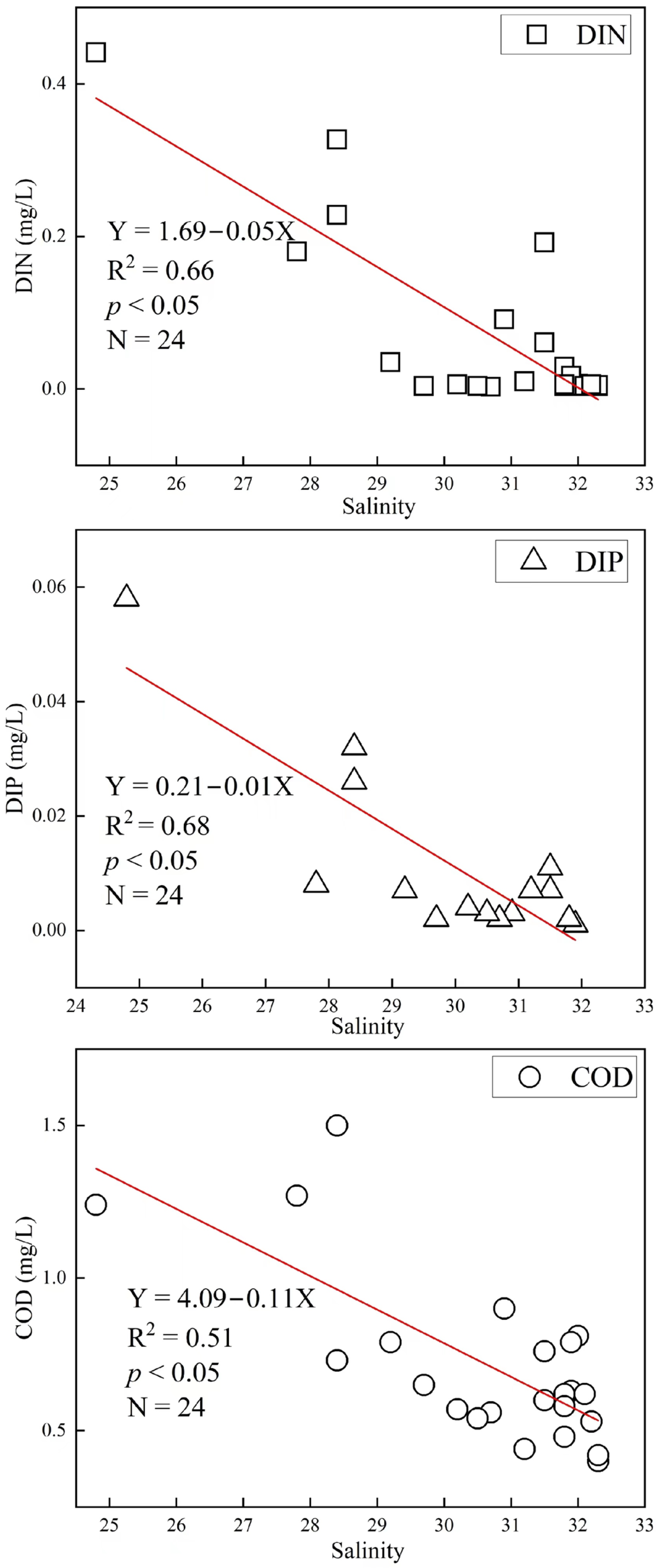
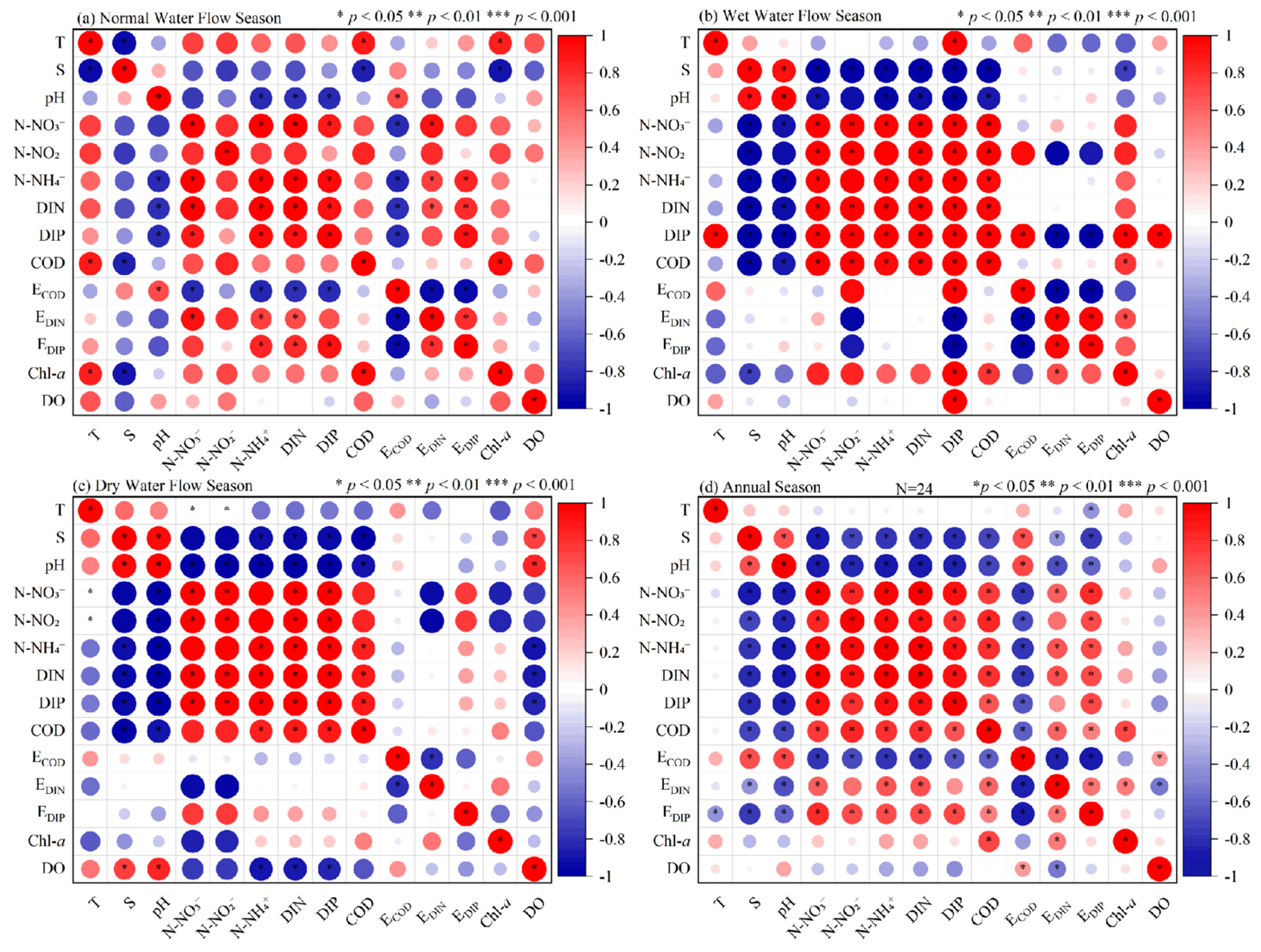
4.4. Key Environmental Factors Affecting Nutrients in Tieshan Bay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication on: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, R.W. Coastal nitrogen pollution: A review of sources and trends globally and regionally. Harmful Algae. 2008, 8, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.D.; Qian, P.Y.; Chen, J.C.; Hsieh, D.P.H.; Harrison, P.J. Dynamics of nutrients and phytoplankton biomass in the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent waters of Hong Kong during summer: Preliminary evidence for phosphorus and silicon limitation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 194, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Zhang, J.P.; Huang, X.P.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wu, Y.C. Distribution, key controlling factors and potential ecological role of particulate nitrogen and phosphorus in Daya bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 696–702+711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.P.; Jiang, Z.J. Problems in Development of Chinese Bays and the Protection Strategy. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2016, 31, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greening, H.; Janicki, A.; Sherwood, E.T.; Pribble, R.; Johansson, J.O.R. Ecosystem responses to long-term nutrient management in an urban estuary: Tampa Bay, Florida, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 151, A1–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, G.L.; Wang, D.R.; Du, J.Z.; Herbeck, L.S.; Zhang, J.; Ren, J.L. The impact of anthropogenic activities on nutrient dynamics in the tropical Wenchanghe and Wenjiaohe Estuary and lagoon system in East Hainan, China. Mar. Chem. 2011, 125, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Qi, X.H.; Li, X.; Ye, H.R.; Wu, Y.; Ren, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.Y. Nutrient dynamics from the Changjiang (Yangtze River) estuary to the East China Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2016, 154, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Qi, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, T.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.J.; Tong, Y.D. Recent change in nutrient discharge from municipal wastewater in China’s coastal cities and implication for nutrient balance in the nearshore waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.; Gowen, R.J.; Harrison, P.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Hoagland, P.; Moschonas, G. Anthropogenic nutrients and harmful algae in coastal waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.J.; Cao, W.Z.; Wang, F.F.; Su, X.L.; Yan, Y.Y.; Guan, Q.S. Riverine nutrient fluxes and environmental effects on China’s estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ruan, H.M.; Dai, P.D.; Zhao, L.R.; Zhang, J.B. Spatiotemporal river flux and composition of nutrients affecting adjacent coastal water quality in Hainan Island, China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 591, 125293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.J.; Hu, X.; Huang, W.J.; Murrell, M.C.; Lehrter, J.C.; Lohrenz, S.E.; Chou, W.C.; Zhai, W.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Wang, Y. Acidification of subsurface coastal waters enhanced by eutrophication. