Abstract
Tartaric acid (TA) is an organic acid whose properties in aquaculture have not yet been comprehensively studied. In the current research, the effect of dietary TA on growth indices, gut microbiota, the level of digestive enzymes, antioxidant and immunological markers, and survival rate following immersion challenge with Vibrio parahaemolyticus (14 days) in Litopenaeus vannamei were investigated. To achieve this, 600 shrimp (3.26 ± 0.05 g) were tested with pellets supplemented with five distinct concentrations of TA including 0 (TA0), 2.5 (TA2.5), 5 (TA5), 7.5 (TA7.5), and 10 g/kg (TA10) for 56 days. The results showed that the growth performance, feed utilization, gut lactic acid bacteria (LAB) count, and activity of digestive enzymes were markedly elevated in the groups receiving diets incorporated with 5 and 7.5 g/kg of TA. The highest total hemocyte count (THC), hyaline cell (HC), and semi-granular cell (SGC) counts were detected in shrimp fed with the TA7.5 diet. Hemolymph immune responses including LYZ (lysozyme), alkaline phosphatase (AKP), acid phosphatase (ACP), and phenol oxidase (PO) activities were significantly enhanced in all TA-treated groups. Dietary TA7.5 significantly boosted all antioxidant enzymes. In addition, malondialdehyde (MDA) content illustrated a significant decrease in shrimp fed with diets supplemented with 2.5–10 g/kg TA when compared with specimens fed with TA0. The survival rate following the immersion challenge with Vibrio parahaemolyticus markedly increased in all shrimp treated with 2.5–10 g/kg TA compared to TA0, irrespective of the dosage. However, the dietary inclusion of TA7.5 resulted in the highest survival rate. Based on the outcomes, dietary TA, especially at the concentration of 7.5 g/kg, is proposed to promote the growth performance and immunological indicators of L. vannamei.
1. Introduction
The Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, is one of the most well-known economical aquatic species that is broadly reared in many countries of the world due to its high growth rate, excellent feed conversion rate, and significant marketability [1,2]. Among the farmed species of crustaceans, the highest share of production (more than 50%) belongs to L. vannamei [3]. However, its production is affected by infectious agents [4] and non-biological stresses such as ammonia stress [5], herbicides [6], insecticides [7], heavy metals [8], low salinity [9], and microplastics [10]. In rearing conditions, it is feasible to achieve sustainable production through improved diets for farmed species such as L. vannamei [11]. Employing biostimulants with capabilities such as high availability, low cost, safety, and antibacterial effects is one of the top options for boosting the growth and immune function of the hosts [12]. In general, the physiological activities of animals can be affected by intestinal microbial communities [13].
Organic acids (OAs) are compounds with antimicrobial properties that have at least a hydroxyl group in their structure [14]. It is stated that organic acids can modulate intestinal microflora, inhibit the growth of opportunistic pathogens (e.g., Vibrio sp., Aeromonas sp.), and reduce antibiotic consumption [15]. In fact, the antibacterial mechanism of OA acts through lowering the cytoplasmic pH of bacteria and disrupting normal cellular reactions [16]. Earlier reports indicated that diets containing OA such as citric acid [17], formic acid [18], and succinic acid [19] effectively improved immune and antioxidant responses in L. vannamei when compared with the un-supplemented group. Moreover, OA boosts the disease resistance of animals by controlling the gut microbial population and stimulating the immune system [20]. In Vibrio harveyi-infected L. vannamei, the survival rate in groups fed with organic acids was up to 50% higher than in the un-supplemented group [21]. The findings on the influence of OAs on weight gain and feed utilization in aquatic organisms have been favorable, but these may be different depending on the chemical structure of OA and species. For instance, the administration of succinic acid markedly increased growth and feed efficiency in L. vannamei [19], while the growth and feed indices of Penaeus monodon were not affected in response to the pellets fortified with OAB (organic acid blend; formic, lactic, malic, and citric acids) [14].
Tartaric acid (TA; synonym: dihydroxybutanol, chemical formula: C4H6O6) is a chemical compound obtained from biological (fermentation) and chemical processes that is also naturally present in different fruits such as grape, banana, lychee, sweet cherry, avocado, and tamarind [22,23]. TA has gained growing popularity in food and pharmaceutical activities due to its various biological properties. Such properties include regulating acidity, improving the shelf life and sensory properties of food, stimulating the immune system, and displaying antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects [24].
V. parahaemolyticus is one of the well-known opportunistic bacteria in the marine aquaculture industry, and is associated with the emergence of the fatal infection of AHPND (acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease) [25]. One of the effective strategies to increase the resistance against vibriosis infection and boost other physiological processes in shrimps is the administration of OAs in their diet [11,21]. Hence, the current work was performed to clarify the possible benefits of tartaric acid on growth and nutritional markers, gut microbiota profile, digestive enzymes, immunohemocyte and antioxidant responses, and survival rate following an immersion challenge with V. parahaemolyticus in L. vannamei.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diet Preparation and Experimental Design
In this work, the effects of dietary tartaric acid (TA, Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) on L. vannamei were tested. Five experimental diets (Table 1), supplemented with different concentrations of TA including 0 (TA0), 2.5 (TA2.5), 5 (TA5), 7.5 (TA7.5), and 10 g/kg (TA10) were formulated. The dietary components were sieved, weighed, and accurately blended. The dietary liquid components such as soybean lecithin and oils were weighed and gently added to other ingredients in a drum mixture to produce a homogeneous mixture. After homogenization, the above mixture was made into a paste using 300 mL of water, and the resulting paste was changed to stable sticks using a meat grinder. The pellets were dehumidified for 36 h and then kept at 4 °C until consumption [26]. Finally, the biochemical status of each diet was analyzed using the standard AOAC [27] protocol.

Table 1.
Feedstuffs and proximate analysis of the basal diet (g/kg in dry matter).
2.2. Shrimp Rearing and Growth Performance
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This work was conducted in the form of a completely randomized design in the laboratory located in the Bardstan site (Dyer city, Bushehr province, Iran). In total, 650 shrimp were purchased by the native supplier, and specimens were macroscopically assayed externally for any signs of damage, lesions, or parasites. Before starting the feeding trial, the shrimp were conditioned for 14 days with new physicochemical parameters including temperature: 30.5 ± 0.7 °C, salinity: 34.5 ± 1 g/L, pH: 8.2 ± 0.3, dissolved oxygen: 6.5 ± 0.5 mg/L, alkalinity: 140.4 ± 6 mg CaCO3/L, ammonia level: 0.05 ± 0.01 mg/l, nitrate (NO3-N): 5.9 ± 0.2 mg/l, and nitrate (NO3-N): 0.2 ± 0.05.
During this period, the shrimp were fed using the control diet (un-supplemented diet, TA0) thrice a day (7:30, 13:00, and 18:00) ad libitum. Then, 600 shrimp (3.26 ± 0.05; mean ± SD) were allocated to 15 fiberglass tanks (300 L, density; 40 specimens per tank) and fed with their respective diets. Aeration of the tanks was performed using two air stones linked to a blower (STREAM-HG-1500B, Zhoushan, China). To block the escape routes of the specimens, the top and outlet of the tanks were enclosed via plastic nets. The water temperature was controlled through a heater attached to each tank wall. The photoperiod was adjusted based on 12 h light/12 h dark [28].
After feeding, the remaining pellets were collected from the bottom of the tanks, dehumidified in an oven (60 °C), and weighed [29]. Water quality parameters were maintained by monitoring the physio-chemical parameters of the water, siphoning suspended particles (shells, feces, etc.), and changing 30% of the water daily [19].
After completing the rearing time, all specimens belonging to each replicate were counted and weighed. The growth performance parameters, feed conversion ratio, protein efficiency ratio, and survival rate were calculated as follows: [26]
where FW: final weight, IW: initial weight, Nf: shrimp number at the final of trial feeding, Ni: shrimp number at the initial of trial feeding, and d: days.
Weight gain (WG, g) = Final weight − Initial weigh
Specific growth rate (SGR, %/day) = 100 × [(ln FW − ln IW)/d]
Feed conversion ratio (FCR) = FI/(FW−IW)
Protein efficiency ratio (PER) = weight gain (g)/protein intake (g)
Survival rate (SR, %) = (Final individual numbers/Initial individual numbers) × 100
2.3. Sampling Procedure
After terminating the 56-day rearing trial, the animals were starved (24 h), and 15 specimens were randomly collected from each tank, immobilized, and euthanized on ice [30]. Three samples were used for the gut microbial analysis, three samples were used for evaluating the response of digestive enzymes, three samples were used to assess the oxidation capacity, and the others were used for hemolymph extraction. The body surface of the animals was disinfected with 70% alcohol, and then the gut was obtained by dissecting the abdominal part. Three samples were instantly prepared for microbial culture according to the previously described procedure (see below) [31].
To evaluate the response of the digestive enzymes, after dissection, the gut of each animal was isolated and washed using distilled water. Then, the samples were dried with a paper towel. The tissues were homogenized using mannitol–Tris buffer (50 mM mannitol, 2 mM Tris–HCl buffer, pH; 7.0) in 30 volumes (v/w) and a homogenizing tool (Heidolph® SilentCrusher-m, Schwabach, Germany) on the ice [32]. The suspension was centrifuged at 10,000× g for 30 min (4 °C), and the supernatant was separated and stored at −80 °C.
The hemolymph was taken from the pericardial cavity of the specimens using a 2 mL syringe, and then it was poured into a 1.5 mL vial containing an anticoagulant substance (Alzor; 336 mM sodium chloride, 115 mM glucose, 27 mM sodium citrate, and 9 mM EDTA) [33]. To ascertain immunological activities, the supernatant of the hemolymph was obtained by centrifuging at 4000× g for 10 min and kept at –80 °C [34].
The oxidation capacity and lipid peroxidation of the shrimps grown in the desired nutritional conditions were determined using the hepatopancreas organ. After collecting the tissues, the samples were weighed and homogenized with PBS solution (sterile phosphate-buffered saline, 0.1 M, pH = 7.4). The liquid containing the antioxidant enzymes was obtained through centrifugation (10,000× g, 4 °C for 15 min) and kept at −80 °C [32].
