Investigating the Erosion Resistance of Different Vegetated Surfaces for Ecological Enhancement of Sea Dikes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Vegetated Clay Layers as Dike Cover
1.2. Erosion on the Seaward Dike Slope Due to Wave Impacts
1.3. Erosion on the Landward Dike Slope Due to Wave Overtopping and Overflow
1.4. Research Aims and Overall Research Methodology
2. Materials and Methods
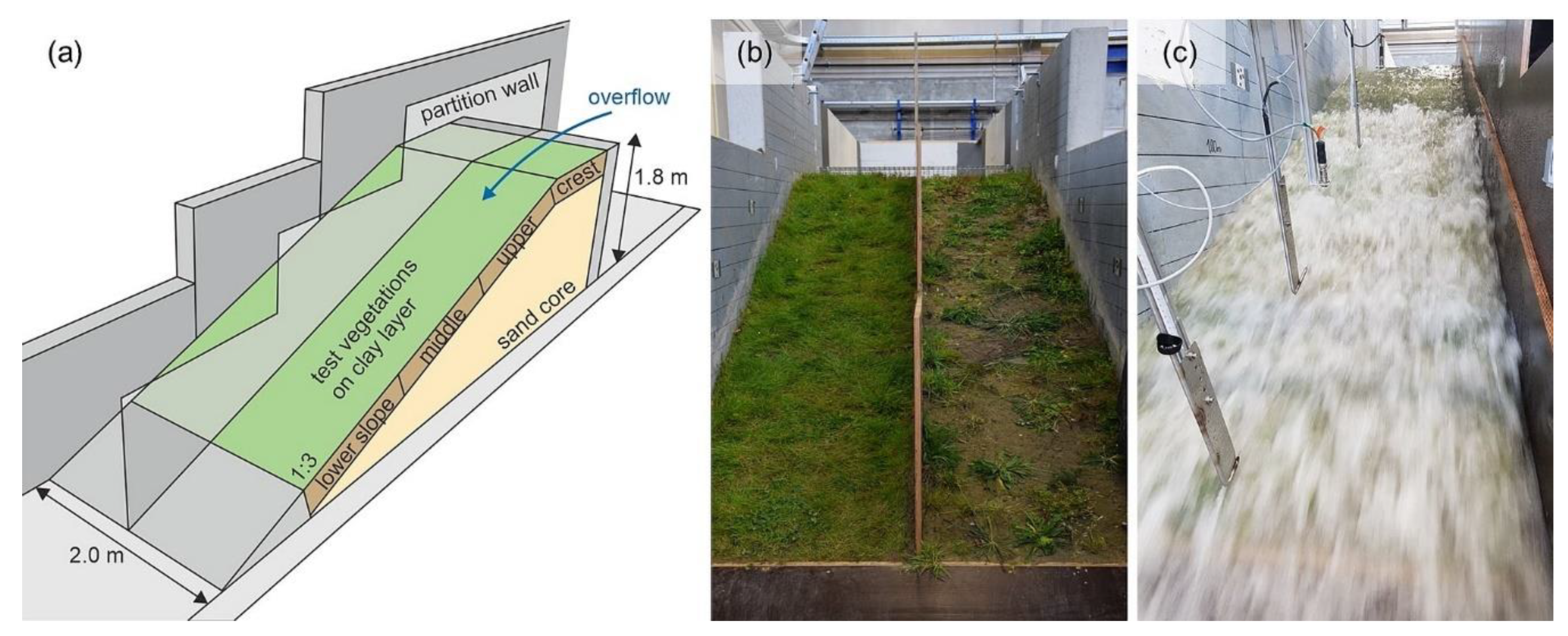
2.1. Test Vegetations and Botanical Analyses
2.2. Wave Impact Simulations
2.3. Overflow Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Vegetation Establishment
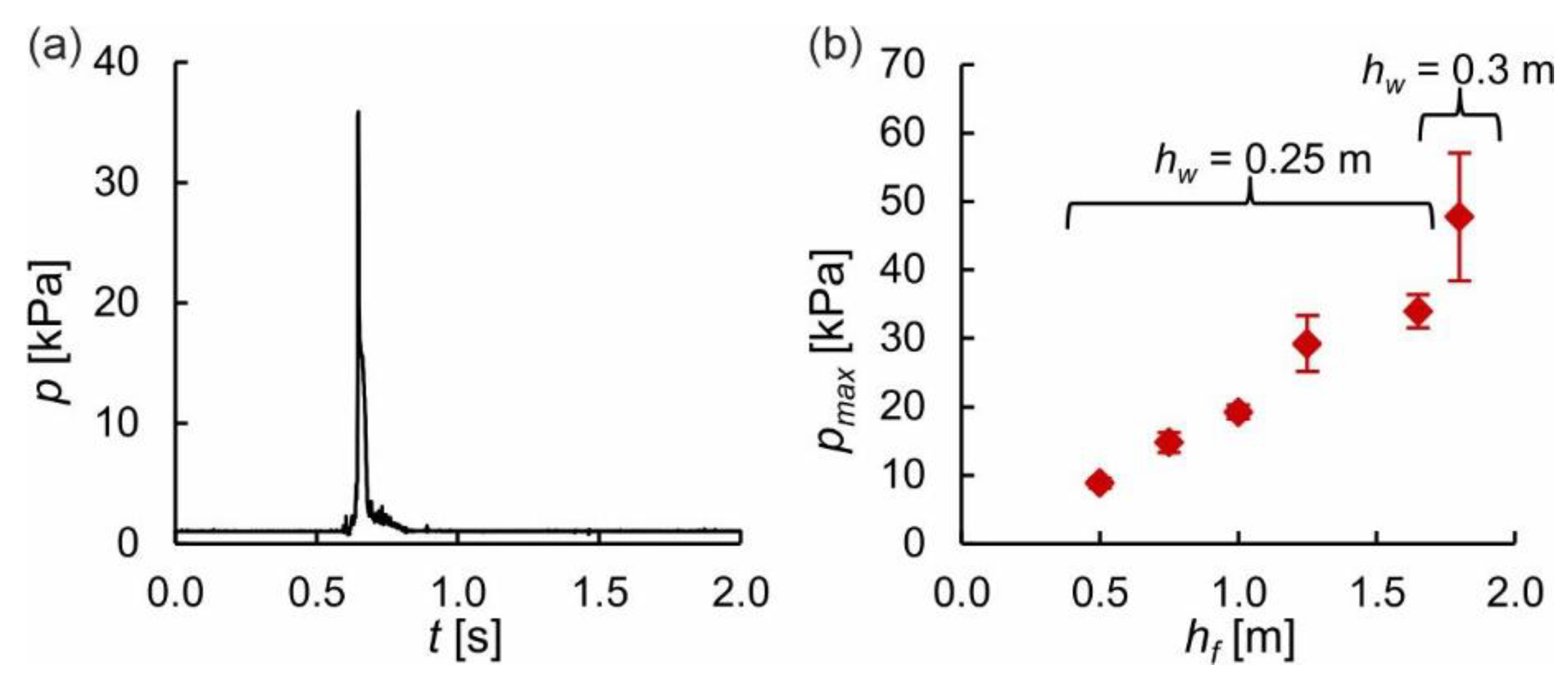
3.2. Wave Impact Simulations
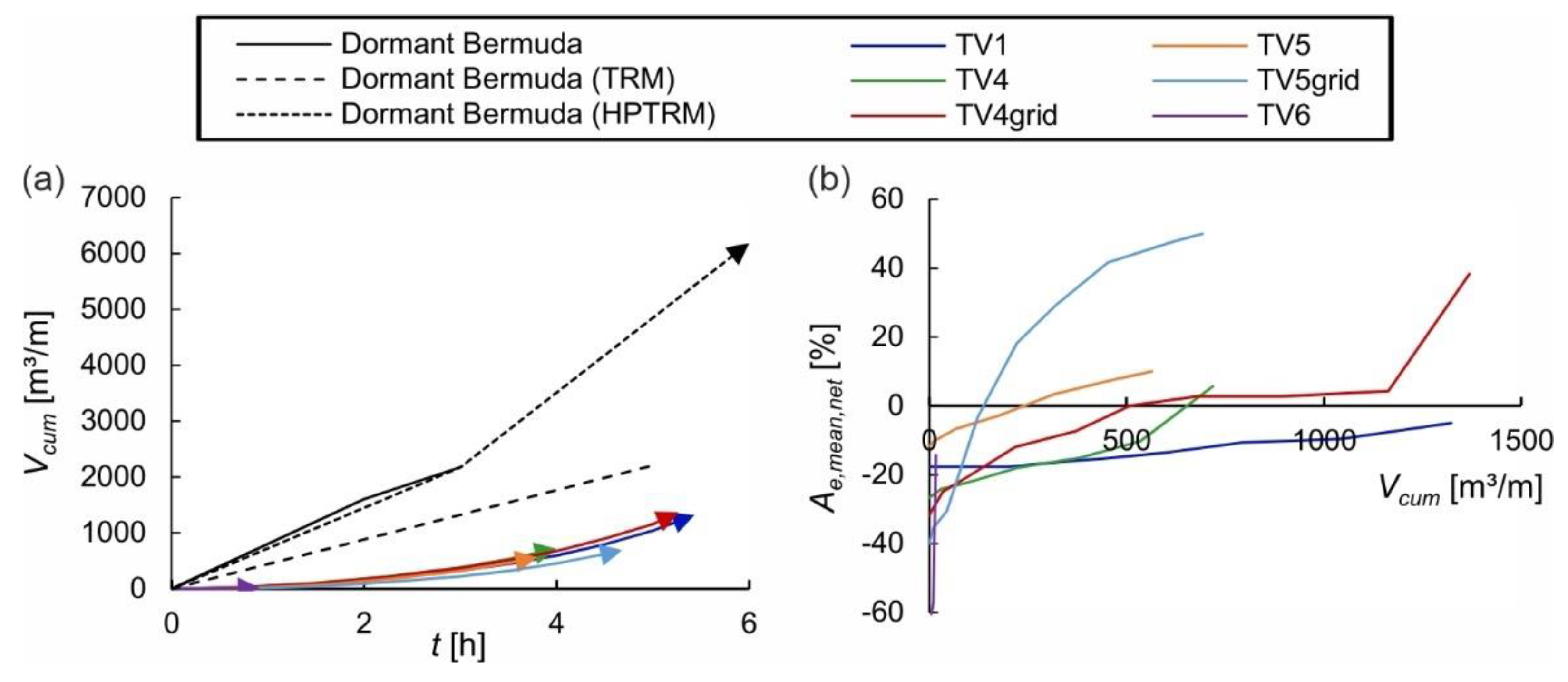
3.2.1. Erosion Patterns
3.2.2. Analysis
3.2.3. Discussion of the Methodology and Results of the Wave Impact Simulations
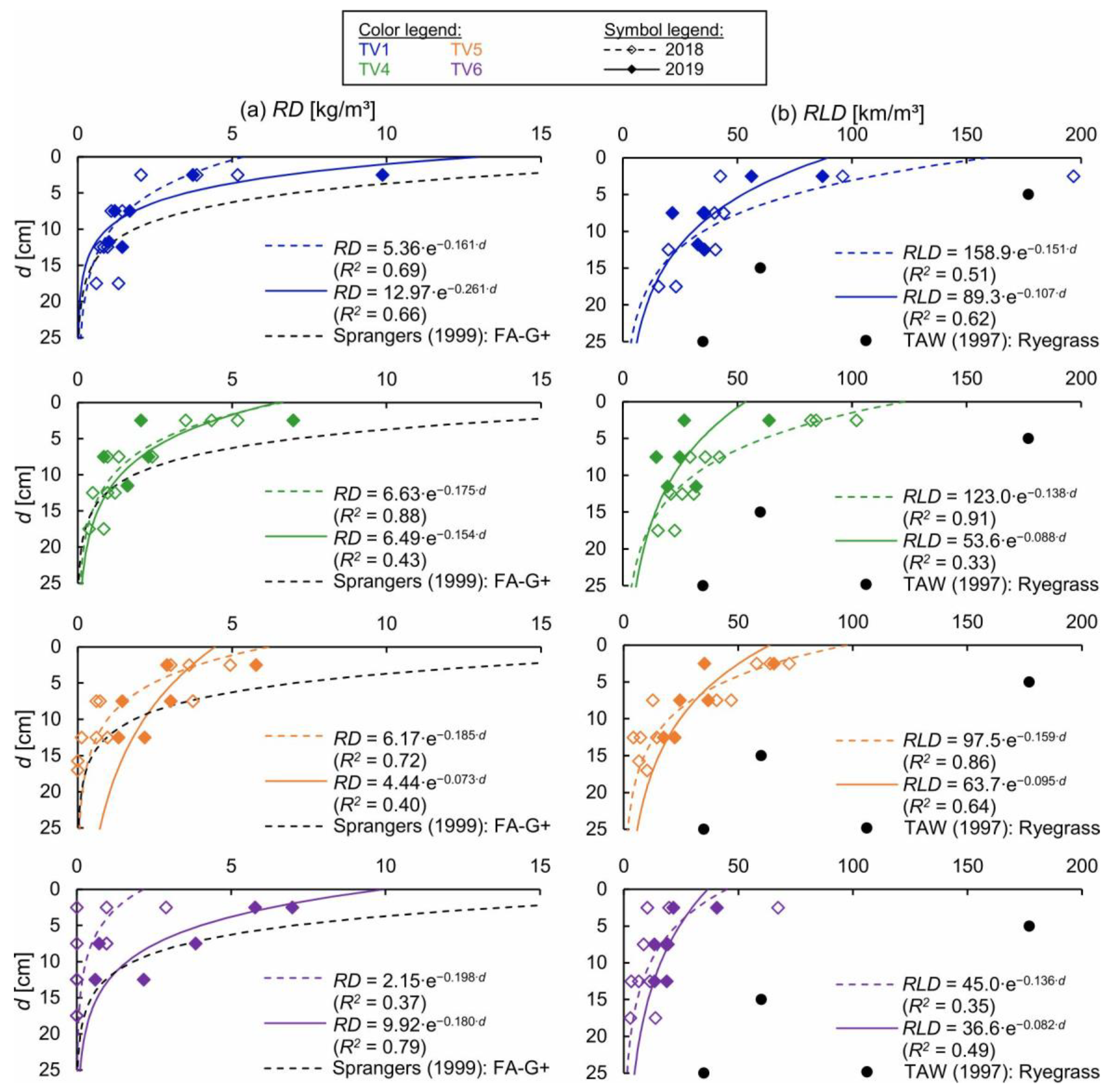
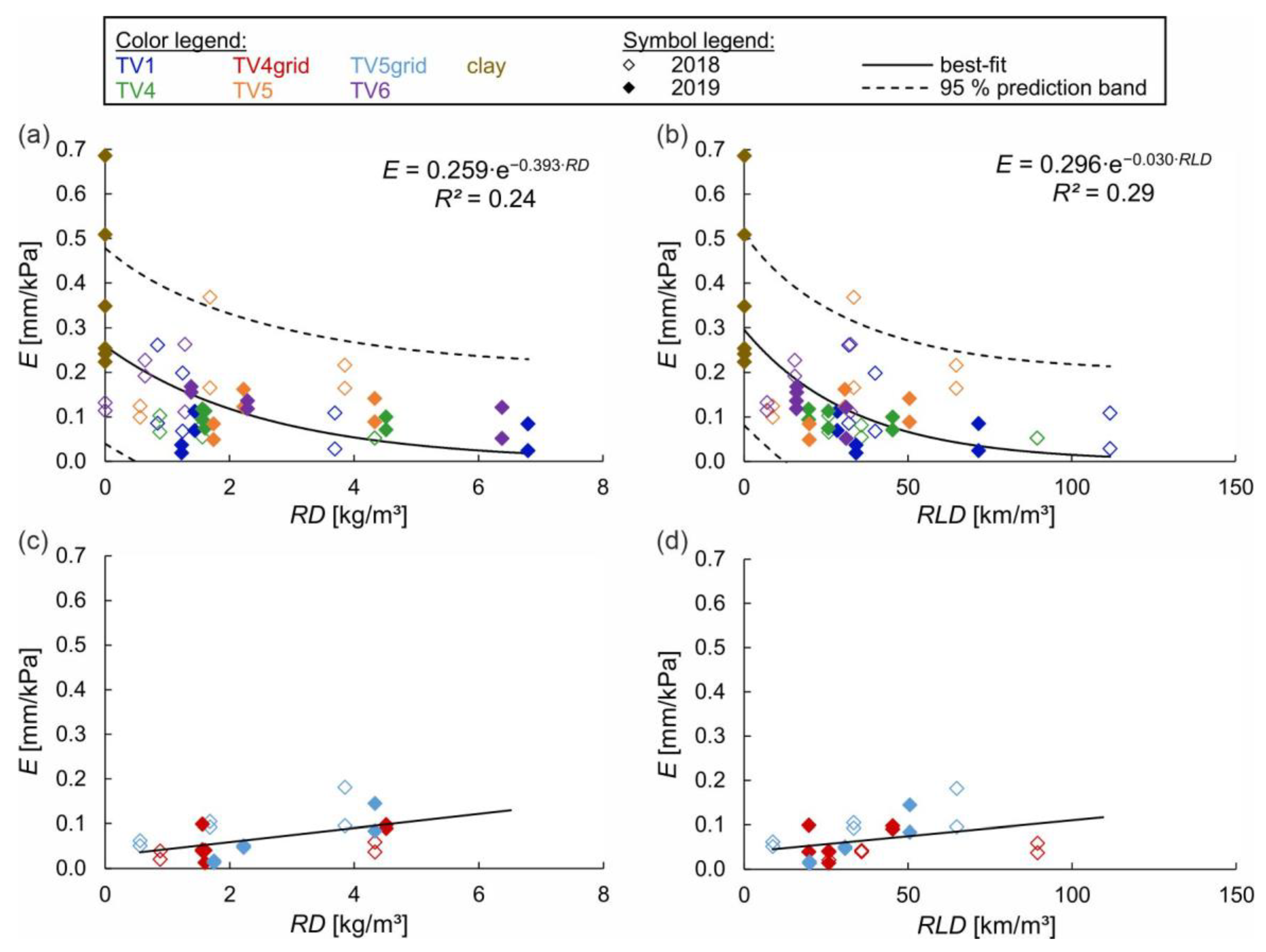
3.3. Overflow Simulations
3.3.1. Erosion Patterns
3.3.2. Analysis
