Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Ballast Water Treatment System Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Description and Methodology
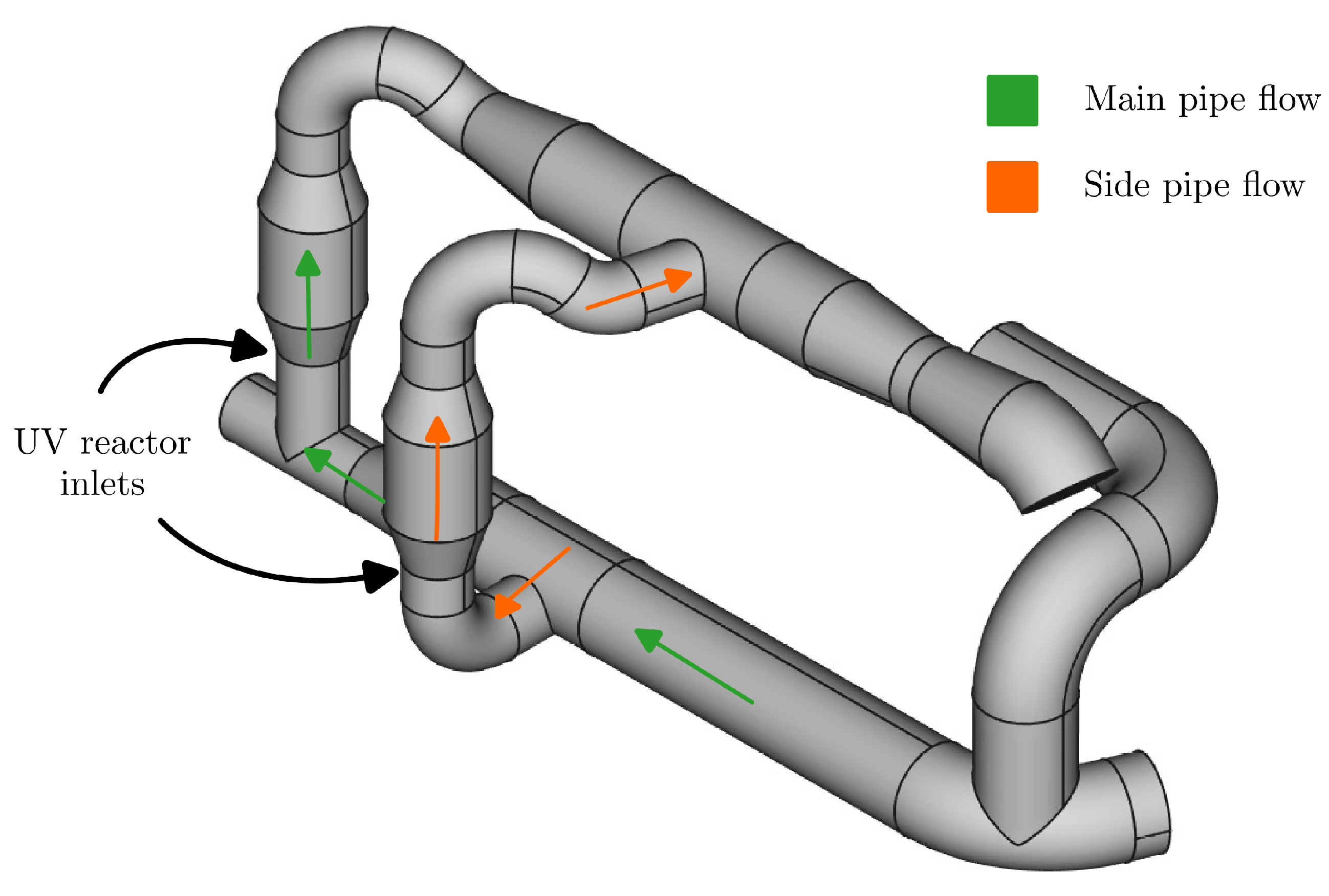
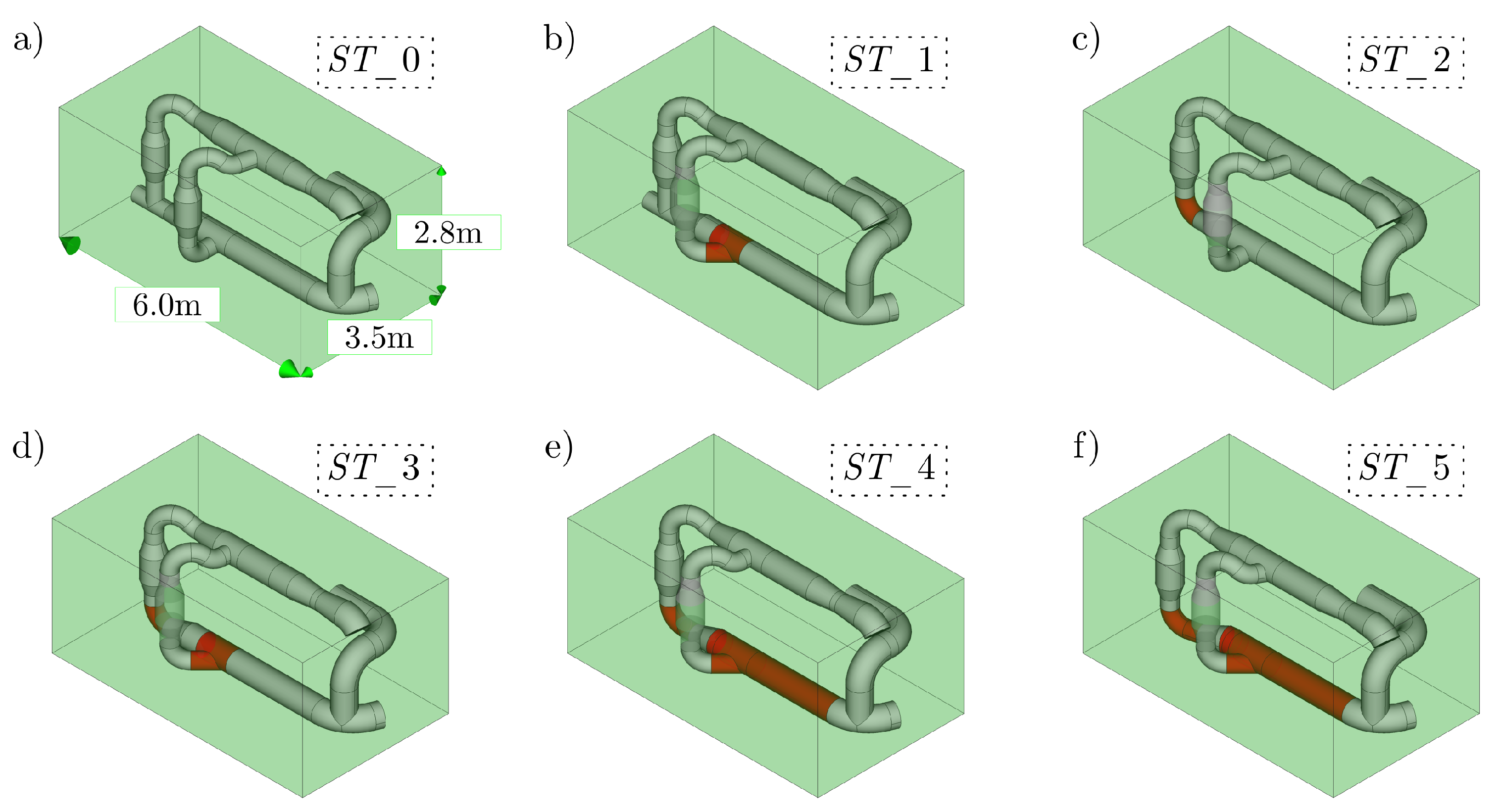
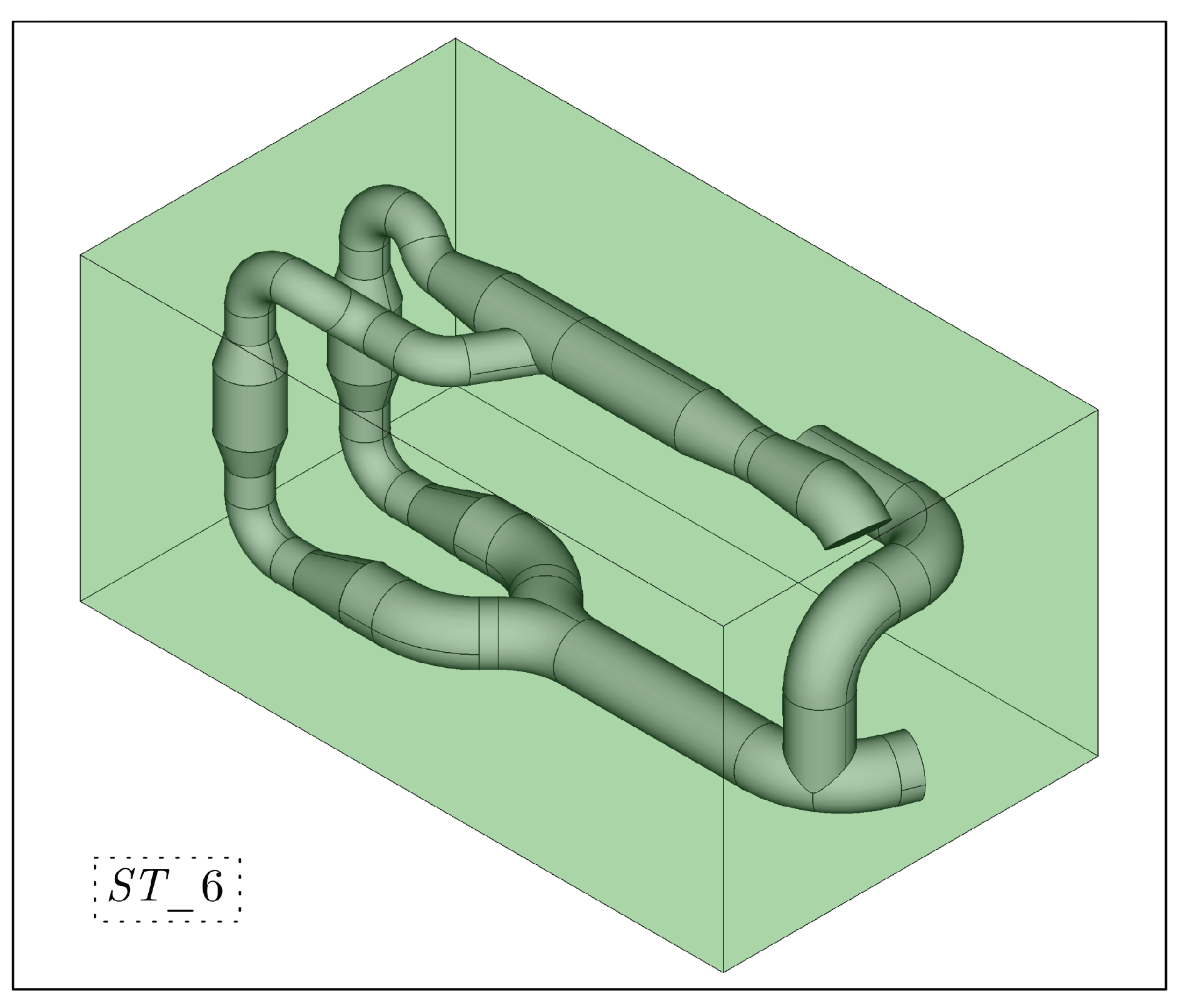
2.1. Ballast Water Treatment System (BWTS) Layout
