Influence of Central Platform on Hydrodynamic Performance of Semi-Submerged Multi-Buoy Wave Energy Converter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Model of the WEC
3. Results of the Numerical Analysis
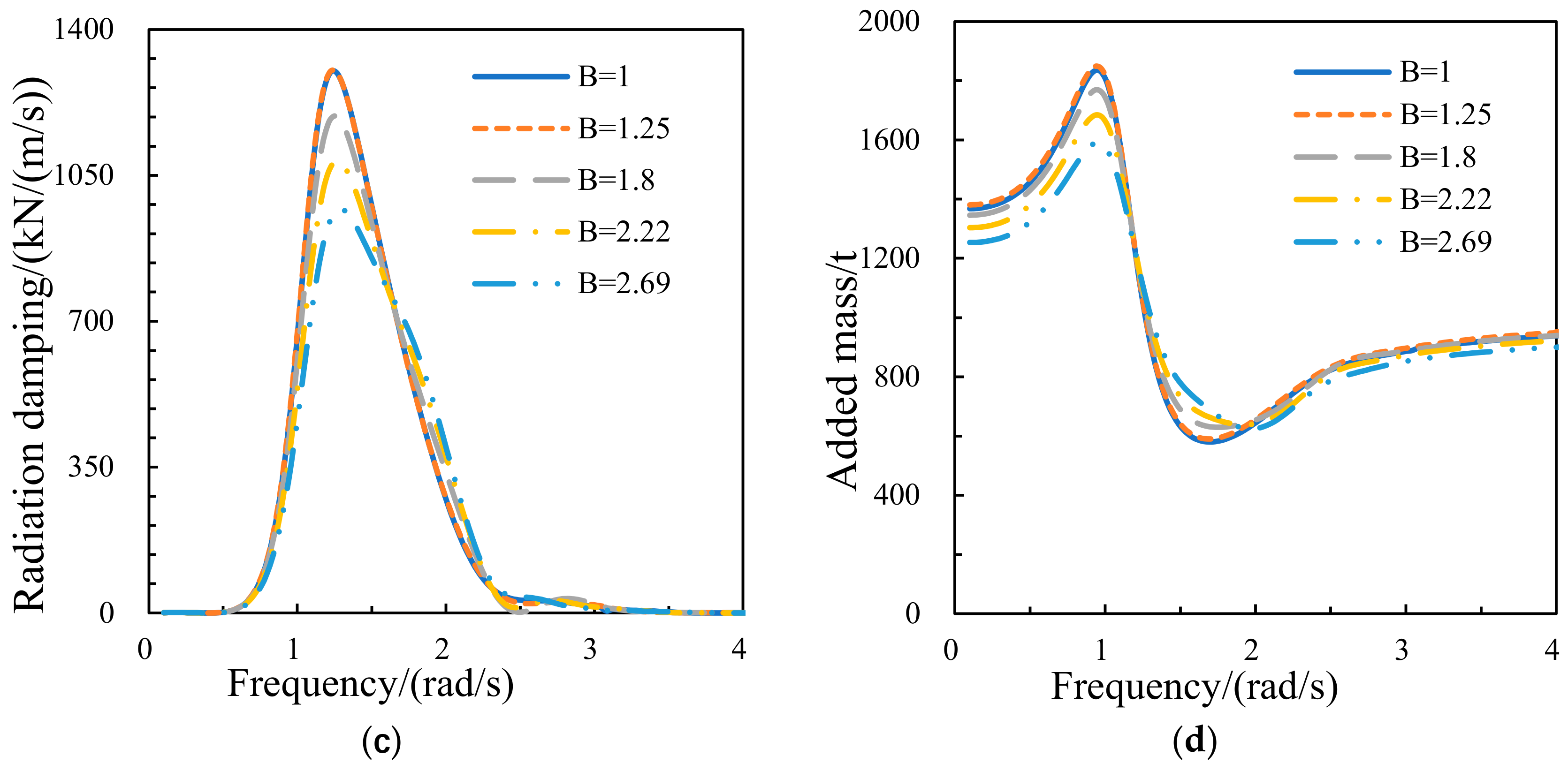
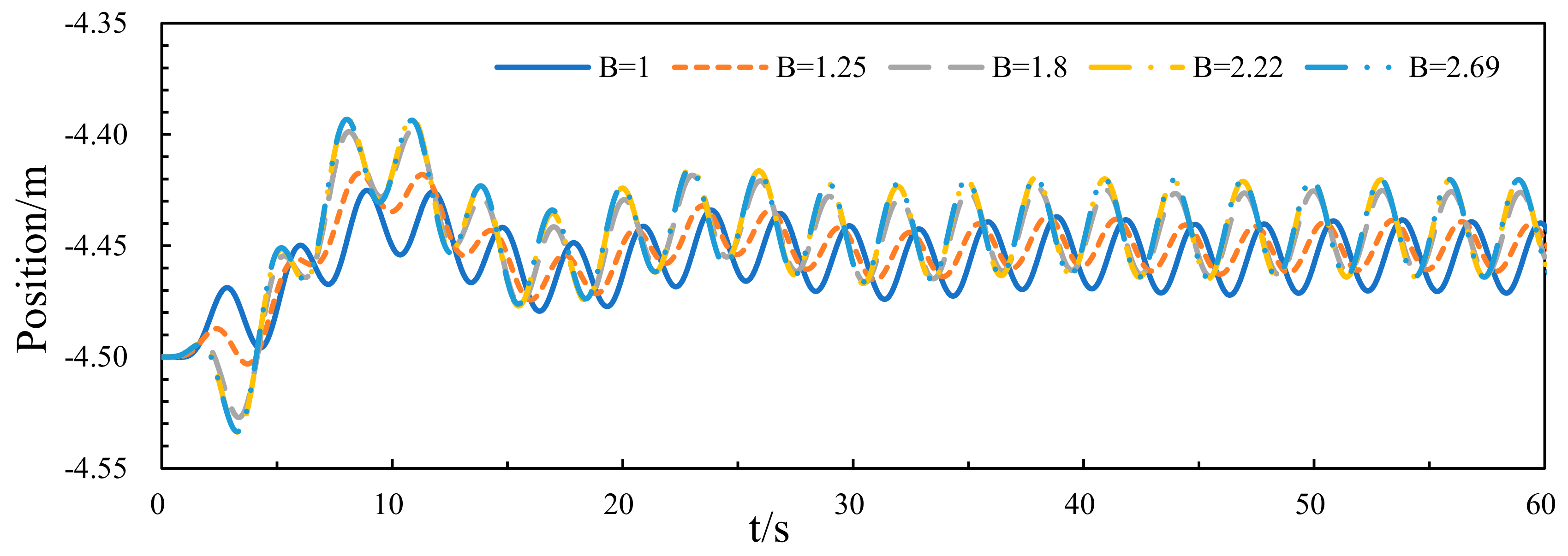
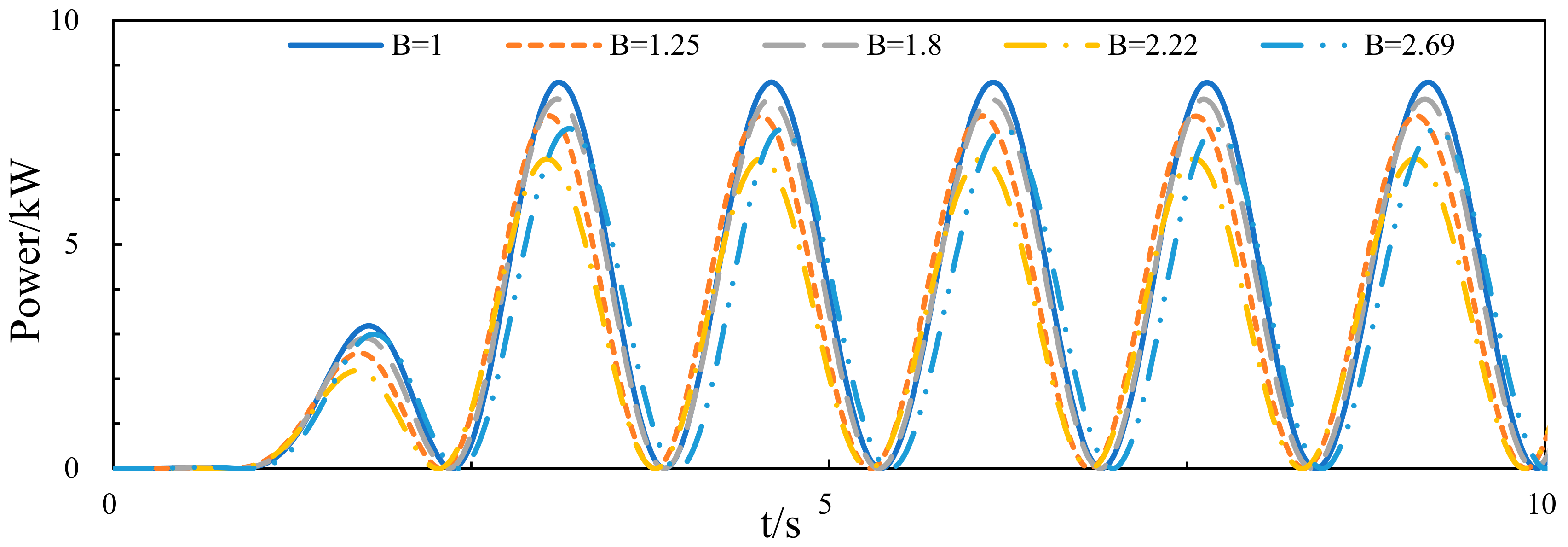
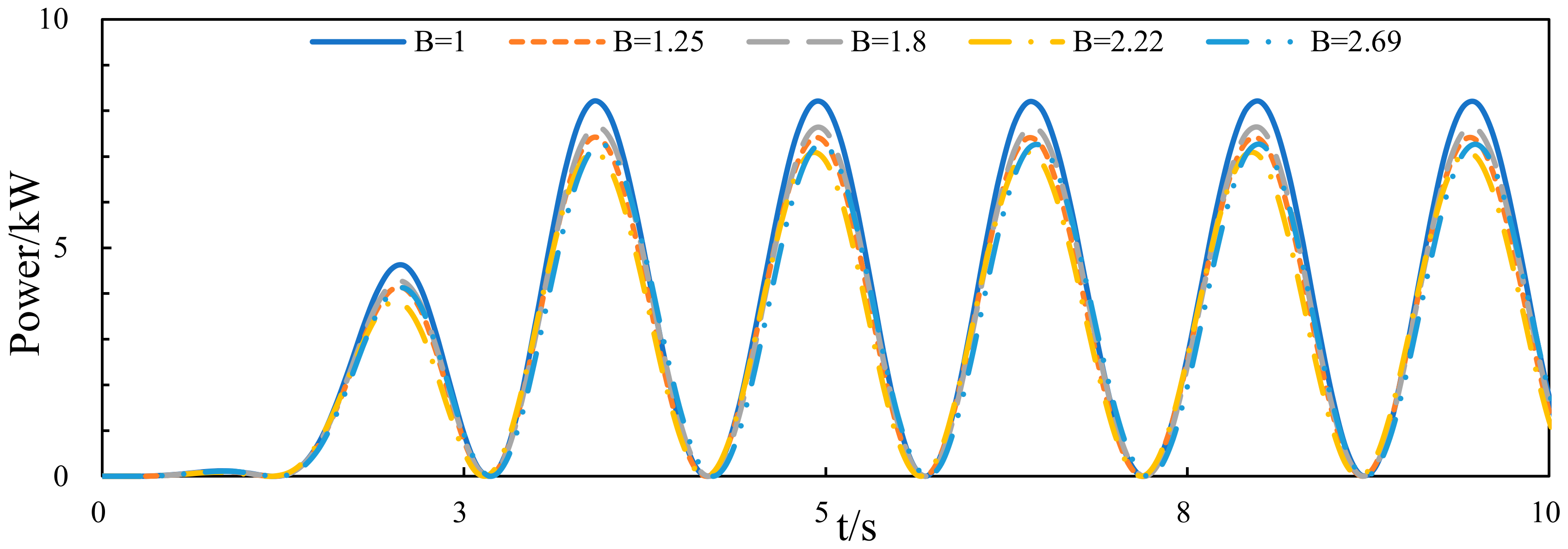
