Effects of the Bioturbating Marine Yabby Trypaea australiensis on Sediment Properties in Sandy Sediments Receiving Mangrove Leaf Litter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
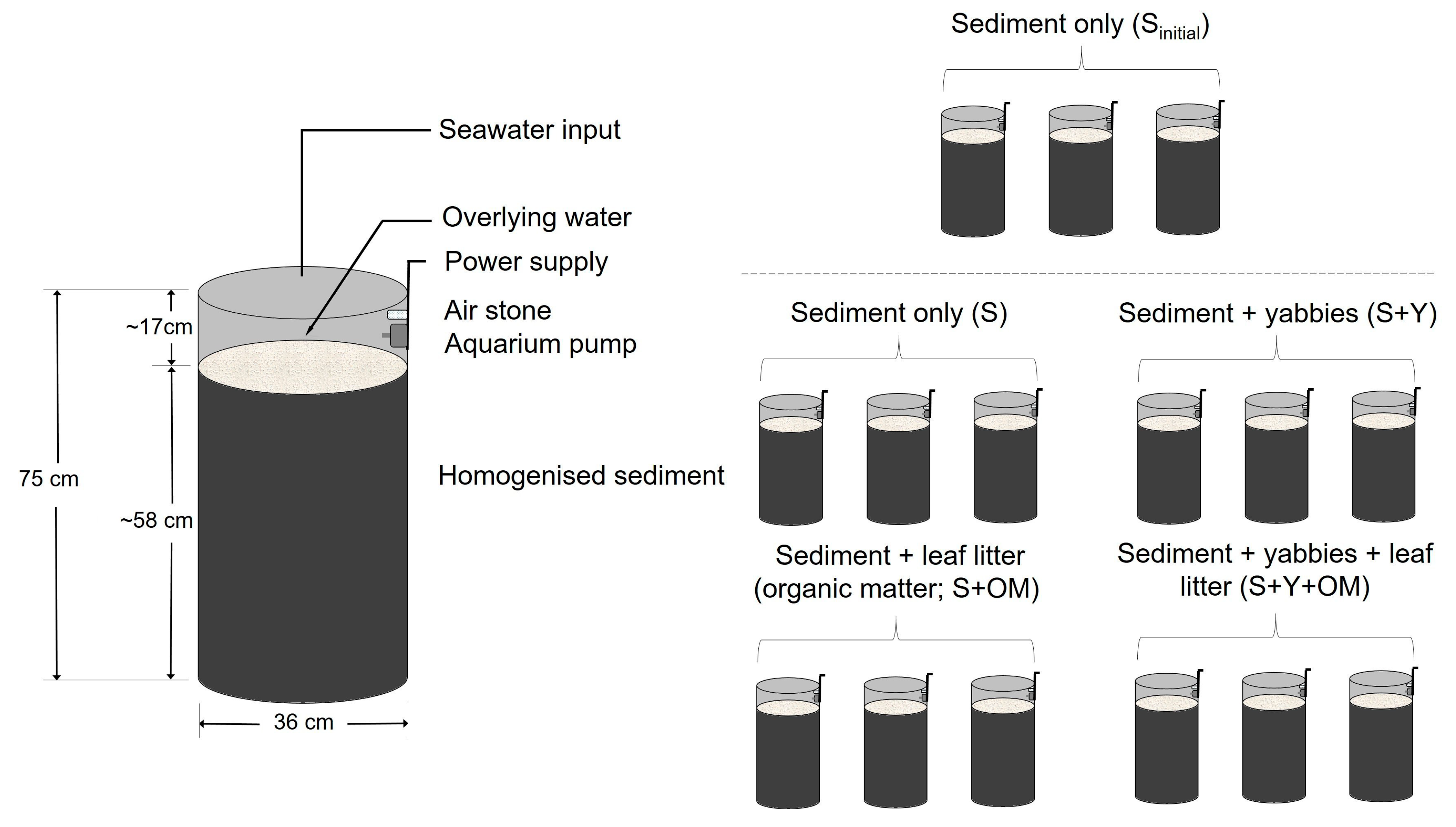
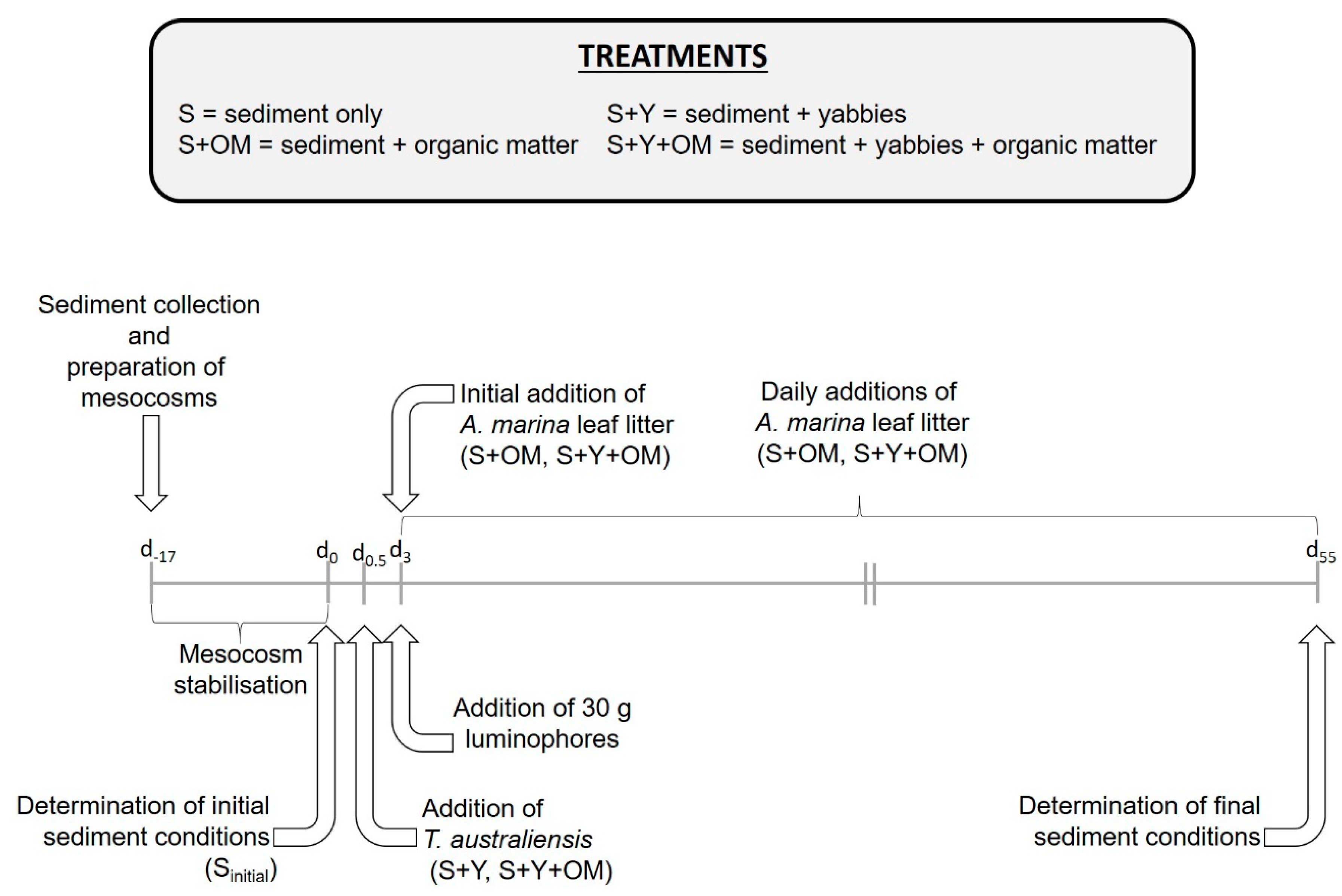
2.1. Experimental Set-up and Design
2.2. Sediment Profile Collection
2.3. Sediment Reworking Quantification
2.4. Analytical Techniques
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Visual Observations
3.2. Sediment Reworking
3.2.1. Tracer Profiles
3.2.2. Sediment Reworking Coefficients
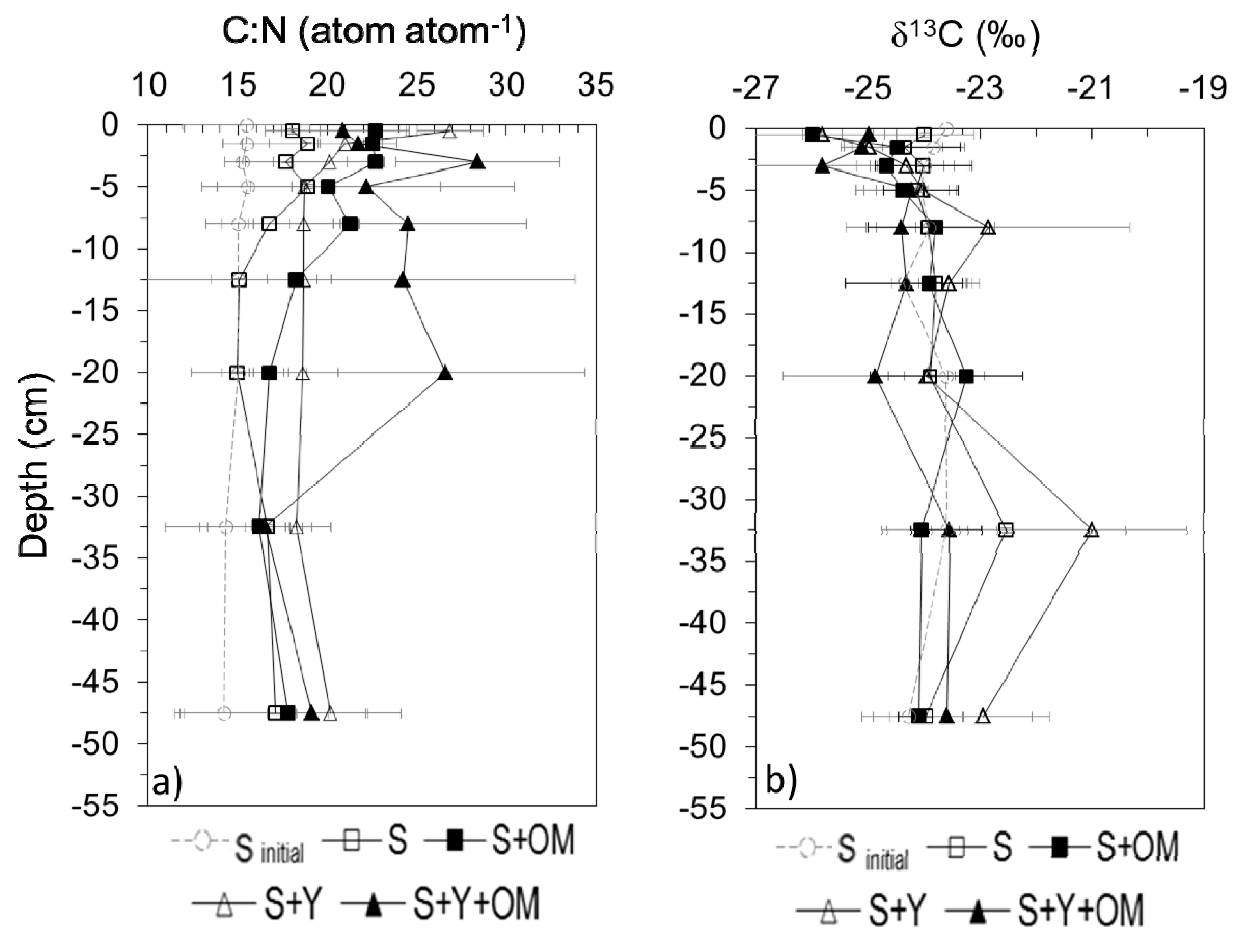
3.3. Physical and Chemical Sediment Profiles
4. Discussion
4.1. Relevance of Experimental Approach and Observed Behaviour
4.2. Sediment Reworking by T. australiensis
4.3. Physical Sediment Characteristics
4.4. Sediment Organic Matter and Nutrient Profiles
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Little, C. Biology of Soft Shores and Estuaries; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, D.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, N.J.; Ma, Z.; Fuller, R.A. Tidal flats of the Yellow Sea: A review of ecosystem status and anthropogenic threats. Aust. Ecol. 2015, 40, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mfilinge, P.L.; Meziane, T.; Bachok, Z.; Tsuchiya, M. Litter dynamics and particulate organic matter outwelling from a subtropical mangrove in Okinawa Island, South Japan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 63, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.K.; Welsh, D.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Lemckert, C.J.; Teasdale, P.R.; Meziane, T. Investigating the distribution and sources of organic matter in surface sediment of Coombabah Lake (Australia) using elemental, isotopic and fatty acid biomarkers. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 2535–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y. Mangrove outwelling: A review. Hydrobiologia 1995, 295, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennerjahn, T.C.; Ittekkot, V. Relevance of mangroves for the production and deposition of organic matter along tropical continental margins. Naturwissenschaften 2002, 89, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katrak, G.; Bird, F.L. Comparative effects of the large bioturbators, Trypaea australiensis and Heloecius cordiformis, on intertidal sediments of Western Port, Victoria, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2003, 54, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.T.; Castadelli, G. Bacterial nitrification activity directly associated with isolated benthic marine animals. Mar. Biol. 2004, 144, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, A.; Kneer, D.; Stapel, J.; Asmus, H. Shrimp burrows in tropical seagrass meadows: An important sink for litter. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 79, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, L.; Maire, O.; Volkenborn, N.; Lecroart, P.; Bichon, S.; de Montaudouin, X.; Grémare, A.; Deflandre, B. Influence of the mud shrimp Upogebia pusilla (Decapoda: Gebiidea) on solute and porewater exchanges in an intertidal seagrass (Zostera noltei) meadow of Arcachon Bay: An experimental assessment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 477, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Aoki, S.; Okamoto, K. Effects of the bioturbating crab Macrophthalmus japonicus on abiotic and biotic tidal mudflat characteristics in the Tama River, Tokyo Bay, Japan. Plankton Benthos Res. 2017, 12, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Organic matter diagenesis at the oxic/anoxic interface in coastal marine sediments, with emphasis on the role of burrowing animals. Hydrobiologia 2000, 426, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.T. It’s a dirty job but someone has to do it: The role of marine benthic macrofauna in organic matter turnover and nutrient recycling to the water column. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 19, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.K.; Welsh, D.T.; Jordan, M.A.; Teasdale, P.R.; Lemckert, C. Influence of natural amphipod (Victoriopisa australiensis) (Chilton, 1923) population densities on benthic metabolism, nutrient fluxes, denitrification and DNRA in sub-tropical estuarine sediment. Hydrobiologia 2009, 628, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzhofer, F.; Glud, R.N. Small-scale spatial and temporal variability in benthic O2 dynamics of coastal sediments: Effect of fauna activity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.; Teasdale, P.R.; Welsh, D.T. A novel gel-based technique for the two-dimensional determination of iron (II) and sulfide in sediment. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2008, 6, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.; Welsh, D.T.; Teasdale, P.R. Investigating biogenic heterogeneity in coastal sediments with two-dimensional measurements of iron (II) and sulphide. Environ. Chem. 2009, 6, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkenborn, N.; Meile, C.; Polerecky, L.; Pilditch, C.A.; Norko, A.; Norkko, J.; Hewitt, J.E.; Thrush, S.F.; Wethey, D.S.; Woodin, S.A. Intermittent bioirrigation and oxygen dynamics in permeable sediments: An experimental and modelling study of three tellinid bivalves. J. Mar. Res. 2012, 70, 794–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Holmer, M. Decomposition of plant material in marine sediment exposed to different electron acceptors (O2, NO3− and SO42−), with emphasis on substrate origin, degradation stage and the role of bioturbation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.; Aller, R.C.; Hulth, S. The influence of biogenic irrigation intensity on benthic nitrification and denitrification; an experimental and model approach. J. Mar. Res. 2003, 61, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, D.T.; Nizzoli, D.; Fano, E.A.; Viaroli, P. Direct contribution of clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) to benthic fluxes, nitrification, denitrification and nitrous oxide emission in a farmed sediment. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.P.; Eyre, B.D. Effect of natural populations of burrowing thalassinidean shrimp on sediment irrigation, benthic metabolism, nutrient fluxes and denitrification. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 268, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkenborn, N.; Polerecky, L.; Wethey, D.S.; Woodin, S.A. Hydraulic activities by ghost shrimp Neotrypaea californiensis induce oxic–anoxic oscillations in sediments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 455, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, K.L.; Long, M.; Bird, F.L. Comparative feeding ecology of two spatially coexisting species of ghost shrimp, Biffarius arenosus and Trypaea australiensis (Decapoda: Callianassidae). Ophelia 2001, 55, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilmont, N.; Meziane, T.; Seuront, L.; Welsh, D.T. Identification of food sources of sympatric ghost shrimp (Trypaea australiensis) and soldier crab (Mictyris longicarpus) using a lipid biomarker dual stable isotope approach. Aust. Ecol. 2009, 34, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contessa, L.; Bird, F.L. The impact of bait-pumping on populations of the ghost shrimp Trypaea australiensis (Decapoda: Callianassidae) and the sediment environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 304, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E.; Penha-Lopes, G.; Delefosse, M.; Valdemarsen, T.; Quintana, C.O.; Banta, G.T. What is bioturbation? The need for precise definition for fauna in aquatic sciences. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 5, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworschak, P.C.; Koller, H.; Abed-Navandi, D. Burrow structure, burrowing and feeding behaviour of Corallianassa longiventris and Pestarella tyrrhena (Crustacea, Thalassinidea, Callianassidae). Mar. Biol. 2005, 148, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.A.; Welsh, D.T.; Dunn, R.J.K.; Teasdale, P.R. Influence of Trypaea australiensis population density on benthic metabolism and nitrogen dynamics in sandy estuarine sediment: A microcosm simulation. J. Sea Res. 2009, 61, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, D.; Branch, G.M. Bioengineering effects of burrowing Thalassinidean shrimps on marine soft-bottom ecosystems. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2011, 49, 137–192. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, R.J.K.; Welsh, D.T.; Jordan, M.A.; Teasdale, P.R.; Lemckert, C.J. Influence of the marine yabby (Trypaea australiensis) and mangrove (Avicennia marina) leaf litter on benthic metabolism and nitrogen cycling in sandy estuarine sediment. Hydrobiologia 2012, 693, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailstone, T.S.; Stephenson, W. The Biology of Callianassa (Trypaea) australiensis Dana 1852 (Crustacea, Thalassinidea); The University of Queensland Press: St. Lucia, Australia, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Rotherham, D. Fisheries Biology, Ecology and Recreational Harvesting of Ghost Shrimp (Trypaea australiensis) in South-Eastern Australia. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Sydney, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rotherham, D.; West, R.J. Comparison of methods for sampling populations of ghost shrimp, Trypaea australiensis (Decapoda: Thalassinidea: Callianassidae). Fish. Res. 2003, 60, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, N. Australia’s Mangroves: The Authoritative Guide to Australia’s Mangrove Plants; University of Queensland: St. Lucia, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Davie, J.D.S. Structural variation, litter production and nutrient status of mangrove vegetation in Moreton bay. In Focus on Stradbroke: New Information on North Stradbroke Island and Surrounding Areas 1974–1984; Colemand, R.J., Covacevich, J., Davie, P., Eds.; Boolarong Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 1984; pp. 208–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hedman, J.H.; Gunnarsson, J.S.; Samuelsson, G.; Gilbert, F. Particle reworking and solute transport by the sediment-living polychaetes Marenzelleria neglecta and Hediste diversicolor. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 407, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahaut, M.L.; Graf, G. A luminophore tracer technique for bioturbation studies. Oceanol. Acta 1987, 10, 323–328. [Google Scholar]
- François, F.; Gérino, M.; Stora, G.; Durbec, J.P.; Poggiale, J.C. Functional approach to sediment reworking by gallery-forming macrobenthic organisms: Modelling and application with the polychaete Nereis diversicolor. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 229, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, J.B.; Lindsay, P.J. Measurement of physical properties of sediments. In Manual of Physico-Chemical Analysis of Aquatic Sediments; Mudroch, A., Azcue, J.M., Murdoch, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; pp. 7–46. [Google Scholar]
- Heiri, O.; Lotter, A.F.; Lemcke, G. Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: Reproducibility and comparability of results. J. Paleolimnol. 2001, 25, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisterkamp, I.M.; Kamp, A.; Schramm, A.T.; de Beer, D.; Stief, P. Indirect control of the intracellular nitrate pool of intertidal sediment by the polychaete Hediste diversicolor. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 445, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stief, P.; Kamp, A.; de Beer, D. Role of diatoms in the spatial-temporal distribution of intracellular nitrate in intertidal sediment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Ainsworth, M. A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 92, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Aust. J. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe, S.; Austen, M.C. Mesocosm investigation into the effects of bioturbation on the diversity and structure of a subtidal macrobenthic community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 189, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, E. Impact of polychaetes (Nereis spp. and Arenicola marina) on carbon biogeochemistry in coastal marine sediments. Geochem. Trans. 2001, 2, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribsholt, B.; Kristensen, E. Effects of bioturbation and plant roots on salt marsh biogeochemistry: A mesocosm study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 241, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papaspyrou, S.; Kristensen, E.; Christensen, B. Arenicola marina (Polychaeta) and organic matter mineralisation in sandy marine sediments: In situ and microcosm comparison. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 72, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, F.; Hulth, S.; Grossi, V.; Poggiale, J.C.; Desrosiers, G.; Rosenberg, R.; Gérino, M.; François-Carcaillet, F.; Michaud, E.; Stora, G. Sediment reworking by marine benthic species from the Gullmar Fjord (Western Sweden): Importance of faunal biovolume. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 348, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, P.G.; Lillebø, A.I.; Lopes, C.B.; Pereira, E.; Duarte, A.C.; Pardal, M.A. Influence of bioturbation by Hediste diversicolor on mercury fluxes from estuarine sediments: A mesocosms laboratory experiment. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2008, 56, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blankson, E.R.; Adhikary, N.R.D.; Klerks, P.L. The effects of lead contamination on bioturbation by Lumbriculus variegatus in a freshwater microcosm. Chemosphere 2017, 167, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Backer, A.; Van Collie, F.; Montserrat, F.; Provoost, P.; Van Colen, C.; Vincx, M.; Degraer, S. Bioturbation effects of Corophium volutator: Importance of density and behavioural activity. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 91, 306–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuominen, L.; Mäkelä, K.; Lehtonen, K.K.; Hietanen, S.; Kuparinen, J. Nutrient fluxes, porewater profiles and denitrification in sediment influenced by algal sedimentation and bioturbation by Monoporeia affinis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1999, 49, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyrou, S.; Thessalou-Legaki, M.; Kristensen, E. Impact of Pestarella tyrrhena on benthic metabolism in sediment microcosms enriched with seagrass and macroalgal detritus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 281, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, F.Ø.; Kristensen, E. The influence of macrofauna on estuarine benthic community metabolism: A microcosm study. Mar. Biol. 1988, 99, 591–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, F.Ø.; Kristensen, E. The importance of benthic macrofauna in decomposition of microalgae in a coastal marine sediment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 1392–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrí, S.P.; Blackburn, T.H. Effect of Bioturbation by Nereis sp., Mya Arenaria and Cerastoderma sp. on nitrification and denitrification in estuarine sediments. Ophelia 1995, 42, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.; Kristensen, E. Impact of macrofaunal recolonization on benthic metabolism and nutrient fluxes in a shallow marine sediment previously overgrown with macroalgal mats. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 45, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, L.; Bernard, G.; Bastrop, R.; Norkko, A.; Norkko, J. Increasing densities of an invasive polychaete enhance bioturbation with variable effects on solute fluxes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamhuis, E.J.; Schreurs, C.E.; Videler, J.J. Burrow architecture and turbative activity of the thalassinid shrimp Callianassa subterranea from the central North Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 151, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grigg, N.J.; Webster, I.T.; Ford, P.W. Non-destructive measurement of the time evolution of burrowing shrimp mound topography. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 329, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duport, E.; Stora, G.; Tremblay, P.; Gilbert, F. Effects of population density on the sediment mixing induced by the gallery-diffusor Hediste (Nereis) diversicolor O.F. Müller, 1776. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 336, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheatcroft, R.A.; Jumars, P.A.; Smith, C.R.; Nowell, A.R.M. A mechanistic view of the particulate biodiffusion coefficient: Step lengths, rest periods and transport directions. J. Mar. Res. 1990, 48, 177–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, O.; Duchȇne, J.C.; Grémare, A.; Malyuga, V.S.; Meysman, F.J.R. A comparison of sediment reworking rates by the surface deposit-feeding bivalve Abra ovata during summertime and wintertime, with a comparison between two models of sediment reworking. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 343, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, C.; Kumblad, L.; Fagrell, A. The use of tracers to evaluate the importance of bioturbation in remobilising contaminants in Baltic sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R. The Interactive Effect of Sandprawn (Callichirus kraussi) Stebbing Bioturbation and Nutrients on Macrofaunal Communities. Master’s Thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Boon, P.I.; Bird, F.L.; Bunn, S.E. Diet of the intertidal callianassid shrimps Biffarus arenosus and Trypaea australiensis (Decapoda: Thalassinidea) in Western Port (southern Australia), determined with multiple stable-isotope analyses. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1997, 48, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, S.N.; Bird, F.L. Temporal changes in burrow structure of the thalassinidan ghost shrimps Trypaea australiensis and Biffarius arenosus. J. Nat. Hist. 2008, 42, 2041–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingalls, A.E.; Aller, R.C.; Lee, C.; Sun, M.Y. The influence of deposit-feeding on chlorophyll-a degradation in coastal sediments. J. Mar. Res. 2000, 58, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandnes, J.; Forbes, T.; Hansen, R.; Sandnes, B. Influence of particle type and faunal activity on mixing of di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in natural sediments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 197, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andrea, A.F.; DeWitt, T.H. Geochemical ecosystem engineering by the mud shrimp Upogebia pugettensis (Crustacea: Thalassinidae) in Yaquina Bay, Oregon: Density-dependent effects on organic matter remineralization and nutrient cycling. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 1911–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziebis, W.; Huettel, J.; Forster, S. Impact of biogenic sediment topography on oxygen fluxes in permeable seabeds. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 140, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowden, A.A.; Jones, M.B.; Morris, A.W. The role of Callianassa subterranea (Montagu) (Thalassinidea) in sediment resuspension in the North Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1998, 18, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, F.L. The interaction between ghost shrimp activity and seagrass restoration. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Ecology of Large Bioturbators in Tidal Flats and Shallow Sublittoral Sediments—From Individual Behaviour to Their Role as Ecosystem Engineers, Nagasaki, Japan, 1–2 November 2003; Tamaki, A., Ed.; Nagasaki University: Nagasaki, Japan, 2004; pp. 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Pillay, D.; Branch, G.M.; Forbes, A.T. The influence of bioturbation by the sandprawn Callianassa kraussi on feeding and survival of the bivalve Eumarcia paupercula and the gastropod Nassarius kraussianus. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2007, 344, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, G.; Rosenberg, R. Bioresuspension and biodeposition: A review. J. Mar. Syst. 1997, 11, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E.D.; Phillips, I.R.; Hawker, D.W. Trace metals and nutrients in bottom sediments of the Southport Broadwater, Australia. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2004, 48, 378–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.K.; Lemckert, C.J.; Teasdale, P.R.; Welsh, D.T. Macroinfauna dynamics and sediment parameters of a subtropical estuarine lake—Coombabah Lake (Southern Moreton Bay, Australia). J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.K.; Robertson, D.; Teasdale, P.R.; Waltham, N.J.; Welsh, D.T. Benthic metabolism and nitrogen dynamics in an urbanised tidal creek: Domination of DNRA over denitrification as a nitrate reduction pathway. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 131, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnken, J.; Dunn, R.J.K.; Teasdale, P.R. Investigation of recreational boats as a source of copper at anchorage sites using time-integrated diffusive gradients in thin film and sediment measurements. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2004, 49, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagès, A.; Welsh, D.T.; Robertson, D.; Panther, J.G.; Schafer, J.; Tomlinson, R.B.; Teasdale, P.R. Diurnal shifts in the co-distributions of porewater sulphide and iron (II), and phosphate and ammonium in the rhizosphere of Zostera capricorni. Estuar. Coastal. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, G.; Corfield, J. Association between the ghost shrimp Trypaea australiensis Dana 1852 (Crustacea: Decapoda) and a small deposit-feeding bivalve Mysella vitrae Laserson 1956 (Mollusca: Leptonidae). Mar. Freshw. Res. 1998, 49, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, M.; Nizzoli, D.; Welsh, D.T.; Viaroli, P. Short-term influence of recolonisation by the polychaete worm Nereis succinea on oxygen and nitrogen fluxes and denitrification: A microcosm simulation. Hydrobiologia 2000, 431, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzoli, D.; Bartoli, M.; Cooper, M.; Welsh, D.T.; Underwood, G.J.C.; Viaroli, P. Implications for oxygen and nutrient fluxes and denitrification