Simulation Study on Detection and Localization of a Moving Target Under Reverberation in Deep Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Models for Active Sonars’ Received Signals in Deep Water
2.1. Scattered Sound Field of Targets
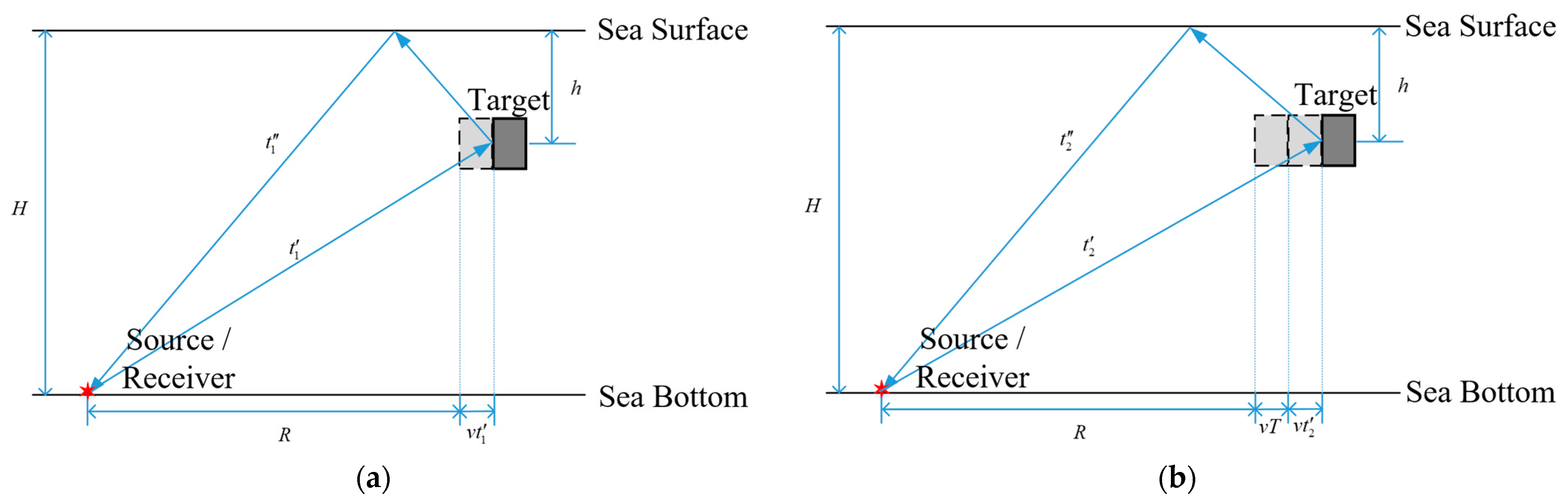
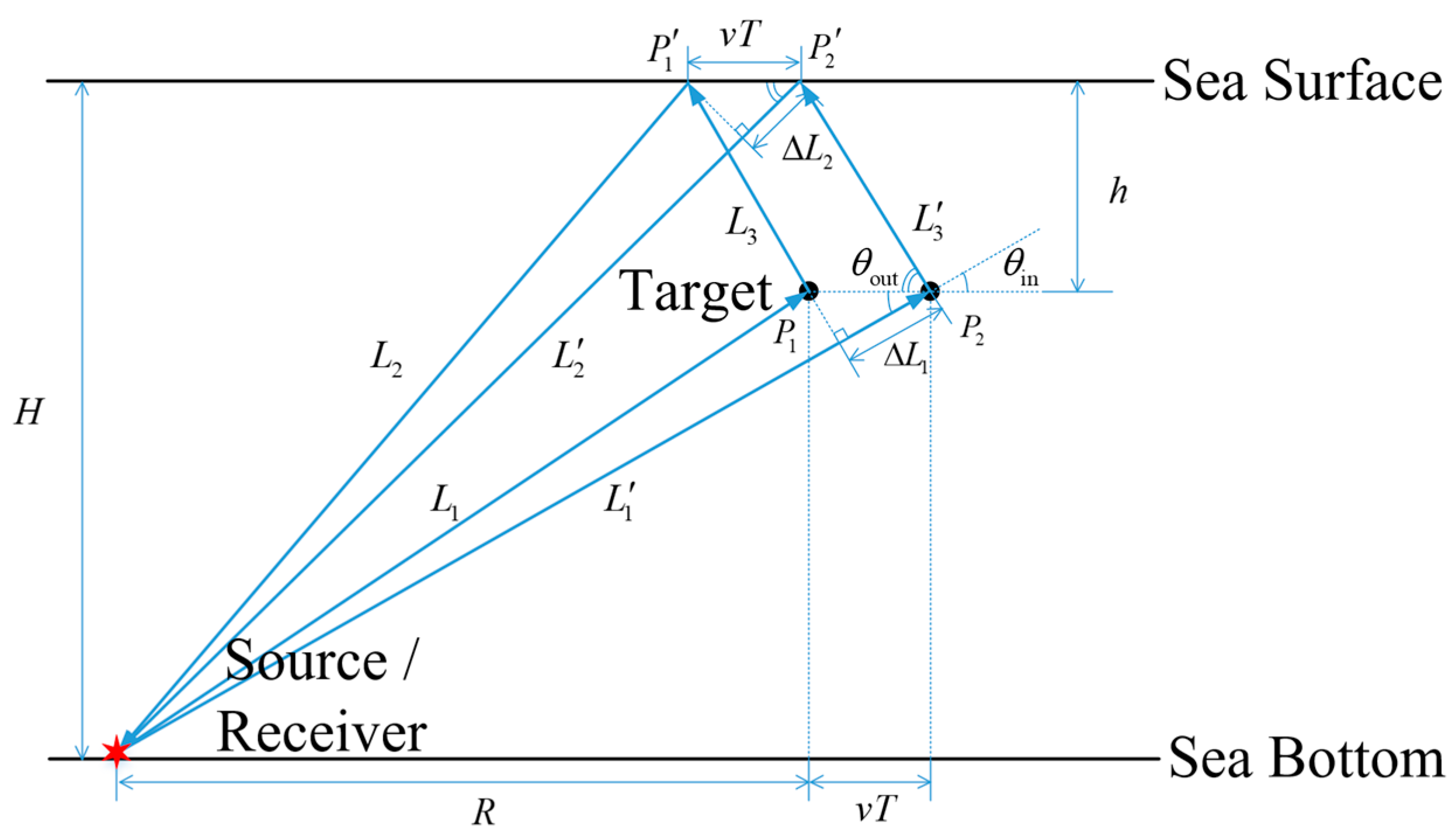
2.2. Echoes of Moving Targets
2.3. Time-Domain Waveforms of Reverberation
3. Methods of Detection and Localization for Moving Targets in Deep Water
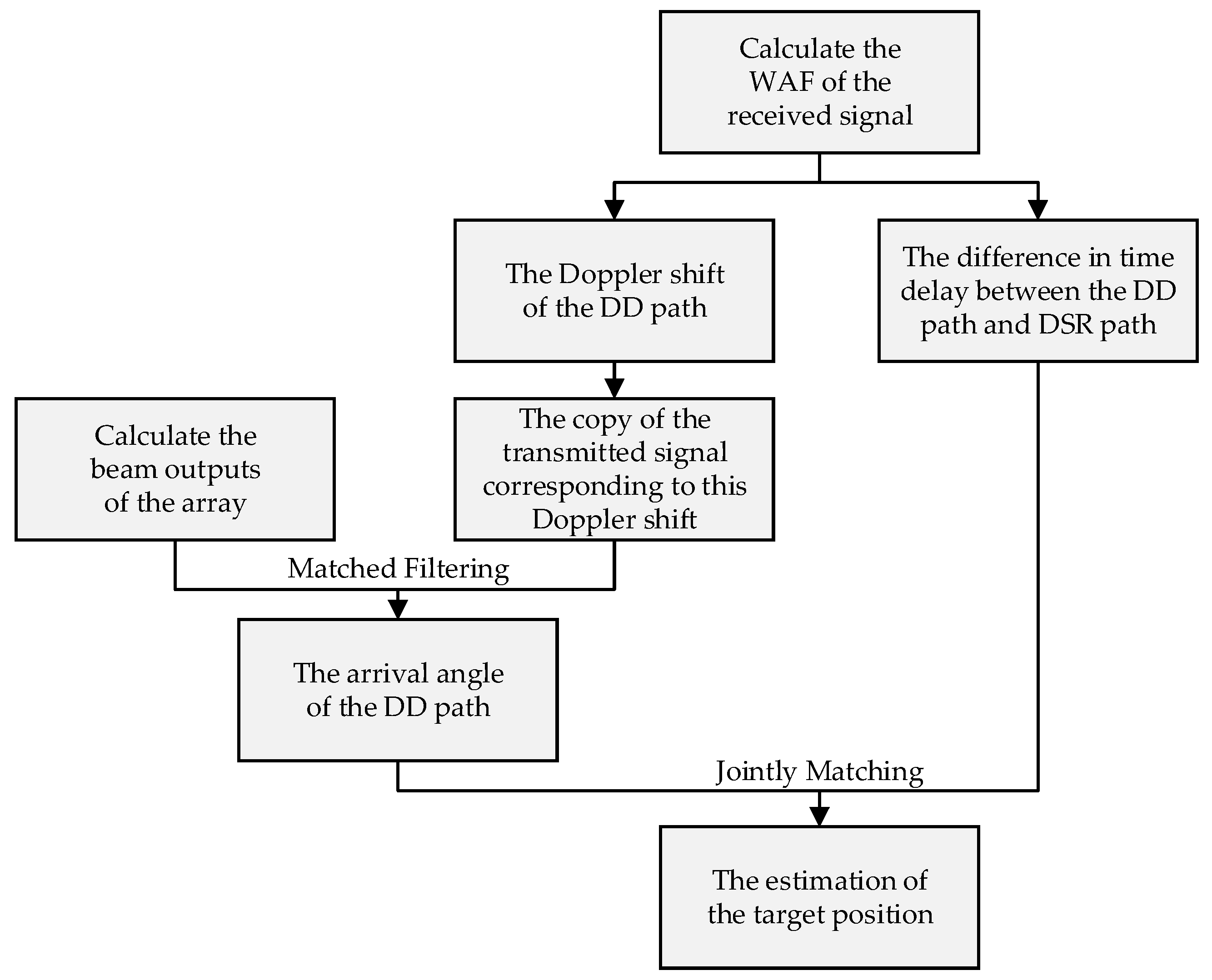
3.1. Algorithm Procedures
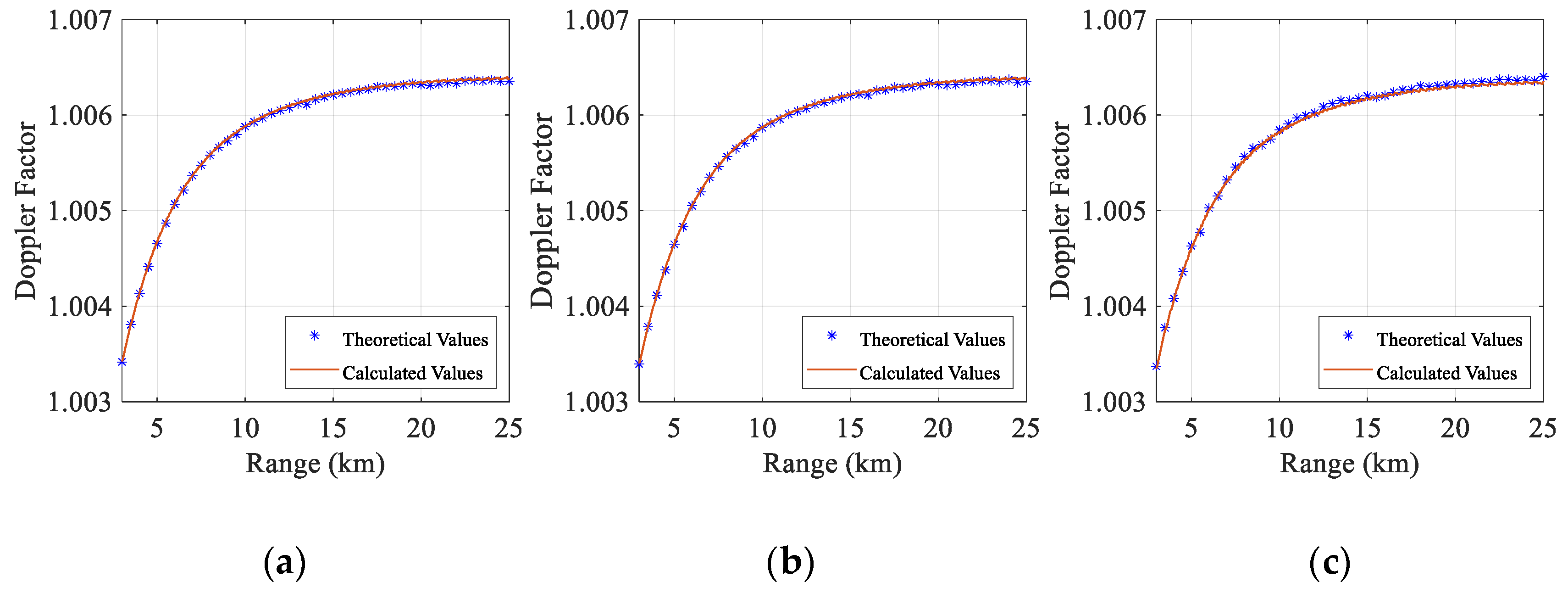
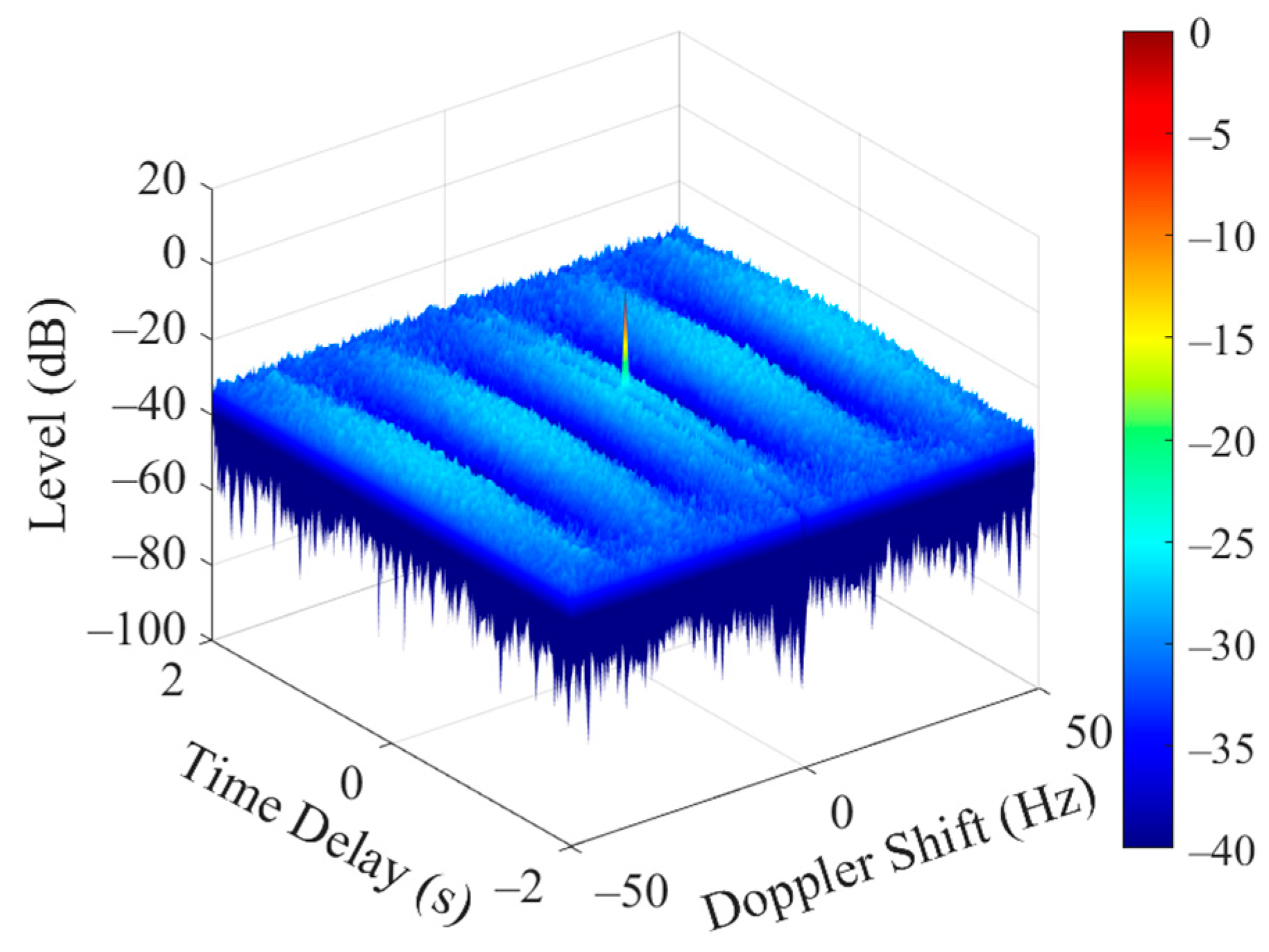
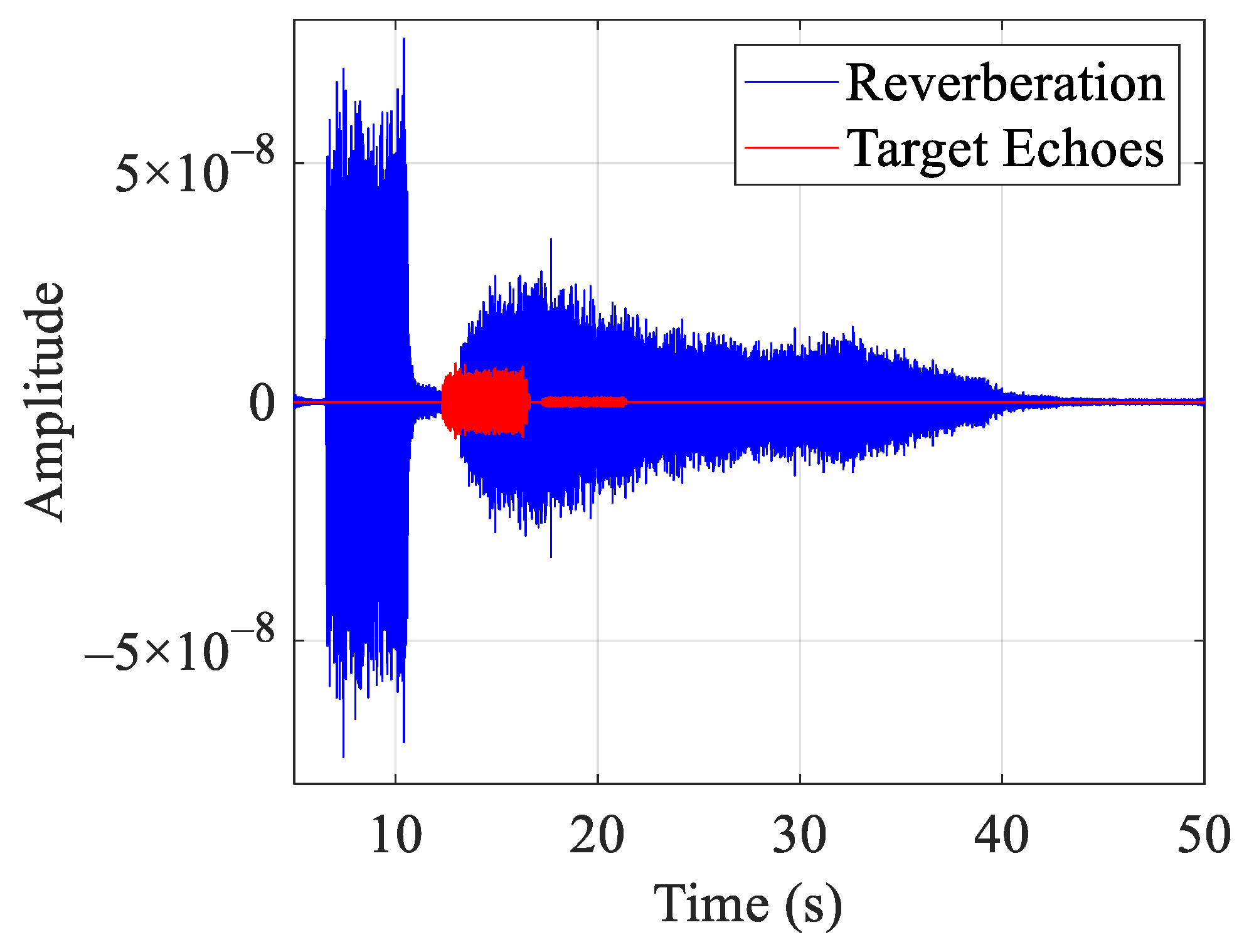
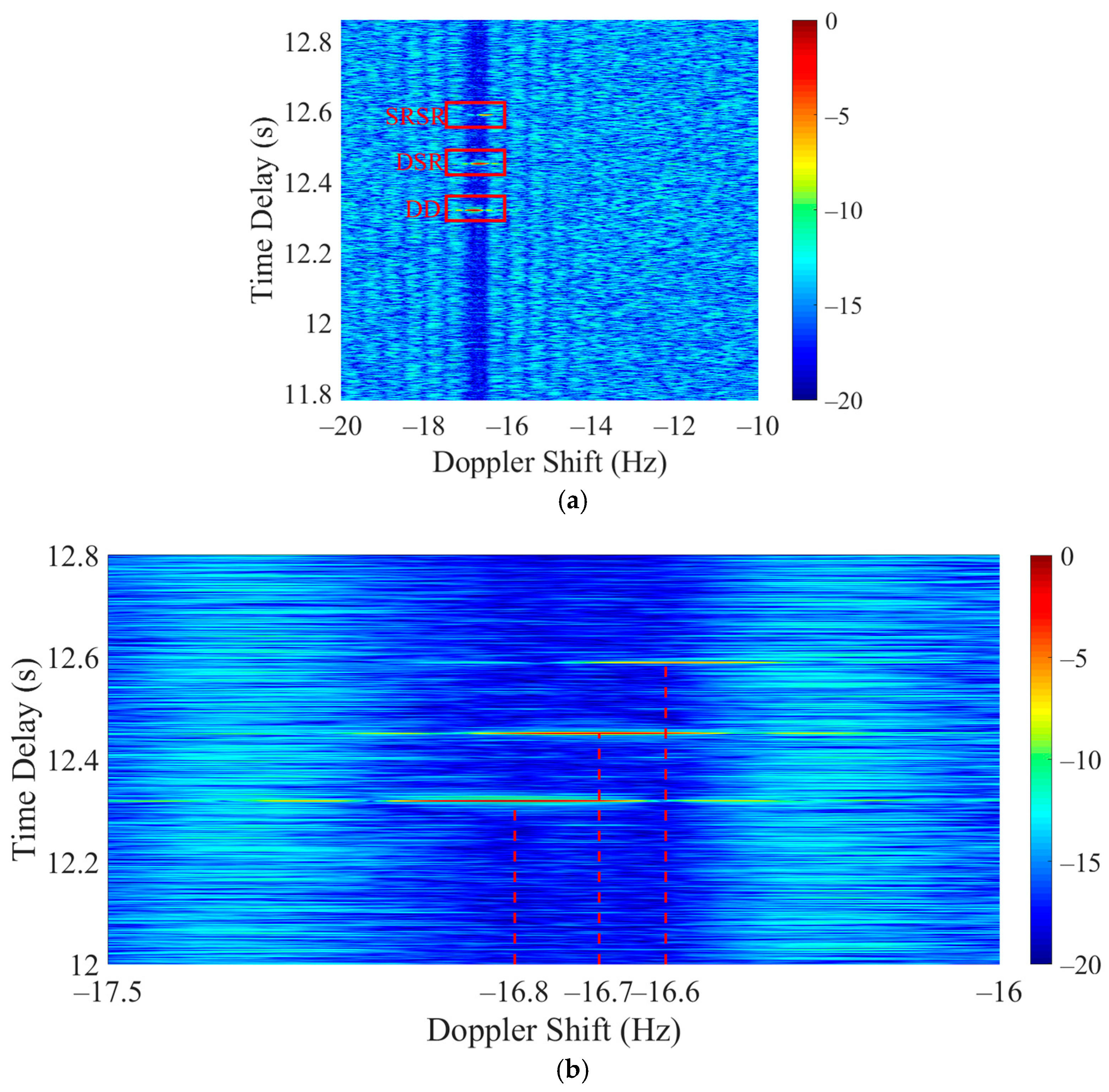
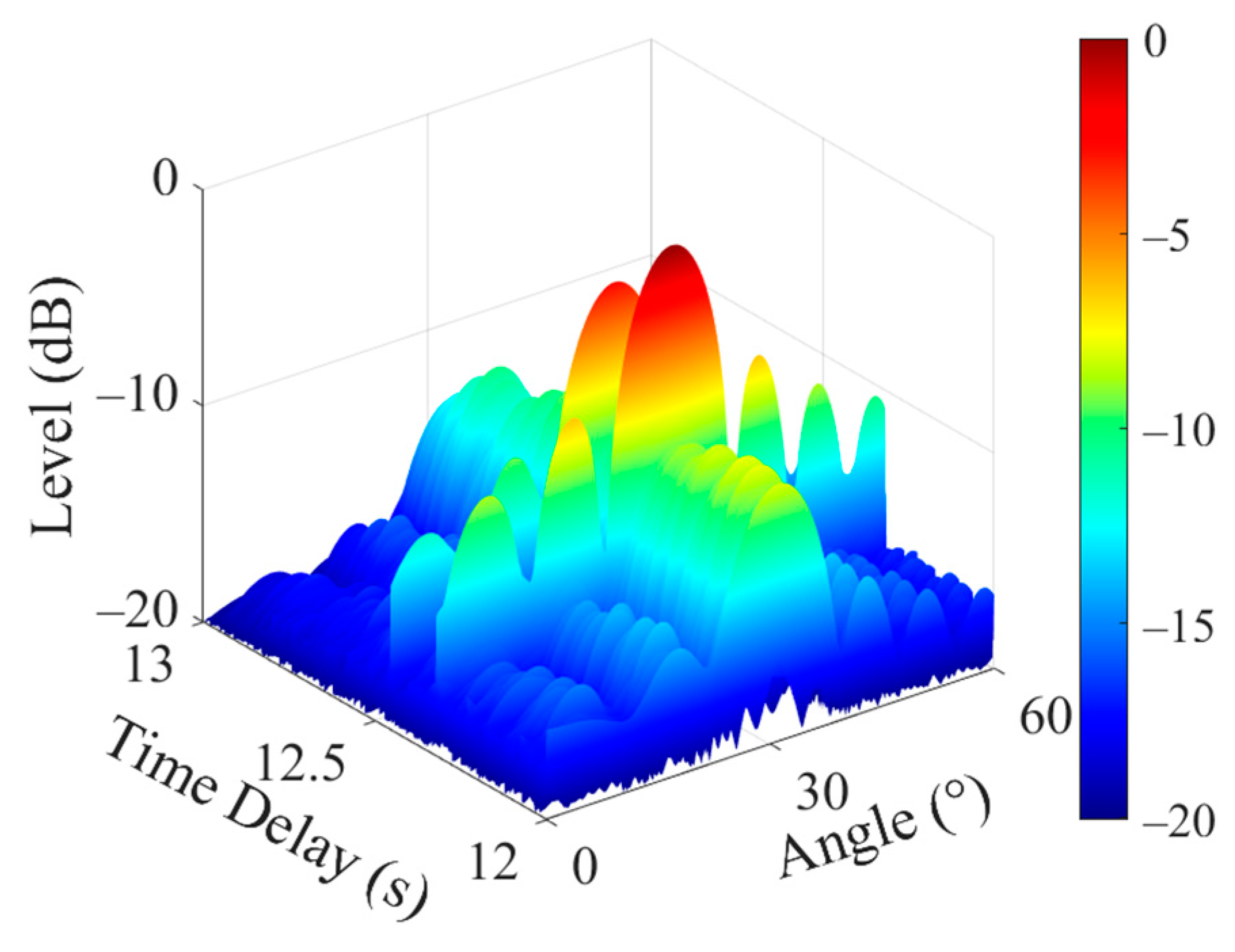
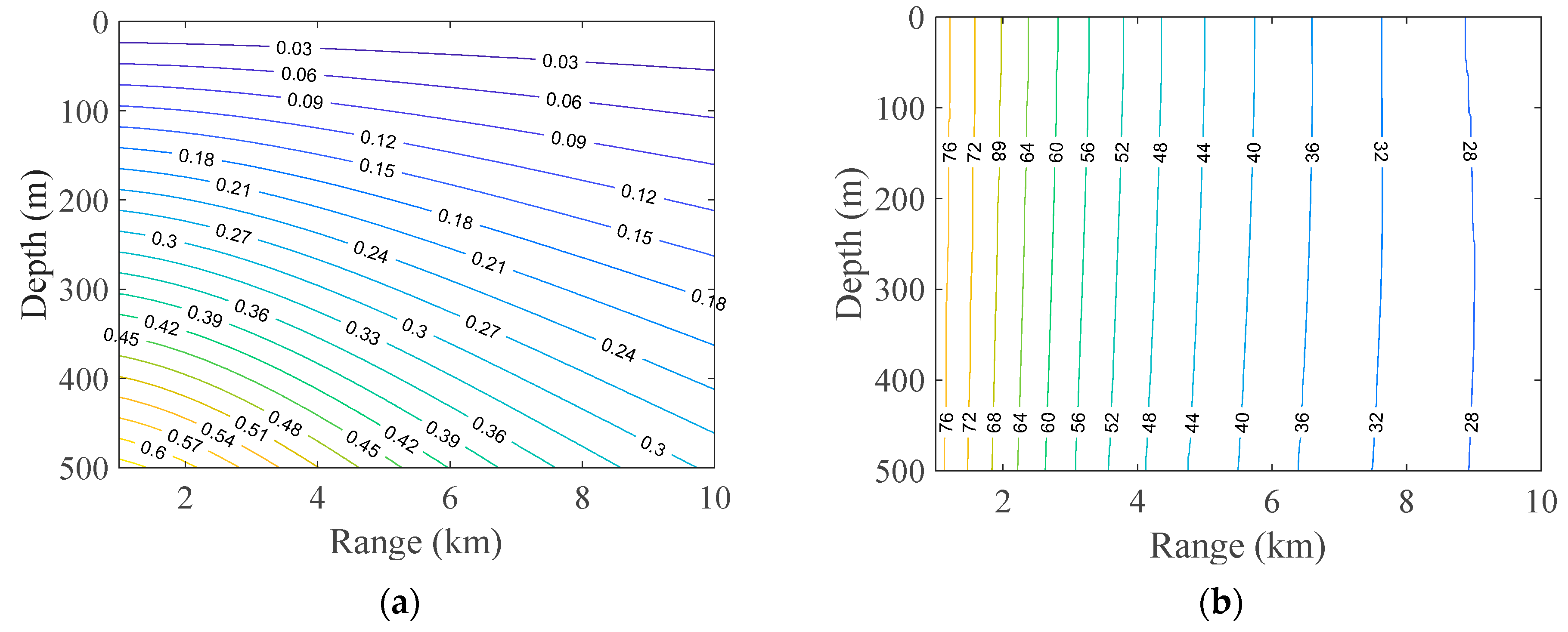
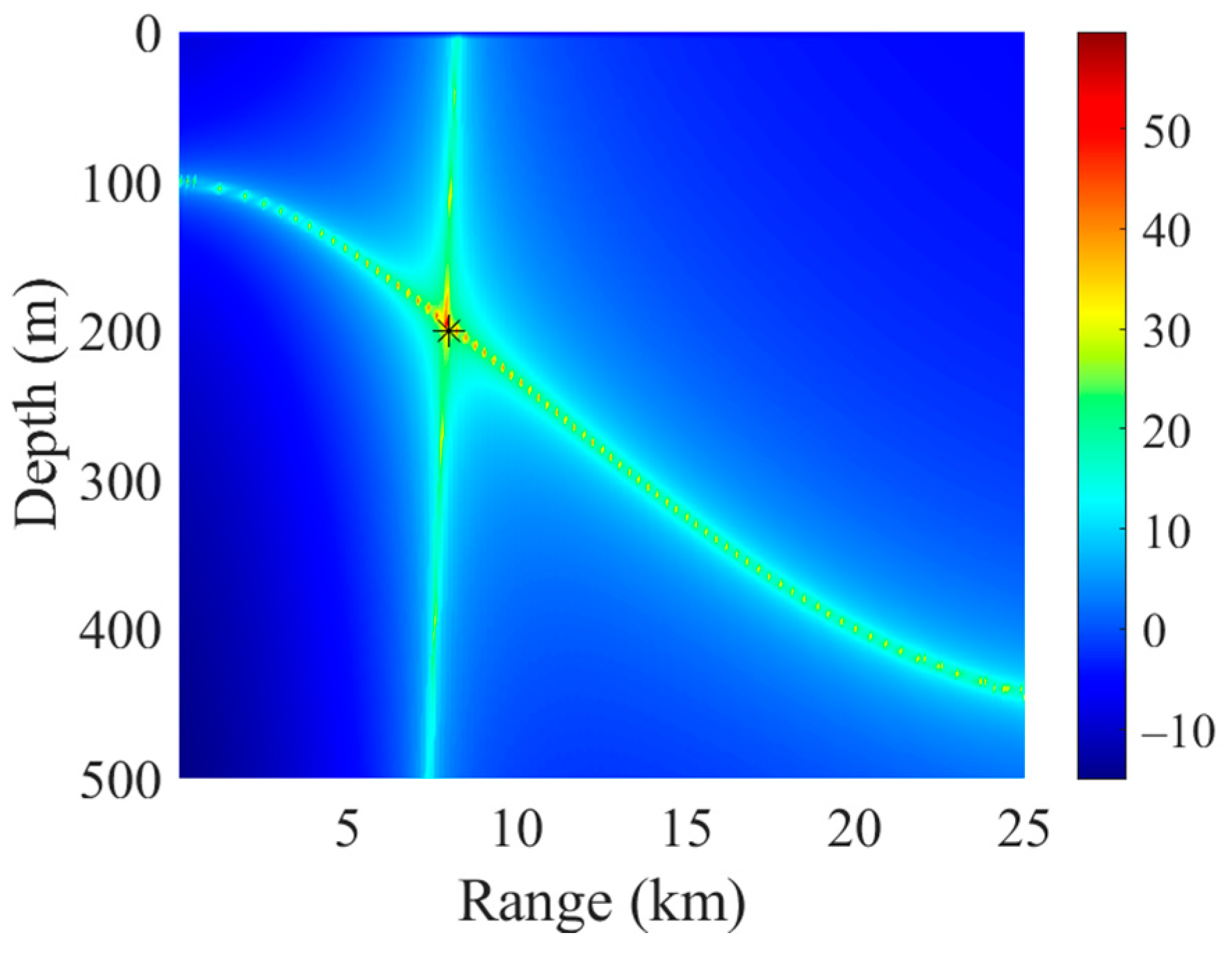
3.2. Simulation Analysis
4. Performance Analysis
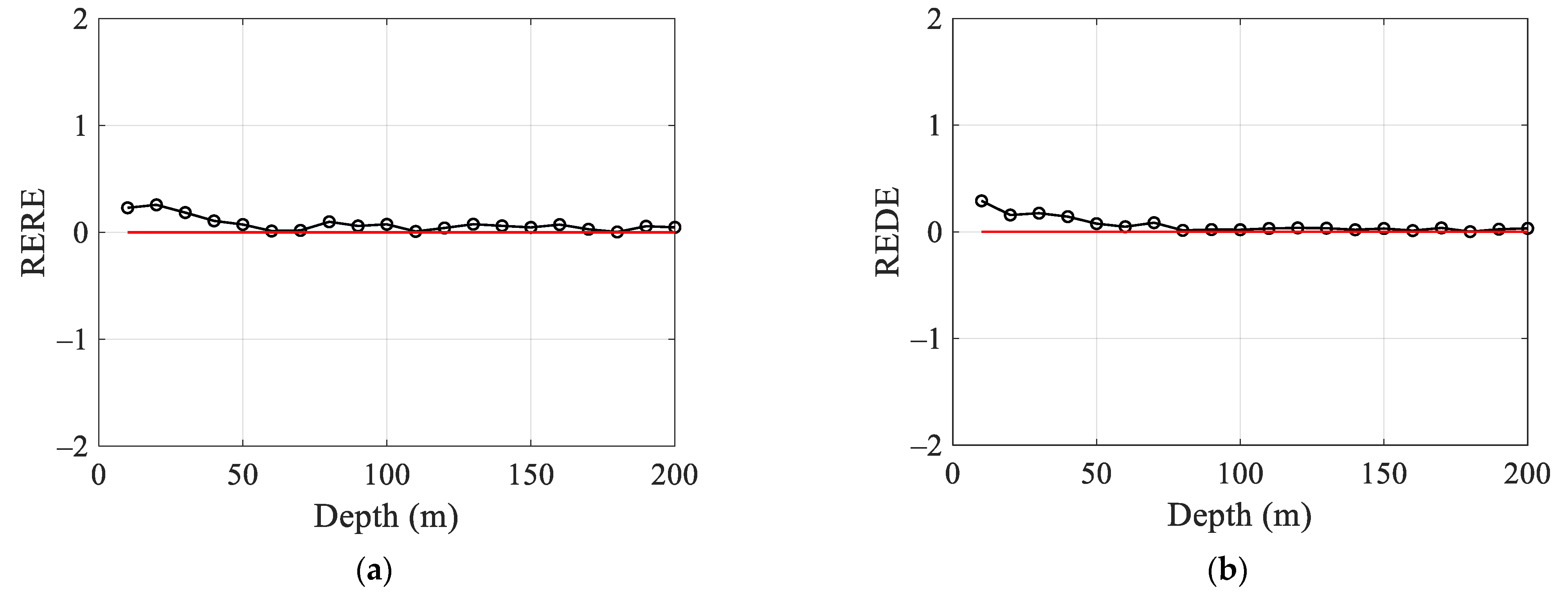
4.1. Target Depth
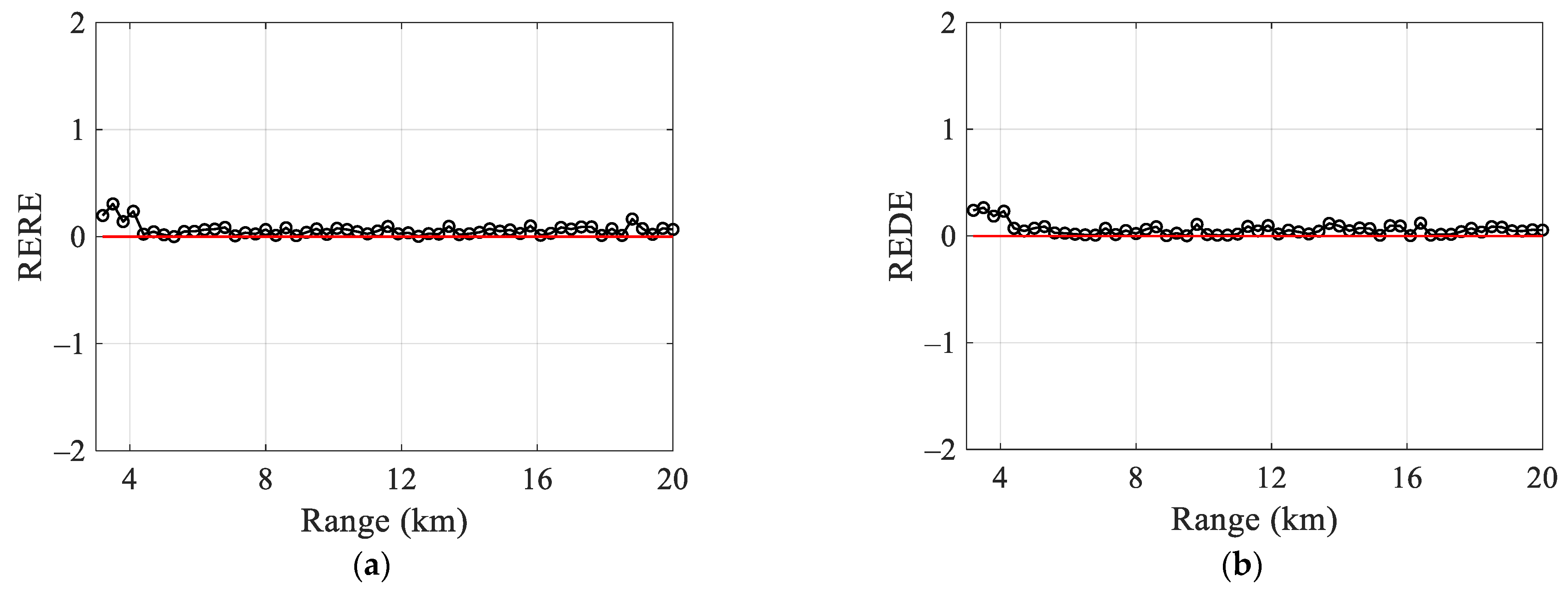
4.2. Horizontal Distance Between the Sonar and the Target
