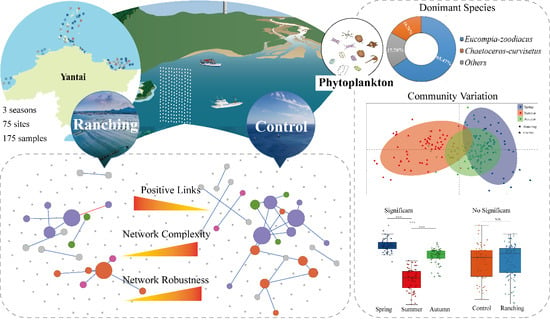
The Phytoplankton Community Exhibited Restored Species Diversity but Fragile Network Stability Under Potential Sustainable Aquaculture Approach of Marine Ranching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
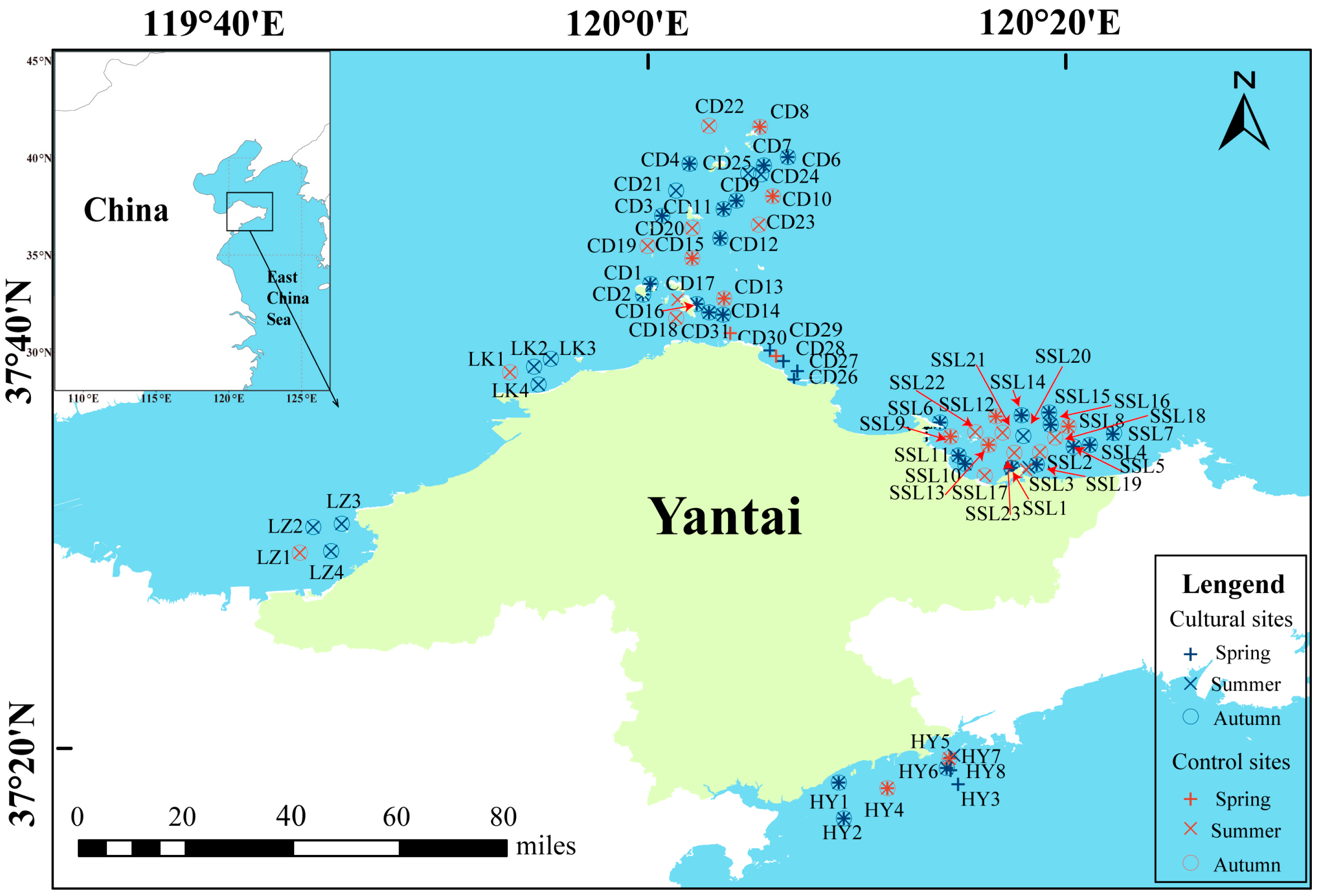
2.1. Description of the Study Area
2.2. Sampling Collection
2.3. Phytoplankton Cell Enumeration
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Network Construction and Stability Analysis
3. Results
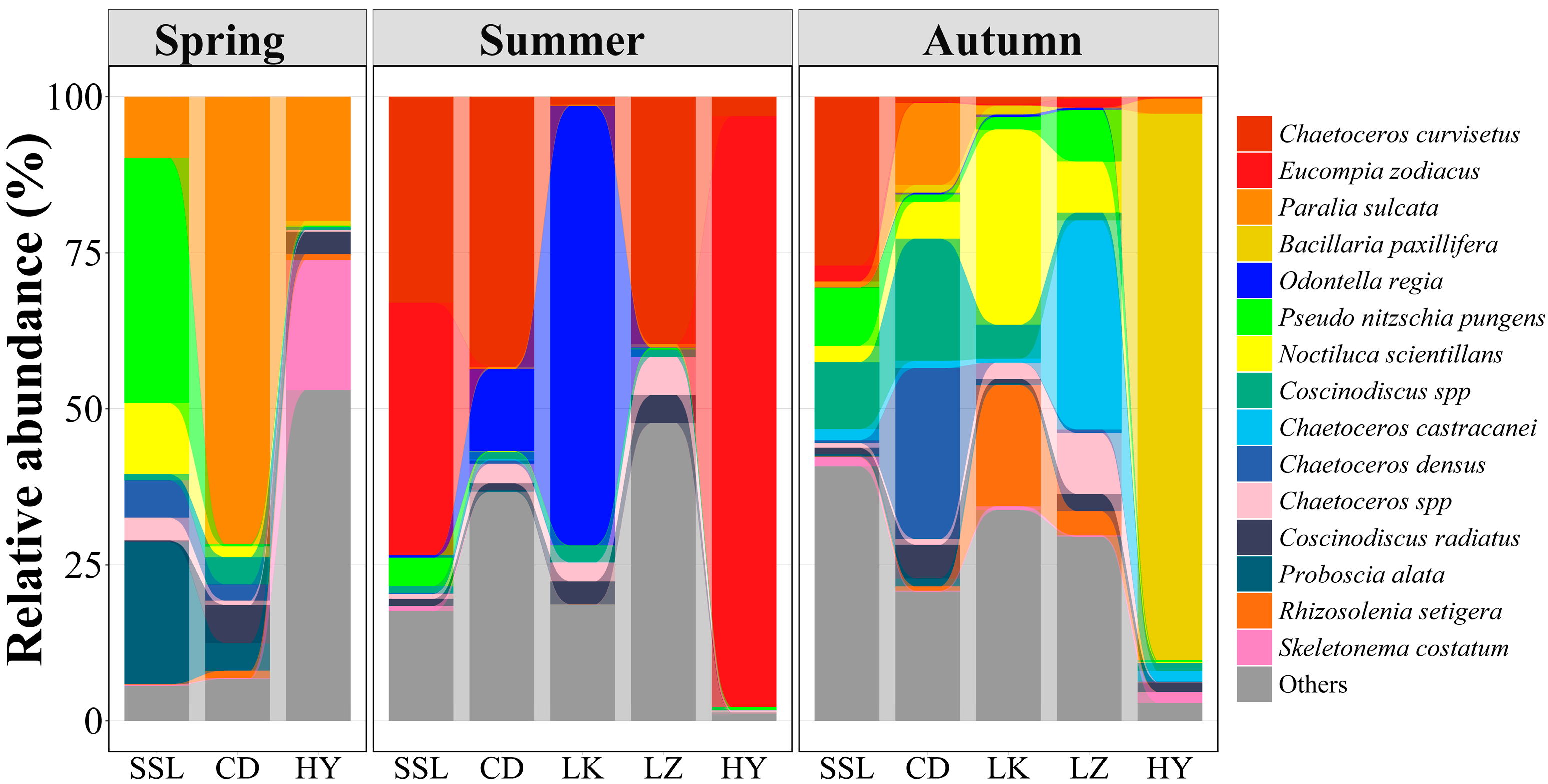
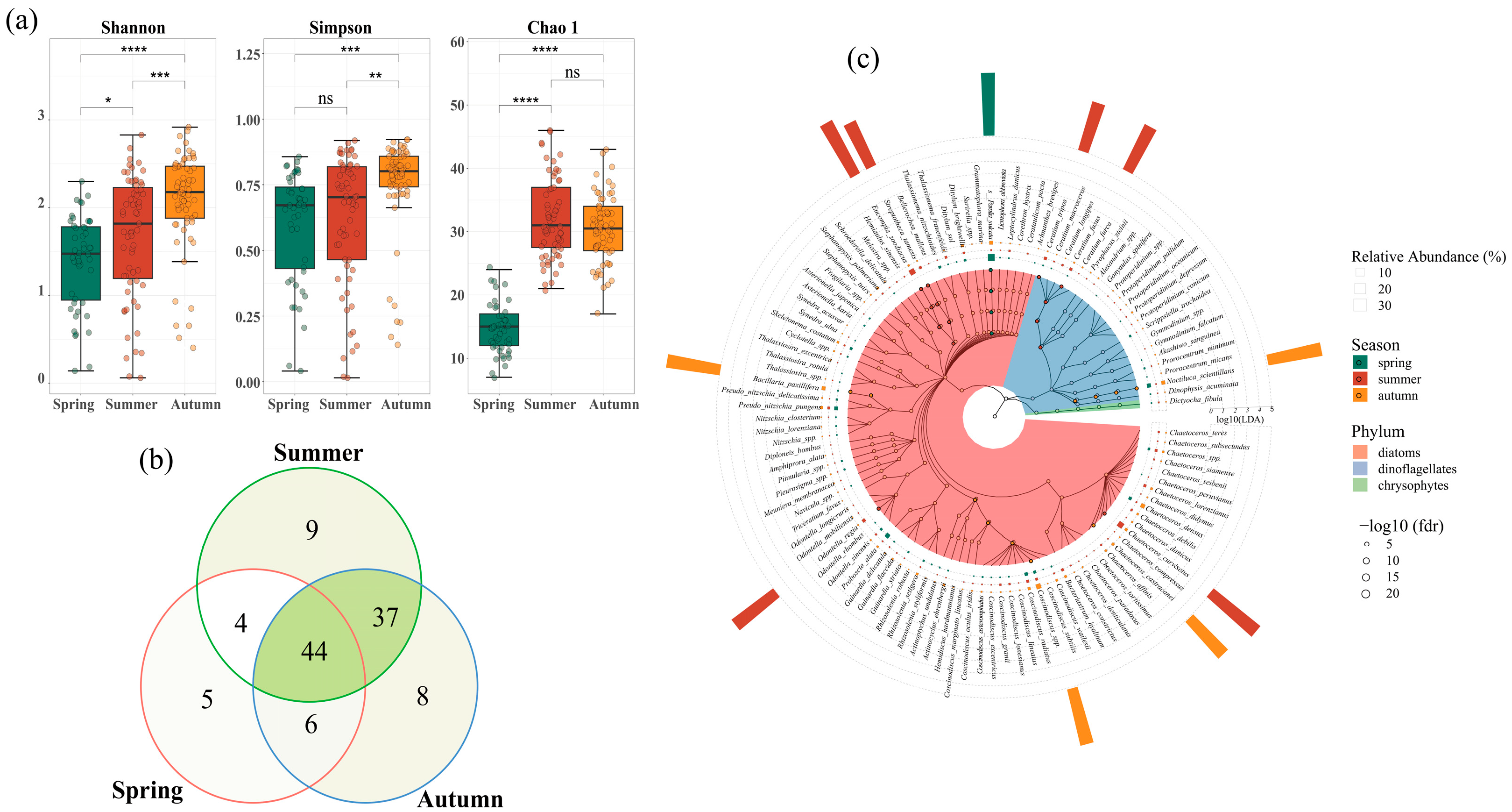
3.1. Phytoplankton Community Abundance and Composition
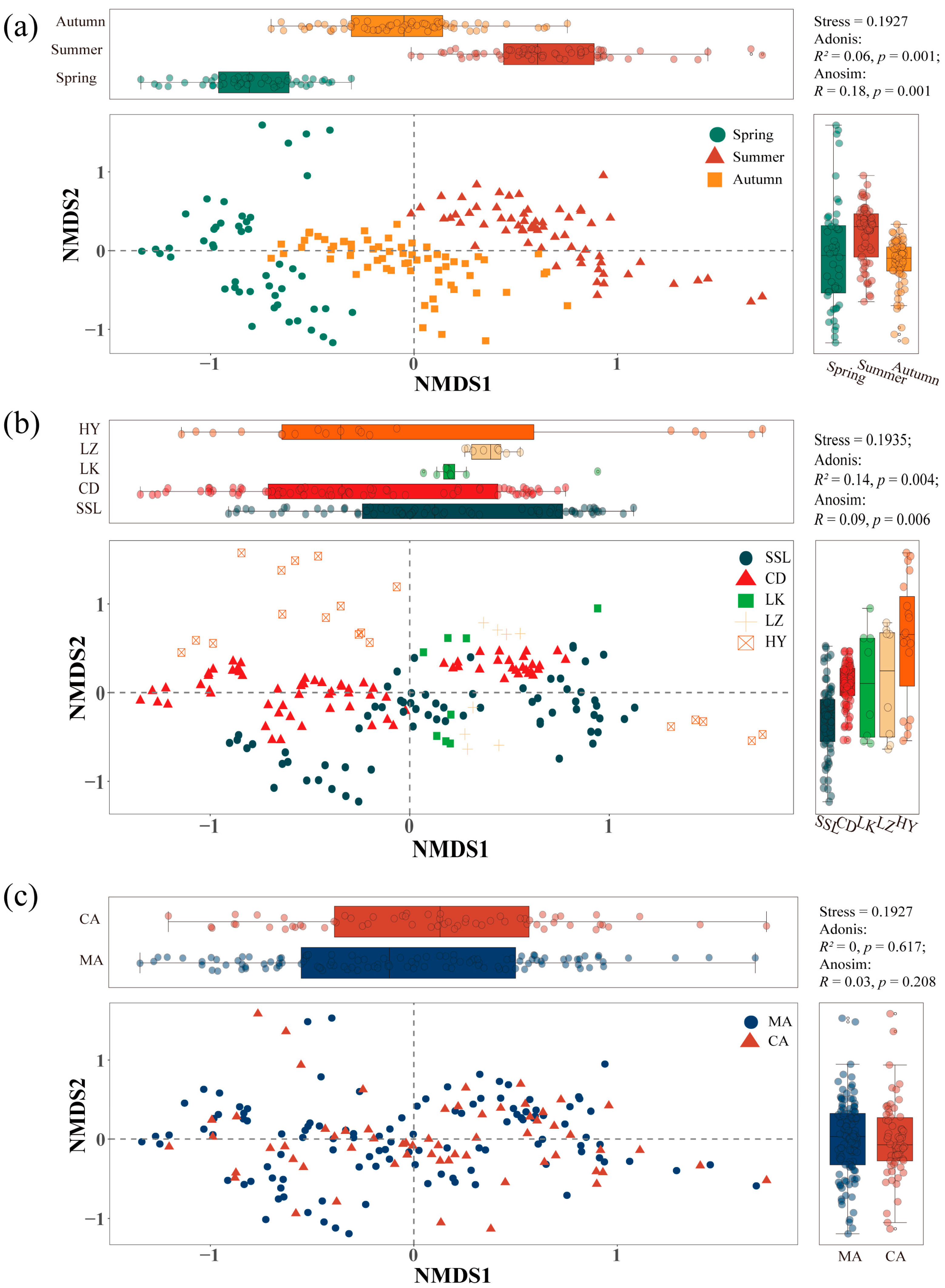
3.2. Seasonal Variations of Phytoplankton Communities
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Phytoplankton Communities
3.4. Impacts of Marine Ranching on Phytoplankton Communities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naylor, R.L.; Hardy, R.W.; Buschmann, A.H.; Bush, S.R.; Cao, L.; Klinger, D.H.; Little, D.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Shumway, S.E.; Troell, M. A 20-year retrospective review of global aquaculture. Nature 2021, 591, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.-X.; He, L.-Y.; Gao, F.-Z.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Jia, W.-L.; Ye, P.; Jia, Y.-W.; Hong, B.; Liu, S.-S.; et al. Mariculture affects antibiotic resistome and microbiome in the coastal environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L. Evolution of marine ranching policies in China: Review, performance and prospects. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 737, 139782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, H. Japanese Efforts in Marine Ranching Development. In Resources and Environment in Asia’s Marine Sector; Taylor and Francis: New York, WA, USA, 1992; pp. 199–216. [Google Scholar]
- Salvanes, A.G.V. Ocean Ranching. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences; Steele, J.H., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; pp. 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, H.; Whitmarsh, D.; Jensen, A. Artificial Reefs as a Tool to Aid Rehabilitation of Coastal Ecosystems: Investigating the Potential. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 37, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.O.; Otake, S.; Kim, J.K. Transition of artificial reefs (ARs) research and its prospects. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2018, 154, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Announcement No.515 of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. 2022. Available online: http://www.moa.gov.cn/nybgb/2022/202202/202203/t20220324_6393765.htm. (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Gao, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C. Temporal and spatial variation patterns of chlorophyll α in marine ranching under global interannual events. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 202, 106760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Mei, L.; Pan, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhou, C. Comparative metabarcoding analysis of phytoplankton community composition and diversity in aquaculture water and the stomach contents of Tegillarca granosa during months of growth. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Chang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. Phytoplankton community succession in relation to water quality changes in the indoor industrial aquaculture system for Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2020, 527, 735441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, L.; Gu, J.; Ye, Z.; Jin, R.; Wu, J. Spatiotemporal variation of phytoplankton communities and water quality among seaweed, shellfish and cage fish culture systems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 896, 165305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Du, P.; Zhu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Shou, L.; Yan, X.; et al. Kelp cultivation effectively improves water quality and regulates phytoplankton community in a turbid, highly eutrophic bay. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 707, 135561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, F.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, A.; Lu, G.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Diversity and annual variation of phytoplankton community in Yesso scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) farming waters of North Yellow Sea of China. Aquaculture 2019, 511, 734266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühe, L.; Cordier, T.; Dully, V.; Breiner, H.W.; Lentendu, G.; Pawłowski, J.; Martins, C.I.M.; Wilding, T.A.; Stoeck, T. Supervised machine learning is superior to indicator value inference in monitoring the environmental impacts of salmon aquaculture using eDNA metabarcodes. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 30, 2988–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wen, S.; Cheng, Z.; Tan, Y. Insights into ecological effects of fish and shellfish mariculture on microeukaryotic community. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strogatz, S.H. Exploring complex networks. Nature 2001, 410, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goberna, M.; Verdú, M. Cautionary notes on the use of co-occurrence networks in soil ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Qin, C.; Ma, H.; Xi, S.; Zuo, T.; Pan, W.; Li, C. Response of protist community dynamics and co-occurrence patterns to the construction of artificial reefs: A case study in Daya Bay, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 742, 140575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, C.; Frankstone, T.; Cao, L. Characterizing the development of Sea ranching in China. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2022, 32, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Du, P.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Shou, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, J. Oyster farming control on phytoplankton bloom promoted by thermal discharge from a power plant in a eutrophic, semi-enclosed bay. Water Res. 2019, 159, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Bruhn, A.; Krause-Jensen, D. A seaweed aquaculture imperative to meet global sustainability targets. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Lü, Y.; Cui, H.; Yuan, Y.L. Observation of the seasonal evolution of the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass in 1996–1998. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 442–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Yuan, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhao, J. Zooplankton community variations in response to summer hypoxia in Sishili Bay, North Yellow Sea, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 42, 1880–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Shan, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Zuo, T. Long-term changes in the fishery ecosystem structure of Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, C. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. 2011, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Package Version 2; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, A.; Ishizaka, J.; Yang, M.; Ouyang, L.; Yin, Y.; Ma, Z. Changes in community structure and photosynthetic activities of total phytoplankton species during the growth, maintenance, and dissipation phases of a Prorocentrum donghaiense bloom. Harmful Algae 2019, 82, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Non parametric estimation of the classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhan, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Q.