2.4. Analysis
2.4.1. Microbiological Determination
After weighing the guts, the samples were changed into a homogeneous suspension using a homogenizer and sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Then, successive dilutions were produced from each sample and 0.1 mL was poured into tryptic soy agar (TSA; Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and de Man–Rogosa–Sharpe agar (MRS, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) plates for the counting of the total count bacteria (TCB) and lactic acid bacteria (LAB), respectively. The MRS plates were incubated at 37 °C for 48 h [35,36], and the TSA plates were kept at 30 °C for 24 h [37,38]. Then, the colonies were counted, and data exhibited as CFU/g gut.
2.4.2. Digestive and Antioxidant Enzymes
The level of amylase activity was detected spectrophotometrically at 540 nm based on the method explained by Rick and Stegbauer [39]. In this procedure, soluble starch and dinitrosalicylic acid are employed as a substrate and color reagent, respectively. The lipase activity was examined as explained by Kiran et al. [40]. For this, 480 μL pNPP (p-nitrophenyl palmitate) was mixed with 20 μL enzyme extract and then kept at 37 °C for 15 min. The supernatant was obtained by centrifuging the mixture at 10,000× g for 10 min. Finally, OD was detected at 410 nm. The quantitation of the protease level was detected using the spectrophotometry method at 500 nm and according to the protocol explained by García-Carreño [41].
The level of hepatopancreas enzymatic activity (superoxide dismutase; SOD, glutathione peroxidase; GPX, and catalase; CAT) and lipid peroxidation content were measured using the kits produced by Zelbio Co. (GmBH Co., Lonsee, Germany) and according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.4.3. Hemolymph Indices and Immunological Assays
The enumeration of the total hemocyte count (THC) was conducted via a Neobar slide and a light microscope device as previously recommended by Abdollahi-Arpanahi et al. [42]. Determining the percentage of hemocyte types was carried out by revealing morphological aspects of hemocytes (nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio, color and granule count, and cell diameter) using the May–Grunwald and Giemsa staining technique and detecting them under a light microscope [43].
The activity of lysozyme (LYZ) in hemolymph was evaluated via turbidity test using a Gram-positive bacterium, Micrococcus lysodeikticus (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA). Accordingly, 25 μL of hemolymph was pipetted into 175 μL of bacterial sample (prepared in PBS: 50 Mm and pH 6.5). The reaction was kept at 22 °C for 15 min, and optical density (OD) was detected at 450 nm [44].
Assaying phenoloxidase activity was carried out using the colorimetric method via the formation of red pigment dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-chromium. In brief, an equal dose (50 μL) of the enzymatic substrate L-dihydroxy phenylalanine (L-DOPA) and hemolymph was kept at 20 °C for 5 min. Then, OD was read at 490 nm [45].