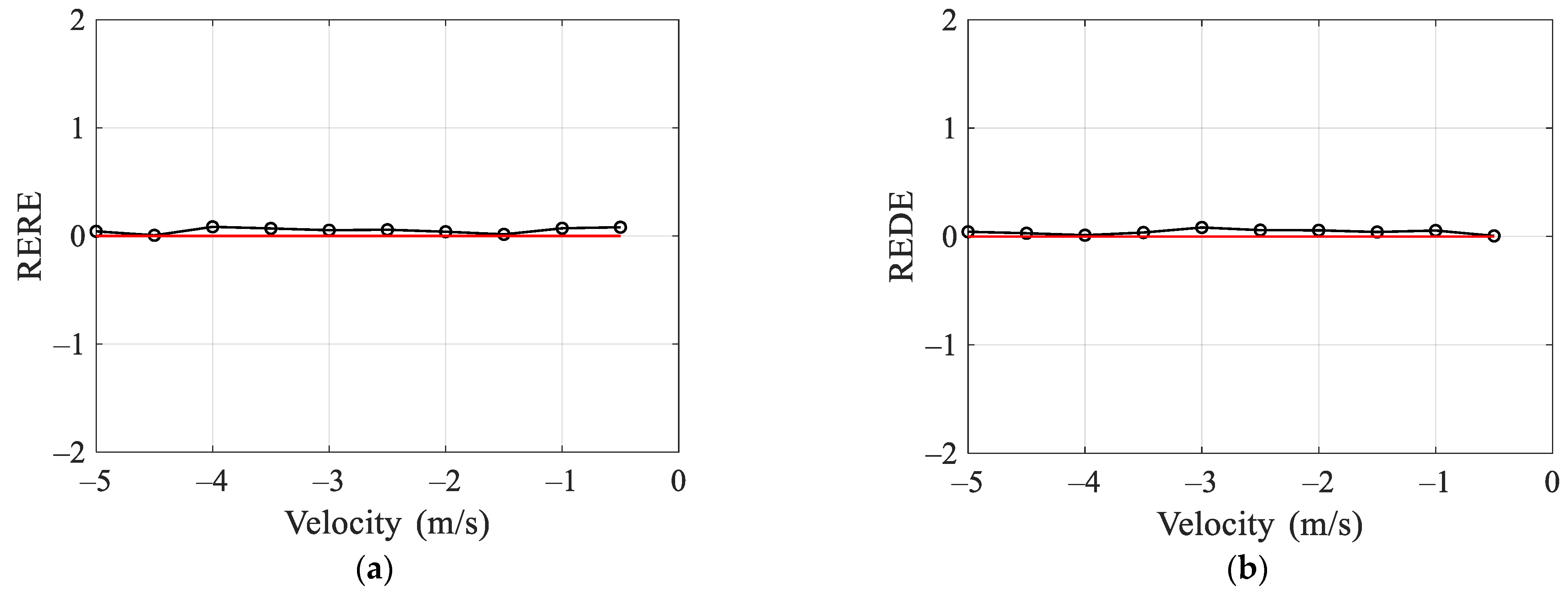
4.3. Target Velocity
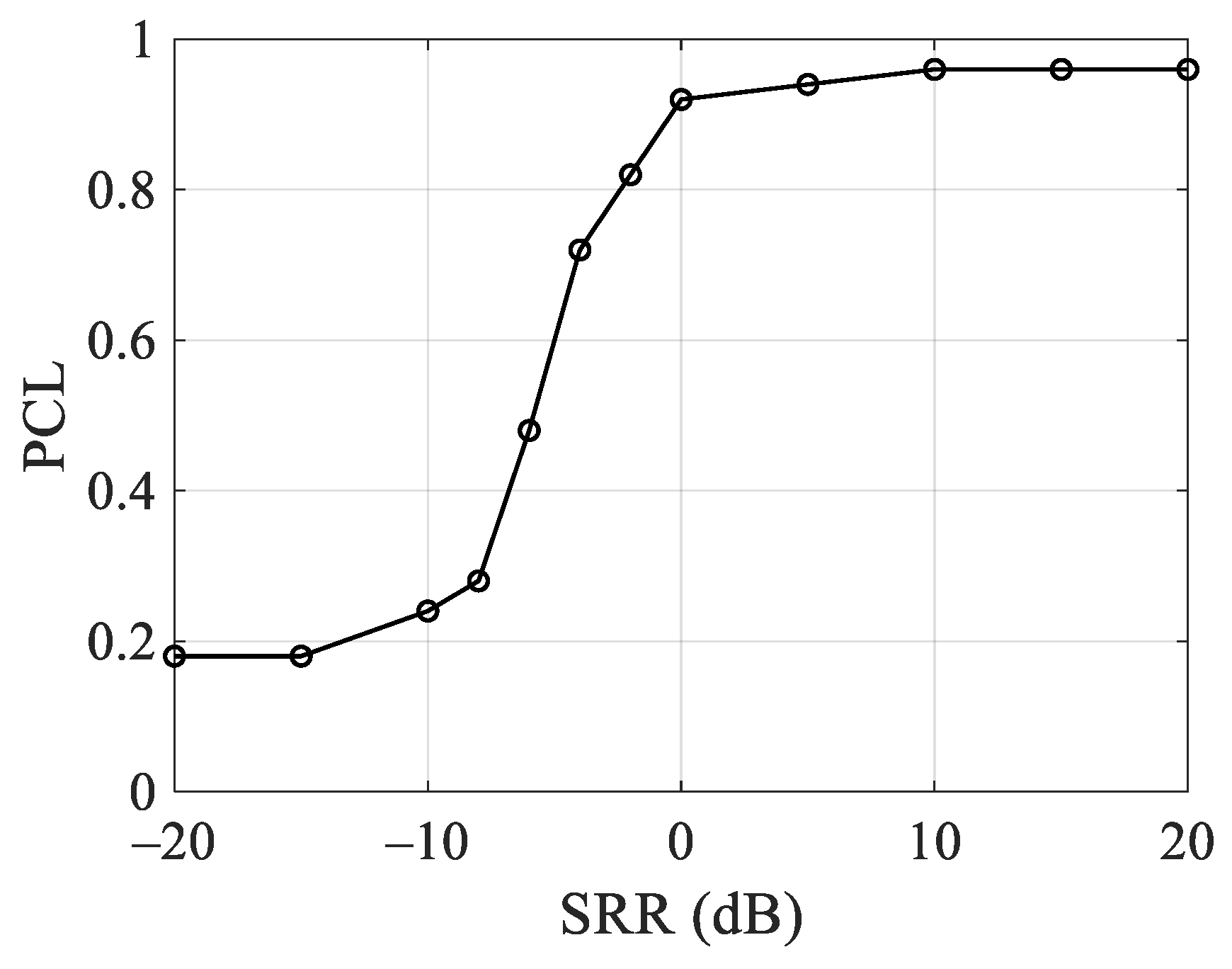
4.4. SRR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Research on detection methods of echo under reverberation condition. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the Underwater Acoustics Branch of the Acoustical Society of China, Nanjing, China, 24–26 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Ma, X. Designs and implementations of broadband beamformers. Acta Acust. 2008, 33, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Hao, C.; Yan, S. Wideband reverberation suppression in beams domain by utilizing angular distribution features. Acta Acust. 2018, 43, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Feng, X.; Huang, H.; Bi, Y. A Space-Time Adaptive Processing Method Based on Sparse Reconstruction of Reverberation Interference. J. Northwest. Polytech. Univ. 2021, 38, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; de Lamare, R.C.; Liu, W. Sparsity-based STAP using alternating direction method with gain/phase errors. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 2756–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, K.; Duan, R.; Wu, F.; Zhang, M. Sparse spatial spectral estimation with heavy sea bottom reverberation in the fractional fourier domain. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 160, 107132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Meng, X. Morphological characteristics separation of underwater target echo and reverberation in time and frequency domain. Acta Acust. 2017, 42, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, Z.; Wang, X.; Mu, L. Blind separation of underwater target echoes in reverberation background. J. Harbin. Eng. Univ. 2015, 36, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, J.C. Underwater Sound Propagation in the Straits of Florida. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1966, 39, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdain, G.; Henrioux, J.P. Use of large bandwidth-duration binary phase shift keying signals in target delay Doppler measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 90, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, M.E.G.D.; Beerens, S.P. False-alarm reduction for low-frequency active sonar with BPSK pulses: Experimental results. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2011, 36, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.C.; Schindall, J.; Huang, C.F.; Liu, J.Y. Clutter reduction using Doppler sonar in a harbor environment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3053–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, Z. Realization of low frequency reverberation sequence in shallow water based on normal-mode theory. J. Appl. Acoust. 2012, 31, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qin, J.; Fu, D.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Weng, J. Bottom reverberation for large receiving depth in deep water. Acta Phys. Sin. 2019, 68, 134303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Fang, S.; Han, N. Analysis of Doppler factor based on