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, L.; Feng, T.; Chen, M.; Wu, T.; Hu, E.; et al. MicrobiotaProcess: A comprehensive R package for deep mining microbiome. Innovation 2023, 4, 100388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Xie, P.; Yang, S.; Niu, G.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xue, C.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yuan, J. ggClusterNet: An R package for microbiome network analysis and modularity-based multiple network layouts. iMeta 2022, 1, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvát, S.; Podkalicki, J.; Csárdi, G.; Nepusz, T.; Traag, V.; Zanini, F.; Noom, D. IGraph/M: Graph theory and network analysis for Mathematica. J. Open Source Softw. 2023, 8, 4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring Correlation Networks from Genomic Survey Data. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Volume 3, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, U. On variants of shortest-path betweenness centrality and their generic computation. Soc. Netw. 2008, 30, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Fair, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Duan, B.; Lu, X. Diversity and co-occurrence networks of bacterial and fungal communities on two typical debris-covered glaciers, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 273, 127409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, G.-S.; Wu, J. Optimal network topology for structural robustness based on natural connectivity. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 2016, 443, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, T. Patchwork: The Composer of Plots, R package version 1.3. 0.9000; 2024; Available online: https://github.com/thomasp85/patchwork (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Chen, Y.-H.; Gao, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-P.; Liang, J.-R.; Sun, L.; Zhen, Y.; Qiao, L. Seasonal variations of phytoplankton assemblages and its relation to environmental variables in a scallop culture sea area of Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Li, A.; Cui, Z.; Ding, D.; Qu, K.