The activity of acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase was measured following the incubation of 100 μL of hemolymph sample with 2 mL of p-nitrophenyl phosphate in citrate buffer at pH = 5 (as ACP substrate) and 2 mL p-nitrophenyl phosphate in glycine-NaOH buffer at pH = 9 (as AKP substrate) for 30 min at a temperature of 37 °C and absorbance reading was taken at 405 nm [46].
2.4.4. Challenge Test
In this study, a disease challenge was performed using the Vibrio parahaemolyticus bacterium ATCC 17,802 obtained from the Center of Genetic and Biological Reserves of Iran. This work was conducted in full compliance with quarantine and health principles and in a completely isolated place far from the rearing farms. This bacterium was grown in optimal conditions including tryptic soy broth (TSB) medium mixed with 2% (w/v) NaCl at 30 °C overnight. The bacterial pellets were obtained by centrifugation of the supernatant at 7000× g at 4 °C for 20 min, and then they were washed twice with the relevant solution (PBS). Finally, the concentration was adjusted using spectrophotometry at 1 × 108 at 600 nm based on significant previous results [47].
The animals were subjected to this strain with a concentration of 106 CFU/mL via the immersion method for 2 h based on results obtained by Sha et al. [48]. In the challenge time, the water quality parameters were similar to the rearing phase. Then, infected samples were stored in tanks (100 L containing 50 L water; 15 shrimp per tank) and losses were recorded daily for 14 days. During this period, the status of the specimens was monitored four times a day, and mortality and abnormalities were detected. Furthermore, the animals were fed, and water quality parameters were monitored in a manner consistent with the rearing phase.
2.4.5. Statistical Analysis
Data analysis was conducted using an ANOVA (one-way analysis of variance) test in an SPSS software (version 20) environment. Tukey’s multiple range test was applied to detect remarkable discrepancies among the experimental treatments (p < 0.05) following checking the normality of the data and homogeneity of the variance using Shapiro–Wilk and Levene tests. Assumptions were met in all cases. The outcomes were illustrated as mean ± SD.
3. Results
3.1. Growth Performance Parameters
The growth performance parameters, FCR, PER, FI, and SR in the Pacific white shrimp fed with different concentrations of TA are exhibited in Table 2. Accordingly, FW, WG, and PER in groups treated with 5–10 g/kg of TA-supplemented diets were markedly higher than the TA0 treatment (p < 0.05). All TA-supplemented diets markedly enhanced SGR value compared to the TA0 group (p < 0.05). Except for TA2.5, the FCR value in other treatments was remarkably lower than the TA0 treatment (p < 0.05).

Table 2.
Growth performance parameters, FCR, PER, FI, and SR of L. vannamei fed with diets containing 0–10 g/kg tartaric acid (TA) for 56 days.