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glibert, P.M.; Al-Azri, A.; Icarus Allen, J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.; Burford, M.A.; Harrison, P.J.; Zhou, M. Key questions and recent research advances on harmful algal blooms in relation to nutrients and eutrophication. Glob. Ecol. Oceanogr. Harmful Algal Bloom. 2018, 232, 229–259. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Q.; Lu, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, H.D.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, H.B.; Yin, K.D. Low dissolved oxygen in the Pearl River estuary in summer: Long-term spatio-temporal patterns, trends, and regulating factors. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.P.; He, W.H.; Cai, S.Q. Seasonal variation of dissolved oxygen in the southeast of the Pearl River Estuary. Water 2020, 12, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Li, J.X.; Xu, J.L.; Luo, X.Q.; Zhao, L.R. Seasonal phosphorus variation in coastal water affected by the land-based sources input in the eutrophic Zhanjiang Bay, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 252, 107277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Zhang, P.; Ou, S.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, J.B. Spatiotemporal nutrient patterns, composition, and implications for eutrophication mitigation in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 266, 107749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Gulf Journal Compilation Committee. Gulf Records of China; The Gulf of Guangxi; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.W.; Zhang, C.Z. Basic Status of Marine Environmental Resources in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Oceanic Bureau. Strategic Plan for the Development of Guangxi’s Maritime Economy (2021–2035); Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Oceanic Bureau: Guangxi, China, 2021. Available online: http://hyj.gxzf.gov.cn/zwgk_66846/hyjj_66894/t10969962.shtml (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, R.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Pan, X.H.; Tang, J.H.; Zhang, G. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in the Beibu Gulf, China: Impacts of river discharge and aquaculture activities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 78, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Wang, W.G.; Zhao, M.W.; Chen, B.; Olusegun, A.D.; Chu, Z.H. Spatial distribution and historical trends of heavy metals in the sediments of petroleum producing regions of the Beibu Spatial distribution and historical trends of heavy metals in the sediments of petroleum producing regions of the Beibu Gulf, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Q.B.; Su, Q.Z.; Liu, G.Q.; Shen, Y.L.; Chen, F.J.; Lei, X.T.; Qing, S.M.; Wei, C.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Gao, J.S. Spatial distribution of and historical changes in heavy metals in the surface seawater and sediments of the Beibu Gulf, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.M.; Wei, M.X. A Preliminary Study of the Relationship between the Self-purifyingability and the Environment Factors of Tieshangang Bay. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2006, 3, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Cai, W.G.; Xu, S.N.; Huang, Z.R.; Qiu, Y.S. Risk assessment of coastal ecosystem in Beibu Gulf, Guangxi of South China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, R.C.; Zhuang, J.L.; Ke, K.; Jiang, F.J.; Xu, M.B. Application the Nemerow lndex to Comprehensive Assessment of Sea Area Environmental Quality of Beibu Gulf Coast in Summer. Guangxi Sci. 2014, 21, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mo, H.L.; Guo, Z. Current Condition and Assessment of Inshore Water Quality in Guangxi. