Evolution Process of Liquefied Natural Gas from Stratification to Rollover in Tanks of Coastal Engineering with the Influence of Baffle Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Object Description
2.1. LNG Thermal Properties Description
2.2. Physical Processes Description
3. Numerical Implementation
3.1. Governing Equations
3.2. Computational Models with Grids
3.3. Assumptions and Boundary Conditions
4. Results and Discussion
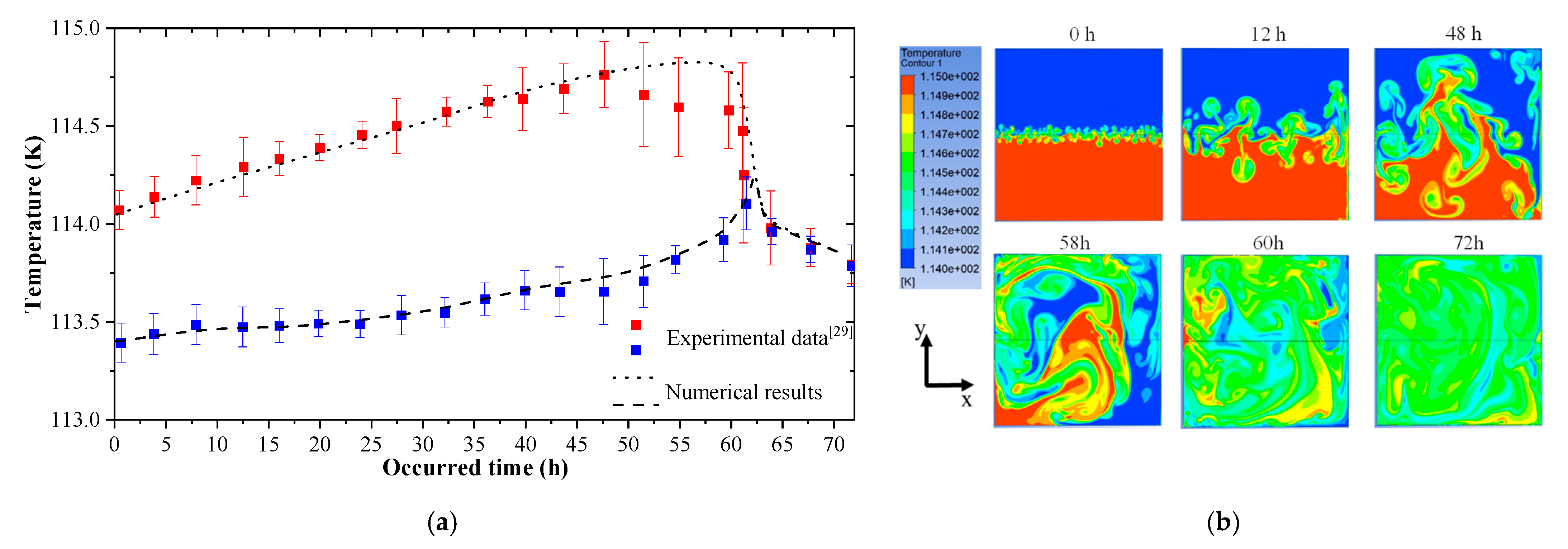
4.1. Numerical Model Validation
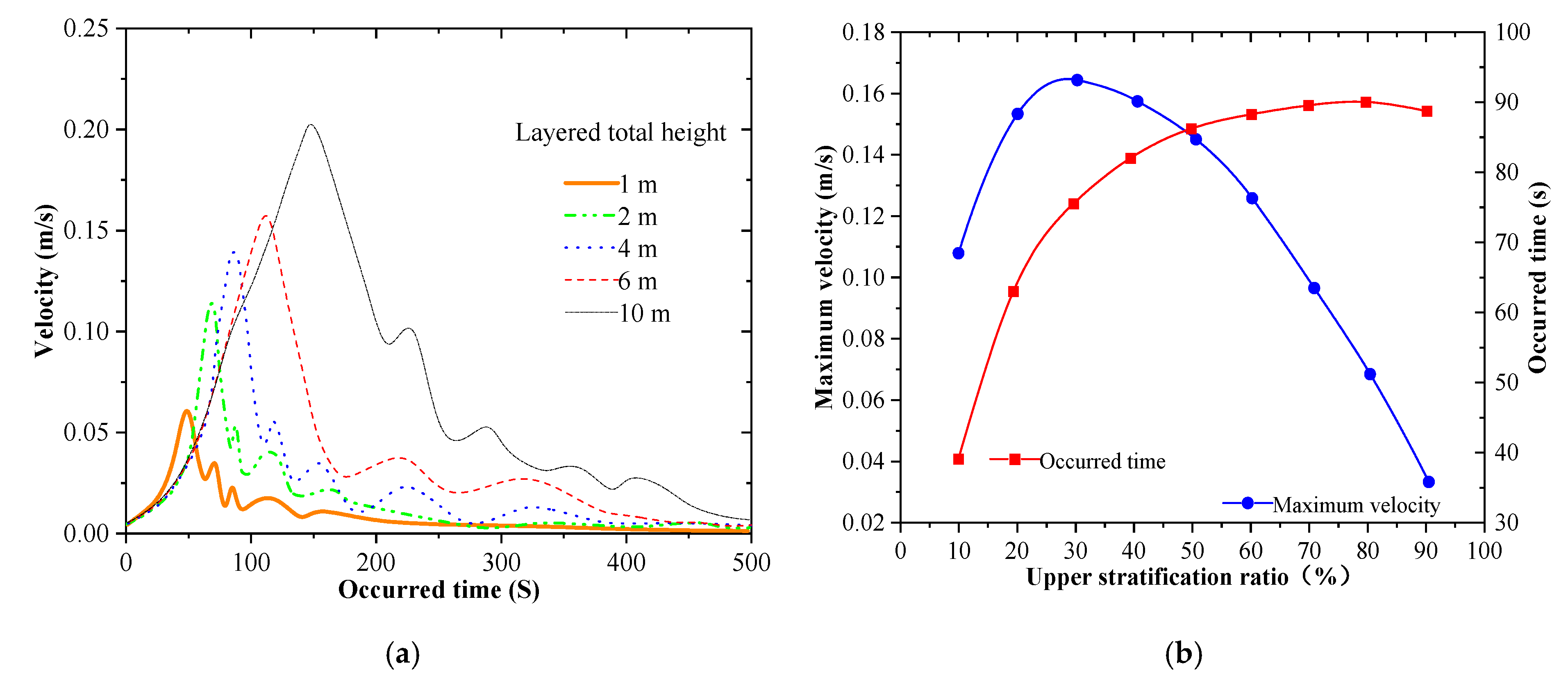
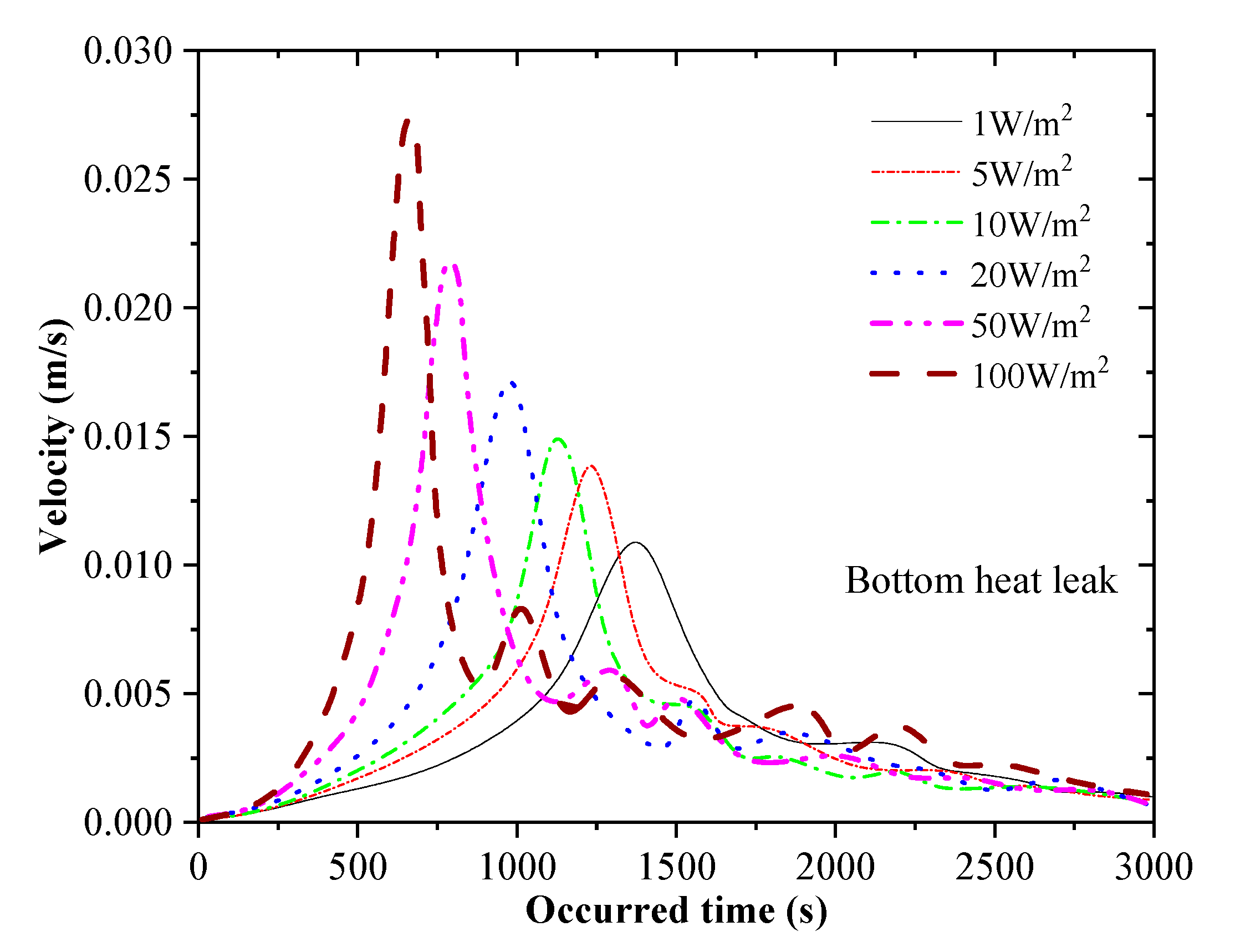
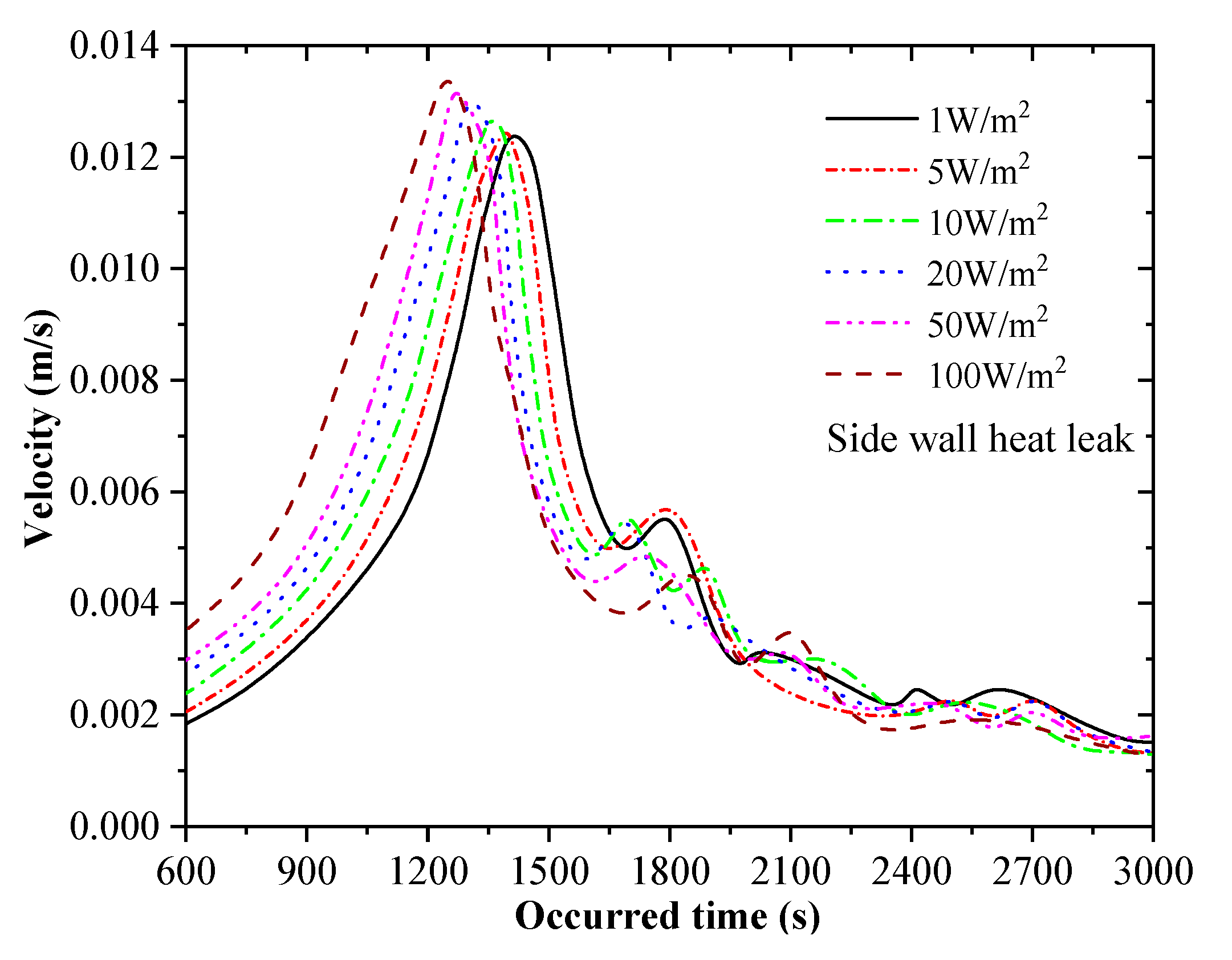
4.2. Effects of Density Difference, Heat Leakage and Stratification on Rollover
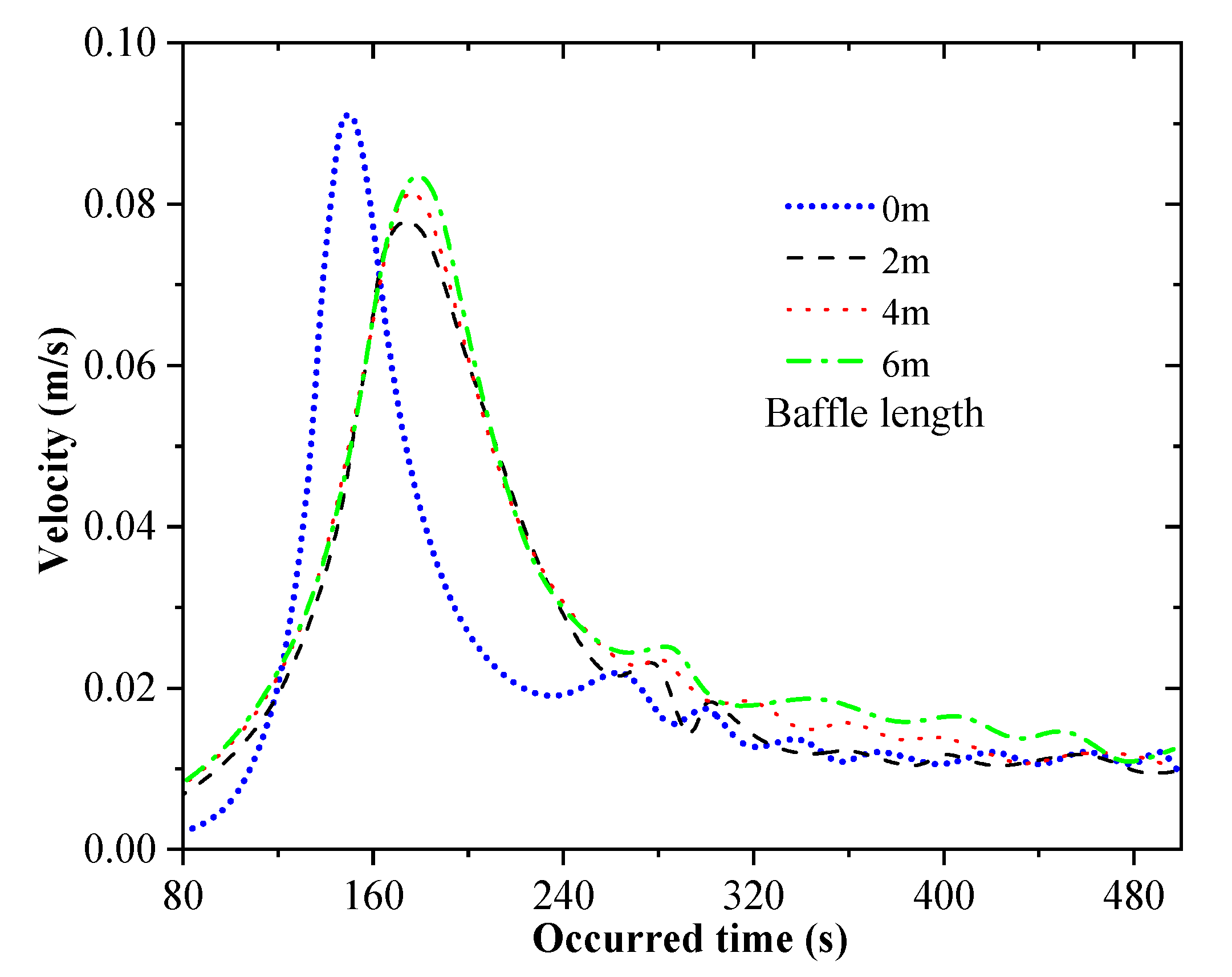
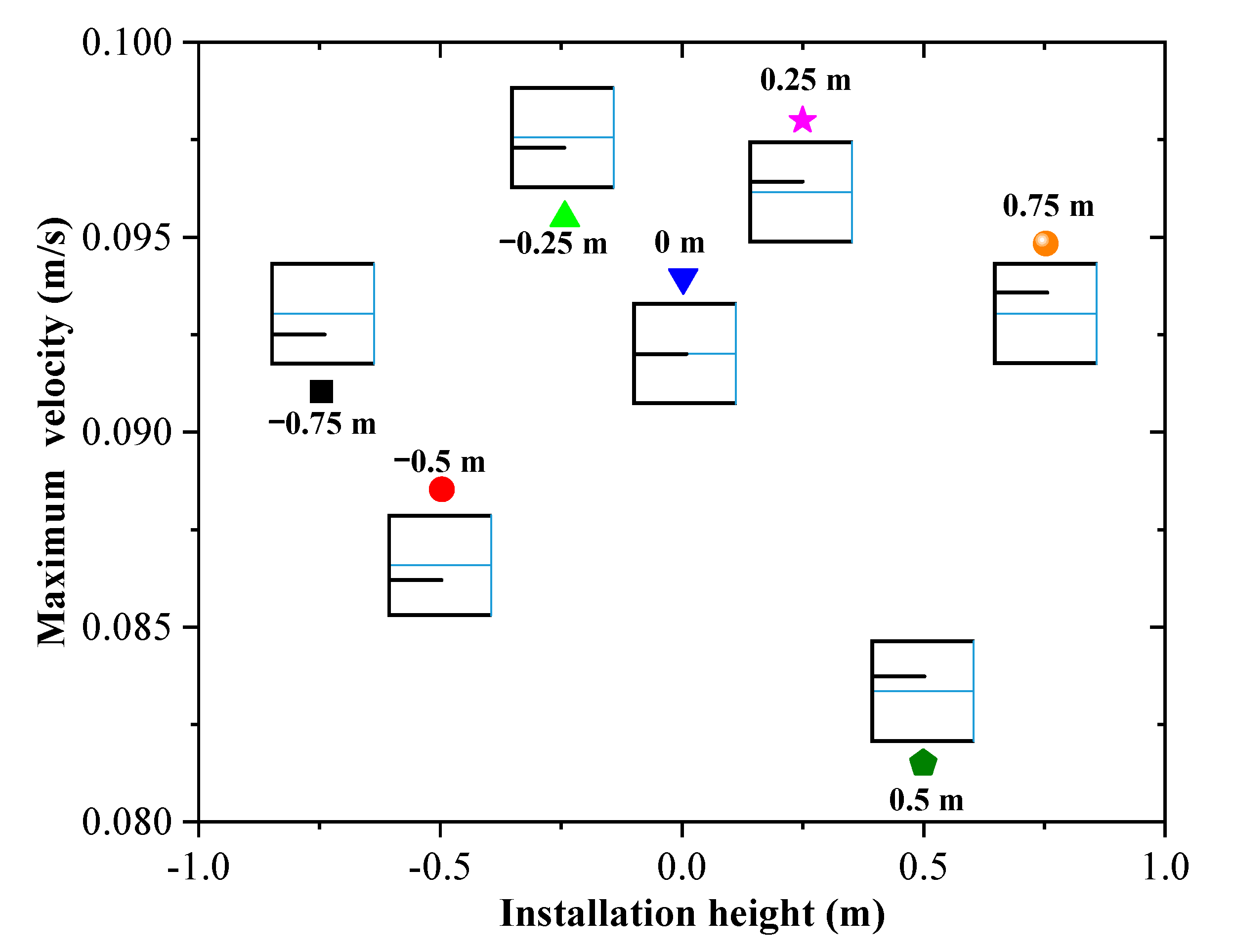
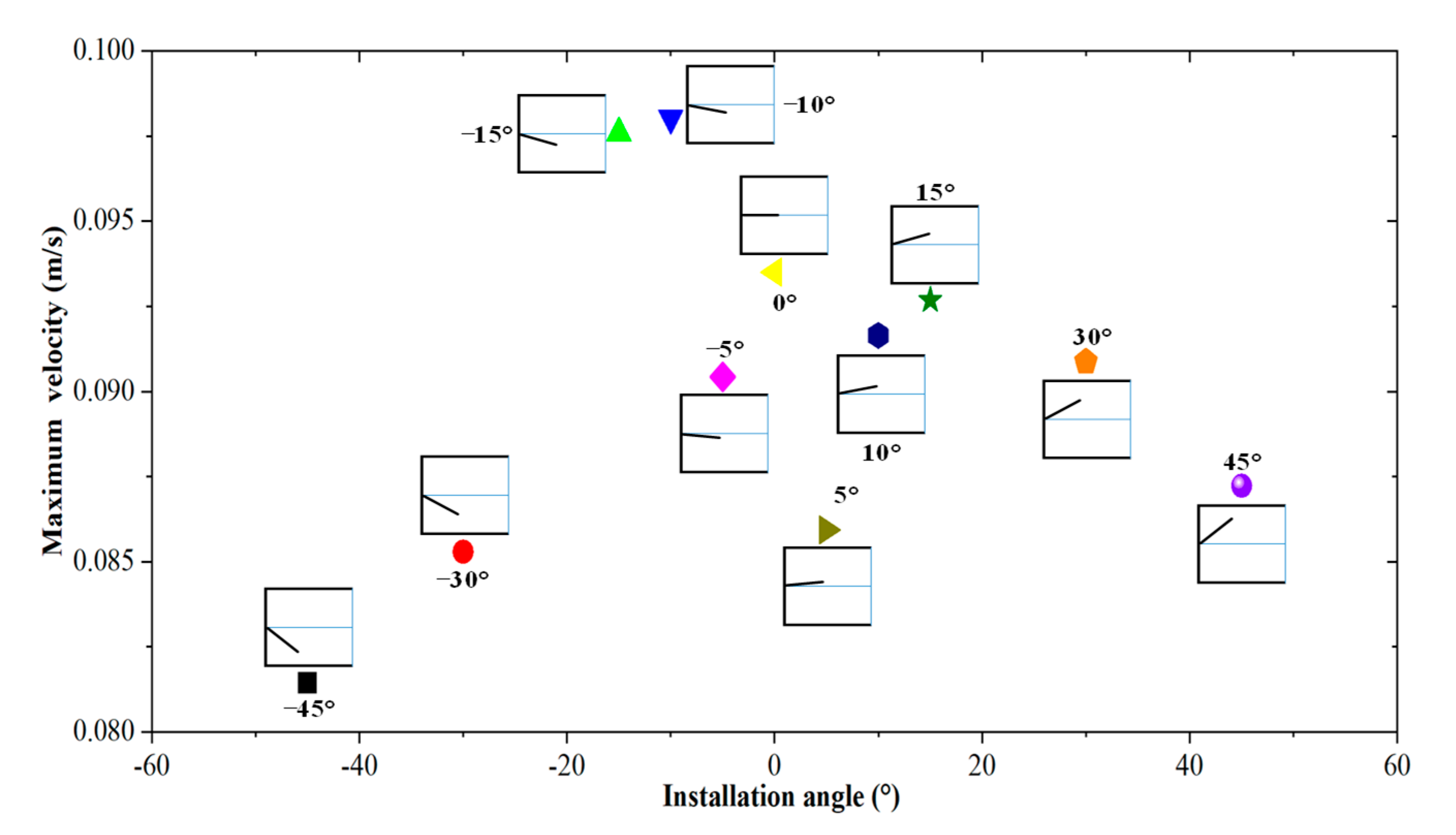
4.3. Effects of Baffle Structure on Rollover
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| cp | Specific heat capacity (J·kg−1·K−1) |
| F | Volume force of fluid (kg·m·s−2) |
| G | Generic term of turbulent kinetic energy (kg·m2·s−2) |
| i | Free coordinates in the Cartesian coordinate system |
| j | Free coordinates in the Cartesian coordinate system |
| k | Turbulent kinetic energy (kg·m−2·s−1) |
| P | Pressure (kPa) |
| Re | Reynolds Number |
| S | Mass fraction and diffusion coefficient |
| T | Temperature (K) |
| t | Time (s) |
| u | Velocities in the x-direction (m/s) |
| v | Velocities in the y-direction (m/s) |
| x | Coordinate direction |
| y | Coordinate direction |
| Greek symbols | |