SR and FI were similar among the different treatments (p > 0.05). Based on the quadratic regression test, there was a remarkable relationship between the shrimp FW (R2 = 0.81), WG (R2 = 0.82), SGR (R2 = 0.84), FCR (R2 = 0.78), and PER (R2 = 0.73) with the dietary TA concentrations (Table 2), and the best levels were acquired at TA concentrations of 7.08 g, 6.22, 6.86 g, 7.14 g, and 7.05 g according to the FW, WG, SGR, FCR, and PER, respectively (Table 2).
3.2. Gut Total and Lactic Acid Bacteria
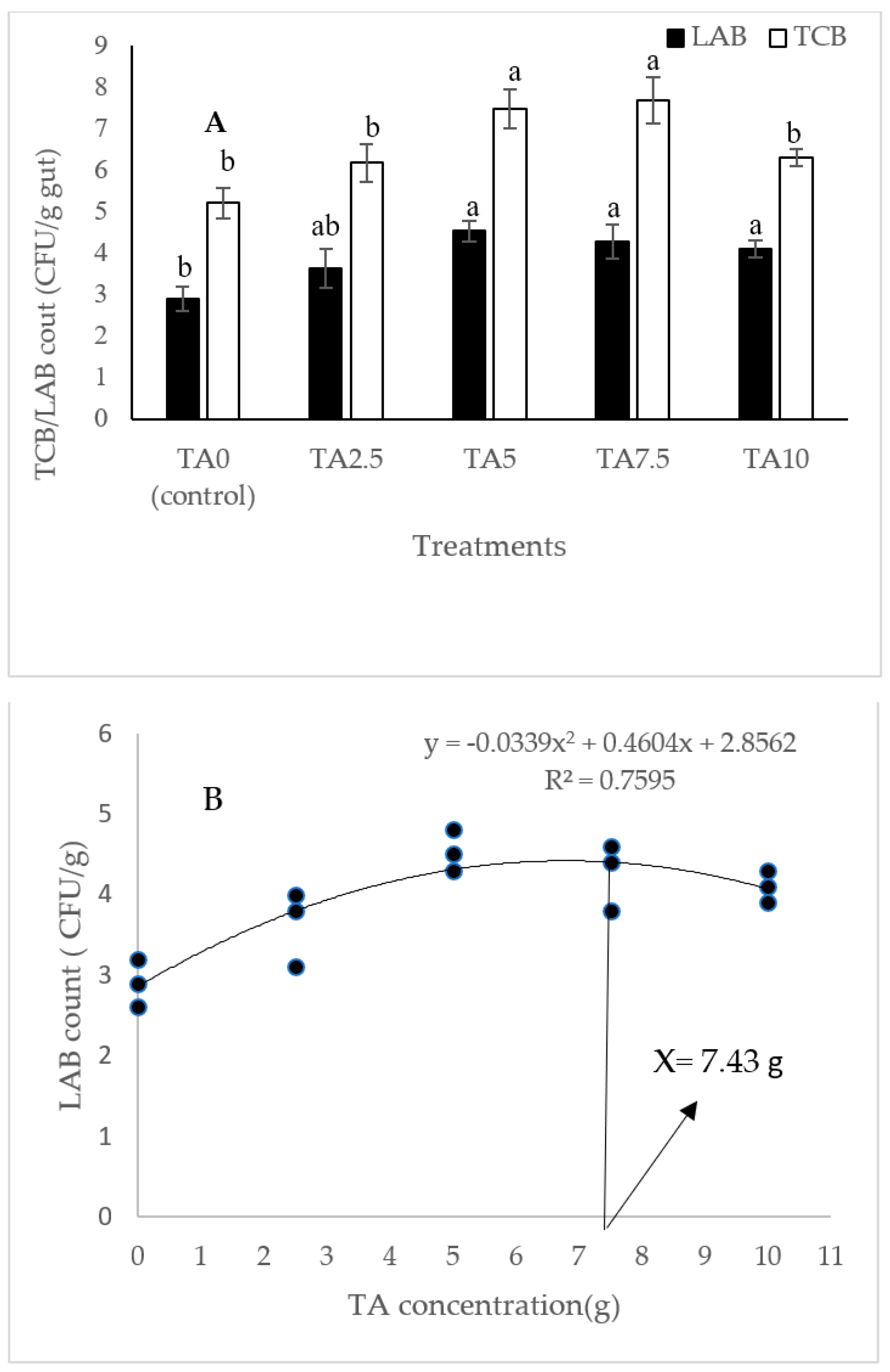
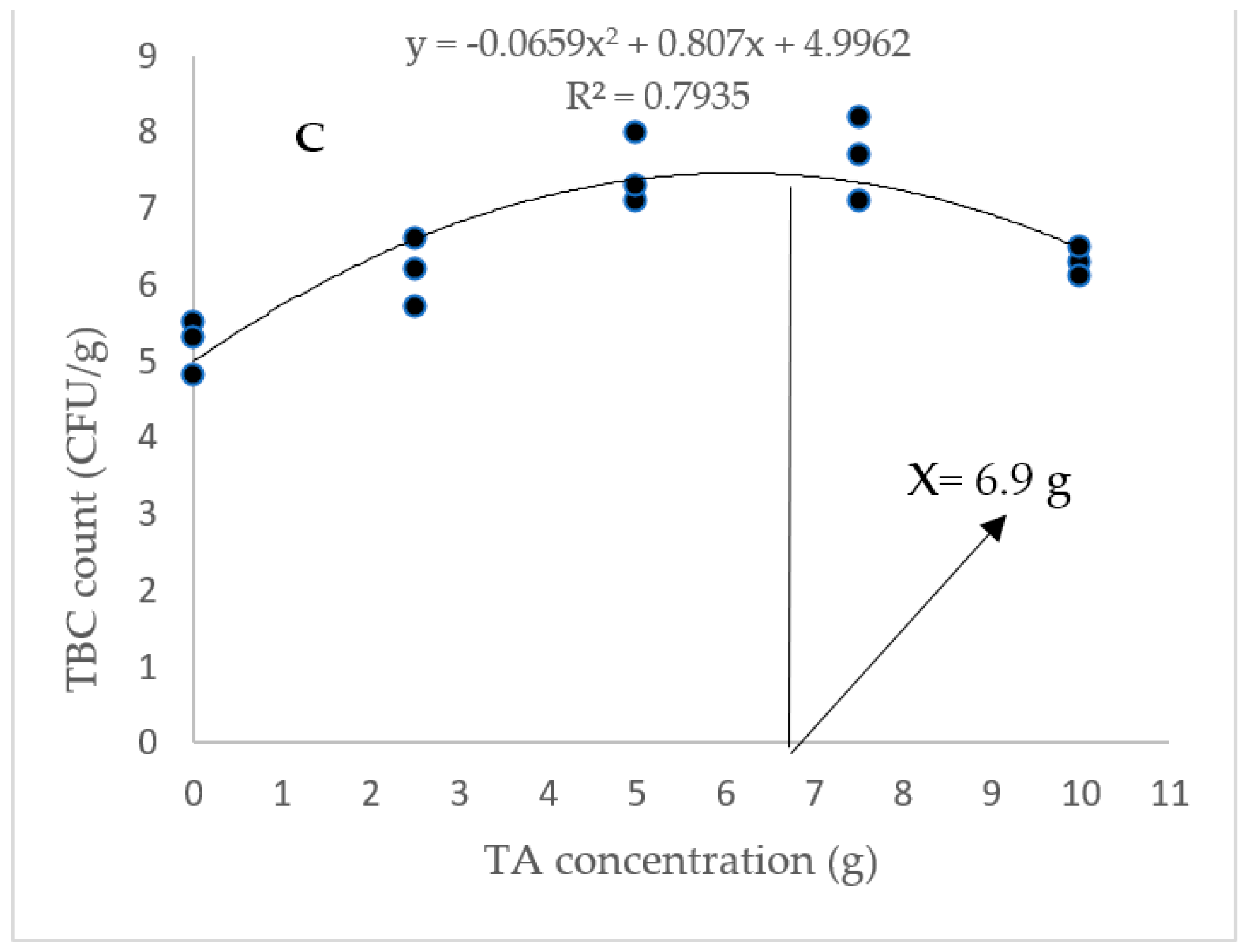
According to Figure 1, the highest gut TCB count was obtained in animals fed with diets containing 5 and 7.5 g/kg of TA (p < 0.05). In addition, the gut LAB count was markedly elevated in response to pellets fortified with 5–10 g/kg of TA (p < 0.05). Based on the quadratic regression test, there was a remarkable relationship between the shrimp LAB (R2 = 0.75) and TBC (R2 = 0.79) with the dietary TA concentrations (Figure 1), and the best levels were acquired at TA concentrations of 7.43 g and 6.9 g according to the LAB and TBC, respectively (Figure 1).
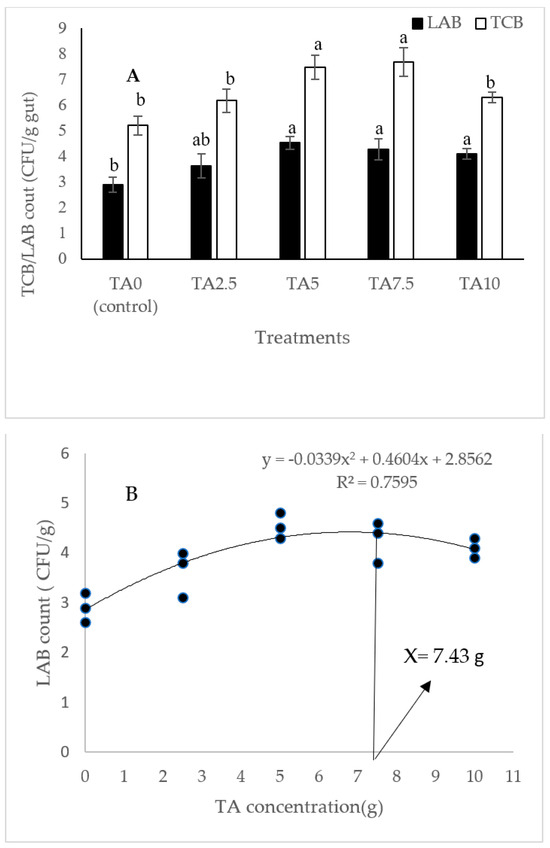
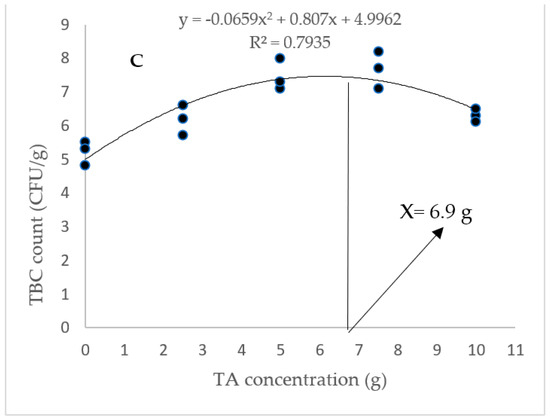
Figure 1.
(A): Gut TCB (total count bacteria) and LAB (lactic acid bacteria) count in L. vannamei after treatment with different concentrations of tartaric acid (TA) (0–10 g/kg) for 56 days. (B,C): Relationships between the dietary TA levels and LAB (count CFU/g) and TBC (count CFU/g) in L. vannamei (n = 3). Dissimilar letters above the bars represent significant differences among the experimental groups (Tukey test; n = 3, p < 0.05). OD: optimum dose; R2: R square.
3.3. Digestive Enzyme Activity
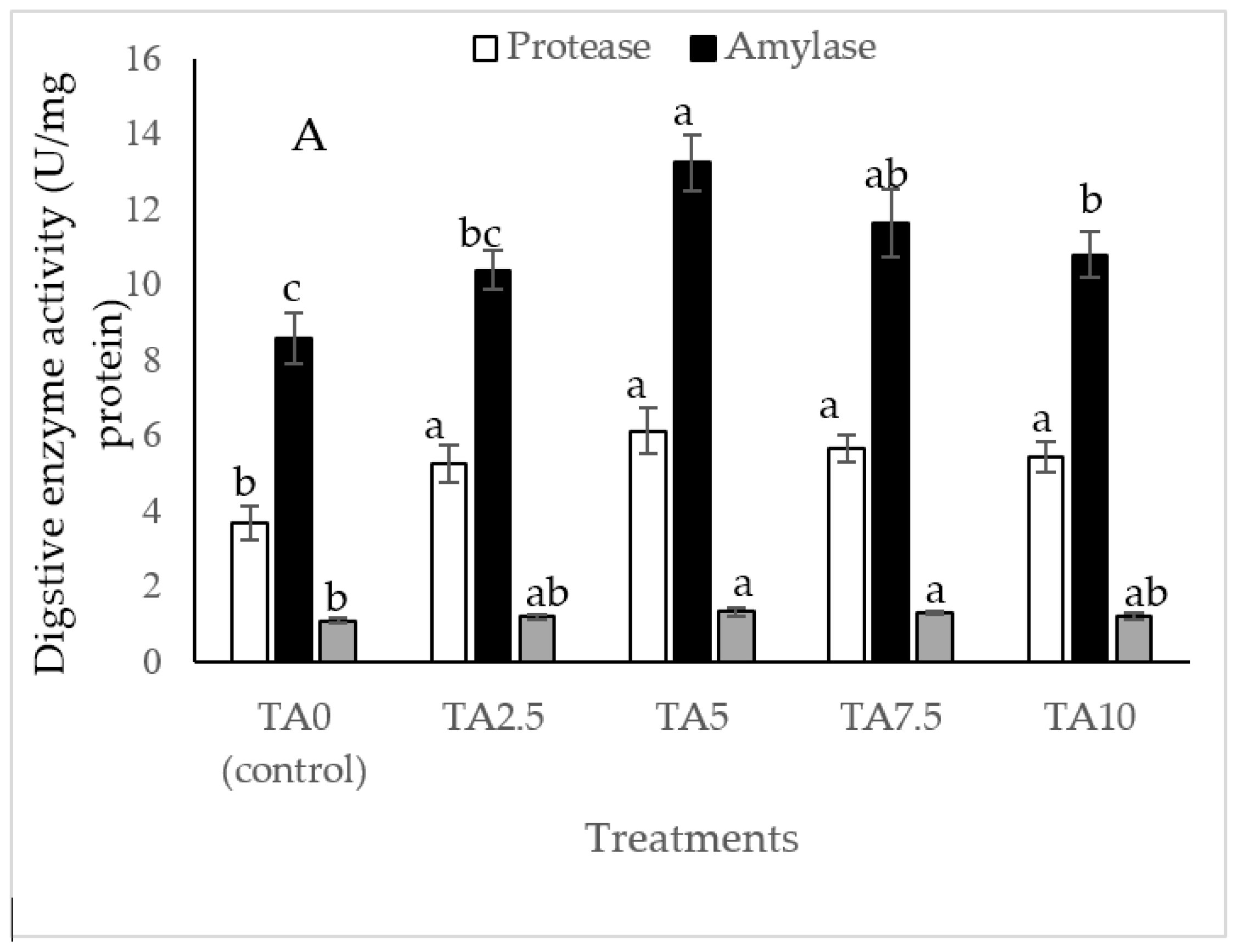
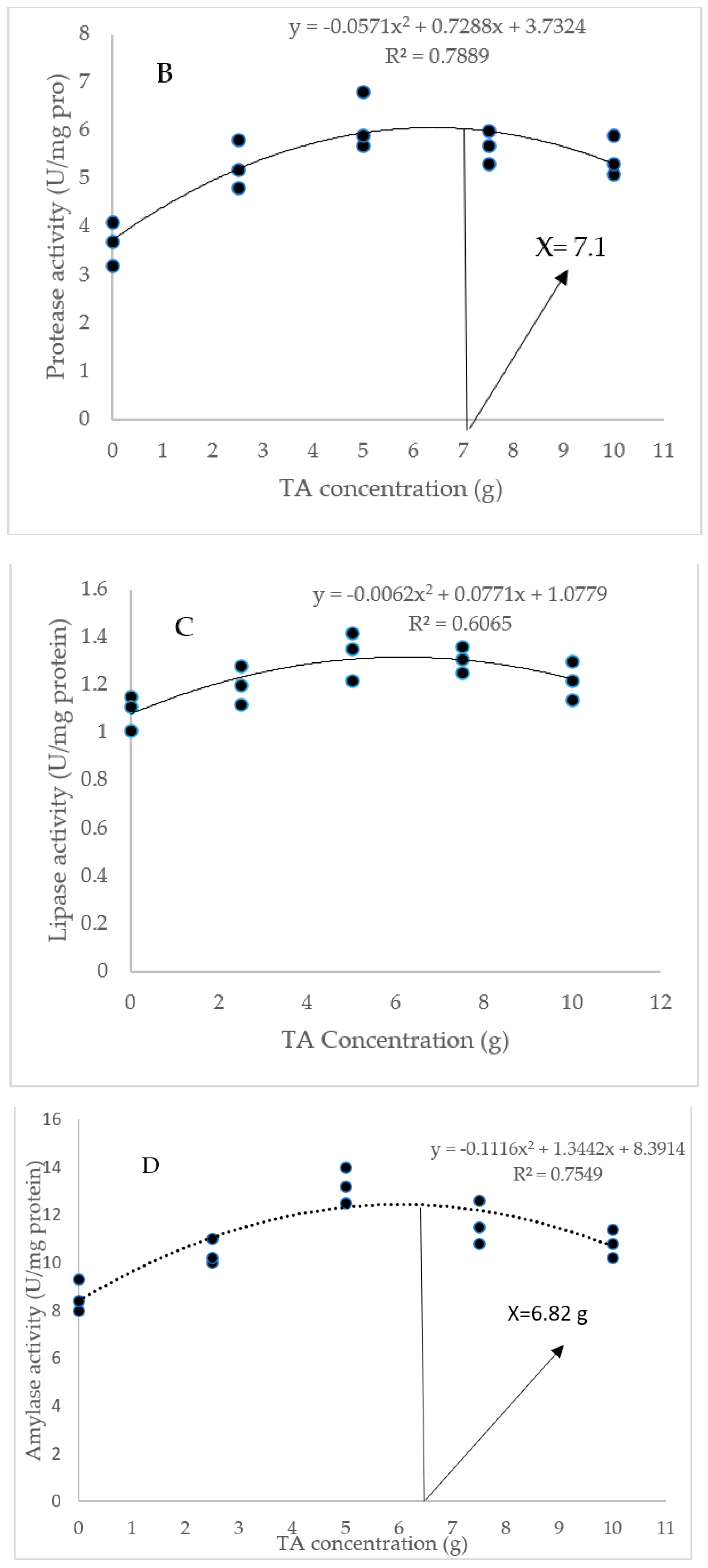
As Figure 2 indicates, the diet of 5, 7.5, and 10 g/kg TA remarkably elevated the amylase level compared to the TA0 treatment (p < 0.05). All TA-treated groups significantly improved protease activity with a similar trend higher than the TA0 (p < 0.05). The shrimp fed with pellets administrated with 5 and 7 g/kg TA presented a higher (p < 0.05) lipase level than the TA0. Based on the quadratic regression test, there was a remarkable relationship between the shrimp protease activity (R2 = 0.78) and amylase activity (R2 = 0.75) with the dietary TA concentrations (Figure 2), and the best levels were acquired at TA concentrations of 7.1 g and 6.82 g according to the protease activity and amylase activity, respectively (Figure 2).
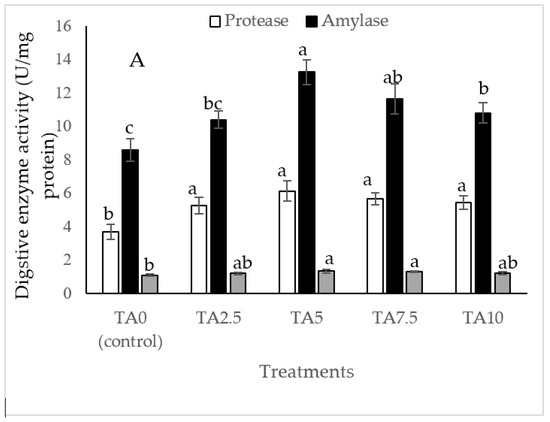
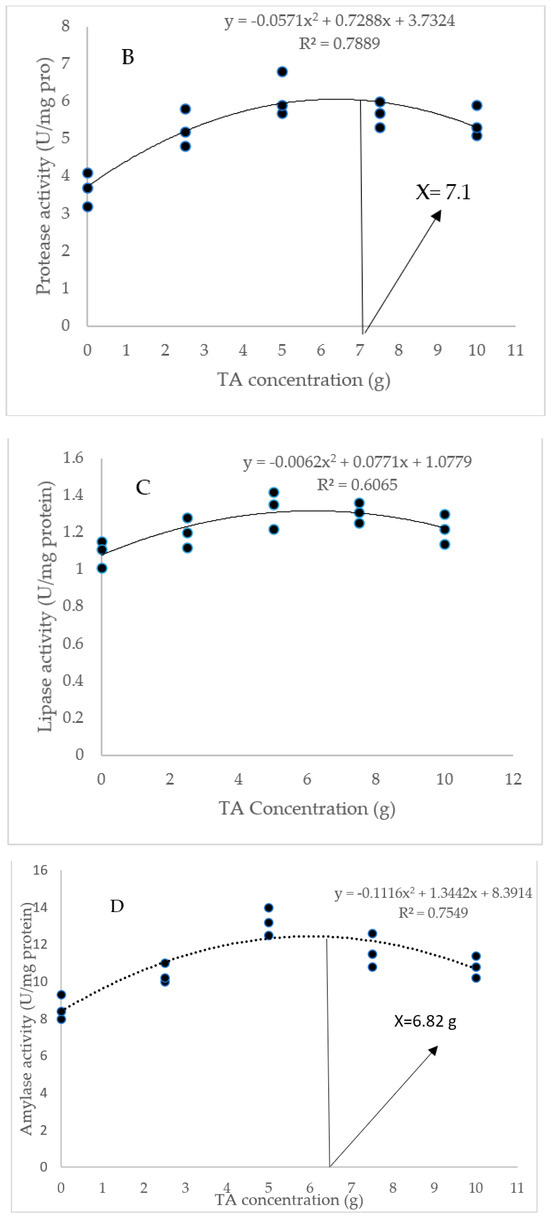
Figure 2.
(A): Digestive enzyme activities in L. vannamei after treatment with different concentrations of tartaric acid (TA) (0–10 g/kg) for 56 days. (B–D): Relationships between the dietary protease activity (U/mg protein), lipase activity (U/mg protein), and amylase activity (U/mg protein) in L. vannamei (n = 3). Dissimilar letters above the bars represent significant differences among the experimental groups (Tukey test; n = 3, p < 0.05).