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, L.; Jiang, T.; Jiang, T. A comparative study of phytoplankton community structure and biomass determined by HPLC-CHEMTAX and microscopic methods during summer and autumn in the central Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 155, 111172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, C.T.; Thomas, M.K.; Litchman, E. Temperature- and size-scaling of phytoplankton population growth rates: Reconciling the Eppley curve and the metabolic theory of ecology. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1658–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.-B.; Chen, Q.-Z.; Zeng, J.-N.; Liao, Y.-B.; Shou, L.; Liu, J. Phytoplankton community distribution in relation to environmental parameters in three aquaculture systems in a Chinese subtropical eutrophic bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 446, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Huang, R.; Xu, H.; Jiao, C. Seasonality overwhelms aquacultural activity in determining the composition and assembly of the bacterial community in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 683, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Bu, J.; Long, H.; Zhang, X.; Cai, X.; Huang, A.; Ren, W.; Xie, Z. Community Structure of Protease-Producing Bacteria Cultivated From Aquaculture Systems: Potential Impact of a Tropical Environment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 638129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, L.; Beusen, A.; Glibert, P.M.; Overbeek, C.; Pawlowski, M.; Herrera, J.; Mulsow, S.; Yu, R.; Zhou, M. Mariculture: Significant and expanding cause of coastal nutrient enrichment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Bernard, C.; Churro, C.; Escalera, L.; Hoppenrath, M.; Iwataki, M.; Larsen, J.; Mertens, K.; Moestrup, Ø.; Murray, S.; et al. (Eds.) IOC UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae. 2009. Available online: www.marinespecies.org/hab (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Riccardi, M.; Guerrini, F.; Roncarati, F.; Milandri, A.; Cangini, M.; Pigozzi, S.; Riccardi, E.; Ceredi, A.; Ciminiello, P.; Dell’aversano, C.; et al. Gonyaulax spinifera from the Adriatic sea: Toxin production and phylogenetic analysis. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, V.M.; Rosa, R.; Costa, P.R. Presence and persistence of the amnesic shellfish poisoning toxin, domoic acid, in octopus and cuttlefish brains. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 133, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabaglo, K.; Chrapusta, E.; Bober, B.; Kaminski, A.; Adamski, M.; Bialczyk, J. Environmental roles and biological activity of domoic acid: A review. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Yu, R.-C.; Richardson, A.J.; Sun, C.; Eriksen, R.; Kong, F.-Z.; Zhou, Z.-X.; Geng, H.-X.; Zhang, Q.-C.; Zhou, M.-J. Marked shifts of harmful algal blooms in the Bohai Sea linked with combined impacts of environmental changes. Harmful Algae 2023, 121, 102370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, U.; Stibor, H.; Katechakis, A.; Sommer, F.; Hansen, T. Pelagic food web configurations at different levels of nutrient richness and their implications for the ratio fish production:primary production. Hydrobiologia 2002, 484, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.M.; Tréguer, P.; Brzezinski, M.A.; Leynaert, A.; Quéguiner, B. Production and dissolution of biogenic silica in the ocean: Revised global estimates, comparison with regional data and relationship to biogenic sedimentation. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1995, 9, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serôdio, J.; Lavaud, J. Diatoms and their ecological importance. In Life Below Water; Filho, W.L., Azul, A.M., Brandli, L., Salvia, A.L., Wall, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 304–312. [Google Scholar]
- Smayda, T.J.; Reynolds, C.S. Strategies of marine dinoflagellate survival and some rules of assembly. J. Sea Res. 2003, 49, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassot, E.; Bonhommeau, S.; Dulvy, N.K.; Mélin, F.; Watson, R.; Gascuel, D.; Le Pape, O. Global marine primary production constrains fisheries catches. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Fu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Dynamics of phytoplankton community in scallop farming waters of the Bohai Sea and North Yellow Sea in China. BMC Evol. Biol. 2022, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Luan, Q.; Shan, X.; Cui, H.; Qu, K.; Cui, Z.; Sun, J. Temperature and nutrients drive distinct successions between diatoms and dinoflagellates over the past 40 years: Implications for climate warming and eutrophication. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 931, 172997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-G.; Kim, H.M.; Min, J.; Park, C.