Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plants on Suspended Sediment Concentrations in Coastal Waters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Suspended Sediment Concentration Measurements
2.3. Particle Size Distribution Measurement
2.4. Heavy Metal Compositions of SS
3. Results
3.1. Linko Power Plant (LPP)
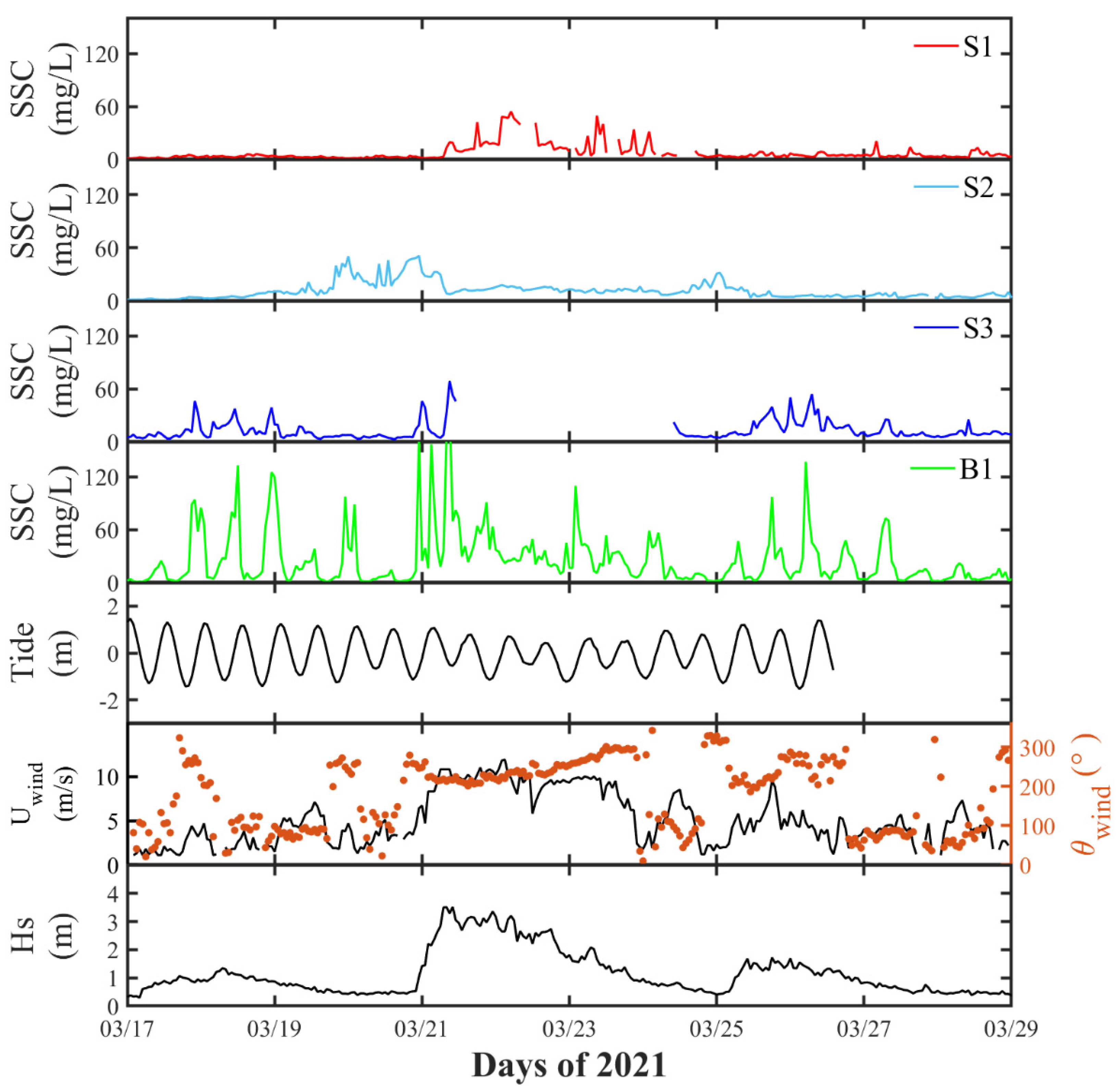
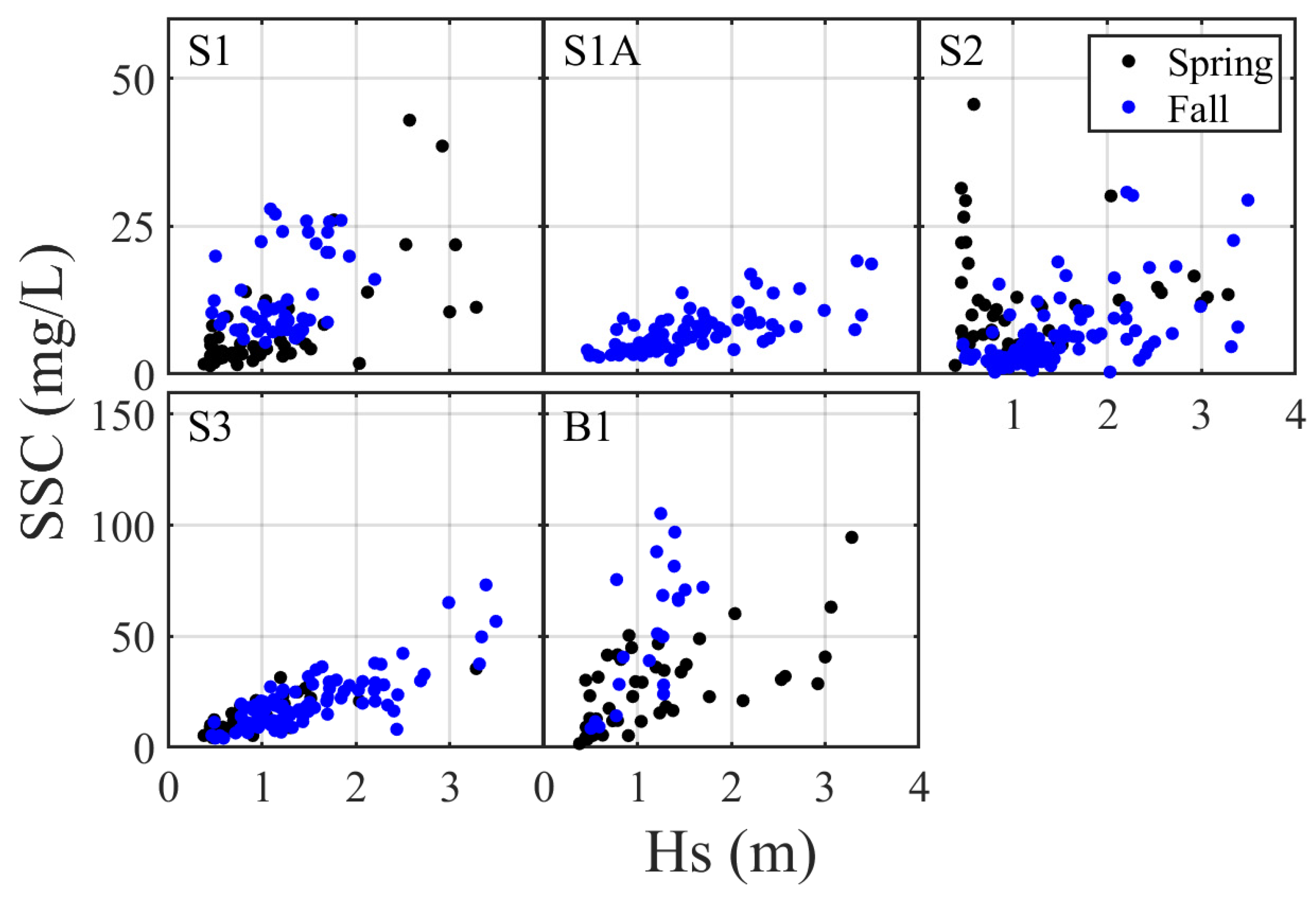
3.1.1. Variation of SSC
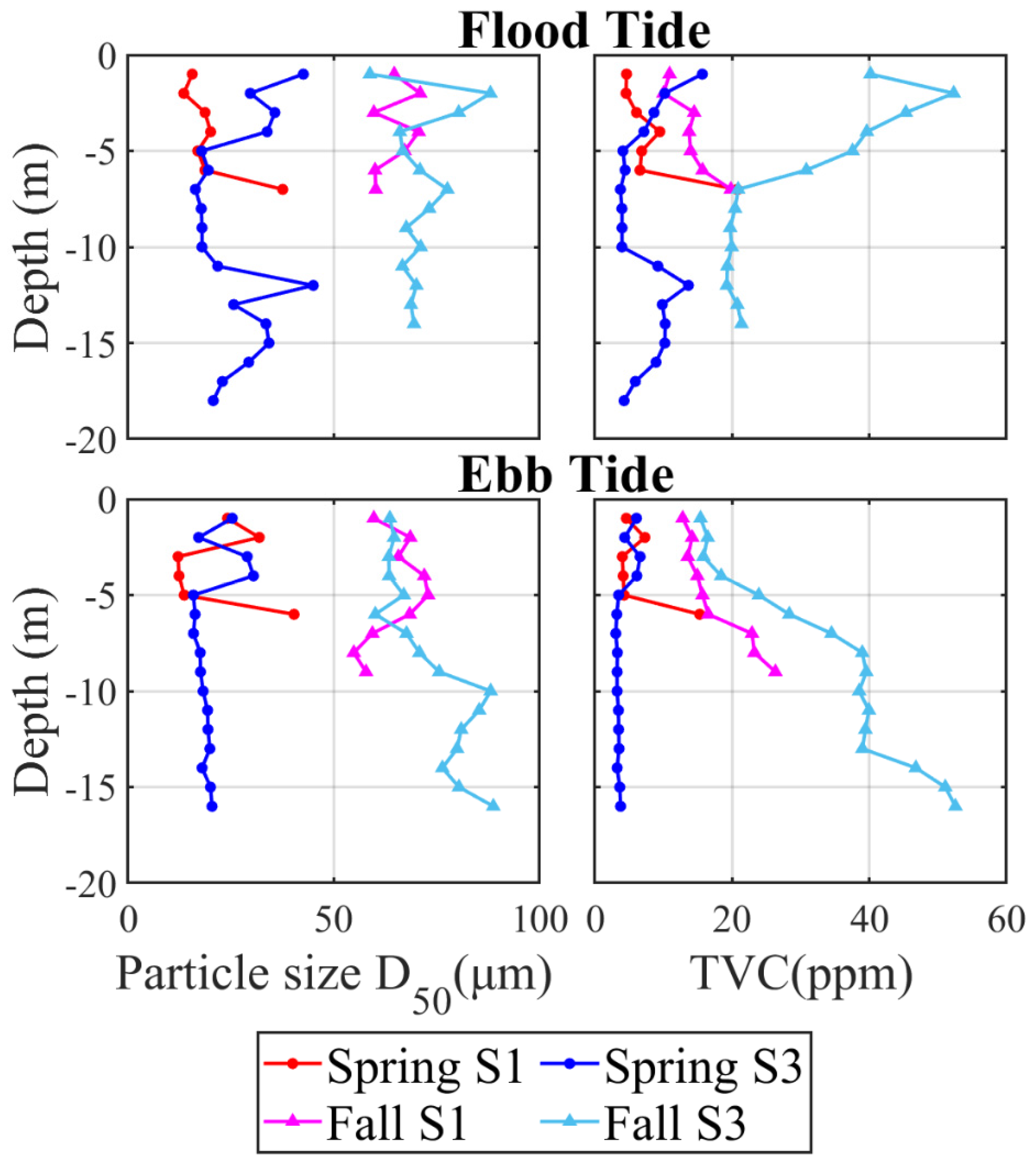
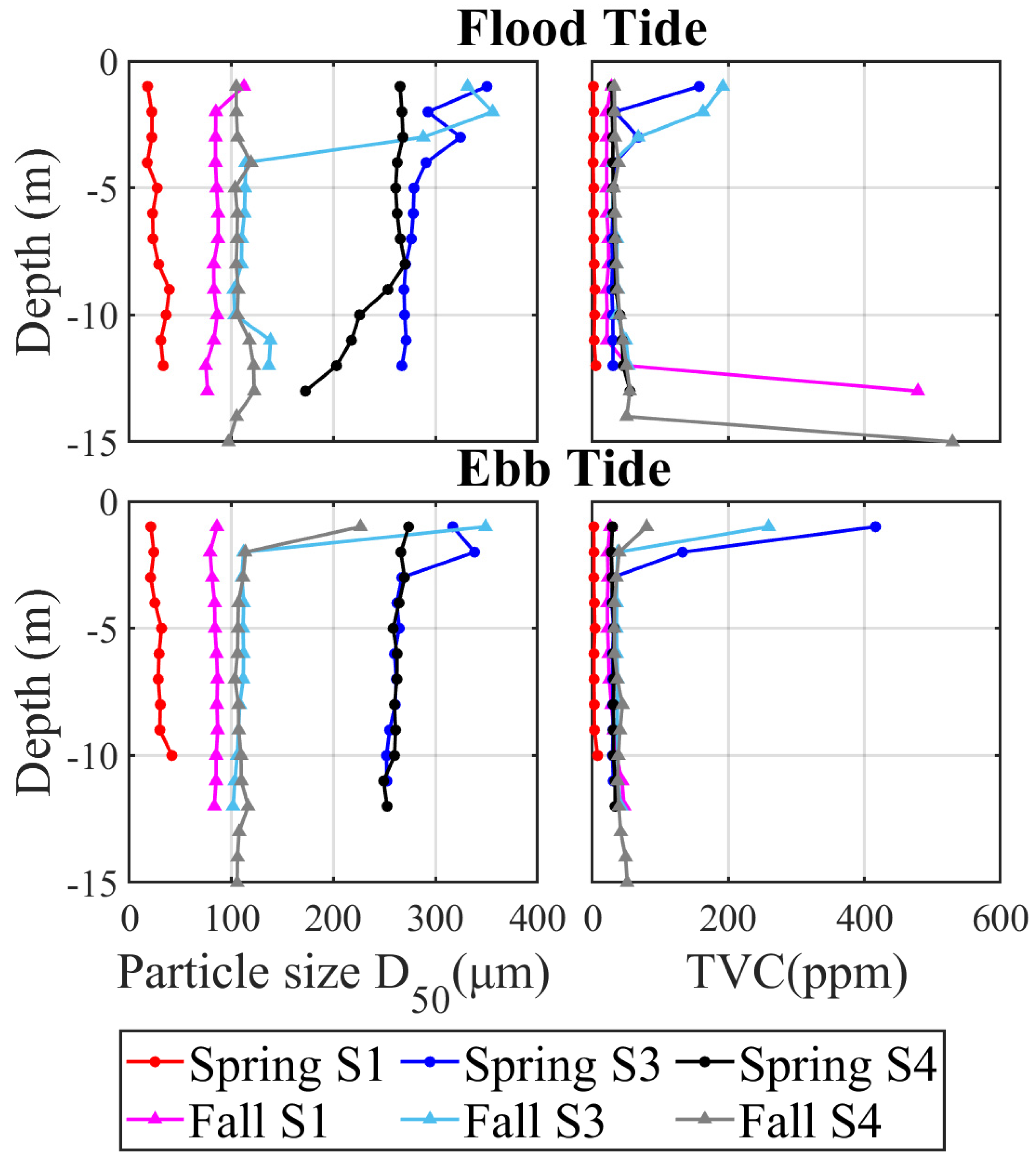
3.1.2. Particle Size and TVC
3.2. Dalin Power Plant (DPP)
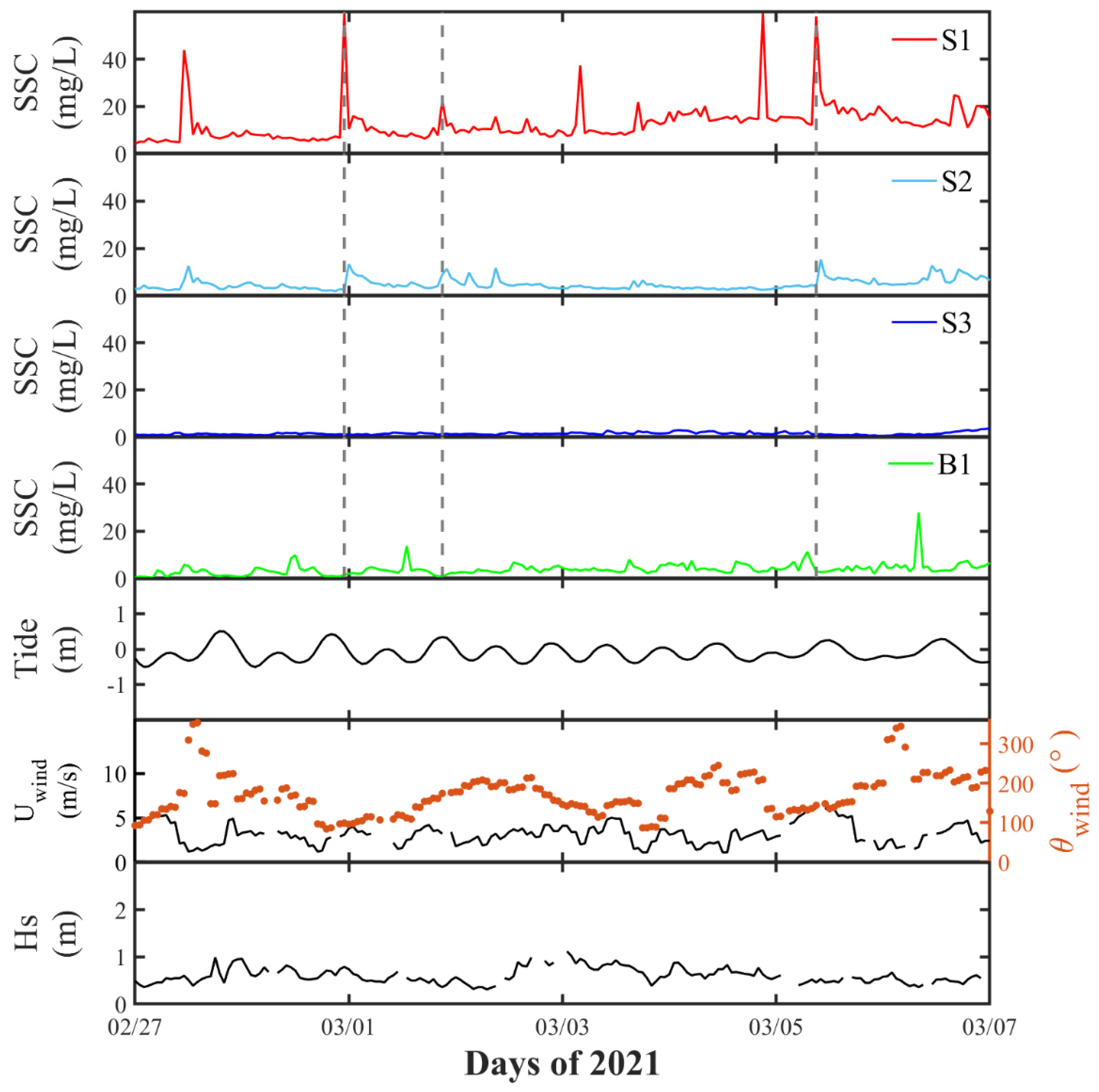
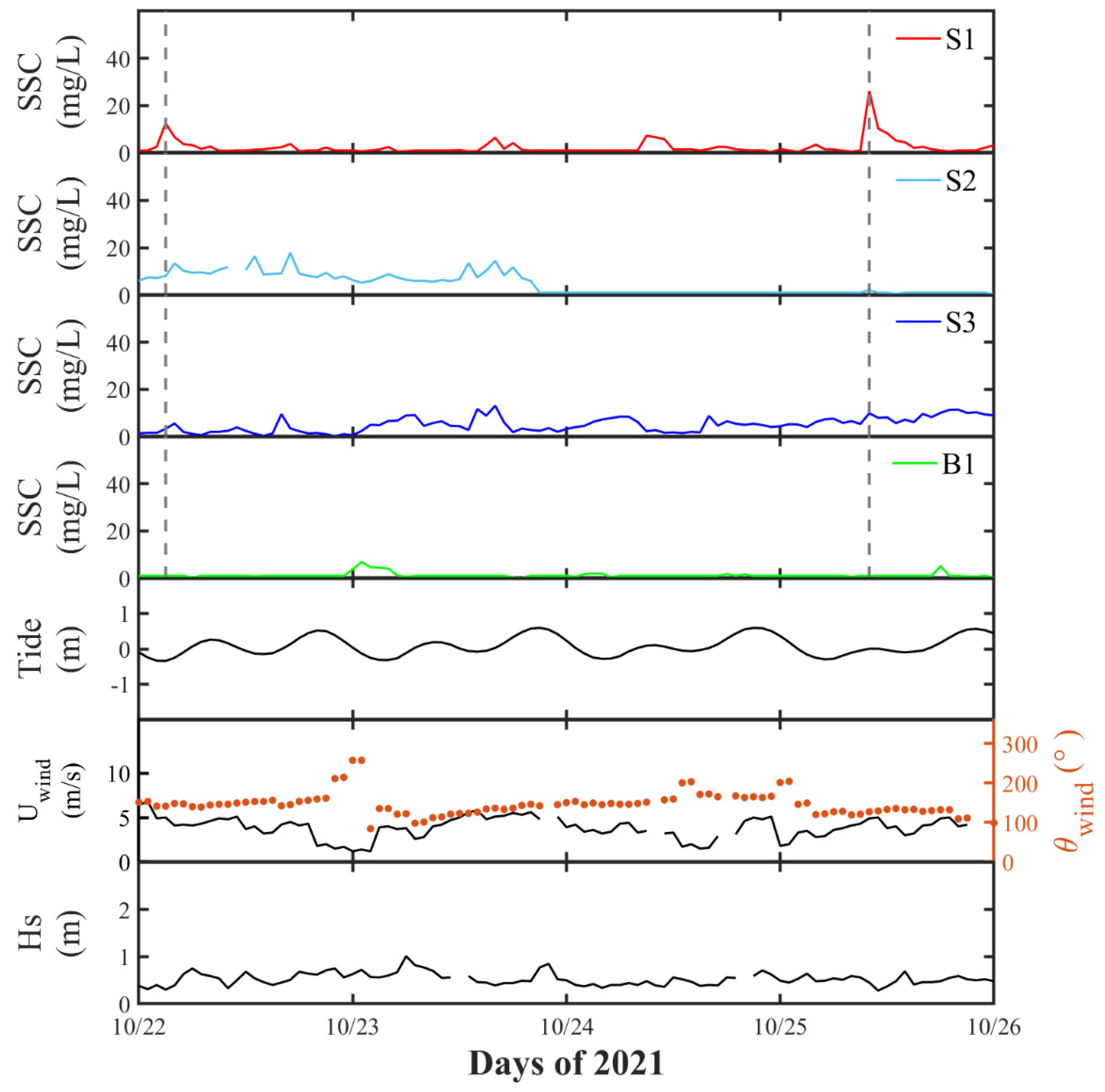
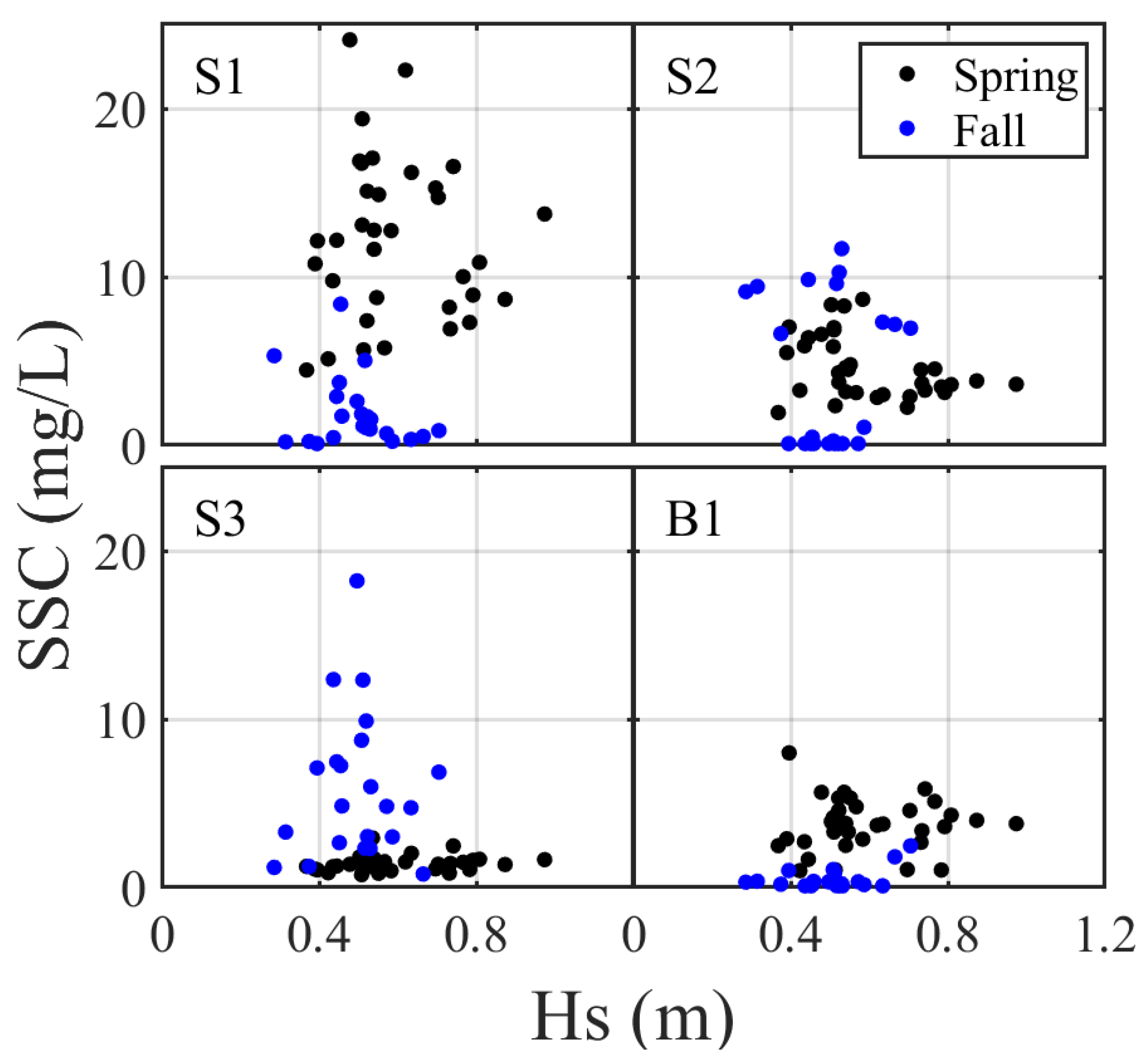
3.2.1. Variation of SSC
3.2.2. Particle Size and TVC
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Heavy Metal Compositions of SSs
4.2. Factors Affecting the Variation of SSC
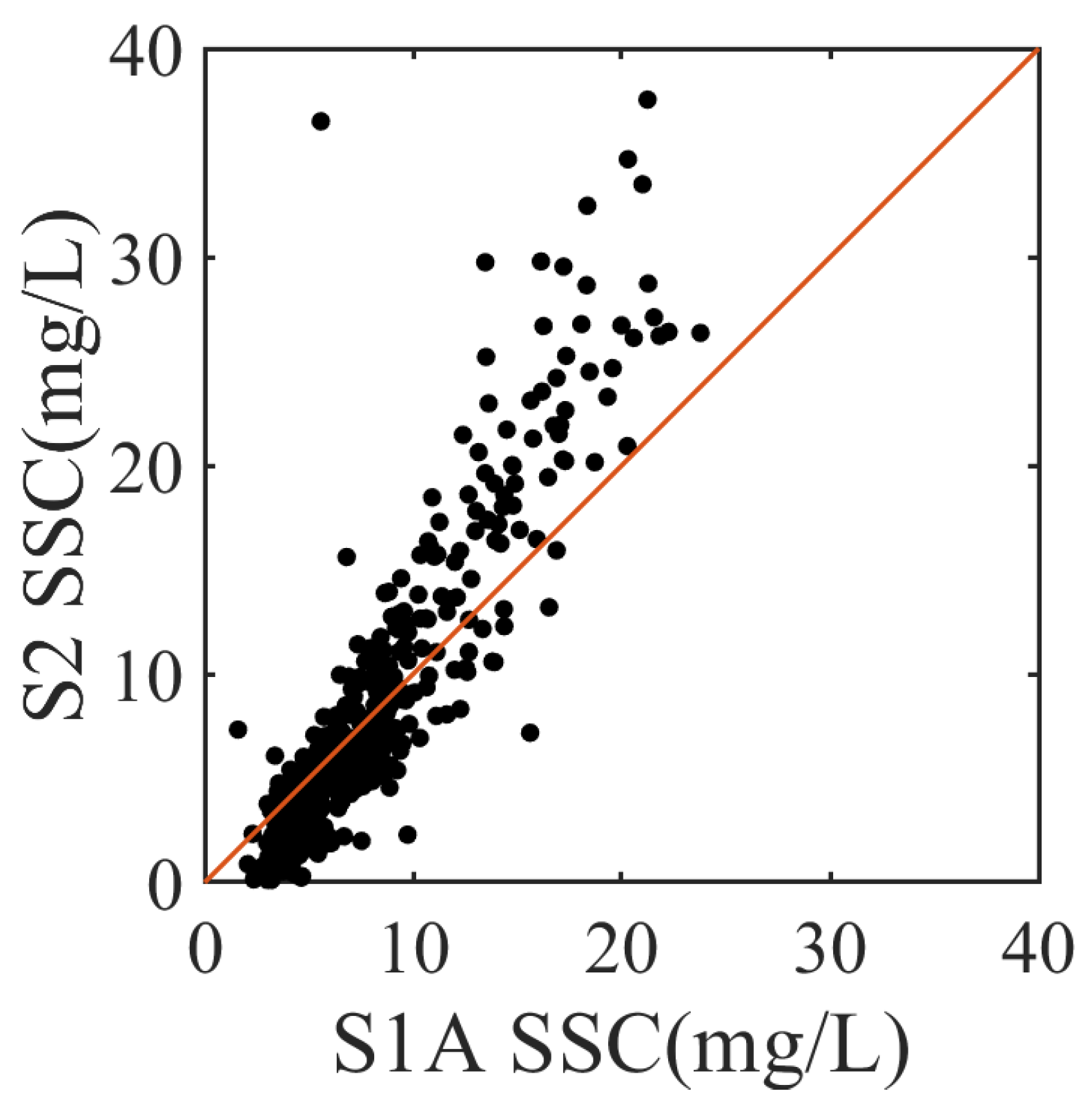
4.3. Change in SSC Between the Intake and Discharge Points
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Calibration of OBS
| Linko Power Plant (LPP) | ||||
| Season | Spring | Fall | ||
| Dates | 2021/03/17~2021/03/29 | 2021/11/05~2021/11/30 | ||
| Depth (m) | Calibration Equations (mg/L) | Depth (m) | Calibration Equations (mg/L) | |
| S1 | ~8 m | SSC = 0.11 mV − 2.32 | ~8 m | SSC = 0.14 mV − 4.29 |
| S1A | ~8 m | SSC = 0.09 mV − 2.44 | ||
| S2 | ~16 m | SSC = 0.08 mV − 1.6 | ~16 m | SSC = 0.12 mV − 9.79 |
| S3 | ~24 m | SSC = 0.12 mV − 0.15 | ~24 m | SSC = 0.09 mV − 4.45 |
| B1 | ~16 m | SSC = 0.17 mV − 3.31 | ~16 m | SSC = 0.17 mV + 0.58 |
| Dalin Power Plant (DPP) | ||||
| Season | Spring | Fall | ||
| Dates | 2021/02/27~2021/03/07 | 2021/10/22~2021/10/26 | ||
| Depth (m) | Calibration Equations (mg/L) | Depth (m) | Calibration Equations (mg/L) | |
| S1 | ~12 m | SSC = 0.12 mV − 0.36 | ~12 m | SSC = 0.11 mV − 1.30 |