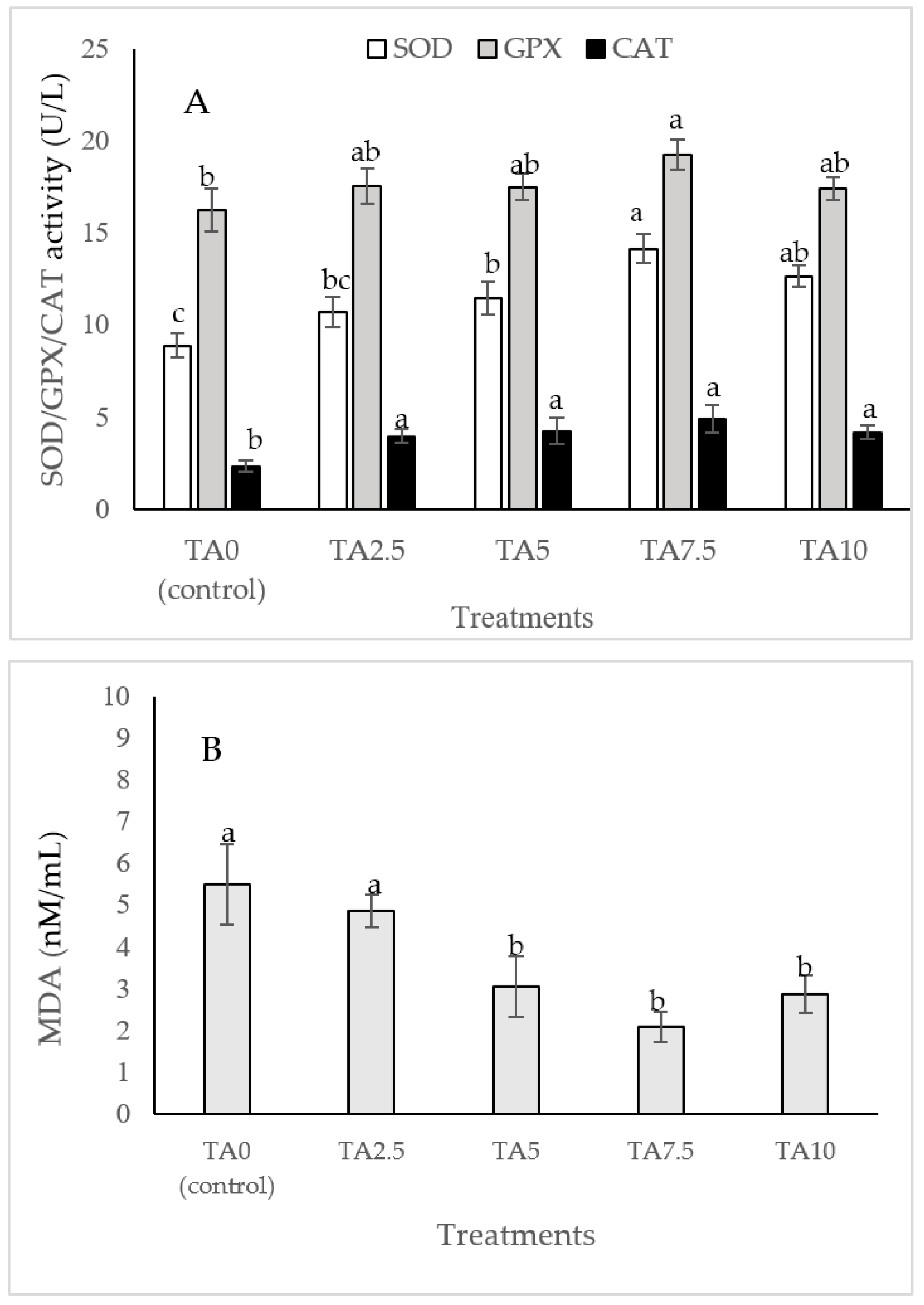
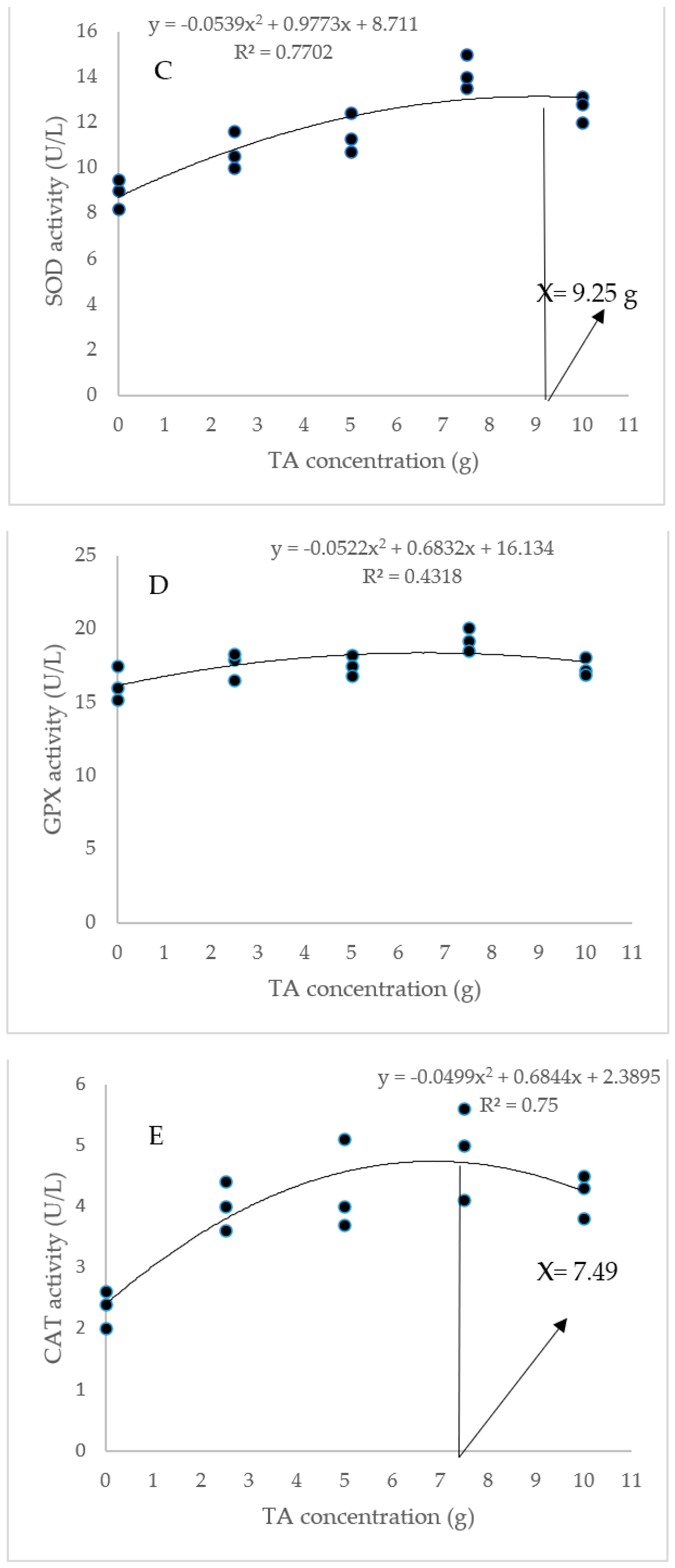
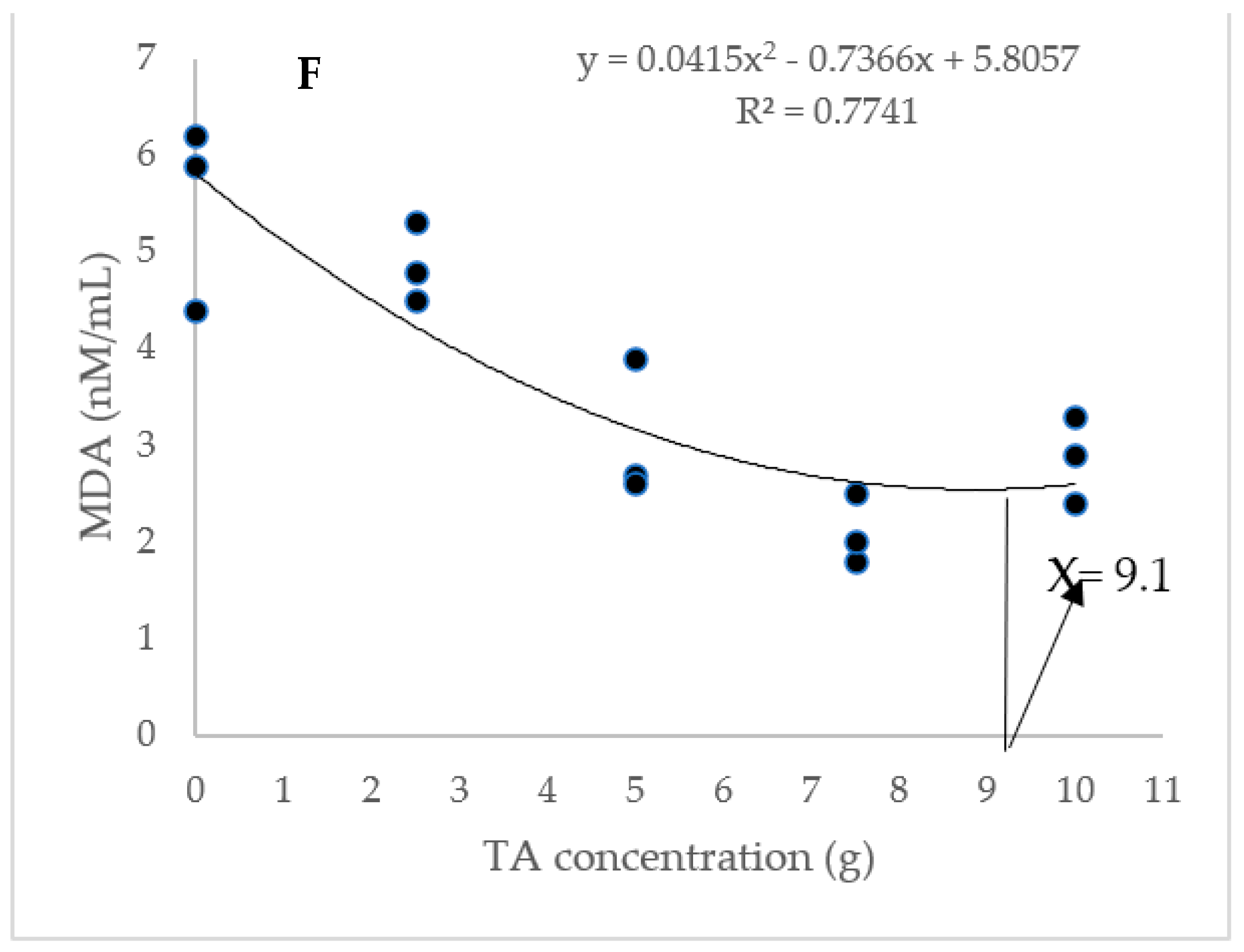
3.4. Measuring the Response of Antioxidant Markers and MDA Content
The dietary administration of 5, 7.5, and 10 g/kg induced a notable increase in the SOD activity compared to the TA0 (Figure 3). The specimens fed with the TA7.5 diet showed a significant improvement in GPX activity compared to the TA0 (p < 0.05). Dietary supplementation of TA at all concentrations markedly boosted the activity of CAT compared to the TA0 (p < 0.05). The dietary supplementation of TA at concentrations of 5–10 g/kg significantly decreased the MDA content when compared to the TA0 group (p < 0.05). Based on the quadratic regression test, there was a remarkable relationship between the shrimp SOD activity (R2 = 0.77), CAT activity (R2 = 0.75), and MDA content (R2 = 0.77) with the dietary TA concentrations (Figure 3) and the best levels were acquired at TA concentrations of 9.25 g, 7.49 g, and 9.1 g according to the SOD activity, CAT activity, and MDA content, respectively (Figure 3).