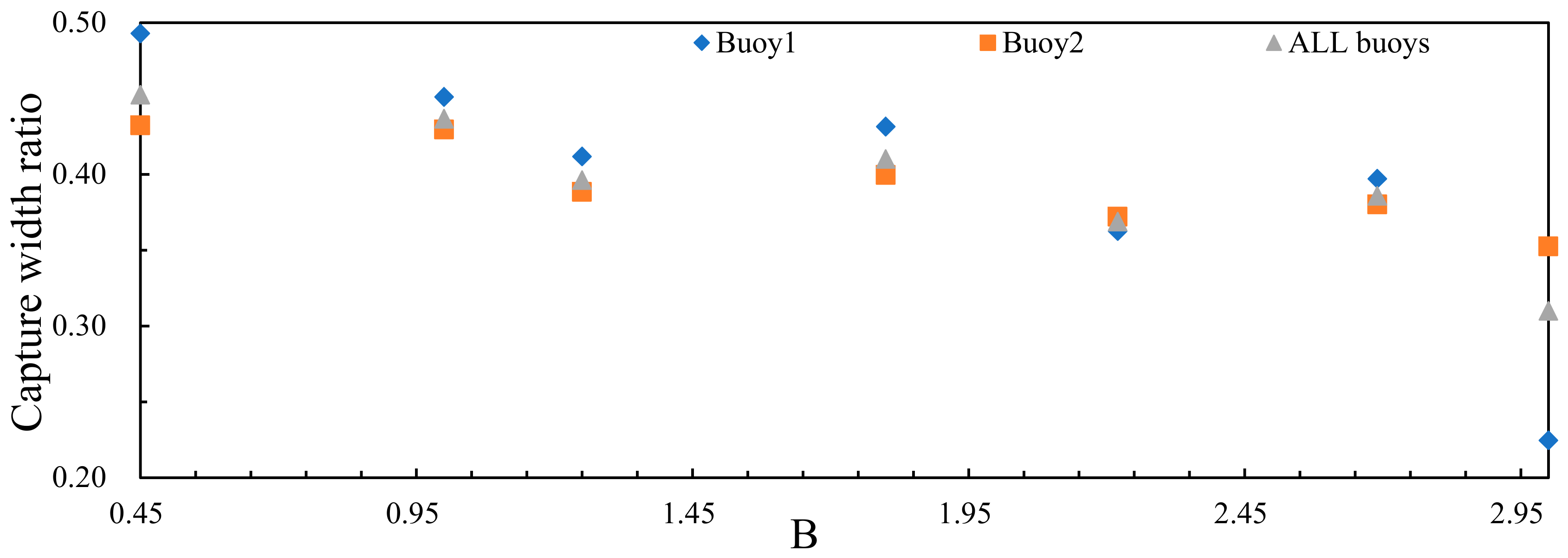
3.1. Numerical Results at Different Aspect Ratio of the Damping Layer
3.1.1. Hydrodynamic Performance of the Central Platform
3.1.2. Wave Energy Capture Width Ratio of the Device
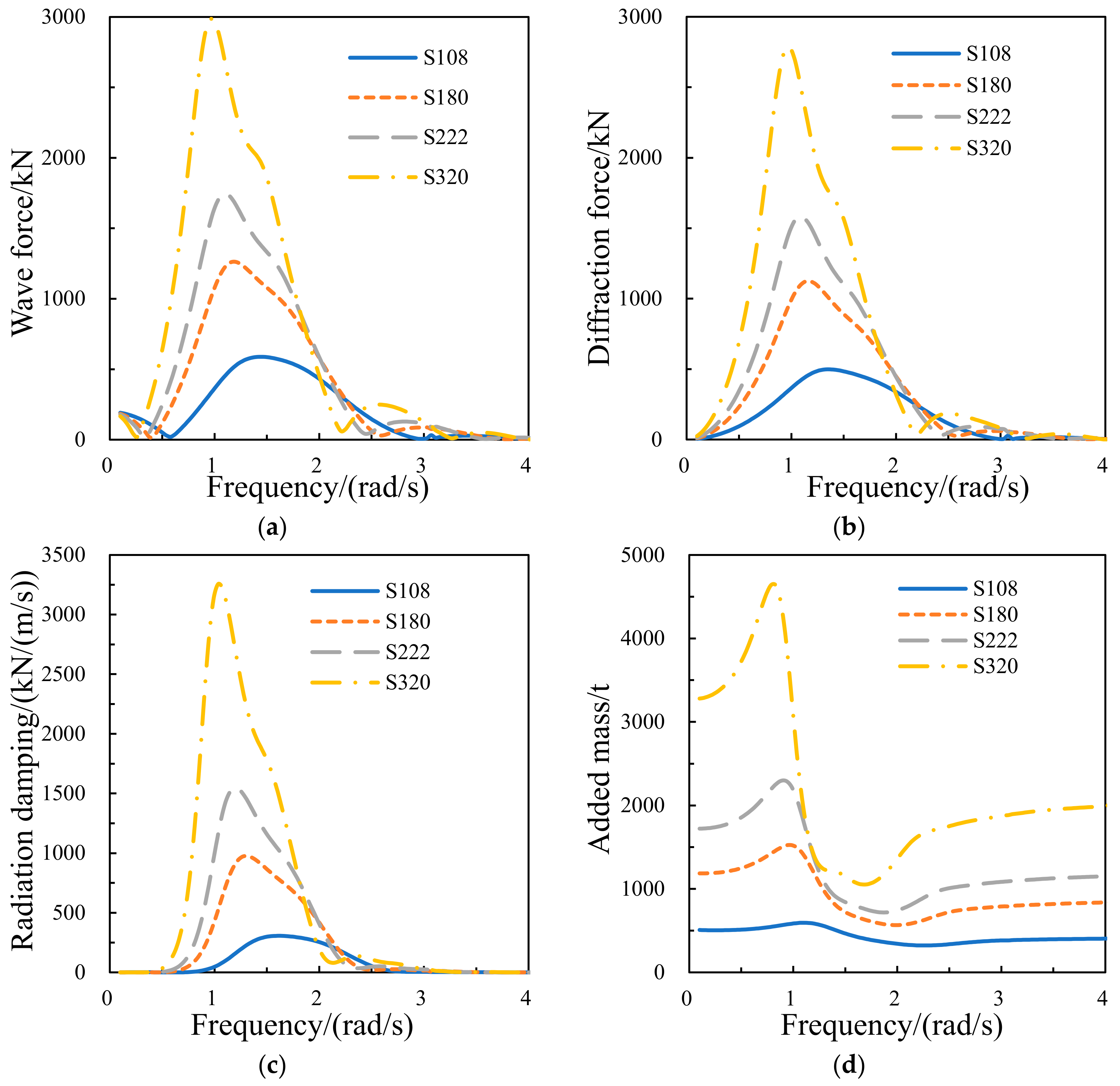
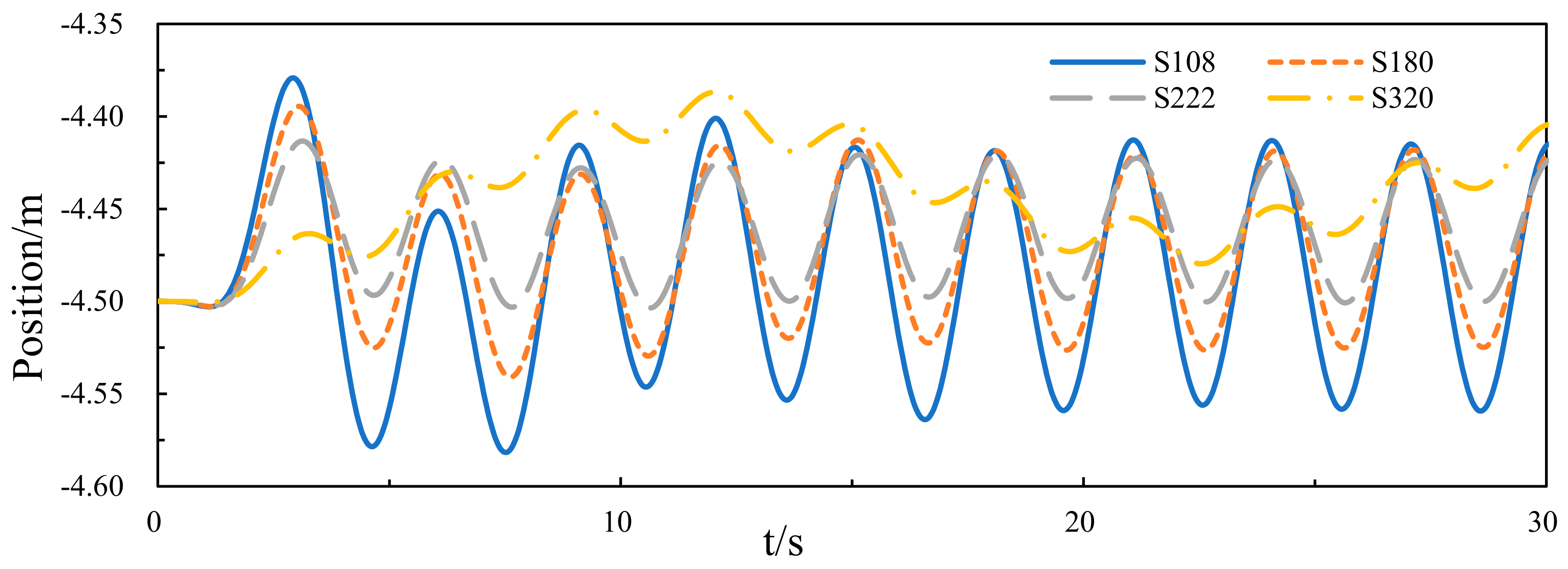
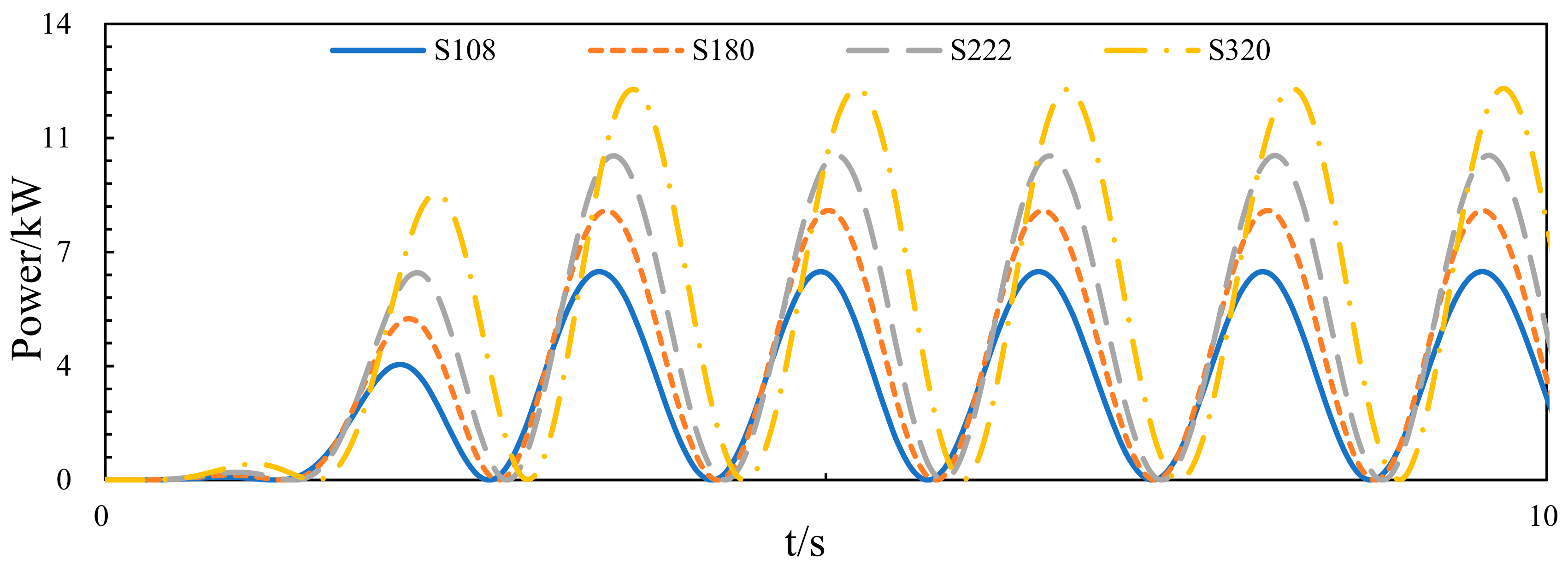
3.2. Numerical Results at Different Areas of the Damping Layer
