Method for Delineating the Formula Limit of the Continental Shelf under the Maximum Area Principle Constraint
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
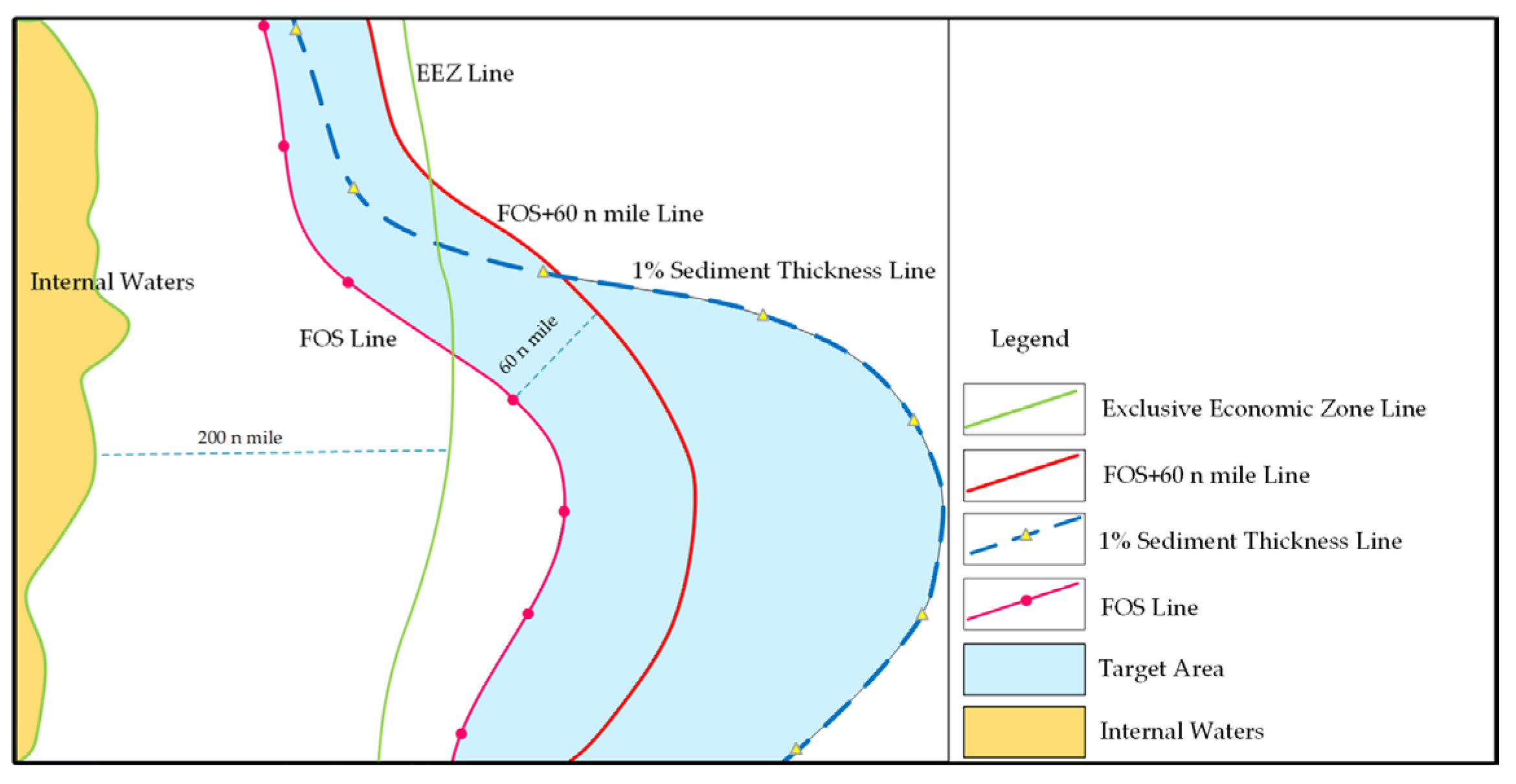
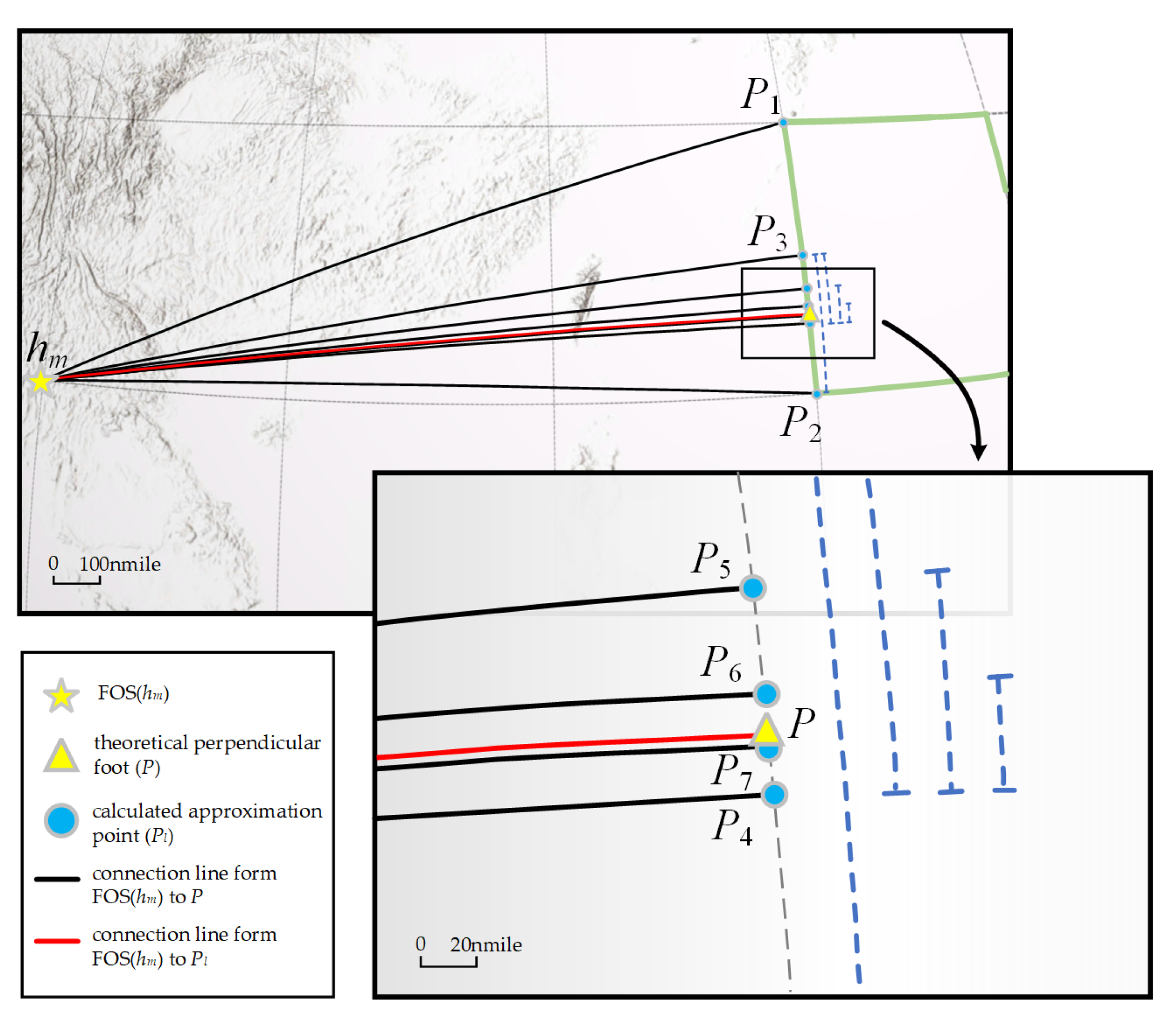
2.1. Calculation of FOS+60 n Mile Line Candidate Points Set
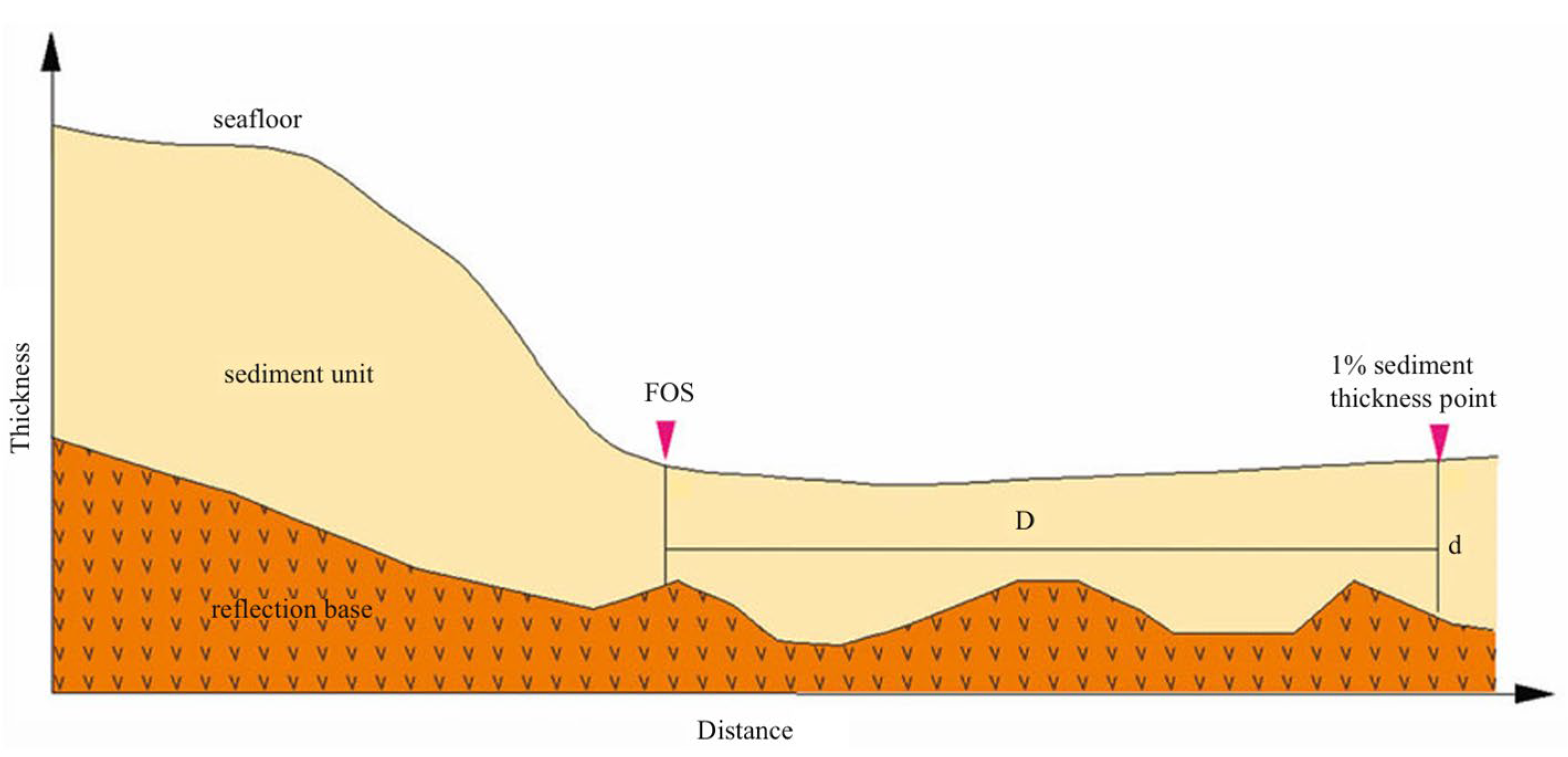
2.2. Calculation of the 1% Sediment Thickness Line Candidate Points Set
2.2.1. Precision Calculation of Distance Interval
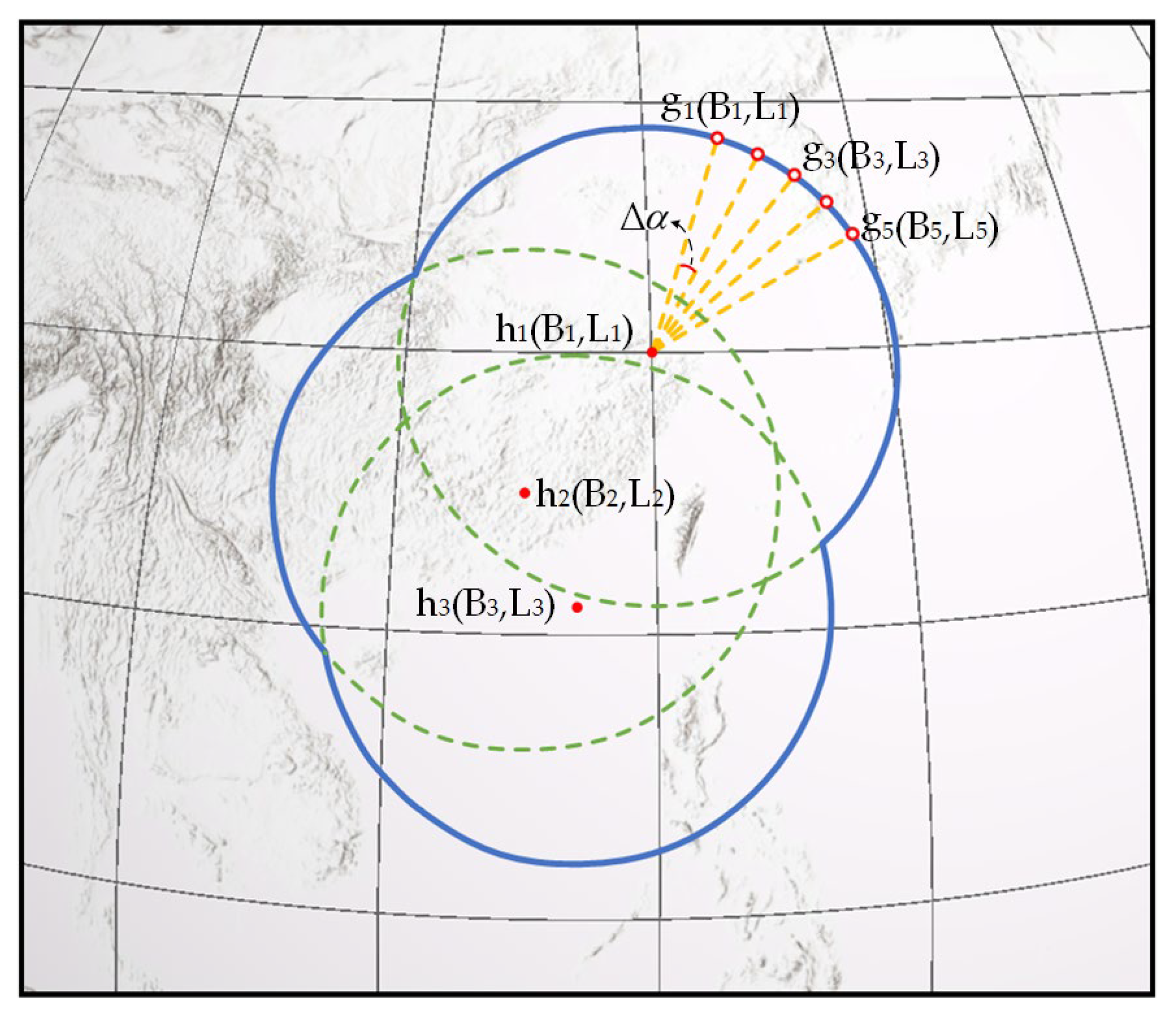
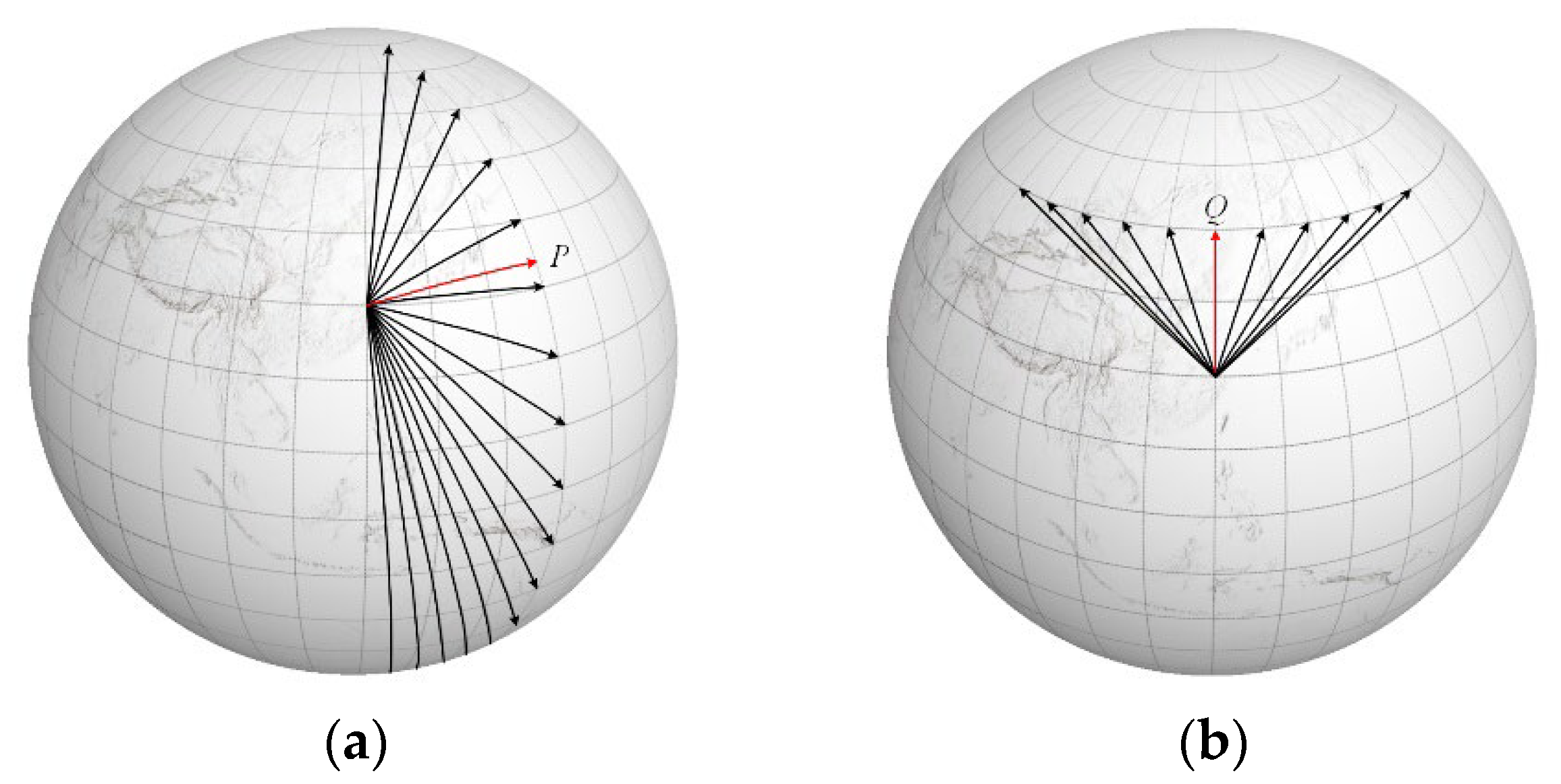
2.2.2. Selecting Candidate Points from Potential Area
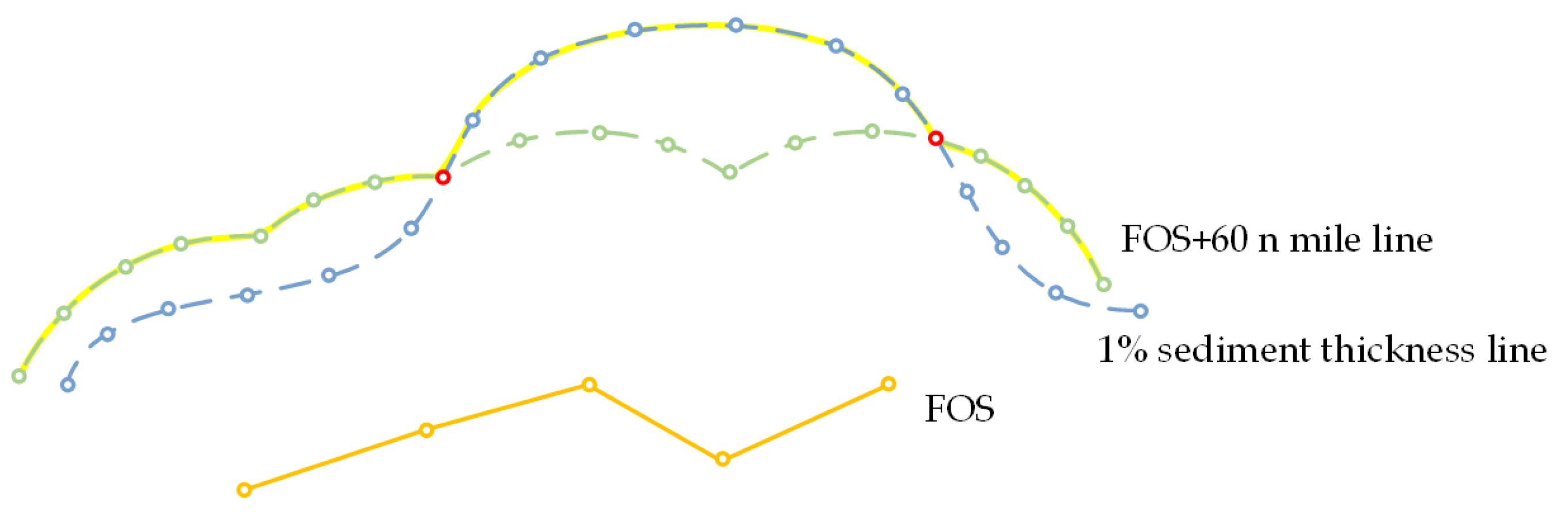
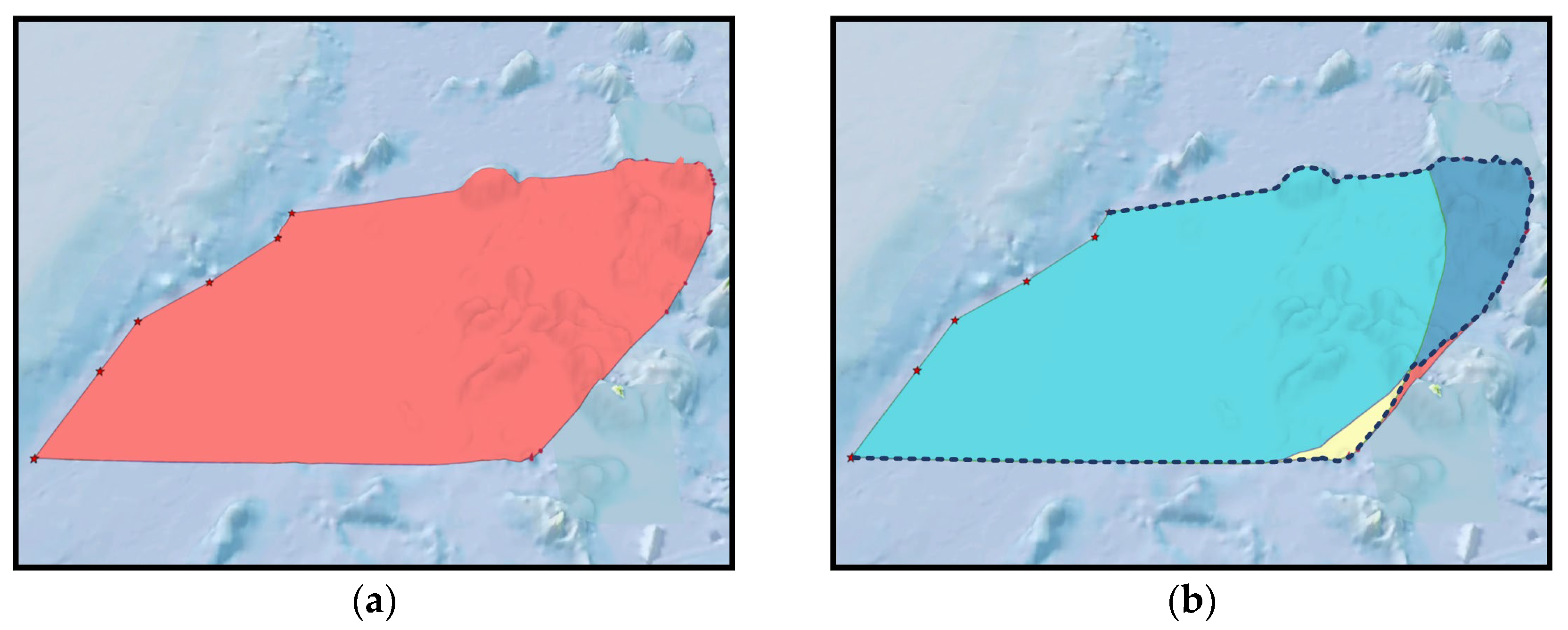
2.3. Constructing Formula Limit Based on Two Candidate Points Sets
3. Experiments and Numerical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Q.; Fang, Y.; Li, J. Science and technology of delimitation of continental shelf and its application in Maritime Silk Road cooperation. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Yin, J. Progress of Work in the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf and Hot Issues on the Extended Continental Shelf Delineation Worldwide. Chin. Rev. Int. Law 