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mo, H.L.; Guo, Z. Annual Assessment of Seawater Quality of Beibu Gulf in 2016. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 1, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.P.; Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Lei, F.; He, X.L. Investigation and Analysis of Water Pollution in Beibu Gulf of Guangxi. Guangxi Sci. 2022, 29, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, W.J.; Zhang, Q.F.; Shi, H.M.; Xu, Y.S.; Wang, B.; Jiang, H.Y. Study on variation trend of nutrients in Bohai Bay. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 238–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, J.R.; Zhang, Y.Q. Relationship between red tide occurrence and environmental factors in offshore waters of East China Sea. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2019, 39, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.X.; Lai, T.H.; He, B.M. Development Trend of the Water Quality Conditions in the Tieshangang Bay. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2001, 21, 69–744. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, J.B.; Sun, S.L. Evaluation on temporal and spatial distribution of nutrients and potential eutrophication in Shenzhen Bay. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.J.; Huang, X.P.; Huang, Z.G. Spatiotemporal variation of TN & TP contents in Enhalus acoroides and responses to nutrient load in Xincun Bay, Hainan. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 40–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Gui, F.K.; Wu, C.W. Effects of nutritional factors on uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus by Halymeniafloresia. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.X.; Tong, W.P.; Lai, T.H.; He, B.M. the Change Characteristics of Biogenic Elements and Theirinfluencing Factors in Tieshangang Port. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2001, 4, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.L.; Peng, X.Y. Variation Characteristics of Nutrient Concentrations in the Tieshangang Bay. Guangxi Sci. 2011, 18, 380–384+391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, P.; Dai, P.D.; Lai, J.Y.; Chen, Y. Spatiotemporal distributions of DIP and the eutrophication in Hainan Island adjacent coastal water. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.G.; Cai, H.S. Theory and Application of Geological Environment Quality Assessment; China University of Geosciences Press: Wuhan, China, 1998; pp. 70–83. [Google Scholar]
- GB3097-1997; Standard for Seawater Quality. British Standard Institute: London, UK, 1997.
- Zou, J.Z.; Dong, L.P.; Qin, B.P. A preliminary study on eutrophication and red tide in Bohai Bay. Marine Environmental Science. 1983, 2, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, X.L.; Han, X.R.; Wang, J.T. Analysis of COD distribution and contribution to seawater eutrophication in the Bohai Sea. Mar. Sci. 2005, 9, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.H.; Liu, S.M.; Li, Y.W.; Zhang, G.L.; Ren, J.L.; Zhang, J. Nutrient dynamics in tropical rivers, lagoons, and coastal ecosystems of eastern Hainan Island, South China Sea. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.L.; Li, T.S.; Han, L.J. Distribution and seasonal variation of nutrition in the adjacent waters of Tieshangang bay in Guangxi. Mar. Sci. 2014, 38, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rishworth, G.M.; Elden, S.V.; Perissinotto, R.; Miranda, N.A.F.; Steyn, P.P.; Bornman, T.G. Environmental influences on living marine stromatolites: Insights from benthic microalgal communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rishworth, G.M.; Perissinotto, R.; Bornman, T.G.; Lemley, D.A. Peritidal stromatolites at the convergence of groundwater seepage and marine incursion: Patterns of salinity, temperature and nutrient variability. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 167, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menció, A.; Casamitjana, X.; Mas-Pla, J.; Coll, N.; Compte, J.; Martinoy, M.; Pascual, J.; Quintana, X.D. Groundwater dependence of coastal lagoons: The case of La Pletera salt marshes (NE Catalonia). J. Hydrol. 2017, 552, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodellas, V.; Stieglitz, T.C.; Risoa, A.; Cook, P.G.; Raimbault, P.; Tamborski, J.J.; Beek, P.V.; Radakovitch, O. Groundwater-driven nutrient inputs to coastal lagoons: The relevance of lagoon water recirculation as a conveyor of dissolved nutrients. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 764–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, Y.; Chaigneau, A.; Okpeitcha, V.O.; Stieglitz, T.; Assogba, A.; Duhaut, T.; Rétif, F.; Peugeot, C.; Sohou, Z. Terrestrial or oceanic forcing? Water level variations in coastal lagoons constrained by river inflow and ocean tides. Adv. Water Resour 2022, 169, 104309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redfield, A.C.; Ketchum, B.H.; Richards, F.A. The Influence of Organisms on the Composition of Sea-Water. Sea 1963, 2, 26–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.A.; Su, J.L.; Hu, C.Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Guan, W.B.; Chen, J.Z. N and P in waters of the Zhujiang River Estuary in summer. J. Oceanogr. 2004, 5, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, L.R.; Lai, J.Y.; Dai, P.D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.B. Concentration, composition and fluxes of land-based nitrogen and phosphorus source pollutants input into Zhanjiang Bay in Summer. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2019, 39, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Peng, C.H.; Dai, P.D.; Lai, J.Y.; Zhao, L.R.; Zhang, J.B. Spatiotemporal variation, composition of DIN and its contribution to eutrophication in coastal waters adjacent to Hainan Island, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 37, 101332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Lin, H.; Zhang, C.H.; Ji, W.D.; Zhou, Q.L.; Lin, L.B.; Lu, M.R.; Huang, H.N.; Chen, C.P.; Gao, Y.H. Changing trends of DIN and PO4--P content in Xiamen Seawaters. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2010, 29, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Ou, S.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Categorizing numeric nutrients criteria and implications for water quality assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1004235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, S.B.; Longstaff, B.; Dennison, W.; Jones, A.; Boicourt, K.; Wicks, C.; Woerner, J. Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation’s estuaries: A decade of change. Harmful Algae. 