Effects of Glyphosate-Based and Derived Products on Sea Urchin Larval Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Adult Specimens
2.2. Experimental Conditions Tested
2.3. Gamete Preparation and Larval Exposure
2.4. Larval Development and Growth Assessment
2.5. Respiration Rate
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Larval Development, Abnormalities and Growth
3.2. Respiration Rate
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tijani, J.O.; Fatoba, O.O.; Babajide, O.O.; Petrik, L.F. Pharmaceuticals, endocrine disruptors, personal care products, nanomaterials and perfluorinated pollutants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Poi, C.; Evariste, L.; Serpentini, A.; Halm-Lemeille, M.P.; Lebel, J.M.; Costil, K. Toxicity of five antidepressant drugs on embryo–larval development and metamorphosis success in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 13302–13314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V.; Fabrello, J.; Marin, M.G. The effects of glyphosate and its commercial formulations to marine invertebrates: A review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, K.E.; Thomas, S.M.; Bodour, A.A. Prioritizing research for trace pollutants and emerging contaminants in the freshwater environment. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3462–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M. Global change ecotoxicology: Identification of early life history bottlenecks in marine invertebrates, variable species responses and variable experimental approaches. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 76, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. Why are Early Life Stages of Aquatic Organisms More Sensitive to Toxicants than Adults? In New Insights into Toxicity and Drug Testing; InTech Open: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gosselin, L.A.; Qian, P.Y. Juvenile mortality in benthic marine invertebrates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 146, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilo, T.; Zygier, L.; Rubin, B.; Wolf, S.; Eizenberg, H. Mechanism of glyphosate control of Phelipanche aegyptiaca. Planta 2016, 244, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbrunn, E.; Eschenburg, S.; Shuttleworth, W.A.; Schloss, J.V.; Amrhein, N.; Evans, J.N.S.; Kabsch, W. Interaction of the herbicide glyphosate with its target enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase in atomic detail. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myers, J.P.; Antoniou, M.N.; Blumberg, B.; Carroll, L.; Colborn, T.; Everett, L.G.; Hansen, M.; Landrigan, P.J.; Lanphear, B.P.; Mesnage, R.; et al. Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: A consensus statement. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benbrook, C.M. Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maggi, F.; la Cecilia, D.; Tang, F.H.M.; McBratney, A. The global environmental hazard of glyphosate use. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.W.; Twilley, R.R.; Stevenson, J.C.; Boynton, W.R.; Means, J.C. The decline of submerged vascular plants in Upper Chesapeake Bay: Summary of results concerning possible causes. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 1983, 17, 78–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Yuan, D.; Ma, J. A simple method for the determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in seawater matrix with high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. Talanta 2016, 161, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amri, S.; Samar, M.F.; Sellem, F.; Ouali, K. Seasonal antioxidant responses in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck 1816) used as a bioindicator of the environmental contamination in the South-East Mediterranean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, P.; Flores, F.; Mueller, J.F.; Carter, S.; Negri, A.P. Glyphosate persistence in seawater. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.M.; Kroes, R.; Munro, I.C. Safety evaluation and risk assessment of the herbicide Roundup and its active ingredient, glyphosate, for humans. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2000, 31, 117–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, L.J.; Fuentes, L.; Rodgers, J.H.; Bowerman, W.W.; Yarrow, G.K.; Chao, W.Y.; Bridges, W.C. Relative toxicity of the components of the original formulation of Roundup® to five North American anurans. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmar, L.C.; Sanders, H.O.; Julin, A.M. Toxicity of the herbicide glyphosate and several of its formulations to fish and aquatic invertebrates. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1979, 8, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borggaard, O.K.; Gimsing, A.L. Fate of glyphosate in soil and the possibility of leaching to ground and surface waters: A review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesy, J.P.; Dobson, S.; Solomon, K.R. Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment for Roundup® Herbicide. In Reviews of Enviromental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2000; Volume 167, pp. 35–120. [Google Scholar]
- Annett, R.; Habibi, H.R.; Hontela, A. Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on the freshwater environment. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 458–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modesto, K.A.; Martinez, C.B.R. Roundup® causes oxidative stress in liver and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in muscle and brain of the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Chemosphere 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uren Webster, T.M.; Santos, E.M. Global transcriptomic profiling demonstrates induction of oxidative stress and of compensatory cellular stress responses in brown trout exposed to glyphosate and Roundup. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uren Webster, T.M.; Laing, L.V.; Florance, H.; Santos, E.M. Effects of glyphosate and its formulation, Roundup, on reproduction in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iummato, M.M.; Di Fiori, E.; Sabatini, S.E.; Cacciatore, L.C.; Cochón, A.C.; Ríos de Molina, M.d.C.; Juárez, Á.B. Evaluation of biochemical markers in the golden mussel Limnoperna fortunei exposed to glyphosate acid in outdoor microcosms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelboin, Y.; Quéré, C.; Pernet, F.; Pichereau, V.; Corporeau, C. Energy and antioxidant responses of pacific oyster exposed to trace levels of pesticides. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcante, D.G.S.M.; Martinez, C.B.R.; Sofia, S.H. Genotoxic effects of Roundup® on the fish Prochilodus lineatus. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2008, 655, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, S.; Gaivao, I.; Santos, M.A.; Pacheco, M. European eel (Anguilla anguilla) genotoxic and pro-oxidant responses following short-term exposure to Roundup®—A glyphosate-based herbicide. Mutagenesis 2010, 25, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guilherme, S.; Gaivão, I.; Santos, M.A.; Pacheco, M. Tissue specific DNA damage in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla) following a short-term exposure to a glyphosate-based herbicide. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 189, S212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, S.A.; Byrne, M. Acclimatization and Adaptive Capacity of Marine Species in a Changing Ocean. In Advances in Marine Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 74, pp. 69–116. [Google Scholar]