| S2 | ~5 m | SSC = 0.10 mV − 2.3 | ~5 m | SSC = 0.09 mV − 8.53 |
| S3 | ~12 m | SSC = 0.07 mV − 0.81 | ~12 m | SSC = 0.13 mV − 3.12 |
| B1 | ~13 m | SSC = 0.20 mV − 3.75 | ~13 m | SSC = 0.09 mV − 3.04 |
References
- Oikawa, K.; Yongsiri, C.; Takeda, K.; Harimoto, T. Seawater flue gas desulfurization: Its technical implications and performance results. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumura, M.; Baba, M.; Znad, H.T.; Kawase, Y.; Yongsiri, C.; Takeda, K. Neutralization of the acidified seawater effluent from the flue gas desulfurization process: Experimental investigation, dynamic modeling, and simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 6339–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.B.; Cui, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, C.S.; Anthony, E.J. Partitioning behavior of Arsenic in circulating fluidized bed boilers co-firing petroleum coke and coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 166, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.J.; Xue, P.; Liu, J.J.; Liao, J.H.; Guo, J.M. A review of removing SO2 and NOX by wet scrubbing. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Sun, L.M.; Yuan, D.X.; Yin, L.Q.; Chen, J.S.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, C.Y.; Liang, Y.; Lin, F.F. Mercury distribution in seawater discharged from a coal-fired power plant equipped with a seawater flue gas desulfurization system. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011, 18, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Feng, L.F.; Yuan, D.X.; Lin, S.S.; Huang, S.Y.; Gao, L.M.; Zhu, Y. The extent of the influence and flux estimation of volatile mercury from the aeration pool in a typical coal-fired power plant equipped with a seawater flue gas desulfurization system. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Peng, J.J.; Yuan, D.X.; Lu, B.Y.; Lin, K.N.; Huang, S.Y. Mercury isotope signatures of seawater discharged from a coal-fired power plant equipped with a seawater flue gas desulfurization system. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoellhamer, D.H.; Mumley, T.E.; Leatherbarrow, J.E. Suspended sediment and sediment-associated contaminants in San Francisco Bay. Environ. Res. 2007, 105, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanders, J.R.; Turner, R.R.; Morrison, T.; Jensen, R.; Pizzuto, J.; Skalak, K.; Stahl, R. Distribution, behavior, and transport of inorganic and methylmercury in a high gradient stream. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1756–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzuto, J.E. Long-term storage and transport length scale of fine sediment: Analysis of a mercury release into a river. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 5875–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Zhang, H.Q.; Jia, Y.G.; Liu, W.Q.; Wang, H. Migration and Diffusion of Heavy Metal Cu from the Interior of Sediment during Wave-Induced Sediment Liquefaction Process. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.N.; Burnett, W.C.; Opsahl, S.P.; Santos, I.R.; Misra, S.; Froelich, P.N. Tracking suspended particle transport via radium isotopes (226Ra and 228Ra) through the Apalachicola-Chattahoochee-Flint River system. J. Environ. Radioact. 2013, 116, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.M.; Lin, S.S.; Feng, L.F.; Huang, S.Y.; Yuan, D.X. The distribution and sea-air transfer of volatile mercury in waste post-desulfurization seawater discharged from a coal-fired power plant. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6191–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, S.G.; Verney, R.; van Prooijen, B.C.; Tran, D.; Hendriks, E.C.M.; Jacquet, M.; Wang, Z.B. Characterizing the Composition of Sand and Mud Suspensions in Coastal and Estuarine Environments Using Combined Optical and Acoustic Measurements. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2021, 126, e2021JC017354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, T.N.; Huang, Z.C. Real-time and long-term monitoring of waves and suspended sediment concentrations over an intertidal algal reef. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoellhamer, D.H. Variability of suspended-sediment concentration at tidal to annual time scales in San Francisco Bay, USA. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, A.W.M.; Lowe, R.J.; Ghisalberti, M.; Winter, G.; Storlazzi, C.; Cuttler, M. Spatial Variability of Sediment Transport Processes Over Intratidal and Subtidal Timescales Within a Fringing Coral Reef System. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 1013–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogston, A.S.; Storlazzi, C.D.; Field, M.E.; Presto, M.K. Sediment resuspension and transport patterns on a fringing reef flat, Molokai, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 2004, 23, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.A.; Riegl, B.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Todd, P.A. Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1737–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadori, M.; Chen, C.R.; Lewis, S.; Wang, J.T.; Shen, J.P.; Hou, E.Q.; Rashti, M.R.; Huang, Q.Y.; Bainbridge, Z.; Stevens, T. The origin of suspended particulate matter in the Great Barrier Reef. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L.; Association, A.P.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaefer, J.A.; Tebbett, S.B.; Bellwood, D.R. The study of sediments on coral reefs: A hydrodynamic perspective. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, J. Twenty-five years with OBS sensors: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 2299–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.P.; Rijnsburger, S.; Meirelles, S.; Horner-Devine, A.R.; Souza, A.J.; Pietrzak, J.D. Incorporating Non-Equlibrium Ripple Dynamics into Bed Stress Estimates Under Combined Wave and Current Forcing. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.R.; Huang, Z.C. Numerical modeling on wave-current flows and bed shear stresses over an algal reef. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2024, 24, 697–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Lian, J.J.; Liu, F.; Yao, Y. Study on the Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Suspended Sediment Driven by Waves and Currents. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, A.A.; Ataie-Ashtiani, B. Analysis of threshold and incipient conditions for sediment movement. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nakamura, T.; Cho, Y.H.; Mizutani, N. Numerical Simulation of Wave-Induced Scour in Front of Vertical and Inclined Breakwaters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P. Coastal Bottom Boundary Layers and Sediment Transport; World Scientific: Singapore, 1992; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, S.; Wang, J.; Chern, C.S.; Chao, S.Y. Seasonal variation of the circulation in the Taiwan Strait. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 35, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Hsu, H.Y.; Chu, C.R.; Liao, C.M. Assessment of wind characteristics and wind turbine characteristics in Taiwan. Renew. Energy 2003, 28, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Kawamura, H.; Li, C.Y.; Hong, H.S.; Jiang, Y.W. Review on Current and Seawater Volume Transport through the Taiwan Strait. J. Oceanogr. 