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.Y. Quantification of the paralytic shellfish poisoning dinoflagellate Alexandrium species using a digital PCR. Harmful Algae 2020, 92, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Needham, D.M.; Sachdeva, R.; Fuhrman, J.A. Ecological dynamics and co-occurrence among marine phytoplankton, bacteria and myoviruses shows microdiversity matters. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippot, L.; Griffiths, B.S.; Langenheder, S. Microbial Community Resilience across Ecosystems and Multiple Disturbances. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e0026-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Dai, S.; Ke, Z.; Guo, J.; Lai, Y.; Tan, Y. Phytoplankton Communities Miniaturization Driven by Extreme Weather in Subtropical Estuary under Climate Changes. Water Res. 2023, 245, 120588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, J.; Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Wu, Q.L. Evaluating the effects of aquaculture on the freshwater lake from the perspective of plankton communities: The diversity, co-occurrence patterns and their underlying mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.E.; Tilman, D.; Estes, J.A.; Menge, B.A.; Bond, W.J.; Mills, L.S.; Daily, G.; Castilla, J.C.; Lubchenco, J.; Paine, R.T. Challenges in the quest for keystones: Identifying keystone species is difficult—But essential to understanding how loss of species will affect ecosystems. Bioscience 1996, 46, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Tan, J.; Sun, K.H.; Jiang, L. Experimental demonstration of the importance of keystone communities for maintaining metacommunity biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Oecologia 2020, 193, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, B.; Hernández-Fariñas, T.; Le Gendre, R.; Schapira, M.; Chapelle, A. Two decades of Pseudo-nitzschia spp. blooms and king scallop (Pecten maximus) contamination by domoic acid along the French Atlantic and English Channel coasts: Seasonal dynamics, spatial heterogeneity and interannual variability. Harmful Algae 2016, 51, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dai, G.X.; Ding, J.; Chen, J. Study on the impact of water environmental factors on dominant species of phytoplankton around the power plant in Xiangshan Bay. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 610–613, 3371–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, L.K.; Bergey, E.A. Exploring the status of motility, lipid bodies, deformities and size reduction in periphytic diatom community from chronically metal (Cu, Zn) polluted waterbodies as a biomonitoring tool. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Pan, D.; Lu, Y.; Liang, Y. Spatial temporal distribution and eutrophication evaluation of nutrients and trace metals in summer surface seawater of Yantai Sishili Bay, China. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