| λ | Fluid thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1) |
| μ | Dynamic viscosity (kg·m−1·s−1) |
| ρ | Density (kg·m−3) |
| τ | Time (s) |
| ε | Turbulent kinetic energy dissipation rate |
Abbreviation
| BOG | Boil-off gas |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| LNG | Liquefied natural gas |
References
- Qadrdan, M.; Abeysekera, M.; Wu, J.; Jenkins, N.; Winter, B. Fundamentals of Natural Gas Networks. In The Future of Gas Networks; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tutak, M.; Brodny, J.; Siwiec, D.; Ulewicz, R.; Bindzár, P. Studying the Level of Sustainable Energy Development of the European Union Countries and Their Similarity Based on the Economic and Demographic Potential. Energies 2020, 13, 6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Thermal Stress Analysis of Process Piping System Installed on LNG Vessel Subject to Hull Design Loads. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guze, S.; Wawrzynski, W.; Wilczynski, P. Determination of Parameters Describing the Risk Areas of Ships Chaotic Rolling on the Example of LNG Carrier and OSV Vessel. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chun, D.-H.; Roh, M.-I.; Ham, S.-H. Optimum Arrangement Design of Mastic Ropes for Membrane-Type LNG Tanks Considering the Flatness of Thermal Insulation Panel and Production Cost. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.K.; Park, S.K. A Study on the Estimation of Facilities in LNG Bunkering Terminal by Simulation—Busan Port Case. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Tank-Level Control of Liquefied Natural Gas Carrier Based on Gaussian Function Nonlinear Decoration. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirbito, W.; Budiyanto, M.A.; Muliadi, R. Performance Analysis of Combined Cycle with Air Breathing Derivative Gas Turbine, Heat Recovery Steam Generator, and Steam Turbine as LNG Tanker Main Engine Propulsion System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, W.; Shen, S.; Hong, W.; Wang, X. Numerical investigation of stratification and rollover characteristics for LNG tanks. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Xi’an, China, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrín, J.L.; Pérez-Pérez, L.J. Numerical simulation of natural convection and boil-off in a small size pressurized LNG storage tank. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 138, 106840. [Google Scholar]
- Scurlock, R.G. Stratification, Rollover and Handling of LNG, LPG and Other Cryogenic Liquid Mixtures; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 40–133. [Google Scholar]
- Haddar, M.; Hammami, M.; Baccar, M. Numerical study of steady natural convection in a liquefied natural gas cylindrical storage tank equipped with baffles. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2019, 234, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germeles, A.E. A model for LNG tank rollover. In Advances in Cryogenic Engineering; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1960; pp. 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, N.; Creed, M. Stratification and rollover in liquefied natural gas storage tanks. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1996, 74, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bralewski, A.; Wolanin, J. Analysis of threats involving Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)—Review of literature sources. Saf. Fire Technol. 2019, 53, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Geist, J.M. Effects of stratification on boil-off rates in LNG tanks. Pipeline Gas J. 1972, 199, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Heestand, J.; Shipman, C.W.; Meader, J.W. A predictive model for rollover in stratified LNG tanks. AlChE J. 1983, 29, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munakata, T.; Lior, N.; Tanasawa, I. A study of double-diffusive rollover in cylinder enclosures. ASME 1995, 317, 279–291. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, K. CFD Simulation on LNG Storage Tank to Improve Safety and Reduce Cost; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W. Simulating on rollover phenomenon in LNG storage tanks and determination of the rollover threshold. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2015, 37, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, C.; Salehi, A.; Vesovic, V. A non-equilibrium approach to modeling the weathering of stored Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG). Energy 2017, 124, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sharafian, A.; Mérida, W. Non-equilibrium thermodynamic