Studying the Impact of the Load Distribution Ratio on the Unsteady Performance of a Dual-Stage Pump-Jet Propulsor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Calculation Method
2.1. Research Object
2.2. Numerical Simulation Methods
2.2.1. Computational Domain and Mesh Generation
2.2.2. Computational Methods and Boundary Conditions
2.3. Numerical Method Validation
2.3.1. Suboff Validation
2.3.2. Propulsor Verification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrodynamic Performance
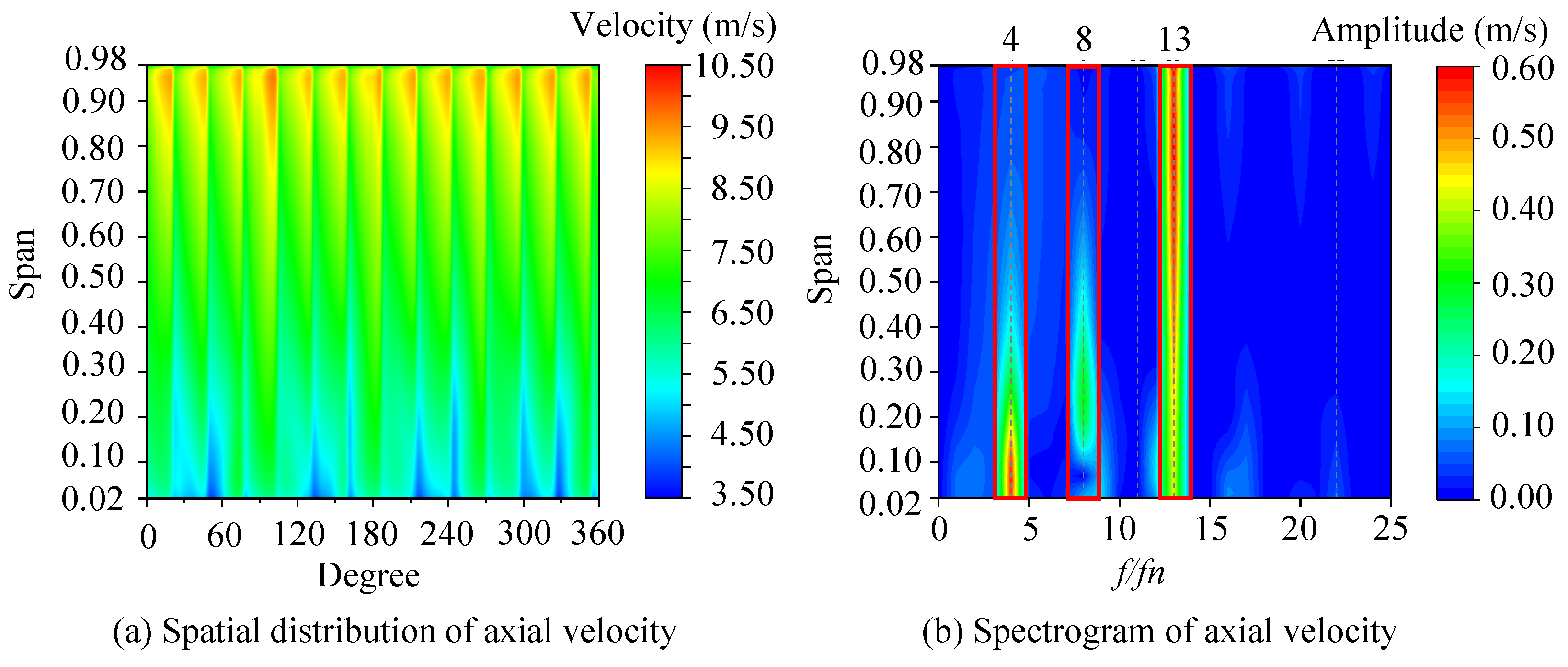
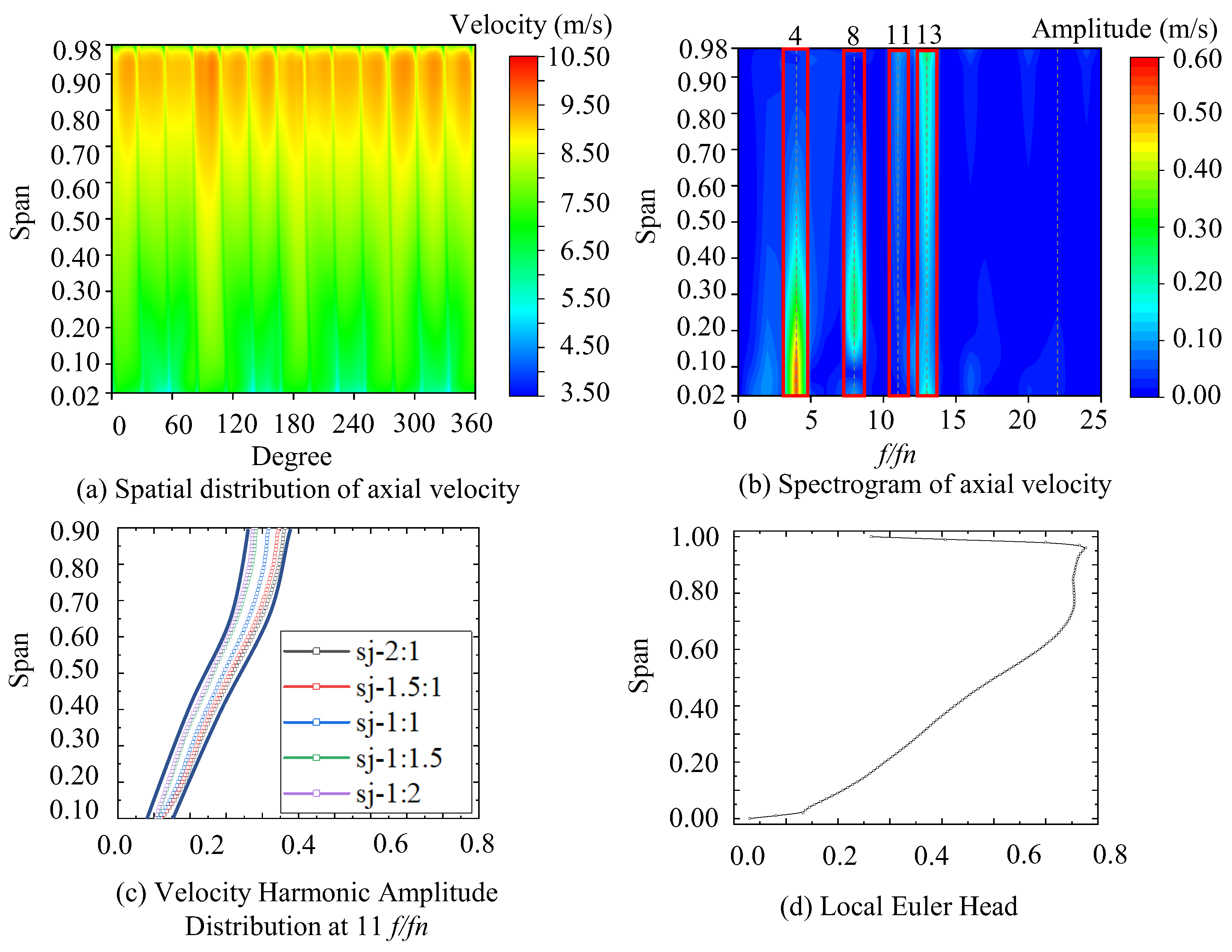
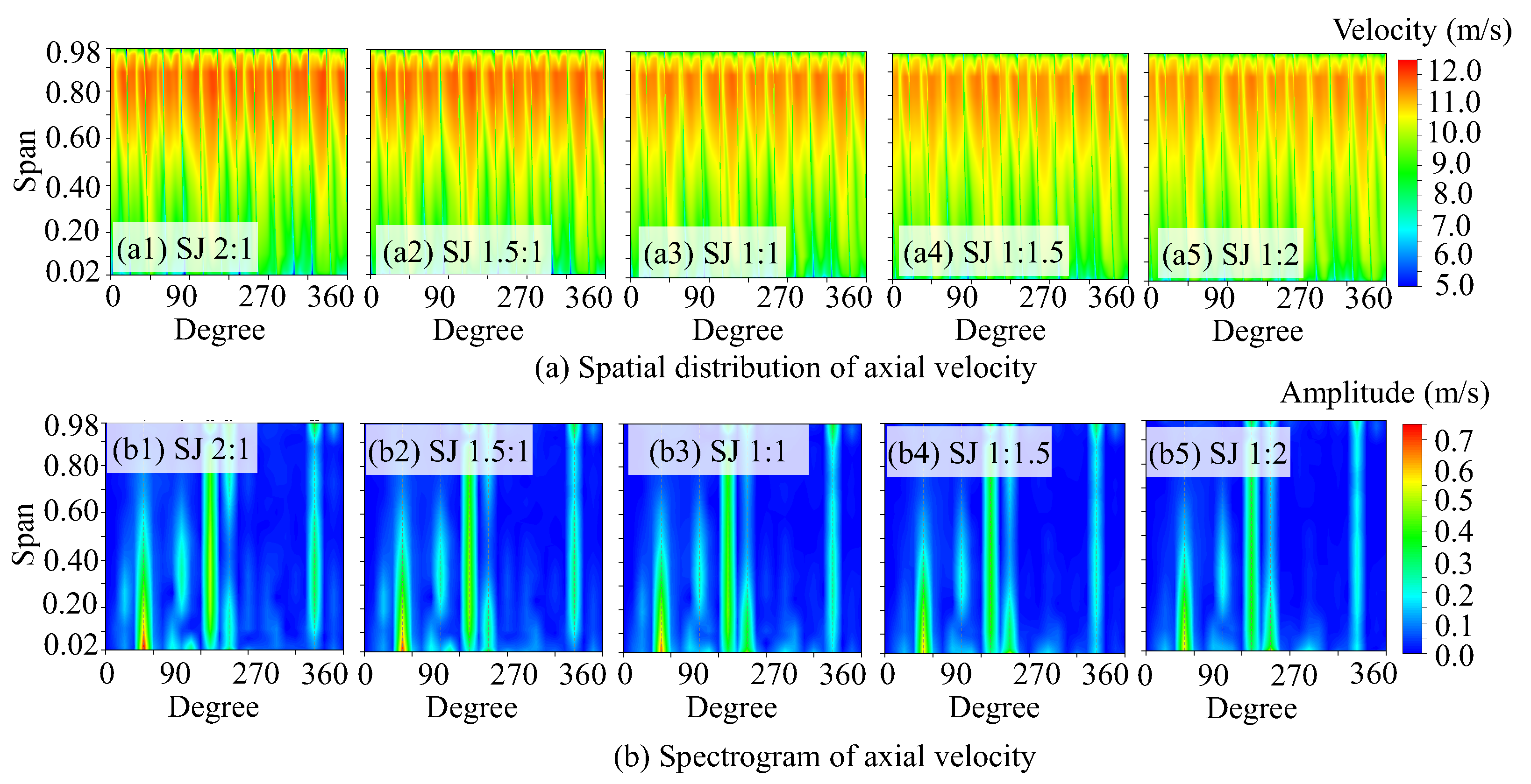
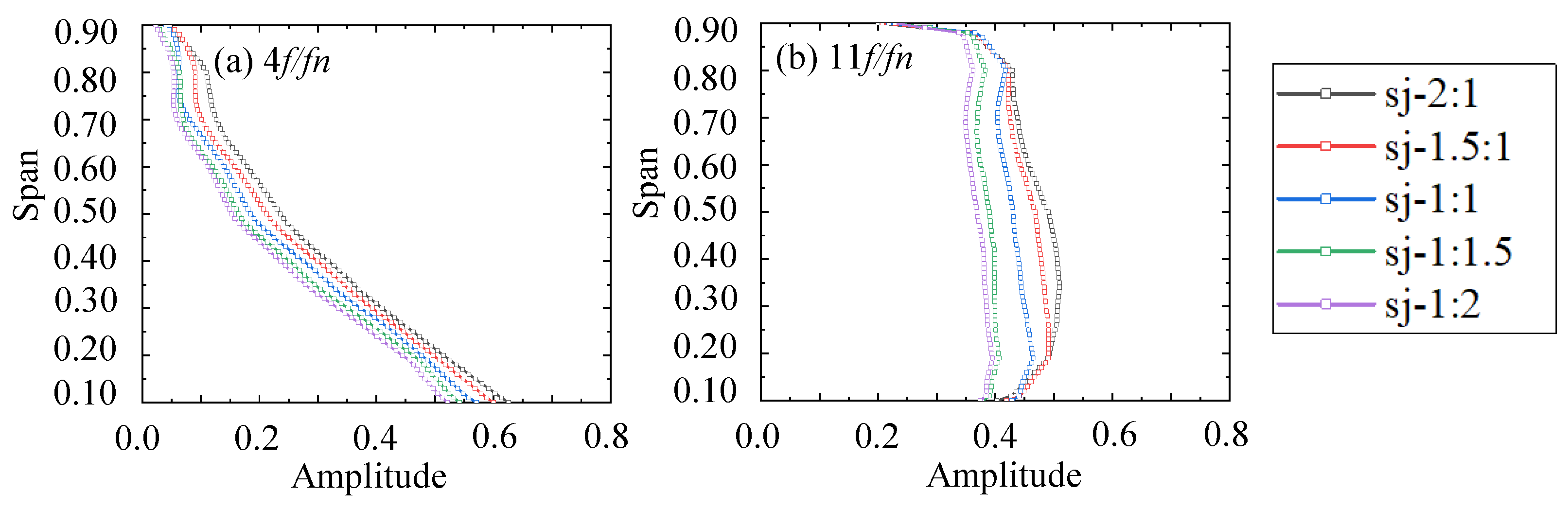
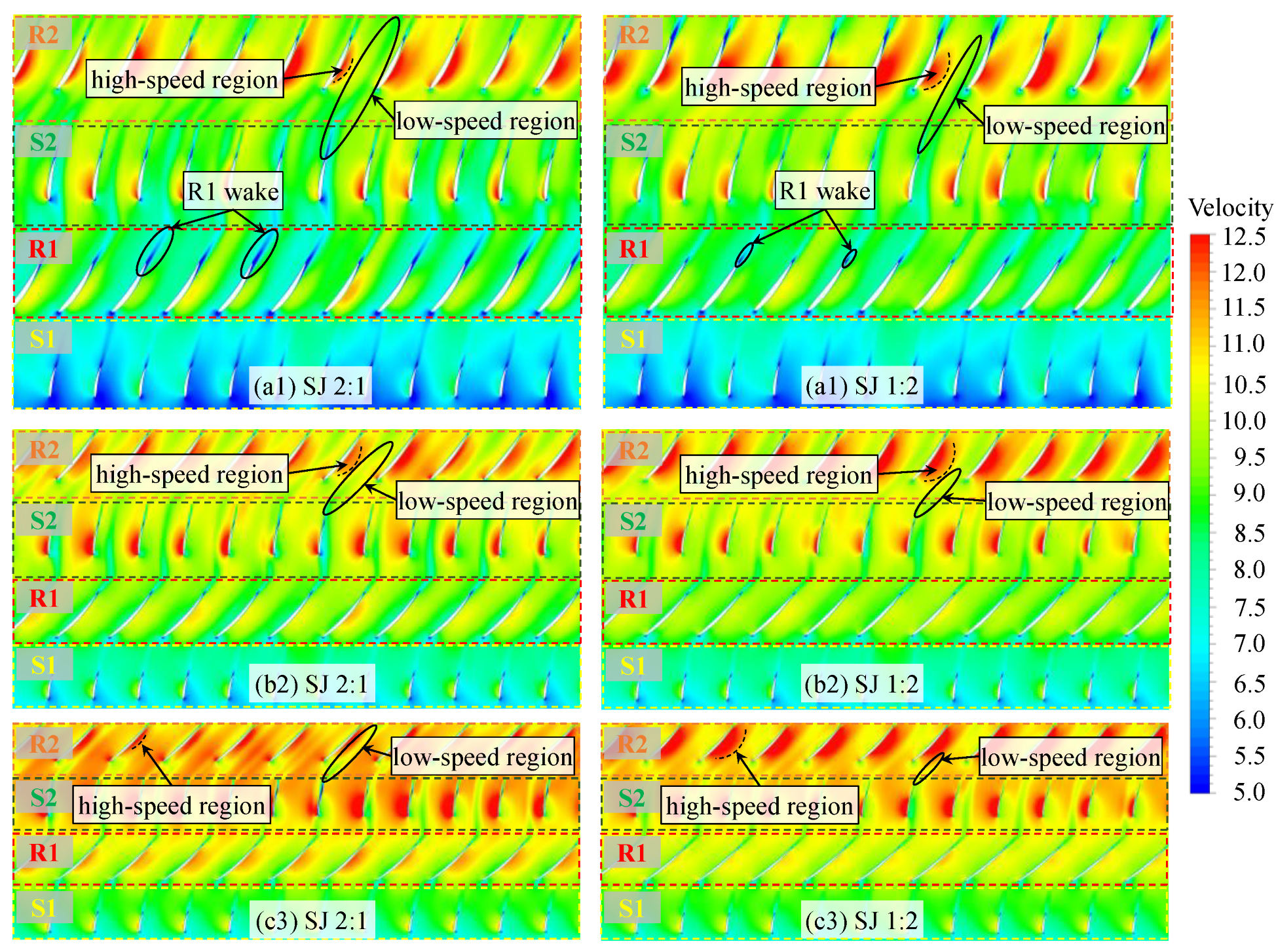
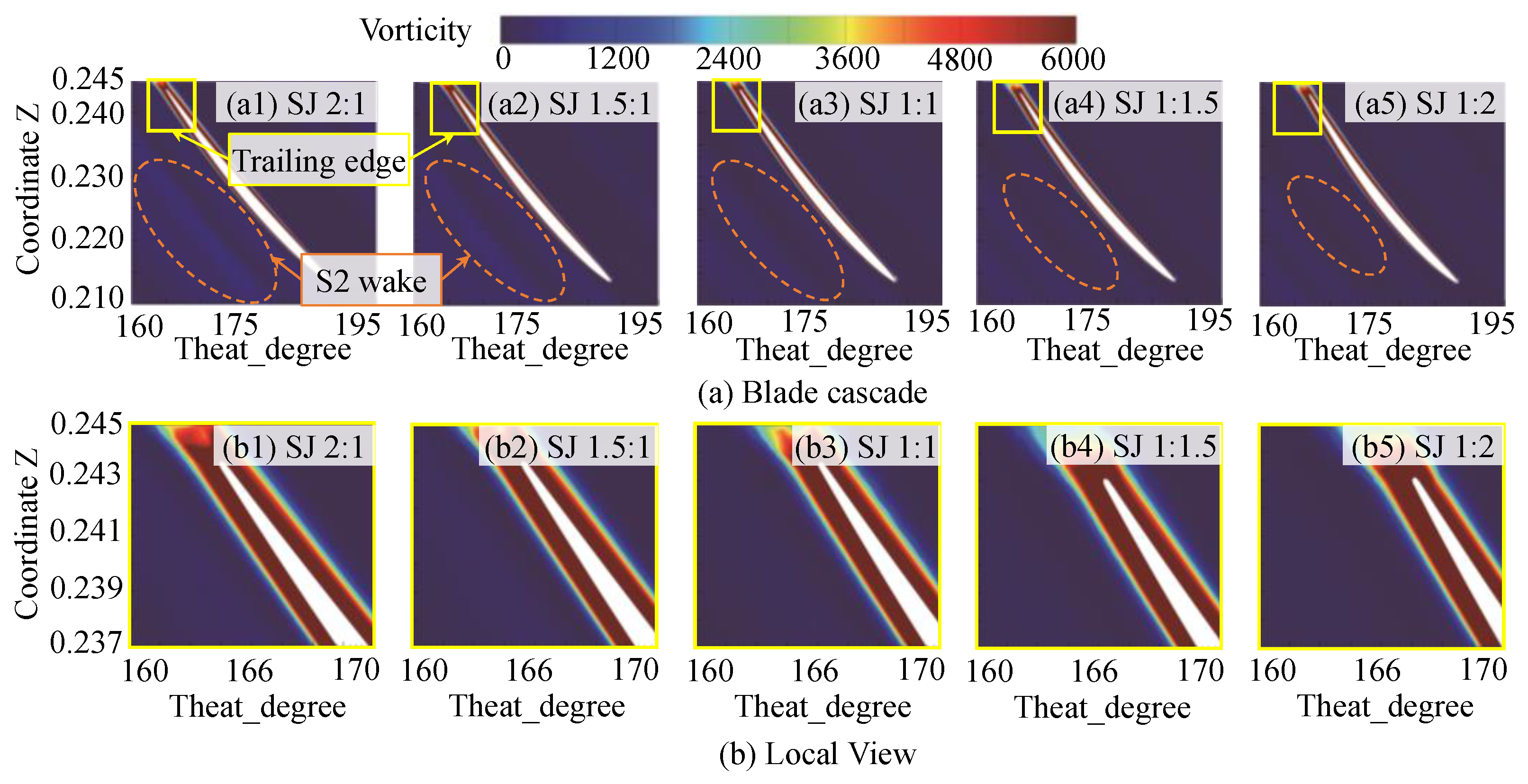
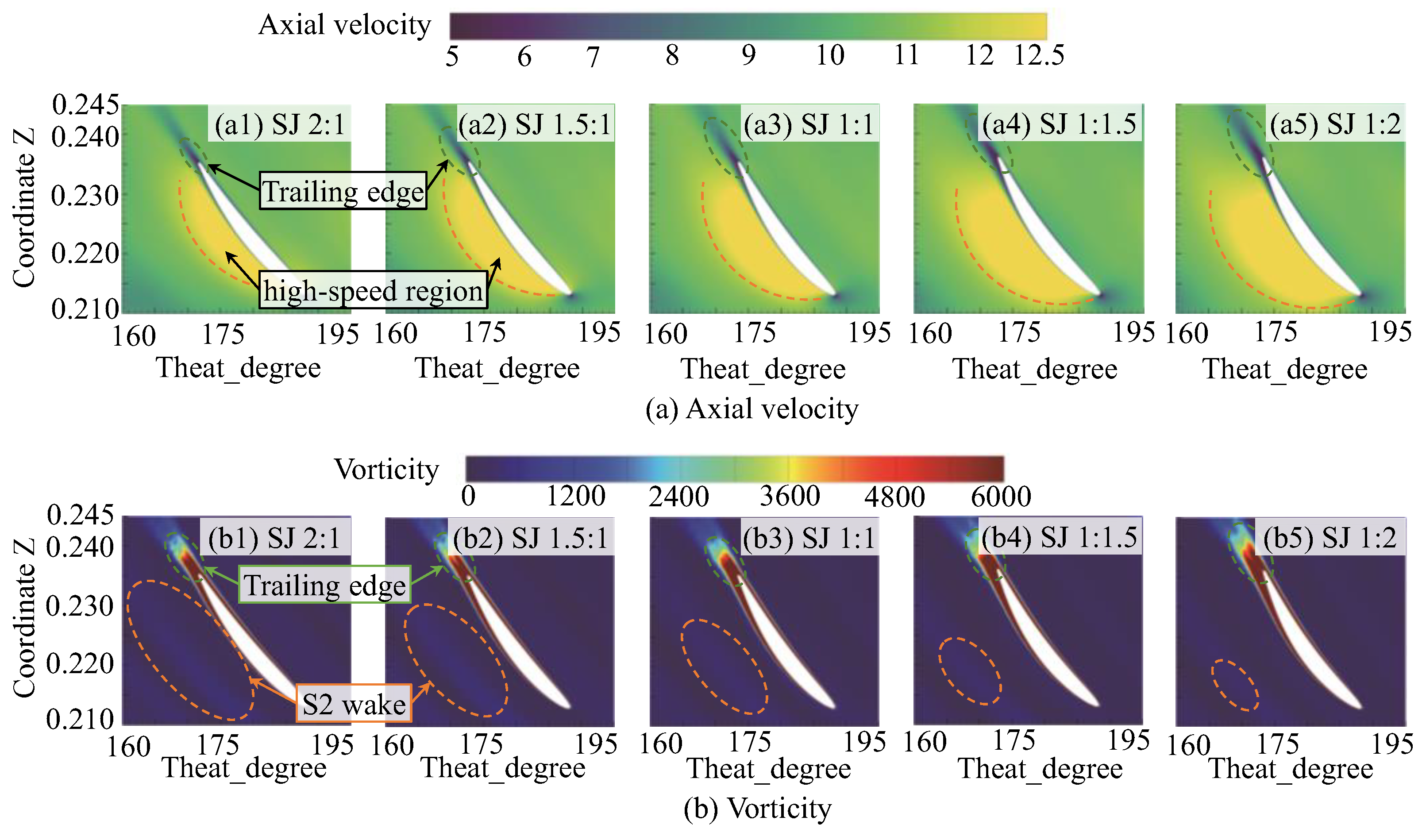
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of the Flow Field
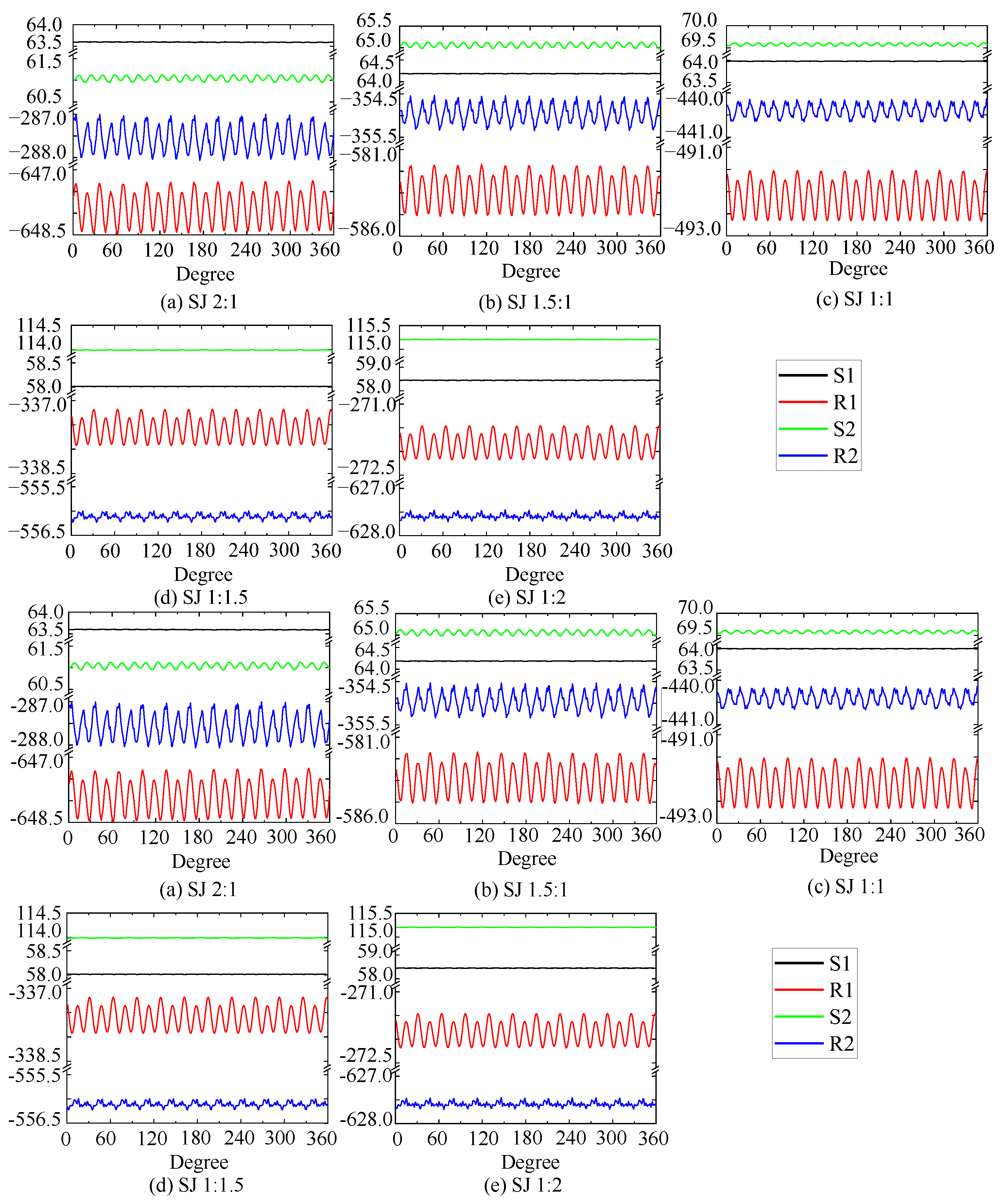
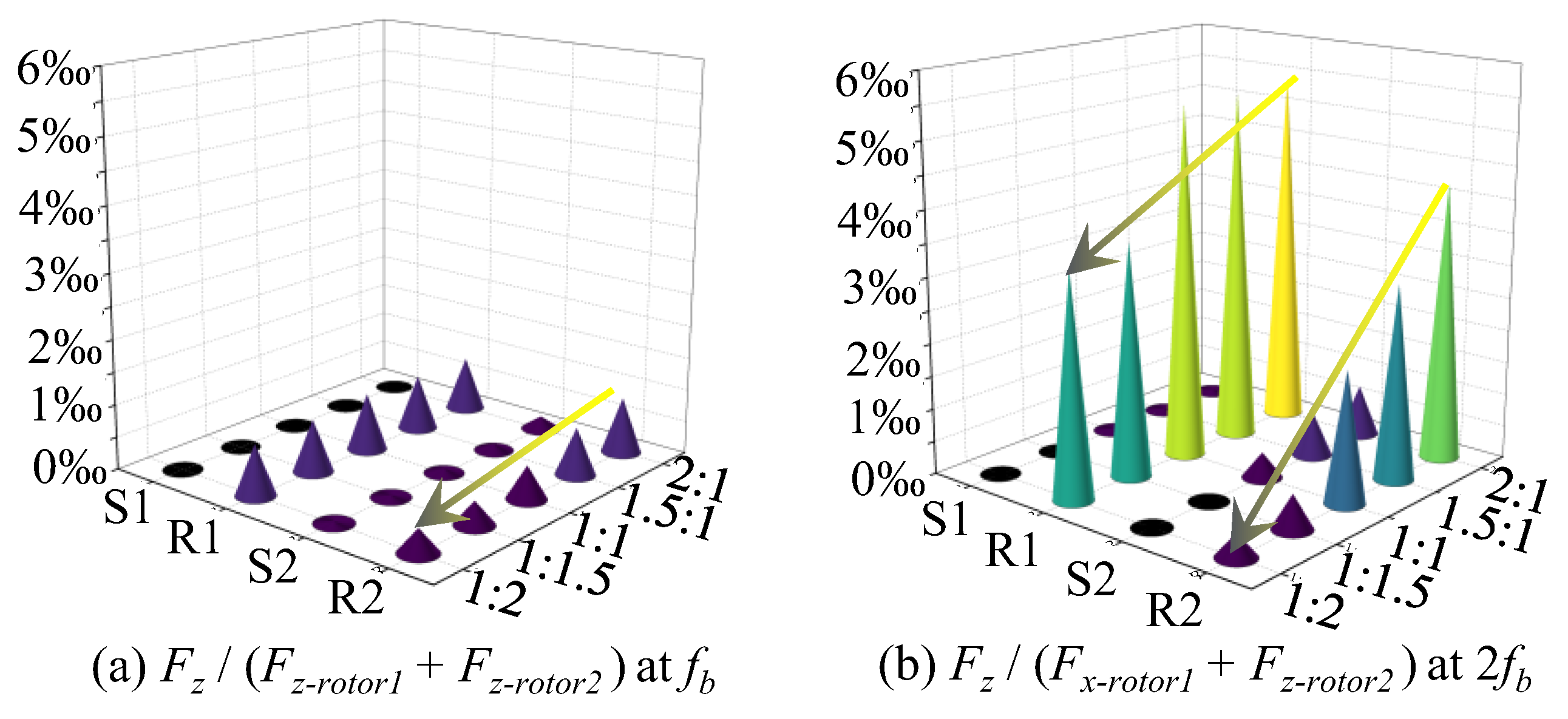
3.3. Effect of Rotor Load Distribution on Unsteady Force
3.4. Effect of Rotor Load Distribution on Radiated Noise Characteristics
4. Conclusions
- Different load distribution ratios have no significant impact on the propulsion performance of dual-stage PJPs. Whether the load is front-heavy and rear-light or front-light and rear-heavy, the propulsion efficiency differs by no more than 1% when the overall propulsion capability is consistent, with only slight differences in the work growth trend observed for first- and second-stage rotors;
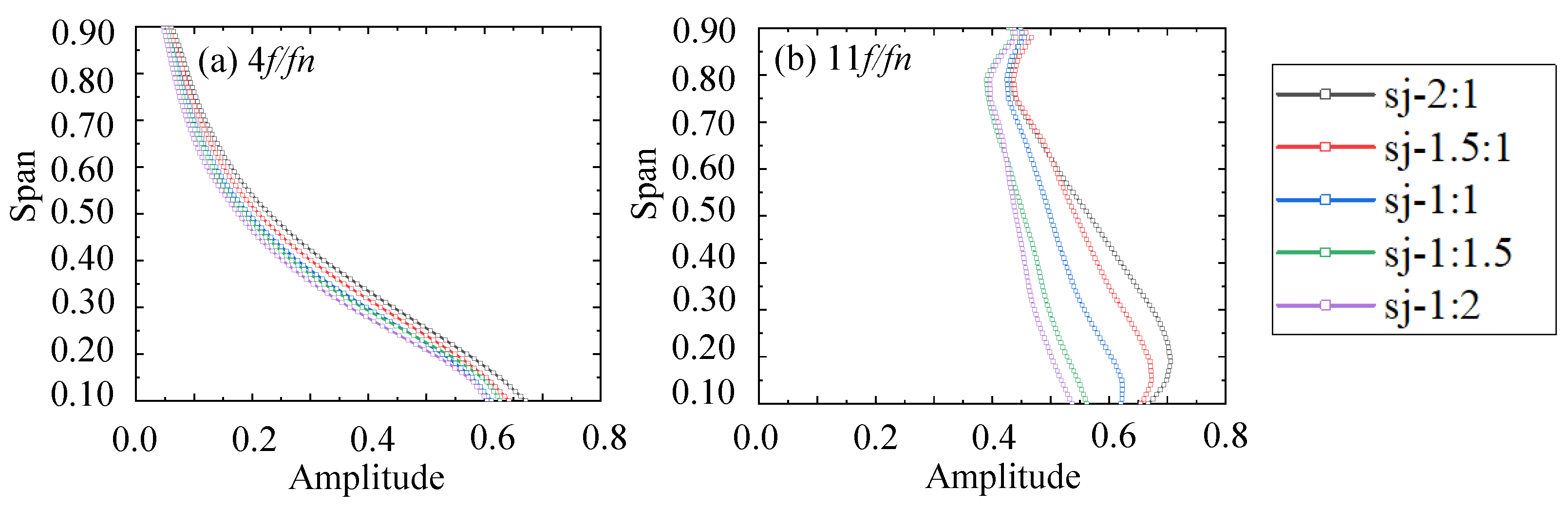
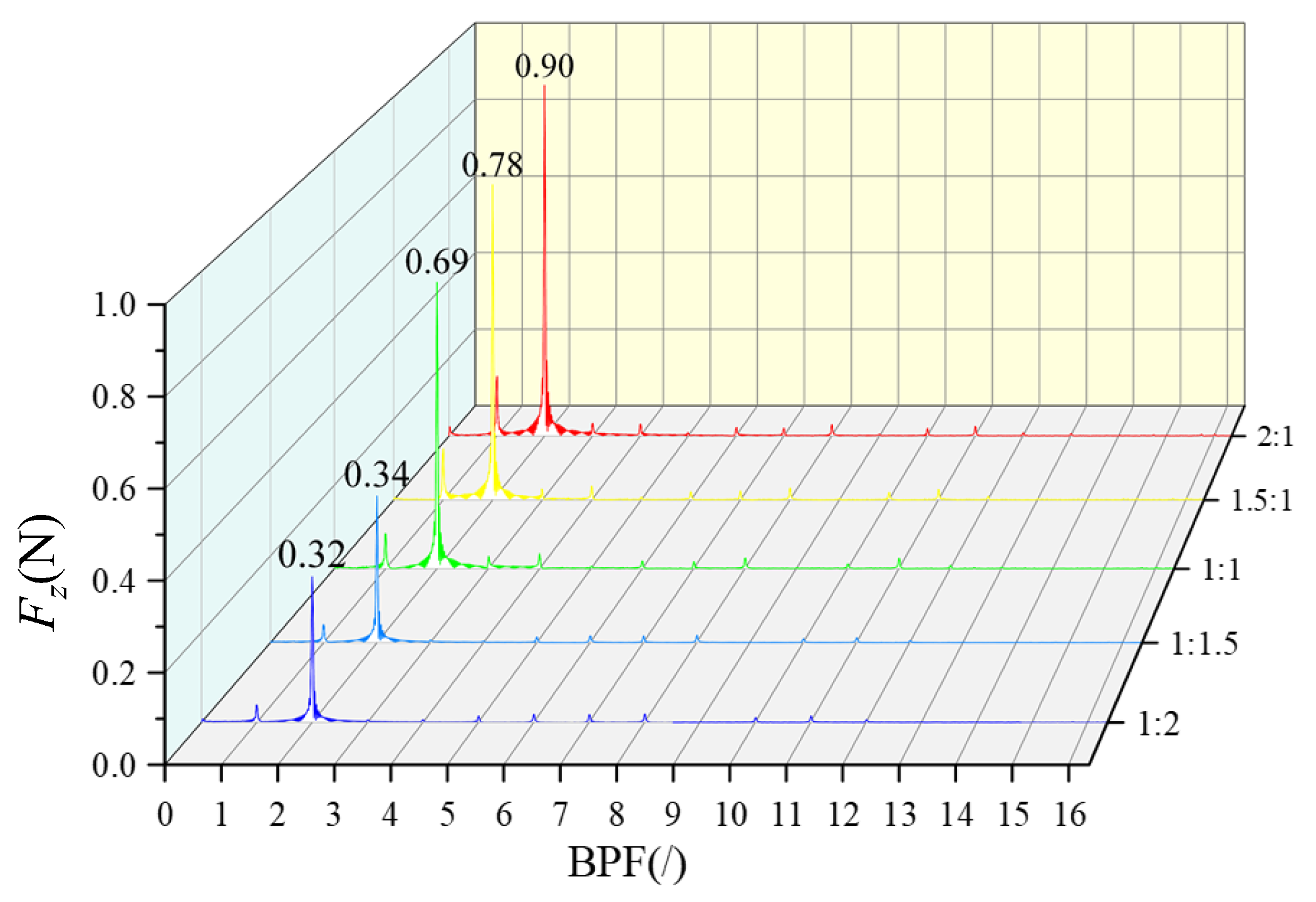
- As the load distribution ratio is aft-shifted, the overall unsteady force of the propulsor decreases continuously. With a load distribution ratio of 1:1, the prototype unsteady force is 0.69 N; with a load distribution ratio of 1:2, the unsteady force decreases to 0.32 N, which is a reduction of 53.6%;
- The principle behind the reduction in the unsteady axial force of the dual-stage PJPs with the aft shift in the load distribution ratio is the simultaneous decrease in the unsteady axial force of both the first- and second-stage rotors: the unsteady force of the first-stage rotor decreases due to the reduction in the axial force and unchanged inflow, while the decrease in the work performed by the first-stage rotor leads to a reduction in the BPFVHC, making the flow field more uniform and significantly improving the inflow conditions at the front of the second-stage rotor, thereby reducing its unsteady force;