3.2.1. Hydrodynamic Performance of the Central Platform
3.2.2. Wave Energy Capture Width Ratio of the Device
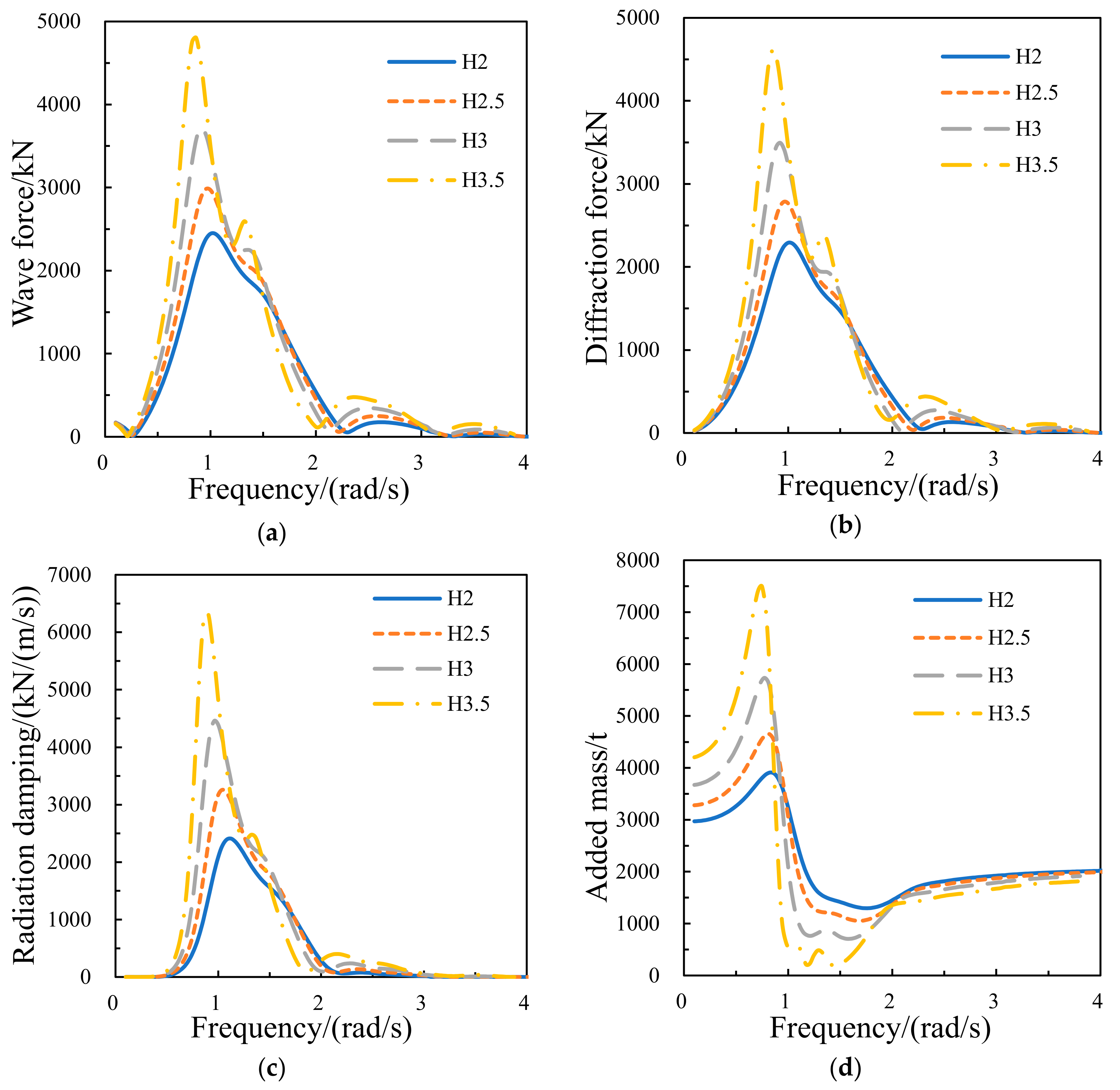
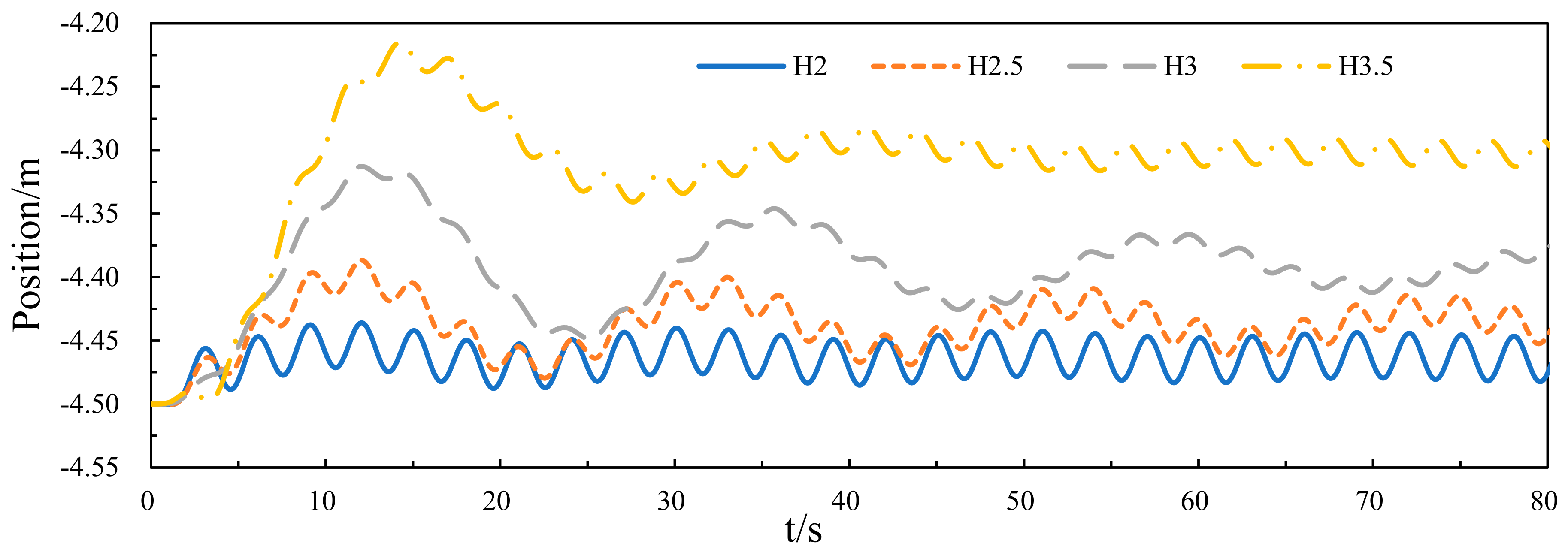
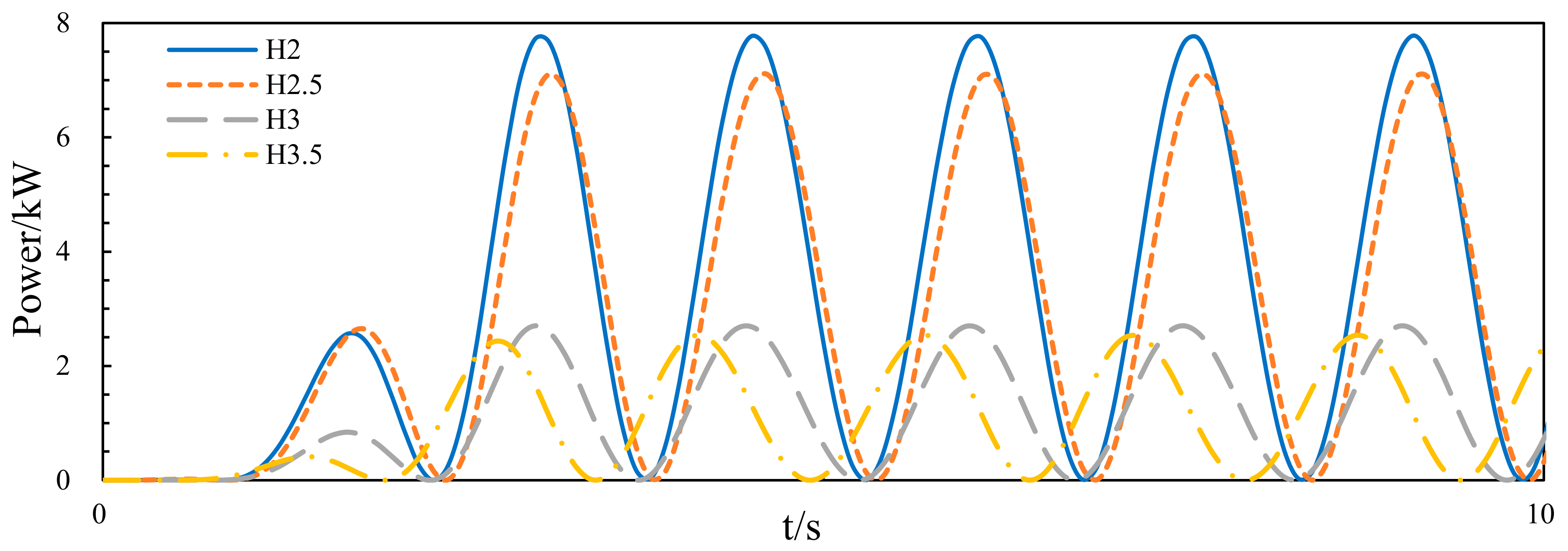
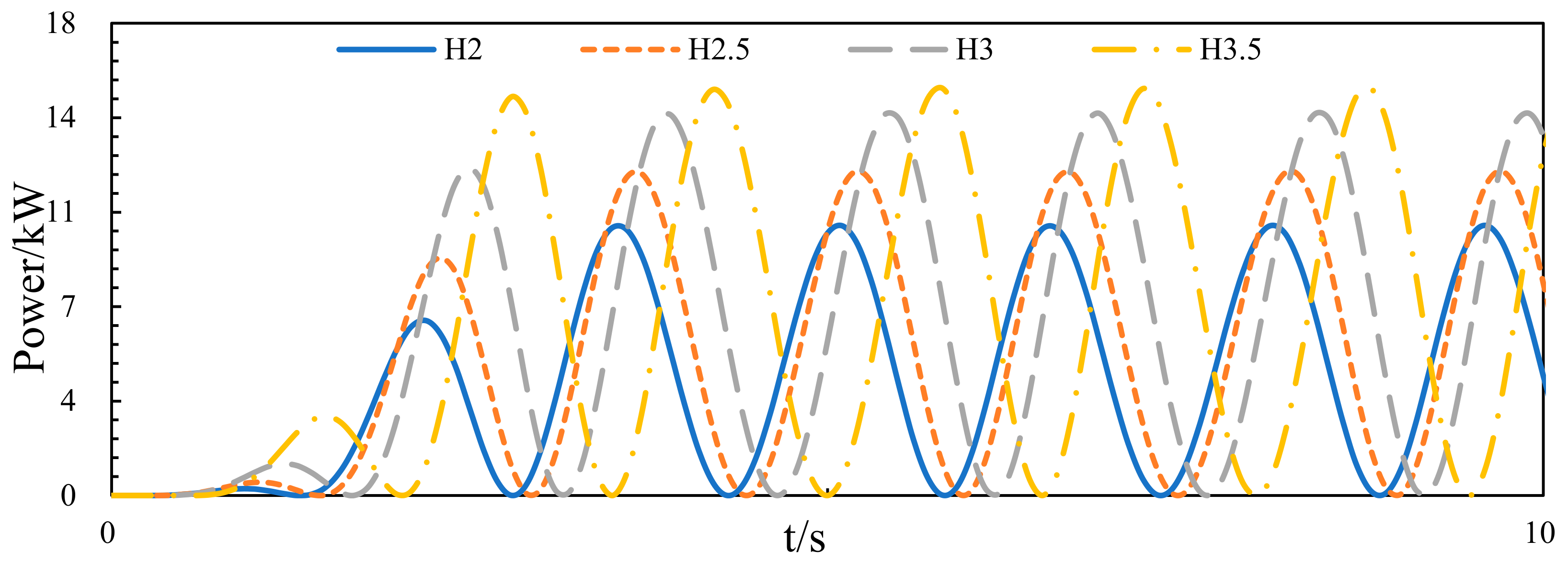
3.3. Numerical Results at Different Heights of the Damping Layer
3.3.1. Hydrodynamic Performance of the Central Platform
