Soil Fabric and Transitional Behavior in Completely Decomposed Granite: An Example of Well-Graded Soil
Abstract
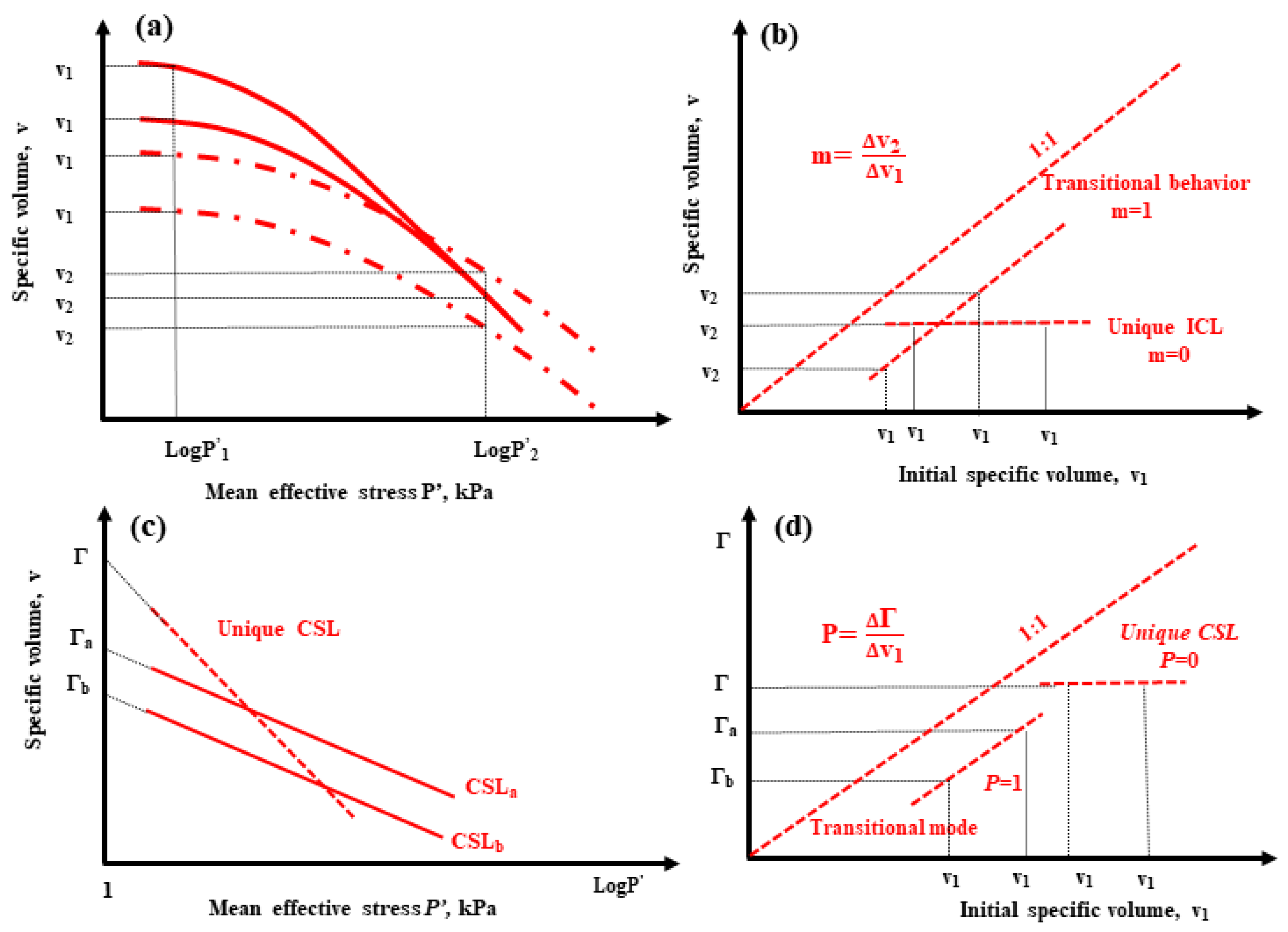
:1. Introduction
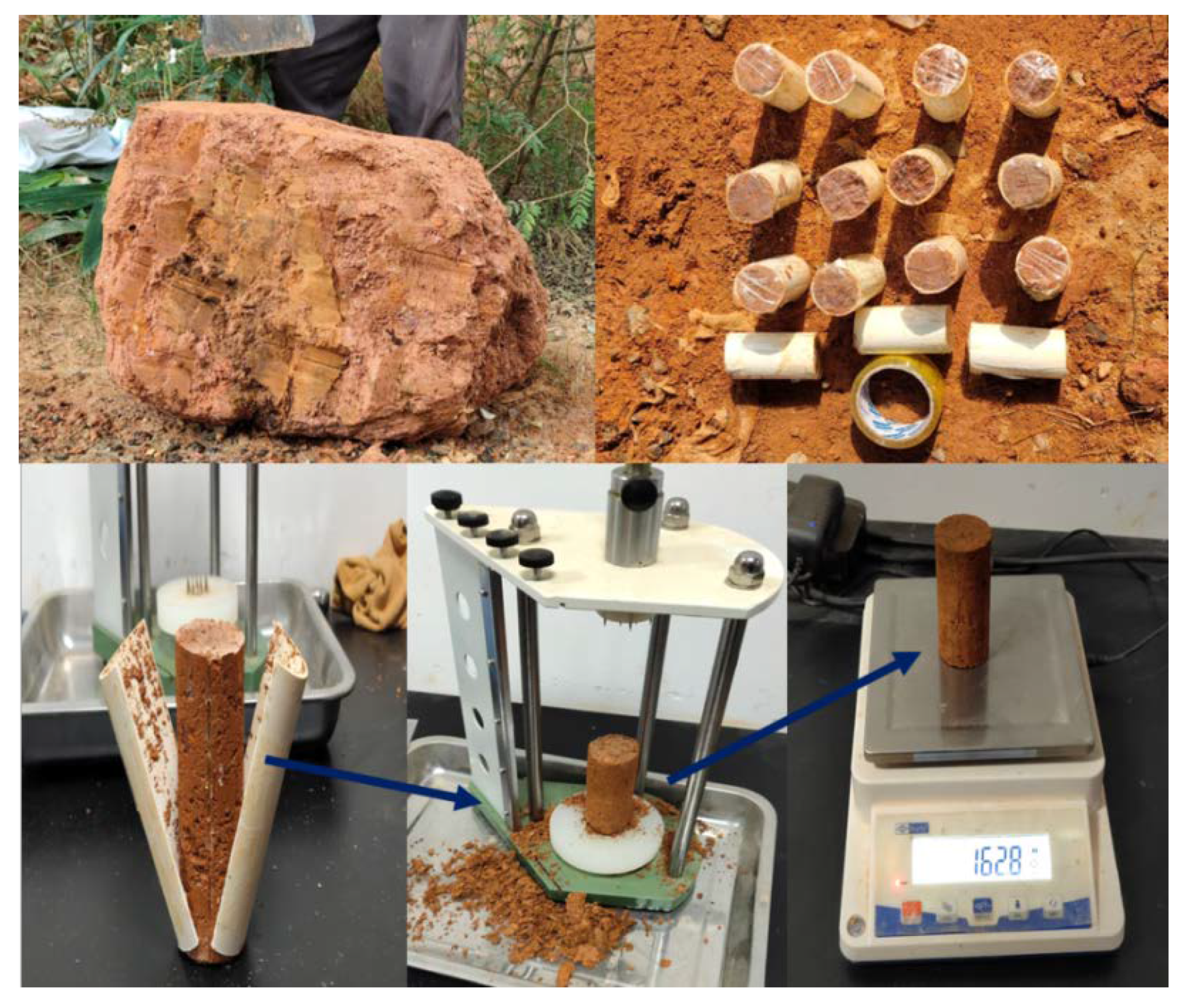
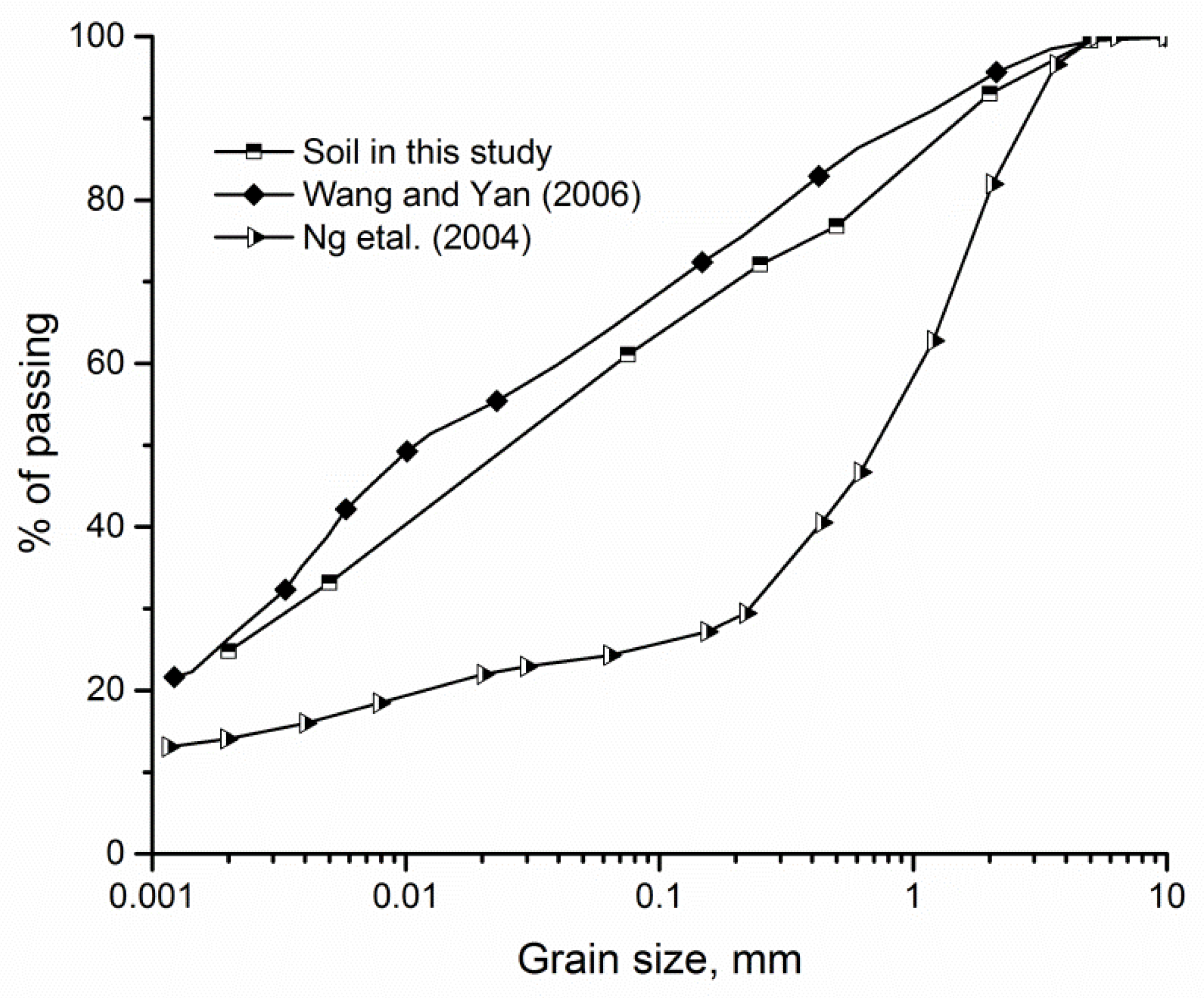
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
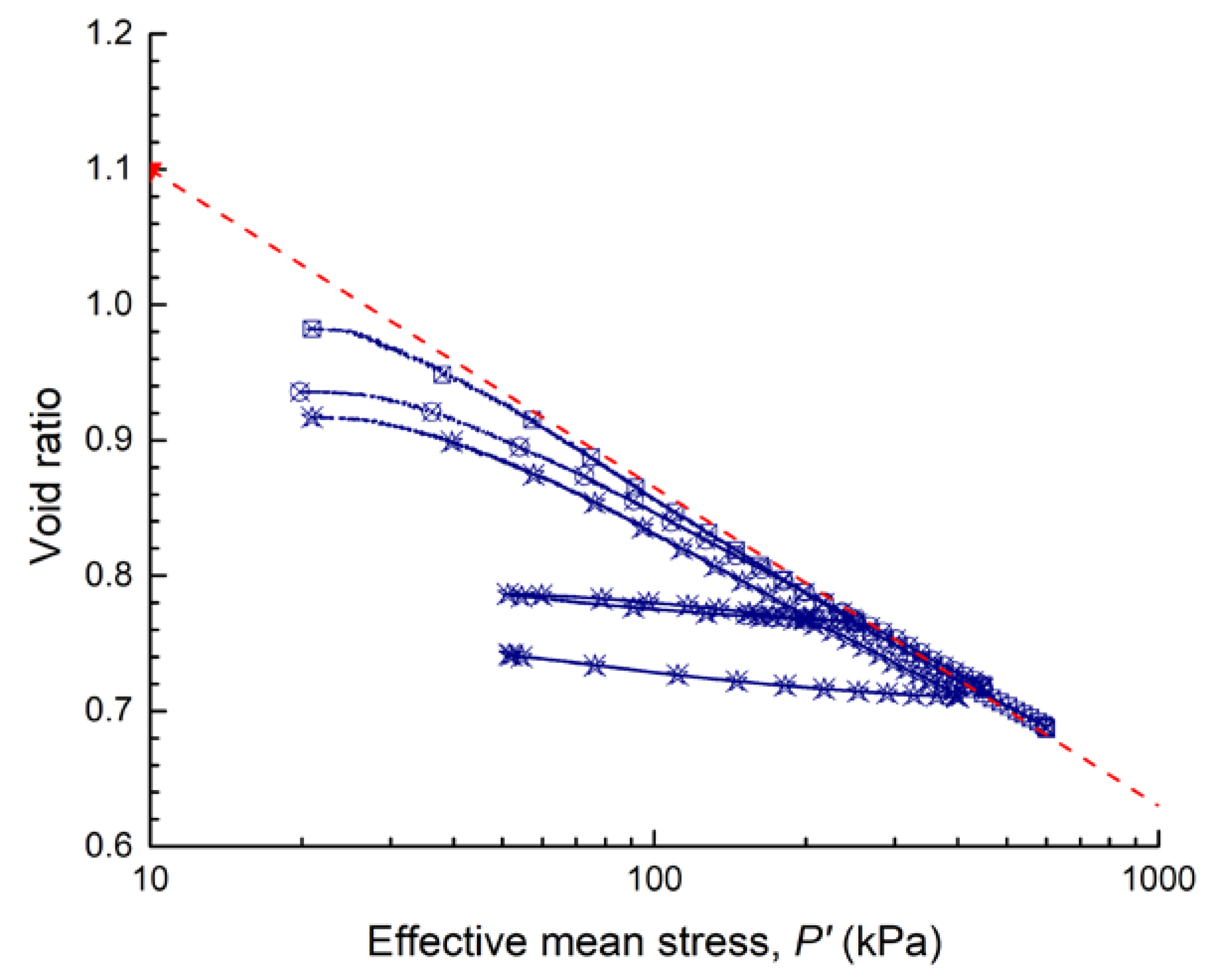
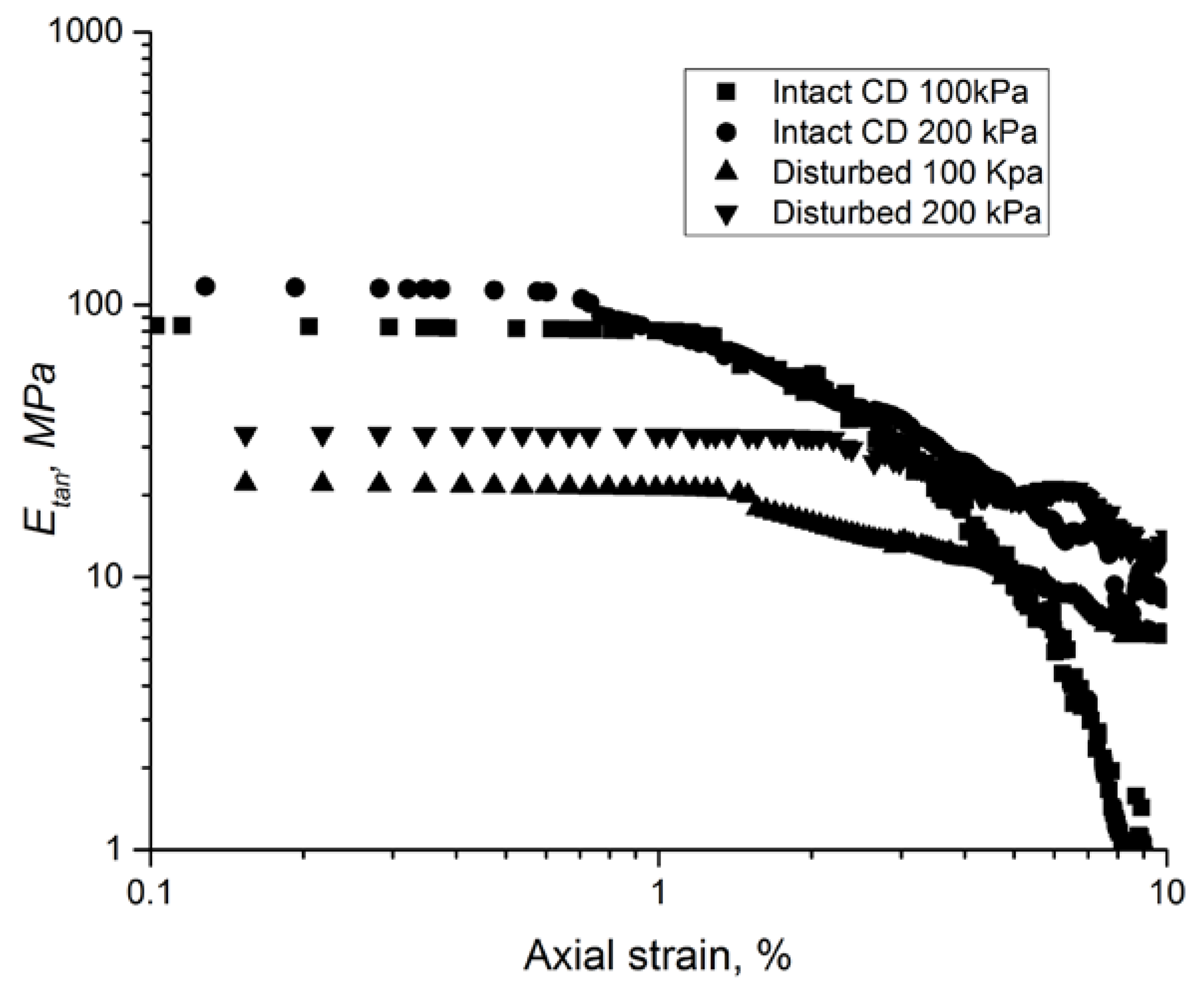
3.1. Compression Response
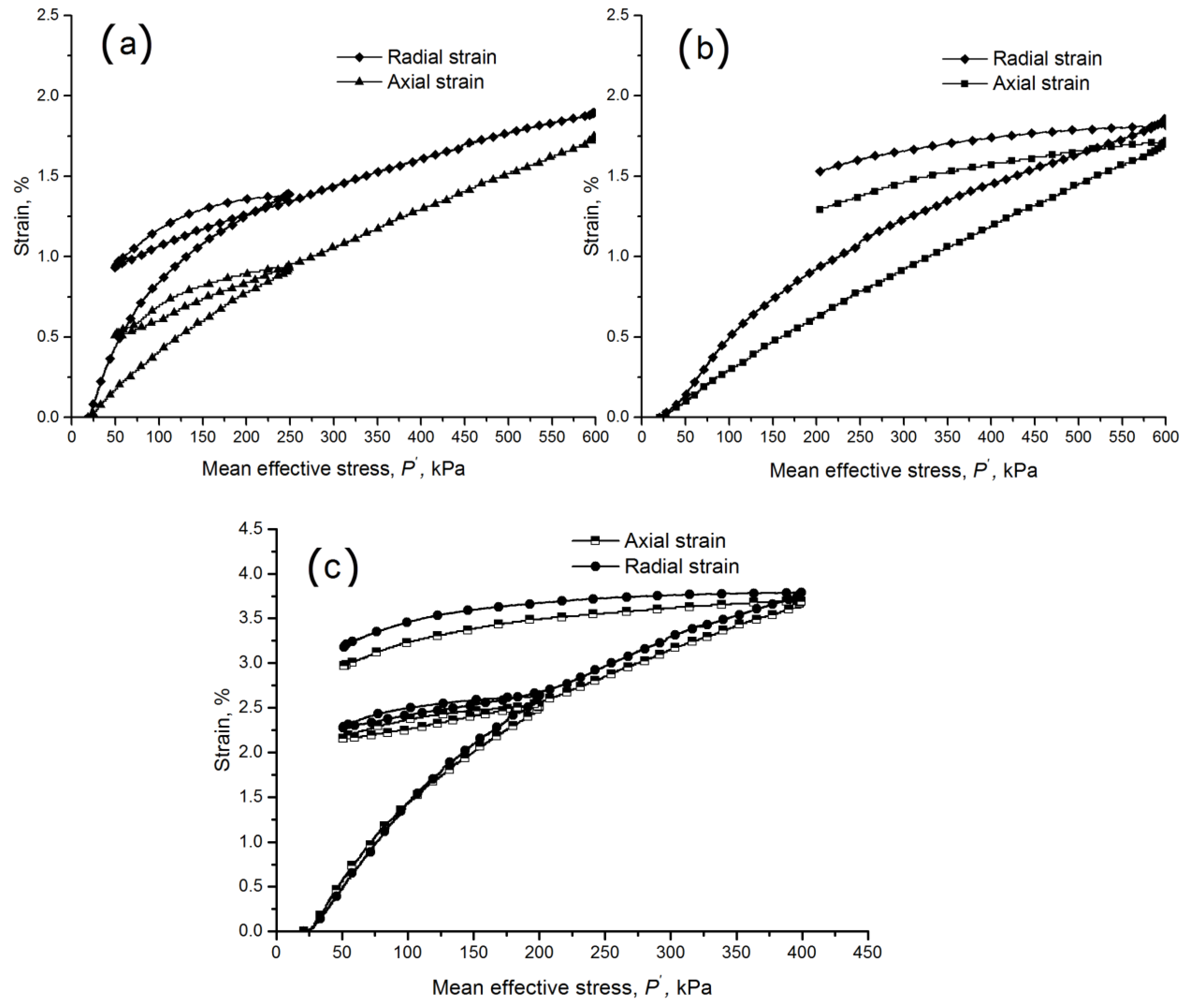
3.2. Volumetric Change
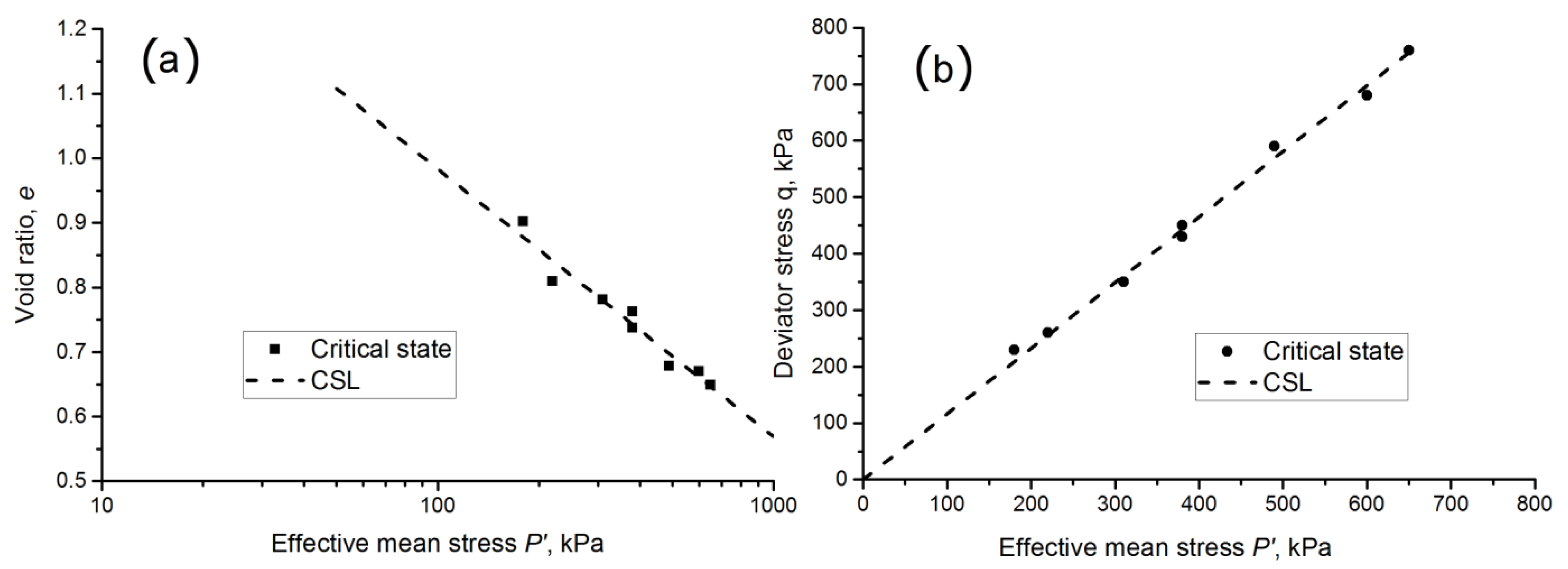
3.3. The Critical State
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elkamhawy, E.; Wang, H.; Zhou, B.; Yang, Z. Failure mechanism of a slope with a thin soft band triggered by intensive rainfall. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ietto, F.; Perri, F.; Cella, F. Weathering characterization for landslides modeling in granitoid rock masses of the Capo Vaticano promontory (Calabria, Italy). Landslides 2018, 15, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhou, X.; He, Y. Bond Yield Characteristics of Undisturbed Completely Decomposed Granite. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coop, M.R.; Lee, I.K. The behaviour of granular soils at elevated stresses. In Predictive Soil Mechanics; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 2015; pp. 186–198. [Google Scholar]