- Opposing flow directions in the inlet and outlet manifolds connected to the UV reactors.
- Extending the CFD domain from the filter outlet to at least three pipe diameters downstream of the last UV reactor.
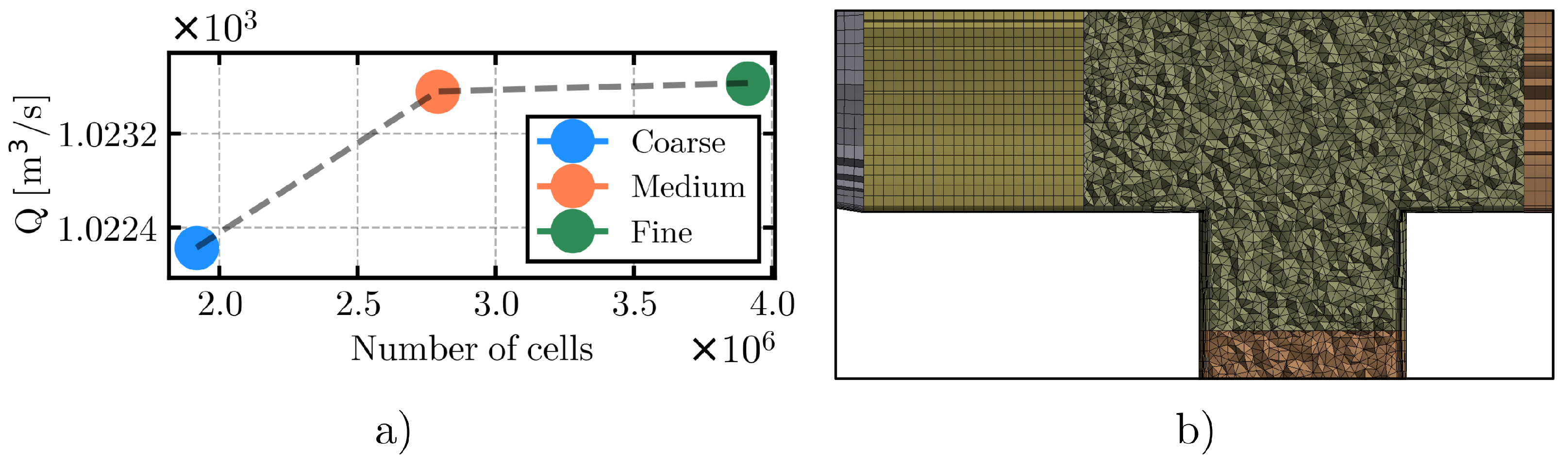
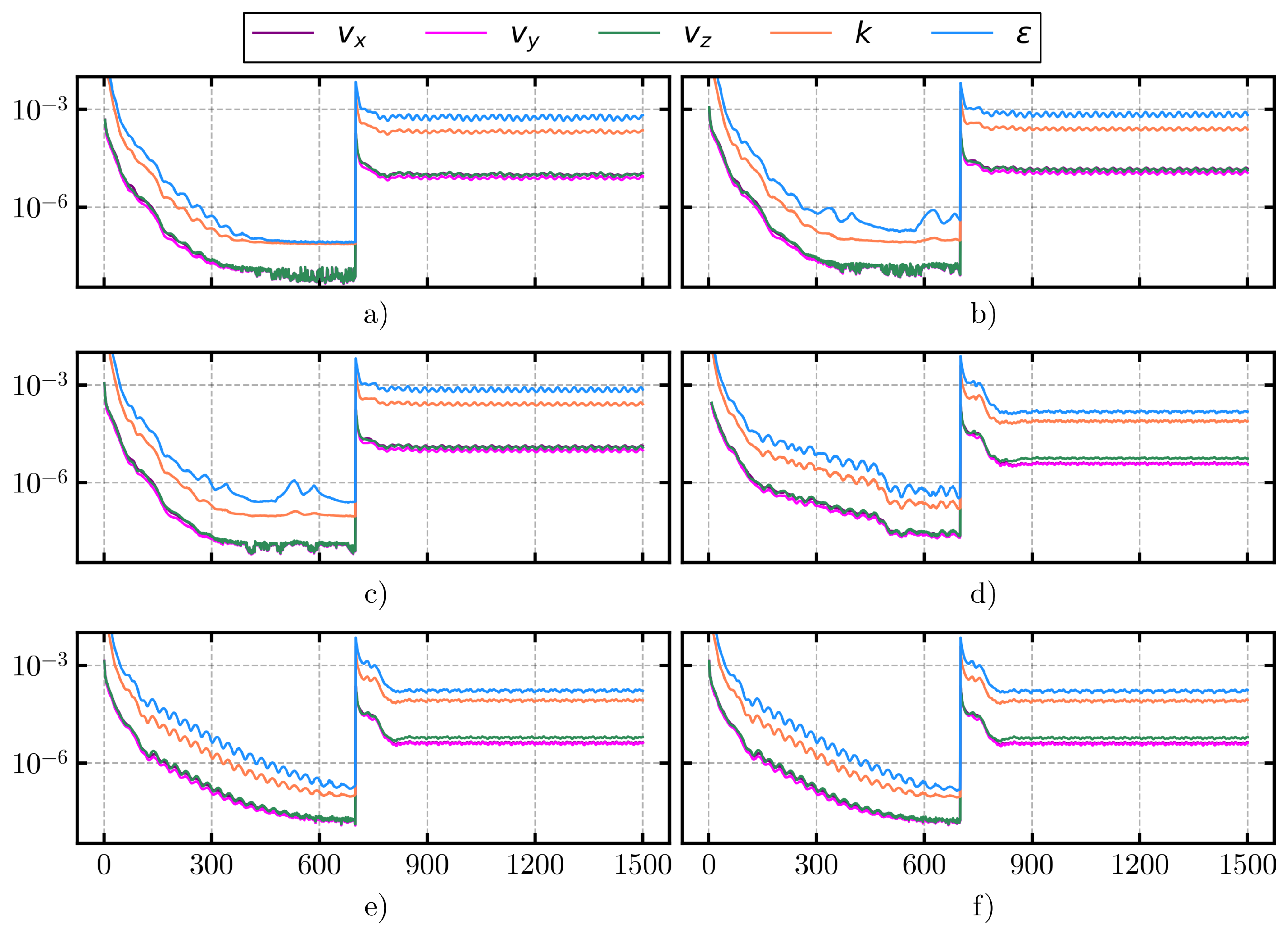
2.2. Numerical Model
- Density: .