3.3.3. Discussion of the Methodology and Results of the Overflow Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. 2019. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/ (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Dangendorf, S.; Hay, C.; Calafat, F.M.; Marcos, M.; Piecuch, C.G.; Berk, K.; Jensen, J. Persistent acceleration in global sea-level rise since the 1960s. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arns, A.; Wahl, T.; Dangendorf, S.; Jensen, J. The impact of sea level rise on storm surge water levels in the northern part of the German Bight. Coast. Eng. 2015, 96, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chini, N.; Stansby, P.; Leake, J.; Wolf, J.; Roberts-Jones, J.; Lowe, J. The impact of sea level rise and climate change on inshore wave climate: A case study for East Anglia (UK). Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, A.; Dangendorf, S.; Jensen, J.; Talke, S.; Bender, J.; Pattiaratchi, C. Sea-level rise induced amplification of coastal protection design heights. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vriend, H.J.; van Koningsveld, M.; Aarninkhof, S.G.J.; de Vries, M.B.; Baptist, M.J. Sustainable hydraulic engineering through building with nature. J. Hydro Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, S.; Meire, P.; Bouma, T.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Ysebaert, T.; de Vriend, H.J. Ecosystem-based coastal defence in the face of global change. Nature 2013, 504, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton-Grier, A.E.; Gittman, R.K.; Arkema, K.K.; Bennett, R.O.; Benoit, J.; Blitch, S.; Burks-Copes, K.A.; Colden, A.; Dausman, A.; DeAngelis, B.M.; et al. Investing in natural and nature-based infrastructure: Building better along our coasts. Sustainability 2018, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Jones, C.; Byers, J.E.; Arkema, K.; Berkenbusch, K.; Commito, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Hacker, S.; Lambrinos, J.; Hendriks, I.E.; et al. Physical ecosystem engineers and the functioning of estuaries and coasts. In Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science; Wolanski, E., McLusky, D.S., Eds.; Elsevier/Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 53–81. ISBN 978-0-12-374711-2. [Google Scholar]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.; Beck, M.W.; Reguero, B.G.; Losada, I.J.; van Wesenbeeck, B.; Pontee, N.; Sanchirico, J.N.; Ingram, J.C.; Lange, G.