Control of Wave Energy Converters with Discrete Displacement Hydraulic Power Take-Off Units
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
1.1. Constant Pressure Configuration
1.2. Variable Pressure
1.3. Variable–Constant Pressure
2. WEC Dynamics
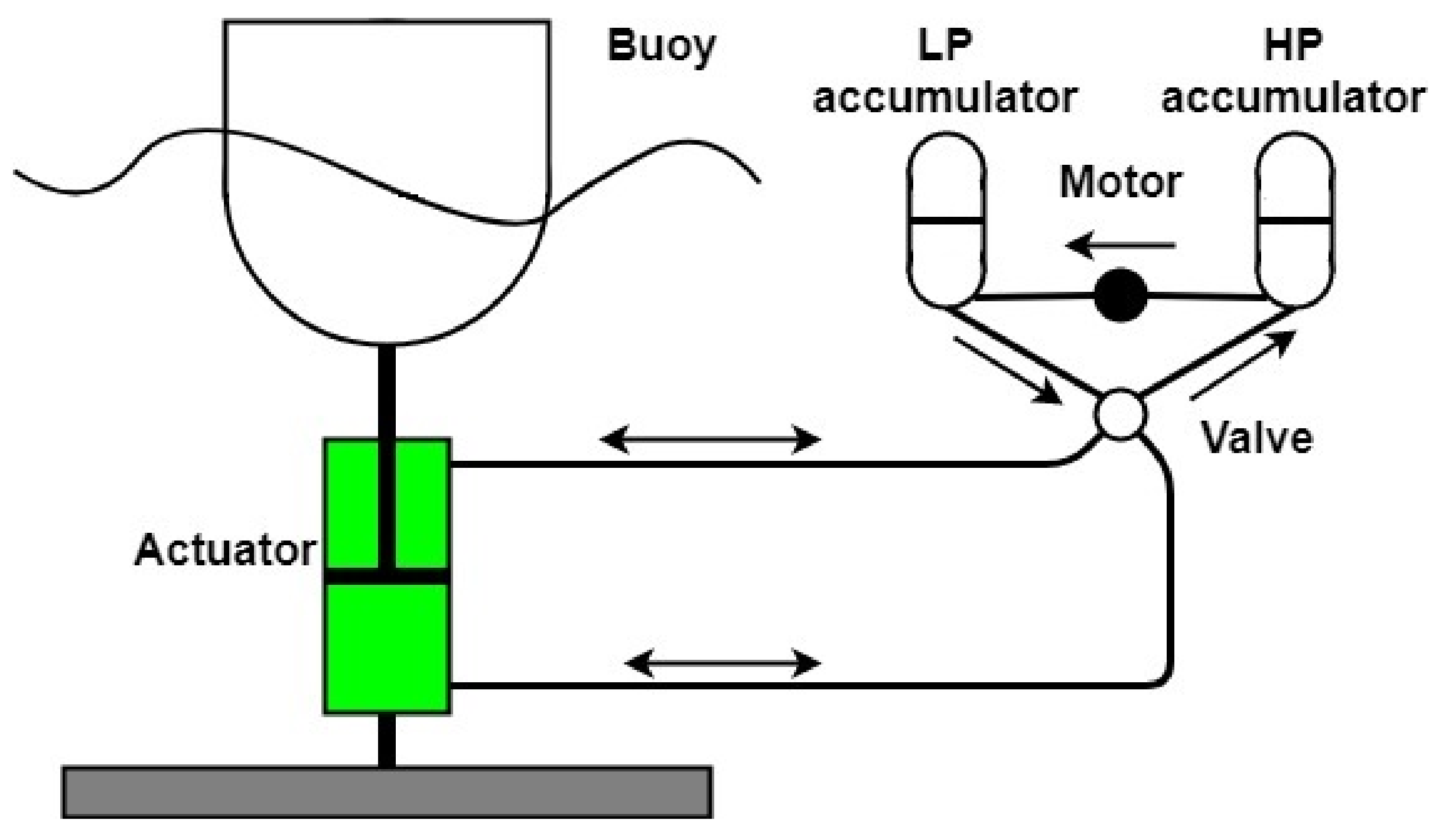
3. The Hydraulic PTO System
3.1. The Hydraulic Cylinder
3.2. The Hoses
3.3. The Directional Valves
3.4. The Pressure Accumulators
3.5. The Hydraulic Motor
4. The Control Algorithm
4.1. The Buoy Control Method
4.2. The Force-Shifting Algorithm
5. Simulation Tool
5.1. Wave Model
5.2. The System Losses
6. Simulation Results
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ymbol | Meaning | I Units |
| Area of the hose | m | |
| Instantaneous opening area of the valve | m | |
| Maximum opening area of the valve | m | |
| Piston area of chamber 1 | m | |
| Piston area of chamber 2 | m | |
| Piston area of chamber 3 | m | |
| Piston area of chamber 4 | m | |
| B | Feedback controller gain on the angular velocity | N.m.s.rad |
| Valve discharge coefficient | - | |
| Flow loss coefficient of the hydraulic motor | m.s.Pa | |
| Gas specific heat at constant volume | J.(kg.K) | |
| Capture width ratio | - | |
| Diameter of the hose | m | |
| D | Characteristic dimension of the buoy | m |
| Total hydraulic motor displacement | m | |
| Hydraulic motor displacement | m | |
| Force applied by the cylinder | N | |
| Friction force of the cylinder | N | |
| Reference control force | N | |
| Wave excitation torque impulse response function | N.m | |
| Radiation torque impulse response function | N.m | |
| Wave significant height | m | |
| Rigid body inertia | kg.m | |
| Moment of the added mass | kg.m | |
| Number of generators | - | |
| Hydrostatic stiffness coefficient | N.m.rad | |
| K | Feedback controller gain on the angular position | N.m.rad |
| Length of the hose | m | |
| Pressure in the accumulator | Pa | |
| Expected average power output | W | |
| Pressure in chamber 1 | Pa | |
| Pressure in chamber 2 | Pa | |
| Pressure in chamber 3 | Pa | |
| Pressure in chamber 4 | Pa | |
| Pressure drop across the hose | Pa | |
| Pressure of the high pressure accumulator | Pa | |
| Pressure of the low pressure accumulator | Pa | |
| Pressure drop of the fitting | Pa | |
| Pressure drop across a straight pipe/hose | Pa | |
| Actuator power extraction | W | |
| Average extracted power | W | |
| Generator power output | W | |
| Motor power output | W | |
| Wave energy transport | W.m | |
| Inlet flow to the accumulator | m.s | |
| Inlet flow to chamber 1 | m.s | |
| Inlet flow to chamber 2 | m.s | |
| Inlet flow to chamber 3 | m.s | |
| Inlet flow to chamber 4 | m.s | |
| Inlet flow of the hose | m.s | |
| Outlet flow of the hose | m.s | |
| R | Ideal gas constant | kg.m.(s.K) |
| Reynold’s number | - | |
| S | Wave spectral density | m.s.rad |
| Valve opening and closing time | s | |
| T | Gas temperature | K |
| Hydraulic accumulator wall temperature | K | |
| Valve opening and closing signal | - | |
