Hydrodynamic Modelling of Severn Bore and Its Dependence on Ocean Tide and River Discharge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Setup and Validation
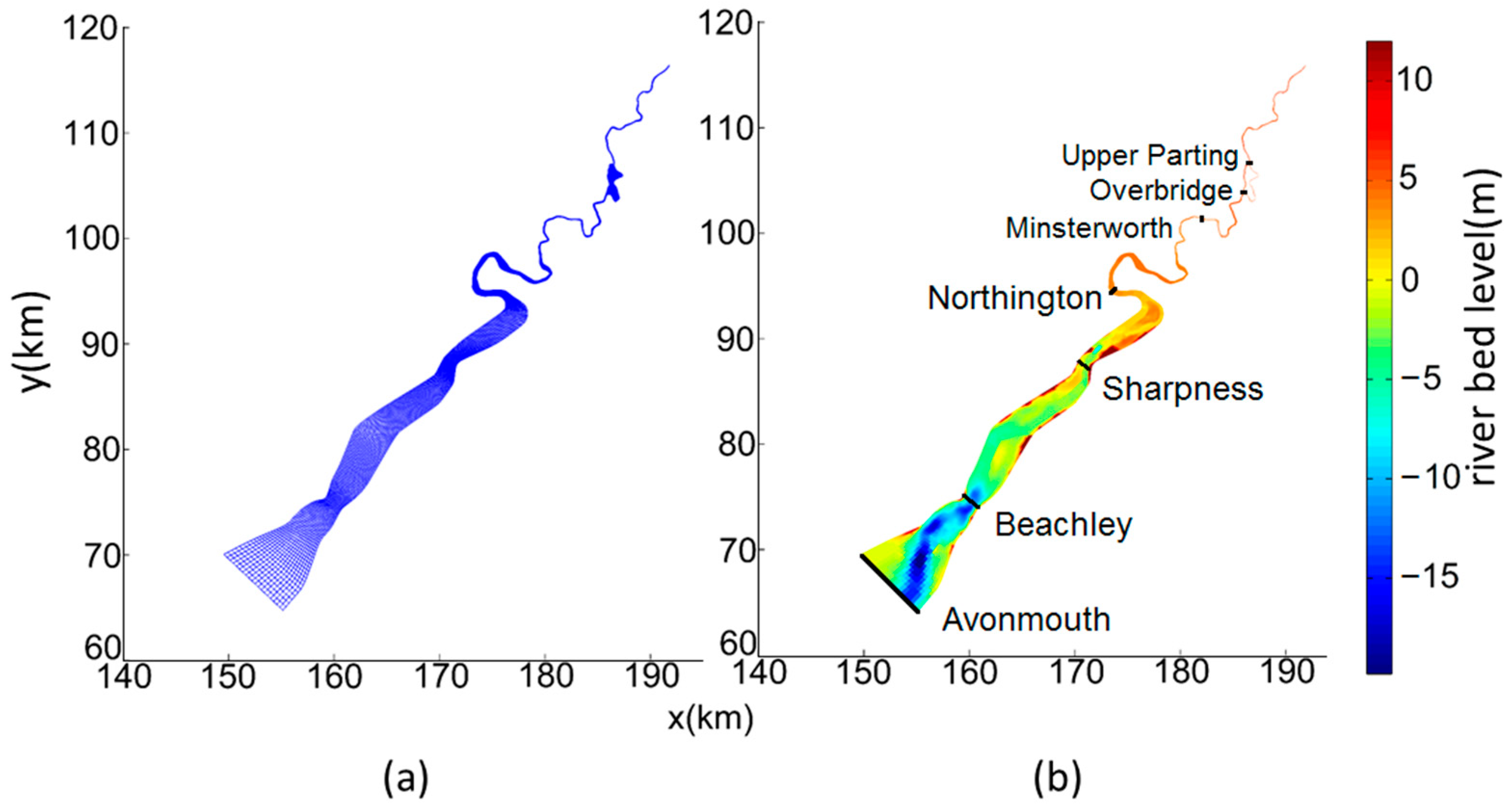
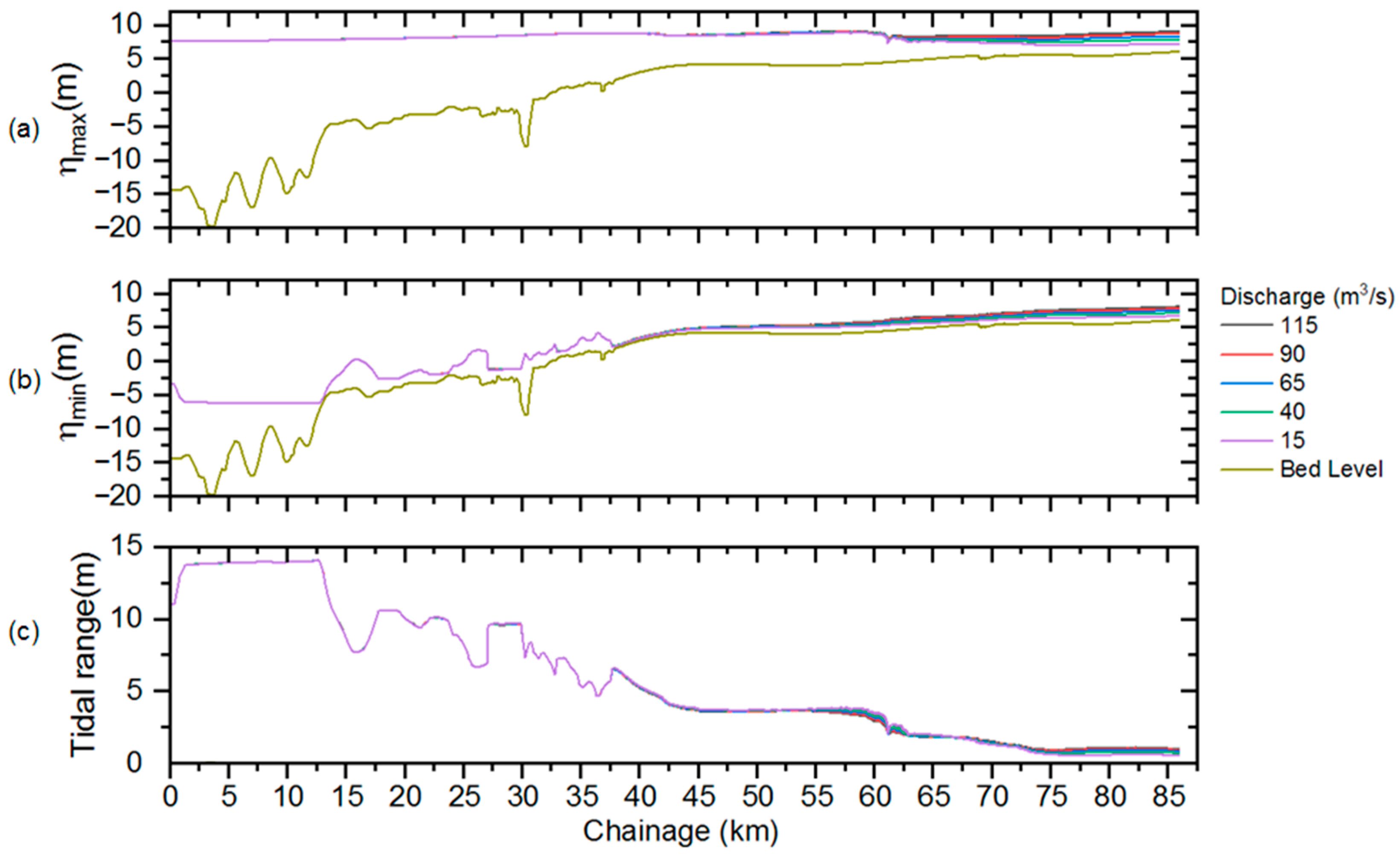
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Model Establishment
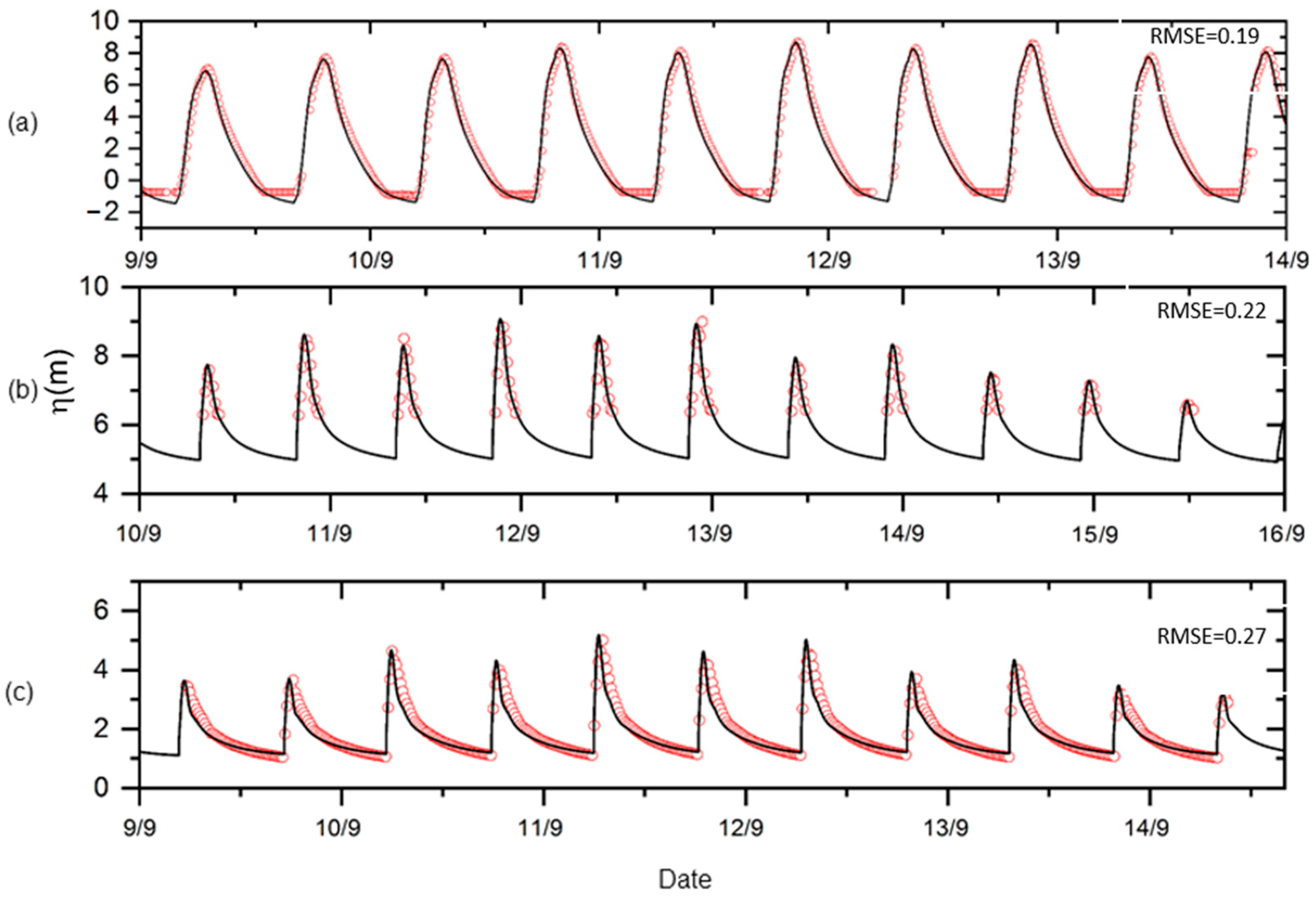
2.3. Model Validation
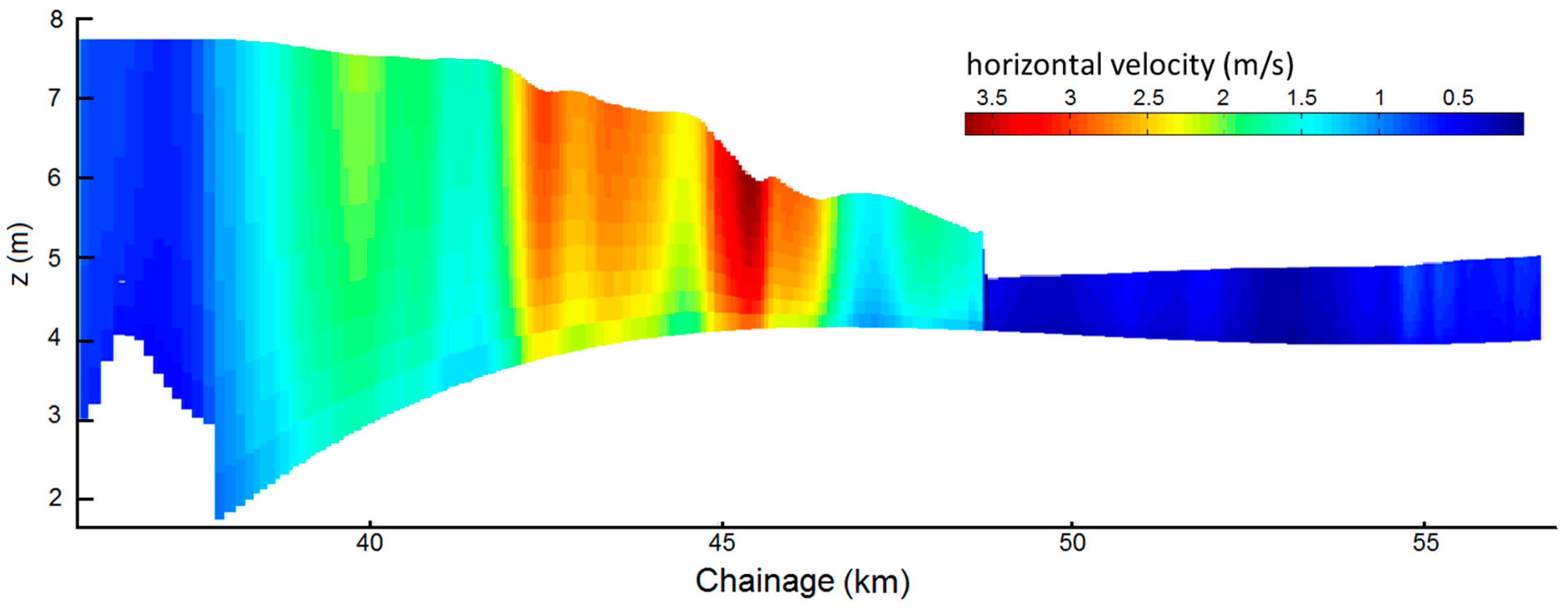
2.4. Tidal Bore Formation and Intensity
3. Results
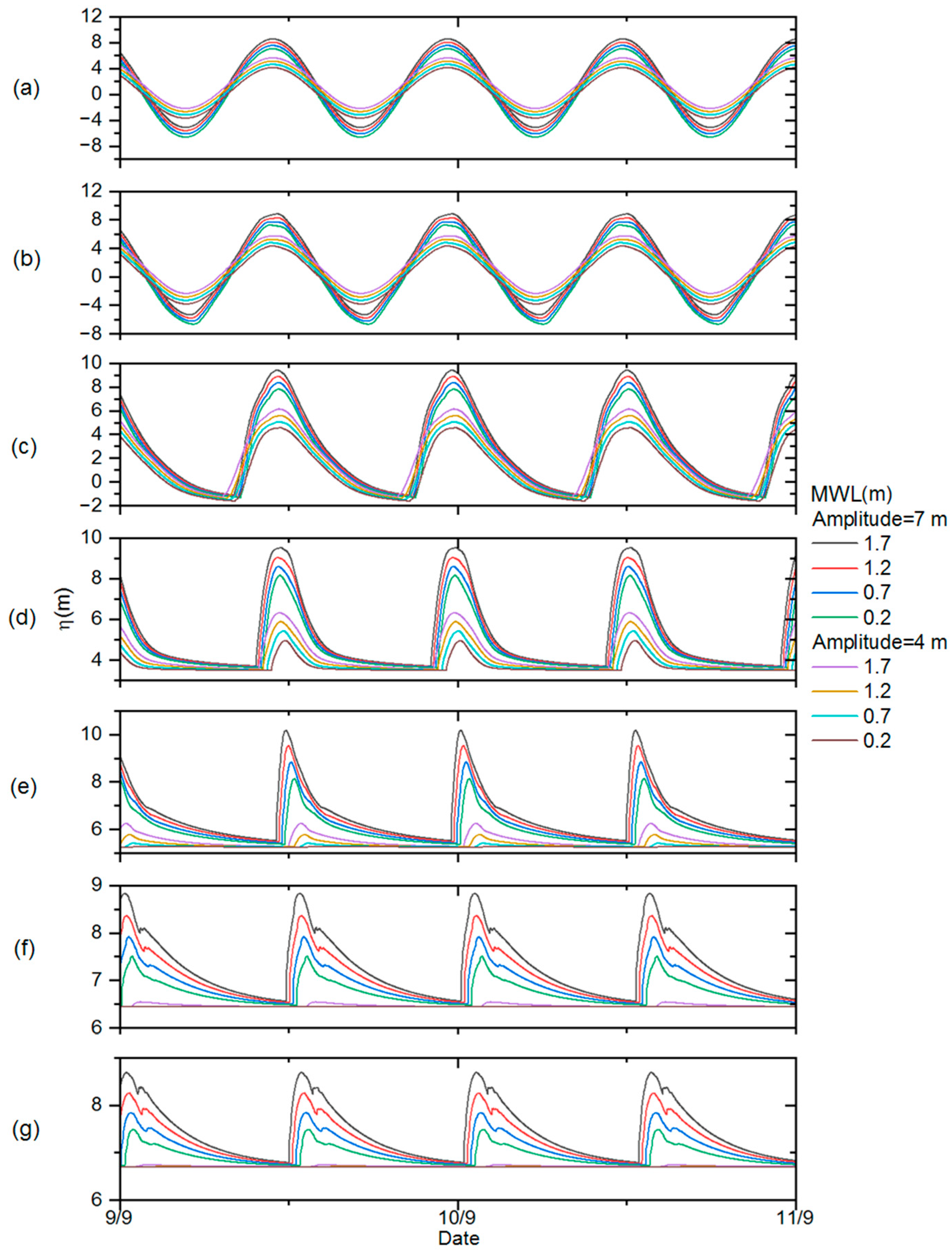
3.1. Scenario Definition
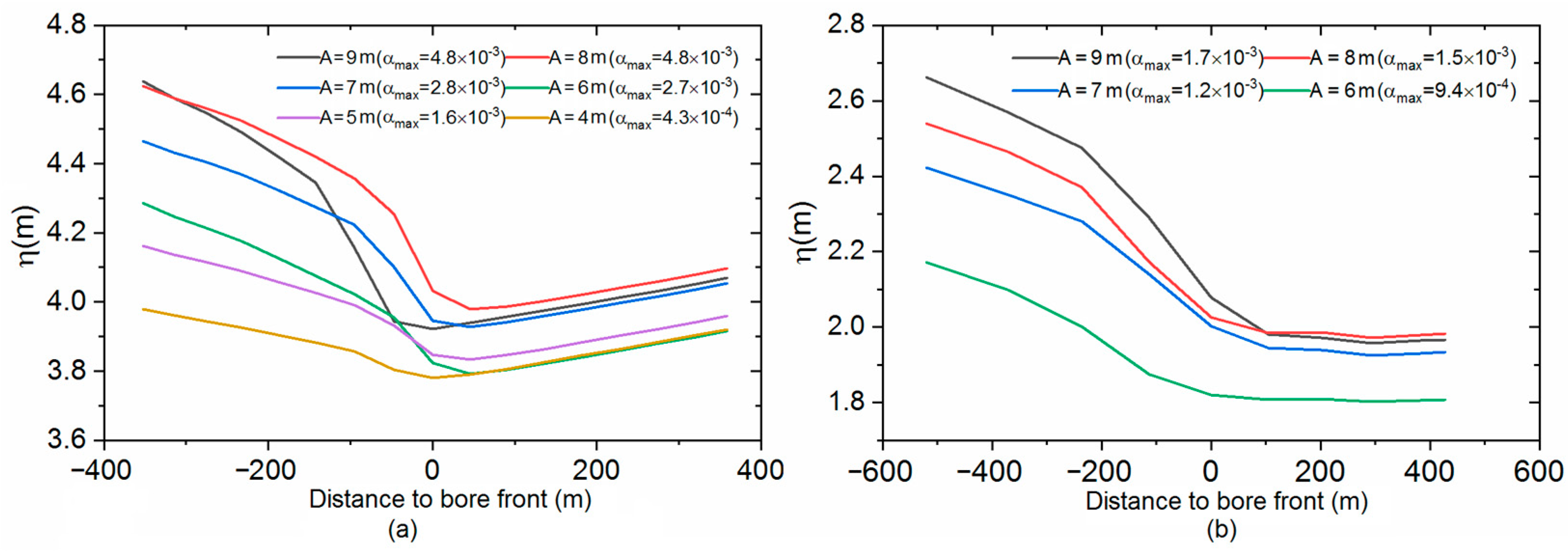
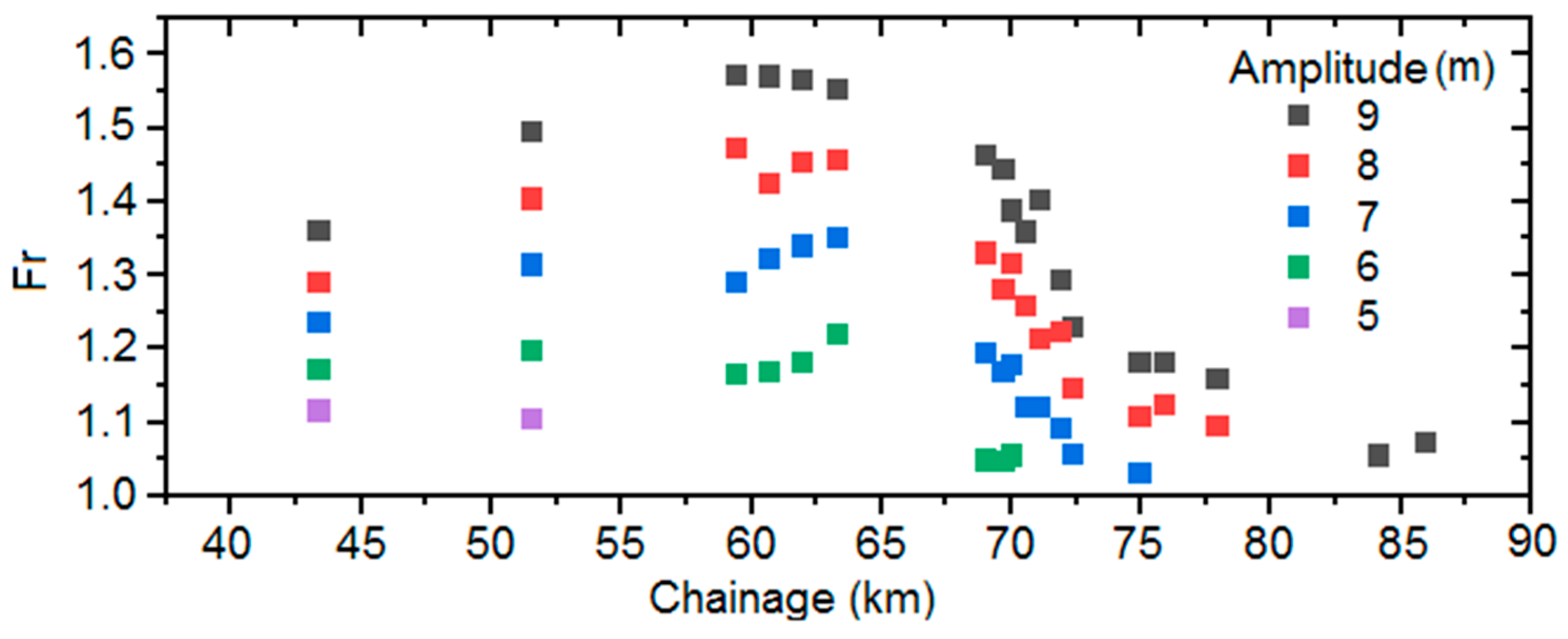
3.2. Influence of Downstream Tidal Amplitude
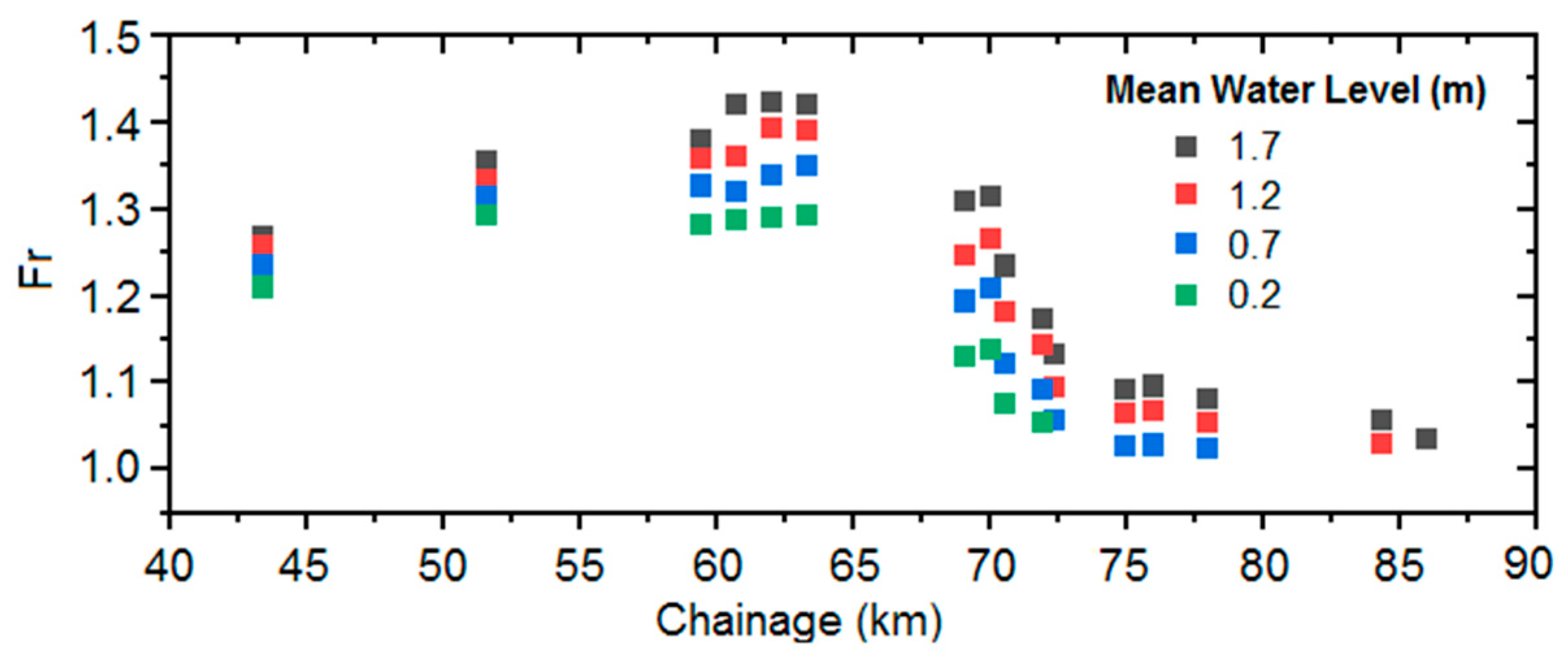
3.3. Influence of Downstream Mean Water Level
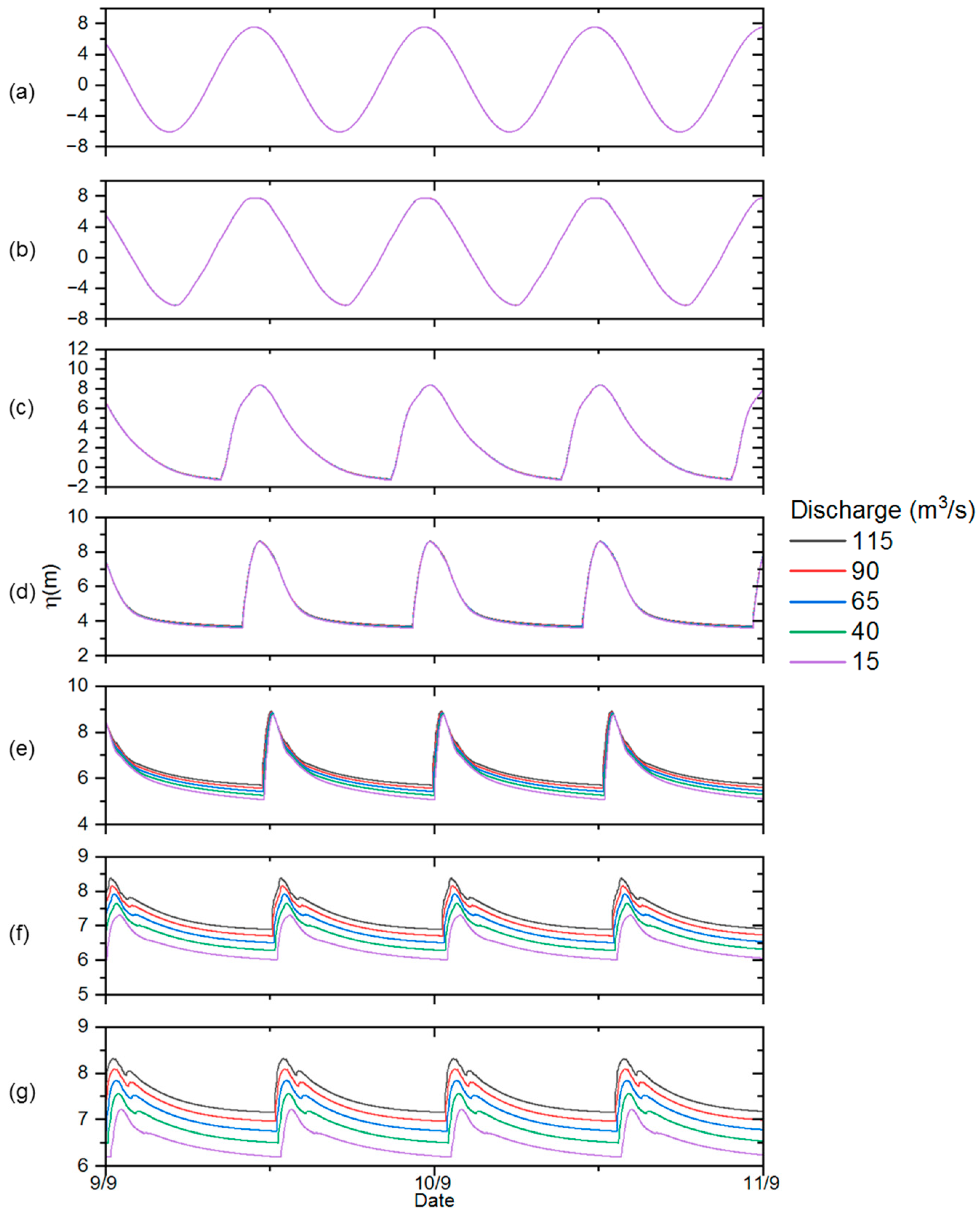
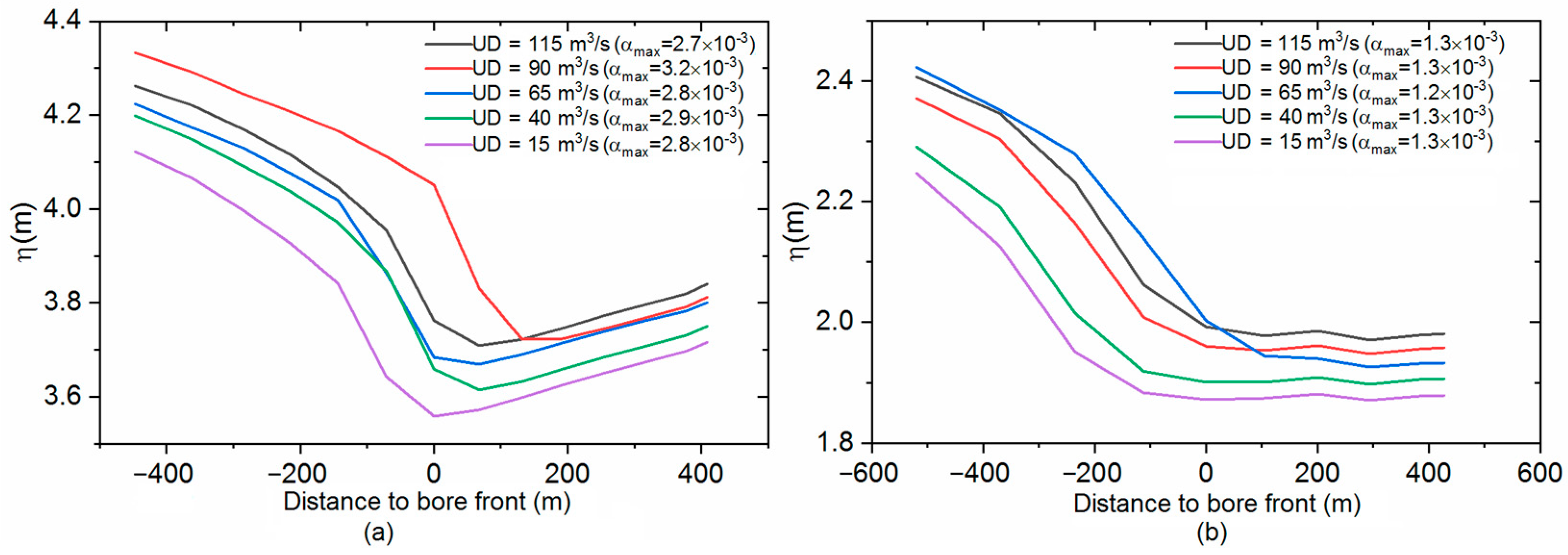
3.4. Influence of River Discharge