-M.; Burks-Copes, K.A. The effectiveness, costs and coastal protection benefits of natural and nature-based defences. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoonees, T.; Gijón Mancheño, A.; Scheres, B.; Bouma, T.J.; Silva, R.; Schlurmann, T.; Schüttrumpf, H. Hard structures for coastal protection, towards greener designs. Estuaries Coasts 2019, 42, 1709–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, E.M.A.; Olabarria, C.; Mayer-Pinto, M.; Cumbo, V.; Morris, R.L.; Bugnot, A.B.; Dafforn, K.A.; Heery, E.; Firth, L.B.; Brooks, P.R.; et al. Eco-engineering urban infrastructure for marine and coastal biodiversity: Which interventions have the greatest ecological benefit? J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 55, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.E.; Herbert, R.J.H.; Britton, J.R.; Hull, S.L. Ecological enhancement techniques to improve habitat heterogeneity on coastal defence structures. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 210, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, T.A.; Alias, N.A.; Ghazali, A.H.; Jaafar, M.S. Evaluation of environmental and hydraulic performance of bio-composite revetment blocks. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 2, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheres, B.; Schüttrumpf, H. Enhancing the ecological value of sea dikes. Water 2019, 11, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CIRIA. The International Levee Handbook; Construction Industry Research and Information Association (CIRIA): London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-0-86017-734-0. [Google Scholar]
- EAK. Empfehlungen für Küstenschutzwerke: Korrigierte Ausgabe 2007. In Die Küste; Kuratorium für Forschung im Küsteningenieurwesen, Ed.; Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau (BAW): Karlsruhe, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Führböter, A.; Dette, H.H.; Grüne, J. Response of Sea Dykes Due to Wave Impacts. Coastal Engineering 1976. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Honolulu, HI, USA, 11–17 July 1976; American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1977; pp. 2604–2622. ISBN 9780872620834. [Google Scholar]
- Witte, H.-H.R. Druckschlagbelastung durch Wellen in deterministischer und stochastischer Betrachtung. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Carolo-Wilhelmina zu Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bölke, S.; Relotius, P.C. Über die wellenerzeugten Druckschlagbelastungen von Seedeichen im Böschungsbereich zwischen 1:4 und 1:6. In Mitteilungen Leichtweiss-Institut für Wasserbau der Technischen Universität Braunschweig; Leichtweiß-Institut für Wasserbau: Braunschweig, Germany, 1974; pp. 358–388. [Google Scholar]
- Führböter, A.; Sparboom, U. Shock Pressure Interactions on Prototype Sea Dykes Caused by Breaking Waves. In Proceedings of the SOWAS’88 (Modelling Soil-Water-Structure Interactions), Delft, The Netherlands, 29 August–2 September 1988; pp. 243–252, ISBN 90.6191.8154. [Google Scholar]
- Stive, R.J.H. Wave impact on uniform steep slopes at approximately prototype scale. In Symposium on Scale Effects in Modelling Hydraulic Structures; IAHR: Esslingen, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Technical Advisory Committee for Flood Defence (TAW). Erosion Resistance of Grassland as Dike Covering; Technical Report; TAW: Delft, The Netherlands, 1997.