| Instantaneous piston velocity | m.s | |
| Velocity of the outlet flow of the hose | m.s | |
| Accumulator size | m | |
| Accumulator external volume of the pipeline | m | |
| Accumulator gas volume | m | |
| External volume of the connecting hose to chamber 1 | m | |
| External volume of the connecting hose to chamber 2 | m | |
| External volume of the connecting hose to chamber 3 | m | |
| External volume of the connecting hose to chamber 4 | m | |
| Instantaneous stroke of the cylinder | m | |
| Maximum stroke of the cylinder | m | |
| Effective bulk modulus of the fluid | Pa | |
| Fitting loss coefficient | - | |
| Wave elevation | m | |
| Cylinder efficiency | - | |
| Electricity generation efficiency | - | |
| Angular position of the arm | rad | |
| Kinematic viscosity of the fluid | m.s | |
| Fluid density | kg.m | |
| Accumulator thermal time constant | s | |
| Wave excitation torque | N.m | |
| Power take-off torque | N.m | |
| Torque due to the radiation wave | N.m | |
| Random phase shift | rad | |
| Motor speed control coefficient | - | |
| Wave frequency | rad.s | |
| Angular velocity of the hydraulic motor | rad.s | |
| Peak frequency of the wave | rad.s |
References
- António, F.d.O.; Justino, P.A.; Henriques, J.C.; André, J.M. Reactive versus latching phase control of a two-body heaving wave energy converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Control Conference (ECC), European, Budapest, Hungary, 23–26 August 2009; pp. 3731–3736. [Google Scholar]
- Bacelli, G.; Ringwood, J.V.; Gilloteaux, J.C. A control system for a self-reacting point absorber wave energy converter subject to constraints. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2011, 44, 11387–11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, P.; Lopez, J.; Santos, M.; Ruiz-Minguela, P.; Villate, J.; Salcedo, F. Control strategies for a wave energy converter connected to a hydraulic power take-off. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2011, 5, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You-Guan, Y.; Guo-fang, G.; Guo-Liang, H. Simulation technique of AMESim and its application in hydraulic system. Hydraul. Pneum. Seals 2005, 3, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, F.; Kracht, P. Implementation of a Hydraulic Power Take-Off for wave energy applications. Department of Civil Engineering, Aalborg University: Aalborg, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Plummer, A.; Cargo, C. Power Transmissions for Wave Energy Converters: A Review. In Proceedings of the 8th International Fluid Power Conference (IFK), Dresden, Germany, 26–28 March 2012; University of Bath: Bath, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Antonio, F.d.O. Modelling and control of oscillating-body wave energy converters with hydraulic power take-off and gas accumulator. Ocean Eng. 2007, 34, 2021–2032. [Google Scholar]