multi-path sound channel. In Proceedings of the 2017 INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference, Hong Kong, China, 27–30 August 2017; Available online: http://www.proceedings.com/37265.html (accessed on 7 December 2017).
- Tang, W.; Fan, J.; Ma, Z. Acoustic Scattering of Underwater Targets; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018; pp. 32–35. ISBN 978-7-03-054027-0. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, W.; Fan, J. The geometrical acoustic method for calculating the echo of targets submerged in a shallow water waveguide. Acta Acust. 2010, 35, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.B.; Bucker, H.P. Gaussian beam tracing for computing ocean acoustic fields. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1987, 82, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B.; Schmidt, H. Computational Ocean Acoustics; Springer New York: New York, USA, 2011; pp. 133–135. ISBN 978-7-118-11202-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkup, S. The Boundary Element Method in Acoustics: A Survey. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, K.; Li, C.; Yang, L. Parameter Estimation for Multi-Scale Multi-Lag Underwater Acoustic Channels Based on Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 4808–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.C.; Porter, M.B. Ray/Beam Tracing for Modeling the Effects of Ocean and Platform Dynamics. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2013, 38, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.H. Sound channel in an exponentially stratified ocean, with application to SOFAR. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1974, 55, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.D. A shallow-water normal-mode reverberation model. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 2804–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, Y. Geometric model of the waveform prediction for the deep-ocean reverberation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference of the Underwater Acoustics