- Lade, P.V.; Yamamuro, J.A. Undrained Sand Behavior in Axisymmetric Tests at High Pressures. J. Geotech. Eng. 1996, 122, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, J.M.; Whittle, A.J. Compression model for cohesionless soils. Géotechnique 1995, 45, 611–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, J.A.; Lade, P.V. Static liquefaction of very loose sands. Can. Geotech. J. 1997, 34, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Been, K.; Jefferies, M.G. A state parameter for sands. Géotechnique 1985, 35, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.B.; Bressani, L.A.; Coop, M.R.; Bica, A.V.D. Some aspects of the compressibility behaviour of a clayey sand. Can. Geotech. J. 2001, 38, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocilla, A.; Coop, M.R.; Colleselli, F. The mechanics of an Italian silt: An example of ‘transitional’ behaviour. Géotechnique 2006, 56, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.M.V.; Bica, A.V.D. Problems in identifying the effects of structure and critical state in a soil with a transitional behaviour. Géotechnique 2006, 56, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzoni, E.; Nocilla, A.; Coop, M.; Colleselli, F. Identification and quantification of transitional modes of behaviour in sediments of Venice lagoon. Géotechnique 2014, 64, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuhafi, F.; Baudet, B.A.; Sammonds, P. The mechanics of subglacial sediment: An example of new “transitional” behaviour. Can. Geotech. J. 2010, 47, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shipton, B.; Coop, M. Transitional behaviour in sands with plastic and non-plastic fines. Soils Found. 2015, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Coop, M.R.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Jiang, J. Transitional Behaviors in Well-Graded Coarse Granular Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2016, 142, 06016018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Coop, M.R. The mechanics of a saturated silty loess with a transitional mode. Géotechnique 2017, 67, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altuhafi, F.; Coop, M. Changes to particle characteristics associated with the compression of sands. Géotechnique 2011, 61, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Yan, W.M. Laboratory Studies of Two Common Saprolitic Soils in Hong Kong. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2006, 132, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.K.; Coop, M.R. The intrinsic behaviour of a decomposed granite soil. Géotechnique 1995, 45, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Chiu, A.C.F. Laboratory Study of Loose Saturated and Unsaturated Decomposed Granitic Soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2003, 129, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Fung, W.T.; Cheuk, C.Y.; Zhang, L. Influence of Stress Ratio and Stress Path on Behavior of Loose Decomposed Granite. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.M.; Li, X.S. Mechanical response of a medium-fine-grained decomposed granite in Hong Kong. Eng. Geol. 2012, 129, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudet, B.; Stallebrass, S. A constitutive model for structured clays. Géotechnique 2004, 54, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipton, B.; Coop, M. On the compression behaviour of reconstituted soils. Soils Found. 2012, 52, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irfan, T.Y. Mineralogy, fabric properties and classification of weathered granites in Hong Kong. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 1996, 29, 5–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Guan, P.; Shang, Y.J. Weathering mechanisms and indices of the igneous rocks of Hong Kong. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2001, 34, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skempton, A.W. The Pore-Pressure CoefficientsAandB. Géotechnique 1954, 4, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, K.H. Manual of Soil Laboratory Testing; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Verdugo, R.; Ishihara, K. The Steady State of Sandy Soils. Soils Found. 1996, 36, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elkamhawy, E.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H. Transitional behavior in well-graded soils: An example of completely decomposed granite. Eng. Geol. 2019, 253, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, E.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H. Mineralogy, Micro-fabric and the Behavior of the Completely Decomposed Granite Soils. Civ. Eng. J. 2019, 5, 2762–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkamhawy, E.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H. Experimental investigation of both the disturbed and undisturbed granitic saprolite soil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Coop, M.R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, G. The