- António, F.d.O. Phase control through load control of oscillating-body wave energy converters with hydraulic PTO system. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, R.H. Design and Control of the Powertake-Off System for a Wave Energy Converter with Multiple Absorbers. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Energy Technology, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Babarit, A.; Guglielmi, M.; Clément, A.H. Declutching control of a wave energy converter. Ocean Eng. 2009, 36, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidsmoen, H. Tight-moored amplitude-limited heaving-buoy wave-energy converter with phase control. Appl. Ocean Res. 1998, 20, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidsmoen, H. Simulation of a Slack-Moored Heaving-Buoy Wave-Energy Converter with Phase Control; Norwegian University of Science and Technology: Trondheim, Norway, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Josset, C.; Babarit, A.; Clément, A. A wave-to-wire model of the SEAREV wave energy converter. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M 2007, 221, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R. Design, simulation, and testing of a novel hydraulic power take-off system for the Pelamis wave energy converter. Renew. Energy 2006, 31, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Ying, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lin, Y.; Bao, J. Wave energy converter of inverse pendulum with double action power take off. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C 2013, 227, 2416–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolín-Urbaneja, J.C.; Cortés, A.; Cabanes, I.; Estensoro, P.; Lasa, J.; Marcos, M. Modeling innovative power take-off based on double-acting hydraulic cylinders array for wave energy conversion. Energies 2015, 8, 2230–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cargo, C.; Hillis, A.; Plummer, A. Optimisation and control of a hydraulic power take-off unit for a wave energy converter in irregular waves. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A 2014, 228, 462–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Ge, W.; Luo, L.; Liang, H.; Xu, C.; Leng, J.; Yuan, Z.; Huang, H. Research on the hydraulic power take-off unit of a hybrid wave energy converter. In Proceedings of the IEEE OCEANS 2016-Shanghai, Shanghai, China, 10–13 April 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, R.H.; Kramer, M.M.; Vidal, E. Discrete displacement hydraulic power take-off system for the wavestar wave energy converter. Energies 2013, 6, 4001–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.H.; Andersen, T.O.; Pedersen, H.C. Model based design of efficient power take-off systems for wave energy converters. In Proceedings of the 12th Scandinavian International Conference on Fluid Power, SICFP, Tampere, Finland, 18–20 May 2011; Tampere University Press: Tampere, Finland, 2011; pp. 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Kamizuru, Y. Development of Hydrostatic Drive Trains for Wave Energy Converters, Shaker Verlag GmbH: Germany, 13 November 2014.