- Kinematic viscosity: .
- Dynamic viscosity: .
3. Results and Discussion
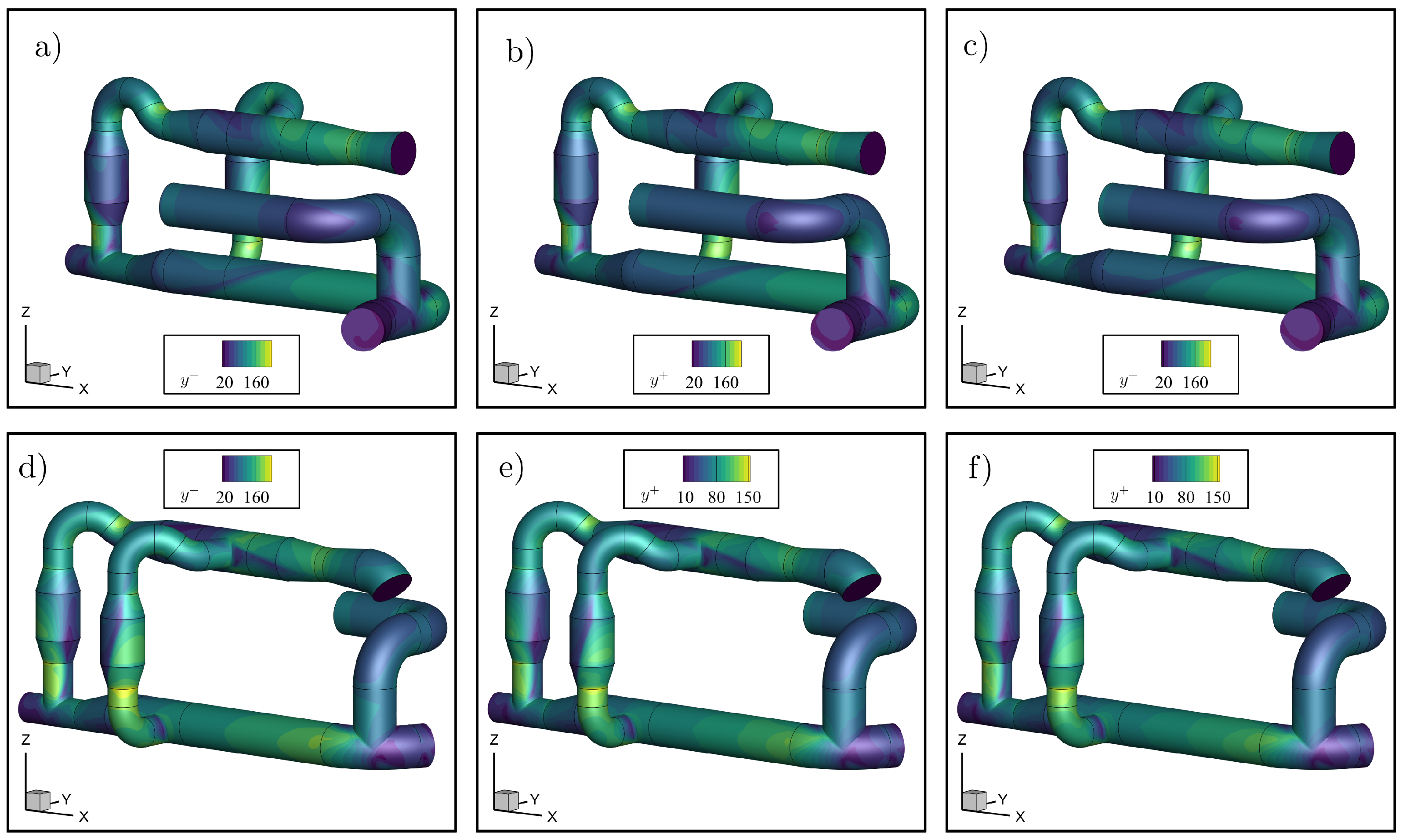
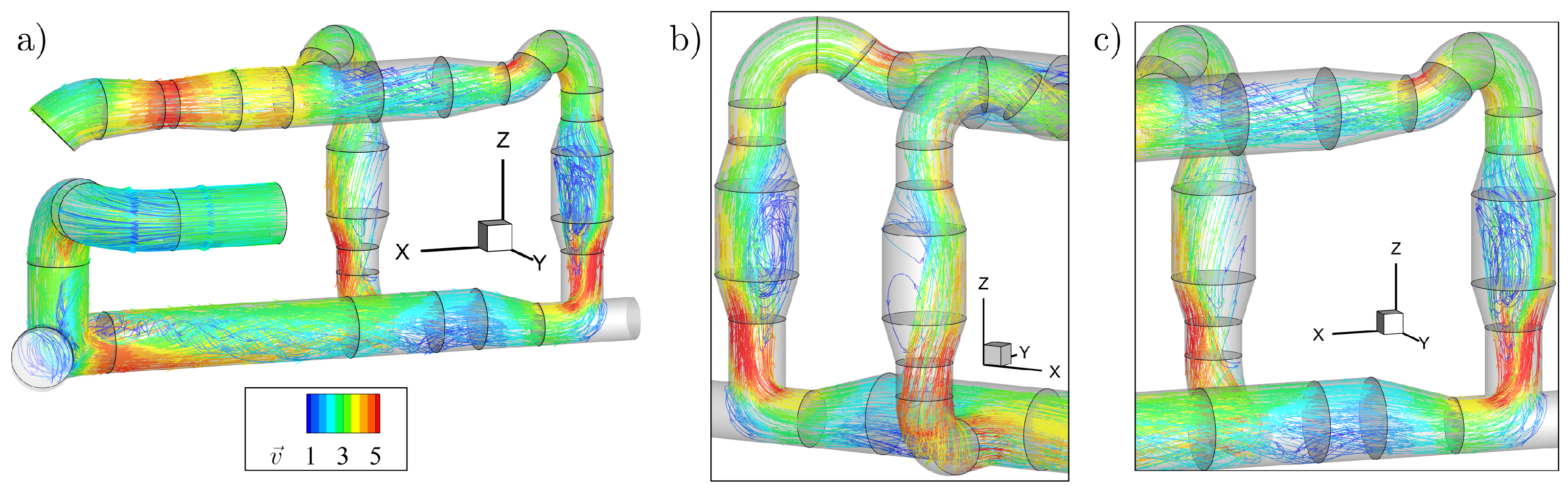
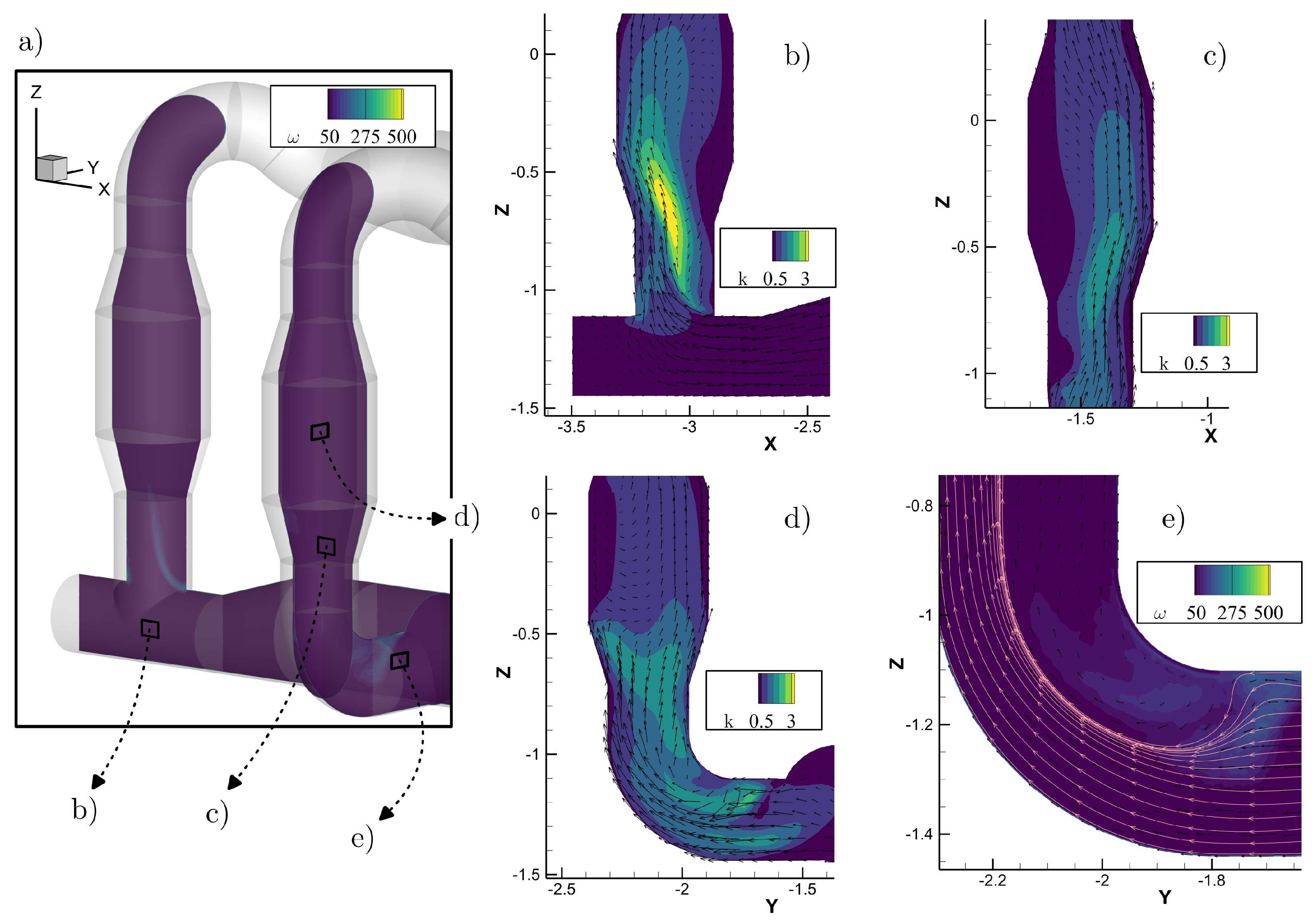
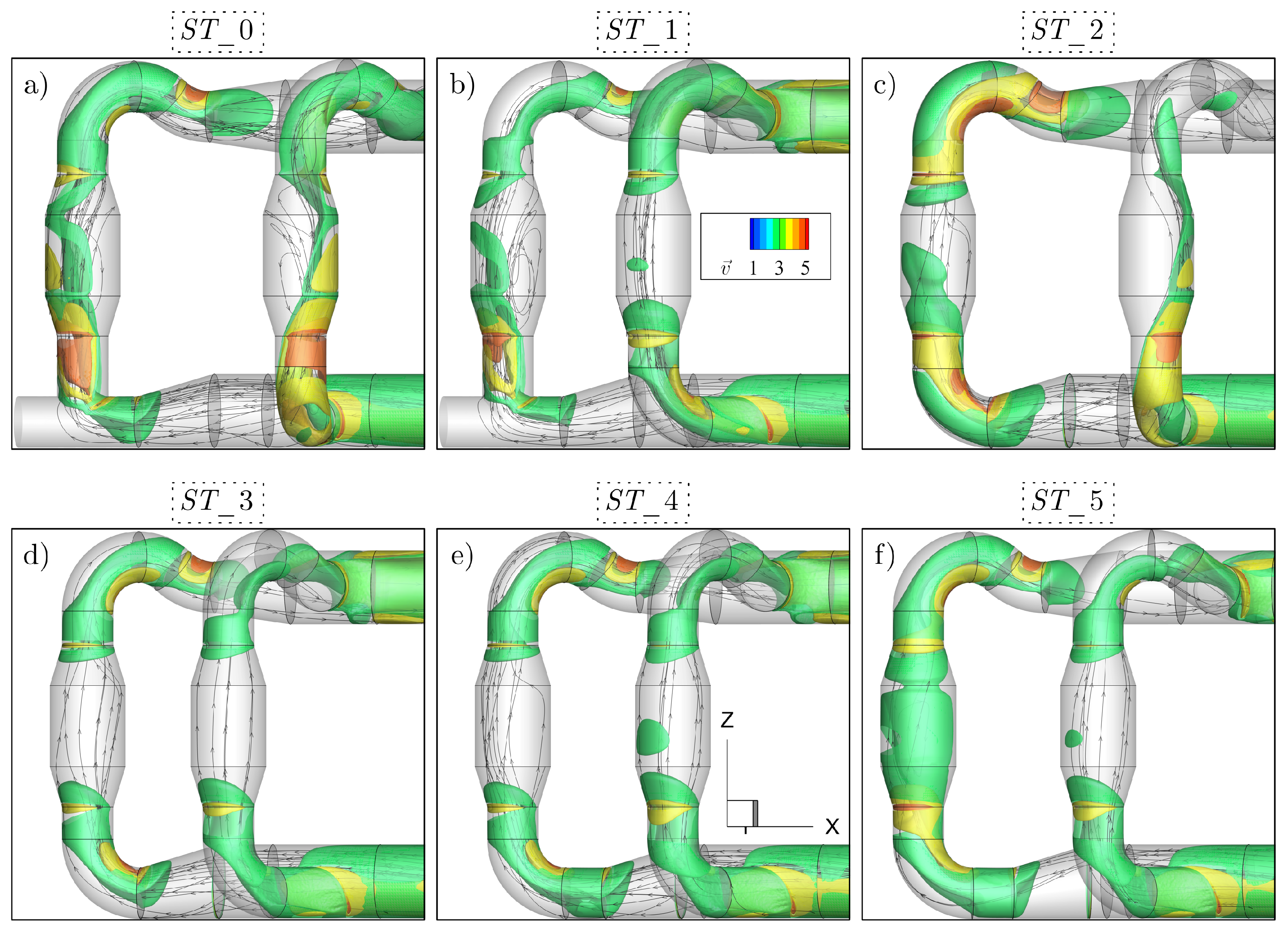
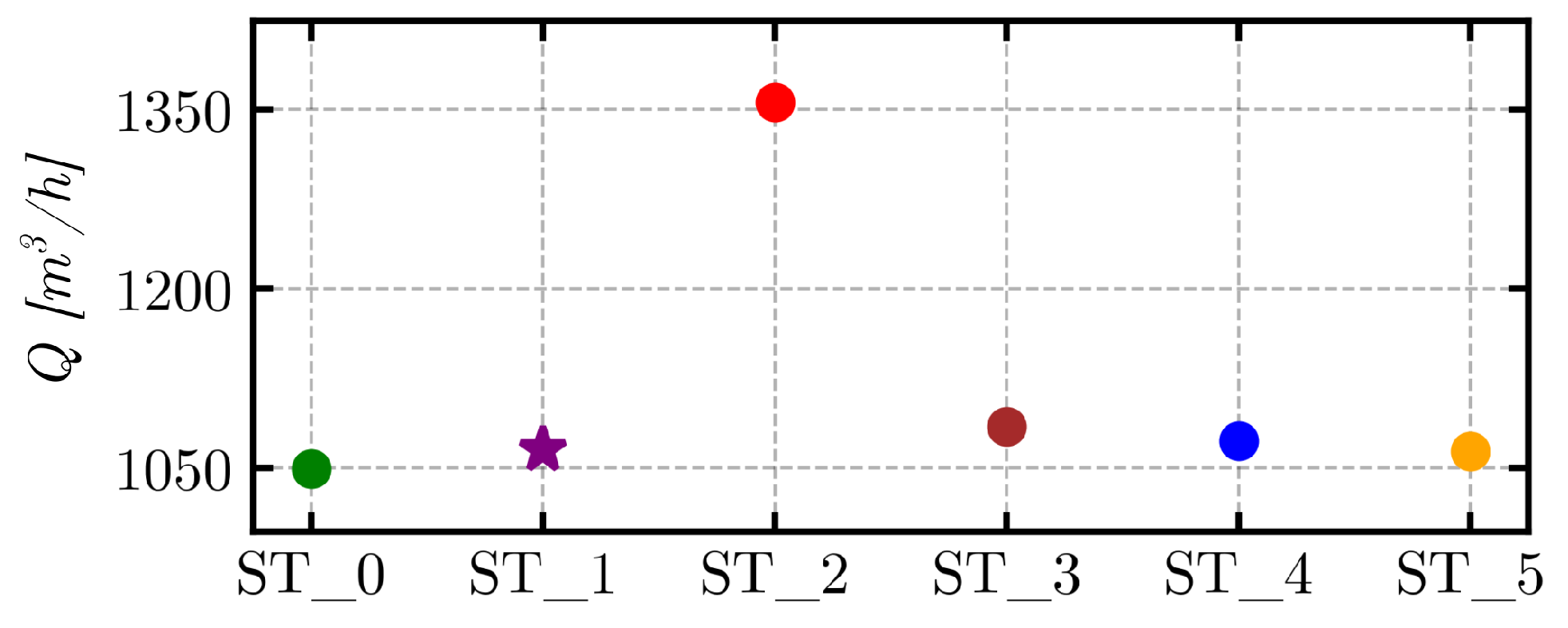
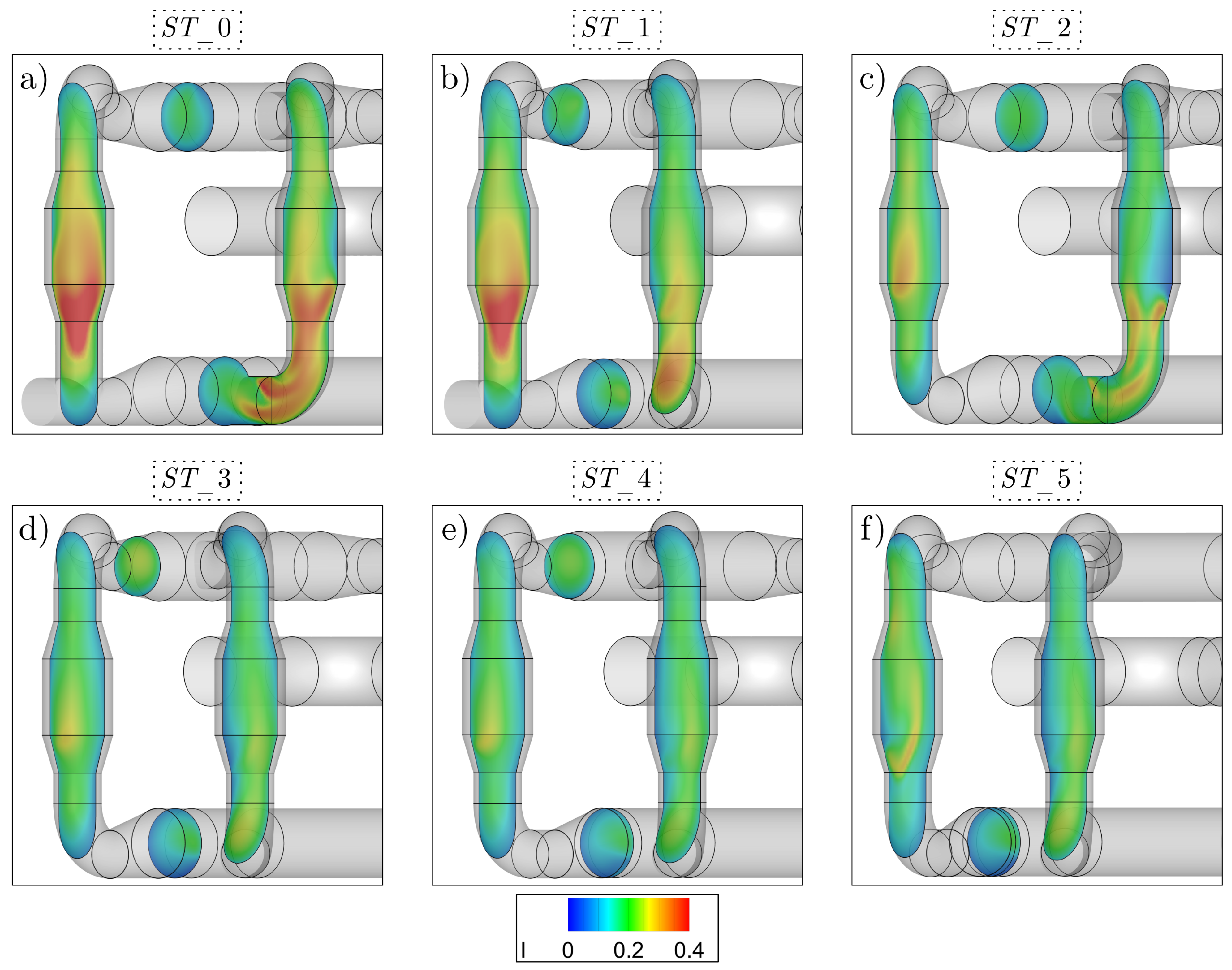
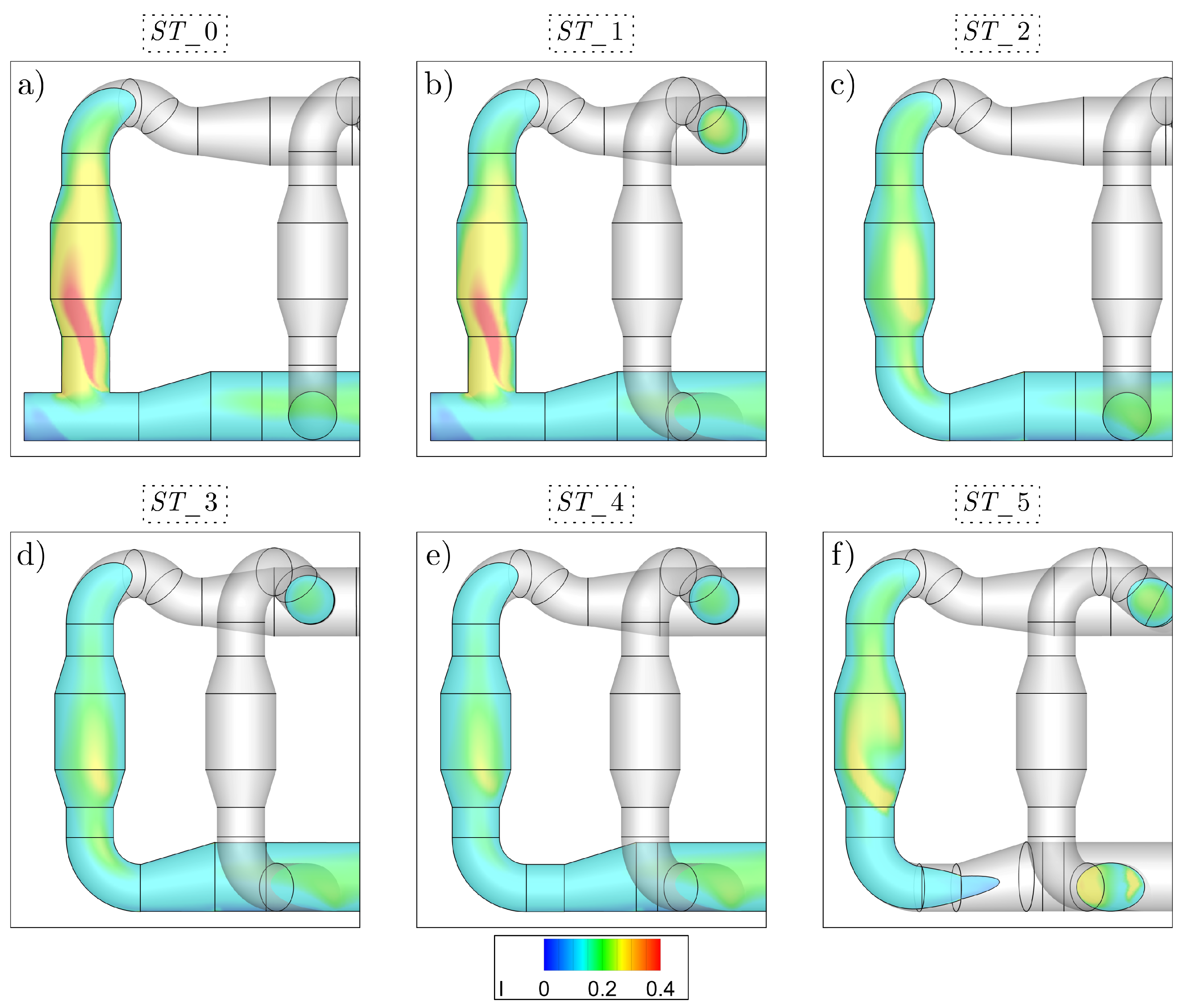
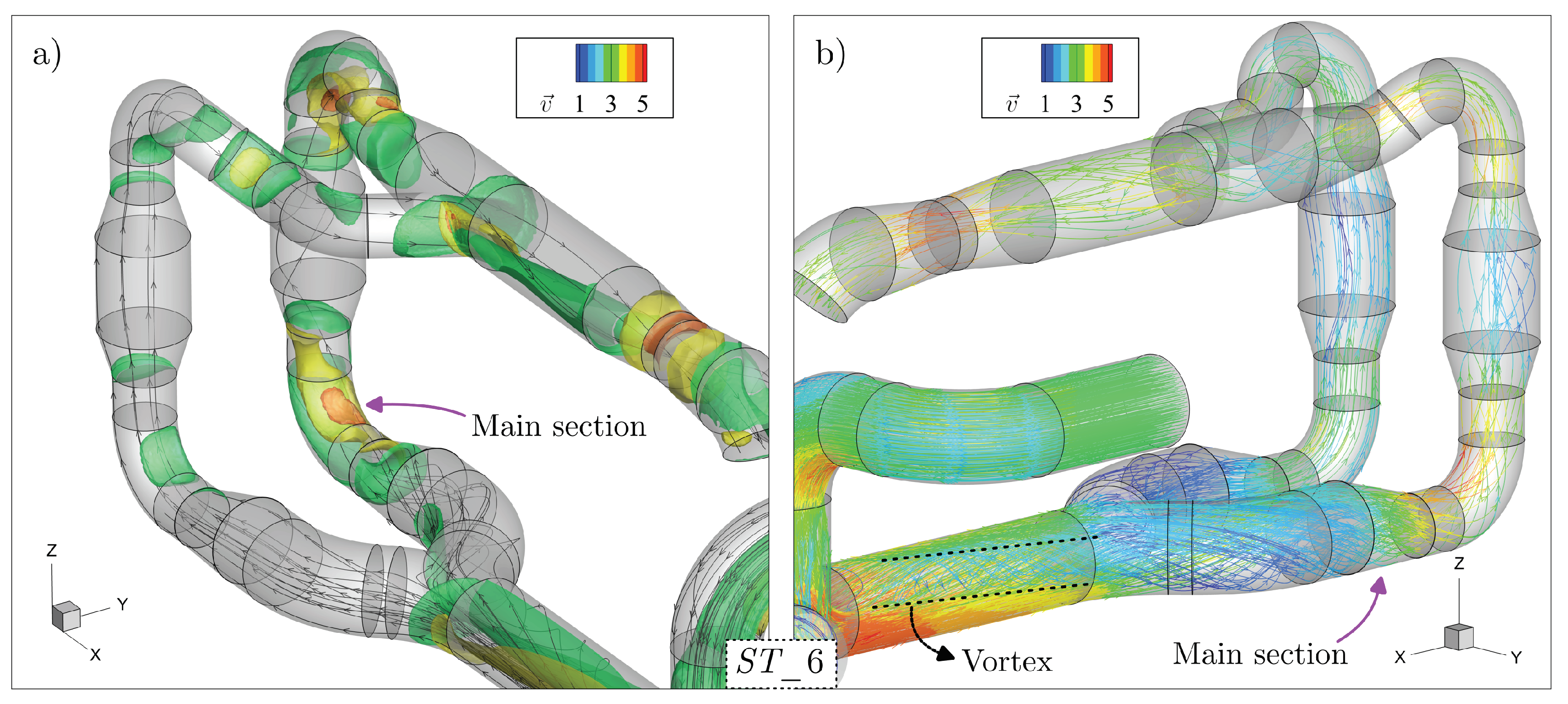
3.1. Pipeline Analysis in Newbuilding Engine Room
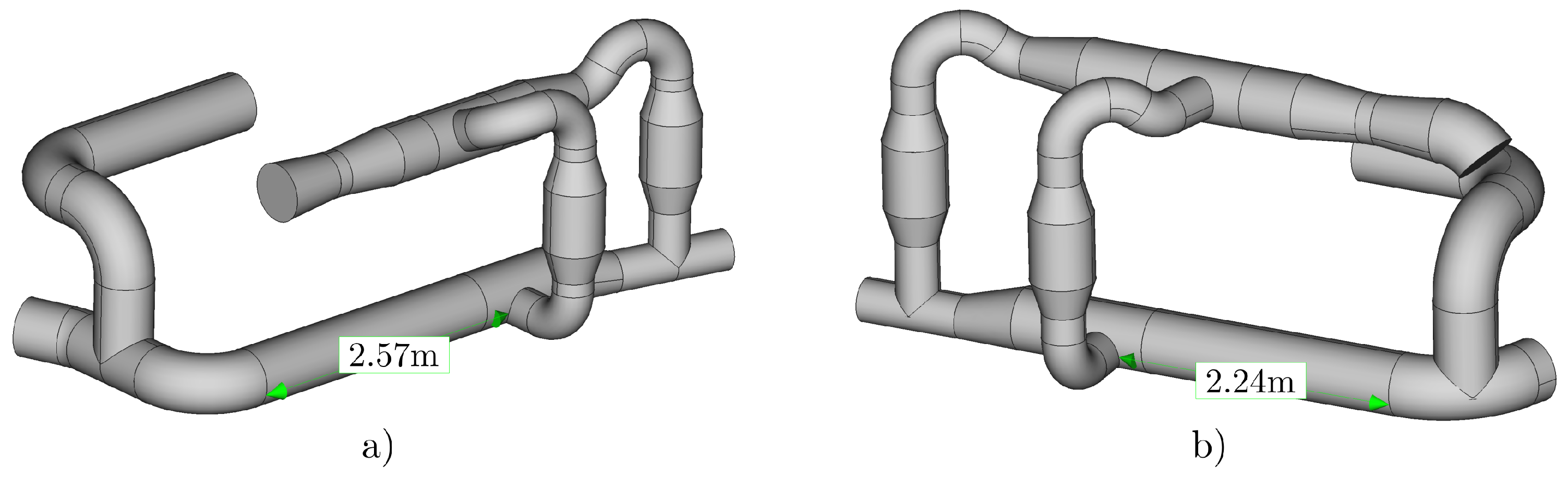
3.2. Analysis of Possible Pipeline Geometry Changes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
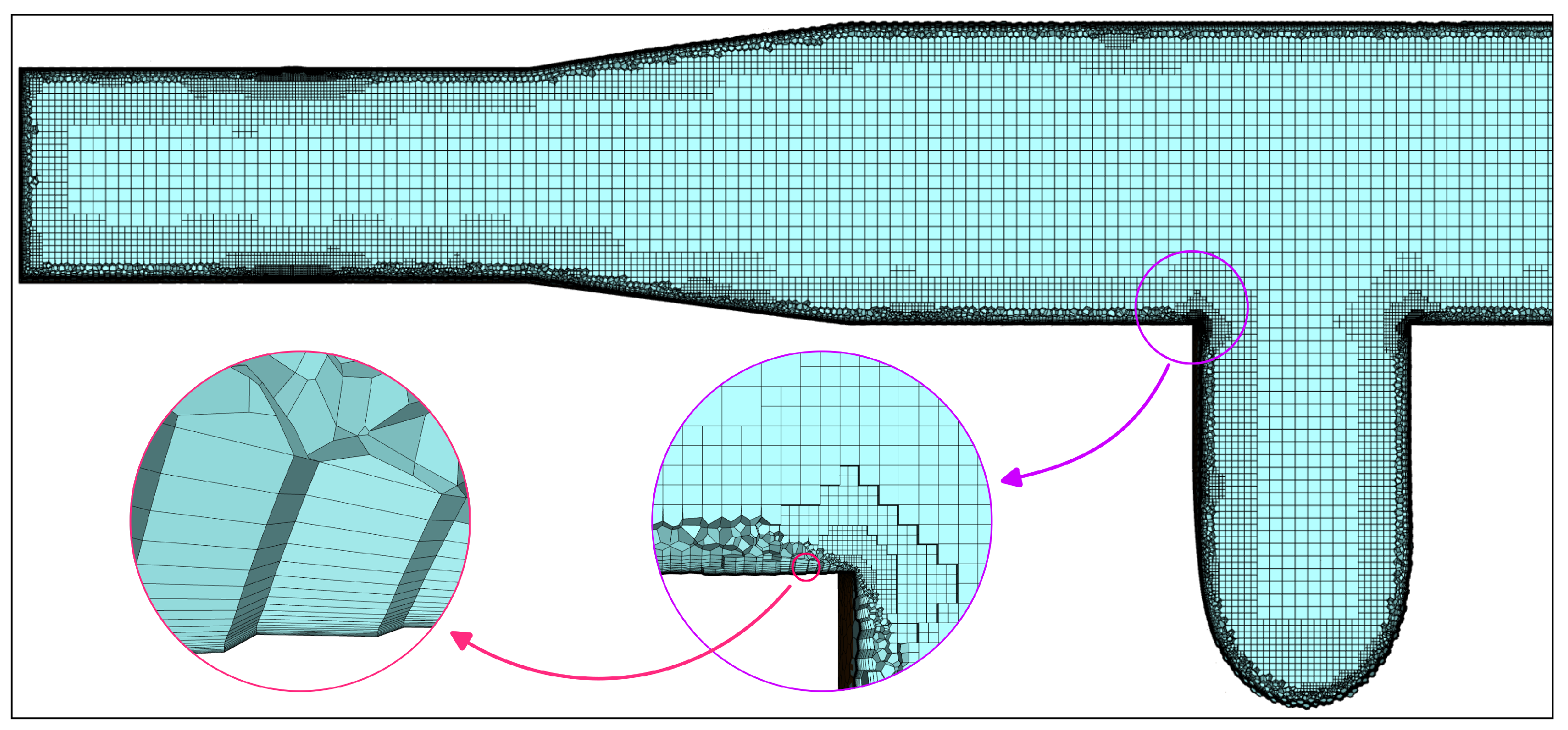
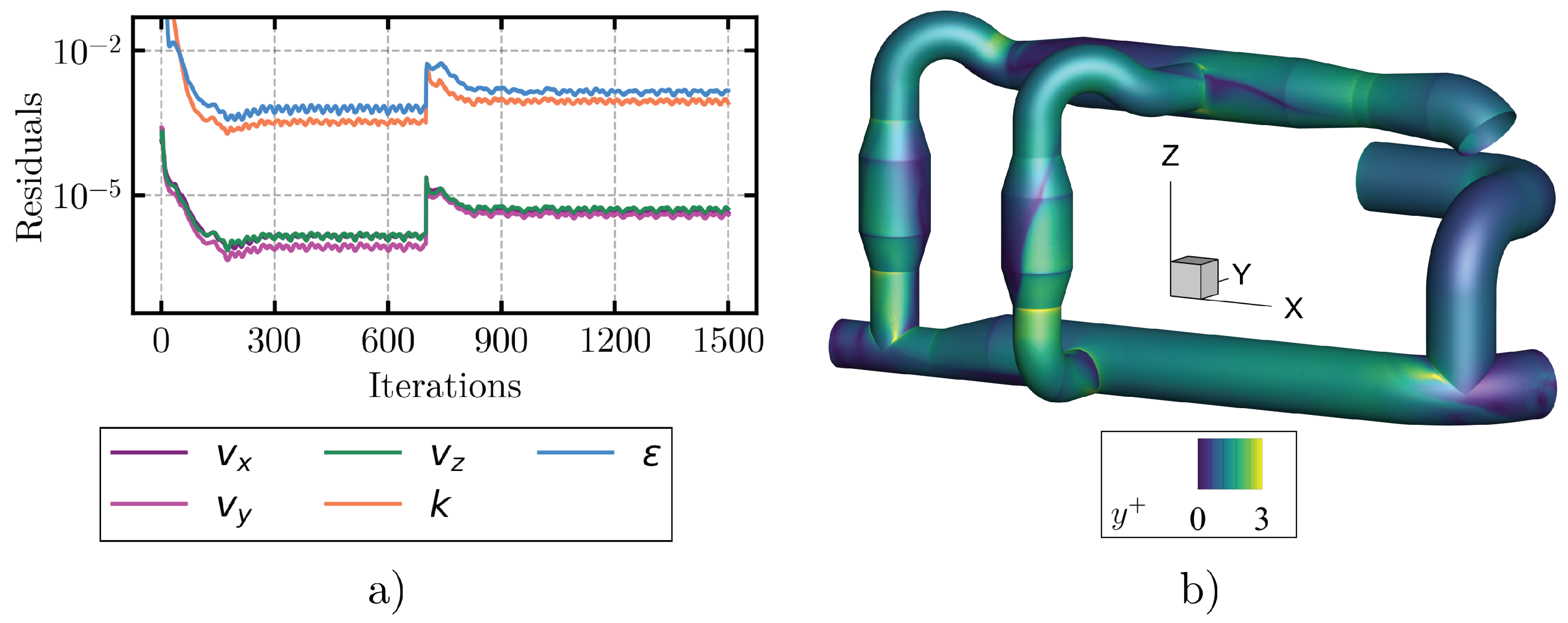

References
- Rebeca, G. Review of Maritime Transport; United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- EMSA—European Maritime Safety Agency. Ballast Water Management—Guidance for Best Practices on Sampling; EMSA—European Maritime Safety Agency: Lisboa, Portugal, 2019.
- Chan, F.T.; Macisaac, H.J.; Bailey, S.A. Relative importance of vessel hull fouling and ballast water as transport vectors of nonindigenous species to the canadian arctic. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 1230–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, A.D.; Dodgshun, T.J. The nature and extent of organisms in vessel sea-chests: A protected mechanism for marine bioinvasions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 54, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argüello, G.; Krabbe, N.; Langlet, D.; Hassellöv, I.M.; Martinson, C.; Helmstad, A. Regulation