2010, 66, 591–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.W.; Ren, J.; Nie, D.; Chen, B.Z.; Lv, X.Y. Wave-current bottom shear stresses and sediment re-suspension in the mouth bar of the Modaomen Estuary during the dry season. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeroy, A.W.M.; Lowe, R.J.; Ghisalberti, M.; Storlazzi, C.; Symonds, G.; Roelvink, D. Sediment transport in the presence of large reef bottom roughness. J. Geophys. Res.-Ocean. 2017, 122, 1347–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, T.; Roche, M.; Lurton, X.; Fezzani, R.; Simmons, S.M.; Gastauer, S.; Fietzek, P.; Mesdag, C.; Berger, L.; Breteler, M.K.; et al. Bottom and Suspended Sediment Backscatter Measurements in a Flume-Towards Quantitative Bed and Water Column Properties. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.W.; Cheng, R.T.; Wang, P.F.; Richter, K. Laboratory and field evaluations of the LISST-100 instrument for suspended particle size determinations. Mar. Geol. 2001, 175, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.C.; Hsu, T.J.; Ly, T.N. Field evidence of flocculated sediments on a coastal algal reef. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lange, S.I.; Sehgal, D.; Martínez-Carreras, N.; Waldschläger, K.; Bense, V.; Hissler, C.; Hoitink, A.J.F. The Impact of Flocculation on In Situ and Ex Situ Particle Size Measurements by Laser Diffraction. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR035176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, Y.C.; Pottsmith, H.C. Instruments for particle size and settling velocity observations in sediment transport. Mar. Geol. 2000, 168, 89–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Liu, D.Z.; Liang, M.G.; Zhang, T.; Huang, E.M.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Jia, L.W. Characteristics and Mechanisms of Spring Tidal Mixing and Sediment Transport in a Microtidal Funnel-Shaped Estuary. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Ha, H.K.; Woo, S.B. Dynamics of sediment disturbance by periodic artificial discharges from the world’s largest tidal power plant. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 190, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, B.P.; Hill, P.S. Rouse revisited: The bottom boundary condition for suspended sediment profiles. Mar. Geol. 2020, 419, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, K.B.J.; Nittrouer, J.A.; Abolfazli, E.; Osborn, R.; Strom, K.B. Hydrodynamically-Driven Deposition of Mud in River Systems. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowbridge, J.H.; Lentz, S.J. The Bottom Boundary Layer. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2018, 10, 397–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, E.L.; Veron, F. Near-surface turbulence and buoyancy induced by heavy rainfall. J. Fluid Mech. 2017, 830, 602–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.F.; Tang, T.Y.; Jan, S.; Chen, C.J. Taiwan strait current in winter. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Season | Site | As | Std | Cr | Std | Cu | Std | Pb | Std | Cd | Std | Ni | Std | Se | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study area: LPP Averaged Concentration (mg/kg) | |||||||||||||||
| Spring | Inlet | N.D. | - | 1.2 | 1.0 | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | N.D. | - |
| Discharge | N.D. | - | 1.9 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | |
| Increment | - | - | 0.7 | 1.2 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| Fall | Inlet | 79.9 | 67.3 | 237.3 | 226.4 | 66.1 | 20.3 | 56.8 | 8.4 | 18.8 | 4.4 | 63.8 | 30.7 | 45.8 | 29.5 |
| Discharge | 79.2 | 58.0 | 523.4 | 426.7 | 96.5 | 83.5 | 39.6 | 19.1 | 12.6 | 2.4 | 68.6 | 31.5 | 144.5 | 92.5 | |
| Increment | −0.7 | 286.1 | 30.4 | −17.2 | −6.2 | 4.8 | 98.7 | ||||||||