- Tato, T.; Salgueiro-González, N.; León, V.M.; González, S.; Beiras, R. Ecotoxicological evaluation of the risk posed by bisphenol A, triclosan, and 4-nonylphenol in coastal waters using early life stages of marine organisms (Isochrysis galbana, Mytilus galloprovincialis, Paracentrotus lividus, and Acartia clausi). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarore, A.; Musco, L.; Bertocci, I.; Gallo, A.; Cannavacciuolo, A.; Mutalipassi, M.; Caramiello, D.; Giomi, F.; Fusi, M.; Danovaro, R.; et al. Sea urchin chronicles. The effect of oxygen super-saturation and marine polluted sediments from Bagnoli-Coroglio Bay on different life stages of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 159, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, S.; Buono, S.; Cremisini, C. Toxic effects of irgarol and diuron on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus early development, fertilization, and offspring quality. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 51, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morroni, L.; Pinsino, A.; Pellegrini, D.; Regoli, F.; Matranga, V. Development of a new integrative toxicity index based on an improvement of the sea urchin embryo toxicity test. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 123, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morroni, L.; Giuliani, S.; Pellegrini, D.; Sartori, D. In situ embryo toxicity test with sea urchin: Development of exposure chamber for test execution. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Granmo, Å.; Beiras, R. Embryotoxicity of the antifouling biocide zinc pyrithione to sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) and mussel (Mytilus edulis). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Nieto, Ó.; Beiras, R. Integrative assessment of coastal pollution: Development and evaluation of sediment quality criteria from chemical contamination and ecotoxicological data. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschino, V.; Marin, M.G. Spermiotoxicity and embryotoxicity of triphenyltin in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus Lmk. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2002, 16, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- His, E.; Heyvang, I.; Geffard, O.; de Montaudouin, X. A comparison between oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) larval bioassays for toxicological studies. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1706–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, Version 2.5-2. CRAN R. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Favret, K.P.; Lynn, J.W. Flow-cytometric analyses of viability biomarkers in pesticide-exposed sperm of three aquatic invertebrates. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.G.; Moschino, V.; Cima, F.; Celli, C. Embryotoxicity of butyltin compounds to the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2000, 50, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Soars, N.A.; Ho, M.A.; Wong, E.; McElroy, D.; Selvakumaraswamy, P.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Davis, A.R. Fertilization in a suite of coastal marine invertebrates from SE Australia is robust to near-future ocean warming and acidification. Mar. Biol. 2010, 157, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Ho, M.; Selvakumaraswamy, P.; Nguyen, H.D.