2020, 7, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Tang, Y.; Yin, J. Principles and methods for the submission consideration of the Commission on the Limits of Continental Shelf-Cases study of recommendations summary made by the Commission. J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, J.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y. Principles and methods for determining the foot of the continental slope. J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 40, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Jin, J. Study to Automatic Drawing of Foot Line of Extended Continental Slope. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2007, 43, 240–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; Tang, Y. High-Resolution Seafloor Survey and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Jin, X.; Fang, Y.; Shang, J.; Li, S. Methods and Procedures to Determine the Outer Limits of the Continental Shelf beyond 200 Nautical Miles. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 32, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y. A Novel Method of Buffer Generation Based on Vector Boundary Tracing. In 2009 International Forum on Information Technology and Applications; IEEE: Chengdu, China, 2009; Volume 1, pp. 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Yang, C.; Rui, X.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Q. An Effective Buffer Generation Method in GIS. In 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing (IGARSS), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 3706–3708. [Google Scholar]
- Bader, M.; Weibel, R. Detecting and Resolving Size and Proximity Conflicts in the Generalization of Polygonal Maps. In Proceedings of the 18th International Cartographic Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 23–27 June 1997; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H. Problem of Buffer Zone Construction in GIS. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 1997, 22, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bolstad, P. GIS Fundamentals: A First Text on Geographic Information Systems, 6th ed.; XanEdu: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Žalik, B.; Zadravec, M.; Clapworthy, G.J. Construction of a Non-Symmetric Geometric Buffer from a Set of Line Segments. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L. A Shape-Based Buffering Method. Environ. Plan. B-Plan. Des. 2008, 35, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Vira, V.; Choksi, D.; Venkatachalam, P. An Algorithm for Generating Geometric Buffers for Vector Feature Layers. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, 16, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Wang, J. A Research on Creating Buffer on the Earth Ellipsoid. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2002, 31, 270–273. [Google Scholar]
- Munkres, J.R. Topology; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, R.; Wang, J.; Tian, Z.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z. A Research for Selecting Baseline Point of the Territorial Sea Based on Technique of the Convex Hull Construction. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2005, 34, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. Study of Optimizing Method for Algorithm of Minimum Convex Closure Building for 2D Spatial Data. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2002, 32, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; He, T.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Tang, R. A Fast Convex Hull Algorithm of Planar Point Set Based On Sorted Simple Polygon. Chin. J. Comput. 1998, 21, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R. Spacial Analysis; Wuhan Techinical University of Surveying and Mapping Press: Wuhan, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Yang, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, K. An Improved Algorithm for Producing Minimum Convex Hull. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2011, 31, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preparata, F.P.; Shamos, M.I. Computational Geometry: An Introduction; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brönnimann, H.; Iacono, J.; Katajainen, J.; Morin, P.; Morrison, J.; Toussaint, G. Space-Efficient Planar Convex Hull Algorithms. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2004, 321, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamby, A.N.; Katajainen, J. Convex-Hull Algorithms: Implementation, Testing, and Experimentation. Algorithms 2018, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avis, D.; Bremner, D.; Seidel, R. How Good Are Convex Hull Algorithms? Comput. Geom.-Theory Appl. 1997, 7, 265–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.B.; Dobkin, D.P.; Huhdanpaa, H. The Quickhull Algorithm for Convex Hulls. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 1996, 22, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, D.G.; Seidel, R. The Ultimate Planar Convex Hull Algorithm? SIAM J. Comput. 1986, 15, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Peng, R.; Li, N.; Liu, G.; Tang, L. Optimal Selection Algorithm of Territorial Sea Baseline Points with the Limitation of Baseline Length Threshold. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2023, 48, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J. Ellipsoidal Geodesy; People’s Liberation Army of China Press: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, J. Marine delimitation method based on earth ellipsoid model. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2013, 38, 16–17+30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W. Algorithm Design and Analysis, 3rd ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gallot, S.; Hulin, D.; Lafontaine, J. Riemannian Geometry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- International Hydrographic Organization. A Manual on Technical Aspects of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, 1982, 6th ed.; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]


| Serial Number (Start–End Points) | FOS+60 n Mile Line (m) | 1% Sediment Thickness Line (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1–2 | 9256.8 | 15,845.6 |
| 2–3 | 9256.8 | 5558.3 |
| 3–4 | 9256.8 | 1978.3 |
| 4–5 | 9256.8 | 1978.3 |
| 5–6 | 9256.8 | 1978.3 |
| 6–7 | 9256.8 | 21,183.1 |
| 7–8 | 9256.8 | 20,443.3 |
| 8–9 | 2101.0 | 12,322.3 |
| 9–10 | 9256.8 | 12,839.9 |
| 10–11 | 9256.8 | 13,193.1 |
| 11–12 | 9256.8 | 15,669.7 |
| 12–13 | 9256.8 | 12,795.9 |
| 13–14 | 9256.8 | 17,752.7 |
| 14–15 | 4629.4 | 11,829.1 |
| 15–16 | -- | 3490.4 |
| FOS+60 n Mile Line | 1% Sediment Thickness Line | Combined Region | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area (m2) | 13,501,729,047 | 14,995,785,392 | 15,218,132,884 |
| Serial Number (Start–End Points) | Geodetic Line Distances (m) |
|---|---|
| 1–2 | 15,845.6 |
| 2–3 | 5558.3 |
| 3–4 | 1978.3 |
| 4–5 | 1978.3 |
| 5–6 | 1978.3 |
| 6–7 | 21,183.1 |
| 7–8 | 20,443.3 |
| 8–9 | 12,322.3 |
| 9–10 | 65,318.7 |
| 10–11 | 4629.4 |
| Intersection Method | Maximum Area Principle | |
|---|---|---|
| Area (m2) | 15,218,132,884 | 15,295,411,311 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, T.; Dong, J.; Tang, L.; Ma, M.; Wang, D. Method for Delineating the Formula Limit of the Continental Shelf under the Maximum Area Principle Constraint. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060949
Xie T, Dong J, Tang L, Ma M, Wang D. Method for Delineating the Formula Limit of the Continental Shelf under the Maximum Area Principle Constraint. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(6):949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060949
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Tian, Jian Dong, Lulu Tang, Mengkai Ma, and Dong Wang. 2024. "Method for Delineating the Formula Limit of the Continental Shelf under the Maximum Area Principle Constraint" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 6: 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060949
APA StyleXie, T., Dong, J., Tang, L., Ma, M., & Wang, D. (2024). Method for Delineating the Formula Limit of the Continental Shelf under the Maximum Area Principle Constraint. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(6), 949. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12060949