Branch of the Acoustical Society of China, Wuhan, China, 5–8 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, D.A. Underwater Acoustic Signal Processing: Modeling, Detection, and Estimation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhou, S.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Du, S.; Dun, J.; Zhou, L. Passive source localization based on multipath arrival angles with a vertical line array using sparse Bayesian learning. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2023, 153, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrovinskaya, E.; Nissen, I.; Casari, P. On the accuracy of passive multipath-aided underwater range estimation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Third Underwater Communications and Networking Conference (UComms), Lerici, Italy, 30 August–1 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y.; Lei, B. A reliable acoustic path: Physical properties and a source localization method. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Niu, H.; Yang, S.; Li, Z. Multiple source localization using learning-based sparse estimation in deep ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 3773–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dun, J.; Zhou, S.; Qi, Y.; Liu, C. Simulation Study on Detection and Localization of a Moving Target Under Reverberation in Deep Water. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122360
Dun J, Zhou S, Qi Y, Liu C. Simulation Study on Detection and Localization of a Moving Target Under Reverberation in Deep Water. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122360
Chicago/Turabian StyleDun, Jincong, Shihong Zhou, Yubo Qi, and Changpeng Liu. 2024. "Simulation Study on Detection and Localization of a Moving Target Under Reverberation in Deep Water" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122360
APA StyleDun, J., Zhou, S., Qi, Y., & Liu, C. (2024). Simulation Study on Detection and Localization of a Moving Target Under Reverberation in Deep Water. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122360