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Davis, A.R. Temperature, but not pH, compromises sea urchin fertilization and early development under near-future climate change scenarios. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.P.; Marshall, D.J. Male-by-female interactions influence fertilization success and mediate the benefits of polyandry in the sea urchin Heliocidaris erythrogramma. Evolution 2005, 59, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeff, W.; Neumann, C.; Schulz-Bull, D.E. Glyphosate and AMPA in the estuaries of the Baltic Sea method optimization and field study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvé, S.; Desrosiers, M. A review of what is an emerging contaminant. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, J.; Hooda, P.S.; Barker, J.; Barton, S.; Swinden, J. Occurrence, fate and transformation of emerging contaminants in water: An overarching review of the field. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowen, R.E.; Depledge, M.H. Rapid Assessment of Marine Pollution (RAMP). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, P.J.; Herwig, H.J.; Zandee, D.I.; Voogt, P.A. Effects of cadmium and PCBs on reproduction of the sea star Asterias rubens: Aberrations in the early development. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1989, 18, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, G.; Cipollaro, M.; Corsale, G.; Esposito, A.; Ragucci, E.; Giordano, G.G.; Trieff, N.M. Comparative toxicities of chlorinated biphenyls on sea urchin egg fertilisation and embryogenesis. Mar. Environ. Res. 1985, 17, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura, R.; Matranga, V. Overview of the molecular defense systems used by sea urchin embryos to cope with UV radiation. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, M.; Marin, M.G.; Brunetti, R. Effects of linear alkylbenzene sulphonate (LAS) on skeletal development of sea urchin embryos (Paracentrotus lividus Lmk). Water Res. 1991, 25, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M.; Lamare, M.; Winter, D.; Dworjanyn, S.A.; Uthicke, S. The stunting effect of a high CO2 ocean on calcification and development in sea urchin larvae, a synthesis from the tropics to the poles. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okazaki, K. Spicule formation by isolated micromeres of the sea urchin embryo. Am. Zool. 1975, 15, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, R.R.; Fenaux, L.; Strathmann, M.F. Heterochronic developmental plasticity in larval sea urchins and its implications for evolution of nonfeeding larvae. Evolution 1992, 46, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.D. Size-specific predation on marine invertebrate larvae. Biol. Bull. 2008, 214, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soars, N.A.; Prowse, T.A.A.; Byrne, M. Overview of phenotypic plasticity in echinoid larvae, ’Echinopluteus transversus’ type vs. typical echinoplutei. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 383, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, M.W. Particle captures and the method of suspension feeding by echinoderm larvae. Biol. Bull. 1991, 180, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.K.; Grunbaum, D.; O’Donnell, M.J. Effects of ocean-acidification-induced morphological changes on larval swimming and feeding. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 3857–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maisano, M.; Cappello, T.; Catanese, E.; Vitale, V.; Natalotto, A.; Giannetto, A.; Barreca, D.; Brunelli, E.; Mauceri, A.; Fasulo, S. Developmental abnormalities and neurotoxicological effects of CuO NPs on the black sea urchin Arbacia lixula by embryotoxicity assay. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Takahashi, C.; Tosuji, H. Inhibition of spicule elongation in sea urchin embryos by the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor eserine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 153, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matozzo, V.; Munari, M.; Masiero, L.; Finos, L.; Marin, M.G. Ecotoxicological hazard of a mixture of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid to the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrini, J.Z.; Rola, R.C.; Lopes, F.M.; Buffon, H.F.; Freitas, M.M.; Martins, C.d.M.G.; da Rosa, C.E. Effects of glyphosate on cholinesterase activity of the mussel Perna perna and the fish Danio rerio and Jenynsia multidentata: In vitro studies. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 130–131, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaee, M.; Akhlaghi, M.; Soltanian, S.; Gholamhosseini, A.; Heidarieh, H.; Fereidouni, M.S. Acute exposure to chlorpyrifos and glyphosate induces changes in hemolymph biochemical parameters in the crayfish, Astacus leptodactylus (Eschscholtz, 1823). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharm. 2019, 222, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pala, F. A survey on weed management in dry lentil fields. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldbusser, G.G.; Hales, B.; Langdon, C.J.; Haley, B.A.; Schrader, P.; Brunner, E.L.; Gray, M.W.; Miller, C.A.; Gimenez, I.; Hutchinson, G. Ocean acidification has multiple modes of action on bivalve larvae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, D.; Wei, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, C. Effects of long-term elevated temperature on covering, sheltering and righting behaviors of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batista de Melo, C.; Côa, F.; Alves, O.L.; Martinez, D.S.T.; Barbieri, E. Co-exposure of graphene oxide with trace elements: Effects on acute ecotoxicity and routine metabolism in Palaemon pandaliformis (shrimp). Chemosphere 2019, 223, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falfushynska, H.; Sokolov, E.P.; Haider, F.; Oppermann, C.; Kragl, U.; Ruth, W.; Stock, M.; Glufke, S.; Winkel, E.J.; Sokolova, I.M. Effects of a common pharmaceutical, atorvastatin, on energy metabolism and detoxification mechanisms of a marine bivalve Mytilus edulis. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 208, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, S.E.; Assidqi, K.; Zamani, N.P.; Appel, D.; Perschke, M.; Huhn, M.; Lenz, M. Suspended micro-sized PVC particles impair the performance and decrease survival in the Asian green mussel Perna viridis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 111, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulletquer, P.; Wolowicz, M.; Latala, A.; Brown, C.; Cragg, S. Application of a micro-respirometric volumetric method to respiratory measurements of larvae of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquat. Living Resour. 2004, 17, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorey, N.; Maboloc, E.; Chan, K.Y.K. Development of the sea urchin Heliocidaris crassispina from Hong Kong is robust to ocean acidification and copper contamination. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 205, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpp, M.; Wren, J.; Melzner, F.; Thorndyke, M.C.; Dupont, S. CO2 induced seawater acidification impacts sea urchin larval development I: Elevated metabolic rates decrease scope for growth and induce developmental delay. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2011, 160, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorey, N.; Lançon, P.; Thorndyke, M.; Dupont, S. Assessing physiological tipping point of sea urchin larvae exposed to a broad range of pH. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3355–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedeke, G.A.; Owagboriaye, F.O.; Ademolu, K.O.; Olujimi, O.O.; Aladesida, A.A. Comparative assessment on mechanism underlying renal toxicity of commercial formulation of Roundup herbicide and glyphosate alone in male albino rat. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, J.; Le Breton, M.; Cormier, P.; Morales, J.; Bellé, R.; Mulner-Lorillon, O. A glyphosate-based pesticide impinges on transcription. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, J.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Boulben, S.; Hureau, D.; Durand, G.; Bellé, R. Pesticide Roundup provokes cell division dysfunction at the level of CDK1/Cyclin B activation. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2002, 15, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, J.; Mulner-Lorillon, O.; Bellé, R. Glyphosate-based pesticides affect cell cycle regulation. Biol. Cell 2004, 96, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iori, S.; Rovere, G.D.; Ezzat, L.; Smits, M.; Ferraresso, S.S.; Babbucci, M.; Marin, M.G.; Masiero, L.; Fabrello, J.; Garro, E.; et al. The effects of glyphosate and AMPA on the mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis and its microbiota. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 108984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matozzo, V.; Marin, M.G.; Masiero, L.; Tremonti, M.; Biamonte, S.; Viale, S.; Finos, L.; Lovato, G.; Pastore, P.; Bogialli, S. Effects of aminomethylphosphonic acid, the main breakdown product of glyphosate, on cellular and biochemical parameters of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 83, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


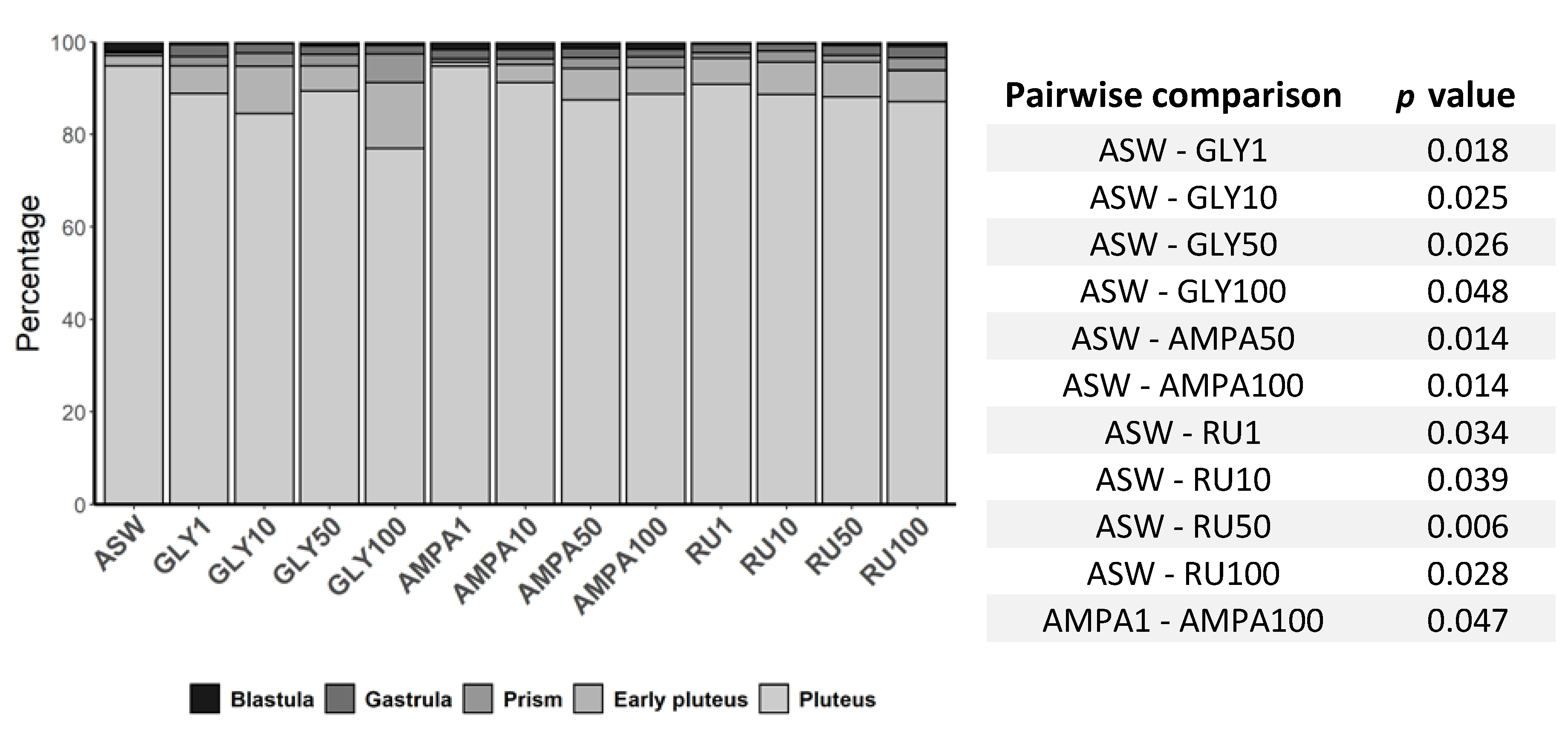



| Developmental Stages 24 hpf | PseudoF(12,60) = 0.671 | <0.050 |
| Developmental Stages 48 hpf | PseudoF(12,98) = 0.978 | <0.050 |
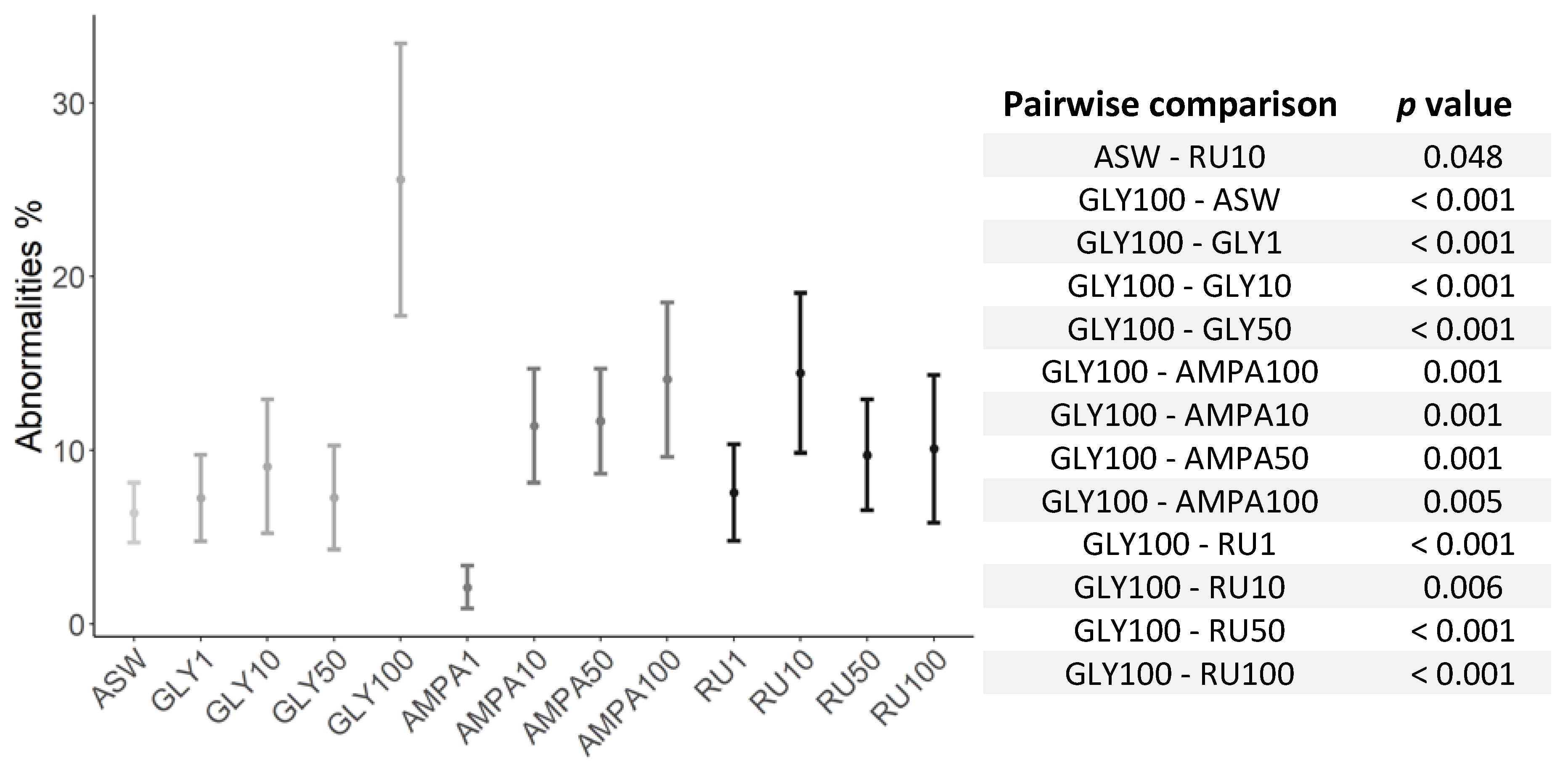
| Anomalies 48 hpf | χ2 (12) = 37.519 | <0.001 |
| Somatic Rod Length 48 hpf | χ2 (12) = 29.263 | <0.010 |
| Post-oral Rod Length 48 hpf | χ2 (12) = 20.810 | <0.050 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asnicar, D.; Cappelli, C.; Sallehuddin, A.S.; Maznan, N.A.; Marin, M.G. Effects of Glyphosate-Based and Derived Products on Sea Urchin Larval Development. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090661
Asnicar D, Cappelli C, Sallehuddin AS, Maznan NA, Marin MG. Effects of Glyphosate-Based and Derived Products on Sea Urchin Larval Development. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(9):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090661
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsnicar, Davide, Costanza Cappelli, Ahmad Safuan Sallehuddin, Nur Atiqah Maznan, and Maria Gabriella Marin. 2020. "Effects of Glyphosate-Based and Derived Products on Sea Urchin Larval Development" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 9: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090661
APA StyleAsnicar, D., Cappelli, C., Sallehuddin, A. S., Maznan, N. A., & Marin, M. G. (2020). Effects of Glyphosate-Based and Derived Products on Sea Urchin Larval Development. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(9), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090661