- The combined comparison of flow field spectrum analysis and unsteady force results under five different load distribution ratios can, to some extent, indicate that when the overall working capacity is consistent, the steady-state flow field distribution results, particularly for the BPFVHC, can predict axial unsteady force. This also lays a foundation for the rapid prediction of unsteady performance in future dual-stage PJPs or axial flow fluid machinery;
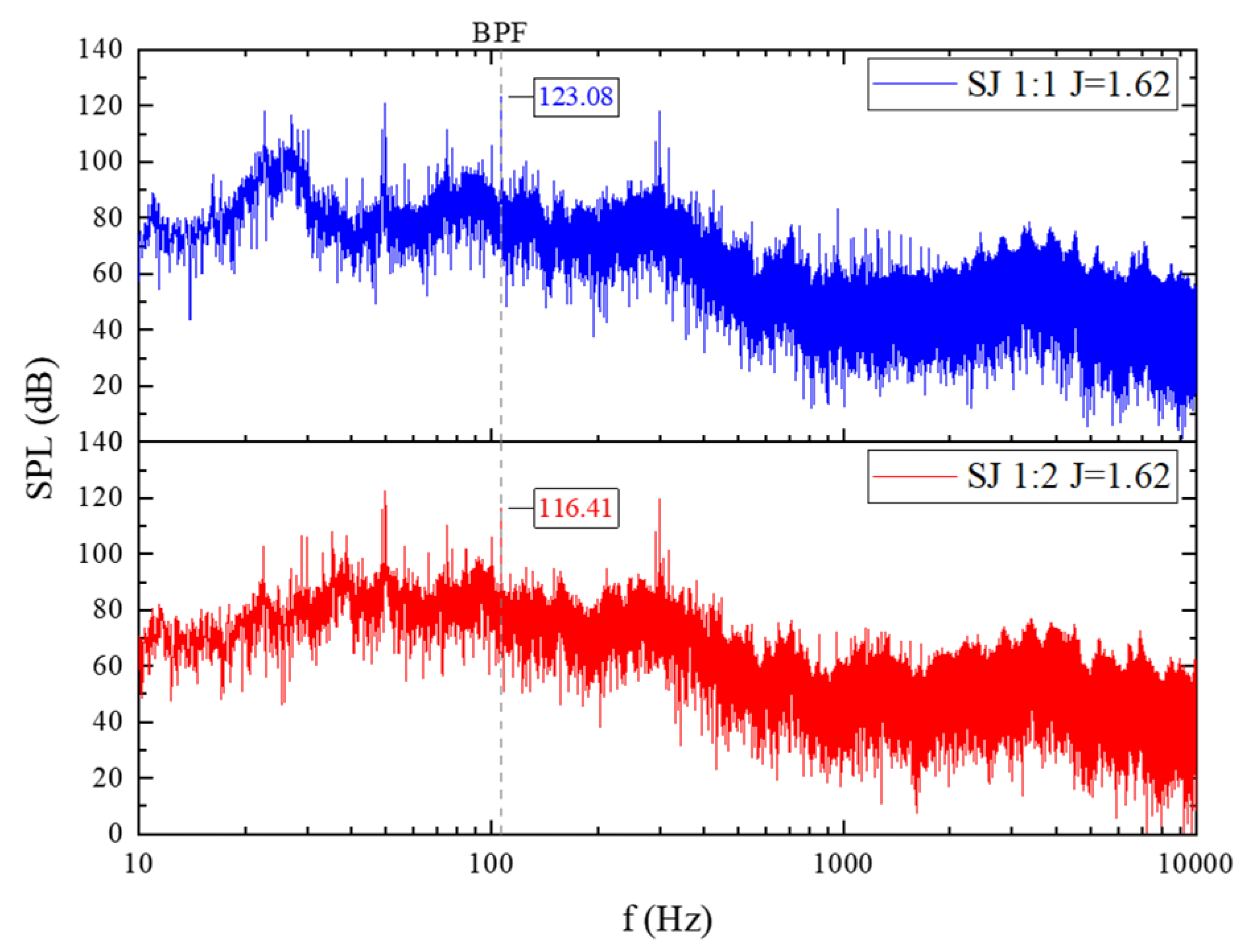
- The sound pressure level results of radiated noise under different load distribution ratios are consistent with the excitation force results. The SJ1:2 pump-jet, compared to the SJ1:1 pump-jet, has a sound pressure level at blade frequency that is reduced by 6.67 dB. This indicates that aft shifting of the load distribution ratio is effective in reducing the unsteady performance of the dual-stage PJPs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| SST | Shear Stress Transport |
| PJP | Pump-jet propulsor |
| Lsub | Length of suboff |
| Dsub | Diameter of suboff |
| NS1 | Number of first-stage stator blades |
| NR1 | Number of first-stage rotor blades |
| NS2 | Number of second-stage stator blades |
| NR2 | Number of second-stage rotor blades |
| Advance coefficient | |
| Thrust coefficient | |
| Torque coefficient | |
| Propulsive efficiency | |
| BPF | Blade-passing frequency |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| BPFVHC | Blade-Passing Frequency Velocity Harmonic Coefficient |
| S1 | First-stage stator |
| R1 | First-stage rotor |
| S2 | Second-stage stator |
| R2 | Second-stage rotor |
| Vertical force | |
| Lateral force | |
| Axial force | |
| Axial force on the First-Stage stator | |
| Axial force on the First-Stage rotor | |
| Axial force on the Second-Stage stator | |
| Axial force on the Second-Stage rotor | |
| fz,fb-R1 | Axial excitation force for the first blade-passing frequency of the first-stage rotor |