of ships at anchor: Safety and environmental implications. Mar. Policy 2022, 140, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.J.; Ribó, M.; Seabrook, S.; Strachan, L.J.; Hale, R.; Lamarche, G. The footprint of ship anchoring on the seafloor. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchin, D. Aquaculture and transport in a changing environment: Overlap and links in the spread of alien biota. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, J.L.; Gamboa, R.L.; Revenga, C.; Spalding, M.D. Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Basnou, C.; Pyšek, P.; Josefsson, M.; Genovesi, P.; Gollasch, S.; Nentwig, W.; Olenin, S.; Roques, A.; Roy, D.; et al. How well do we understand the impacts of alien species on ecosystem services? A pan-European, cross-taxa assessment. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.; Gollasch, S.; Pavliha, M. Global ballast water management and the “same location” concept: A clear term or a clear issue? Ecol. Appl. 2013, 23, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L. Alien species in fresh waters: Ecological effects, interactions with other stressors, and prospects for the future. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 152–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.T.; Hong, J.H.; Tayyab, M.; Kim, D.W.; Jeon, P.R.; Lee, C.H. Continuous bubble reactor using carbon dioxide and its mixtures for ballast water treatment. Water Res. 2019, 154, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, E.; Priya, M.; Achari, V.S. An overview on the treatment of ballast water in ships. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 199, 105296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drillet, G.; Gianoli, C.; Gang, L.; Zacharopoulou, A.; Schneider, G.; Stehouwer, P.; Bonamin, V.; Goldring, R.; Drake, L.A. Improvement in compliance of ships’ ballast water discharges during commissioning tests. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Maritime Organization. International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments; Convention BWM/CONF/36; International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization. Guidelines for Approval of Ballast Water Management Systems (G8); Resolution MEPC.174(58); International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- International Maritime Organization. Procedure for Approval of Ballast Water Management Systems That Make Use of Active Substances (G9); Resolution MEPC.169(57); International Maritime Organization: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Campara, L.; Francic, V.; Maglic, L.; Hasanspahic, N. Overview and Comparison of the IMO and the US Maritime Administration Ballast Water Management Regulations. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolaki, E.; Diamadopoulos, E. Technologies for ballast water treatment: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werschkun, B.; Sommer, Y.; Banerji, S. Disinfection by-products in ballast water treatment: An evaluation of regulatory data. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4884–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, R.; Yaakob, O.; Koh, K.K. A review of developments in ballast water management. Environ. Rev. 2014, 22, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werschkun, B.; Banerji, S.; Basurko, O.C.; David, M.; Fuhr, F.; Gollasch, S.; Grummt, T.; Haarich, M.; Jha, A.N.; Kacan, S.; et al. Emerging risks from ballast water treatment: The run-up to the International Ballast Water Management Convention. Chemosphere 2014, 112, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakalar, G. Comparisons of interdisciplinary ballast water treatment systems and operational experiences from ships. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorkapić, A.; Radonja, R.; Zec, D. Cost efficiency of ballast water treatment systems based on ultraviolet irradiation and electrochlorination. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2018, 30, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayinli, B.; Dong, Y.; Park, Y.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. Recent progress and challenges facing ballast water treatment—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehouwer, P.P.; Buma, A.; Peperzak, L. A comparison of six different ballast water treatment systems based on UV radiation, electrochlorination and chlorine dioxide. Environ. Technol. 