rates during the early stage of sediment colonisation by the polychaete Nereis spp. in four estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 75, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzoli, D.; Welsh, D.T.; Viaroli, P. Seasonal nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics during benthic clam and suspended mussel cultivation. Mar. Poll. Bull. 2011, 62, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stief, P. Stimulation of microbial nitrogen cycling in aquatic ecosystems by benthic macrofauna: Mechanisms and environmental implications. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 2829–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelegrí, S.P.; Nielsen, L.P.; Blackburn, T.H. Denitrification in estuarine sediment stimulated by the irrigation activity of the amphipod Corophium volutator. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1994, 105, 258–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatment | S+Y | |||
| Mesocosm replicate | 1 | 2 | 3 | Mean ± Standard deviation |
| Db (cm2 y−1) | 4.5 | 8.2 | 6.5 | 6.4 ± 1.9 |
| r (y−1) | 2.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 3.7 ± 2.1 |
| Treatment | S+Y+OM | |||
| Mesocosm replicate | 1 | 2 | 3 | Mean ± Standard deviation |
| Db (cm2 y−1) | 5.5 | 4.0 | 8.1 | 5.9 ± 2.1 |
| r (y−1) | 2.5 | 0.1 | 5.8 | 2.8 ± 2.9 |
| Source | df | Sediment Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet-bulk Density | Porosity | LOI550 | C:N | δ15N | δ13C | NH4+bio | ||
| Treatment | 3 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.356 | 0.001 | 0.141 | 0.114 | 0.003 |
| Depth | 8 | 0.649 | 0.004 | 0.026 | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 |
| Treatment × Depth | 24 | 0.859 | 0.997 | 0.196 | 0.842 | 0.159 | 0.849 | 0.100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dunn, R.J.K.; Welsh, D.T.; Teasdale, P.R.; Gilbert, F.; Poggiale, J.-C.; Waltham, N.J. Effects of the Bioturbating Marine Yabby Trypaea australiensis on Sediment Properties in Sandy Sediments Receiving Mangrove Leaf Litter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120426
Dunn RJK, Welsh DT, Teasdale PR, Gilbert F, Poggiale J-C, Waltham NJ. Effects of the Bioturbating Marine Yabby Trypaea australiensis on Sediment Properties in Sandy Sediments Receiving Mangrove Leaf Litter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2019; 7(12):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120426
Chicago/Turabian StyleDunn, Ryan J. K., David T. Welsh, Peter R. Teasdale, Franck Gilbert, Jean-Christophe Poggiale, and Nathan J. Waltham. 2019. "Effects of the Bioturbating Marine Yabby Trypaea australiensis on Sediment Properties in Sandy Sediments Receiving Mangrove Leaf Litter" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 7, no. 12: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120426
APA StyleDunn, R. J. K., Welsh, D. T., Teasdale, P. R., Gilbert, F., Poggiale, J.-C., & Waltham, N. J. (2019). Effects of the Bioturbating Marine Yabby Trypaea australiensis on Sediment Properties in Sandy Sediments Receiving Mangrove Leaf Litter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 7(12), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse7120426