3.3.2. Wave Energy Capture Width Ratio of the Device
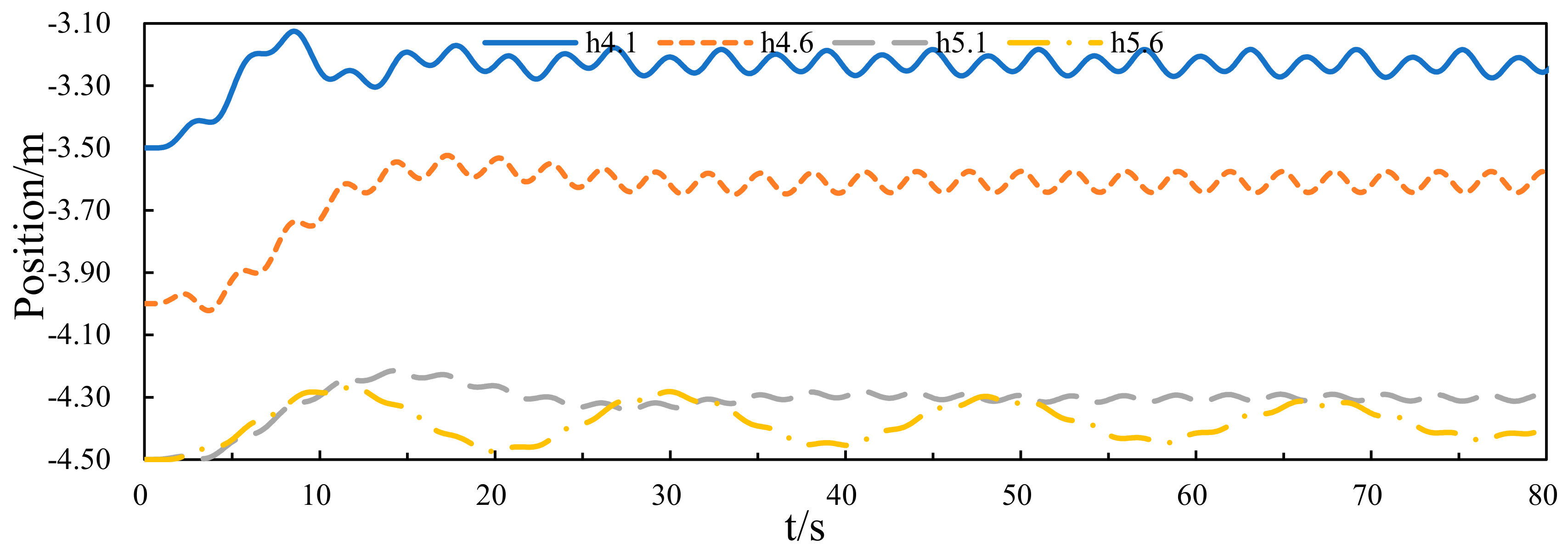
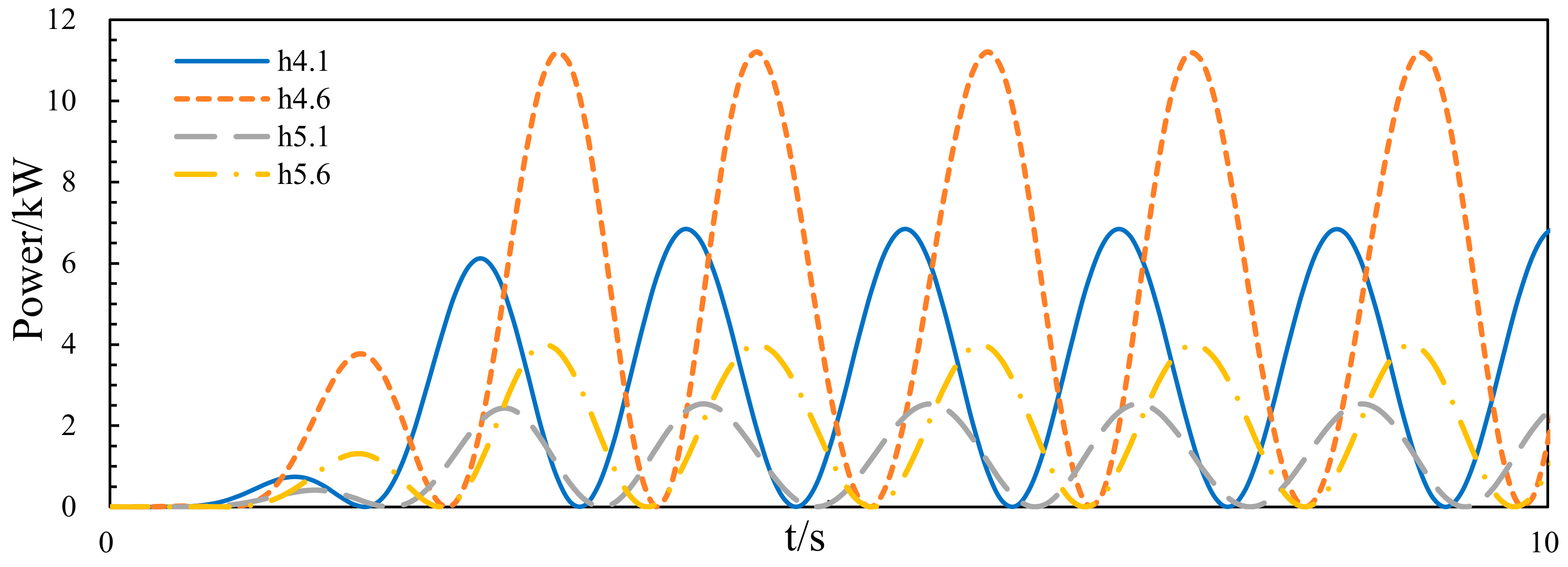
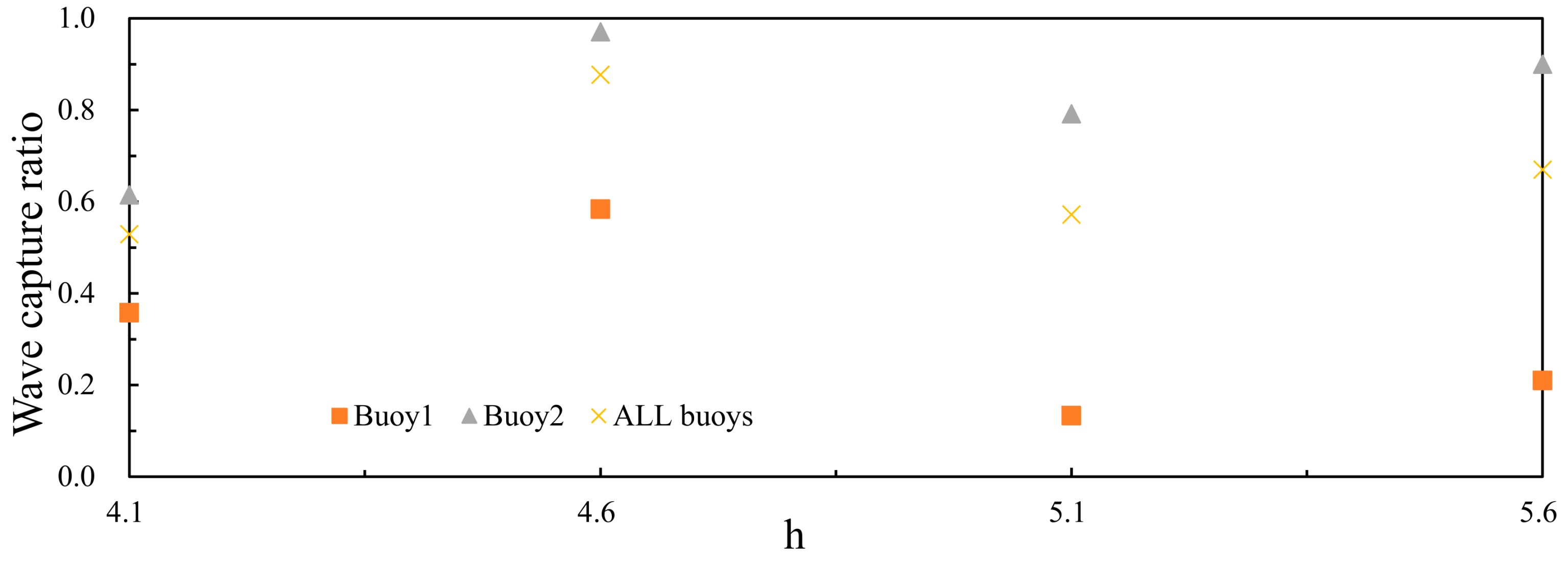
3.4. Numerical Results at Different Drafts of the Damping Layer
3.4.1. Hydrodynamic Performance of the Central Platform
3.4.2. Wave Energy Capture Width Ratio of the Device
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- There exists a relationship between the hydrodynamic performance of the WEC and the geometry of central platform.
- (2)
- For a certain wave condition, there exists an optimal geometry of the central platform. At the wave condition mentioned in the paper, when the aspect ratio of the damping layer is 0.45, the area of the damping layer is 320 m2 and the height of the damping layer is 3.5 m, the wave energy capture width ratio of the WEC is better, so that more wave energy can be extracted from the ocean.
- (3)
- It is found that increasing the draft of the central platform is conducive to improving the wave energy capture width ratio of the WEC, and in this paper, the wave energy capture width ratio of the WEC is the largest when the draft of the central platform is 4.6 m.