2008, 8, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, V.S.; Gutierrez, M.F.; Regaldo, L.; Paira, A.R.; Repetti, M.R.; Gagneten, A.M. Influence of rainfall and sea-sonal crop practices on nutrient and pesticide runoff from soybean dominated agricultural areas in Pampean streams, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Lan, W.L. Assessment of the Eutrophication Level of the Marine Environment and Its Effect on Phytoplankton Chlorophyll a in Oinzhou Bay. Ocean Dev. Manag. 2020, 37, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, M.Q. Analysis of Seawater Quality Variation and Influencing Factors in Fangchenggang Bay for the Past Ten Years. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci. 2021, 37, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Q.F.; Tu, J.B.; Ma, Y.Y.; Yi, C.L.; Wang, B. Distribution and influencing factors of COD, along with the relationship with eutrophication in Tianjin coastal area. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2017, 36, 343–348+371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H. The Variations of Nutrients and Phytoplankton Assemblages in the Bohai Bay and Their Correlation Analysis; Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Niu, L.X.; Dang, H.M.; Yang, Q.S. Effects of seasonal variation of the river discharge input on nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in Pearl River Estuary. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madron, X.D.; Denis, L.; Diaz, F.; Garcia, N.; Guieu, C.; Grenz, C.; Loÿe-Pilot, M.D.; Ludwig, W.; Moutin, T.; Raimbault, P.; et al. Nutrients and carbon budgets for the Gulf of Lion during the Moogli cruises. Oceanol. Acta. 2003, 26, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabouille, C.; Conley, D.J.; Dai, M.H.; Cai, W.J.; Chen, C.T.A.; Lansard, B.; Green, R.; Yin, K.; Harrison, P.J.; Dagg, M.; et al. Comparison of hypoxia among four river-dominated ocean margins: The Changjiang (Yangtze), Mississippi, Pearl, and Rhone rivers. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1527–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N.; Alexander, R.B.; Mcisaac, G.; Howarth, R.W. Characterization of nutrient, organic carbon, and sediment loads and concentrations from the Mississippi River into the northern Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries Coasts 2007, 30, 773–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.M.; Wei, M.X.; Fan, H.Q.; Pan, L.H.; Cao, Q.X. Spatio-temporal change of inorganic nitrogen content and the evaluation ofeutrophication in the surface seawaters of mangrove areas in Guangxi bays. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2014, 33, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Y.; Lan, C.B.; Xu, M.B.; Lai, J.X.; Ling, H.J. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on Phaeocystis globosa colon growth in Qinzhou Bay. Mar. Sci. 2022, 46, 30–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, S.; Cai, Z.M.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, J.X. Effects of river input flux on spatiotemporal patterns of total nitrogen and phosphorus in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1129712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Jia, X.P.; Lin, Q.; Li, C.H.; Gan, J.L.; Cai, W.G.; Wang, Z.H.; Lu, X.Y. Research on the Distributional Features of and Interrelationships Between the Dissolved Oxygen, Salinity, pH Value and nutrients in the Honghai Bay Waters. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2000, 1, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.B. Marine Chemistry; China Ocean University Press: Qingdao, China, 2004; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.X.; Peng, D.M.; Shi, X.; Yang, S.Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.B. Seasonal Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus Variation, Speciation, and Composition in the Maowei Sea Affected by Riverine Flux Input, South China Sea. Water 2022, 14, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraert, N.; Archana, A.; Xu, M.N.; Kao, S.J.; Baker, D.M.; Thibodeau, B. Investigating the link between Pearl River-induced eutrophication and hypoxia in Hong Kong shallow coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, J.; Chandra, S.D.; Rani, K.S.; Ahmed, M.; Haque, S.M.; Haque, F.; Ahsan, M.E.; Ahmed, S.; Hossain, M.I.; Salam, M.A. Outwelling of nutrients into the Pasur River estuary from the Sundarbans mangrove creeks. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H.; Tilman, G.D.; Nekola, J.C. Eutrophication: Impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1999, 100, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbeck, L.S.; Unger, D.; Wu, Y.; Jennerjahn, T.C. Effluent, nutrient and organic matter export from shrimp and fish ponds causing eutrophication in coastal and back-reef waters of NE Hainan, tropical China. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 57, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Qu, L.; Huang, B.G.; Li, Q.; You, Q.M. Status and evaluation on nutrients for the adjacent sea water of the Yellow River estuary in autumn of 2014. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Q.; Ding, D.S.; Gu, T.; Xu, Y.; Sun, X.M.; Qu, K.M.; Sun, J.; Cui, Z.G. Ocean acidification and warming significantly affect coastal eutrophication and organic pollution: A case study in the Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.B.; Fu, M.J.; Zhang, P.; Sun, D.; Peng, D.M. Unravelling Nutrients and Carbon Interactions in an Urban Coastal Water during Algal Bloom Period in Zhanjiang Bay, China. Water 2023, 15, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Luo, W.; Fu, M.; Zhang, J.B.; Cheng, M.Y.; Xie, J. Effects of tidal variations on total nitrogen concentration, speciation, and exchange flux in the Shuidong Bay coastal water, South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 961560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njock, P.G.A.; Zhou, A.N.; Yin, Z.Y.; Shen, S.L. Integrated risk assessment approach for eutrophication in coastal waters: Case of Baltic Sea. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokulil, M.; Chen, W.; Cai, Q. Anthropogenic impacts to large lakes in China: The Tai Hu example. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gaoa, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, Z.; Noori, R.; Siadatmousavi, S.M.; Afzalimehr, H.; Azizpour, J. Satellite-Based Monitoring of Eutrophication in the Earth’s Largest Transboundary Lake. GeoHealth 2023, 7, e2022GH000770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. Land-water interfaces: Metabolic and limnological regulators. SIL Proc. 1990, 24, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M. Harmful algal blooms and eutrophication: Nutrient sources, composition, and consequences. Estuaries 2002, 25, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.C.S.; Marinho, M.; Huszar, V.L.M.; Branco, C.W.C.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. The effects of water retention time and watershed features on the limnology of two tropical reservoirs in Brazil. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2008, 13, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troell, M.; Halling, C.; Neori, A.; Chopin, T.; Buschmann, A.H.; Kautsky, N.; Yarish, C. Integrated mariculture: Asking the right questions. Aquaculture 2003, 226, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, R.; Berndtsson, R.; Adamowski, J.F.; Abyaneh, M.R. Temporal and depth variation of water quality due to thermal stratification in Karkheh Reservoir, Iran. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 19, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohollah, N.; Elmira, A.; YongWook, J.; Saber, A.; Mohsen, M.; Majid, H.; Sayed, M.B. Hyper-Nutrient Enrichment Status in the Sabalan Lake, Iran. Water 2021, 13, 2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Projects | Average Single Factor Pollution Index | Single Factor Pollution Index Range | Station Exceedance Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIN normal water flow Season | 0.174 ± 0.143 | 0.002~0.384 | 0.0 |
| DIN wet water flow season | 0.120 ± 0.209 | 0.013~0.654 | 0.0 |
| DIN dry water flow season | 0.203 ± 0.294 | 0.010~0.882 | 0.0 |
| DIP normal water flow Season | 0.153 ± 0.138 | 0.033~0.467 | 0.0 |
| DIP wet water flow season | 0.135 ± 0.218 | 0.033~0.711 | 0.0 |
| DIP dry water flow season | 0.409 ± 0.381 | 0.067~1.289 | 12.5 |
| Area | DIN (mg/L) | DIP (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | EI | DIN/DIP | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oinzhou Bay | 0.21 | 0.018 | 1.44 | 1.73 | 35–154 | [58,66,67] |
| Fangchenggang Bay | 0.126 | 0.019 | Nd | Nd | Nd | [59] |
| Bohai Bay | 0.125 | 0.002 | 1.81 | Nd | Nd | [60,61] |
| Daya bay | 0.128 | 0.005 | Nd | Nd | Nd | [4] |
| Pearl River Estuary | 0.688 | Nd | 1.02 | 8.64 | 42.6 | [18,62] |
| Zhenzhu Bay | Nd | Nd | Nd | 1.52 | Nd | [66] |
| Lianzhou Bay | Nd | Nd | Nd | 28.48 | Nd | [66] |
| Yellow River Estuary | Nd | Nd | Nd | 0.56 | 51.1 | [68] |
| Rhone River Estuary, France | 1.876 | 0.017 | Nd | Nd | 110.7 | [63,64] |
| Mississippi River | 1.125 | 0.029 | Nd | Nd | 38.31 | [65] |
| Tieshan Bay | 0.071 ± 0.115 | 0.008 ± 0.013 | 0.71 ± 0.219 | 0.519 ± 1.536 | 30.2 ± 13.2 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Wu, S.; Xu, M.; Luo, X.; Peng, X.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Nutrient Patterns, Stoichiometry, and Eutrophication Assessment in the Tieshan Bay Coastal Water, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081602
Zhang P, Wu S, Xu M, Luo X, Peng X, Ren C, Zhang J. Spatiotemporal Nutrient Patterns, Stoichiometry, and Eutrophication Assessment in the Tieshan Bay Coastal Water, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(8):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081602
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, Siying Wu, Menghan Xu, Xiaojun Luo, Xi Peng, Chaoxing Ren, and Jibiao Zhang. 2023. "Spatiotemporal Nutrient Patterns, Stoichiometry, and Eutrophication Assessment in the Tieshan Bay Coastal Water, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 8: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081602
APA StyleZhang, P., Wu, S., Xu, M., Luo, X., Peng, X., Ren, C., & Zhang, J. (2023). Spatiotemporal Nutrient Patterns, Stoichiometry, and Eutrophication Assessment in the Tieshan Bay Coastal Water, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(8), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11081602