2015, 36, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, N.B.; Madsen, T.; Glaring, M.A.; Dobbs, F.C.; Jørgensen, N.O. Ballast water treatment and bacteria: Analysis of bacterial activity and diversity after treatment of simulated ballast water by electrochlorination and UV exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pećarević, M.; Mikuš, J.; Prusina, I.; Juretić, H.; Cetinić, A.B.; Brailo, M. New role of hydrocyclone in ballast water treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgreen, K.; Holbech, H.; Pedersen, K.L.; Petersen, G.I.; Andreasen, R.R.; George, C.; Drillet, G.; Andersen, M. UV fluences required for compliance with ballast water discharge standards using two approved methods for algal viability assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Martínez, L.; van Slooten, C.; van Harten, M.; Nebot, E.; Peperzak, L. Comparative assessment of four ballast water compliance monitoring devices with natural UV-treated water using IMO’s monitoring approaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thach, N.D.; Hung, P.V. Development of UV reactor controller in ballast water treatment system to minimize the biological threat on marine environment. J. Sea Res. 2024, 198, 102465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Jung, G.; Oh, I.; Rhee, T. Validation test on real scale uv reactor for ballast water treatment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 190455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Hu, K.; Shan, B. Ballast water treatment using UV/TiO2 advanced oxidation processes: An approach to invasive species prevention. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 243, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