- Hals, J.; Taghipour, R.; Moan, T. Dynamics of a force-compensated two-body wave energy converter in heave with hydraulic power take-off subject to phase control. In Proceedings of the 7th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference, Porto, Portugal, 11–13 September 2007; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, R.; Ringwood, J.; Weber, J. Comparison of two alternative hydraulic PTO concepts for wave energy conversion. In Proceedings of the 9th European Wave and Tidal Energy Conference (EWTEC), Southampton, UK, 5–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kamizuru, Y.; Liermann, M.; Murrenhoff, H. Simulation of an ocean wave energy converter using hydraulic transmission. In Proceedings of the 7th International Fluid Power Conference, Aachen, Germany, 22–24 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Penalba, M.; Sell, N.P.; Hillis, A.J.; Ringwood, J.V. Validating a wave-to-wire model for a wave energy converter—Part I: The Hydraulic Transmission System. Energies 2017, 10, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, K.; Fuchshumer, F.; Böhmer, N.; Costello, R.; Villegas, C. Design and control of a hydraulic power take-off for an axi-symmetric heaving point absorber. In Proceedings of the 9th European Wave and Tidal Conference, Southampton, UK, 5–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gaspar, J.F.; Calvário, M.; Kamarlouei, M.; Soares, C.G. Power take-off concept for wave energy converters based on oil-hydraulic transformer units. Renew. Energy 2016, 86, 1232–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E.V.; Hansen, R.H.; Kramer, M.M. Control performance assessment and design of optimal control to harvest ocean energy. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 40, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.H.; Pedersen, H.C. Reducing pressure oscillations in discrete fluid power systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I 2016, 230, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.H.; Andersen, T.O.; Pedersen, H.C.; Hansen, A.H. Control of a 420 kn discrete displacement cylinder drive for the wavestar wave energy converter. In Proceedings of the ASME/BATH 2014 Symposium on Fluid Power and Motion Control, Bath, UK, 10–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.; Abdelkhalik, O.; Robinett, R.; Bacelli, G.; Wilson, D. Optimal control of wave energy converters. Renew. Energy 2017, 103, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hals, J.; Falnes, J.; Moan, T. Constrained Optimal Control of a Heaving Buoy Wave-Energy Converter. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2011, 133, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelkhalik, O.; Robinett, R.; Zou, S.; Bacelli, G.; Coe, R.; Bull, D.; Wilson, D.; Korde, U. On the control design of wave energy converters with wave prediction. J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy 2016, 2, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Abdelkhalik, O.; Robinett, R.; Bacelli, G.; Wilson, D.; Korde, U. Multi-resonant feedback control of heave wave energy converters. Ocean Eng. 2016, 127, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herber, D.R.; Allison, J.T. Wave energy extraction maximization in irregular ocean waves using pseudospectral methods. In Proceedings of the 39th Design Automation Conference, Portland, OR, USA, 4–7 August 2013; p. V03AT03A018. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, M.; Marquis, L.; Frigaard, P. Performance evaluation of the wavestar prototype. In Proceedings of the 9th European Wave and Tidal Conference, Southampton, UK, 5–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]



















| Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| kg m | ||
| Nm/rad | ||
| The transfer function | ||
| * | ||
| ** | ||
| The transfer function | ||
| *** | ||
| **** |
| Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length of the arms | ||
| 3 | m | |
| m | ||
| m | ||
| Length of the hoses C2M | ||
| 1 | m | |
| 1 | m | |
| 1 | m | |
| 1 | m | |
| Diameter of the hoses C2M | ||
| in | ||
| in | ||
| in | ||
| in | ||
| Maximum stroke | ||
| 3 | m | |
| Area of the chambers | ||
| m | ||
| m | ||
| m | ||
| m | ||
| Max Area of the valves | ||
| m | ||
| m | ||
| m | ||
| m | ||
| Accumulator size | ||
| m | ||
| Pressure drop coef | ||
| 1 | ||
| Specific time constant S | ||
| 23 | s | |
| 34 | s | |
| Initial pressure of the accumulators | ||
| 20 | bar | |
| 130 | bar | |
| Initial angle | ||
| rad | ||
| Control parameters | ||
| K | Nm/rad | |
| B | Nms/rad | |
| Valve opening time | ||
| s | ||
| Wall temperature | ||
| 50 | oC | |
| Ideal gas constant | ||
| R | 276 | J/kg/K |
| Gas specific heat at constant volume | ||
| 760 | J/kg/K | |
| Motor displacement | ||
| 100 | cc/rev | |
| Flow loss coefficient | ||
| m/s/Pa | ||
| Fluid bulk modulus | ||
| Pa |
| Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The SA controller | ||
| 3705 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW | ||
| The PD controller | ||
| 1119 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW | ||
| The PDC3 controller | ||
| 1404 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW |
| Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The SA controller | ||
| 215 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW | ||
| The PD controller | ||
| 215 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW | ||
| The PDC3 controller | ||
| 215 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW | ||
| The SB controller | ||
| 215 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW | ||
| The MPC controller | ||
| 215 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW | ||
| The PS controller | ||
| 215 | kN | |
| m | ||
| kW |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, S.; Abdelkhalik, O. Control of Wave Energy Converters with Discrete Displacement Hydraulic Power Take-Off Units. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6020031
Zou S, Abdelkhalik O. Control of Wave Energy Converters with Discrete Displacement Hydraulic Power Take-Off Units. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2018; 6(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6020031
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Shangyan, and Ossama Abdelkhalik. 2018. "Control of Wave Energy Converters with Discrete Displacement Hydraulic Power Take-Off Units" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 6, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6020031
APA StyleZou, S., & Abdelkhalik, O. (2018). Control of Wave Energy Converters with Discrete Displacement Hydraulic Power Take-Off Units. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 6(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse6020031