4. Discussions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chanson, H. Environmental, Ecological and Cultural Impacts of Tidal Bores, Benaks, Bonos and Burros. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Hydraulics: Theoretical, Experimental and Computational Solutions, Valencia, Spain, 29 October 2009; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chanson, H. Current Knowledge in Tidal Bores and Their Environmental, Ecological and Cultural Impacts. Environ. Fluid. Mech. 2011, 11, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, O.; Fairclough, L. Sounding Grief: The Severn Estuary as an Emotional Soundscape. Emot. Space Soc. 2016, 20, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, M. River of Many Voices: Oral and Environmental Histories of the Severn. In Telling Environmental Histories: Intersections of Memory, Narrative and Environment; Holmes, K., Goodall, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 81–106. ISBN 978-3-319-63772-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch-Winkler, S.; Lynch, D.K. Catalog of Worldwide Tidal Bore Occurrences and Characteristics; U.S. Geological Survey Circular; U.S. Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1988; Volume 1022.
- Chanson, H. Tidal Bores, Aegir, Eagre, Mascaret, Pororoca: Theory and Observations; World Scientific: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, D.K. Tidal Bores. Sci. Am. 1982, 247, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H.; Reungoat, D.; Simon, B.; Lubin, P. High-Frequency Turbulence and Suspended Sediment Concentration Measurements in the Garonne River Tidal Bore. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 95, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.H.; Fisher, N.R.; Wiles, P. Reynolds Stress and TKE Production in an Estuary with a Tidal Bore. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolanski, E.; Williams, D.; Spagnol, S.; Chanson, H. Undular Tidal Bore Dynamics in the Daly Estuary, Northern Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneton, P.; Van de Loock, J.; Parisot, J.-P.; Bonneton, N.; Sottolichio, A.; Detandt, G.; Castelle, B.; Marieu, V.; Pochon, N. On the Occurrence of Tidal Bores—The Garonne River Case. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 64, 1462–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.F.; Pan, C.H.; Wu, X.G. Modeling the Tidal Bore on the Qiantang River, China: An Application of FVCOM. In Proceedings of the the 6th International Symposium on Environmental Hydraulics, Athens, Greece, 23–25 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, C.; Huang, W. Numerical Modeling of Suspended Sediment Transport Affected by Tidal Bore in Qiantang Estuary. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-H.; Lu, H. 2D Numerical Simulation of Tidal Bore on Qiantang River Using KFVS Scheme. Int. Conf. Coastal. Eng. 2011, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, D.-Z.; Chanson, H.; Pan, C.-H. Real-Time Characteristics of Tidal Bore Propagation in the Qiantang River Estuary, China, Recorded by Marine Radar. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 180, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, H.; Huai, Z.; YaoLin, S.H.I. Numerical simulation of the tidal bore in the Qiantang River based on Boussinesq-type equations. Chin. J. Geophys. 2022, 65, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-Biswas, T.; Sen, D. Tidal Bore Dynamics of a Mixed Estuary: The Hooghly River, India. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 2023, 149, 05022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayu, A.; Pudjaprasetya, S.; Wisha, U.; Husrin, S. Numerical Simulation of Tidal Bore Bono at Kampar River. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2019, 12, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. Numerical Modelling of Shallow-Water Wave Propagation in Coastal and Estuarine Environments; University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kurniawan, A.; Wisha, U.J.; Husrin, S.; Karjadi, E.A. Tidal Bore Generation at Hte Estuaries of the East Coast of Sumatra. In Proceedings of the 37th IAHR World Congress, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13 August 2017; pp. 3587–3593. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, F.A.R.; Ningsih, N.; Rachmayani, R. Numerical Simulation of Tidal Bore in Kampar River: A Preliminary Study. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 339, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Falconer, R.A.; Lin, B. Hydrodynamic Impact of a Tidal Barrage in the Severn Estuary, UK. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, R.; Falconer, R.; Bockelmann-Evans, B. Far-Field Modelling of the Hydro-Environmental Impact of Tidal Stream Turbines. Renew. Energy 2012, 38, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Xia, J.; Falconer, R.; Zhang, J. Study on Tidal Resonance in Severn Estuary and Bristol Channel. Coast. Eng. J. 2015, 56, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Adcock, T.A.A. Modification of Tidal Resonance in the Severn Estuary by a Barrage and Lagoon. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy 2020, 6, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severn Estuary Commission. Available online: https://www.severncommission.co.uk/ (accessed on 7 November 2024).