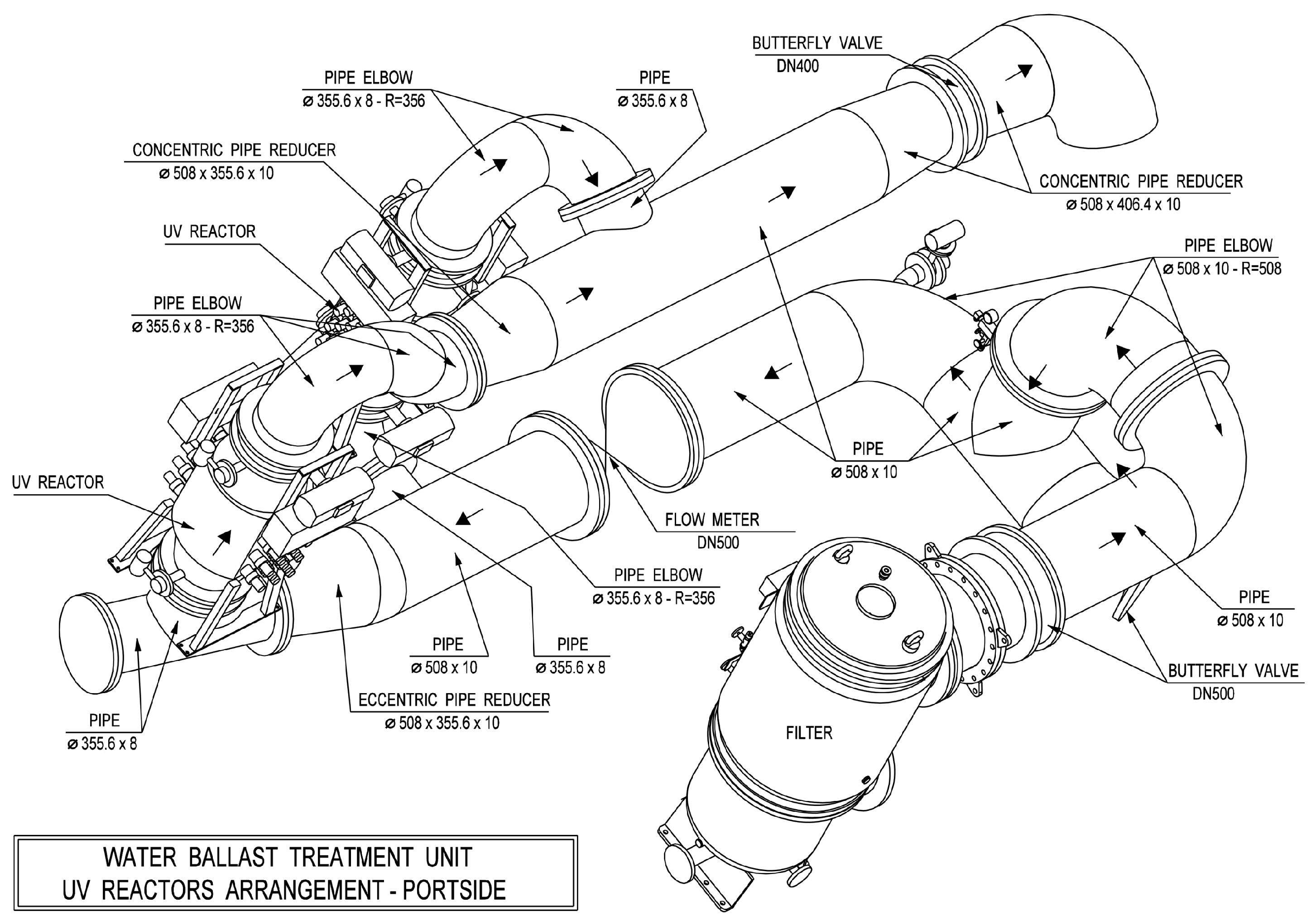
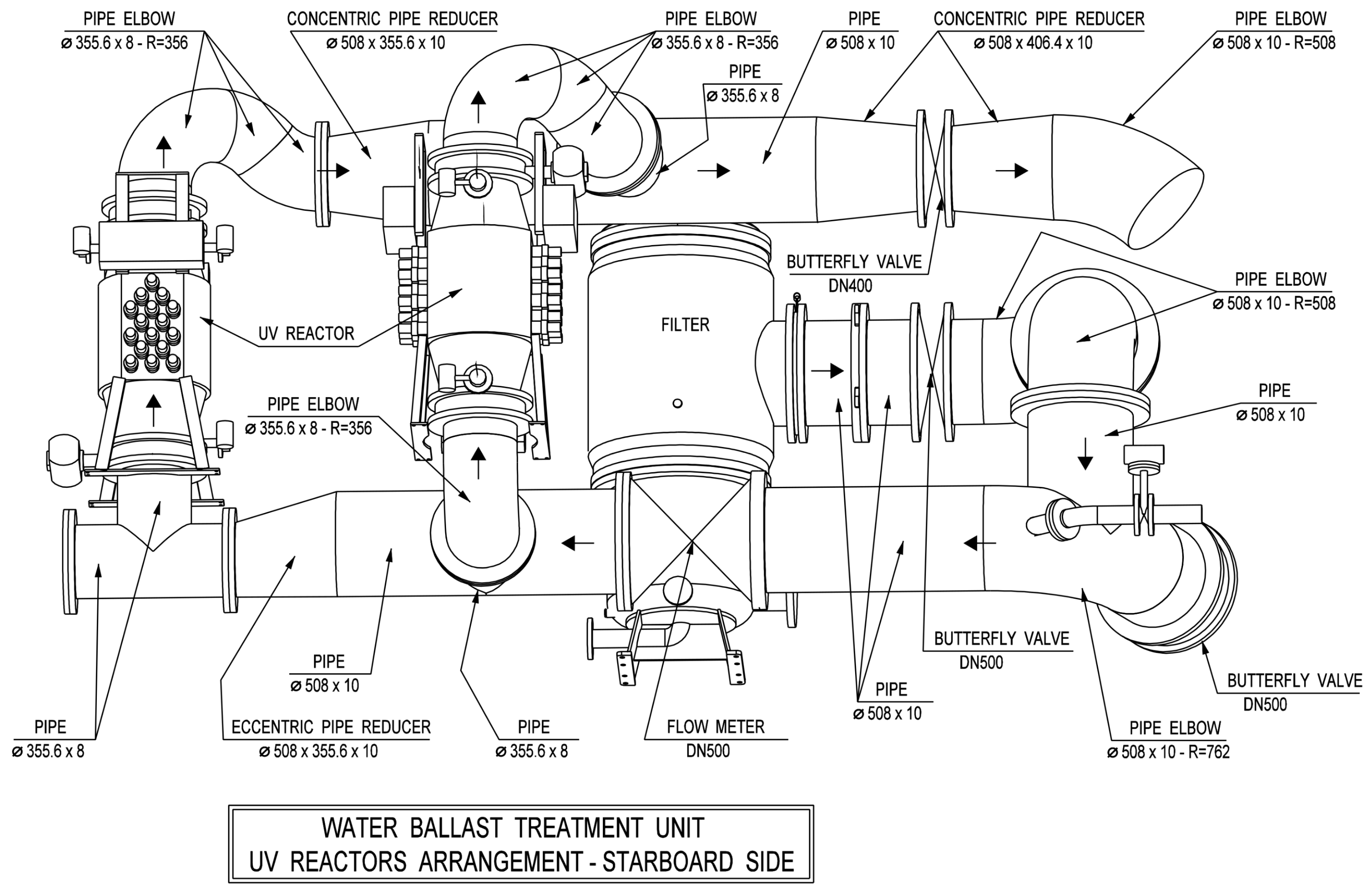



| Nominal Flow | Port-Side BWTU | Starboard-Side BWTU | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pipe Type | [m3/h] | [%] | Pipe Type | [m3/h] | [%] | |
| 2000 | Main Pipe | 1023.54 | 2.35 | Main Pipe | 1049.49 | 4.95 |
| 2000 | Side Pipe | 973.06 | −2.69 | Side Pipe | 947.35 | −5.26 |
| 1900 | Main Pipe | 972.54 | −2.75 | Main Pipe | 996.96 | −0.30 |
| 1900 | Side Pipe | 924.43 | −7.56 | Side Pipe | 899.98 | −10.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rak, A.; Mrakovčić, T.; Mauša, G.; Kranjčević, L. Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Ballast Water Treatment System Design. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040743
Rak A, Mrakovčić T, Mauša G, Kranjčević L. Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Ballast Water Treatment System Design. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040743
Chicago/Turabian StyleRak, Andro, Tomislav Mrakovčić, Goran Mauša, and Lado Kranjčević. 2025. "Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Ballast Water Treatment System Design" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040743
APA StyleRak, A., Mrakovčić, T., Mauša, G., & Kranjčević, L. (2025). Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis of Ballast Water Treatment System Design. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040743