| Study area: DPP Averaged Concentration (mg/kg) | |||||||||||||||
| Spring | Inlet | N.D. | - | 2.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | 1.5 | 3.0 | N.D. | - |
| Discharge | N.D. | - | 3.1 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | N.D. | - | N.D. | - | 0.5 | 0.4 | N.D. | - | |
| Increment | - | 0.2 | −0.1 | - | - | −1.0 | - | ||||||||
| Fall | Inlet | 60.6 | 7.8 | 322.2 | 48.5 | 129.3 | 10.5 | 132.3 | 37.7 | 15.3 | 4.6 | 108.2 | 20.8 | 120.2 | 130.6 |
| Discharge | 78.3 | 54.8 | 317.7 | 189.6 | 122.7 | 44.7 | 103.3 | 51.5 | 11.1 | 4.3 | 74.9 | 37.7 | 125.1 | 121.7 | |
| Increment | 17.7 | −4.5 | −6.6 | −29.0 | −4.2 | −33.3 | 4.9 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.-C.; Lin, P.-C.; Lin, P.-H.; Chuang, S.-H. Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plants on Suspended Sediment Concentrations in Coastal Waters. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030563
Huang Z-C, Lin P-C, Lin P-H, Chuang S-H. Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plants on Suspended Sediment Concentrations in Coastal Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(3):563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030563
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhi-Cheng, Po-Chien Lin, Po-Hsun Lin, and Shun-Hsing Chuang. 2025. "Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plants on Suspended Sediment Concentrations in Coastal Waters" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 3: 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030563
APA StyleHuang, Z.-C., Lin, P.-C., Lin, P.-H., & Chuang, S.-H. (2025). Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plants on Suspended Sediment Concentrations in Coastal Waters. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(3), 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030563