- (4)
- Further related research should be carried out in a physical prototype test and focused on fluid analysis of the central platform, to find out the influence of different shaped platforms on wave distribution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.G.; Isberga, J. Review of control strategies for wave energy conversion systems and their validation, the wave-to-wire approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khana, N.; Kalaira, A.; Haiderc, N.A. Review of ocean tidal, wave and thermal energy technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 72, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H. Marine renewable energy in the Mediterranean Sea: Status and perspectives. Energies 2017, 10, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; He, H.Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. Dynamic properties and energy conversion efficiency of a floating multi-body wave energy converter. China Ocean Eng. 2017, 3, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Marquis, H.; Frigaard, P. Performance evaluation of the Wavestar prototype. In Proceedings of the 9th European Wave and Tidal Conference (EWTEC), Southampton, UK, 5–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, R.H.; Kramer, M.; Vida, E. Discrete displacement hydraulic power take-off system for the Wavestar WEC. Energies 2013, 6, 4001–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambühl, S.; Kramer, M.; Sørensen, J.D. Reliability-based structural optimization of WECs. Energies 2014, 7, 8178–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.H.; He, H.Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H. Design and experimental study of raft array type wave energy generating system. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 11, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Yang, S.H.; He, H.Z.; Zhang, J.; Li., H. Modeling and simulation analysis of array type wavy energy generator. Ocean Eng. 2017, 2, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, K.L.; Wang, Z.P.; Lin, H.J.; Ye, Y. Research on the wave energy generating device of Eagle1. Ship Eng. 2015, 9, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, K.L.; Lin , H.J.; Wang, W.S.; Chen, A. Overview of the overall design of the Eagle device Wanshan. Ship Eng. 2015, 37, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.S.; Sheng, S.Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y. Frequency domain motion analysis and optimization design of eagle1 wave energy device. Ocean Technol. 2018, 2, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, K.L.; Ye, Y.; You, Y. Research on generation system of eagle wave energy generator. Renew. Energy Resour. 