| fz,2fb-R1 | Axial excitation force for the second blade-passing frequency of the first-stage rotor |
References
- Mccormick, B.W.; Elsenhuth, J.J. Design and performance of propellers and pumpjets for underwater propulsion. Aiaa J. 1963, 1, 2348–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Dong, X.; Yang, C. Attenuation of the tip-clearance flow in a pump-jet propulsor by thickening and raking the tips of rotor blades: A numerical study. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2021, 113, 102723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Huang, Q.; Pan, G.; He, X. Multi-path deep learning framework on discrete pressure points to predict velocity field of pump-jet propulsor. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2022, 123, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.K.; Pavesi, G.; Yuan, J.P.; Fu, Y.X.; Gao, Q.L. Effects of duct profile parameters on flow characteristics of pump-jet: A numerical analysis on accelerating and decelerating ducts distinguished by cambers and angles of attack. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 281, 114733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, M.C.; Park, I.; Seol, H.; Kim, M.J.; Jin, W.S. Parametric study of the hydrodynamic characteristics of the pumpjet propulsor for the SUBOFF submarine. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L. Study on Rotor-Rotor Interaction Contra and Hydraulic Optimal Design of Pump, Rotating Water-Jet. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, A.; Shigemitsu, T.; Watanabe, S. Performance test and flow measurement of contra-rotating axial flow pump. J. Therm. Sci. 2007, 16, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momosaki, S.; Usami, S.; Okuma, K.; Watanabe, S.; Furukawa, A. Experimental study on rotational speed control of contra-rotating axial flow pump. In Proceedings of the 3rd Asian Joint Workshop on Thermophysics and Fluid Science, Matsue, Japan, 10–14 September 2010; p. JP-02. [Google Scholar]