mechanics of a saturated silty loess and implications for landslides. Eng. Geol. 2018, 236, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Guimaraes, M.; Santamarina, J.C. Micaceous Sands: Microscale Mechanisms and Macroscale Response. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, T.-G.; Nakata, Y.; Orense, R.; Hyodo, M. Strength Anisotropy of Compacted Decomposed Granite Soils. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2011, 30, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, J.B. On the compressibility and shear strength of natural clays. Géotechnique 1990, 40, 329–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futai, M.M.; Almeida, M.S.S.; Lacerda, W.A. Yield, Strength, and Critical State Behavior of a Tropical Saturated Soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

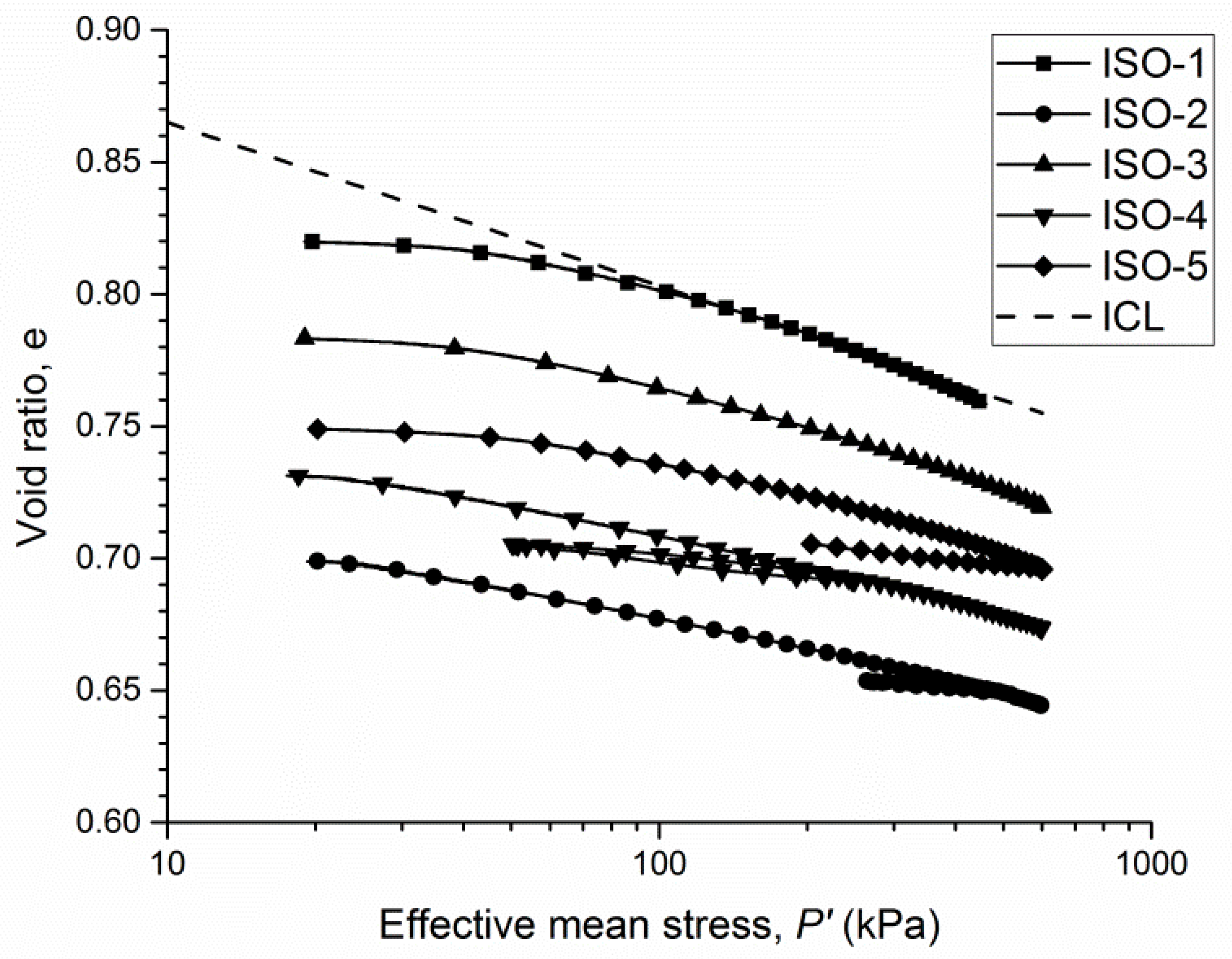
| Test ID | Loading Path, P’ kPa | Initial Void Ratio | Final Void Ratio | Slope of Parallel ICLs (ξ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO-1 | 20–450 | 0.8198 | 0.7583 | 0.027 |
| ISO-2 | 20–450–275–600 | 0.6988 | 0.6442 | |
| ISO-3 | 20–600 | 0.7833 | 0.7194 | |
| ISO-4 | 20–250–50–600 | 0.7312 | 0.6733 | |
| ISO-5 | 20–600–200 | 0.7490 | 0.7057 |