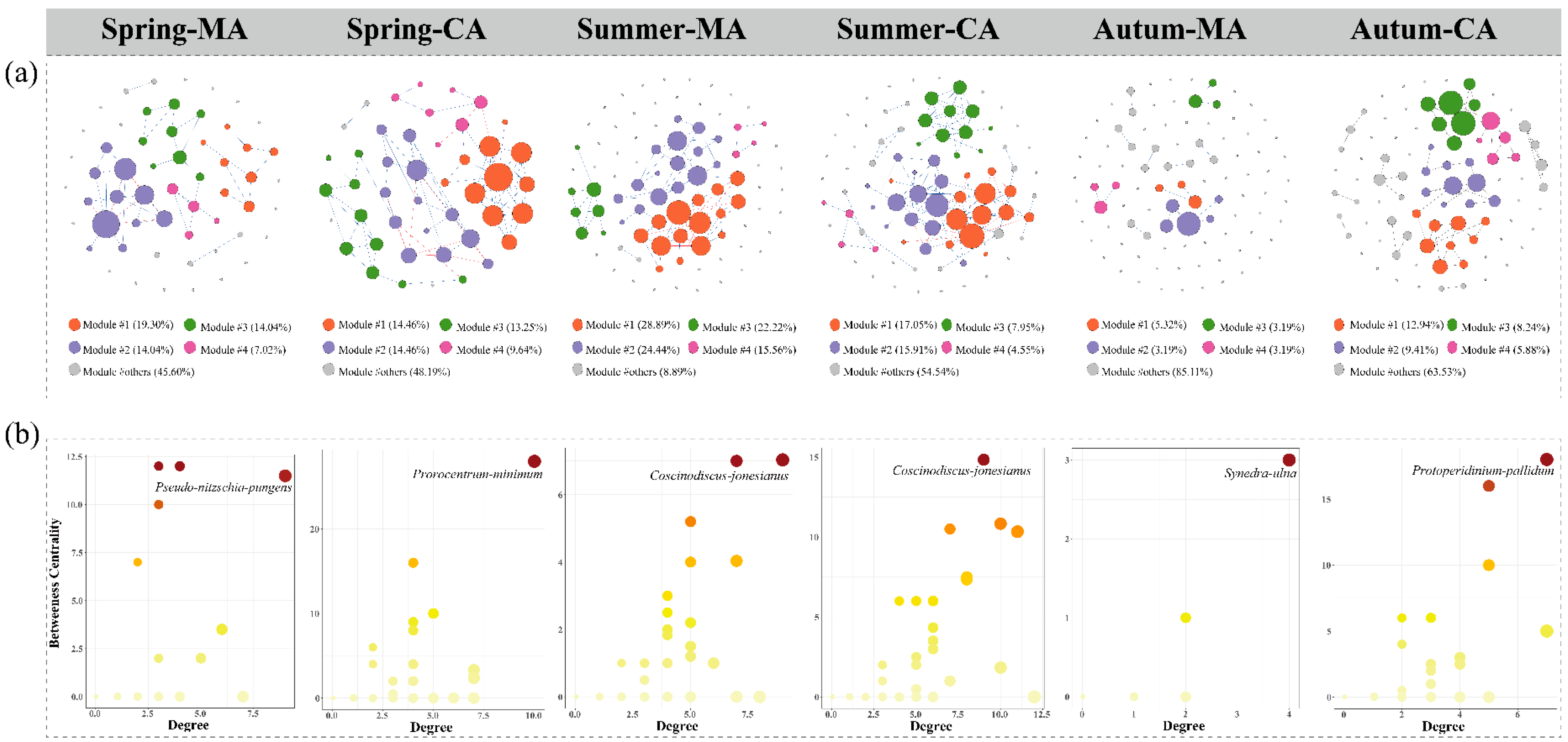
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MA | CA | Adding Percent (%) | MA | CA | Adding Percent (%) | MA | CA | Adding Percent (%) | |
| Node | 57 | 45 | 26.67 | 88 | 83 | 6.02 | 94 | 85 | 10.59 |
| Edge | 47 | 79 | −40.51 | 79 | 107 | −26.17 | 17 | 65 | −73.85 |
| Positive connections (%) | 85.11 | 84.81 | 0.35 | 82.28 | 83.18 | −1.08 | 100 | 92.31 | 8.33 |
| Negative connections (%) | 14.89 | 15.19 | −1.97 | 17.72 | 16.82 | 5.35 | 0 | 7.69 | −100.00 |
| Average degree | 0.825 | 1.756 | −53.02 | 0.898 | 1.289 | −30.33 | 0.181 | 0.765 | −76.34 |
| Modularity | 0.679 | 0.655 | 3.66 | 0.605 | 0.59 | 2.54 | 0.851 | 0.794 | 7.18 |
| Average clustering coefficient | 0.139 | 0.205 | −32.20 | 0.089 | 0.134 | −33.58 | 0.012 | 0.140 | −91.43 |
| Average path length | 1.698 | 1.743 | −2.58 | 1.432 | 1.529 | −6.34 | 1.190 | 1.690 | −29.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, D.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Ji, D.; Qu, L.; Li, B.; Wei, X.; Qin, S. The Phytoplankton Community Exhibited Restored Species Diversity but Fragile Network Stability Under Potential Sustainable Aquaculture Approach of Marine Ranching. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050835
Wei D, Xie Z, Li J, Ji D, Qu L, Li B, Wei X, Qin S. The Phytoplankton Community Exhibited Restored Species Diversity but Fragile Network Stability Under Potential Sustainable Aquaculture Approach of Marine Ranching. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050835
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Dongqun, Zeping Xie, Jialin Li, Diansheng Ji, Lin Qu, Baoquan Li, Xiao Wei, and Song Qin. 2025. "The Phytoplankton Community Exhibited Restored Species Diversity but Fragile Network Stability Under Potential Sustainable Aquaculture Approach of Marine Ranching" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050835
APA StyleWei, D., Xie, Z., Li, J., Ji, D., Qu, L., Li, B., Wei, X., & Qin, S. (2025). The Phytoplankton Community Exhibited Restored Species Diversity but Fragile Network Stability Under Potential Sustainable Aquaculture Approach of Marine Ranching. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050835