model for liquefied natural gas storage tanks. Energy 2020, 190, 116412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, Y.; Kubota, A.; Muraki, S. Rollover test in LNG storage tank and simulation model. In Advances in Cryogenic Engineering; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 805–811. [Google Scholar]
- Muro, M. Experimental and analytical study of the rollover phenomenon using LNG. In Proceedings of the International Cryogenic Engineering Conference, Berlin, Germany, 22–25 April 1986; pp. 633–637. [Google Scholar]
- Marcel, O. Measurement of the velocity of natural convection movements in an LNG storage tank. In Proceedings of the Gas Technology Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 21–22 May 1990; pp. 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Munakata, T.; Tanasawa, I. Numerical Study on Effect of Initial Concentration Difference on Onset of Rollover. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. 1994, 60, 3512–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansawa, I. Experimental Techniques in Natural Convection. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1995, 10, 403518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.; Morrison, D.S. Modelling the behaviour of stratified liquid natural gas in storage tanks: A study of the rollover phenomenon. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1997, 40, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorieu, O.; Uznanski, D.; DuPont, P. How to operate LNG terminals with flexibility/safety despite the diversification of unloaded LNG qualities. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference and Exhibition of Liquefied Natural Gas, Doha, Qatar, 21–24 March 2004; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Ang, K.K.; Jin, J.; Wang, C.M.; Hellan, Ø.; Watn, A. Large Floating Structure with Free-Floating, Self-Stabilizing Tanks for Hydrocarbon Storage. Energy 2019, 12, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Yang, S. Effect of Different Zigzag Channel Shapes of PCHEs on Heat Transfer Performance of Supercritical LNG. Energy 2019, 12, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Li, C.; He, Y.; Jia, W. Dynamic Modeling of the Two-Phase Leakage Process of Natural Gas Liquid Storage Tanks. Energy 2017, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakaria, Z.; Kamarulzaman, K.; Samsuri, A. Rollover phenomena in liquefied natural gas storage: Analysis on heat and pressure distribution through CFD simulation. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 2017, 8, 392–400. [Google Scholar]
- Degawa, T.; Fukue, S.; Uchiyama, T.; Ishikawa, A.; Motoyama, K. Behavior of a Jet Issuing Diagonally Upward into Two-Layer Density-Stratified Fluid in a Cylindrical Tank. J. Flow Control. Meas. Vis. 2017, 5, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Han, S.; Xu, L.; Shi, C.; Gao, D.; Zhang, Y.D. Rollover Mechanism Methodology of LNG Tank with Gas-Liquid Stratification Based on Curvelet Finite Element Method and Large Eddy Simulation Technology. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2018, 11, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Ren, J.; Wang, C.; Bi, M.; Bo, Y. Dynamic characteristics of the initial interface in stratified multi-composition liquid tanks during rollover. App. Therm. Eng. 2018, 145, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, A.; Dembele, S.; Denissenko, P.; Wen, J. Predicting Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) rollovers using Computational Fluid Dynamics. J. Loss Prev. Process. Ind. 2019, 62, 103922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, F.; Vesovic, V. A realistic vapour phase heat transfer model for the weathering of LNG stored in large tanks. Energy 2019, 174, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovidi, F.; Pagni, E.; Landucci, G.; Galletti, C. Numerical study of pressure build-up in vertical tanks for cryogenic flammables storage. App. Therm. Eng. 2019, 161, 114079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaws, C.L. Chemical Properties Handbook: Physical, Thermodynamic, Environmental, Transport, Safety, and Health Related Properties for Organic and Inorganic Chemicals; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, A.; Farooq, S.; Karimi, I.A.; Banerjee, R. CFD Analysis of Stratification and Rollover Phenomena in an Industrial-Scale LNG Storage Tank. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 14126–14144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Theoretical Derivation | Fitting Formula | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| ρ (kg/m3) | ρu = 21.67 T − 19,998.39 ρl = −1.45 T + 590.12 | 100 K~125 K | |