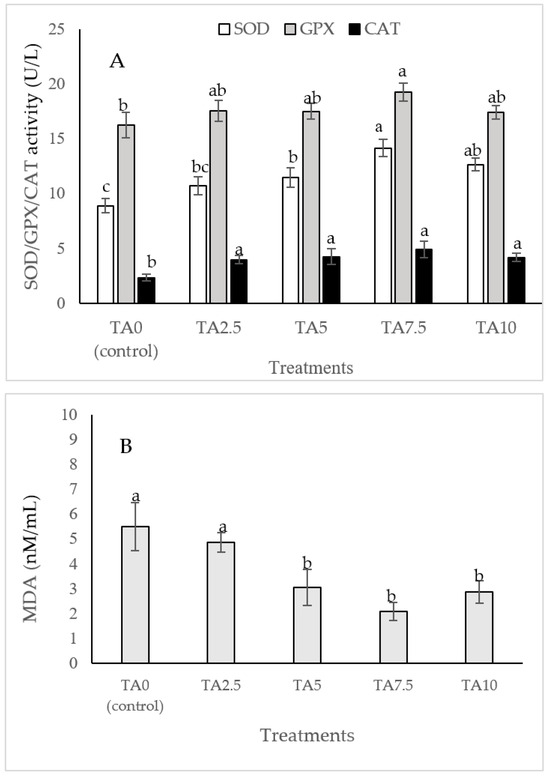
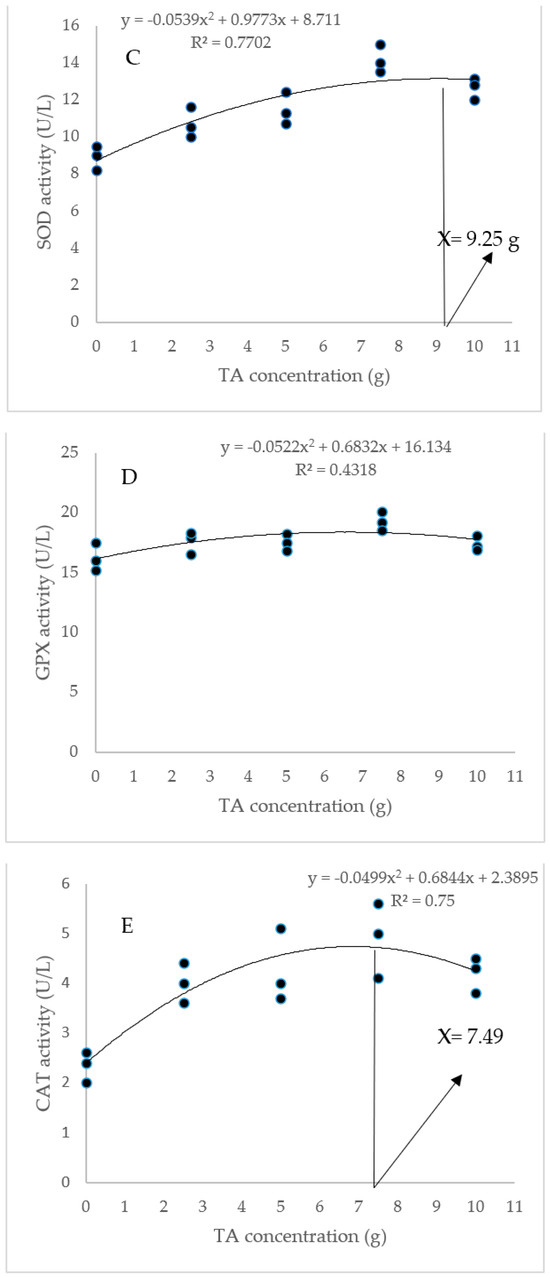
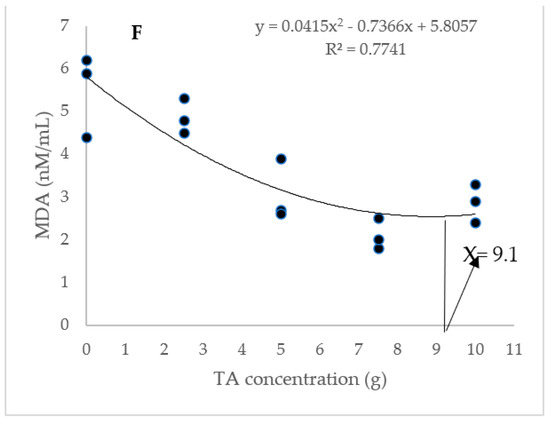
Figure 3.
(A,B): Serum SOD (superoxide dismutase), GPX (glutathione peroxidase), CAT (catalase) activity, and MDA (malondialdehyde) value in L. vannamei after treatment with different concentrations of tartaric acid (TA) (0–10 g/kg) for 56 days. (C–F): Relationships between the dietary TA levels and SOD (U/L), GPX (U/L), CAT (U/L) and MDA (nM/mL) in L. vannamei (n = 3). Dissimilar letters above the bars represent significant differences among the experimental groups (Tukey test; n = 3, p < 0.05), OD; optimum dose, R2; R square.
3.5. Innate Immune Responses
As indicated in Table 3, the SGC and HC counts were remarkably elevated in TA7.5 compared with the TA0 treatment (p < 0.05). In addition, the THC count was markedly enhanced in all specimens receiving TA compared to animals fed with the diet without TA (TA0). Moreover, the maximum THC count was observed in the TA7.5 group (p < 0.05). The LGC count was similar between the different treatments (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Immunity parameters in L. vannamei fed with diets containing 0–10 g/kg tartaric acid (TA) for 56 days.
Interestingly, hemolymph immune responses including LYZ, PO, AKP, and ACP in the specimens fed with all dietary TA levels were higher than the TA0 group (p < 0.05). Based on the quadratic regression test, there was a remarkable relationship between the shrimp THC count (R2 = 0.71), LYZ activity (R2 = 0.79), PO activity (R2 = 0.82), AKP activity (R2 = 0.72), and ACP activity (R2 = 0.80) with the dietary TA concentrations and the best levels were acquired at TA concentrations of 7.49 g, 7.73 g, 8.04 g 7.11 g, and 7.62 g according to the THC count, LYZ activity, PO activity, AKP activity, and ACP activity, respectively.
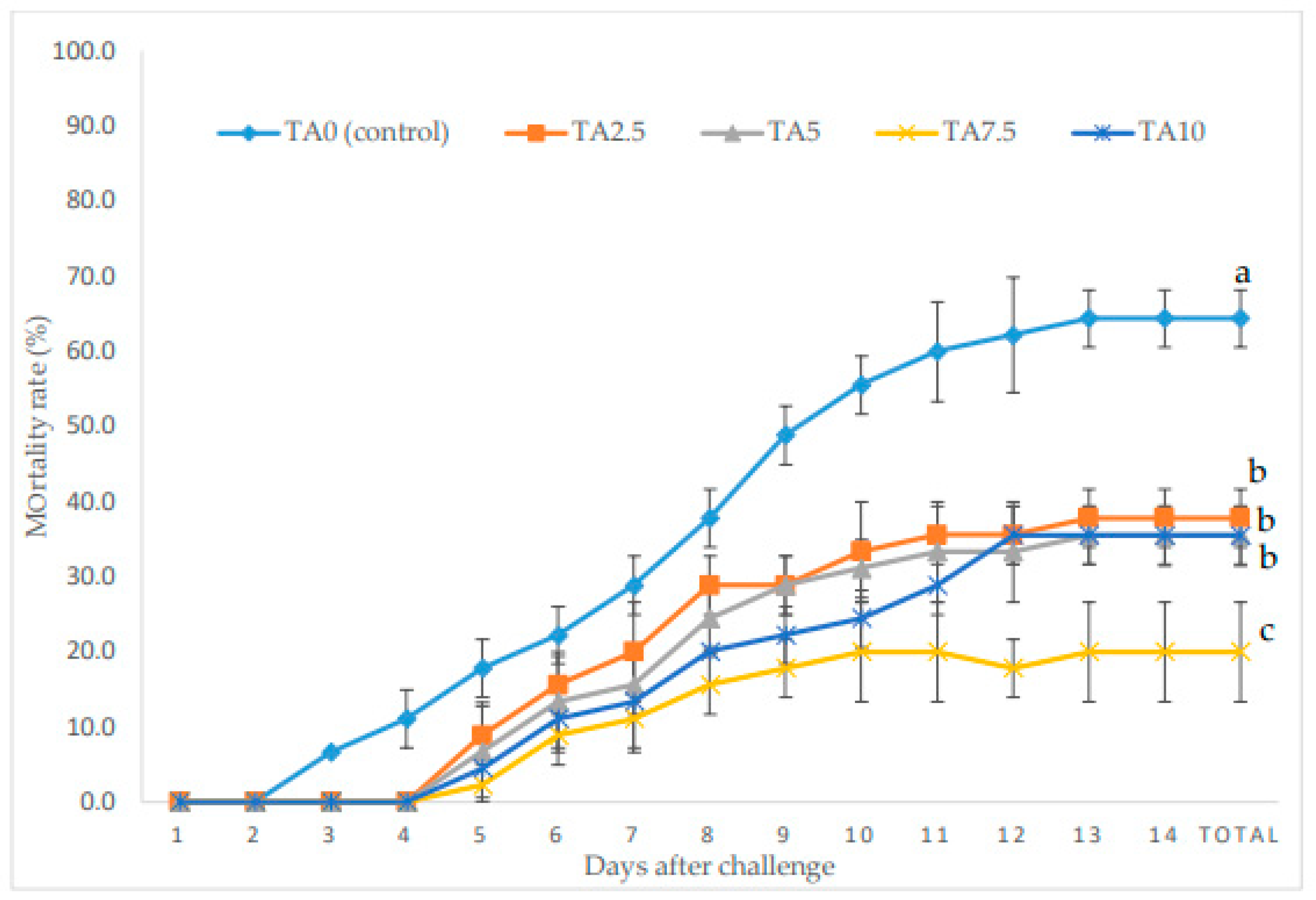
3.6. Challenge Test
The mortality rate (MR) of L. vannamei exposed to V. parahaemolyticus during a 14-day period is exhibited in Figure 4. At the end of the bacterial challenge period, all supplemented groups revealed a remarkably lower MR compared to the TA0 (p < 0.05). Moreover, the minimum MR was observed in the TA7.5 group, which presented a lower MR than the other TA groups (p < 0.05).
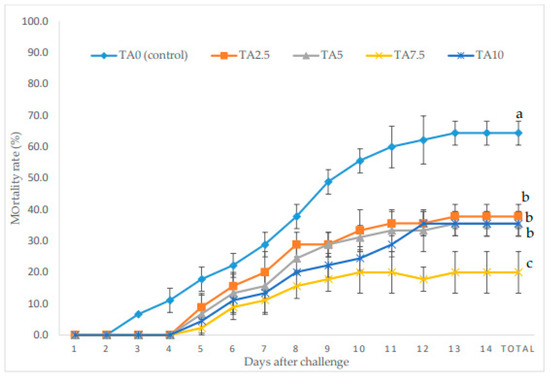
Figure 4.