- Piontkowitz, T. EroGRASS. Failure of Grass Cover Layers at Seaward and Shoreward Dike Slopes. Performance, Results and Conclusions. 2012. Available online: http://www.masterpiece.dk/UploadetFiles/10852/36/EroGrassreportB.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2020).
- Smith, G.M.; Seijffert, J.W.W.; van der Meer, J.W. Erosion and overtopping of grass dike large scale model tests. Coast. Eng. 1994, 2639–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Seijffert, J.W.; Verheij, H. Grass covers and reinforcement measures. In Dikes and Revetments: Design, Maintenance and Safety Assessment; Pilarczyk, K.W., Ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 289–302. ISBN 9781315141329. [Google Scholar]
- van Steeg, P.; Klein Breteler, M.; Labrujere, A. Use of wave impact generator and wave flume to determine strength of outer slopes of grass dikes under wave loads. Int. Conf. Coast. Eng. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewlett, H.W.M.; Boorman, L.A.; Bramley, L.A. Design of Reinforced Grass Waterways; Construction Industry Research and Information Association (CIRIA): London, UK, 1987; ISBN 9780860172857. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer, J.W.; Allsop, N.W.H.; Bruce, T.; de Rouck, J.; Kortenhaus, A.; Pullen, T.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Troch, P.; Zanuttigh, B. EurOtop. Manual on Wave Overtopping of Sea Defences and Related Structures. An Overtopping Manual Largely Based on European Research, but for Worldwide Application. 2018. Available online: www.overtopping-manual.com (accessed on 31 May 2020).
- Van der Meer, J.; Schrijver, R.; Hardeman, B.; van Hoven, A.; Verheij, H.; Steendam, G.J. Guidance on Erosion Resistance of Inner Slopes of Dikes from Three Years of Testing with the Wave Overtopping Simulator. In Coasts, Marine Structures and Breakwaters: Adapting to Change; Allsop, W., Ed.; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2010; pp. 460–473. ISBN 0-7277-4159-4. [Google Scholar]
- Trung, L.H. Overtopping on Grass Covered Dikes: Resistance and Failure of the Inner Slopes. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Le, H.T.; Verhagen, H.J.; Vrijling, J.K. Damage to grass dikes due to wave overtopping. Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 849–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.G.; Rosati, J.D.; Walton, T.L.; Edge, B.L. Erosional equivalences of levees: Steady and intermittent wave overtopping. Ocean Eng. 2010, 37, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; Thornton, C. Tolerable time-varying overflow on grass-covered slopes. JMSE 2015, 3, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Meer, J.W.; Hardeman, B.; Steendam, G.J.; Schuttrumpf, H.; Verheij, H. Flow depths and velocities at crest and landward slope of a dike, in theory and with the wave overtopping simulator. Int. Conf. Coastal. Eng. 2010, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Damme, M.; Ponsioen, L.; Herrero, M.; Peeters, P.; Lang, M.; Klijn, F.; Samuels, P. Comparing overflow and wave-overtopping induced breach initiation mechanisms in an embankment breach experiment. In Proceedings of the FLOODrisk 2016—3rd European Conference on Flood Risk Management, Lyon, France, 17–21 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ponsioen, L.; van Damme, M.; Hofland, B.; Peeters, P. Relating grass failure on the landside slope to wave overtopping induced excess normal stresses. Coast. Eng. 2019, 148, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VTV. Voorschrift Toetsen op Veiligheid Primaire Waterkeringen; Ministerie van Verkeer en Waterstaat: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 978-90-369-5762-5.