| cp (J/kg·K) | cp_u = −180.36 T − 23,585.1 cp_l = 6.901 T + 2658.2 | 100 K~125 K | |
| μ (W/m2·K) | μu = 0.0059 T − 0.4753 μl = −0.0013 T + 0.3392 | 100 K~125 K | |
| λ (Pa·s) | λu = 0.00029 T + 0.031 λl = −0.000002 T + 0.0004 | 100 K~125 K |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Han, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Evolution Process of Liquefied Natural Gas from Stratification to Rollover in Tanks of Coastal Engineering with the Influence of Baffle Structure. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010095
Wang Z, Han F, Liu Y, Li W. Evolution Process of Liquefied Natural Gas from Stratification to Rollover in Tanks of Coastal Engineering with the Influence of Baffle Structure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(1):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhe, Fenghui Han, Yuxiang Liu, and Wenhua Li. 2021. "Evolution Process of Liquefied Natural Gas from Stratification to Rollover in Tanks of Coastal Engineering with the Influence of Baffle Structure" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 1: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010095
APA StyleWang, Z., Han, F., Liu, Y., & Li, W. (2021). Evolution Process of Liquefied Natural Gas from Stratification to Rollover in Tanks of Coastal Engineering with the Influence of Baffle Structure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(1), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9010095