Cumulative mortality during bacterial challenge with Vibrio parahaemolyticus in L. vannamei after treatment with different concentrations of tartaric acid (TA) (0–10 g/kg) for 56 days. Different letters following the lines of each treatment represent the significant differences among the experimental groups (Tukey test; n = 3, p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Markers, Gut LAB, and Digestive Enzyme Activities
In recent years, the acidification of aquafeed using OA has created several benefits for the digestive system health and growth of aquatic animals [12,19]. To date, no research has examined the properties of a dietary administration of TA on shrimp. In the current research, pellets fortified with TA at 5–10 g/kg significantly improved WG, FW, SGR, and FCR. Similarly, feeding L. vannamei with succinic acid at a concentration of 5 g/kg diet resulted in elevated FW, SGR, and FCR [19]. Similar data were also documented in L. vannamei fed with a diet supplemented with 2% potassium diformate (KDF) [12]. Several studies have reported that the dietary inclusion of OA boosted nutrient digestibility, protein, and energy storage, leading to a notable increase in PER, FCR, and SGR in shrimp [2,17,21]. It has been indicated that OA increases the availability of nutrients by lowering the pH. This action is accompanied by the chelation of minerals and the dephosphorylation of phytate, which facilitate the absorption of phosphorus and minerals, respectively [14,49]. In addition, OA participates in metabolic activities such as the carboxylic acid cycle, thereby increasing the generation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which, in turn, improves growth performance and feed utilization [37,50].
It has been demonstrated that the acidification of aquafeed with OA could regulate the gut microbiota by increasing beneficial strains resistant to acidity (e.g., LAB) and lysing bacteria sensitive to low pH [2,17,20]. Previous reports have revealed that gut LAB plays a vital role in the modulation of gut enzymatic capacity, thereby enhancing the growth performance of the host [51,52]. In this study, the inclusion of TA in the pellet at the concentration of 5–10 g/kg was able to fortify the abundance of indigenous LAB in the intestine, which was associated with the increase in intestinal digestive enzyme activity and growth performance. Similarly, other findings indicated that enhancing the LAB population led to improving digestive enzyme activity, such as yellowfin seabream (Acanthopagrus latussodium) [53] and L. vannamei [1,19] fed with an organic acid blend (propionate (Na-P) and sodium acetate) and succinic acid, respectively.
4.2. Immune Status
Shrimp and other crustaceans lack evolved specific immune responses, and, unlike fish, rely mainly on innate immune responses such as phagocytosis ability, antimicrobial peptides, and phenoloxidase activity; hence, boosting the innate immune system of shrimp in commercial conditions is essential [54]. Circulating hemocytes including hyaline cells, large granular cells, and semi-granular cells are the main mediators in creating cellular and humoral responses in crustaceans [55]. Therefore, measuring their count is one of the most reliable indicators to determine the effect of manipulated diets on immunity [56]. In the present research, the THC count markedly increased in all supplemented groups, which could be related to the maximum release of minerals such as copper and iron (Reda et al. [37]). Consistent with our results, feeding L. vannamei with sodium butyrate significantly improved the THC count [57]. In addition, the THC count was markedly elevated in L. vannamei supplemented with formic acid plus astaxanthin [18]. Alterations in the hemocyte count can also influence innate immune responses [54].
Phenol oxidase is a main metabolite in the prophenoloxidase system and presents varied immunity responses against pathogens including phagocytosis activity, melanization reaction, the liberation of cytotoxic substances, the encapsulation of parasites, and nodule formation [49]. Lysozyme is one of the well-known components of the innate immune system of aquatic animals, which is mainly responsible for the destruction of Gram-positive bacteria [58]. Our findings showed that the activity level of LYZ and PO were increased in all TA-treated shrimps compared to the control group, regardless of the dosage. No research has been performed to investigate the immunoprotective effects of TA on LYZ and PO in shrimp. However, other findings demonstrated that OA has the potential to stimulate the natural immune response in fish and shellfish. Su et al. [17] found that the dietary administration of citric acid at levels of 2 and 3 g/kg significantly boosted LYZ and PO activities in L. vannamei. Maslowski and Mackay [59] reported that different organic acids act as ligands for G protein-coupled receptor 43 and regulate immune reactions in aquatic animals.
In this work, ACP and AKP levels, as two lysosomal enzymes involved in hydrolytic activities, increased in all TA-treated animals. The mechanism of OAs on ACP or AKP levels in fish or shrimp has not been precisely identified. However, in poultry, some findings claimed that the increase in AKP in poultry serum is due to increased phosphorus digestibility and absorption [60,61,62]. They reported that the addition of OAs to the diet led to a decrease in gut pH and an increase in the transport of minerals from the digestive tract into the bloodstream. In fact, OA facilitates the activity of phytase enzyme to hydrolyze phytate by reducing gut pH and improving the absorption of minerals [11]. Recently, Liu et al. [2] reported a notable increase in the activity of ACP in L. vannamei fed with diets containing sodium butyrate/tributyrin. In addition, the addition of sodium benzoate to pellets significantly influenced the activity of AKP and ACP in L. vannamei [63].
However, the AKP activity was not affected by the mentioned diets in the same study. The properties of TA in stimulating the immune system may be related to regulating the intestinal microbial population or directly through stimulating the secretion of immune components by lymphoid tissues and altering some inflammatory responses.
4.3. Antioxidant Markers
Boosting the enzymatic or non-enzymatic reactions of the antioxidant system during the growth period plays a vital role in improving the health of crustaceans against biological or non-biological stress factors [64]. The inclusion of OA in the diet is one of the most practical and effective techniques used to improve the antioxidant status of L. vannamei. In this study, increasing the availability of minerals as cofactors for antioxidant enzymes can be one of the possible reasons for boosting the antioxidant status in supplemented groups [53,65]. Huang et al. [63] reported that dietary sodium benzoate could boost the activity of antioxidant enzymes in L. vannamei. Also, the SOD activity was significantly enhanced in L. vannamei fed with pellets fortified with formic acid plus astaxanthin [18].
Moreover, the ability of TA in ROS (reactive oxygen species) to scavenge or increase the level of mitochondrial enzymes is well speculated in in vitro conditions [24].
4.4. Challenge Test
Increasing the survival rate against fatal infections is one of the main goals of adding biostimulants to aquafeed [47]. In this research, the pellets fortified with TA at all concentrations led to a significant decrease in the mortality rate of the specimens fed with this diet compared to those given the TA0 treatment. Moreover, the minimum MR was obtained in the TA 7.5 group, which was three times lower than the control group. This can be related to the better regulation of the intestine microflora, increasing the immune and antioxidant capacity of shrimp belonging to this treatment. Similarly, the disease resistance against V. parahaemolyticus was enhanced in the Pacific white shrimp fed with formic acid [18] and citric acid plus sorbic acid [11].
5. Conclusions
The findings indicated that dietary tartaric acid boosted the growth markers and defense systems of L. vannamei. The notable improvements in growth indices, feed utilization, gut LAB, digestive enzyme activities, hemolymph immune parameters, antioxidant status, and disease resistance against V. parahaemolyticus were particularly recorded in the shrimp fed with TA7.5 diet. These results showed that TA could be considered a novel immunopotentator and growth stimulator for L. vannamei rearing. However, more research is recommended to explore the properties of tartaric acid alone or in combination with other biostimulants such as probiotics on gut morphology, the expression of genes related to growth, immunity, and antioxidant capacity, as well as its benefits against environmental stresses in fish/shellfish.
Author Contributions
M.Y.: Supervision, conceptualization, resources, funding acquisition, and reviewing the draft. M.N.F.: Supervision, conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft. A.A.-K.: Conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology. S.A.: methodology, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by the RUDN University Strategic Academic Leadership Program dedicated to Morteza Yousefi.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Xiong, D.; Zhang, J. Response of intestine microbiota, digestion, and immunity in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei to dietary succinate. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zou, H.; Wang, C. Effect of dietary supplementation with sodium butyrate and tributyrin on the growth performance and intestinal microbiota of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 2477–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, J.T.; dos Santos Rocha, R.; Maggioni, R. Structural and functional diversity of lectins associated with immunity in the marine shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 129, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Ng, T.H.; Wang, H.C. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in penaeid shrimp. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, A.S.K.; Mok, W.Y.; Tamrin, M.L.M.; Shapawi, R.; Kim, Y.S. Effects of dietary nucleotides on growth, survival and metabolic response in whiteleg shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei against ammonia stress condition. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, B.; Li, J.; Liao, G.; Wang, L.; Fan, L. Toxic effects of glyphosate on histopathology and intestinal microflora of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 255, 106399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Han, F.; Huang, K.; Zhang, J.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L.; Li, E. Impact of imidacloprid exposure on the biochemical responses, transcriptome, gut microbiota and growth performance of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Xu, C.; Chen, C.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L.; Li, E. Toxic effect of chronic waterborne copper exposure on growth, immunity, anti-oxidative capacity and gut microbiota of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 100, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Leal, H.M.; Ponce-Palafox, J.T.; Cervantes-Cervantes, C.M.; Valenzuela-Quiñónez, W.; Luna-González, A.; López-Álvarez, E.S.; Vázquez-Montoya, N.; López-Espinoza, M.; Gómez-Peraza, R.L. Effects of low salinity exposure on immunological, physiological and growth performance in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xiong, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. Toxicological effects of microplastics in Litopenaeus vannamei as indicated by an integrated microbiome, proteomic and metabolomic approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Rahimnejad, S.; Wang, L.; Song, K.; Lu, K.; Zhang, C. Effects of organic acids and essential oils blend on growth, gut microbiota, immune response and disease resistance of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, M.; Amirtharaj, K.V.; Chrisolite, B.; Sivasankar, P.; Subash, P. Dietary organic acids on growth, immune response, hepatopancreatic histopathology and disease resistance in Pacific white shrimp, Penaeus vannamei against Vibrio harveyi. Res. Squ. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, A.; Mehrgan, M.S.; Islami, H.R. Optimizing turmeric and green tea fermentation with Lactobacillus brevis to enhance growth performance, digestive enzymes, and immunity in rainbow trout. Aquaculture 2023, 577, 739962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.-K.; Koh, C.-B.; Teoh, C.-Y.; Romano, N. Farm-raised tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon, fed commercial feeds with added organic acids showed enhanced nutrient utilization, immune response and resistance to Vibrio harveyi challenge. Aquaculture 2015, 449, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, S.; Boopathy, R. Effect of organic acids on shrimp pathogen, Vibrio harveyi. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathod, N.B.; Ranveer, R.C.; Benjakul, S.; Kim, S.K.; Pagarkar, A.U.; Patange, S.; Ozogul, F. Recent developments of natural antimicrobials and antioxidants on fish and fishery food products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4182–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Li, X.; Leng, X.; Tan, C.; Liu, B.; Chai, X.; Guo, T. The improvement of growth, digestive enzyme activity and disease resistance of white shrimp by the dietary citric acid. Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuchird, N.; Rorkwiree, P.; Rairat, T. Effect of dietary formic acid and astaxanthin on the survival and growth of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) and their resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Springer Plus 2015, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Dietary effects of succinic acid on the growth, digestive enzymes, immune response and resistance to ammonia stress of Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 78, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busti, S.; Rossi, B.; Volpe, E.; Ciulli, S.; Piva, A.; D’Amico, F.; Soverini, M.; Candela, M.; Gatta, P.P.; Bonaldo, A. Effects of dietary organic acids and nature identical compounds on growth, immune parameters and gut microbiota of European sea bass. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Koh, C.-B.; Ng, W.K. Dietary microencapsulated organic acids blend enhances growth, phosphorus utilization, immune response, hepatopancreatic integrity and resistance against Vibrio harveyi in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2015, 435, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantwal, A.; Durgapal, S.; Upadhyay, J.; Joshi, T.; Kumar, A. Tartaric acid, Antioxidants Effects in Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; You, L.; Khan, R.A.A.; Yu, Y. Phenolic contents, organic acids, and the antioxidant and bio activity of wild medicinal Berberis plants-as sustainable sources of functional food. Molecules 2022, 27, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, I.; Shamim, S.; Ameen, F.; Hussain, Z.; Bhat, S.A.; Qadri, T.; Hussain, M.A. combinatorial approach towards antibacterial and antioxidant activity using tartaric acid capped silver nanoparticles. Process 2022, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethalakshmi, P.; Rajeev, R.; Kiran, G.S.; Selvin, J. Shrimp disease management for sustainable aquaculture: Innovations from nanotechnology and biotechnology. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 1591–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Hamidoghli, A.; Farris, N.W.; Olowe, O.S.; Choi, W.; Lee, S.; Won, S.; Ohh, M.; Lee, S.; Bai, S.C. Dietary γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) promotes growth and resistance to Vibrio alginolyticus in whiteleg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Nutr. 2022, 2022, 9105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists). Official Methods of Analysis of Official Analytical Chemists International, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Irani, M.; Islami, H.R.; Bahabadi, M.N.; Shekarabi, S.P.H. Production of Pacific white shrimp under different stocking density in a zero-water exchange biofloc system: Effects on water quality, zootechnical performance, and body composition. Aquac. Eng. 2023, 100, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Hu, S.Y.; Chiu, C.-S.; Liu, C.-H. Multiple-strain probiotics appear to be more effective in improving the growth performance and health status of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, than single probiotic strains. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.-C.; Lin, T.-Y.; Chi, C.-C.; Liu, C.-H. Probiotic, Bacillus subtilis E20 alters the immunity of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei via glutamine metabolism and hexosamine biosynthetic pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Farsani, M.N.; Ghafarifarsani, H.; Raeeszadeh, M. Dietary Lactobacillus helveticus and Gum Arabic improves growth indices, digestive enzyme activities, intestinal microbiota, innate immunological parameters, antioxidant capacity, and disease resistance in common carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023, 135, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarizadeh, A.; Sotoudeh, E.; Mozanzadeh, M.T.; Sanati, A.M.; Ghasemi, A. Supplementing dietary selenium nano-particles increased growth, antioxidant capacity and immune-related genes transcription in Pacific whiteleg shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) juveniles. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonwachai, T.; Purivirojkul, W.; Limsuwan, C.; Chuchird, N.; Velasco, M.; Dhar, A.K. Growth, nonspecific immune characteristics, and survival upon challenge with Vibrio harveyi in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) raised on diets containing algal meal. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, H.; Sourinejad, I.; Johari, S.A. Dietary turmeric, curcumin and nanoencapsulated curcumin can differently fight against salinity stress in Pacific white shrimp Penaeus vannamei Boone, 1931. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabawati, E.; Hu, S.Y.; Chiu, S.-T.; Balantyne, R.; Risjani, Y.; Liu, C.H. A synbiotic containing prebiotic prepared from a by-product of king oyster mushroom, Pleurotus eryngii and probiotic, Lactobacillus plantarum incorporated in diet to improve the growth performance and health status of white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 120, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanez-Lemus, F.; Moraga, R.; Smith, C.T.; Aguayo, P.; Sánchez-Alonzo, K.; García-Cancino, A.; Valenzuela, A.; Campos, V.L. Selenium nanoparticle-enriched and potential probiotic, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum S14 strain, a diet supplement beneficial for rainbow trout. Biology 2022, 11, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reda, R.M.; Mahmoud, R.; Selim, K.M.; El-Araby, I.E. Effects of dietary acidifiers on growth, hematology, immune response and disease resistance of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016, 50, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasim, S.A.; Hafsan, H.; Saleem, H.D.; Kandeel, M.; Khudhair, F.; Yasin, G.; Iswanto, A.H.; Mohammed, H.T.; Izzat, S.E.; Dadras, M. The synergistic effects of the probiotic (Lactobacillus fermentum) and cinnamon, Cinnamomum sp. powder on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, immunity, antioxidant defence and resistance to Yersinia ruckeri infection in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) under high rearing density. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5957–5970. [Google Scholar]
- Rick, W.; Stegbauer, H.P. α-Amylase Measurement of Reducing Groups, Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1974; pp. 885–890. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, G.S.; Priyadharshini, S.; Sajayan, A.; Ravindran, A.; Priyadharshini, G.B.; Ramesh, U.; Suarez, L.E.C.; Selvin, J. Dietary administration of gelatinised polyhydroxybutyrate to Penaeus vannamei improved growth performance and enhanced immune response against Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Carreño, F.L. Protease inhibition in theory and practice. J. Biol. Educ. 1992, 3, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi-Arpanahi, D.; Soltani, E.; Jafaryan, H.; Soltani, M.; Naderi-Samani, M.; Campa-Córdova, A.I. Efficacy of two commercial and indigenous probiotics, Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, immuno-physiology and resistance response of juvenile white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture 2018, 496, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moullac, G.; Le Groumellec, M.; Ansquer, D.; Froissard, S.; Levy, P. Haematological and phenoloxidase activity changes in the shrimp Penaeus stylirostrisin relation with the moult cycle: Protection against vibriosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 1997, 7, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, A. Lysozyme assays. Techniques in Fish Immunology; Stolen, J.S., Fletcher, T.C., Anderson, D.P., Kaattari, S.L., Rowley, A.F., Eds.; SOS Publications: Fair Haven, NJ, USA, 1990; pp. 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-López, J.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Vargas-Albores, F. Activation of the prophenoloxidase system of the brown shrimp Penaeus californiensis Holmes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. 1996, 113, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, K.; Liu, J.-Y.; Ling, F.; Liu, X.-L.; Lu, L.; Xia, L.; Wang, G.X. Effects of dietary administration of Shewanella haliotis D4, Bacillus cereus D7 and Aeromonas bivalvium D15, single or combined, on the growth, innate immunity and disease resistance of shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2014, 428, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogeley, J.L.; Interaminense, J.A.; Buarque, D.S.; da Silva, S.M.B.C.; Coimbra, M.R.M.; Peixoto, S.M.; Soares, R.B. Growth and immune gene expression of Litopenaeus vannamei fed Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus circulans supplemented diets and challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Jiang, K.; Xin, F.; Wang, B. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and the corresponding supernatant on the survival, growth performance, immune response and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Pandey, A.; Satoh, S. Effects of organic acids on growth and phosphorus utilization in red sea bream Pagrus major. Fish Sci. 2007, 73, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.J.; Satoh, S.; Kiron, V. Supplementation of citric acid and amino acid chelated trace elements in low-fish meal diet for rainbow trout affect growth and phosphorus utilization. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2012, 43, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, P.; Shamna, N.; Sahu, N. Acidifiers in aquafeed as an alternate growth promoter: A short review. Anim. Nutr. Feed Technol. 2020, 20, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Dawood, M.A.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; El-Matbouli, M. Benefits of dietary butyric acid, sodium butyrate, and their protected forms in aquafeeds: A review. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 28, 421–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoudeh, E.; Sangari, M.; Bagheri, D.; Morammazi, S.; Torfi Mozanzadeh, M. Dietary organic acid salts mitigate plant protein induced inflammatory response and improve humoral immunity, antioxidative status and digestive enzyme activities in yellowfin seabream, Acanthopagrus latus. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Krishnan, S.; Anand, D.; Kokkattunivarthil Uthaman, S.; Otta, S.K.; Karunasagar, I.; Kooloth Valappil, R. Immune responses and immunoprotection in crustaceans with special reference to shrimp. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 431–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bossier, P.; Norouzitallab, P.; Vanrompay, D. Trained immunity and perspectives for shrimp aquaculture. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 2351–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, C.J.; Söderhäll, K. The stress–immunity axis in shellfish. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 186, 107492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarahmadi, P.; Mirghaed, A.T.; Shekarabi, S.P.H. Zootechnical performance, immune response, and resistance to hypoxia stress and Vibrio harveyi infection in Pacific white shrimp (Litopeneaus vannamei) fed different fishmeal diets with and without addition of sodium butyrate. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 26, 101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aweya, J.J.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, X.; Yao, D.; Zhang, Y. The expanding repertoire of immune-related molecules with antimicrobial activity in penaeid shrimps: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1907–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslowski, K.M.; Mackay, C.R. Diet, gut microbiota and immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafacz-Livingston, K.; Parsons, C.; Jungk, R. The effects of various organic acids on phytate phosphorus utilization in chicks. Poult. Sci. J. 2005, 84, 1356–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liem, A.; Pesti, G.; Edwards, H., Jr. The effect of several organic acids on phytate phosphorus hydrolysis in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. J. 2008, 87, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Kaya, A.; Gül, M.; Çelebi, Ş.; Timurkaan, S.; Apaydin, B. Effects of supplementation of different levels of organic acids mixture to the diet on performance, egg quality parameters, serum traits and histological criteria of laying hens. Eur. Poult. Sci. 2014, 78, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Lou, G.; Man, Z.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, X.; Guo, Y.; Ge, R.; Liu, H.; Tong, M.; Liu, X.; et al. Dietary sodium benzoate improves growth, morphology, antioxidant capacity and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquac. Rep. 2023, 33, 101778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trestrail, C.; Nugegoda, D.; Shimeta, J. Invertebrate responses to microplastic ingestion: Reviewing the role of the antioxidant system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 138559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, R.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Kavandi, M. Modulation of antioxidant defense and immune response in zebra fish (Danio rerio) using dietary sodium propionate. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 42, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).