- Momosaki, S.; Usami, S.; Watanabe, S.; Furukawa, A. Numerical simulation of internal flow in a contra-rotating axial flow pump. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2010, 12, 12046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Watanabe, S.; Momosaki, S.; Imanishi, T.; Furukawa, A. Low Speed Design of Rear Rotor in Contra-Rotating Axial Flow Pump. Int. J. Fluid Mach. Syst. 2013, 6, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D. Mechanics of Underwater Noise; Pergamon Press: Tarrytown, New York, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Merz, S.; Kinns, R.; Kessissoglou, N. Structural and acoustic responses of a submarine hull due to propeller forces. J. Sound. Vib. 2009, 325, 266–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessup, S.D. Measurement of Multiple Blade Rate Unsteady Propeller Forces; David Taylor Research Center: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, X.D.; Chen, H.Y.; Dong, X.Q.; Chen, Y. Experimental and numerical investigations on the unsteady thrust of a propeller in presence of an upstream rudder. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 237, 109644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.T.; Zhang, Z.G.; Hua, H.X. Numerical investigation of tip clearance effects on propulsion performance and pressure fluctuation of a pump-jet propulsor. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 192, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Duan, N.; Hua, H.; Zhang, Z. Propulsion performance and unsteady forces of a pump-jet propulsor with different pre-swirl stator parameters. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2020, 100, 102184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, Q.; Pan, G.; Dong, X. The transient prediction of a pre-swirl stator pump-jet propulsor and a comparative study of hybrid RANS/LES simulations on the wake vortices. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 203, 107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, Q.; Pan, G.; Dong, X.; Li, F. Effects of blade number on the propulsion and vortical structures of pre-swirl stator pump-jet propulsors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Cao, L.; Wu, D.; Yu, F.; Huang, B. Generation and distribution of turbulence-induced forces on a propeller. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 206, 107255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.Y.; Cao, L.L.; Wu, D.Z.; Huang, B.; Qin, S.J.; Yu, F.X. Unsteady responses and correlation characteristics of propeller blades under turbulence excitation. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 266, 112631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.T.; Huang, B.; Zhang, D.H.; Wu, D.Z. Control method of line spectrum excitation force for pump-jet propeller: Random unevenly spaced rotor blades. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 097104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.T.; Huang, B.; Zhang, D.H.; Wu, D.Z. Excitation force on a pump-jet propeller: The effect of the blade number. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 281, 114727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, J.T.; Huang, B.; Zhang, D.H.; Wu, D.Z. Suppression method for exciting force of pump jet propellers based on sinusoidal unevenly spaced rotor blades. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 262, 112198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, Q.G.; Pan, G.; Dong, X.G.; Xu, L.H. Study on the thrust fluctuation and vortices of a pump-jet propulsor under different duct. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 271, 113788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Z.; Li, F.Z.; Huang, Q.G.; Pan, G.; Wang, S.X.; Tian, X.S. On the space-time decomposition and reconstruction of the pump-jet propulsor flow field. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 286, 115521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Z.; Huang, Q.G.; Sun, G.C.; Pan, G.; Li, H.; Bai, C.A. Numerical simulation of the flow field and radiation noise from a pump-jet propulsor under various stator pre-whirl angles. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2023, 135, 103558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujun, W. Research Progress of Computational Model for Rotating Turbulent Flow in Fluid Machinery. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2016, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C. Research on the Influence of the Wake Field of Underwater Vehicles on Propulsor Exciting Force Characteristics; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, D.; Pan, G.; Lee, S.; Huang, Q.; Shi, Y. Underwater radiated noise reduction technology using sawtooth duct for pumpjet propulsor. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 188, 106228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Z.; Liu, G.S.; Huang, Q.G.; Sun, G.C.; Pan, G.; Qin, D.H. Influence of asymmetric pre-whirl stator spacing on unsteady characteristics of pump-jet propulsor. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 273, 113896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.C.; Shi, S.K.; Su, Z.W.; Tang, W.H.; Hua, H.X. Reducing underwater radiated noise of a SUBOFF model propelled by a pump-jet without tip clearance: Numerical simulation. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 243, 110277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.L.; Lv, F.R.; Ta, N.; Rao, Z.S. Study on bearing force of marine propeller induced by longitudinal vibration of propulsion-shafting. Ships Offshore Struct. 2020, 15, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.L.; Jiao, C.X.; Ta, N.; Rao, Z.S. Theoretical study on the axial excitation force transmission characteristics of marine propellers. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 189, 106364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.K.; Tang, W.H.; Huang, X.C.; Dong, X.Q.; Hua, H.X. Experimental and numerical investigations on the flow-induced vibration and acoustic radiation of a pump-jet propulsor model in a water tunnel. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 258, 2022258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. 2-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. Aiaa J. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Feng, D.K.; Liu, L.W.; Wang, X.Z.; Yao, C.B. Research on the Performance of Pumpjet Propulsor of Different Scales. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R.; Kuntz, M.; Langtry, R. Ten years of industrial experience with the SST turbulence model. In Reviews in Turbulence, Heat and Mass Transfer; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Summary of DARPA Suboff Experimental Program Data; Naval Surface Warfare Center, Carderock Division (NEWCCD): Bethesda, MD, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, L.; Cui, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D. Effects of non-uniform inflow on the spatial and temporal distribution of impeller excitation in axial flow pumps in water tunnels. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 5251–5262. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Research on Acoustic Characteristics Analysis and Characteristic Line Spectrum Extraction Method of Propulsion Pump Noise; Zhejiang University: Hangzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
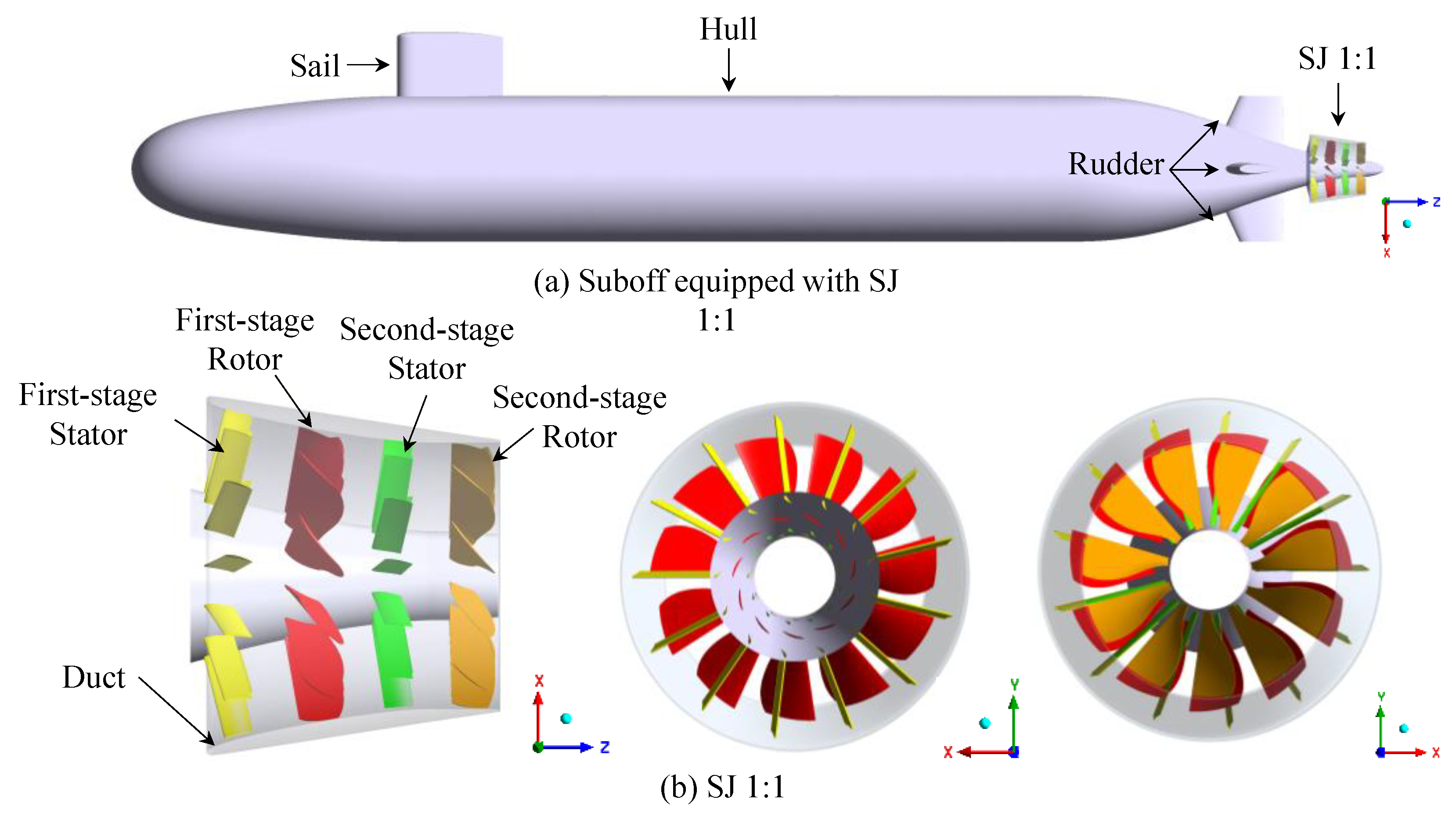
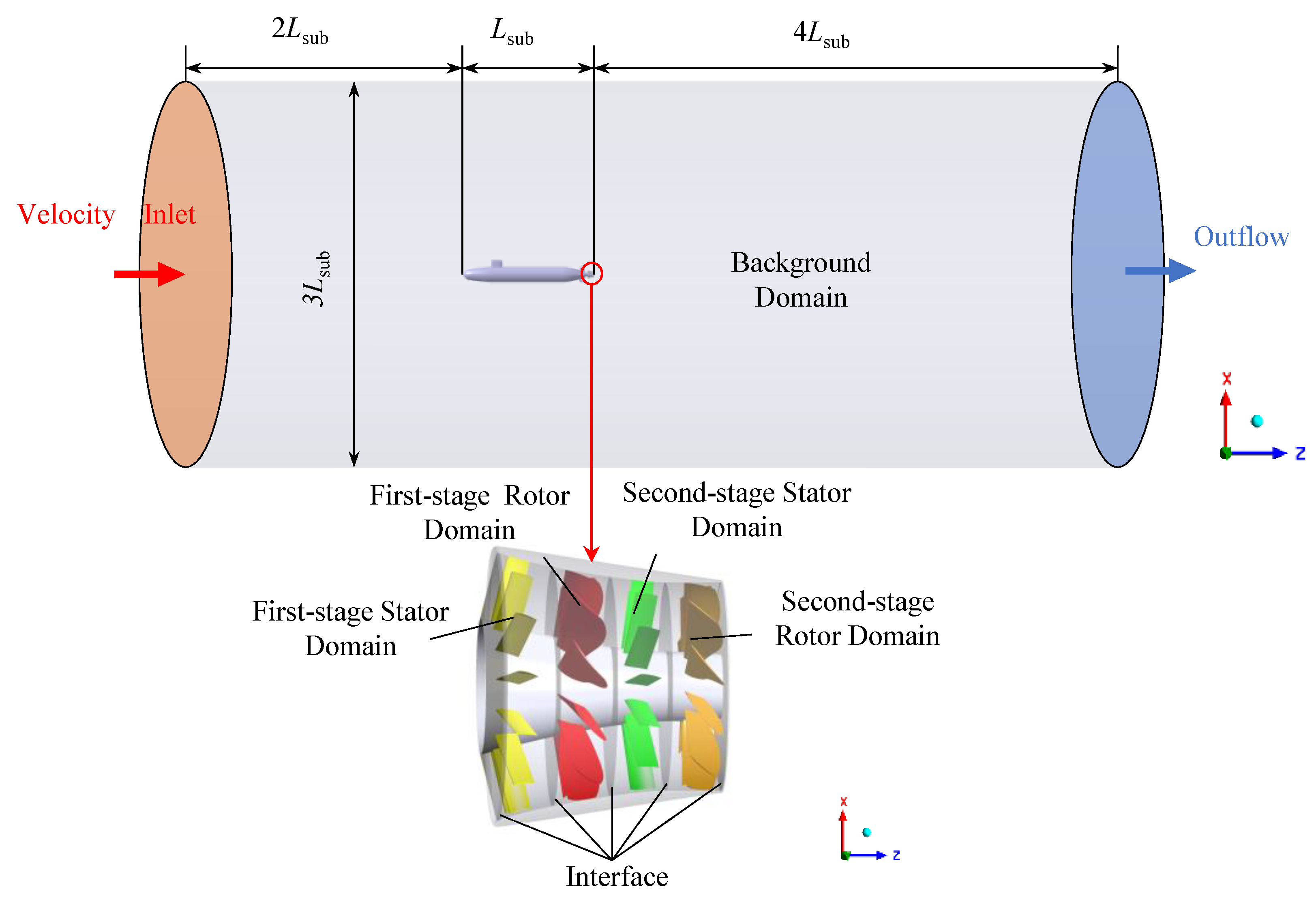
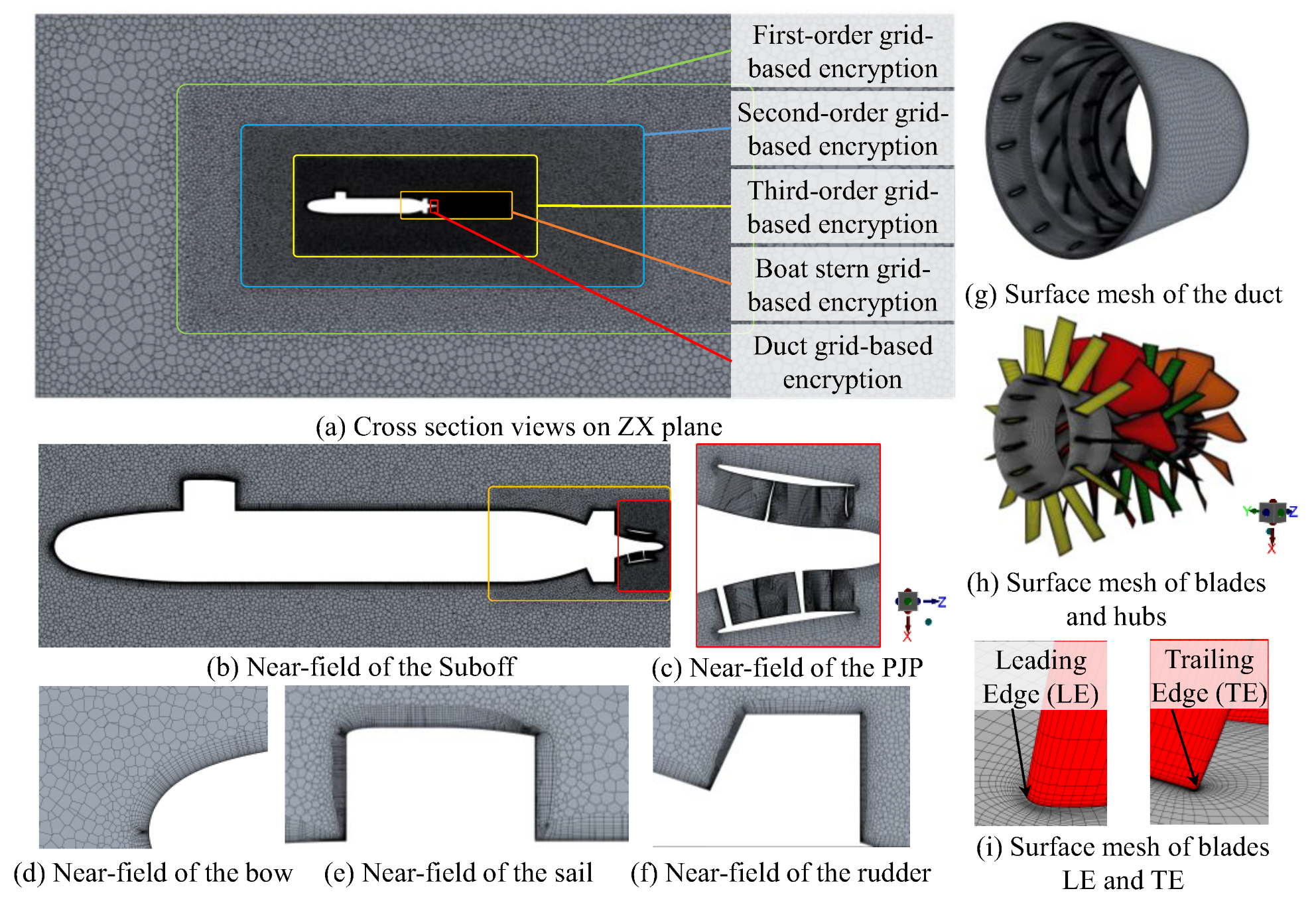
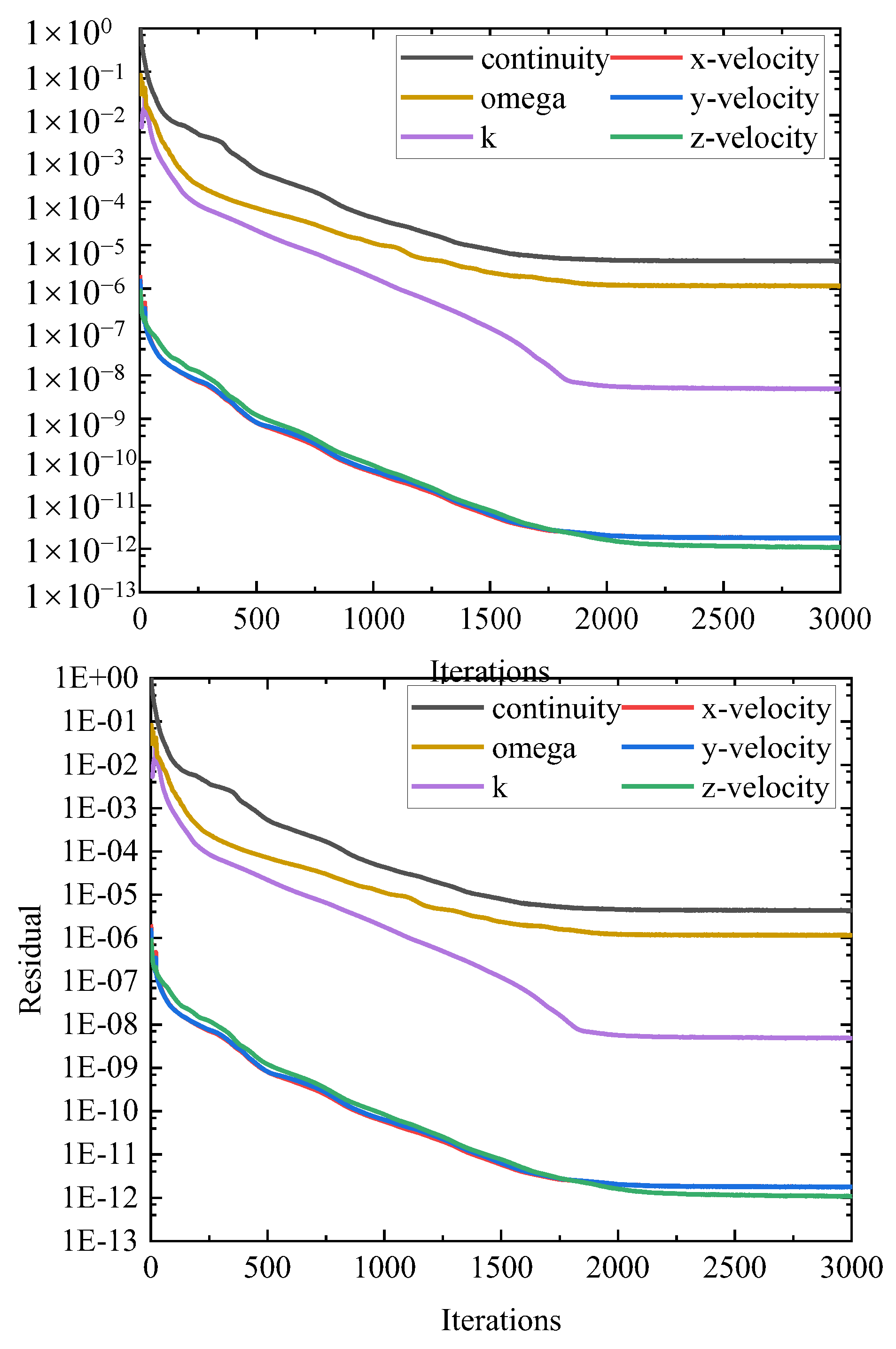
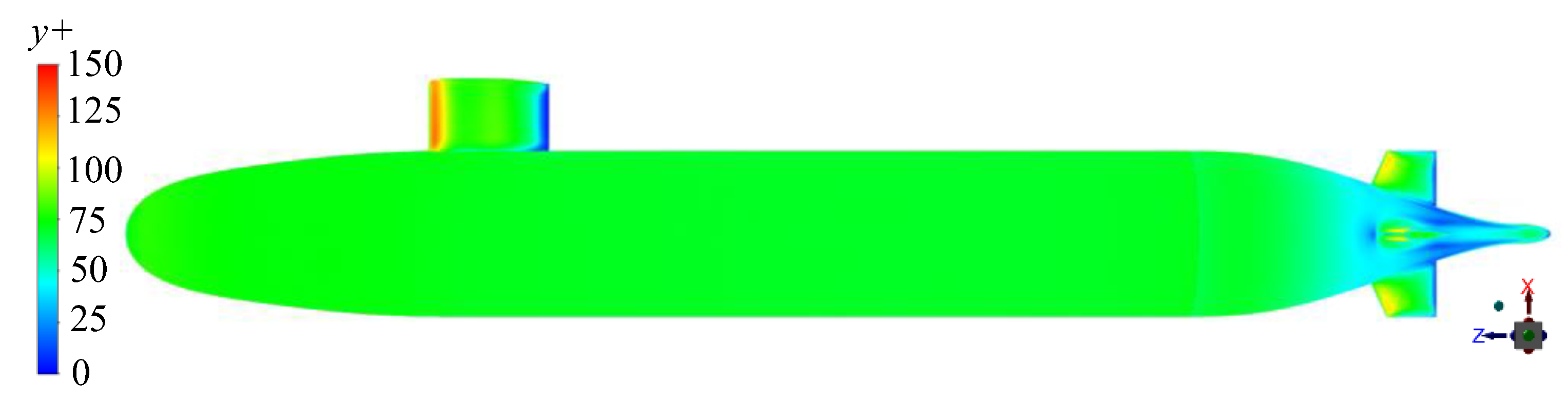
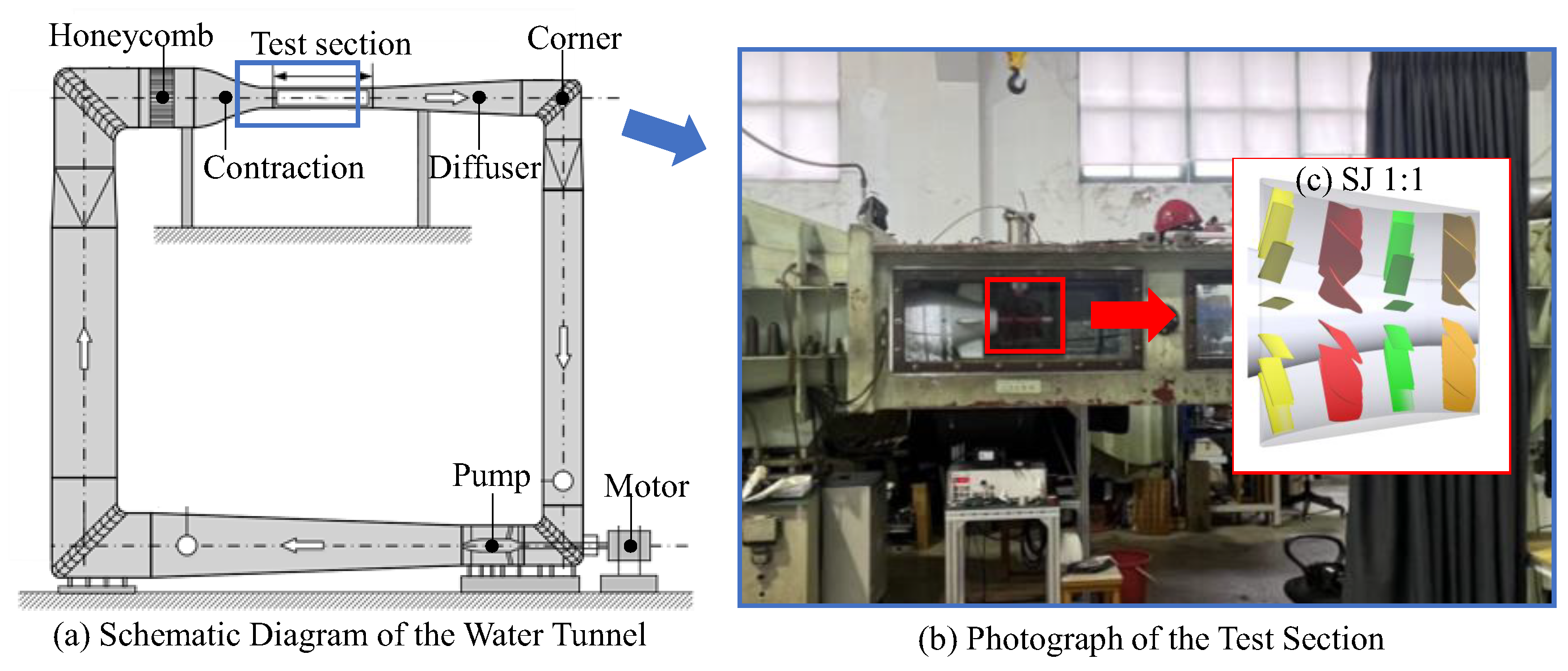
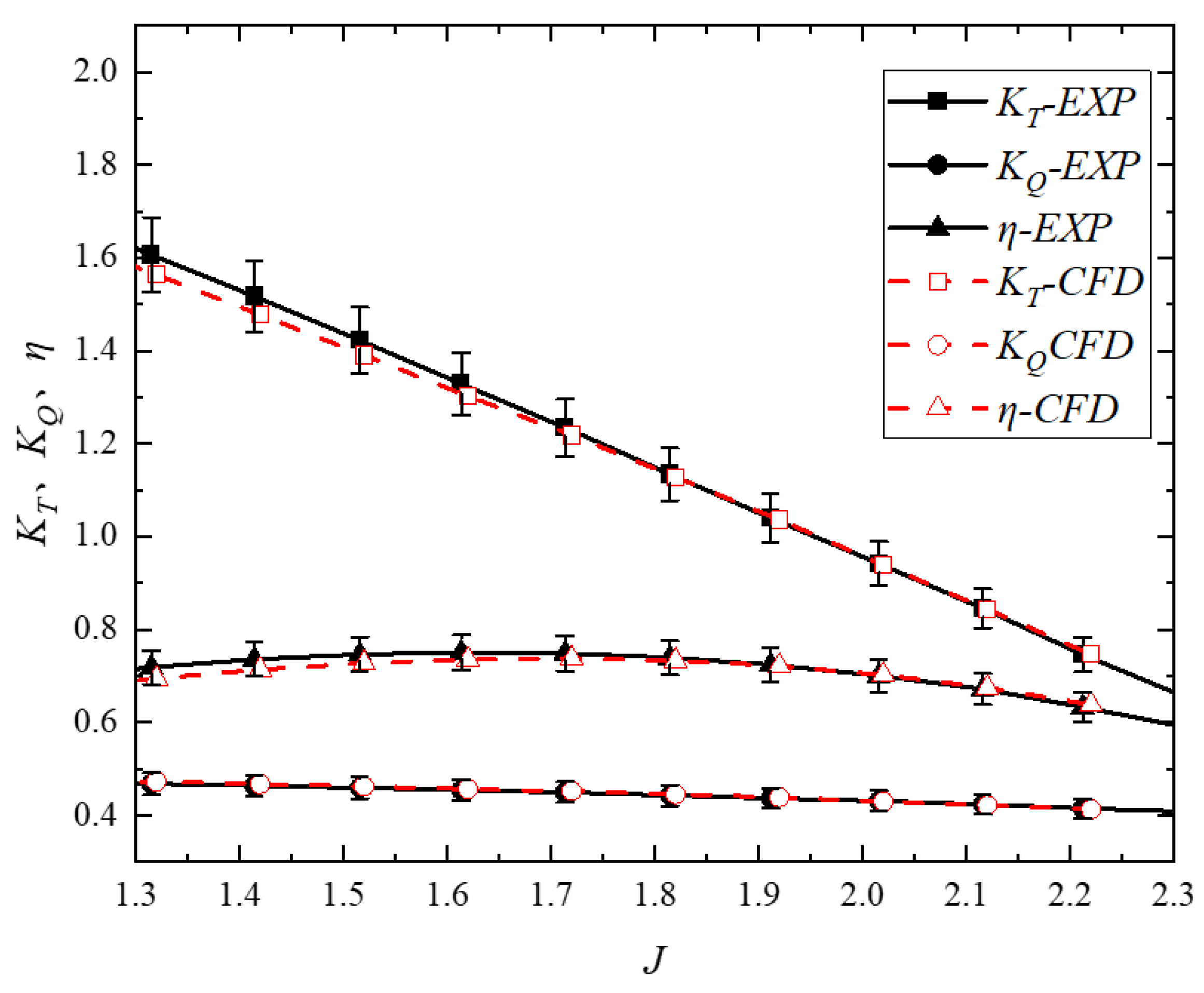
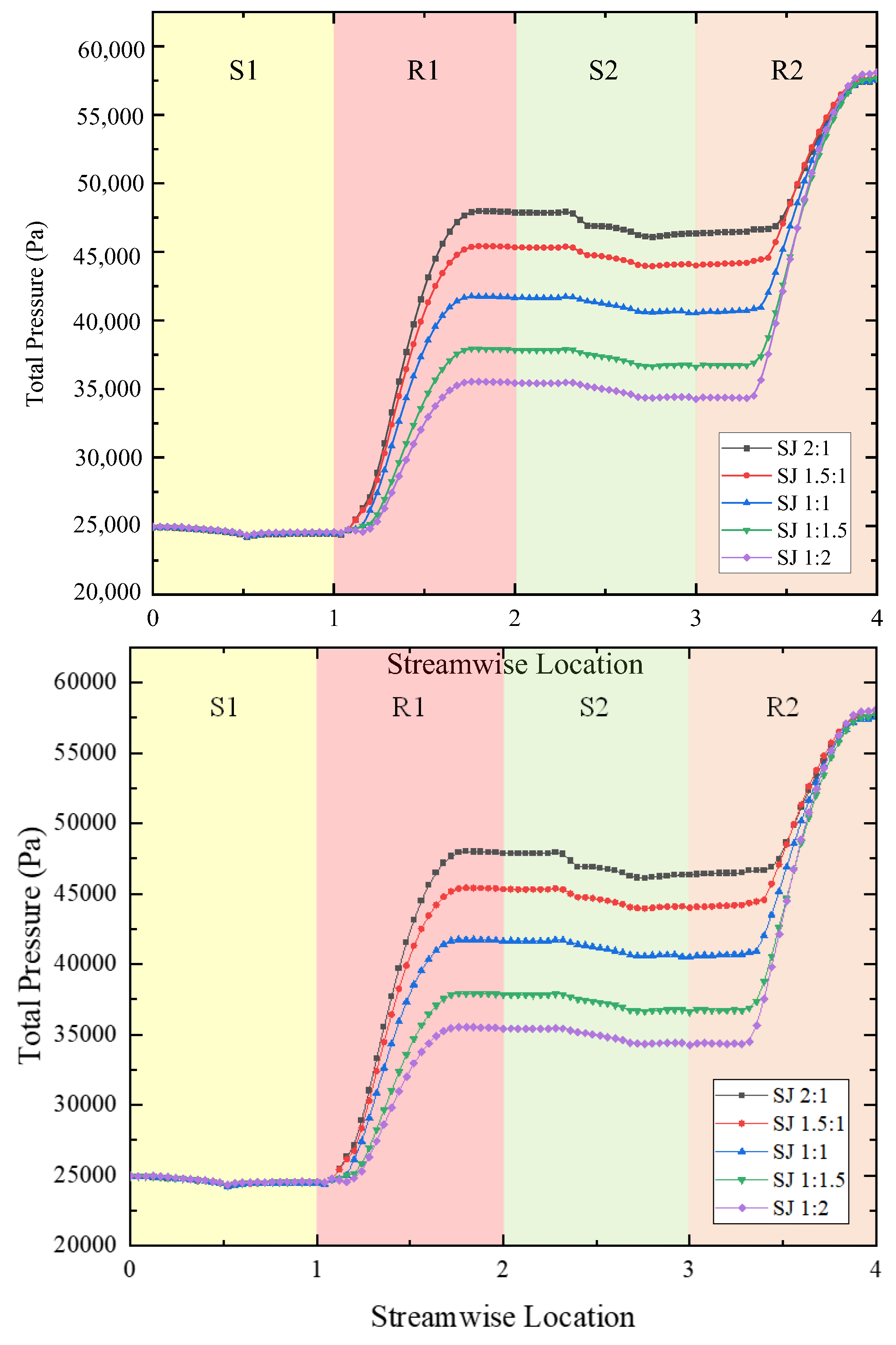
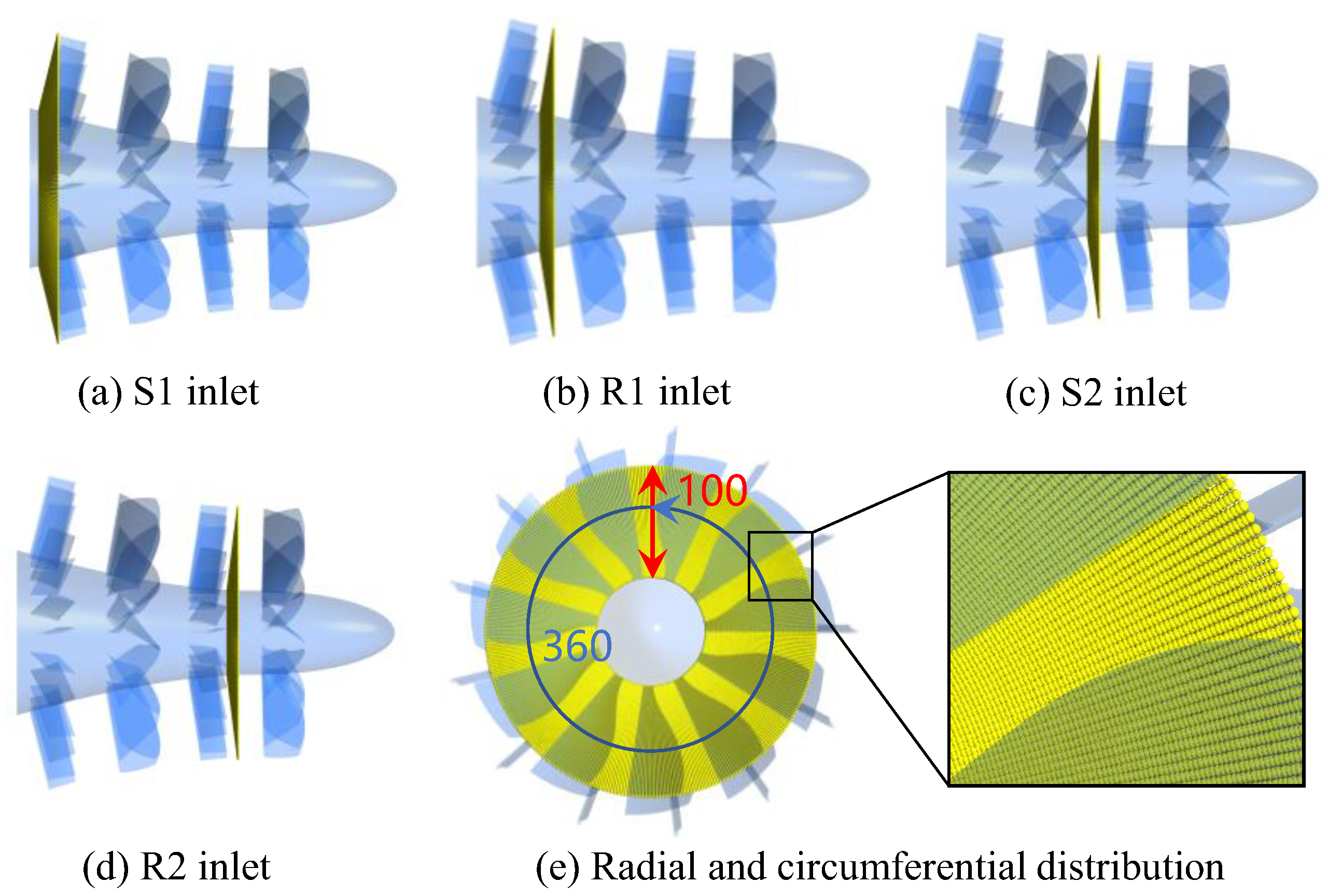


| Components | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Duct | Diameter (mm) | 232 |
| First-stage stator | Number of first-stage stator blades, NS1 (/) | 13 |
| First-stage rotor | Number of first-stage rotor blades, NR1 (/) | 11 |
| Hub-to-diameter ratio (/) | 0.42 | |
| Tip clearance (mm) | 0.5 | |
| Direction of rotation | Counterclockwise | |
| Second-stage stator | Number of second-stage stator blades, NS2 (/) | 13 |
| Second-stage rotor | Number of second-stage rotor blades, NR2 (/) | 11 |
| Hub-to-diameter ratio (/) | 0.33 | |
| Tip clearance (mm) | 0.5 | |
| Direction of rotation | Counterclockwise |
| Components (deg) | SJ 2:1 | SJ 1.5:1 | SJ 1:1 | SJ 1:1.5 | SJ 1:2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-stage stator | 68.00 | 68.00 | 68.00 | 68.00 | 68.00 |
| First-stage rotor | 45.37 | 43.37 | 41.72 | 40.98 | 40.59 |
| Second-stage stator | 72.00 | 72.00 | 72.00 | 72.00 | 72.00 |
| Second-stage rotor | 42.50 | 43.25 | 44.61 | 45.01 | 46.25 |
| Number of Mesh Cells (Million) | Drag (N) | Deviation (/) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh 1 | 4.33 | 841.04 | 0.61% |
| Mesh 2 | 7.45 | 842.53 | 0.44% |
| Mesh 3 | 13.19 | 842.94 | 0.39% |