- Abbott, M.R.; Lighthill, M.J. A Theory of the Propagation of Bores in Channels and Rivers. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1956, 52, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langston, W.J.; Jonas, P.J.C.; Millward, G.E. The Severn Estuary and Bristol Channel: A 25 Year Critical Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 61, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holgate, S.J.; Matthews, A.; Woodworth, P.L.; Rickards, L.J.; Tamisiea, M.E.; Bradshaw, E.; Foden, P.R.; Gordon, K.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Pugh, J. New Data Systems and Products at the Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level. J. Coast. Res. 2012, 29, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrological Open Data—Data.Gov.UK. Available online: https://www.data.gov.uk/dataset/98a4d46e-23e7-4430-883c-9e5f14645e8f/hydrological-open-data (accessed on 8 November 2024).
- Bonneton, P.; Bonneton, N.; Parisot, J.-P.; Castelle, B. Tidal Bore Dynamics in Funnel-Shaped Estuaries. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowbotham, F. The Severn Bore; David & Charles: London, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, C.; Lin, B.; Mao, X. New Development in the Numerical Simulation of the Tidal Bore. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Estuaries & Coasts, Hangzhou, China, 9 November 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Viero, D.P.; Defina, A. Consideration of the Mechanisms for Tidal Bore Formation in an Idealized Planform Geometry. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5670–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treske, A. Undular Bores (Favre-Waves) in Open Channels—Experimental Studies. J. Hydraul. Res. 1994, 32, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouaze, D.; Chanson, H.; Simon, B. Field Measurements in the Tidal Bore of the Sélune River in the Bay of Mont Saint Michel; The University of Queensland: Brisbane, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, J.; Fan, D. Flow and Turbulence Structure in a Hypertidal Estuary with the World’s Biggest Tidal Bore. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 3417–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalrymple, R.W. Sedimentation on High-Energy Sand Flats in the Bay of Fundy: The Record of Tidal-Bore Activity and Deposition from High-Concentration Suspensions of Sand. Sedimentology 2021, 68, 2195–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kästner, K.; Hoitink, A.J.F.; Torfs, P.J.J.F.; Deleersnijder, E.; Ningsih, N.S. Propagation of Tides along a River with a Sloping Bed. J. Fluid. Mech. 2019, 872, 39–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Lin, B.-Y.; Mao, X.-Z. Case Study: Numerical Modeling of the Tidal Bore on the Qiantang River, China. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2007, 133, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wang, X.; Bockelmann-Evans, B.N.; Falconer, R.A. Study on Nutrient Distribution and Interaction with Sediments in a Macro-Tidal Estuary. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 52, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, C. Three-Dimensional Modelling of Sediment Transport under Tidal Bores in the Qiantang Estuary, China. J. Hydraul. Res. 2018, 56, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| River | Date | Bore Type | Fr | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Garonne | 10 August 2010 | Undular | 1.3 | [8] |
| Sélune | 24 September 2010 | Breaking | 2.35 | [36] |
| Qiantang | 25 October 2012 | Breaking | 1.92 | [37] |
| Hooghly | 9 April 2020 | Undular | 1.37 | [17] |
| Salmon | 21 June 2020 | Breaking | 2–3 | [38] |
| Test | Tidal Amplitude (m) | Mean Water Level (m) | Discharge (m3/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (validation) | measurement (≈7) | measurement (≈0.7) | 65 |
| 2–9 | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 | 0.7 | 65 |
| 10–13 | 4 | 0.2, 0.7, 1.2, 1.7 | 65 |
| 14–17 | 7 | 0.2, 0.7, 1.2, 1.7 | 65 |
| 18–22 | 7 | 0.7 | 15, 40, 65, 90, 115 |
| Amplitude (m) | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| Bore Height (m) | 1.8 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Mean Water Level (m) | 1.7 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 |
| Bore Height (m) | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Discharge (m3/s) | 115 | 90 | 65 | 15 | 40 |
| Bore Height (m) | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che, B.; Hu, H.; Ma, J.; Liang, D. Hydrodynamic Modelling of Severn Bore and Its Dependence on Ocean Tide and River Discharge. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122319
Che B, Hu H, Ma J, Liang D. Hydrodynamic Modelling of Severn Bore and Its Dependence on Ocean Tide and River Discharge. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122319
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe, Bowen, Hao Hu, Jun Ma, and Dongfang Liang. 2024. "Hydrodynamic Modelling of Severn Bore and Its Dependence on Ocean Tide and River Discharge" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122319
APA StyleChe, B., Hu, H., Ma, J., & Liang, D. (2024). Hydrodynamic Modelling of Severn Bore and Its Dependence on Ocean Tide and River Discharge. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122319