2015, 9, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Sheng, S.W.; You, Y.G.; Huang, Z.X.; Wang, W.S. Study of hydrodynamic characteristics of a sharp eagle WEC. China Ocean Eng. 2017, 3, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Lin, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; You, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, A.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Ye, Y. Model research and open sea tests of 100 kW wave energy convertor sharp eagle Wanshan. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, S.H.; He, H.Z.; Chen, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, D. Hydrodynamic performance analysis of semi-submersible multi-body wave power plant. J. Ocean Eng. 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sheng, W.A. Numerical study on the dynamics of a two-raft wave energy conversion device. J. Fluids Struct. 2015, 58, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babarit, A.; Hals, J.; Muliawan, M.J.; Kurniawan, A.; Moan, T.; Krokstad, J. Numerical benchmarking study of a selection of wave energy converteors. Renew. Energy 2012, 41, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babarit. A database of capture width ratio of WECs. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 610–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferys, E.R. Device characterization. In Power from Sea Waves; Count, B., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1980; pp. 413–438. [Google Scholar]
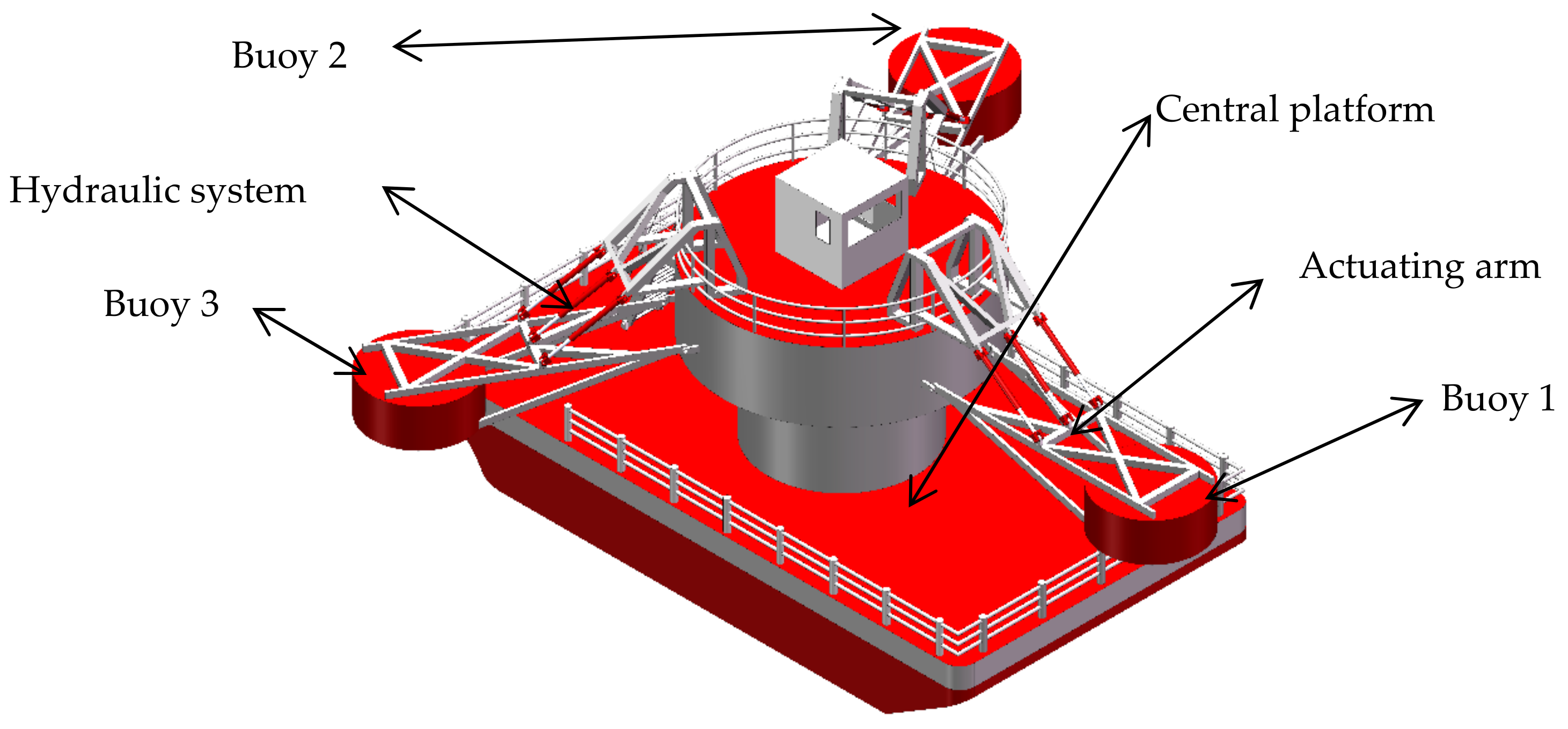
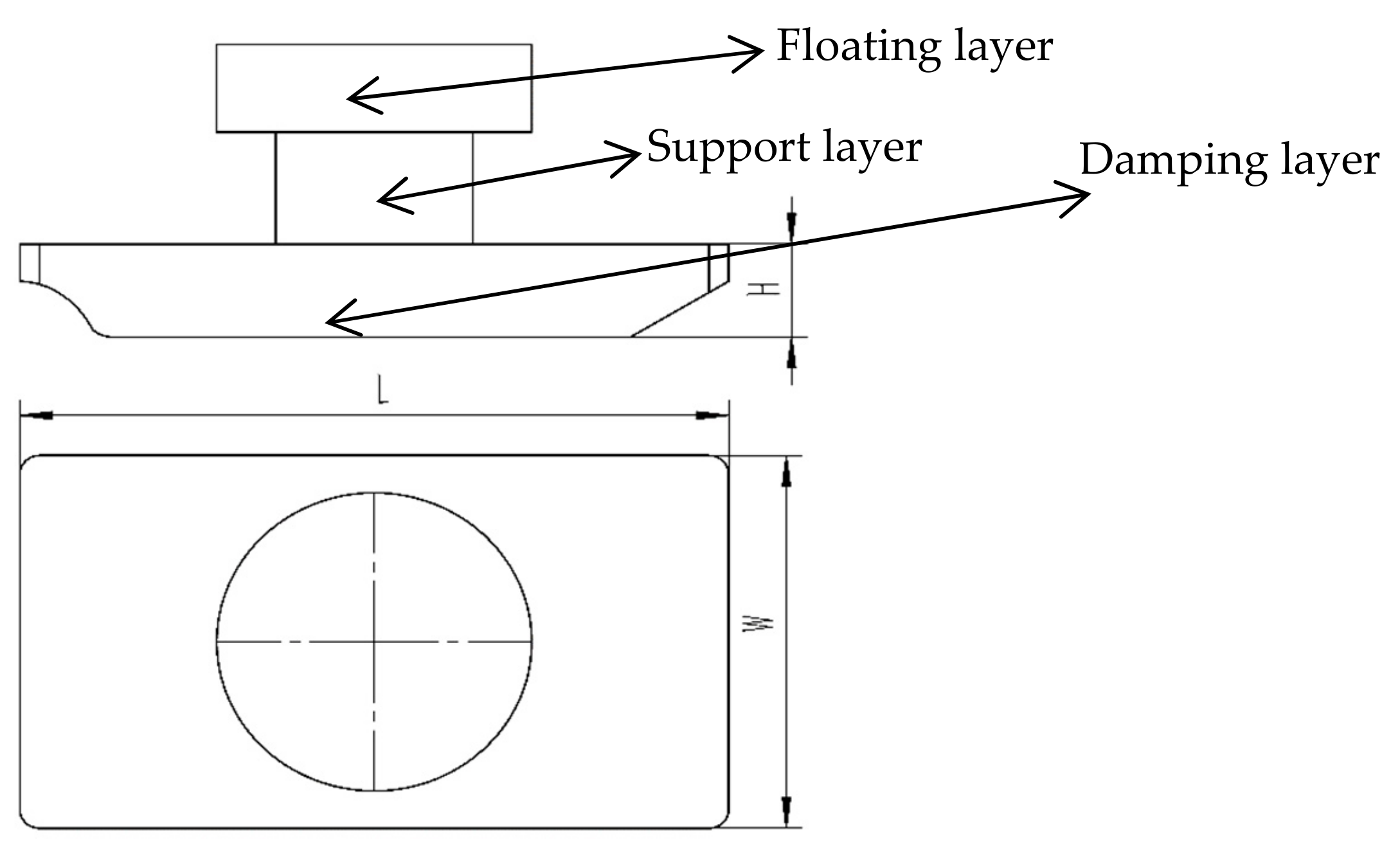
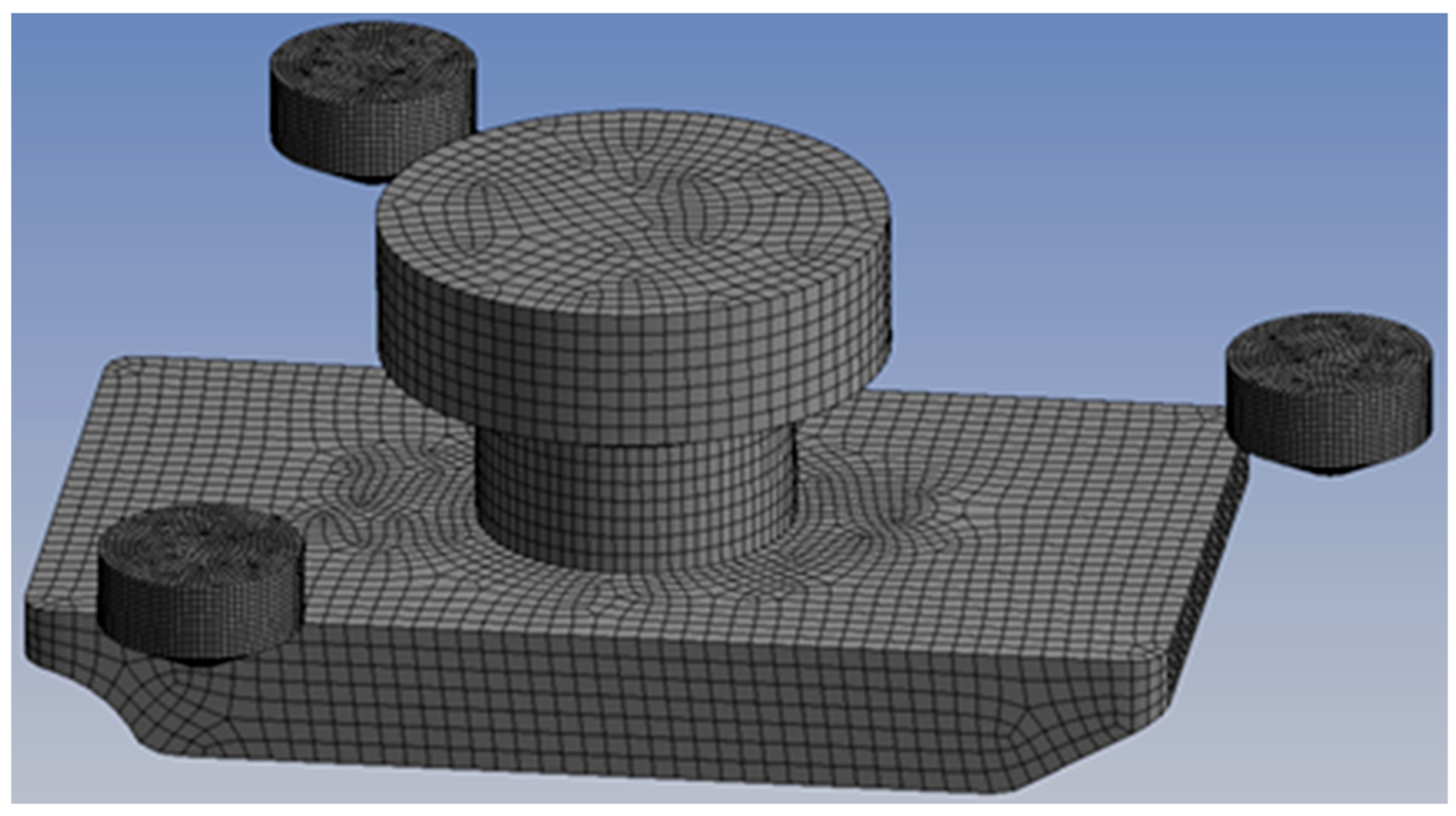






| Designation | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Molded length | 18 m |
| Molded width | 10 m |
| Molded height | 2.5 m |
| Diameter of buoy | 3.2 m |
| Height of buoy | 2 m |
| Draft depth of the device | 5.1 m |
| B | L/W (m) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 13.4/13.4 |
| 1.25 | 15/12 |
| 1.8 | 18/10 |
| 2.22 | 20/9 |
| 2.69 | 22/8.18 |
| S (m2) | LW (m) |
|---|---|
| 108 | 7 × 5.56 |
| 180 | 9 × 20 |
| 222 | 10 × 22.2 |
| 320 | 12 × 26.67 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Yang, S.; He, H.; Chen, H. Influence of Central Platform on Hydrodynamic Performance of Semi-Submerged Multi-Buoy Wave Energy Converter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8010012
Hu Y, Yang S, He H, Chen H. Influence of Central Platform on Hydrodynamic Performance of Semi-Submerged Multi-Buoy Wave Energy Converter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yuan, Shaohui Yang, Hongzhou He, and Hu Chen. 2020. "Influence of Central Platform on Hydrodynamic Performance of Semi-Submerged Multi-Buoy Wave Energy Converter" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8010012
APA StyleHu, Y., Yang, S., He, H., & Chen, H. (2020). Influence of Central Platform on Hydrodynamic Performance of Semi-Submerged Multi-Buoy Wave Energy Converter. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8010012