| Rotor Rotation Angle(deg) | fz,fb-R1 (N)/Fluctuation Range (/) | fz,2fb-R1 (N)/Fluctuation Range (/) | fz,fb-R2 (N)/Fluctuation Range (/) | fz,2fb-R2 (N)/Fluctuation Range (/) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0.101/19% | 0.386/23% | 0.029/40% | 0.048/74% |
| 1 | 0.082/36% | 0.503/10% | 0.048/39% | 0.187/38% |
| 0.5 | 0.128/- | 0.561/- | 0.079/- | 0.304/- |
| SJ 2:1 | SJ 1.5:1 | SJ 1:1 | SJ 1:1.5 | SJ 1:2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head (m) | 3.35 | 3.38 | 3.36 | 3.40 | 3.45 |
| Propulsive efficiency (/) | 80.14% | 80.76% | 80.84% | 80.50% | 79.91% |
| First-stage rotor torque (Nm) | 48.84 | 43.96 | 36.71 | 29.19 | 24.69 |
| Second-stage rotor torque (Nm) | 24.70 | 29.65 | 35.96 | 44.17 | 49.92 |
| First-stage rotor thrust (N) | 636.47 | 575.85 | 486.30 | 369.16 | 307.24 |
| Second-stage rotor thrust (N) | 301.27 | 364.83 | 443.66 | 567.29 | 633.57 |
| First-stage rotor head (m) | 2.47 | 2.20 | 1.80 | 1.39 | 1.14 |
| Second-stage rotor head (m) | 1.13 | 1.40 | 1.75 | 2.20 | 2.50 |
| Torque ratio (/) | 1.98 | 1.48 | 1.02 | 0.66 | 0.49 |
| Thrust ratio (/) | 2.11 | 1.58 | 1.10 | 0.65 | 0.48 |
| Head ratio (/) | 2.20 | 1.57 | 1.03 | 0.64 | 0.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Liang, N.; Zhang, J.; Cao, L.; Wu, D.; Zhao, W.; Han, H. Studying the Impact of the Load Distribution Ratio on the Unsteady Performance of a Dual-Stage Pump-Jet Propulsor. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040726
Zhang J, Liang N, Zhang J, Cao L, Wu D, Zhao W, Han H. Studying the Impact of the Load Distribution Ratio on the Unsteady Performance of a Dual-Stage Pump-Jet Propulsor. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040726
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jiansheng, Ning Liang, Jianwei Zhang, Linlin Cao, Dazhuan Wu, Wei Zhao, and Hanqiao Han. 2025. "Studying the Impact of the Load Distribution Ratio on the Unsteady Performance of a Dual-Stage Pump-Jet Propulsor" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040726
APA StyleZhang, J., Liang, N., Zhang, J., Cao, L., Wu, D., Zhao, W., & Han, H. (2025). Studying the Impact of the Load Distribution Ratio on the Unsteady Performance of a Dual-Stage Pump-Jet Propulsor. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040726