- Thornton, C.; Hughes, S.; Scholl, B.; Youngblood, N. Estimating grass slope resiliency during wave overtopping: Results from full-scale overtopping simulator testing. Int. Conf. Coast. Eng. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vannoppen, W.; Vanmaercke, M.; de Baets, S.; Poesen, J. A review of the mechanical effects of plant roots on concentrated flow erosion rates. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 150, 666–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graunke, A.; Wrage-Mönnig, N. Grüne Seedeiche für den Küstenschutz. In Leistungen von Gras und Klee-Gras auf Acker und Grünland, Proceedings of the 62. Jahrestagung der AGGF 2018 in Kiel, Germany, 30 August–1 September 2018; Institut für Pflanzenbau und Pflanzenzüchtung, Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel: Kiel, Germany, 2018; pp. 95–99. ISBN 978-3-00-060516-1. [Google Scholar]
- Berendse, F.; van Ruijven, J.; Jongejans, E.; Keesstra, S. Loss of plant species diversity reduces soil erosion resistance. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheres, B.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Felder, S. Flow resistance and energy dissipation in supercritical air-water flows down vegetated chutes. Water Resour. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehlker, H. Eine Hilfstafel zur Schätzung von Deckungsgrad und Artmächtigkeit. In Mitteilungen der Florist.-Soziol. Arbeitsgemeinschaft NF; Floristisch-soziologischen Arbeitsgemeinschaft e.V.: Göttingen, Germany, 1977; Volume 19, pp. 427–429. [Google Scholar]
- Lobet, G.; Pagès, L.; Draye, X. A novel image-analysis toolbox enabling quantitative analysis of root system architecture. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanczak, G. Breaching of Sea Dikes Initiated from the Seaside by Breaking Wave Impacts. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany, University of Florence, Florence, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Führböter, A. Model and prototype tests for wave impact and run-up on a uniform 1:4 slope. Coast. Eng. 1986, 10, 49–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprangers, H. Vegetation Dynamics and Erosion Resistance of Sea Dyke Grassland. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]








| Erosion Model | Notation |
|---|---|
| Seijffert and Verheij (1998) [27] | E: erosion rate (mm/h) cE: erosion coefficient (1/(ms)), see [27] HS: significant wave height (m) |
| van Steeg et al. (2015) [28] | E: erosion rate (mm/h or m²/h) ax: erosion coefficient (mm/(hm) or m²/(hm)), see [28] HS: significant wave height (m) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scheres, B.; Schüttrumpf, H. Investigating the Erosion Resistance of Different Vegetated Surfaces for Ecological Enhancement of Sea Dikes. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070519
Scheres B, Schüttrumpf H. Investigating the Erosion Resistance of Different Vegetated Surfaces for Ecological Enhancement of Sea Dikes. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(7):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070519
Chicago/Turabian StyleScheres, Babette, and Holger Schüttrumpf. 2020. "Investigating the Erosion Resistance of Different Vegetated Surfaces for Ecological Enhancement of Sea Dikes" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 7: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070519
APA StyleScheres, B., & Schüttrumpf, H. (2020). Investigating the Erosion Resistance of Different Vegetated Surfaces for Ecological Enhancement of Sea Dikes. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(7), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070519