| Test ID | Compaction Ratio | Load Path, P’ kPa | Initial Void Ratio | Final Void Ratio | Slope of the Unique ICL (ξ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disturbed soil | 85% | 20–600 | 0.982 | 0.686 | 0.1 |
| 87.5% | 20–250–150–450 | 0.935 | 0.709 | ||
| 90% | 20–200–50–400–50 | 0.916 | 0.741 |
| Test Type | Consolidation Stress p’, kPa | Void Ratio before Shearing | Void Ratio after Shearing | Slope of the CSL (λ) in the e-log p’ Space | Slope of the CSL (M) in the q-p’ Space |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | 100 | 0.8882 | 0.9016 | 0.18 | 1.17 |
| 200 | 0.7841 | 0.7810 | |||
| 300 | 0.7060 | 0.6684 | |||
| 400 | 0.6791 | 0.6493 | |||
| CU | 100 | 0.8096 | 0.8096 | ||
| 200 | 0.7626 | 0.7626 | |||
| 300 | 0.7370 | 0.7370 | |||
| 400 | 0.6797 | 0.6797 |
| Test ID | Consolidated Stress p’(kPa) | Void Ratio before Shearing | Void Ratio after Shearing | Slope of the CSL (λ) in the e-log p’ Space | Slope of the CSL (M) in the q-p’ Space |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | 100 | 0.8140 | 0.7578 | 0.083 | 1.03 |
| 200 | 0.7818 | 0.6981 | |||
| 300 | 0.7451 | 0.6635 | |||
| 400 | 0.7069 | 0.6272 | |||
| CU | 100 | 0.8164 | 0.8164 | ||
| 200 | 0.7808 | 0.7808 | |||
| 300 | 0.7447 | 0.7447 | |||
| 400 | 0.7066 | 0.7066 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkamhawy, E.; Wang, H.; Salem, T.N.; Vranay, F.; Zelenakova, M. Soil Fabric and Transitional Behavior in Completely Decomposed Granite: An Example of Well-Graded Soil. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9101046
Elkamhawy E, Wang H, Salem TN, Vranay F, Zelenakova M. Soil Fabric and Transitional Behavior in Completely Decomposed Granite: An Example of Well-Graded Soil. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(10):1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9101046
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkamhawy, Elsayed, Huabin Wang, Tarek N. Salem, František Vranay, and Martina Zelenakova. 2021. "Soil Fabric and Transitional Behavior in Completely Decomposed Granite: An Example of Well-Graded Soil" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 10: 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9101046
APA StyleElkamhawy, E., Wang, H., Salem, T. N., Vranay, F., & Zelenakova, M. (2021). Soil Fabric and Transitional Behavior in Completely Decomposed Granite: An Example of Well-Graded Soil. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(10), 1046. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9101046








